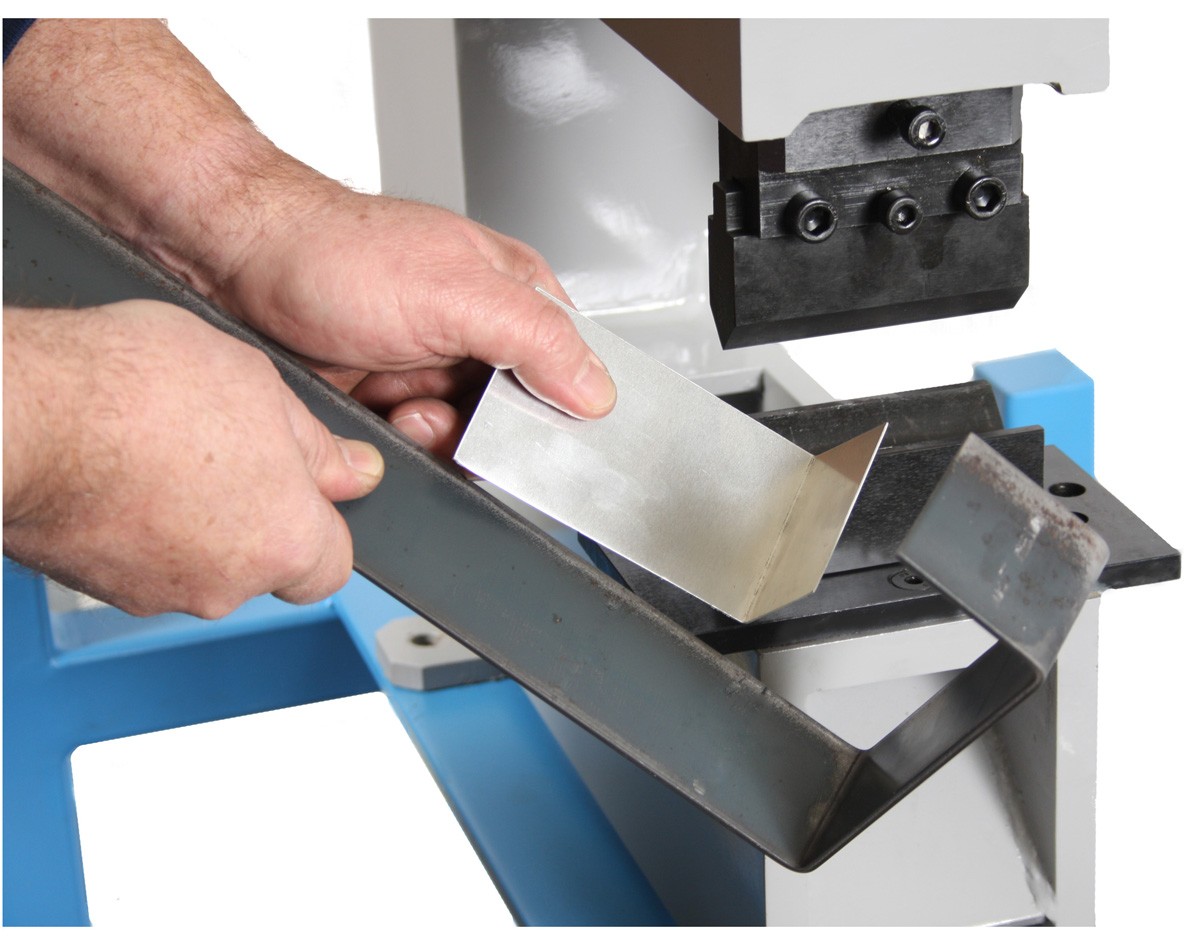
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sheet metal bending dies
In the ever-evolving landscape of metal fabrication, sourcing high-quality sheet metal bending dies presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. These essential tools are critical for achieving precision in bending operations, yet navigating the myriad options available can be daunting. This guide delves into the various types of sheet metal bending dies, their applications across different industries, and best practices for supplier vetting to ensure optimal quality and reliability.
Understanding the nuances of bending dies—from general-purpose 90-degree dies to specialized acute and gooseneck designs—can greatly enhance operational efficiency and product quality. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost considerations, material compatibility, and the importance of adjusting press brake parameters to reduce wear and extend the lifespan of tooling.
By empowering buyers with in-depth knowledge and actionable insights, this comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for decision-makers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Nigeria. With the right information, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs, ensuring they select the most suitable sheet metal bending dies for their specific applications.
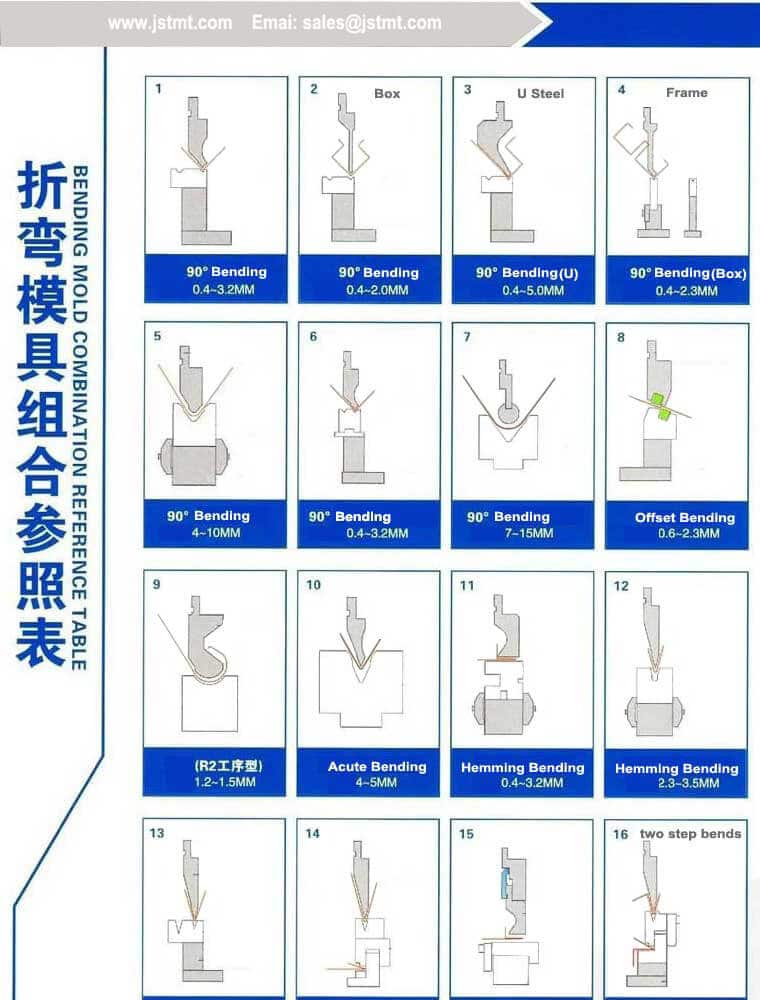
Understanding sheet metal bending dies Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90-Degree Press Brake Dies | Designed for forming standard 90-degree bends. | General metal fabrication, HVAC, automotive. | Pros: Versatile for many applications; easy to use. Cons: Limited to 90-degree bends only. |
| Acute Press Brake Dies | Allows for shallow bends, typically 30 degrees or less. | Aerospace, precision engineering. | Pros: Ideal for intricate designs; minimal material wastage. Cons: Requires skilled operators for precision. |
| Gooseneck Dies | Features a unique curve to accommodate deeper bends. | Heavy machinery, structural components. | Pros: Excellent for complex shapes; reduces need for secondary operations. Cons: Higher tooling costs; may require specialized machinery. |
| Hemming Dies | Designed to fold the edge of sheet metal over itself. | Automotive, appliance manufacturing. | Pros: Increases strength and aesthetics; improves safety. Cons: Can be more complex to set up; requires precise alignment. |
| 3-Way and 4-Way Bottom Dies | Allows for multiple bending angles and configurations. | Versatile applications across industries. | Pros: Flexible usage for various bends; reduces tooling changeover time. Cons: May require additional training for staff to operate effectively. |
What Are the Characteristics of 90-Degree Press Brake Dies?
90-degree press brake dies are essential tools in metal fabrication, specifically designed to create standard right-angle bends in sheet metal. Their simplicity and effectiveness make them a staple in various industries, including HVAC and automotive manufacturing. When purchasing these dies, buyers should consider the material thickness they will work with, as the die’s design directly impacts the bending process. Additionally, understanding the tonnage requirements of the press brake machine is crucial for optimal performance.
How Do Acute Press Brake Dies Differ from Other Types?
Acute press brake dies are characterized by their ability to create bends of 30 degrees or less, making them particularly suited for industries requiring precision, such as aerospace and high-end engineering applications. These dies allow for intricate designs while minimizing material waste. Buyers should be aware that operating acute dies often requires skilled labor to ensure precision and accuracy, which could influence labor costs and training requirements.
What Are the Benefits of Using Gooseneck Dies?
Gooseneck dies are specifically designed for producing deeper bends and complex shapes in sheet metal. Their unique curvature allows for more flexibility in design, making them ideal for heavy machinery and structural components. However, buyers should consider the higher initial investment in tooling and potential compatibility issues with existing machinery. The long-term benefits often justify the costs, especially when high-quality, complex parts are needed.
Why Choose Hemming Dies for Your Production Needs?
Hemming dies are designed to fold the edge of sheet metal over itself, enhancing both strength and aesthetics. Commonly used in the automotive and appliance industries, they improve safety by eliminating sharp edges. Buyers must consider the complexity of setup and the need for precise alignment when implementing hemming dies. The investment in these dies can yield significant returns in product quality and customer satisfaction.
How Do 3-Way and 4-Way Bottom Dies Enhance Flexibility?
3-way and 4-way bottom dies provide the advantage of accommodating multiple bending angles and configurations, making them versatile tools across various applications. This flexibility can significantly reduce the time and effort required for tooling changeovers, which is a critical consideration for manufacturers looking to optimize production efficiency. However, the complexity of operating these dies may necessitate additional training for staff, which should be factored into the overall cost of investment.
Key Industrial Applications of sheet metal bending dies
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sheet metal bending dies | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Forming chassis components and body panels | Enhances structural integrity and reduces assembly time | Precision requirements, material compatibility, and lead times |
| HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning) | Creating ducts and fittings | Improves energy efficiency and airflow in installations | Custom die designs, durability for repeated use, and cost-effectiveness |
| Aerospace | Fabricating aircraft components and enclosures | Ensures safety and compliance with stringent regulations | Lightweight materials, precision tolerances, and certification standards |
| Construction | Producing structural steel components and reinforcements | Increases strength and longevity of structures | Material specifications, load-bearing capacities, and local regulations |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing enclosures for devices | Protects sensitive components and enhances aesthetics | Surface finish requirements, design complexity, and production scalability |
How Are Sheet Metal Bending Dies Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, sheet metal bending dies are essential for forming chassis components and body panels. These dies allow manufacturers to create precise bends that enhance the structural integrity of vehicles while also reducing assembly time. Buyers in this sector must consider the precision of the dies to ensure compatibility with high-strength steel and aluminum materials commonly used in modern vehicles. Additionally, the ability to customize dies for specific designs can significantly impact production efficiency and cost.
What Role Do Sheet Metal Bending Dies Play in HVAC Applications?
Sheet metal bending dies are critical in the HVAC sector for creating ducts and fittings that optimize airflow and energy efficiency. The ability to produce accurate bends ensures that installations fit together seamlessly, reducing air leakage and improving overall system performance. Buyers should prioritize sourcing dies that are durable enough for high-volume production and capable of handling various sheet metal thicknesses. Customization options are also essential for accommodating unique design requirements in different geographical markets.
How Are Sheet Metal Bending Dies Utilized in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In aerospace manufacturing, sheet metal bending dies are used to fabricate components and enclosures that must adhere to stringent safety and regulatory standards. The precision offered by these dies is crucial for ensuring that parts meet the necessary specifications for weight and strength. Buyers in this industry must consider the lightweight materials used, such as aluminum and titanium, and ensure that the dies can accommodate these materials without compromising quality. Certification for aerospace applications is also a significant factor in sourcing decisions.
What Are the Applications of Sheet Metal Bending Dies in Construction?
In the construction industry, sheet metal bending dies are used to produce structural steel components and reinforcements, which are vital for enhancing the strength and longevity of buildings. These dies facilitate the efficient bending of steel plates and bars, allowing for the creation of custom shapes that meet specific engineering requirements. Buyers need to focus on the load-bearing capacities of the components produced and ensure compliance with local building regulations, which can vary significantly across regions.
How Are Sheet Metal Bending Dies Applied in Consumer Electronics?
In consumer electronics, sheet metal bending dies are employed to manufacture enclosures for devices, protecting sensitive components while enhancing product aesthetics. The precision of the bends is crucial for ensuring that the enclosures fit correctly and provide adequate protection against environmental factors. Buyers should look for dies that can produce intricate designs with high-quality surface finishes. Additionally, scalability in production is essential for meeting the demands of rapidly evolving consumer electronics markets.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sheet metal bending dies’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Achieving Accurate Bend Angles
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges in achieving precise bend angles when using sheet metal bending dies. This issue is particularly pronounced when working with materials that exhibit springback, such as stainless steel and aluminum. If the bending dies are not correctly specified or if the press brake settings are off, manufacturers may end up with inconsistent product quality, leading to increased scrap rates and higher operational costs. This can also result in project delays, which can be detrimental to client relationships.
The Solution: To overcome this problem, it is essential to select the right type of bending die for the specific material and application. For instance, using a die with an acute angle can help achieve sharper bends, while a gooseneck punch can be beneficial for forming channels. Additionally, it’s crucial to adjust the press brake settings correctly—particularly the depth of punch travel—to avoid bottoming out and causing premature wear on the tooling. Buyers should consult with suppliers about the material properties and desired bend angles to ensure they are using dies that compensate for springback effectively. Implementing a rigorous quality control process to measure the angles post-bend can also help maintain consistency.
Scenario 2: Tooling Wear and Maintenance Challenges
The Problem: Another common pain point for buyers is the rapid wear and tear of bending dies, which can lead to frequent replacements and downtime. Factors contributing to this issue include using inappropriate die materials, inadequate maintenance, or incorrect operational settings. This not only impacts production efficiency but also inflates costs, as buyers must allocate additional budget for tooling replacements and repairs, thus straining their overall operational budget.
The Solution: To extend the lifespan of bending dies, buyers should consider investing in high-quality materials such as those that undergo flame hardening or are specifically designed for high-wear applications. Regular maintenance practices should be established, including cleaning and inspecting dies after each use to prevent the buildup of debris that can cause damage. Buyers should also train their operators to understand the importance of using the right tonnage settings, as excessive force can accelerate wear. Creating a maintenance schedule and engaging with suppliers for periodic assessments can also enhance the longevity and performance of the dies.
Scenario 3: Sourcing Compatible Dies for Diverse Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges in sourcing sheet metal bending dies that are compatible with their existing press brake machinery. This is especially problematic for companies that operate a range of machines from different manufacturers, leading to complications in compatibility. Incompatibility can result in operational inefficiencies, as the wrong dies may not fit correctly or function as intended, leading to production delays and increased labor costs.
The Solution: To mitigate sourcing issues, buyers should conduct thorough research on the specifications of their press brake machines before purchasing dies. This includes understanding the ram stroke, tonnage capacity, and die holder configuration. Engaging directly with manufacturers or suppliers to obtain recommendations based on their machinery can provide valuable insights. Additionally, buyers can consider investing in modular die systems that offer flexibility for various applications. Building strong relationships with suppliers can also lead to better support when it comes to sourcing dies that meet specific operational needs, ensuring that the company can maintain productivity without costly interruptions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sheet metal bending dies
What Are the Key Materials for Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
When selecting materials for sheet metal bending dies, several factors such as durability, cost, and compatibility with specific applications must be considered. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these dies: Tool Steel, Aluminum, Stainless Steel, and Composite Materials.
How Does Tool Steel Perform as a Material for Bending Dies?
Key Properties: Tool steel is known for its high hardness, wear resistance, and ability to maintain a sharp cutting edge. It typically withstands high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of tool steel is its exceptional durability, which results in a longer lifespan for the dies. However, it is relatively expensive and can be challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing complexity. Tool steel is ideal for high-volume production where precision is crucial.
Impact on Application: Tool steel dies are particularly effective for bending harder metals and can handle the stresses involved in high-tolerance operations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A681 for tool steels is essential. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East often prefer tool steel dies due to their reliability in industrial applications.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum for Bending Dies?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It is often used in applications requiring lower weight and easier handling.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and ease of machining, which reduces manufacturing time. However, it lacks the durability of tool steel and may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications, limiting its lifespan in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum dies are particularly effective for softer materials and are often used in industries like HVAC and automotive for lighter components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is important. Buyers in regions like Africa may prefer aluminum for its lower cost, while European buyers may focus on its recyclability.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare for Bending Dies?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and strength. It can withstand harsh environments, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals. However, it is more expensive than carbon steel and can be more difficult to machine.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel dies are particularly useful for bending materials that require hygiene and cleanliness, such as in food and medical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM A276 is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East may prioritize stainless steel for its durability in high-temperature environments.
What Role Do Composite Materials Play in Bending Dies?
Key Properties: Composite materials combine various substances to achieve desirable properties such as reduced weight and enhanced strength. They can be tailored for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of composites is their versatility and potential for lower weight, which can improve handling and reduce machinery wear. However, they can be more expensive and may not offer the same level of durability as metals.
Impact on Application: Composite dies are often used in specialized applications where weight and corrosion resistance are critical, such as in aerospace or automotive industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific certifications for composites in their region. In Europe, for instance, adherence to standards like EN 15534 is important.
Summary Table of Material Comparisons
| Material | Typical Use Case for sheet metal bending dies | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tool Steel | High-volume production of hard metals | Exceptional durability and longevity | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Bending softer metals in HVAC and automotive | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Limited durability in heavy-duty use | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and medical applications | Corrosion resistance and strength | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Composite Materials | Specialized applications in aerospace | Lightweight and customizable | Potentially higher cost and lower durability | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials used in sheet metal bending dies, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sheet metal bending dies
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
The manufacturing of sheet metal bending dies involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and functionality of the final product. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality tooling that meets their operational needs.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used for Bending Dies?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality steel is typically chosen for bending dies due to its excellent strength and durability. Common materials include tool steels such as D2, A2, or S7, which are selected based on their hardness and wear resistance.
Before fabrication begins, the raw material undergoes rigorous inspections to ensure it meets specified mechanical properties and chemical compositions. This stage is crucial for preventing defects in the finished dies.
How Are Bending Dies Formed?
Once the material is prepared, the next stage is forming. This process involves cutting and shaping the steel into the desired die profile using techniques such as:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is widely employed for precision cutting and shaping. This technique allows for intricate designs and ensures high repeatability.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): This method is utilized for creating complex geometries that are difficult to achieve through traditional machining. EDM is especially beneficial for creating intricate shapes and fine details in the die.
- Grinding: Grinding processes are applied to achieve tight tolerances and smooth surfaces. This step enhances the die’s performance and reduces wear during operation.
What Is Involved in the Assembly of Bending Dies?
The assembly stage combines various components to form a complete die set. This can include the upper punch, lower die, and any additional features such as alignment pins and support structures. Proper alignment and fitment are critical during assembly to ensure consistent performance.
Quality checks are integrated into the assembly process to verify that all components meet design specifications. This might include visual inspections and dimensional checks using calibrated measuring tools.
Finishing: What Are the Final Treatments for Dies?
The finishing stage typically involves surface treatments to enhance the die’s performance and longevity. Common finishing processes include:
- Heat Treatment: To increase hardness and durability, dies often undergo heat treatment processes such as quenching and tempering.
- Coating: Applying specialized coatings, such as titanium nitride (TiN) or chromium plating, can significantly reduce friction and wear, thus prolonging the life of the die.
These finishing touches not only improve performance but also help in reducing maintenance costs over time.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of sheet metal bending dies to ensure they meet industry standards and customer expectations. Implementing robust QA practices helps mitigate risks associated with defects and performance issues.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, understanding relevant international standards is vital. The ISO 9001 standard for quality management systems is a foundational requirement that ensures manufacturers have robust processes in place to meet customer and regulatory requirements.
In addition, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for European markets) or API specifications (for the oil and gas sector) are crucial indicators of compliance and quality. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold the necessary certifications relevant to their industry.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Effective quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage assesses raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers should have protocols to verify material specifications and quality.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections during the manufacturing process help catch defects early. This can include dimensional checks and surface inspections at various stages of production.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a comprehensive inspection should occur to ensure the final product meets all specifications and quality standards.
Each of these checkpoints should be documented, providing traceability and accountability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers have several avenues to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturer’s QA processes firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation, inspecting machinery, and evaluating workforce capabilities.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including inspection records and material certifications, provides insight into the supplier’s QA practices.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures, ensuring compliance with international standards.
What Are the QC Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers must navigate specific nuances in quality control that can vary by region. For example, buyers from Africa or South America might face different regulatory requirements compared to their European counterparts. Understanding these differences is essential for ensuring compliance and quality.
Additionally, cultural differences in business practices can influence quality expectations. Buyers should foster open communication with suppliers to clarify quality standards and requirements, ensuring alignment throughout the manufacturing process.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for sheet metal bending dies empowers B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. By prioritizing suppliers that adhere to international standards and maintain rigorous quality control measures, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sheet metal bending dies’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide provides a structured checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure sheet metal bending dies. The goal is to streamline the sourcing process by highlighting essential steps that ensure quality, compatibility, and supplier reliability. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions that meet their specific operational needs.
1. Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes the type of metal to be bent, the thickness of the material, and the desired bend angles.
– Consider the specific applications, such as whether you need acute or obtuse bends, as these factors will significantly influence the type of dies you require.
2. Assess Your Production Needs
Evaluate the volume of production and the frequency of use for the bending dies. This assessment will help determine whether you need general-purpose dies or specialized tools.
– For high-volume production, investing in more durable, high-quality dies may reduce long-term costs associated with frequent replacements.
3. ✅ Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications that comply with international quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management.
– Check for any industry-specific certifications that might apply to your region or sector, as this can enhance the credibility of the supplier.
4. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, conduct a thorough vetting of potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Look for suppliers with a proven track record in providing bending dies that meet your specifications and deadlines. Don’t rely solely on their website; seek independent reviews and testimonials.
5. Compare Product Offerings
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, compare their product offerings. Pay attention to the variety of dies available, including specialized options like gooseneck or hemming dies.
– Assess the compatibility of their dies with your existing machinery and the flexibility of their offerings to adapt to future needs.
6. Request Samples and Conduct Tests
Whenever possible, request samples of the bending dies before making a bulk order. This allows you to test the dies with your materials to ensure they meet your specifications.
– Testing helps identify any potential issues related to fit, finish, or performance, which can save time and costs associated with returns or replacements.
7. Negotiate Terms and Finalize Orders
After selecting a supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. Be clear about your expectations to avoid misunderstandings.
– Ensure that the terms include warranty coverage and options for future orders, as this can provide peace of mind and establish a long-term relationship with the supplier.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing sheet metal bending dies, ensuring they select the right tools for their manufacturing needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sheet metal bending dies Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
When sourcing sheet metal bending dies, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
- Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality steel or specialized alloys may incur higher costs but offer enhanced durability and performance.
- Labor: Skilled labor is essential for the manufacturing process. Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographic location and the complexity of the dies being produced.
- Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient production processes can help reduce overhead, thus lowering overall costs.
- Tooling: The design and production of dies require precision tooling. Custom tooling may increase costs but can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the bending process.
- Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the dies meet industry standards and specifications. This can add to the costs but is essential for maintaining quality and minimizing defects.
- Logistics: Transportation and handling costs should not be overlooked, especially for international shipments. Factors like distance, shipping methods, and customs duties can significantly affect the final cost.
- Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding typical industry margins can help buyers assess the fairness of the quotes received.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Bending Dies?
Several factors can influence the pricing of sheet metal bending dies:
- Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often come with price breaks. Buyers should consider minimum order quantities (MOQ) that can maximize cost efficiency.
- Specifications and Customization: Custom designs tailored to specific applications can increase costs. Clearly defining requirements can mitigate unnecessary expenses.
- Materials: The type and quality of materials chosen will have a direct impact on pricing. High-strength materials or those requiring special treatment will cost more.
- Quality and Certifications: Suppliers that adhere to international quality standards (such as ISO certifications) may charge a premium, but this often translates to better reliability and performance.
- Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and location can also influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
- Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. The choice of terms affects who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and customs, thereby influencing the total cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Bending Die Procurement?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to optimize costs when sourcing sheet metal bending dies:
- Negotiation: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better negotiation outcomes. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts on larger orders or longer-term contracts.
- Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not only the purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to lower long-term expenses.
- Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East should be aware of additional costs such as tariffs and import taxes. Familiarize yourself with local regulations that may impact overall costs.
- Request Multiple Quotes: Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers can provide insight into market pricing and help identify the best value. Compare not just prices, but also terms, delivery times, and service options.
- Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in Europe or regions with developing manufacturing sectors, sourcing locally can reduce logistics costs and lead times, potentially resulting in a more favorable total cost.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of sheet metal bending dies is essential for B2B buyers. By considering various cost components, price influencers, and practical tips, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Always remember that prices may vary, and it’s advisable to seek indicative quotes while considering the overall value and service provided.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sheet metal bending dies With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Sheet Metal Bending Dies
When it comes to bending sheet metal, there are various solutions available to manufacturers and fabricators. While sheet metal bending dies are a popular choice due to their precision and efficiency, it is essential to explore alternative methods to identify the best fit for specific applications. This analysis will compare sheet metal bending dies with two viable alternatives: Press Brakes and Roll Forming.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Sheet Metal Bending Dies | Press Brakes | Roll Forming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for various angles | Versatile, ideal for complex bends | Continuous forming, efficient for long runs |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Higher upfront cost but versatile | Lower per-unit cost for large volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor for setup | Easier to operate with training | Requires specialized machinery and setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate; wear over time | Low, but needs regular calibration | Low; minimal wear with proper usage |
| Best Use Case | Custom parts with specific angles | Complex shapes and profiles | High-volume production of uniform shapes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Press Brakes?
Press brakes are a widely adopted alternative to sheet metal bending dies, offering versatility in bending angles and shapes. They utilize a punch and die setup, similar to bending dies, but allow for more complex bending operations, including multi-step bends. The initial investment for press brakes can be higher, but they often justify the cost through their ability to handle various materials and thicknesses. However, press brakes require trained operators to ensure optimal performance and safety during operation.
How Does Roll Forming Compare to Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
Roll forming is an efficient method for producing long lengths of uniform shapes, making it an excellent choice for high-volume manufacturing. This method involves continuously feeding sheet metal through a series of rollers that shape it into the desired profile. While roll forming can significantly reduce per-unit costs, it is less adaptable to custom shapes and angles compared to sheet metal bending dies. The initial setup for roll forming can be time-consuming and requires specialized machinery, making it less suitable for small production runs or one-off custom parts.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the right solution for sheet metal bending, it is crucial for B2B buyers to consider their specific production needs, budget constraints, and the complexity of the components they intend to manufacture. Sheet metal bending dies excel in precision and customization for intricate parts, while press brakes provide versatility for a variety of bending operations. In contrast, roll forming is ideal for high-volume production of uniform shapes. Ultimately, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sheet metal bending dies
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
Understanding the essential technical specifications of sheet metal bending dies is crucial for international B2B buyers. These properties directly impact the efficiency, accuracy, and longevity of your bending operations. Here are several critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material used in manufacturing bending dies, typically tool steel or carbide, affects durability and performance. Tool steel is common for its hardness and resistance to wear, while carbide provides superior longevity and strength, particularly for high-volume production. Selecting the right material grade can enhance die life and reduce replacement frequency, leading to cost savings. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions. Precision in tolerances ensures that the bends meet design specifications, which is vital for high-quality end products. Tight tolerances may be necessary for intricate designs, while looser tolerances might suffice for more straightforward applications. A thorough understanding of tolerance levels helps avoid production errors and rework. -
Bend Radius
The bend radius is the curvature of the bend formed by the die. It is critical for preventing material cracking, especially when working with materials like aluminum or stainless steel. A proper bend radius can also enhance the aesthetic quality of the finished product. Different materials may require specific bend radii, so understanding these requirements is essential for optimal performance. -
Die Size and Configuration
The size and configuration of the die are integral to the bending process. Dies can come in various shapes and sizes, influencing the types of bends achievable. A well-chosen die configuration enables efficient production and can minimize the risk of defects. Matching die size to the material thickness and type ensures that operations are carried out smoothly. -
Hardness
The hardness of a bending die, typically measured on the Rockwell scale, indicates its resistance to deformation and wear. A harder die will last longer under high-stress conditions but may also be more brittle. Understanding the hardness requirements based on the materials being bent can guide buyers in selecting the right dies for their operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Sheet Metal Bending Die Transactions?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEMs are companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help assess the quality and reliability of the bending dies offered. OEM products often meet strict quality standards and can be critical in ensuring compatibility with existing machinery. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should evaluate their production needs against the MOQ to avoid overstocking or underutilizing resources. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. It is a vital step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare pricing and terms. A well-crafted RFQ can streamline negotiations and lead to more favorable purchasing agreements. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for transportation, insurance, and risk at various stages of the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers navigate logistics and avoid misunderstandings in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when evaluating suppliers to ensure timely delivery and maintain operational efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing sheet metal bending dies, ultimately enhancing their production capabilities and competitiveness in the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sheet metal bending dies Sector
What are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Sheet Metal Bending Dies Sector?
The global sheet metal bending dies market is witnessing significant growth, driven by increased demand for precision-engineered components across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. As manufacturers seek to enhance operational efficiency, the integration of advanced technologies like CNC machining and automation in the bending process is becoming prevalent. This technological advancement allows for higher production rates and better accuracy, which is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to maintain competitive advantages.
In regions like Africa and South America, there is a notable shift towards local sourcing as manufacturers aim to reduce lead times and shipping costs. Conversely, buyers in Europe, particularly in Germany, are increasingly focused on sourcing high-quality dies that adhere to stringent industrial standards. Moreover, as the global market becomes more interconnected, businesses are leveraging digital platforms for sourcing, facilitating easier access to suppliers across different geographies.
Emerging trends also include the customization of dies to cater to specific bending requirements, which is essential for businesses involved in niche markets. Additionally, the rising emphasis on reducing waste and improving yield in manufacturing processes is shaping sourcing decisions, prompting buyers to consider suppliers that offer optimized tooling solutions.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Sheet Metal Bending Dies Market?
Sustainability is becoming a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the sheet metal bending dies sector. With growing awareness of environmental issues, manufacturers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains to minimize their ecological footprint. The production of bending dies often involves significant energy consumption and raw material use, making it essential for companies to adopt sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are now prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to responsible manufacturing processes. This includes the use of recycled materials, adherence to fair labor practices, and compliance with environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can provide assurance to buyers regarding the sustainability of their sourcing choices.
Furthermore, suppliers that incorporate eco-friendly materials and processes into their product offerings are likely to gain a competitive edge in the market. This shift not only helps in reducing environmental impact but also aligns with the corporate social responsibility goals of many organizations, making it a critical factor in sourcing decisions.
What is the Brief Evolution and History of Sheet Metal Bending Dies?
The history of sheet metal bending dies can be traced back to the early industrial revolution when basic manual tools were utilized for metal forming. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and machining technology led to the development of more sophisticated dies capable of producing complex shapes and angles. The introduction of hydraulic press brakes in the mid-20th century revolutionized the bending process, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher precision and efficiency.
As industries evolved, so did the requirements for bending dies, leading to innovations such as air bending and the creation of specialized dies for different materials like aluminum and stainless steel. Today, with the rise of digital manufacturing and automation, the sheet metal bending dies sector is on the cusp of further transformation, promising exciting opportunities for international B2B buyers seeking cutting-edge solutions to enhance their production capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sheet metal bending dies
-
How do I choose the right sheet metal bending die for my project?
Choosing the right sheet metal bending die involves understanding your project’s specific requirements, including material type, thickness, and the desired bend angle. For general applications, 90-degree dies are most common, but for more complex shapes, consider acute or gooseneck dies. Additionally, assess the tonnage capacity of your press brake and the radius of the bends needed. Consulting with suppliers about your project’s specifics can help you identify the most suitable die and avoid costly mistakes. -
What is the best material for sheet metal bending dies?
The best material for sheet metal bending dies typically includes high-strength steel or tool steel, which offers durability and resistance to wear. For applications involving stainless steel or aluminum, consider dies that have undergone flame hardening or surface polishing to enhance longevity and reduce marking on the material. The choice of material will depend on the type of metal being bent and the complexity of the bending operations, so be sure to discuss these factors with your supplier. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering custom sheet metal bending dies?
Lead times for custom sheet metal bending dies can vary significantly based on the complexity of the design and the manufacturer’s production capabilities. Generally, you can expect a lead time of 4 to 8 weeks for custom orders. However, for urgent needs, some suppliers may offer expedited services. It’s advisable to communicate your timeline expectations clearly with potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your deadlines. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for sheet metal bending dies?
Minimum order quantities for sheet metal bending dies can vary by supplier and the specific type of die required. Many manufacturers have MOQs ranging from one unit for standard dies to larger quantities for custom or specialized dies. When sourcing, inquire about MOQs upfront to understand the financial implications of your order and to ensure that the supplier can accommodate your needs without excessive inventory. -
How can I verify the quality of sheet metal bending dies before purchasing?
To verify the quality of sheet metal bending dies, request samples or detailed specifications, including material certifications and manufacturing processes. Look for suppliers who provide quality assurance documentation and have a robust return policy. Additionally, consider checking customer reviews or testimonials to gauge the supplier’s reputation. If possible, visit their facility or request third-party inspections to ensure they meet your quality standards. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing sheet metal bending dies?
Payment terms for sheet metal bending dies can vary by supplier and region. Common terms may include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the remaining balance due upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60 days) based on your credit history or relationship with them. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing your order to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
How can I ensure efficient logistics for shipping sheet metal bending dies internationally?
To ensure efficient logistics for shipping sheet metal bending dies internationally, work closely with your supplier and a reliable freight forwarder. Discuss shipping options, including air or sea freight, and choose the method that balances cost and speed. Ensure that all customs documentation is prepared in advance to avoid delays. Additionally, consider factors such as insurance coverage and delivery timelines, especially when shipping to regions with complex customs regulations. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing sheet metal bending dies from international suppliers?
Common challenges when sourcing sheet metal bending dies from international suppliers include language barriers, differing quality standards, and variations in lead times. Time zone differences can complicate communication, making it essential to establish clear expectations upfront. Additionally, familiarize yourself with the supplier’s production capabilities and quality assurance practices to mitigate risks. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can help navigate these challenges effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Sheet Metal Bending Dies Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Offset Press Brake Dies – Metalworking Tools
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: {“title”:”Offset Press Brake Dies – Metalworking Sheet Metal Bending Tools”,”condition”:”New”,”price”:”Approx. HKD 302.53 ($38.54)”,”quantity_available”:”More than 10 available”,”item_number”:”125699431191″,”treated_material”:”Metal”,”category”:”Business & Industrial > CNC, Metalworking & Manufacturing > Metalworking Equipment > Press Brakes”,”seller”:”EisenholzDesign”,”seller_feedback”:”100% posi…
2. McMaster – Bend Dies & Tube Bender Sets
Domain: mcmaster.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: This company, McMaster – Bend Dies & Tube Bender Sets, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. PolyProd – Urethane V-Dies for Press Brake Forming
Domain: polyprod.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Urethane V-Dies for Press Brake Forming are designed for making mar-free bends in pre-polished stainless steel, aluminum, and pre-finished surfaces in high volume production runs. Available in 1-V, 2-V, and 4-V designs for different gauges and types of metals, these molded urethane dies are sized like steel V-dies (V = 8 x metal thickness) and are typically available in 8 ft. lengths. They are sui…
4. SendCutSend – Die Marks in Sheet Metal Bending
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Die marks in sheet metal bending are surface marks left by tooling used in press brakes, also known as die lines or witness marks. These marks are difficult to prevent, but can be minimized by choosing harder materials like stainless steel, which have less deep witness marks compared to softer materials. A dual action (DA) orbital sander is recommended for blending out the marks. SendCutSend does …
5. METALpro – Brake Die Sets
Domain: metalprocorp.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Brake Die Sets – METALpro offers a variety of Brake Die Sets based on bending style, degree of bend, and material thickness. Priced per inch, options include Offset Brake Dies, Gooseneck Brake Dies, Flattening Brake Dies, Custom Brake Dies, 30 Degree Brake Dies, and 90 Degree Brake Dies. Lengths start at 4″ and increase by 1″ increments. All Brake Die Sets are rated for mild steel. Custom Brake Di…
6. Reddit – Custom Sheet Metal Bending Tool
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Sheet metal, 10mm thick, 1.8m across, with small “ears” that need to be bent 90 degrees, bends approximately 15cm wide. Requires a narrow tool for bending without affecting other parts of the plate.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sheet metal bending dies
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of sheet metal bending dies is pivotal for businesses aiming to enhance their manufacturing efficiency and product quality. By understanding the variety of dies available—such as general-purpose, acute, and specialized options—buyers can tailor their investments to meet specific production needs. Sourcing dies that accommodate different materials, like aluminum and stainless steel, while considering their unique properties and springback effects, ensures optimal performance and longevity of the tooling.
Moreover, leveraging partnerships with reliable suppliers can lead to significant cost savings and improved access to innovative technologies. As the global market continues to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of trends and aligning with trusted manufacturers will be crucial for competitive advantage.
Looking forward, international B2B buyers are encouraged to proactively engage with suppliers, seek out the latest advancements in die technology, and consider the implications of their sourcing decisions on their overall operational success. Investing in quality sheet metal bending dies today will not only enhance production capabilities but also secure a robust position in the marketplace for tomorrow.