Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Sheet Metal Fastening Methods
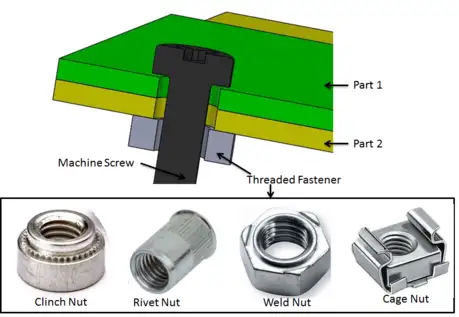
Selecting optimal sheet metal fastening methods is critical for ensuring structural integrity, assembly efficiency, and long-term reliability in fabricated components. At Honyo Prototype, our engineering-driven Sheet Metal Fabrication services integrate deep expertise in fastening technologies—from precision PEM® inserts and self-clinching hardware to advanced welding studs and structural rivets—to solve complex joining challenges across aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. We prioritize method selection based on your specific material thickness, load requirements, and environmental exposure, ensuring every fastener enhances rather than compromises your design’s performance.
Our end-to-end capabilities extend beyond fabrication to seamless prototyping and low-volume production, backed by rigorous quality control and material traceability. To accelerate your development cycle, Honyo Prototype offers an Online Instant Quote platform that delivers precise, transparent pricing in seconds—not days—by analyzing your uploaded STEP or DWG files against real-time production parameters. This eliminates traditional quoting bottlenecks while maintaining engineering accuracy.
The efficiency difference is quantifiable:
| Quoting Process | Traditional Workflow | Honyo Prototype Instant Quote |
|---|---|---|
| Time to Pricing | 24–72 hours | Under 60 seconds |
| Engineering Review | Manual assessment | Automated DFM validation |
Leverage our fastening proficiency and instant quoting to transform your sheet metal designs from concept to certified hardware faster. Submit your files today at honyoprototype.com/quote for immediate cost analysis and manufacturability feedback.
Technical Capabilities
Sheet Metal Fastening Methods – Technical Specifications
The following table outlines key technical specifications for common sheet metal fastening methods—laser cutting, bending, and welding—with consideration to material compatibility for Aluminum, Steel, ABS, and Nylon. These processes are critical in precision fabrication and assembly within manufacturing environments.
| Process | Tolerances | Minimum Feature Size | Material Compatibility | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | ±0.1 mm | 0.5 mm (hole diameter) | Aluminum, Steel (mild and stainless), ABS (limited), Nylon (not recommended) | High-precision cutting; not suitable for thermoplastics due to melting and charring |
| Bending | ±0.25° angular, ±0.2 mm | Bend radius ≥ material thickness | Aluminum, Steel (good springback control), ABS (possible with heated dies), Nylon (poor due to low stiffness) | Requires tooling (punch/die); not ideal for brittle or flexible polymers |
| Welding | ±0.5 mm alignment | N/A | Aluminum (TIG/MIG), Steel (MIG, spot, laser), ABS (ultrasonic/spot welding only), Nylon (vibration/ultrasonic welding) | Thermoplastics require specialized joining; not fusion-welded like metals |
Notes on Material Behavior:
Aluminum: Excellent for laser cutting and welding (with proper shielding gas). Bends well with controlled springback; requires clean edges to avoid weld defects.
Steel (Carbon & Stainless): Ideal for all three processes. High weldability and formability; laser cutting provides clean, burr-free edges.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Can be laser cut with CO₂ lasers but risks melting and fume generation. Not suitable for traditional welding; limited to ultrasonic or adhesive joining. Bending possible with heat-assisted forming.
Nylon (Polyamide): Poor candidate for laser cutting and conventional welding due to low melting point and high thermal expansion. Joining typically done via mechanical fasteners, adhesives, or ultrasonic welding.
These specifications are applicable for industrial-grade equipment and assume proper fixturing, material preparation, and process controls. Selection of method depends on design requirements, production volume, and material properties.
From CAD to Part: The Process
Honyo Prototype executes sheet metal fastening method selection and implementation through a tightly integrated digital workflow designed for precision and manufacturability. This process ensures fastening solutions align with structural requirements, cost targets, and assembly efficiency from initial design to final delivery.
Upon CAD file upload, our system immediately analyzes geometric features relevant to fastening. The AI Quote engine identifies critical parameters including material thickness, hole patterns, clearance zones, and proximity to bends. It cross-references these against Honyo’s proprietary fastening database—which catalogs hundreds of methods including PEM® inserts, self-clinching hardware, weld studs, blind rivets, and threaded standoffs—to generate real-time cost and lead time estimates. Fastener selection directly impacts pricing; for example, PEM inserts in 1.5mm aluminum may add 12% to part cost versus standard tapped holes but reduce assembly time by 30%.
The DFM phase rigorously validates fastening feasibility. Our engineers review AI-generated flags such as insufficient material thickness for self-clinching hardware or inadequate bend clearance for rivet guns. We provide specific alternatives: if a design specifies weld nuts on a 0.8mm sheet (below the 1.0mm minimum for reliable welding), the DFM report recommends switching to PEM SMS screws with revised hole tolerances. All fastening-related DFM feedback includes technical justification per ISO 13920 dimensional standards and ASME B18.2.1 fastener specifications.
During production, fastening method execution follows strict protocols. CNC punch/laser operations incorporate precise hole tolerances per fastener type (e.g., +0.05/-0.00mm for PEM inserts versus +0.10/-0.00mm for rivets). In the fastening cell, automated feeders verify fastener material grade (e.g., 303 stainless vs. 1215 steel) against the work order, while torque-controlled presses document insertion force curves for traceability. Critical assemblies undergo pull-test validation per ASTM F606.
Delivery includes comprehensive fastening documentation. Each shipment contains a Fastening Compliance Report detailing installed hardware specifications, process validation data, and conformity to the approved DFM. For high-reliability sectors like medical or aerospace, we provide PPAP Level 3 documentation including fastener material certs and process capability studies (CpK ≥1.33).
This closed-loop approach ensures fastening methods are not merely selected but validated at every stage—from AI-driven initial assessment through metrology-backed delivery—minimizing assembly line disruptions and liability risks for our clients.
The table below summarizes how key fastening methods are evaluated during Honyo’s DFM phase:
| Fastening Method | Critical DFM Checkpoints | Minimum Material Thickness | Typical Tolerance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Clinching PEM | Bend proximity (>3xD), hole concentricity, material hardness | 1.0mm | +0.05/-0.00mm |
| Weld Nuts/Studs | Sheet flatness, weld zone accessibility | 0.9mm | ±0.10mm |
| Blind Rivets | Backside clearance, grip range validation | 0.7mm | +0.10/-0.00mm |
| Threaded Standoffs | Counterbore depth, torque retention | 1.2mm | ±0.05mm |
Start Your Project

Explore reliable sheet metal fastening solutions engineered for precision and durability. From PEM fasteners to weld studs and custom configurations, our expertise ensures optimal assembly performance for your sheet metal applications.
All manufacturing is supported by our ISO-certified factory in Shenzhen, where tight process control and advanced tooling deliver consistent quality for prototyping and low-volume production.
Contact Susan Leo for technical guidance or project support.
Email: [email protected]
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.