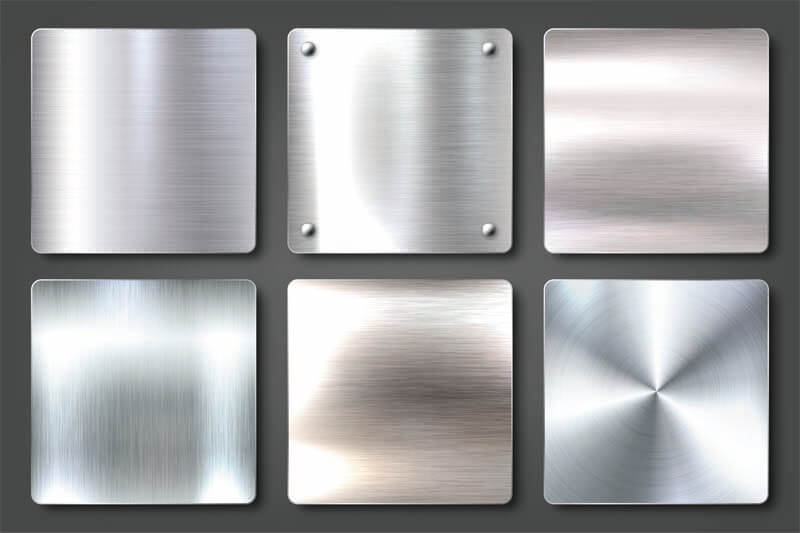
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sheet metal finishes
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing the right sheet metal finishes poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers. With varying requirements across industries and regions, understanding the nuances of sheet metal finishes is critical for ensuring quality, performance, and compliance with local standards. This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of finishes available—from raw and anodized to powder-coated and electropolished—highlighting their unique properties and applications.
By examining factors such as cost, performance, and aesthetic appeal, this guide equips international buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Germany—with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. Additionally, we provide insights into effective supplier vetting processes, enabling businesses to identify reliable partners who can meet their specific finishing needs.
Whether you are in the automotive, aerospace, or construction industry, understanding the intricacies of sheet metal finishes will empower you to enhance your product offerings and maintain a competitive edge in your market. This guide serves as your essential resource for navigating the complex world of sheet metal finishes, ensuring that you can confidently select the right solutions for your business.
Understanding sheet metal finishes Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw Finish | Unfinished surface, may exhibit natural texture and imperfections. | Pharmaceutical, automotive, and HVAC. | Pros: Cost-effective, suitable for certain environments. Cons: Less aesthetic appeal, limited corrosion resistance. |
| Electroplating | Thin layer of metal applied for aesthetic and protective purposes. | Jewelry, faucets, automotive components. | Pros: Enhanced appearance, corrosion protection. Cons: Can be more expensive, may wear over time. |
| Anodizing | Electrochemical process creating a durable oxide layer. | Automotive parts, architectural elements. | Pros: High corrosion resistance, customizable colors. Cons: Limited to aluminum, initial cost can be higher. |
| Powder Coating | Dry powder applied and baked for a durable finish. | Industrial equipment, consumer products. | Pros: Excellent durability, wide color range. Cons: Requires specialized application and curing equipment. |
| Electropolishing | Removes surface imperfections using an electrical current. | Food processing, medical devices, automotive. | Pros: Smooth surface, improved hygiene, corrosion resistance. Cons: Higher cost and requires specific equipment. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Raw Finish?
The raw finish is characterized by its untouched surface, often displaying natural textures and imperfections. This type of finish is suitable for environments where aesthetic appeal is less critical than functionality, such as in pharmaceutical equipment or HVAC systems. Buyers should consider the application environment since raw finishes may offer adequate corrosion resistance, particularly when using materials like stainless steel. However, the lack of finishing may not meet aesthetic requirements for consumer-facing products.
How does Electroplating enhance the quality of sheet metal finishes?
Electroplating involves applying a thin layer of metal to a substrate, enhancing both aesthetics and protection against corrosion. This finish is common in high-end applications like jewelry and automotive components, where appearance is paramount. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of a more attractive product against the potential for increased costs and the longevity of the finish. While electroplated surfaces can enhance product life, they may require maintenance over time as the coating can wear down.
Why is Anodizing a preferred choice for aluminum products?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that creates a durable oxide layer on aluminum surfaces, providing excellent corrosion resistance and a visually appealing finish. This type of finish is particularly suitable for automotive parts and architectural applications where durability and aesthetics are essential. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment in anodizing, which can be higher than other finishes, but recognize the long-term benefits of reduced maintenance and enhanced product lifespan.
What advantages does Powder Coating offer to industrial applications?
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to sheet metal, which is then baked to create a tough, durable finish. This method is widely used in industrial equipment and consumer products due to its excellent durability and availability in various colors. Buyers should evaluate the cost implications of powder coating, as it requires specialized equipment and processes. However, the long-lasting nature of powder-coated surfaces often justifies the investment, especially in high-traffic or outdoor applications.
How does Electropolishing improve surface quality for critical applications?
Electropolishing is a finishing process that uses an electrical current to remove surface imperfections, resulting in a smooth, shiny finish. This technique is particularly beneficial for industries like food processing and medical devices, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical. B2B buyers should consider the higher costs associated with electropolishing, but recognize its value in enhancing product quality and compliance with stringent industry standards. The investment in electropolishing can lead to reduced cleaning times and improved product performance.
Key Industrial Applications of sheet metal finishes
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sheet metal finishes | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Exterior body panels | Enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal | Ensure compliance with industry standards; consider lead times for finishing processes |
| Aerospace | Aircraft components | Weight reduction and improved durability | Seek finishes that meet strict safety and performance regulations; assess global sourcing capabilities |
| Food and Beverage | Processing equipment | Hygiene compliance and easy cleaning | Look for finishes that prevent bacterial growth; verify certifications for food safety |
| Construction | Architectural elements | Weather resistance and design versatility | Evaluate finishes suitable for outdoor exposure; assess local regulations and environmental impact |
| Electronics | Enclosures for devices | Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection | Ensure finishes that provide adequate protection; consider compatibility with electronic components |
In the automotive industry, sheet metal finishes are crucial for exterior body panels, where aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance are paramount. Finishes such as anodizing and powder coating not only enhance the visual quality but also protect against environmental wear. Buyers must ensure that the chosen finishes comply with stringent automotive standards and consider the lead times associated with various finishing processes to align with production schedules.
In aerospace, the application of sheet metal finishes on aircraft components is vital for weight reduction and durability. Anodizing and electropolishing are commonly used to achieve lightweight, corrosion-resistant surfaces. International buyers must be aware of the strict safety and performance regulations governing aerospace materials, necessitating a thorough assessment of suppliers’ certifications and capabilities to meet these standards.
The food and beverage sector utilizes sheet metal finishes in processing equipment to ensure hygiene and ease of cleaning. Finishes like electropolishing provide smooth, non-porous surfaces that minimize bacterial growth. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that offer finishes certified for food safety, as compliance with health regulations is critical for operational success.
In construction, architectural elements often require finishes that provide both aesthetic value and weather resistance. Powder coating and phosphate coatings are popular choices for their durability and color retention in outdoor applications. Buyers should evaluate finishes based on their suitability for specific climates and ensure compliance with local building regulations to guarantee longevity and safety.
Finally, in the electronics industry, sheet metal finishes are essential for device enclosures, providing electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection. Finishes must be compatible with electronic components to prevent interference and ensure reliability. Buyers should seek suppliers that can offer finishes designed for ESD protection, along with certifications that validate the quality and safety of the materials used.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sheet metal finishes’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding Finish Quality Standards
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in industries like automotive or aerospace, struggle to comprehend the varying quality standards of sheet metal finishes. Confusion often arises between Class A, B, and C finishes, leading to improper specifications that can affect the quality and functionality of their final products. For instance, a buyer may mistakenly order a Class C finish for components that require a Class A finish, resulting in aesthetic imperfections and potential rejection during quality assurance checks.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding the classification of finishes and their implications on product performance. This can be achieved by engaging with reputable suppliers who offer detailed specifications and samples of each finish class. Create a checklist that outlines the requirements for each project, ensuring that the finish class aligns with the application’s needs. For example, if parts will be exposed to harsh environments or require a high degree of aesthetic quality, specify a Class A finish. Additionally, consider collaborating with suppliers who can provide a mock-up or prototype to visualize the finish before mass production. This proactive approach minimizes misunderstandings and ensures that the right finish is applied from the outset.
Scenario 2: Managing Lead Times for Custom Finishes
The Problem: International buyers often face delays in lead times when ordering custom sheet metal finishes, especially when different finishing processes are required. For instance, a manufacturer in South America may request a specialized powder coating that requires additional curing time, inadvertently pushing back the entire production schedule. Such delays can disrupt supply chains and lead to missed deadlines, impacting business relationships and financial performance.
The Solution: To effectively manage lead times, buyers should establish clear communication with suppliers regarding their finishing requirements upfront. It is essential to provide suppliers with detailed specifications, including the desired finish type, quantity, and any specific deadlines. Consider implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory strategy that allows for flexibility in ordering based on real-time production needs. Additionally, maintaining a good relationship with multiple suppliers can provide alternatives in case of unforeseen delays. Regularly scheduled check-ins during the production process can also help buyers stay informed about the status of their orders and make necessary adjustments in a timely manner.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Consistent Quality Across Multiple Orders
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter issues with consistency when ordering sheet metal finishes over time. A company might receive a batch of components with a finish that varies significantly from previous orders, leading to quality control issues and increased rework costs. For example, a buyer in Europe may notice that the anodized finish on aluminum parts varies in color and texture from one shipment to the next, which can compromise the integrity of the final product.
The Solution: To ensure consistent quality, buyers should establish a comprehensive quality assurance protocol with their suppliers. This includes setting clear expectations for finish specifications and implementing regular audits of the supplier’s finishing processes. Requesting certificates of compliance and detailed reports on the finishing techniques used can also help in maintaining standards. Additionally, consider building a feedback loop where any discrepancies can be reported and addressed promptly. Utilizing a standardized finish specification sheet can serve as a reference point for both buyers and suppliers to align expectations and reduce variability in future orders. Engaging in long-term partnerships with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality can further enhance consistency in finishes across multiple orders.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sheet metal finishes
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Sheet Metal Finishes?
When selecting materials for sheet metal finishes, understanding the properties and implications of each option is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four common materials: stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, and galvanized steel, focusing on their performance characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international markets.
Stainless Steel: A Durable Choice for Corrosion Resistance
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It is often rated for high-pressure applications, making it suitable for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and aesthetic appeal, which makes it ideal for visible applications. However, it tends to be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with various media, including water, chemicals, and food products, making it a versatile choice for many industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards like ASTM and DIN, as well as the importance of certifications for food-grade applications.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has excellent thermal conductivity. It is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can lead to cost savings in transportation and installation. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not perform well under high-pressure conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications involving low to moderate pressures and is commonly used for decorative finishes due to its aesthetic versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum grades that meet local standards (e.g., JIS in Japan or EN in Europe) and the implications for recycling, which is increasingly important in sustainable practices.
Carbon Steel: Cost-Effective and Strong
Key Properties: Carbon steel offers high strength and is often used in structural applications. It is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel and aluminum, making it necessary to apply protective finishes.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for large-scale projects. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can limit its application unless properly finished or coated.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is often used in construction and heavy machinery but requires careful consideration of environmental factors to prevent degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards and consider the need for additional coatings or finishes to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid or coastal regions.
Galvanized Steel: Protection Against Corrosion
Key Properties: Galvanized steel is carbon steel that has been coated with zinc to enhance corrosion resistance. This makes it suitable for outdoor applications and environments prone to moisture.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of galvanized steel is its affordability and effective protection against rust. However, the zinc coating can wear off over time, especially in harsh environments, requiring maintenance.
Impact on Application: Galvanized steel is widely used in construction, automotive, and agricultural applications where exposure to the elements is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with high humidity or industrial pollution should consider the long-term performance of galvanized finishes and adhere to relevant standards for coating thickness and durability.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Sheet Metal Finishes
| Material | Typical Use Case for sheet metal finishes | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive components | Lightweight and versatile | Less durable under high-pressure | Medium |
| Carbon Steel | Structural applications | Cost-effective for large projects | Susceptible to rust and corrosion | Low |
| Galvanized Steel | Outdoor structures and automotive parts | Affordable with good corrosion protection | Zinc coating can wear off | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of common sheet metal materials, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sheet metal finishes
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Sheet Metal Finishes?
The manufacturing processes for sheet metal finishes are critical in determining the final product’s quality, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding these processes helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers for their projects. The main stages in manufacturing sheet metal finishes include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Sheet Metal Finishing?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting the appropriate sheet metal type based on the project’s requirements. Common materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and carbon steel, each offering unique properties such as corrosion resistance or strength.
After material selection, the sheets undergo cleaning to remove any contaminants, oils, or residues that may affect the finish quality. Techniques such as chemical cleaning, ultrasonic cleaning, or sandblasting are often employed. This ensures that the surface is free from impurities before proceeding to the next stage.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Sheet Metal?
Forming processes shape the prepared sheet metal into desired forms. Common techniques include:
- Bending: Using presses or brakes to create angles and curves.
- Punching: Creating holes or cutouts using punches and dies.
- Laser Cutting: Utilizing high-powered lasers for precise cuts, allowing for complex geometries.
- Stamping: Employing dies to produce specific shapes in mass production.
These forming techniques not only affect the structural integrity of the parts but also influence the finish quality. For instance, sharp edges from punching or bending may require additional finishing to ensure safety and aesthetics.
How Does Assembly Fit into the Manufacturing Process?
Assembly is often a crucial stage, especially for complex parts that require multiple components. This process can involve welding, riveting, or using fasteners to join parts together. Attention to detail during assembly is essential, as any misalignment can affect the final finish and performance of the product.
What Are the Main Finishing Techniques for Sheet Metal?
Finishing is perhaps the most critical phase in enhancing the functionality and appearance of sheet metal products. Various techniques are employed based on the desired outcome:
- Electroplating: Applying a metallic layer to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Powder Coating: Spraying a dry powder that is baked to create a durable finish.
- Anodizing: An electrochemical process that enhances aluminum’s corrosion resistance and allows for dyeing.
- Electropolishing: Using an electrical current to create a smooth, shiny surface.
Each finishing technique has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific application requirements.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Sheet Metal Finishes?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in ensuring that sheet metal finishes meet both international standards and customer specifications. A robust QA process not only prevents defects but also instills confidence in B2B buyers regarding their suppliers.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Sheet Metal Finishing?
B2B buyers should be familiar with international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that suppliers consistently deliver quality products and services.
Additionally, industry-specific standards such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in the oil and gas sector may also apply. Understanding these standards helps buyers assess whether a supplier can meet their specific regulatory and quality requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Checking raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing processes to detect any deviations from quality standards during production.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive inspections of finished products before shipment to ensure they meet customer specifications.
By implementing these checkpoints, manufacturers can reduce defects and improve overall product quality.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s QC processes:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with quality standards.
- Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports that outline inspection results, defect rates, and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engaging independent inspection agencies to verify the quality of the finished products.
These measures provide transparency and help buyers ensure that suppliers adhere to the highest quality standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, which can affect the certification process.
Additionally, cultural differences may impact communication regarding quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear lines of communication with suppliers and understanding local regulations is crucial for successful international transactions.
Moreover, buyers should be aware of logistical considerations, such as shipping times and customs regulations, which may affect the delivery and inspection of products.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for sheet metal finishes is vital for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with material preparation, forming techniques, finishing methods, and quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. This knowledge not only enhances product quality but also fosters stronger business relationships in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sheet metal finishes’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure sheet metal finishes. Understanding the various finishing options and the procurement process is essential for ensuring that the chosen finishes meet project specifications, performance requirements, and budget constraints. This step-by-step guide will help you navigate the complexities of sourcing sheet metal finishes effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of a successful procurement process. Determine the required finish type based on the application, whether it’s aesthetic, functional, or both. Consider factors such as corrosion resistance, surface texture, and compliance with industry standards relevant to your region, such as ISO or ASTM.
- Identify Application Requirements: Understand the end-use of the finished product to choose the right finish (e.g., anodizing for corrosion resistance in automotive parts).
- Consider Environmental Factors: Evaluate how environmental conditions may impact the finish, such as exposure to moisture or chemicals.
Step 2: Research Different Finishing Options
Familiarize yourself with the various types of sheet metal finishes available in the market. Options range from basic mill finishes to advanced processes like anodizing and powder coating. Each finish has unique properties and applications, which can significantly affect performance and cost.
- Assess Finishing Processes: Understand the advantages and limitations of each finishing technique to make informed decisions.
- Match Finishes to Specifications: Ensure that the finishes align with your defined technical requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to conduct thorough evaluations. Request company profiles, certifications, and case studies that demonstrate their capabilities and experience in your industry.
- Check References: Contact previous clients to gather feedback on quality, delivery times, and customer service.
- Assess Manufacturing Capabilities: Ensure that the supplier has the necessary equipment and technology to produce the required finishes.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Confirm that potential suppliers possess the necessary certifications and quality management systems, such as ISO 9001. Certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to international quality standards and maintains consistent processes.
- Request Documentation: Ask for copies of relevant certifications and quality assurance protocols.
- Review Compliance with Industry Standards: Ensure that suppliers can meet any specific regulatory requirements relevant to your project.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the finishes you are considering. This allows you to evaluate the quality and suitability of the finishes for your specific application.
- Conduct Performance Testing: Assess the samples against your technical specifications and application requirements.
- Evaluate Aesthetic Qualities: Review the visual appeal of the finishes to ensure they align with your branding and design goals.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you’ve selected a supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize pricing, lead times, and payment terms. Be clear about your expectations regarding quality and delivery schedules.
- Establish Clear Terms: Define all terms of the agreement, including warranty and after-sales support.
- Consider Long-Term Partnerships: Evaluate the potential for a long-term relationship, which could lead to better pricing and service.
Step 7: Monitor Production and Quality Control
After placing your order, maintain open communication with the supplier to monitor the production process. Regular updates and quality checks can help ensure the finished products meet your expectations.
- Schedule Regular Check-Ins: Establish a timeline for updates on production status and quality inspections.
- Be Prepared for Adjustments: Stay flexible to address any potential issues that may arise during production.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can ensure a more streamlined and effective procurement process for sheet metal finishes, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sheet metal finishes Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sheet Metal Finishes Sourcing?
When sourcing sheet metal finishes, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of finish directly influences material costs. For instance, anodized finishes may require higher-grade aluminum, while powder coating involves specific polymers that can vary in price based on color and performance specifications.
-
Labor: Labor costs are tied to the complexity of the finishing process. Techniques like electroplating or anodizing require skilled technicians, which can increase overall labor expenses. In contrast, simpler methods like bead blasting or raw finishing may demand less labor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory rent. Advanced processes that require specialized machinery, such as electropolishing, typically incur higher overhead.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specific finishes, particularly for unique product shapes or sizes. This upfront investment can significantly affect pricing, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the finished product meets industry standards often requires robust QC processes, which can add to costs. Certifications (like ISO or ASTM) may also be necessary, particularly for industries like aerospace or automotive.
-
Logistics: Transporting finished products can influence pricing, especially for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and Incoterms will all play a role in the overall logistics cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin varies based on market competition, supplier reputation, and demand for specific finishes.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sheet Metal Finishing Costs?
Several key factors can influence the pricing of sheet metal finishes:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts on larger quantities, making it more economical for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom finishes or specific requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their needs to avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Premium materials and certifications can substantially raise costs. For example, finishes that require compliance with environmental or safety regulations may have additional fees.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capacity can influence pricing. Suppliers in regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, while those with established reputations may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is essential. Different Incoterms (like FOB, CIF, etc.) affect responsibility and risk, which can impact the overall cost of the sourced finishes.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Help Buyers Achieve Cost-Efficiency?
International B2B buyers can employ several strategies to negotiate better pricing on sheet metal finishes:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Consolidating orders can provide leverage for negotiating bulk pricing. Engage suppliers with forecasts of future orders to negotiate better rates.
-
Clarify Specifications Early: Clearly define product specifications and desired finishes upfront to avoid costly changes later in the process.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the upfront cost but the total cost over the product’s lifecycle, including maintenance, durability, and potential rework costs.
-
Research Market Rates: Stay informed about prevailing market prices for different finishes. This knowledge can empower negotiations and help identify fair pricing.
-
Utilize Local Knowledge: For buyers in regions like Africa or South America, leveraging local suppliers or manufacturers familiar with regional dynamics can lead to cost savings and improved logistics.
What Should International Buyers Know About Pricing Nuances?
International B2B buyers must be aware of the unique pricing nuances when sourcing sheet metal finishes across regions:
-
Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rates can impact pricing, especially for long-term contracts. Consider negotiating in stable currencies to mitigate risks.
-
Import Duties and Taxes: Understand the tariffs and taxes applicable to imported goods, as these can significantly increase overall costs.
-
Cultural Differences in Business Practices: Negotiation styles and pricing expectations can vary by region. Understanding local customs can facilitate smoother negotiations.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
The prices associated with sheet metal finishes can vary significantly based on the factors discussed. Buyers are encouraged to obtain tailored quotes from multiple suppliers and consider the comprehensive cost structure to make informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sheet metal finishes With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Sheet Metal Finishes
In the realm of manufacturing and metal fabrication, selecting the right finishing process can significantly impact the durability, aesthetics, and overall performance of products. While sheet metal finishes offer a variety of options tailored to specific applications, alternative methods and technologies exist that can achieve similar goals. This section explores these alternatives, providing a comprehensive comparison to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Sheet Metal Finishes | Powder Coating | Anodizing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | High durability; scratch and fade resistant | Enhanced corrosion resistance; aesthetic appeal |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on finish class | Generally cost-effective for large runs | Higher initial cost, but long-term savings due to durability |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and expertise | Relatively straightforward application process | Requires precise control during the electrochemical process |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance if properly applied | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Moderate maintenance; may require re-coating |
| Best Use Case | Automotive, aerospace, and consumer products | Industrial equipment, furniture, and appliances | Aerospace components, architectural applications, and consumer electronics |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Powder Coating
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to metal surfaces, which is then cured under heat to create a tough, protective layer. This method is particularly advantageous for large-scale manufacturing due to its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Its high durability makes it suitable for industrial equipment and consumer products, while its resistance to scratches and fading enhances the longevity of the finish. However, the initial setup can be capital-intensive, and it may require additional equipment for effective application.
2. Anodizing
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminum and other metals, significantly improving corrosion resistance and surface hardness. This method is favored in industries like aerospace and architecture due to its aesthetic qualities and ability to be dyed in various colors. While anodizing offers long-term durability and minimal maintenance, it typically involves higher initial costs and requires specialized equipment and expertise for implementation. Its complexity may also limit its application to specific types of metals.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When considering sheet metal finishes versus alternative solutions like powder coating and anodizing, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific project requirements, including performance needs, budget constraints, and the intended application. Each finishing method has its strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to align the choice with the end-use of the product. By thoroughly assessing factors such as durability, cost, and maintenance, buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their immediate needs but also provide long-term value.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sheet metal finishes
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Sheet Metal Finishes?
When selecting sheet metal finishes, understanding the critical specifications is essential for ensuring product quality and performance. Here are some key properties that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the metal used, which impacts its durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications. For example, stainless steel (such as 304 or 316) is often preferred for its excellent corrosion resistance, especially in environments like the Middle East or coastal areas. Understanding material grades helps buyers select the right type for their industry requirements, influencing long-term performance and maintenance costs.
2. Surface Finish Type
The surface finish type can significantly affect aesthetic appeal and functionality. Options range from raw finishes, which have no additional treatment, to anodized or powder-coated finishes that enhance durability and appearance. The choice of finish type can influence factors like adhesion for paints or coatings, making it crucial for buyers to align their selection with the intended application.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the metal part. Tighter tolerances often indicate higher precision, which is vital for components used in industries like aerospace or automotive where safety and performance are critical. Buyers need to specify tolerances to ensure compatibility with other components and systems, ultimately affecting the overall quality of the final product.
4. Thickness
Thickness is a critical property that determines the strength and weight of the sheet metal. Different applications require varying thicknesses; for instance, automotive parts may need thinner sheets for weight reduction, while structural components may require thicker sheets for strength. Understanding the required thickness helps in optimizing material usage and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is essential for extending the lifespan of metal products, especially in harsh environments. The choice of finish can enhance corrosion resistance; for example, anodizing aluminum creates a protective oxide layer. Buyers should assess the environmental conditions their products will face to select finishes that offer the necessary level of protection.
6. Finish Class
Sheet metal finishes can be classified into different categories, such as Class A, B, and C. Class A finishes are the highest quality, often used in visible applications requiring a flawless appearance, while Class C finishes are more basic and less expensive. Understanding these classes helps buyers determine the appropriate level of finish for their projects, balancing cost with quality requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Sheet Metal Finishing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and purchasing processes. Here are some common trade terms relevant to sheet metal finishes:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in another company’s final product. Understanding OEM relationships can aid buyers in sourcing high-quality components that meet specific standards, which is crucial in industries like automotive and aerospace.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and manage inventory effectively, ensuring they meet production needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. A well-prepared RFQ can expedite the procurement process, allowing for better comparison of suppliers and pricing, ultimately leading to more informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in international transactions, as they clarify the logistics and legalities involved in shipping sheet metal products.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays, allowing businesses to maintain their competitive edge.
6. Surface Treatment
Surface treatment encompasses various processes applied to the surface of sheet metal to enhance its properties, such as corrosion resistance or aesthetic appeal. Recognizing different surface treatments helps buyers select the right finish for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance in their applications.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing sheet metal finishes, aligning their choices with operational requirements and market standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sheet metal finishes Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in Sheet Metal Finishes
The global sheet metal finishes market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand across various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, international B2B buyers are focusing on advanced finishing techniques that enhance product durability and aesthetic appeal. For instance, the automotive industry is leaning towards anodizing and powder coating for their ability to provide corrosion resistance and improved surface quality.
Emerging technologies, including automated finishing processes and digital supply chain management systems, are reshaping sourcing strategies. These advancements allow buyers to track quality and consistency in finishes while optimizing lead times. In addition, the rise of Industry 4.0 is pushing manufacturers to adopt smart factories, integrating IoT and AI to enhance operational efficiency. International buyers, particularly in Germany and Saudi Arabia, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide detailed certifications and transparency in their processes, ensuring adherence to quality standards.
Furthermore, the demand for customized finishes is on the rise, as companies strive to differentiate their products in competitive markets. Buyers are also increasingly aware of the implications of sourcing decisions, focusing on suppliers that can offer a comprehensive range of finishes tailored to specific applications. This trend is particularly pronounced in the Middle East and Europe, where quality and innovation are paramount.
How is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Sheet Metal Finishes?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become crucial considerations for international B2B buyers in the sheet metal finishes sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led to a growing demand for finishes that minimize waste and energy consumption. For instance, powder coating is favored not only for its aesthetic qualities but also for its low VOC emissions and recyclability.
Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly coatings. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and LEED for green building materials are becoming essential criteria for selecting suppliers. Additionally, ethical supply chains are gaining traction, with buyers demanding transparency regarding labor practices and sourcing conditions.
In regions such as Europe and South America, where regulatory frameworks around sustainability are tightening, companies must adapt to these expectations or risk losing market share. The trend towards sustainability is not merely a compliance issue; it is increasingly seen as a competitive advantage that can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What is the Historical Context of Sheet Metal Finishes in B2B Markets?
The evolution of sheet metal finishes has been shaped by technological advancements and changing market demands. Initially, finishes were primarily functional, focusing on corrosion resistance and basic aesthetic qualities. However, as industries evolved, particularly post-World War II, the emphasis shifted towards more refined finishes that not only serve practical purposes but also enhance the visual appeal of products.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of advanced coatings and finishes, such as powder coating and anodizing, revolutionized the industry. These innovations provided enhanced durability and customization options, catering to the growing demand for high-quality products in sectors like automotive and electronics. Today, the sheet metal finishes market continues to adapt, with an increasing focus on sustainability and technological integration, ensuring that suppliers can meet the complex needs of international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sheet metal finishes
-
How do I select the right sheet metal finish for my project?
Choosing the appropriate sheet metal finish involves evaluating the specific requirements of your project, including environmental conditions, aesthetic preferences, and functionality. Consider factors such as corrosion resistance, surface texture, and the intended application (e.g., automotive, medical). Consult with suppliers who can provide detailed information on various finishes, including their advantages and limitations. Additionally, you may want to request samples to assess how each finish aligns with your project’s needs. -
What is the best sheet metal finish for outdoor applications?
For outdoor applications, finishes that offer superior corrosion resistance are essential. Anodizing, powder coating, and electroplating are excellent options, as they provide a protective layer against environmental factors. Anodized aluminum, for instance, is renowned for its durability and resistance to UV rays. When selecting a finish, consider the local climate conditions, such as humidity and salt exposure, which can significantly impact the longevity of the finish. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for sheet metal finishes?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) vary by supplier and the type of finish required. Generally, suppliers may impose an MOQ to ensure cost-effectiveness and efficient production. For specialized finishes, the MOQ might be higher due to the additional processing involved. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your budget and project timelines. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in sheet metal finishes?
To guarantee quality assurance in your sheet metal finishes, choose suppliers with established QA processes. Request documentation of their quality control measures, including certifications and testing methods. Regular inspections and adherence to industry standards, such as ISO certifications, can provide additional assurance. Additionally, consider implementing your own QA checks by requesting samples or conducting on-site inspections during production. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing sheet metal finishes internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms upfront and ensure they align with your budget and cash flow requirements. Additionally, consider negotiating favorable terms that protect both parties, such as partial payments tied to production milestones. -
What logistical considerations should I be aware of when importing sheet metal finishes?
When importing sheet metal finishes, logistical considerations include shipping methods, customs regulations, and lead times. Choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping to navigate customs clearance efficiently. Be aware of the import tariffs and duties applicable in your country, which can affect overall costs. Additionally, plan for potential delays due to customs inspections or shipping disruptions, especially during peak seasons. -
How do I vet suppliers for sheet metal finishes?
Vetting suppliers involves evaluating their experience, reputation, and capacity to meet your specific requirements. Start by checking their certifications, client testimonials, and case studies. Conducting site visits or virtual tours can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Additionally, consider requesting references from other B2B buyers in your industry to gauge their reliability and service quality. -
Can I customize sheet metal finishes to suit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for sheet metal finishes. Customization can include specific colors, textures, and finishes tailored to your project requirements. When discussing your needs with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and examples of desired outcomes. Keep in mind that custom finishes may impact lead times and costs, so it’s essential to clarify these factors early in the negotiation process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Sheet Metal Finishes Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. TFG USA – Sheet Metal Finishes Guide
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: 10 Types of Sheet Metal Finishes: 1. Raw or Rough Finish – No finishing applied, used for corrosion-resistant materials. 2. Electroplating – Applying a layer of metal for aesthetic and protective purposes. 3. Bead Blasting – Uses sand or glass beads for a matte finish, removing blemishes. 4. Anodizing – Electrochemical process for corrosion resistance, available in three types (Type I, II, III). 5…
2. Protolabs – Sheet Metal Fabrication Services
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers a comprehensive sheet metal fabrication service with a variety of finishing options. Key details include: 1. **Surface Finishes**: Two main options – Orbital Sander (for internal components) and Straight Grain/Brushed (for cosmetic applications). 2. **Powder Coating**: Provides a durable finish with custom colors, available in 50 stocked colors. 3. **Plating and Coatings**: Option…
3. Uptive MFG – Key Materials in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: uptivemfg.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Key Materials in Sheet Metal Fabrication: Steel (Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Galvanized Steel), Aluminum, Copper, Brass. Finishing Options for Steel: Powder Coating, Electroplating, Anodizing (for Stainless Steel), Hot-Dip Galvanizing (for Carbon Steel), Polishing. Finishing Options for Aluminum: Anodizing, Powder Coating, Brushing, Clear Coating. Finishing Options for Copper and Brass: Polishi…
4. Timesavers – Sheet Metal Finishing Machines
Domain: timesaversint.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Timesavers offers a range of machines for sheet metal finishing, including rotary brush machines and abrasive belt systems. Key features include: non-directional finishing, various finishes such as Hairline, Duplo, Microlon, and brushed finishes, and the ability to achieve No. 3 or No. 4 finishes with abrasive belts ranging from grit 120 to 320. Specific machine series include the 62 series for co…
5. Protocase – Bare Metal Finish Options
Domain: protocase.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Bare Metal Finish options include: 1. No Finish: CNC Sheet Metal – De-burred with no additional finishing, best for functional parts, not decorative, minor surface scratches expected. 2. Grained Finish: CNC Sheet Metal – Aesthetically superior, applied to accessible flat exterior faces, can be digitally printed and silkscreened. 3. Vibratory Finish: CNC Sheet Metal – Smooths and imparts a random f…
6. Metal Supermarkets – Metal Finishing Processes
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Different types of metal finishing processes include: 1. Plating (or conversion coatings) – Involves covering a substrate with thin layers of another metal (e.g., zinc, nickel, chromium, cadmium) to improve durability, surface friction, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics. 2. Electroplating – Immerses the component in a bath with metal ions and applies direct current to deposit ions on the metal …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sheet metal finishes
In navigating the diverse landscape of sheet metal finishes, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to enhance their procurement processes. Understanding the various finishing options—ranging from anodizing and powder coating to electroplating and abrasive blasting—allows businesses to select finishes that not only meet functional and aesthetic requirements but also align with industry standards. This knowledge is vital for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring product longevity, particularly in sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
The value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated; it fosters strong supplier relationships, enhances negotiation leverage, and ultimately drives cost savings. As the global market continues to evolve, the demand for high-quality, customized sheet metal finishes will only grow.
Looking ahead, buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should remain proactive in exploring innovative finishing technologies and suppliers. Engaging with industry experts and leveraging comprehensive resources can empower organizations to stay ahead of market trends. Connect with trusted partners today to unlock new opportunities and ensure your projects achieve the highest standards in quality and performance.