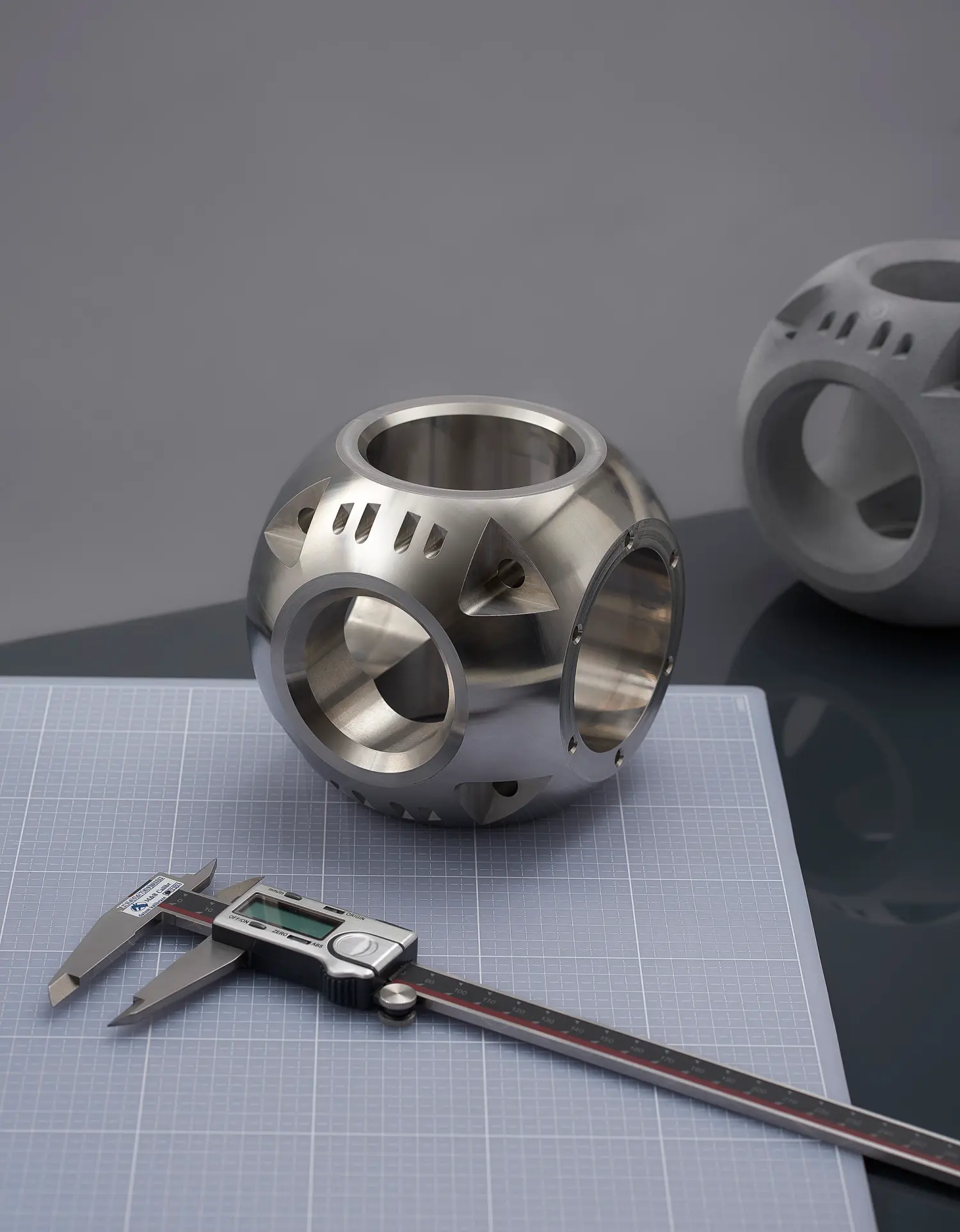
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for servicio cnc
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable CNC services is a critical challenge for international B2B buyers seeking precision and efficiency in manufacturing. As businesses expand globally, the need for high-quality, custom CNC machining services becomes paramount, particularly for industries ranging from aerospace to electronics. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of the global market for servicio CNC, detailing various types of machining processes, application areas, and the importance of supplier vetting to ensure quality and reliability.
Navigating the complexities of sourcing CNC services can be daunting, especially for buyers in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil. This guide not only addresses key considerations like cost analysis, material selection, and production capabilities but also provides actionable insights into establishing strong supplier relationships. By leveraging the information presented here, B2B buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right service providers that align with their operational needs and quality standards.
Ultimately, this guide serves as an essential resource for international buyers, empowering them to confidently navigate the global CNC machining landscape and secure the best solutions for their manufacturing challenges.
Understanding servicio cnc Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Milling | Uses rotating cutting tools for shaping material; available in 3, 4, and 5-axis configurations. | Aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices. | Pros: High precision, suitable for complex geometries. Cons: Setup costs can be high for low-volume runs. |
| CNC Turning | Involves rotating the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool; ideal for cylindrical parts. | Manufacturing of shafts, bushings, and fittings. | Pros: Efficient for round parts, high-speed production. Cons: Limited to parts with rotational symmetry. |
| CNC Routing | Utilizes a spindle to cut flat materials; effective for both wood and plastics. | Furniture, signage, and custom cabinetry. | Pros: Versatile for various materials, good for large sheets. Cons: Less suitable for intricate metal parts. |
| CNC Laser Cutting | Employs a laser beam to cut or engrave materials; offers high precision and speed. | Signage, automotive, and electronics. | Pros: Clean edges and fine details, minimal material waste. Cons: Limited thickness for certain materials. |
| CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) | Uses electrical discharges to remove material; ideal for hard metals. | Tool and die making, aerospace components. | Pros: High precision for intricate shapes, suitable for hard materials. Cons: Slower than traditional machining methods. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Milling?
CNC milling is a versatile machining process that uses rotating cutting tools to remove material from a stationary workpiece. It can operate in various axes, including 3, 4, and 5-axis configurations, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries. This type of machining is particularly suitable for industries such as aerospace and medical, where precision and quality are paramount. Buyers should consider their specific part requirements, including tolerance levels and material types, as well as the potential setup costs associated with low-volume production.
How Does CNC Turning Benefit B2B Manufacturers?
CNC turning is characterized by the rotation of the workpiece against a fixed cutting tool, making it ideal for producing cylindrical components. This method is widely used in sectors such as automotive and manufacturing for parts like shafts and bushings. The efficiency of CNC turning allows for high-speed production, which can significantly reduce lead times. However, businesses should ensure their designs are suitable for rotational symmetry, as this limits the types of parts that can be effectively produced.
In What Scenarios is CNC Routing Preferred?
CNC routing employs a spindle to cut flat materials and is particularly effective for non-metal materials like wood and plastics. This method is commonly used in the furniture and signage industries, where large sheets of material need to be shaped or engraved. Its versatility allows for quick adjustments and changes in design, making it a favorite among custom fabricators. However, businesses should be aware that CNC routing may not be the best choice for intricate metal components that require tighter tolerances.
What Are the Advantages of CNC Laser Cutting?
CNC laser cutting utilizes a high-powered laser beam to cut or engrave materials with remarkable precision. This technique is ideal for applications in signage and electronics, where clean edges and detailed designs are crucial. The speed of laser cutting can significantly reduce production time, and its minimal material waste is an added advantage. Nevertheless, businesses should consider the material thickness limitations when opting for laser cutting, as it may not be suitable for thicker metals.
When Should B2B Buyers Consider CNC EDM?
CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a specialized process that uses electrical discharges to precisely remove material, making it ideal for hard metals and complex shapes. This technique is widely employed in tool and die making as well as aerospace components. The high precision and ability to work with hard materials are significant advantages for industries requiring intricate designs. However, buyers should keep in mind that EDM is generally slower than traditional machining methods, which could impact production schedules.
Key Industrial Applications of servicio cnc
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of servicio cnc | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft and spacecraft | Enhanced safety and performance through reliable parts | Certifications (e.g., AS9100D), material traceability |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Improved patient outcomes and compliance with health standards | Regulatory compliance (ISO 13485), biocompatibility |
| Automotive | Engine components and assembly fixtures | Increased efficiency and reduced production costs | High-volume capabilities, material specifications |
| Electronics | Enclosures and circuit boards for devices | Improved product reliability and market competitiveness | Quick turnaround times, surface finish requirements |
| Industrial Automation | Custom tooling and fixtures for machinery | Enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Tolerances, material selection, and lead times |
How is ‘servicio cnc’ Used in the Aerospace Sector?
In the aerospace industry, CNC machining is critical for producing precision components such as brackets, housings, and turbine parts. These components must meet stringent safety and performance standards. By utilizing CNC services, aerospace manufacturers can achieve the required tolerances and material specifications essential for flight safety. International buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers with AS9100D certification and a proven track record in aerospace applications to ensure compliance and reliability.
What Role Does CNC Machining Play in Medical Devices?
CNC machining is widely used in the medical device sector for crafting custom surgical instruments and implants. The precision and repeatability of CNC processes enable manufacturers to produce complex geometries that are crucial for functionality. Additionally, compliance with ISO 13485 standards is vital for ensuring product safety. International buyers should focus on suppliers that offer biocompatible materials and extensive quality control measures, particularly in South America and Africa, where regulatory frameworks may vary.
How is CNC Machining Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, CNC machining is employed to manufacture engine components, transmission parts, and assembly fixtures. The ability to produce high-quality, durable parts quickly allows automotive companies to optimize production lines and reduce costs. Buyers should consider sourcing from suppliers with high-volume machining capabilities and expertise in automotive-grade materials to ensure compliance with industry standards. This is particularly important for markets in Brazil and Saudi Arabia, where local regulations may impact sourcing decisions.
What Are the Benefits of CNC Machining in Electronics Manufacturing?
CNC machining is essential in the electronics industry for creating enclosures, circuit boards, and intricate components. The precision offered by CNC processes enhances product reliability and allows for rapid prototyping, which is crucial in a fast-paced market. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that can meet specific surface finish requirements and provide quick turnaround times. This is particularly advantageous for businesses in Europe, where time-to-market can significantly impact competitiveness.
Why is CNC Machining Important for Industrial Automation?
In industrial automation, CNC machining facilitates the production of custom tooling and fixtures that enhance the efficiency of manufacturing processes. These components are vital for automating tasks and improving operational workflows. Buyers should consider sourcing CNC services that offer tight tolerances and a variety of material options to meet specific application needs. Understanding the lead times and production capabilities of suppliers is crucial for businesses in Africa and South America, where supply chain dynamics can differ significantly.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘servicio cnc’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Ensuring Quality and Compliance in CNC Machining
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges in ensuring that their CNC machined parts meet stringent quality and compliance standards. This is particularly critical in industries like aerospace and medical, where even minor deviations can lead to catastrophic failures or regulatory penalties. Buyers might struggle to verify the certifications of their suppliers, leading to uncertainty about whether the parts will meet industry-specific standards such as ISO 9001:2015 or AS9100D.
The Solution: To mitigate these risks, buyers should prioritize sourcing CNC machining services from suppliers that are not only certified but also transparent about their quality assurance processes. When evaluating potential vendors, request documentation that confirms their compliance with relevant standards. Additionally, consider implementing a dual-sourcing strategy where parts are procured from multiple suppliers. This approach not only diversifies risk but also allows for comparisons in quality and service. Finally, establishing clear communication channels for feedback and inspection reports can foster a more collaborative relationship with suppliers, ensuring that any quality issues are addressed promptly.
Scenario 2: Long Lead Times Affecting Production Schedules
The Problem: One of the most pressing issues B2B buyers encounter is the unpredictability of lead times in CNC machining services. Delays in production can cascade through supply chains, resulting in missed deadlines and lost business opportunities. This is especially problematic for companies that require rapid prototyping or need to scale production quickly in response to market demands.
The Solution: To tackle lead time challenges, buyers should leverage online CNC machining platforms that offer instant quoting and streamlined ordering processes. These platforms often have a network of vetted suppliers, enabling them to choose the one that can fulfill their order within the required timeframe. It is also beneficial to discuss specific timelines upfront with suppliers, ensuring they understand your urgency. For ongoing projects, consider establishing a safety stock of critical components to buffer against potential delays. Additionally, using advanced planning and forecasting tools can help buyers better align their production schedules with supplier capabilities, minimizing the impact of lead time variability.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Customizing Complex Designs
The Problem: Customization is key in many industries, yet B2B buyers often find it challenging to translate complex designs into feasible CNC machining processes. This is particularly true for buyers who may not have a strong technical background, leading to miscommunications with suppliers about design specifications and manufacturability. As a result, designs may be rejected or require costly revisions, impacting both time and budget.
The Solution: To enhance the customization process, buyers should invest time in creating detailed CAD models that clearly articulate their design intentions. When submitting designs, use online CNC machining services that provide design-for-manufacturability feedback. This feature allows buyers to receive insights on potential production challenges before the machining process begins. Furthermore, fostering a collaborative relationship with CNC engineers can lead to valuable suggestions for optimizing designs for manufacturing. Regular communication during the design phase can help in making necessary adjustments early on, thus avoiding delays and unexpected costs during production. Finally, consider utilizing simulation tools to visualize machining processes, enabling buyers to anticipate issues before they arise.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for servicio cnc
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in CNC Machining?
Aluminum is a highly versatile material commonly used in CNC machining due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance. It is lightweight, making it ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. Aluminum alloys, particularly 6061 and 7075, offer good machinability and can withstand moderate temperatures, making them suitable for various environments.
Pros and Cons: The advantages of aluminum include its durability, ease of machining, and relatively low cost compared to other metals. However, it can be less suitable for high-stress applications due to its lower tensile strength compared to steel. Additionally, while aluminum is resistant to corrosion, it can be susceptible to wear and tear in abrasive environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media makes it a preferred choice for components in industries like electronics and automotive. It is often used in parts that require good thermal conductivity and lightweight properties.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers, especially from regions like the Middle East and Europe, should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN for aluminum specifications. Understanding local regulations regarding aluminum recycling and sustainability can also be beneficial.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in CNC Machining?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance and high-temperature performance. It is particularly useful in environments where exposure to moisture or chemicals is prevalent, such as in the food processing and medical industries. Common grades like 304 and 316 offer good machinability and can be used for both structural and aesthetic applications.
Pros and Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, which makes it ideal for long-lasting applications. However, it is generally more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine due to its toughness. This can lead to increased manufacturing complexity and costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including acidic and alkaline substances, making it suitable for applications in chemical processing and food handling. Its aesthetic appeal also makes it a popular choice for consumer products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa and South America should be aware of the different grades of stainless steel and their certifications, such as ASTM A240. Ensuring that suppliers can provide material certifications is crucial for compliance with local regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Using Engineering Plastics in CNC Machining?
Engineering plastics, such as PEEK and Nylon, are increasingly popular in CNC machining due to their lightweight and excellent mechanical properties. These materials can withstand high temperatures and offer good chemical resistance, making them suitable for a variety of applications, including aerospace and medical devices.
Pros and Cons: The key advantages of engineering plastics include their resistance to corrosion and lower density, which can lead to cost savings in shipping and handling. However, they may not be as strong as metals and can be more susceptible to wear over time, which could limit their use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Engineering plastics are often used in applications requiring electrical insulation or reduced weight, such as in automotive components and electronic housings. Their versatility allows for customization in various designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with international standards like ISO and ASTM for engineering plastics. Understanding the specific requirements for applications in different industries can help in selecting the right material.
How Does Brass Compare in CNC Machining Applications?
Brass is a copper alloy known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. It is often used in applications requiring good electrical conductivity and aesthetic appeal, such as in fittings and decorative items.
Pros and Cons: The main advantage of brass is its ability to be easily machined into complex shapes, making it suitable for precision components. However, it is generally more expensive than aluminum and can be less durable under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application: Brass is compatible with various media, particularly in plumbing and electrical applications, where its conductivity and resistance to corrosion are beneficial.
Considerations for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of the specific grades of brass and their certifications, such as ASTM B16. Understanding the local market preferences for brass components can aid in sourcing decisions.
| Material | Typical Use Case for servicio cnc | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Engineering Plastics | Electrical housings, automotive components | Lightweight and good chemical resistance | Less strength than metals | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, decorative items | Excellent machinability and conductivity | More expensive and less durable under stress | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for servicio cnc
What Are the Main Stages of CNC Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process for CNC (Computer Numerical Control) services is intricate, comprising several key stages that ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages is critical for B2B buyers, especially those engaged in industries like aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical devices.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Material Selected and Processed?
The first step in CNC manufacturing involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which can include metals such as aluminum, steel, titanium, and plastics like PEEK and Teflon. This selection is crucial because the material properties directly affect the performance and durability of the final product. Once chosen, the materials undergo preparation, which may include cutting them to size, cleaning, and ensuring they meet the required specifications.
This stage may also involve checking for defects in the raw materials, as any imperfections can compromise the integrity of the final components. Suppliers often provide material certifications to affirm that the materials meet industry standards, which is particularly important for international buyers requiring compliance with specific regulations.
Forming: What Techniques Are Employed in CNC Machining?
The forming stage utilizes various CNC machining techniques, including milling, turning, and routing. Each technique serves specific functions:
- CNC Milling: This process employs rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. Mills can be 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis, allowing for complex geometries and precision cutting.
- CNC Turning: Here, the workpiece is rotated while a stationary cutting tool removes material, ideal for producing cylindrical parts.
- CNC Routing: This technique is primarily used for softer materials like plastics and involves a similar method to milling but focuses more on creating shapes and designs.
These processes are often complemented by advanced techniques such as Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and laser cutting for intricate designs. Each method’s choice depends on the part’s geometry, the required tolerances, and material properties.
Assembly: How Are CNC Components Joined Together?
In many cases, CNC machined parts are not standalone; they need to be assembled into larger systems or products. The assembly process may involve welding, fastening, or bonding components together. It’s crucial to maintain the precision achieved during machining to ensure that assembled parts function correctly.
For international buyers, ensuring that the assembly process aligns with their operational needs is vital. This may involve understanding the assembly techniques used by suppliers and ensuring they have the capability to meet specific design requirements.
Finishing: What Are the Common Techniques for Enhancing CNC Parts?
Finishing processes are essential for improving the aesthetic and functional qualities of CNC machined parts. Common techniques include:
- Deburring: Removing sharp edges and burrs left from the machining process.
- Surface Treatments: Applying coatings, anodizing, or plating to enhance corrosion resistance or aesthetic appeal.
- Polishing: Achieving a smooth, shiny surface finish for cosmetic purposes.
These finishing techniques not only improve the appearance of parts but also influence their performance in specific applications, such as reducing friction in moving parts or enhancing durability.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for CNC Services?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of CNC manufacturing, particularly for international B2B transactions where compliance with various standards is necessary.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Several international standards are pivotal in ensuring quality and reliability in CNC services:
- ISO 9001:2015: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- ISO 13485: Particularly relevant for medical devices, this standard ensures that manufacturers meet regulatory requirements consistently.
- IATF 16949: This standard is crucial for the automotive industry, focusing on the development of a QMS that emphasizes defect prevention and the reduction of variation and waste.
- AS9100D: Specific to the aerospace sector, this standard incorporates ISO 9001 with additional requirements tailored to the aerospace industry.
These certifications not only signify a commitment to quality but also enhance buyer confidence, particularly for those sourcing from different continents.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, often segmented into various checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, operators and quality engineers monitor production to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the parts are completed, they undergo thorough inspections and testing to ensure they meet all specifications before shipment.
B2B buyers should inquire about the QC processes in place at potential suppliers to ensure they meet their quality expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when dealing with international suppliers. Here are some strategies:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits can help assess compliance with quality standards. Buyers should consider both announced and unannounced audits to get an accurate picture of a supplier’s operations.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into a supplier’s performance over time, including defect rates and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can validate the quality claims made by suppliers. This step is especially important for high-stakes industries where safety and reliability are paramount.
What Are the Nuances of QC and Certification for International B2B Buyers?
For international buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential. Different regions may have specific compliance requirements, and certifications recognized in one area may not hold the same weight in another.
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure that their suppliers not only comply with local regulations but also align with international standards that facilitate trade and acceptance across borders. This understanding can prevent costly delays and ensure smoother operations when sourcing CNC services globally.
By grasping the intricacies of CNC manufacturing processes and quality assurance, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who prioritize quality and reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘servicio cnc’
The following guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure CNC machining services. It outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process, tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulating your technical requirements is the foundation of a successful CNC machining project. This includes defining dimensions, tolerances, materials, and desired finishes. Providing detailed CAD files can significantly streamline the quoting process and help suppliers understand your needs more accurately.
- Considerations: Specify the type of CNC processes needed (e.g., milling, turning, routing) and any necessary certifications for the materials or processes involved.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in CNC machining services. Look for companies with a proven track record and experience in your specific industry. Online reviews, case studies, and industry forums can provide valuable insights into supplier reliability and quality.
- Tip: Utilize platforms that aggregate supplier information and ratings to streamline your research process.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Supplier certifications are a critical indicator of quality and compliance. Look for ISO certifications such as ISO 9001:2015 or industry-specific standards relevant to your project. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality management and operational excellence.
- Why it Matters: Certifications help ensure that the supplier adheres to industry best practices, which can mitigate risks related to product quality and delivery timelines.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline pricing, lead times, and any additional costs such as shipping or tariffs. Comparing quotes will help you identify the best value for your specific project needs.
- Important Note: Ensure that quotes include all relevant details, including the potential for volume discounts or additional services like post-processing.
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s production capabilities is essential to ensure they can meet your requirements. Evaluate their machinery, technology, and workforce expertise. Ask about their capacity for rapid prototyping, small-batch production, or high-volume orders.
- Inquiry Tip: Inquire about their ability to handle complex geometries or specific materials that are critical to your project.
Step 6: Verify Quality Control Processes
A robust quality control process is vital for ensuring that your CNC machined parts meet your specifications. Inquire about their inspection methods and whether they provide documentation such as Certificates of Conformance (CoCs) or material certifications.
- Key Focus: Look for suppliers that incorporate rigorous testing and inspection protocols to guarantee the quality and accuracy of their work.
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication is crucial throughout the sourcing process. Establish clear lines of communication with your chosen supplier to facilitate updates on project status, changes in specifications, or any issues that may arise.
- Recommendation: Utilize project management tools or regular check-ins to maintain transparency and alignment on project goals.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC machining services, ensuring that they select a supplier capable of delivering high-quality, precise components tailored to their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for servicio cnc Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of CNC machining services is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and offers practical tips for effective negotiation and procurement.
What Are the Key Cost Components in CNC Machining Services?
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts costs. Common materials like aluminum, steel, and plastics can vary in price based on market fluctuations and sourcing locations. Specialty materials, such as titanium or high-performance plastics, generally incur higher costs due to their unique properties and processing requirements.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass skilled machinists and technicians who operate CNC machinery. Labor rates can vary widely depending on geographic location, with higher wages typically found in regions with advanced manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, labor costs may increase if specialized skills or certifications are required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead includes expenses related to facility operations, utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient production environments can help keep these costs down, making it vital for buyers to consider suppliers with streamlined operations.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are incurred for the creation and maintenance of the tools used in CNC machining. These costs can be significant, particularly for custom parts requiring specialized tooling. Buyers should clarify whether tooling costs are included in quotes or billed separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring high-quality output often necessitates additional QC processes, including inspections and testing. Certification standards, such as ISO 9001, can lead to higher prices but also enhance reliability and quality assurance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the size and weight of the order, as well as the distance to the destination. International shipments may also involve customs duties and tariffs, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on competition, demand, and the supplier’s operational efficiency.
How Do Various Factors Influence CNC Machining Prices?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher order volumes can lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, smaller orders may attract higher pricing due to the fixed costs associated with production.
-
Specifications and Customization: Complex designs or custom features can increase production time and tooling costs, impacting the overall price. Standard designs often come with a more competitive price point.
-
Material Choices: As mentioned, the selected material plays a crucial role in pricing. Buyers should be aware that premium materials will command higher prices.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with higher quality standards and certifications may charge more due to the assurance of better product reliability. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can all influence pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technologies may offer better quality but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can affect costs. Choosing the right Incoterm can help mitigate unexpected expenses related to logistics.
What Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Their CNC Machining Costs?
-
Negotiate Wisely: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Building a good relationship can lead to better terms and discounts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial price but the long-term costs associated with quality, reliability, and maintenance. A higher upfront cost may be justified by better performance or lower failure rates.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices can vary significantly based on geographic location and market conditions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should research local suppliers to understand pricing dynamics.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of costs to identify potential areas for negotiation or cost-saving opportunities.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Regularly monitor material prices and industry trends to anticipate changes that could affect future sourcing decisions.
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis for CNC machining services enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions, negotiate effectively, and ultimately enhance their supply chain efficiencies. Keep in mind that prices are indicative and can fluctuate based on various market conditions and supplier-specific factors.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing servicio cnc With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Servicio CNC
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, B2B buyers often seek the most efficient and cost-effective solutions for their production needs. While servicio CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a leading choice for precision manufacturing, several alternative technologies and methods can also fulfill similar requirements. Understanding these alternatives enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific operational goals and budget constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Servicio CNC | Alternative 1: 3D Printing | Alternative 2: Traditional Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Good for complex shapes but limited in material strength | High precision but slower than CNC |
| Cost | Moderate to high (depends on volume and complexity) | Lower initial costs, but can be high for larger volumes | Generally lower for high-volume runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires CAD files and setup | User-friendly, minimal setup needed | Requires skilled labor and setup |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Low maintenance, but printer parts may need replacement | High maintenance due to wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, medical devices, and automotive components | Prototyping, small runs, and complex geometries | High-volume production with simple parts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Pros and Cons of 3D Printing as an Alternative?
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, offers unique advantages, particularly for prototyping and creating complex geometries. The technology allows for rapid production of parts without the need for extensive tooling. This is especially beneficial for custom designs that would be costly or impractical with traditional methods. However, the material properties of 3D printed parts can be a limitation; they may not match the strength and durability of CNC machined components, especially in high-stress applications. Additionally, while initial costs are lower, the price can escalate for larger production runs.
How Does Traditional Machining Compare to Servicio CNC?
Traditional machining encompasses various methods like turning and milling, often using manual processes. This technique is known for its ability to produce high-quality parts, particularly in high-volume scenarios where unit costs can be lower. However, traditional machining lacks the automation and speed of CNC machining, resulting in longer lead times. Furthermore, it requires a skilled workforce to operate the machinery effectively, which can increase operational costs. This method is best suited for straightforward designs where high production volumes justify the investment in setup and labor.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing solution requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance. While servicio CNC provides unparalleled precision and versatility, alternatives like 3D printing and traditional machining offer viable options depending on specific project requirements. B2B buyers should evaluate their production volume, material needs, and design complexity to determine the most suitable approach. By aligning the manufacturing method with their operational goals, businesses can optimize their production processes and achieve greater efficiency.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for servicio cnc
What Are the Key Technical Properties of CNC Services Important for B2B Buyers?
When considering CNC machining services, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several essential specifications that play a significant role in the quality and suitability of CNC machined parts:
-
Material Grade
The choice of material directly impacts the performance, durability, and application of the finished part. Common materials used in CNC machining include aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061, 7075), stainless steel (e.g., 304), and engineering plastics (e.g., PEEK). Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the component meets the required strength, weight, and corrosion resistance for its intended use. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In CNC machining, tolerances can range from standard (±0.005 inches) to precision (sub ±0.001 inches), depending on the complexity of the part. Tighter tolerances are crucial for applications in industries such as aerospace and medical, where precision is paramount. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers ensure that parts fit correctly and function as intended. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from order placement to delivery of the finished product. Quick lead times (often as short as 3 to 5 business days) are essential for businesses that require rapid prototyping or urgent production runs. Knowing the lead times offered by suppliers allows buyers to plan their projects more effectively and manage inventory levels. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a CNC machined part affects both its aesthetic appeal and functional performance. Common finishes include “as-machined,” bead blasted, and anodized. The choice of surface finish can influence factors such as friction, wear resistance, and the ability to hold coatings or paints. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure compatibility with their applications. -
Minimum Feature Size
This specification indicates the smallest detail that can be reliably machined. For example, a minimum feature size of 0.020 inches (0.50 mm) may apply to certain materials and geometries. Understanding this property is essential for designers to avoid creating features that may be too small to manufacture effectively. -
Edge Condition
Edge condition describes the treatment of edges after machining, such as deburring or sharp edge removal. This property is vital for ensuring the safety and functionality of parts, particularly in applications where sharp edges could pose risks. Buyers should inquire about the default edge treatments offered by their CNC service provider.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in CNC Machining Services?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation with CNC service providers. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts that are used in the assembly of larger products. In CNC machining, understanding OEM relationships can help businesses identify suppliers who specialize in their specific industry needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ can help buyers assess whether a supplier can meet their production requirements, especially for custom parts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. This document typically includes details such as material specifications, tolerances, and quantities. Submitting a well-defined RFQ can streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms used to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping, insurance, and delivery obligations, minimizing potential disputes. -
CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to the software used to create detailed 2D and 3D models of parts. Suppliers often require CAD files for accurate quoting and machining. Providing high-quality CAD files can significantly enhance the efficiency of the CNC machining process. -
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
EDM is a precision machining process used for intricate shapes and hard materials. Familiarity with EDM can be beneficial for buyers needing complex geometries that standard CNC machining may not accommodate.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing CNC machining services, ensuring they select the right partners for their manufacturing needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the servicio cnc Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing the CNC Service Sector?
The CNC service sector is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several global factors. Increased demand for precision manufacturing across diverse industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics is pushing the growth of CNC services. As international B2B buyers look for agile production solutions, the shift towards on-demand manufacturing and rapid prototyping has become pronounced. This trend is particularly evident in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where businesses are leveraging advanced CNC technologies to reduce lead times and lower production costs.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and IoT are also reshaping the CNC landscape. These technologies enable predictive maintenance, automated quality control, and enhanced production efficiency. For international buyers, this means accessing suppliers with advanced capabilities that can offer real-time insights into production processes, ensuring high-quality outcomes. Additionally, the growth of e-commerce platforms is simplifying the procurement process, allowing buyers to obtain instant quotes and streamline their sourcing efforts.
Furthermore, geopolitical factors and supply chain disruptions have led to an increased focus on regional sourcing. Companies are seeking local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global supply chains, especially in light of recent challenges posed by the pandemic and trade tensions. This shift not only enhances reliability but also allows for more tailored services that cater to specific regional needs.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Becoming Integral to CNC Services?
In the current landscape, sustainability and ethical sourcing have emerged as critical considerations for international B2B buyers in the CNC service sector. Environmental impact is a growing concern, prompting companies to adopt practices that minimize waste and energy consumption. This trend is particularly relevant for industries that are under pressure to meet stringent regulatory requirements and consumer expectations regarding sustainability.
Ethical supply chains have gained prominence, as companies increasingly recognize the importance of transparency in sourcing materials and manufacturing processes. Buyers are now seeking CNC service providers that demonstrate commitment to ethical practices, including fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming essential benchmarks for assessing potential suppliers.
Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials in CNC machining, such as recycled metals and biodegradable plastics, is on the rise. This shift not only reduces the environmental footprint but also resonates with consumers and businesses that prioritize sustainability in their operations. As a result, international buyers are encouraged to evaluate their CNC partners based on their sustainability practices and certifications, ensuring that they align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Historical Context of CNC Services and Its Relevance to B2B Buyers?
The evolution of CNC services dates back to the 1940s when the first numerical control machines were developed. Initially, these machines were limited in capabilities and primarily used in specialized industries. However, the advent of computer technology in the 1960s revolutionized CNC machining, enabling more complex designs and greater precision.
As the technology advanced, CNC machining became accessible to a broader range of industries, leading to the proliferation of CNC service providers. Today, CNC machining is integral to modern manufacturing, providing critical solutions for rapid prototyping, customized production, and high-volume manufacturing. For international B2B buyers, understanding this historical context is essential, as it highlights the technological advancements that have shaped the capabilities of CNC services. This knowledge can guide buyers in selecting suppliers that not only meet current demands but are also equipped to adapt to future trends in manufacturing technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of servicio cnc
-
How do I ensure quality when sourcing CNC services internationally?
To ensure quality when sourcing CNC services internationally, start by vetting suppliers through certifications such as ISO 9001:2015 or AS9100D, which indicate adherence to quality management standards. Request samples of previous work to assess precision and finish. Establish clear communication regarding specifications and tolerances, and consider using third-party inspection services to verify compliance with your quality requirements before accepting the final product. -
What are the common materials used in CNC machining services?
CNC machining services typically utilize a wide range of materials, including aluminum alloys (e.g., 6061, 7075), stainless steel, brass, and plastics like PEEK and Teflon. The choice of material depends on the application, required strength, and environmental factors. Discuss your specific needs with suppliers to ensure they can accommodate the materials best suited for your project. -
What customization options are available for CNC machined parts?
Customization options for CNC machined parts include variations in material selection, surface finishes, tolerances, and part geometries. Many suppliers offer the ability to create complex designs based on your CAD files. It’s essential to communicate your specific requirements upfront, including any special features such as threading or intricate shapes, to ensure the final product meets your expectations. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC services?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for CNC services can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Some suppliers may offer prototyping services with no MOQ, while others might require a minimum order of 10 or more units for production runs. Always clarify MOQs with potential suppliers to align your project needs with their capabilities. -
How do I manage logistics when sourcing CNC services internationally?
Managing logistics for international CNC services involves considering shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Work with suppliers who offer comprehensive logistics support, including handling tariffs and providing tracking information. It’s advisable to choose a supplier experienced in international shipping to avoid delays and ensure compliance with local regulations in your country. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with CNC suppliers?
Payment terms for CNC suppliers can vary widely; common practices include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net 30/60 terms. Discussing payment terms early in the negotiation process is crucial to ensure they align with your cash flow and project timeline. Be aware of any potential additional costs, such as shipping or customs fees, that may affect your overall budget. -
What should I look for in a supplier’s experience and capabilities?
When evaluating a CNC supplier, consider their industry experience, the range of services offered, and the types of machinery they use. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry, as well as those who can demonstrate the ability to handle projects similar to yours. Certifications and customer testimonials can also provide insight into their reliability and quality of work. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of CNC machined parts?
To ensure timely delivery of CNC machined parts, establish clear deadlines and communicate them to your supplier during the initial discussions. Choose suppliers with a solid reputation for meeting deadlines and who offer transparent lead times based on your project specifications. Implementing a project timeline with milestones can help track progress and address any potential delays proactively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Servicio Cnc Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Proto Labs – CNC Machining Services
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Online CNC Machining Service offering cost-efficient machined parts at any quantity. Capabilities include CNC Milling (3-axis and 5-axis indexed), CNC Turning (with live tooling), and production machining for prototypes and production parts in as fast as 1 day. Materials available include various metals (Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, Steel Alloy, Mild Low Carbon, Titanium) and plastics…
2. Servicio CNC – Diseño y Decoración en Madera
Domain: serviciocnc.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Diseño y decoración en madera, servicio de corte CNC, productos decorativos en madera, biombos en madera plegable, separadores de espacios, diseño y fabricación de mobiliario, mobiliario corbatines, avisos y logos en CNC, cabeceros para camas, cuadros de madera, cuadros geométricos de madera MDF, espejos en madera, paredes en madera, servicio de corte CNC, tablas para picar en madera curada, diseñ…
3. SendCutSend – Precision CNC Routing Services
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: SendCutSend offers online CNC routing services for a variety of materials including composites, acrylics, and wood. Key features include precision cuts with tolerances as tight as ±0.005, kerf compensation, fast turnarounds (1-3 days shipping), and automatic nesting. The CNC routing service is ideal for materials that do not respond well to laser cutting, providing smoother edges and better finish…
4. 3DEXPERIENCE – CNC Machining Service
Domain: 3ds.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Service offered by 3DEXPERIENCE Make is an On-Demand Manufacturing platform connecting designers with industrial CNC Machining service providers primarily in North America and Europe. The service caters to small and large runs, including mockups and prototypes. Key features include an instant quote engine providing quotes in seconds, secure payments, and protected intellectual proper…
5. CNC Machine Services – Mazak EZ Series
Domain: cncmachineservice.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: CNC Machine Services, Inc. offers a range of manufacturing solutions including machine tools, services, software, and accessories. Key products include the Mazak EZ Series, which is designed and built in the USA, focusing on advanced manufacturing technology for improved part-production efficiency. The company provides machine tool and automation solutions, OEM quality parts without OEM prices, an…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for servicio cnc
In the ever-evolving landscape of CNC machining, strategic sourcing emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement processes. By leveraging a network of certified suppliers, companies can secure high-quality, custom machined parts that meet specific tolerances and material requirements. This not only enhances product quality but also accelerates time-to-market through rapid prototyping and flexible production capabilities.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the value of strategic sourcing cannot be overstated. It provides access to a diverse range of materials and machining techniques, allowing businesses to adapt to varying industry demands while maintaining cost efficiency. Additionally, the emphasis on certifications like ISO and ITAR compliance ensures that the highest quality standards are upheld throughout the manufacturing process.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, remember that the future of CNC machining is not just about cost savings; it’s about building partnerships that foster innovation and reliability. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore new technologies, and position your business to thrive in a competitive global market. Start your journey today by requesting quotes and exploring options that align with your strategic goals.