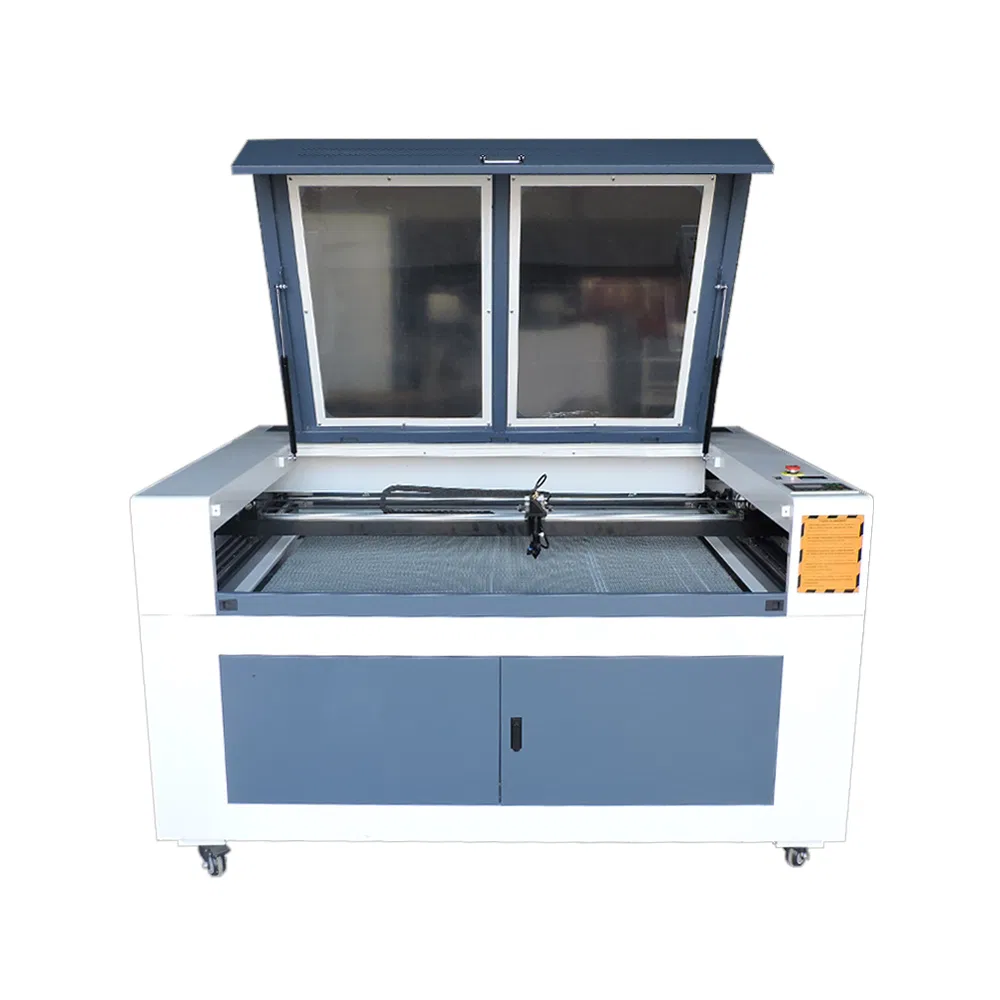
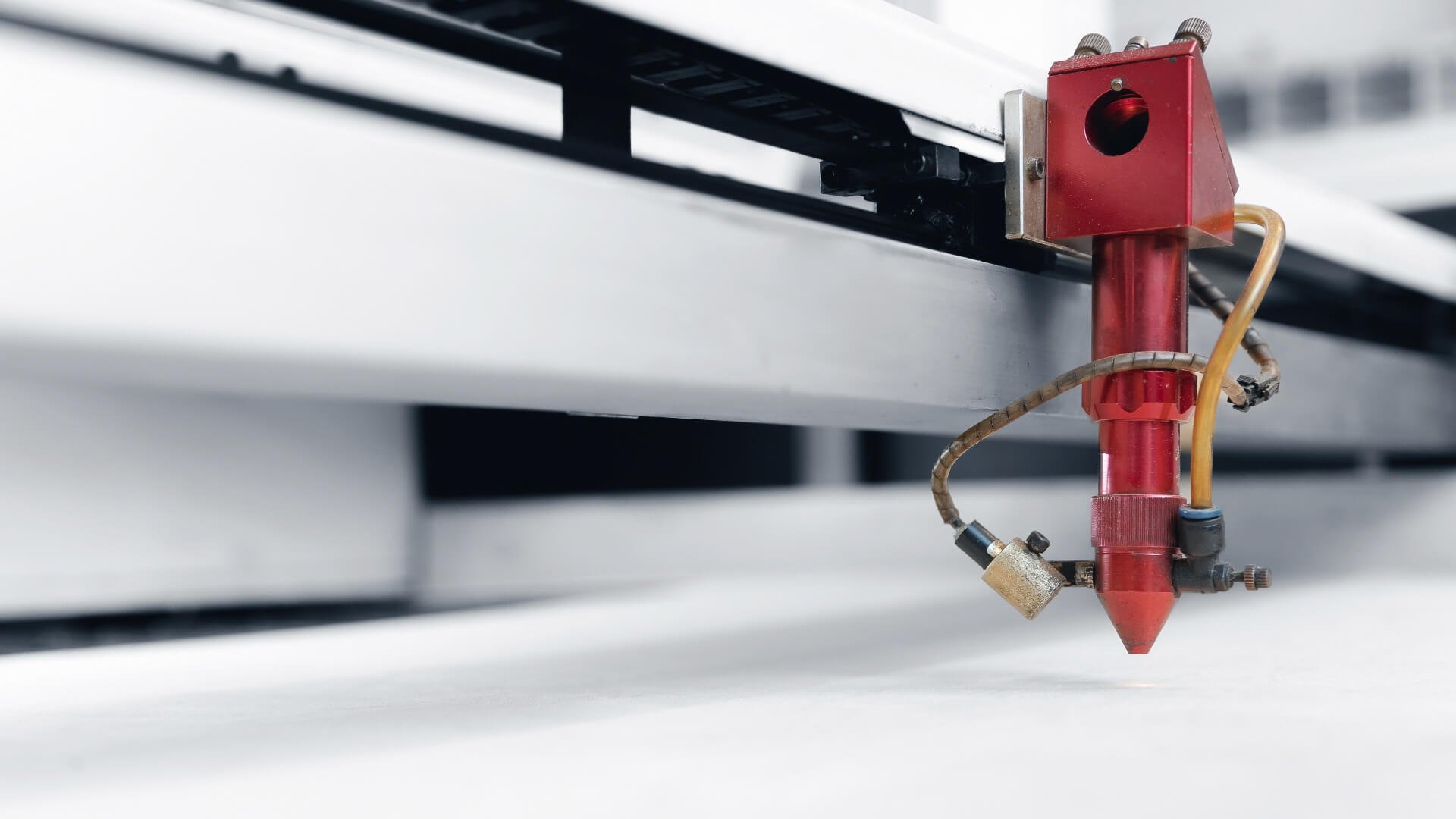
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for second hand laser cutter
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing a reliable second-hand laser cutter can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. With budget constraints and the need for high-quality equipment, businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as Nigeria and Brazil—often struggle to navigate the complex market of pre-owned machinery. This guide aims to simplify that process by providing a comprehensive overview of the second-hand laser cutter market, covering essential aspects such as types of machines available, their applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
Buyers will gain insights into the different categories of laser cutters, including CO2 and fiber models, which are tailored for various industrial applications—from metal marking to intricate engraving tasks. Additionally, this guide will equip you with strategies for evaluating suppliers, ensuring that you invest in machines that are not only functional but also meet your operational standards.
By addressing key challenges and offering actionable insights, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re looking to enhance your production capabilities or reduce operational costs, understanding the second-hand laser cutter market is vital for maximizing your investment and staying competitive in a global economy.
Understanding second hand laser cutter Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutters | Utilizes a gas laser, ideal for non-metal materials. | Woodworking, textiles, acrylic cutting | Pros: Versatile and cost-effective. Cons: Slower than fiber lasers. |
| Fiber Laser Cutters | Uses fiber optics for high-speed metal cutting. | Metal fabrication, signage, jewelry | Pros: High precision and speed. Cons: Generally more expensive. |
| MOPA Fiber Laser Cutters | Offers adjustable pulse width for better material control. | Advanced engraving, high-contrast marking | Pros: Versatile for various materials. Cons: Complexity in operation. |
| Desktop Laser Engravers | Compact machines for small-scale projects. | Personalization, small business applications | Pros: Space-efficient and user-friendly. Cons: Limited cutting capacity. |
| Split Fiber Laser Cutters | Combines laser and camera for enhanced marking accuracy. | High-precision marking on small parts | Pros: Increases accuracy and efficiency. Cons: Requires more setup. |
What are CO2 Laser Cutters and Their B2B Applications?
CO2 laser cutters are widely recognized for their ability to cut and engrave a variety of non-metal materials such as wood, acrylic, and textiles. They operate using a gas laser, which makes them particularly effective for applications in woodworking and signage production. When considering a second-hand CO2 laser cutter, businesses should evaluate the machine’s condition, available working area, and whether it meets their specific material requirements. While these machines are generally more affordable, their cutting speed may not match that of fiber lasers.
How Do Fiber Laser Cutters Stand Out in the Market?
Fiber laser cutters are known for their efficiency and precision, particularly in metal cutting applications. They utilize advanced fiber optic technology, enabling them to achieve high speeds and fine details in metal fabrication, including signage and jewelry production. For B2B buyers, investing in a second-hand fiber laser cutter can significantly enhance production capabilities. However, potential purchasers should consider the initial investment cost and ensure that the machine’s specifications align with their production needs.
What Makes MOPA Fiber Laser Cutters Unique?
MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) fiber laser cutters provide advanced control over pulse width, allowing for improved engraving and marking on various materials. This flexibility makes them suitable for applications requiring high contrast and detail. When purchasing a second-hand MOPA fiber laser, buyers should assess the machine’s adaptability to different materials and the complexity of operation, which may require skilled personnel. Their versatility can justify the higher price point compared to standard fiber lasers.
Why Choose Desktop Laser Engravers for Small Scale Projects?
Desktop laser engravers are compact, user-friendly machines designed for small-scale projects, making them ideal for personalization and small business applications. They are particularly advantageous for businesses that require limited space and flexibility in operations. Buyers should consider the engraving capacity and the types of materials the machine can handle when evaluating second-hand options. While these machines may have a lower cutting capacity, their affordability and ease of use are significant advantages for startups and small enterprises.
How Do Split Fiber Laser Cutters Enhance Accuracy?
Split fiber laser cutters integrate a built-in camera system, allowing for enhanced marking accuracy on small parts. This feature is particularly beneficial for high-precision applications, such as electronics or intricate designs. When looking at second-hand options, businesses should assess the functionality of the camera system and the overall condition of the machine. While the initial setup may be more complex, the efficiency gained through improved accuracy can lead to substantial time and cost savings in production.
Key Industrial Applications of second hand laser cutter
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Second Hand Laser Cutter | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision Cutting of Components | Reduces waste and improves production efficiency | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery and materials |
| Signage and Advertising | Custom Sign Fabrication | Enables unique branding and fast turnaround times | Look for machines with varied cutting sizes and capabilities |
| Textile and Fashion | Fabric Engraving and Cutting | Enhances design possibilities and reduces manual labor | Verify the machine’s ability to handle different fabric types |
| Electronics | PCB and Component Marking | Increases accuracy in manufacturing and reduces errors | Check for precision and reliability in laser performance |
| Arts and Crafts | Personalized Gifts and Decorative Items | Attracts customers with unique offerings | Assess the machine’s engraving capabilities and material versatility |
How is a Second Hand Laser Cutter Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing sector, second hand laser cutters are primarily used for precision cutting of components from various materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. They significantly reduce waste through accurate cuts, which is essential for cost management. Buyers should consider the compatibility of the laser cutter with their existing machinery and the materials they typically use, ensuring that the machine can handle the specific requirements of their production line.
What Role Does a Second Hand Laser Cutter Play in Signage and Advertising?
In the signage and advertising industry, second hand laser cutters are utilized for custom sign fabrication, allowing businesses to create unique branding materials quickly. The ability to cut intricate designs and letters enhances the visual appeal of signs, leading to better customer engagement. When sourcing these machines, companies should look for options that offer various cutting sizes and capabilities, ensuring flexibility in their design processes.
How Can Second Hand Laser Cutters Benefit the Textile and Fashion Industry?
The textile and fashion industry leverages second hand laser cutters for fabric engraving and cutting, which enhances design possibilities while reducing manual labor. This technology allows for complex patterns and custom designs that can elevate a brand’s offerings. Buyers should verify that the machines can accommodate different fabric types and thicknesses to meet their specific production needs effectively.
In What Ways Do Second Hand Laser Cutters Aid Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics, second hand laser cutters are essential for PCB and component marking, where precision is paramount. These machines improve accuracy in manufacturing processes, leading to fewer errors and higher quality products. Buyers should focus on the precision and reliability of the laser performance when sourcing these machines, ensuring they can meet the stringent requirements of electronic component production.
How Do Second Hand Laser Cutters Enhance Arts and Crafts?
For the arts and crafts sector, second hand laser cutters enable the creation of personalized gifts and decorative items, providing a competitive edge in a market driven by uniqueness. This technology allows artisans to produce intricate designs that attract customers. When sourcing a laser cutter, it is crucial to assess the machine’s engraving capabilities and material versatility to ensure it can handle a wide range of crafting projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘second hand laser cutter’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Uncertainty About Machine Condition
The Problem: When purchasing a second-hand laser cutter, many B2B buyers are concerned about the machine’s condition and performance. Unlike new equipment, pre-owned machines may come with undetected wear or hidden issues that could lead to downtime or costly repairs. This uncertainty can be particularly daunting for businesses in regions with limited access to technical support or replacement parts, such as parts of Africa and South America. Buyers may fear that they are investing in a piece of equipment that won’t meet their production needs or will require significant additional investment to bring it to operational standards.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing from reputable dealers who provide detailed inspections and certifications for their second-hand machines. Request comprehensive documentation, including maintenance records, usage history, and any refurbishing work done. Additionally, consider opting for sellers who offer warranties or guarantees on their machines. This assurance can help build confidence in the purchase. If possible, arrange a visit to inspect the machine in person or request a video demonstration to verify its functionality before finalizing the deal. Engaging in thorough due diligence ensures that buyers can make informed decisions, reducing the risk associated with pre-owned laser cutters.
Scenario 2: Lack of Technical Support and Knowledge
The Problem: Many businesses, particularly smaller enterprises or startups, may lack the in-house technical expertise to effectively operate and maintain a second-hand laser cutter. This situation can be exacerbated in regions with limited training resources or access to skilled technicians. As a result, users may struggle with machine setup, operation, and troubleshooting, leading to inefficient production processes and potential wastage of materials.
The Solution: To address the knowledge gap, buyers should seek out suppliers who provide training and support as part of the purchase agreement. This can include on-site training sessions, online tutorials, or access to a dedicated support hotline. Furthermore, joining industry forums and local trade associations can connect buyers with peers who can share valuable insights and tips on operating specific models of laser cutters. Investing in training not only enhances the operational capabilities of the workforce but also helps in troubleshooting common issues effectively, thus maximizing the return on investment in the laser cutter.
Scenario 3: Compatibility with Existing Systems and Materials
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is ensuring that a second-hand laser cutter is compatible with their existing production systems and the materials they intend to use. This concern is particularly relevant for companies looking to integrate new technology into established workflows, which may involve specific software or hardware configurations. For instance, a buyer might find a great deal on a laser cutter, only to discover later that it cannot work with their current design software or is unsuitable for the materials they commonly use.
The Solution: Before purchasing, buyers should conduct a thorough compatibility assessment. This involves checking the specifications of the second-hand laser cutter against the materials (such as wood, acrylic, or metal) and design software currently in use. Buyers should also inquire about any necessary adapters, software upgrades, or additional accessories that may be required to ensure seamless integration. If possible, consult with the manufacturer or the dealer to confirm compatibility and request demonstrations of the machine with the intended materials. Additionally, consider reaching out to other businesses in similar industries to gather feedback on the performance of the specific model with different applications. This proactive approach can save buyers from unexpected operational hurdles post-purchase.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for second hand laser cutter
What Are the Key Materials for Second Hand Laser Cutters?
When considering the purchase of a second-hand laser cutter, the choice of materials that the machine can effectively process is crucial. This section analyzes four common materials—wood, acrylic, metal, and leather—focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Do Wood Materials Perform in Laser Cutting Applications?
Key Properties: Wood is a natural material that is generally easy to cut and engrave with laser technology. It has a low melting point, which allows for precise cuts without significant burning or charring.
Pros & Cons: Wood is widely available and relatively inexpensive, making it a popular choice for various applications, including signage and decorative items. However, its durability can vary significantly based on species, and it may warp or crack over time, particularly in humid environments.
Impact on Application: Wood is compatible with a wide range of laser cutters, making it suitable for both CO2 and fiber lasers. It can be used for intricate designs, but the choice of wood type can affect the final product’s finish.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding the importation of wood products, as certain species may be restricted. Compliance with standards such as ASTM for material quality is essential, particularly in markets like Europe and North America.
What Are the Benefits of Using Acrylic in Laser Cutting?
Key Properties: Acrylic is a thermoplastic that can be easily cut and engraved. It has excellent optical clarity and is available in a variety of colors and thicknesses.
Pros & Cons: Acrylic is lightweight and shatter-resistant, making it ideal for applications like displays and signage. However, it can be more expensive than wood and may require additional finishing processes to achieve a polished edge.
Impact on Application: Acrylic is best suited for CO2 lasers, which provide the necessary precision for detailed cuts and engravings. The material’s versatility allows for creative applications, including awards and custom displays.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the acrylic meets local safety standards, especially if used in consumer products. Understanding the differences in grades and types of acrylic can also influence purchasing decisions.
How Do Metals Perform in Laser Cutting Applications?
Key Properties: Metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, and brass, are durable materials that require higher power laser cutters for effective processing. They have high melting points and can withstand significant pressure.
Pros & Cons: Metal cutting offers high precision and durability, making it suitable for industrial applications. However, the cost of metal materials can be significantly higher than non-metals, and cutting may require specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application: Fiber lasers are particularly effective for cutting metals, allowing for intricate designs and high-speed processing. The choice of metal can greatly influence the end product’s strength and application.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM or ISO is critical for metal products, especially in industries such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific metals in their region.
What Are the Unique Properties of Leather in Laser Cutting?
Key Properties: Leather is a natural material that offers a unique texture and aesthetic. It can be easily cut and engraved, with a low melting point that allows for clean edges.
Pros & Cons: Leather is durable and has a premium feel, making it popular for fashion and accessories. However, it can be more expensive than synthetic alternatives, and the quality can vary widely based on the source.
Impact on Application: Leather is compatible with both CO2 and fiber lasers, allowing for detailed engravings and cuts. The type of leather used can affect the final product’s appearance and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regulations regarding animal products, as these can vary significantly across regions. Ensuring compliance with standards for leather quality can also influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Second Hand Laser Cutters
| Material | Typical Use Case for second hand laser cutter | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Signage, decorative items | Readily available and inexpensive | Can warp or crack | Low |
| Acrylic | Displays, signage | Lightweight and shatter-resistant | Higher cost than wood | Medium |
| Metal | Industrial applications | High precision and durability | Requires specialized equipment | High |
| Leather | Fashion accessories | Unique texture and premium feel | Variable quality and higher cost | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly processed by second-hand laser cutters, offering valuable insights for international B2B buyers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will aid in making informed purchasing decisions that align with market demands and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for second hand laser cutter
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Second-Hand Laser Cutters?
The manufacturing processes for second-hand laser cutters involve several critical stages that ensure the machines meet operational standards and provide value to buyers. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Material Preparation: What Is Involved?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This stage involves sourcing high-quality components such as laser tubes, optics, and frames. Suppliers often use a combination of new and refurbished parts to balance cost and performance. For second-hand laser cutters, the focus is on inspecting existing components for wear and compatibility with modern technology. This inspection can include checking the laser source for efficiency and the frame for structural integrity.
How Is the Forming Process Conducted?
Next is the forming stage, where materials are shaped into parts. This process typically involves cutting, bending, and machining components to precise specifications. Advanced CNC machining tools are often employed to ensure high accuracy. For second-hand equipment, the forming stage may include retrofitting older components to enhance performance or replace outdated technology. The goal is to maintain the cutter’s operational capabilities while ensuring that it meets current industry standards.
What Happens During the Assembly Phase?
The assembly phase is crucial for integrating all components into a fully functional machine. Skilled technicians carefully assemble the laser cutter, ensuring that all parts are aligned and secured. This includes installing the laser source, optics, and cooling systems. Attention to detail is paramount, as even minor misalignments can lead to significant operational issues. In the case of second-hand machines, this stage may also involve reconditioning parts, such as cleaning optics and recalibrating laser sources to ensure optimal performance.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used?
Once assembled, the laser cutter undergoes finishing techniques to prepare it for operation. This may include painting or coating to prevent corrosion and enhance aesthetics. Additionally, final adjustments are made to calibrate the machine, ensuring that it meets the specified cutting and engraving standards. For second-hand machines, this stage can also involve thorough cleaning and polishing to restore the machine’s appearance and functionality.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Implemented?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for second-hand laser cutters. It ensures that the machines meet safety and operational standards, which is particularly important for international buyers.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers should be familiar with international quality standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, and CE marking, which indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Understanding these certifications can provide assurance that the equipment has been manufactured to a recognized quality standard.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before manufacturing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, regular inspections are conducted to monitor quality and identify any deviations from specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the machine is fully assembled, a comprehensive inspection is performed to verify that it meets all operational and safety standards before shipment.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the laser cutter’s functionality and safety. Common tests include:
- Functional Testing: Assessing the machine’s performance under operational conditions to ensure it meets specified cutting and engraving capabilities.
- Safety Testing: Verifying that all safety features are operational, including emergency stop functions and protective covers.
- Calibration Checks: Ensuring that the laser aligns correctly and that the cutting parameters are set accurately for different materials.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for B2B buyers, especially when purchasing second-hand laser cutters from international sources. Here are some effective methods:
What Audit Processes Should Be Conducted?
Conducting audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing practices and quality control measures. Buyers should look for:
- Documentation: Request quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports and compliance certificates.
- On-Site Audits: If feasible, visiting the manufacturing facility can provide firsthand insight into production practices and the condition of the machines.
How to Utilize Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance. These independent entities can verify that the equipment meets specified standards and provide unbiased reports on the condition and quality of the machines.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding QC and certification nuances is crucial. Buyers should be aware of:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have varying standards and certifications. For instance, CE marking is essential for European markets, while other regions may require compliance with local regulations.
- Import Regulations: Familiarity with import regulations in the buyer’s home country can prevent complications during the shipping and customs process.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for second-hand laser cutters is essential for B2B buyers. By being informed about the stages of production, quality control checkpoints, and verification methods, buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This knowledge is particularly valuable in navigating the complexities of international trade, ensuring that investments in laser cutting technology yield optimal returns.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘second hand laser cutter’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing and fabrication, sourcing a second-hand laser cutter can be a cost-effective way to enhance your production capabilities. This checklist is designed to guide B2B buyers through the crucial steps of acquiring a pre-owned laser cutter, ensuring that you make a well-informed decision that meets your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before embarking on your search, clearly outline the technical requirements of the laser cutter. Consider factors such as the type of materials you’ll be cutting or engraving, the desired cutting area dimensions, and the laser technology (e.g., CO2, fiber). Having specific criteria will help narrow down your options and ensure you select a machine that aligns with your production goals.
Step 2: Research the Market and Pricing
Conduct thorough market research to understand the pricing landscape for second-hand laser cutters. Prices can vary significantly based on brand, model, and condition. Look for reputable online marketplaces and auction sites, and compare prices to gauge a fair market value. This step is essential to avoid overpaying and to identify potential deals.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
It’s critical to vet suppliers before making a purchase. Request company profiles, customer testimonials, and case studies from businesses that have sourced equipment from them. Ensure that the supplier has a solid reputation in the industry and offers warranties or service agreements for their machines. This due diligence can protect you from potential risks associated with purchasing used equipment.
Step 4: Inspect the Equipment Thoroughly
Whenever possible, inspect the laser cutter in person or request detailed video demonstrations. Look for signs of wear, ensure all components are functioning properly, and verify that the machine meets your technical specifications. Pay attention to the maintenance history, as well-maintained equipment is likely to perform better and require fewer repairs.
Step 5: Confirm Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the laser cutter complies with local regulations and safety standards. Check for necessary certifications, especially if the machine will be used in a regulated environment. This is crucial not only for operational safety but also for legal compliance, which can have significant implications for your business.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve found a suitable machine, engage in negotiations regarding price, delivery, and warranty terms. Don’t hesitate to ask for additional support during installation and setup. Having clear terms can protect your investment and provide peace of mind.
Step 7: Plan for Installation and Training
Finally, consider how the laser cutter will be integrated into your existing operations. Arrange for installation by qualified technicians and ensure that your team receives adequate training on the machine’s operation and maintenance. This preparation will maximize the benefits of your new equipment and enhance productivity from day one.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing a second-hand laser cutter with confidence, ultimately leading to a successful acquisition that supports their business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for second hand laser cutter Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Second Hand Laser Cutters?
When analyzing the costs associated with sourcing second-hand laser cutters, several key components must be considered:
-
Materials: The materials used in the construction of the laser cutters significantly influence their cost. High-quality components, such as optics and lasers, can increase the initial price but may offer better longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both the original manufacturing and any refurbishment work done on the second-hand equipment. Skilled technicians are required for inspections, repairs, and upgrades, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses incurred during the production of laser cutters. These overheads are often factored into the pricing of refurbished machines.
-
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): Tooling costs refer to the equipment used to produce or refurbish the laser cutters. Quality control measures ensure that the refurbished machines meet industry standards, which may involve additional testing and certification expenses.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the size and weight of the machinery, as well as the distance from the supplier to the buyer. International shipping may also involve tariffs or customs duties that can further affect pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers often apply a markup on second-hand equipment to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the margin is crucial for buyers aiming to negotiate effectively.
How Do Price Influencers Impact the Cost of Second Hand Laser Cutters?
Several factors can influence the pricing of second-hand laser cutters:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchases often yield better pricing. Suppliers may offer discounts for larger orders, making it beneficial for businesses that require multiple machines.
-
Specifications and Customization: Machines with specialized features or configurations may command higher prices. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid overpaying for unnecessary features.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that come with certifications or warranties typically carry higher prices due to the assurance of quality. Buyers should weigh the benefits of these assurances against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but they often provide better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms and responsibilities (Incoterms) is essential. Costs can vary significantly depending on whether the buyer or seller is responsible for shipping, insurance, and duties.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency When Sourcing Second Hand Laser Cutters?
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate the price. Many suppliers expect some back-and-forth discussion and may have flexibility in their pricing, especially for second-hand equipment.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with the equipment, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A cheaper machine may incur higher operational costs over time.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and import regulations that can affect overall costs. It’s advisable to secure quotes in the buyer’s local currency and factor in all potential additional costs.
-
Inspect Before Purchase: If possible, inspect the machine in person or request detailed documentation regarding its condition and history. This can help avoid unexpected issues after purchase.
-
Research and Compare: Take the time to research multiple suppliers and compare prices. Utilize platforms that aggregate listings to find the best deals and ensure you’re getting a fair price.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for second-hand laser cutters can vary significantly based on condition, specifications, and market demand. The figures provided are indicative and may not reflect the final price. Buyers should conduct thorough research and consider all factors before making a purchase decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing second hand laser cutter With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Second Hand Laser Cutters
When considering the procurement of laser cutting equipment, B2B buyers often weigh various options available in the market. While second hand laser cutters present an attractive choice due to their affordability and functionality, it is essential to compare them against other viable solutions. This analysis will focus on two alternatives: CNC Plasma Cutters and Waterjet Cutters, both of which can achieve similar cutting and engraving results.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Second Hand Laser Cutter | CNC Plasma Cutter | Waterjet Cutter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for intricate designs; limited by material types (e.g., metals, plastics) | Excellent for thicker materials; lower precision on fine details | Versatile with various materials; very precise, especially for thin sheets |
| Cost | Generally 30% less than new; lower upfront investment | Moderate to high; depends on the machine and setup | High initial costs and operational expenses |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training for optimal use; setup can be straightforward | Easier to operate for basic cuts; may need skilled operators for complex tasks | Complex setup; requires specialized knowledge and training |
| Maintenance | Requires regular maintenance; parts may be harder to source | Generally low; consumables (nozzles, electrodes) need replacing | High maintenance due to wear on parts and water filtration systems |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for engraving and cutting detailed designs in thinner materials | Best for heavy-duty cutting of metals and thicker materials | Excellent for cutting intricate designs in various materials without heat-affected zones |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Plasma Cutters
CNC Plasma Cutters utilize a high-velocity jet of ionized gas (plasma) to cut through electrically conductive materials. They are particularly effective for projects that require speed and efficiency in cutting thicker metals. The initial investment can be moderate, but the operational costs can vary depending on the power source and consumables. While they are easier to operate for basic cuts, achieving intricate designs may require skilled operators. Additionally, the heat generated during cutting can lead to warping, making them less suitable for delicate applications.
Waterjet Cutters
Waterjet Cutters use a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through a wide range of materials, including metals, glass, and composites. This technology is highly versatile and allows for precise cuts without introducing heat, thereby preventing material distortion. However, the initial investment is significant, and operational costs can be high due to the need for water filtration systems and regular maintenance. The complexity of setup and operation requires specialized knowledge, making it less accessible for smaller businesses or those without technical expertise.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate cutting technology requires careful consideration of your specific business needs, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. Second hand laser cutters offer an economical solution for businesses focusing on precision engraving and cutting of thinner materials. In contrast, CNC plasma and waterjet cutters excel in different applications—CNC plasma for heavier materials and speed, and waterjet for versatility and precision without heat distortion. Assessing these factors will help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their production goals and operational efficiencies.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for second hand laser cutter
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Second-Hand Laser Cutter?
When considering the purchase of a second-hand laser cutter, understanding its technical properties is crucial for making informed decisions. Below are essential specifications that influence performance, cost-effectiveness, and suitability for specific applications.
1. Laser Type and Power Rating
Laser cutters primarily use CO2 or fiber lasers, with power ratings typically ranging from 30W to 100W or more. The type of laser affects the materials that can be processed—CO2 lasers excel in cutting non-metal materials like wood and acrylic, while fiber lasers are better suited for metals. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate laser type and power rating ensures that the machine meets production needs efficiently.
2. Working Area Dimensions
The working area (or bed size) is the maximum size of the material that can be processed in the machine. Common dimensions include 16” x 24” or larger formats for industrial applications. Buyers must evaluate their typical material sizes to ensure the cutter can handle their production volumes without the need for excessive repositioning or material handling.
3. Speed and Precision
The cutting speed (measured in inches per minute) and precision (often indicated by tolerances such as ±0.01mm) are critical for operational efficiency. Higher speeds can increase productivity, but precision is vital for maintaining quality, especially in detailed designs. Understanding these metrics helps businesses assess whether a second-hand laser cutter can meet their production standards.
4. Cooling System
A reliable cooling system, such as a water chiller, is essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and prolonging the lifespan of the laser cutter. An efficient cooling system prevents overheating, which can lead to equipment failure and costly downtime. B2B buyers should inquire about the condition and effectiveness of the cooling system in any second-hand machine they consider.
5. Maintenance History and Condition
The maintenance history and overall condition of the second-hand laser cutter are important indicators of its reliability and potential longevity. Machines that have been regularly serviced and maintained will likely perform better and require fewer repairs. Buyers should request documentation that outlines previous maintenance activities to assess the machine’s current state.
6. Software Compatibility
Modern laser cutters are often integrated with software that controls design and cutting processes. Compatibility with popular design software (like AutoCAD or CorelDRAW) is essential for seamless operation. Buyers should ensure that the second-hand machine supports the software they currently use or plan to use in their operations.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Second-Hand Laser Cutters?
Understanding trade terminology is vital for navigating the purchasing process. Here are some commonly used terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to the original manufacturer of the equipment. In the context of laser cutters, knowing the OEM can help buyers assess the machine’s quality, support, and spare parts availability. It’s advisable to prioritize machines from reputable OEMs to ensure long-term reliability.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. For second-hand laser cutters, this term may apply if purchasing multiple machines or parts. Understanding MOQ helps buyers negotiate better pricing and ensures they meet supplier requirements.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. When purchasing a second-hand laser cutter, submitting an RFQ can help buyers get competitive pricing and terms from multiple suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping. Understanding these terms is crucial for determining who bears the cost and risk at various stages of the shipping process. This knowledge is particularly important for international B2B buyers to avoid unexpected expenses.
5. Refurbished vs. Used
Refurbished machines have been restored to like-new condition and typically come with some form of warranty, while used machines may show signs of wear and lack any guarantees. Knowing the difference can significantly impact a buyer’s decision-making process regarding reliability and cost.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in second-hand laser cutters, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost savings.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the second hand laser cutter Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics Affecting the Second Hand Laser Cutter Sector?
The second-hand laser cutter market is experiencing significant growth, driven by several global factors. First, the demand for cost-effective manufacturing solutions is increasing among businesses in emerging economies, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These regions are witnessing a surge in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require affordable technology to enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. As a result, the availability of pre-owned laser cutters at competitive prices—often up to 30% lower than new models—has become an attractive option for international buyers.
Another emerging trend is the increasing adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which are transforming traditional manufacturing processes. Businesses are seeking laser cutters equipped with advanced features such as automation, precision, and connectivity. This trend is further supported by the rise of e-commerce platforms that facilitate easy sourcing and purchasing of used machinery. B2B buyers can now access detailed listings, compare prices, and read reviews, making the procurement process more transparent and efficient.
The market is also witnessing a shift towards sustainability. As environmental regulations become stricter, companies are looking for ways to minimize waste and optimize resource usage. This has led to a growing interest in refurbished laser cutters that not only meet operational needs but also align with sustainability goals.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Second Hand Laser Cutters?
The importance of sustainability in the sourcing of second-hand laser cutters cannot be overstated. As businesses become more environmentally conscious, they are increasingly seeking equipment that contributes to a circular economy. This involves reusing and recycling machinery to minimize waste and reduce the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing.
Ethical supply chains are gaining traction, with buyers prioritizing vendors that adhere to sustainable practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Moreover, sourcing second-hand equipment can significantly reduce the environmental impact compared to purchasing new machines, as it lessens the demand for raw materials and energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
B2B buyers should also consider the operational efficiencies gained from using refurbished laser cutters, which often come with warranties and support services. This not only ensures that the equipment operates at optimal levels but also reinforces the supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing.
What Historical Developments Have Shaped the Second Hand Laser Cutter Market?
The evolution of the laser cutter market has been marked by rapid technological advancements and changing consumer preferences. Originally, laser cutting technology was primarily used in large-scale industrial applications, making it prohibitively expensive for smaller businesses. However, as technology improved, the cost of laser cutters began to decrease, leading to wider adoption across various sectors.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of CO2 and fiber laser technology revolutionized the market by providing more versatile and efficient cutting solutions. This transition made laser cutting accessible to SMEs, particularly in developing regions. The rise of e-commerce has further accelerated the growth of the second-hand market, enabling buyers to easily find and purchase pre-owned machines that meet their specific needs.
As the market continues to evolve, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing is likely to shape future developments, ensuring that the second-hand laser cutter sector remains a vital component of the global manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of second hand laser cutter
-
How do I determine the quality of a second-hand laser cutter?
To assess the quality of a second-hand laser cutter, start by reviewing the machine’s operational history and maintenance records. Look for certifications from reputable manufacturers that indicate the machine has been inspected and refurbished by qualified technicians. It’s also advisable to request a demonstration of the machine to evaluate its performance firsthand. Finally, consider customer reviews and testimonials from previous buyers to gauge reliability and performance. -
What are the essential specifications to consider when buying a second-hand laser cutter?
When purchasing a second-hand laser cutter, focus on key specifications such as cutting speed, power output (measured in watts), working area dimensions, and the type of laser technology (CO2 or fiber). Additionally, check compatibility with various materials you plan to work with, such as metals, plastics, or wood. Understanding these specifications will help ensure the machine meets your production needs effectively. -
How can I verify the legitimacy of a supplier for second-hand laser cutters?
To verify a supplier’s legitimacy, start by checking their business credentials, including registration details and industry affiliations. Request references from past clients and look for reviews online. It’s also wise to conduct a site visit if possible, or ask for a video tour of their facility. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides warranties and clear return policies to protect your investment. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a second-hand laser cutter?
Payment terms for second-hand laser cutters can vary widely by supplier and region. Common options include full upfront payment, a deposit followed by the balance upon delivery, or installment plans. Be sure to discuss and clarify payment terms before finalizing the purchase, including acceptable payment methods (bank transfer, credit card, etc.). Always ensure that terms are documented to avoid disputes later. -
Are there customization options available for second-hand laser cutters?
Many suppliers offer customization options for second-hand laser cutters to better fit your specific production requirements. This may include modifications to software, additional attachments, or upgrades to enhance cutting capabilities. Discuss your needs with the supplier to explore available customization options, and ensure that any changes do not compromise the machine’s warranty or functionality. -
What should I know about logistics and shipping when buying internationally?
When sourcing a second-hand laser cutter from another country, consider logistics aspects such as shipping costs, import duties, and customs regulations in your region. Work with suppliers who can provide comprehensive shipping solutions, including handling customs documentation. Additionally, ensure that the shipping terms are clear, including insurance coverage during transit to protect against potential damages. -
What is the typical lead time for delivery of a second-hand laser cutter?
The lead time for delivery of a second-hand laser cutter can vary depending on the supplier’s location, the machine’s condition, and any required refurbishments. Generally, you can expect lead times to range from a few weeks to several months. Always confirm the expected delivery timeline with the supplier and factor this into your production scheduling to avoid delays. -
How can I ensure the second-hand laser cutter meets my quality assurance standards?
To ensure the second-hand laser cutter meets your quality assurance standards, request detailed documentation of its operational performance, including any quality tests conducted. Consider implementing a trial period where you can test the machine in your production environment to assess its capabilities. Additionally, establish a maintenance schedule post-purchase to keep the machine in optimal working condition, ensuring ongoing quality in your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Second Hand Laser Cutter Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. OMTech – Pre-Owned Laser Engravers
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Pre-Owned Fiber, CO2 Laser Engravers Machines – OMTech Certified CO2 laser engravers and Fiber laser metal marking machines priced up to 30% below new machine purchases. Each refurbished machine is thoroughly inspected by OMTech engineers, guaranteeing full functionality and restoration to original condition. Example product: Pre-Owned MF1624-60 – 60W CO2 Laser Engraver Cutting Machine with 16” x …
2. AMADA – BODOR A SERIES (2024)
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Laser Cutters available from various brands including AMADA, MITSUBISHI, MAZAK, TRUMPF, BYSTRONIC, and more. Types of CNC laser cutters include gas laser cutting, crystal laser cutting, and fiber laser cutting. Key models listed are BODOR A SERIES (2024), HYPERUSA HYPERBEAM (2023), IPG PHOTONICS YLS6000C (2022), NUKON REX 315 (2021), and several others from brands like TROTEC, AP LAZER, a…
3. Cloudray – CO2 Laser Power Supply
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Metalworking Laser Cutting Machines for sale on eBay. Popular products include Cloudray 110V 100W CO2 Laser Power Supply for CO2 Engraver Cutter priced at $169.99 and Cloudray 110V 80W CO2 Laser Power Supply for CO2 Cutting Machine. Related searches include Laser Cutting Machine, Metal Laser Cutter Machine, Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machine, and more. Categories include various types of metalworki…
4. OMTech – 80W CO2 Laser
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Used/secondhand laser cutters, specifically CO2 lasers, with mentions of brands like OMTech and Rabbit Laser. Users discussed purchasing from Facebook Marketplace, Craigslist, and directly from manufacturers. Specific models mentioned include an 80W red and black laser with a CW5200 chiller and a chuck rotary. Prices mentioned include $2500 for a nearly new unit. Users also mentioned issues with m…
5. Laser Resale – Used Industrial & Scientific Lasers
Domain: laserresale.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Marketplace for used industrial and scientific lasers, including pre-owned lasers, laser systems, laser associated equipment, and optical equipment. Key product categories include: Industrial Lasers (CO₂ Lasers, Nd:YAG Lasers, Fiber Lasers, etc.), Scientific Lasers (Argon Lasers, He:Ne Lasers, Ti:Sapphire, etc.), Optical Laboratory Equipment, and Laser Related Equipment (Chillers, Power Supplies, …
6. CNC Laser Cutters – Used Equipment for Sale
Domain: kdcapital.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Laser Cutter for Sale – KD Capital Equipment. Available brands include Amada, BLM, Bystronic, Cincinnati, Coherent, Durma, Ermaksan, FiberCab, Gravotech, Grizzly, HK, Hymson, IPG, Kasu, Komatsu, MVD, Mazak, Mitsubishi, Multicam, PIA, PrimaLaser, Richpeace, Style CNC, Trotec, Trumpf. Key specifications include year of manufacture, table width, table length, and max wattage. Types of lasers…
7. AtomStack – A5 Pro Laser Engraver
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, AtomStack – A5 Pro Laser Engraver, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. TRUMPF – Laser Cutters
Domain: machinetools.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutters for sale listings – MachineTools.com. A machine that cuts materials by directing the output of a high-power laser, by computer, at the material to be cut. Key brands include TRUMPF (96), AMADA (80), BYSTRONIC (78), MITSUBISHI (36), MAZAK (26). Available wattage ranges from 30 w to 12000000 w. Listings include various models such as ACCURL MASTERLINE 3015, ADIGE LT803D, ALPHA CNC HD-F…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for second hand laser cutter
The strategic sourcing of second-hand laser cutters presents an invaluable opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By acquiring pre-owned equipment, businesses can significantly reduce capital expenditures—often saving up to 30% compared to new machines. This cost-effectiveness does not compromise quality, as many refurbished models undergo thorough inspections to ensure they meet industry standards.
Moreover, sourcing second-hand laser cutters allows companies to stay agile and competitive in a rapidly evolving market. As laser technology continues to advance, investing in pre-owned equipment can facilitate quicker adoption of new capabilities without the associated financial strain of purchasing new machinery.
As you explore your options, consider the specific needs of your operations, such as the type of materials you’ll be cutting or engraving and the desired functionalities. By strategically sourcing second-hand laser cutters, your business can enhance productivity while optimizing costs.
Looking ahead, embrace this opportunity to elevate your manufacturing capabilities. Engage with reputable suppliers and take the next step towards a more efficient and cost-effective production process.