Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for saw to cut through metal
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right saw to cut through metal can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexity of metal cutting—encompassing various materials, thicknesses, and applications—demands a thorough understanding of the tools available. This guide aims to demystify the diverse range of metal cutting saws, providing insights into their specifications, applications, and operational efficiencies.
From heavy-duty industrial chop saws to versatile circular saws, this comprehensive resource covers the intricacies of each type, helping buyers navigate through critical factors such as performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, we delve into essential considerations for supplier vetting, ensuring that you partner with reputable manufacturers who meet international quality standards.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Whether you’re in Nigeria, Brazil, or elsewhere, understanding the nuances of metal cutting tools will enhance your operational capabilities, streamline project execution, and ultimately drive your business success. Embrace the knowledge provided here to confidently invest in the right saws that meet your specific metal cutting needs.
Understanding saw to cut through metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chop Saw | Uses a rotating blade; ideal for straight cuts; often corded. | Construction, metal fabrication | Pros: Fast cuts, precise angles. Cons: Limited to straight cuts. |
| Circular Saw | Portable, versatile, can cut various thicknesses; corded. | Metalworking, HVAC, plumbing | Pros: Lightweight, adaptable to different materials. Cons: Requires skill for accuracy. |
| Band Saw | Continuous loop blade; ideal for intricate cuts; stationary. | Manufacturing, repair shops | Pros: Smooth cuts, can handle complex shapes. Cons: More expensive, requires floor space. |
| Magnetic Drill | Uses magnetic base for stability; ideal for drilling holes. | Structural steel fabrication, installation | Pros: Portable, precise, reduces risk of slipping. Cons: Limited to drilling, not cutting. |
| Plasma Cutter | Uses high-temperature plasma; effective for thick materials. | Heavy manufacturing, automotive | Pros: Cuts through thick metal, fast. Cons: Requires training, can be costly. |
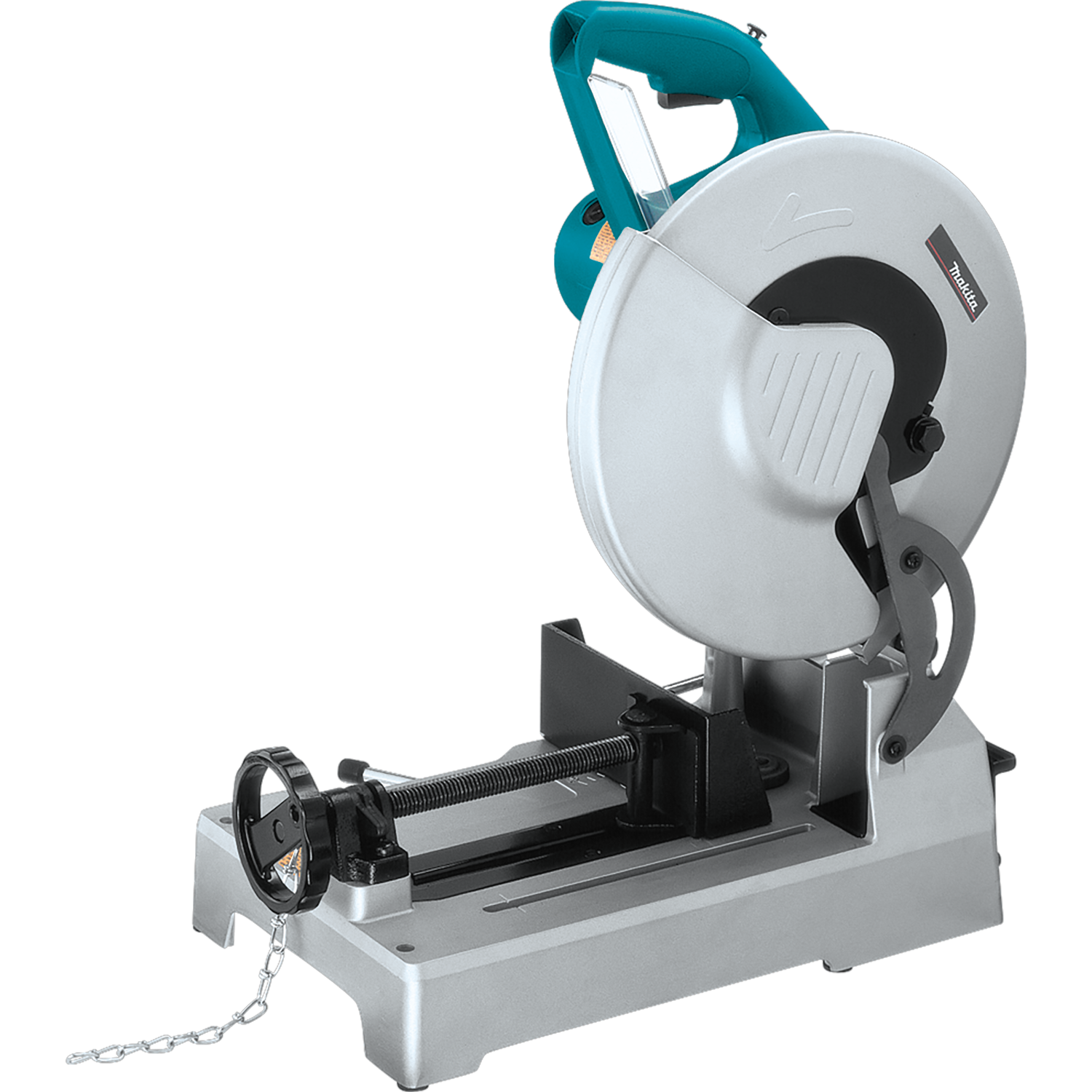
What Are the Key Characteristics of Chop Saws for Metal Cutting?
Chop saws are powerful tools equipped with a rotating blade that excels in making straight cuts through metal. Typically used in construction and metal fabrication, these saws are essential for cutting rebar, metal pipes, and structural steel. When considering a chop saw, businesses should evaluate features such as blade size, cutting capacity, and whether the saw can handle the specific types of metal they work with. The speed and precision of chop saws can significantly enhance productivity on job sites.
How Do Circular Saws Fit Into Metal Cutting Applications?
Circular saws offer versatility, allowing users to cut various thicknesses of metal efficiently. They are portable, making them suitable for on-site work in industries like HVAC and plumbing. Buyers should look for models that provide adjustable cutting depths and compatible blades for different metal types. While circular saws may require a skilled operator to achieve precise cuts, their adaptability and lightweight design make them a valuable addition to any metalworking toolkit.
What Advantages Do Band Saws Offer for Intricate Metal Cuts?
Band saws are characterized by their continuous loop blade, which allows for intricate and smooth cuts, making them ideal for manufacturing and repair shops. They can handle a wide range of materials and thicknesses, which is a significant advantage for businesses that require precision in their metalwork. However, the initial investment and the need for dedicated workspace can be a consideration for potential buyers. Band saws are particularly useful for fabricating custom parts or performing detailed work on metal components.
Why Choose Magnetic Drills for Metal Fabrication?
Magnetic drills are specialized tools that utilize a magnetic base to securely attach to metal surfaces, providing stability during drilling operations. They are particularly beneficial in structural steel fabrication and installation projects. Buyers should assess the drill’s weight, magnetic strength, and the size of the drill bits it can accommodate. While magnetic drills are limited to drilling rather than cutting, their portability and precision make them an excellent choice for fieldwork where accuracy is paramount.
What Makes Plasma Cutters Essential for Heavy Metal Work?
Plasma cutters are high-performance tools that use a jet of ionized gas to cut through thick metal materials quickly and efficiently. They are widely used in heavy manufacturing and the automotive industry, where cutting speed and thickness capability are critical. Businesses interested in plasma cutters should consider factors such as the cutter’s amperage, portability, and the types of metals it can effectively cut. Although plasma cutters require a higher level of training and investment, their ability to handle tough materials makes them invaluable in demanding applications.
Key Industrial Applications of saw to cut through metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of saw to cut through metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Cutting structural steel beams and reinforcements | Ensures precision in structural integrity | Durability, blade compatibility, and cutting capacity |
| Manufacturing | Fabrication of metal components for machinery | Increases efficiency in production processes | Speed, blade quality, and material compatibility |
| Automotive | Production of vehicle frames and parts | Enhances safety and performance of vehicles | Precision cutting, blade longevity, and cost-effectiveness |
| Metal Fabrication | Custom metal designs and prototypes | Allows for creativity and customization | Versatility of saw types and support for various metals |
| Shipbuilding | Cutting hull plates and structural components | Supports robust construction and safety standards | Corrosion resistance, cutting speed, and blade life |
What Are the Key Applications of Saws to Cut Through Metal in Construction?
In the construction industry, saws designed to cut through metal are crucial for precision cutting of structural steel beams and reinforcements. These tools enable contractors to achieve precise dimensions, essential for maintaining structural integrity. Buyers in this sector often prioritize durability and compatibility with various blade types to handle different steel grades, ensuring they can meet diverse project requirements efficiently.
How Are Saws Used in Manufacturing Metal Components?
In manufacturing, saws are integral to fabricating metal components for machinery. The ability to cut through various metal types quickly and accurately improves production efficiency. Manufacturers should consider the speed of the saw, the quality of the blades, and compatibility with the materials they work with. These factors directly influence the overall productivity and cost-effectiveness of their operations.
What Role Do Saws Play in Automotive Production?
In the automotive sector, saws are employed to cut vehicle frames and parts, ensuring safety and performance. Precision is vital here, as even minor inaccuracies can lead to significant safety issues. Buyers need to focus on saws that offer precision cutting capabilities and blade longevity to minimize downtime and replacement costs, which are critical for maintaining competitive production schedules.
Why Are Saws Important in Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication relies heavily on saws for creating custom designs and prototypes. The versatility of these tools allows fabricators to experiment with various shapes and sizes, catering to specific client needs. When sourcing saws, businesses should look for tools that can handle multiple metal types and thicknesses to facilitate a broader range of projects, enhancing their service offerings.
How Do Saws Contribute to Shipbuilding?
In the shipbuilding industry, saws are essential for cutting hull plates and other structural components. These applications demand tools that can withstand harsh marine environments while providing robust performance. Buyers must ensure that the saws they invest in have corrosion-resistant features, high cutting speeds, and extended blade life to meet the rigorous demands of shipbuilding projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘saw to cut through metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Achieving Clean Cuts Without Excess Heat
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges B2B buyers face when utilizing saws to cut through metal is the issue of overheating during the cutting process. This overheating can lead to warping of the metal, compromised structural integrity, and a poor finish, which may require additional processing to rectify. For businesses that rely on precision components, such as those in the automotive or aerospace sectors, this can result in costly delays and quality control issues.
The Solution: To mitigate the overheating problem, buyers should invest in saws specifically designed for metal cutting, such as those equipped with TCT (tungsten carbide-tipped) blades. These blades are engineered to cut through metal efficiently while minimizing heat generation. Additionally, incorporating a coolant system can significantly enhance performance by keeping both the blade and the workpiece cool during operation. When sourcing these saws, look for models that offer variable speed settings, allowing operators to adjust the cutting speed based on the material thickness and type. This adaptability can further reduce heat buildup and improve cut quality.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Cutting Performance Across Different Metals
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter challenges when using a single type of saw for cutting various metal types, such as aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. Each metal possesses unique properties—some are softer and easier to cut, while others are harder and more abrasive. This inconsistency can lead to tool wear and tear, inefficient production cycles, and increased operational costs due to frequent blade replacements.
The Solution: To address this issue, businesses should consider investing in a versatile metal cutting saw that can accommodate different blade types designed for specific metals. For instance, a saw that can use both TCT blades for ferrous metals and specialized blades for non-ferrous materials will enhance versatility. When selecting saws, ensure that they come with clear compatibility specifications for various blade types. Additionally, training operators on the appropriate blade selection and cutting techniques for each metal type can optimize performance and extend the lifespan of the tools. Regularly scheduled maintenance checks to inspect blades for wear can also prevent suboptimal cutting performance.
Scenario 3: Safety Risks During Metal Cutting Operations
The Problem: Safety remains a paramount concern in any metalworking environment. B2B buyers are often worried about the potential hazards associated with using saws to cut through metal, including flying debris, noise pollution, and the risk of injury from improper handling or equipment malfunctions. These safety issues can lead to workplace accidents, increased insurance costs, and regulatory scrutiny.
The Solution: To enhance safety, companies should prioritize the acquisition of saws that come with advanced safety features, such as blade guards, automatic shut-off systems, and ergonomic designs to minimize operator fatigue. It is also essential to implement comprehensive safety training programs for all personnel involved in metal cutting operations. This training should cover proper equipment handling, personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, and emergency procedures. Additionally, creating a culture of safety by encouraging open communication about potential hazards and regular safety audits can significantly reduce risks. Investing in noise reduction solutions, such as soundproofing materials or quieter saw models, can also contribute to a safer working environment.
By addressing these common pain points, B2B buyers can enhance their metal cutting operations, ensuring efficiency, safety, and high-quality results.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for saw to cut through metal
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used for Metal Cutting Saws?
When selecting a saw to cut through metal, understanding the properties of the materials involved is crucial. Different metals exhibit unique characteristics that affect performance, durability, and suitability for various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials: Mild Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Cast Iron.
How Does Mild Steel Perform in Metal Cutting Applications?
Mild steel is a widely used material due to its excellent machinability and cost-effectiveness. It has a low carbon content, which provides good weldability and ductility. Mild steel typically has a temperature rating of around 600°C and is not highly resistant to corrosion unless treated.
Pros:
– Cost-effective and readily available.
– Good machinability, making it easier to cut and shape.
– Suitable for a variety of applications, including structural components.
Cons:
– Lower corrosion resistance compared to other metals.
– Can deform under high pressure or temperature.
Impact on Application: Mild steel is ideal for general fabrication and construction, but it may require protective coatings for outdoor use to prevent rust.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is common for mild steel products. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure that local suppliers meet these standards to guarantee quality.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Stainless Steel?
Stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance and strength, making it a popular choice for applications requiring durability. It typically has a higher temperature rating than mild steel, often exceeding 800°C, depending on the alloy.
Pros:
– Exceptional corrosion resistance, suitable for harsh environments.
– High strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for structural applications.
Cons:
– More expensive than mild steel.
– Requires specialized cutting tools due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in food processing, medical equipment, and outdoor applications where rust resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with DIN standards is crucial for stainless steel products, especially in Europe. Buyers should also consider local availability of specific grades, such as 304 or 316, which are commonly used.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Terms of Cutting?
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it a preferred material in aerospace and automotive industries. It has a lower melting point than steel, which can affect cutting techniques.
Pros:
– Lightweight, reducing overall product weight.
– Excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
Cons:
– Softer than steel, leading to potential wear on cutting tools.
– Can be more expensive than mild steel.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aircraft and automotive components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with JIS standards, particularly in Japan and some parts of Asia. Understanding the local market for aluminum alloys is also essential for sourcing.
What Should Buyers Know About Cutting Cast Iron?
Cast iron is known for its brittleness and high wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It typically has a temperature rating of around 1200°C, which allows for high-performance cutting.
Pros:
– Excellent wear resistance and durability.
– Good machinability when using the right tools.
Cons:
– Brittle nature can lead to chipping during cutting.
– Heavier than other materials, impacting overall design.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in heavy machinery and automotive components, where durability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is essential for cast iron products. Buyers should also consider the availability of appropriate cutting tools designed for this material.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Metal Cutting Saws
| Material | Typical Use Case for saw to cut through metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild Steel | General fabrication and construction | Cost-effective and readily available | Lower corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and medical equipment | Exceptional corrosion resistance | More expensive than mild steel | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive components | Lightweight with excellent corrosion resistance | Softer, leading to tool wear | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Heavy machinery and automotive components | Excellent wear resistance | Brittle nature can lead to chipping | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials used in metal cutting applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and local standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for saw to cut through metal
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for Metal Cutting Saws?
The manufacturing process for metal cutting saws involves several critical stages designed to ensure high performance and durability. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions about their suppliers.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing metal cutting saws is material preparation. This involves sourcing high-grade materials, such as carbide or high-speed steel, which are essential for producing robust and long-lasting blades. Suppliers often prioritize materials that meet international standards, as this enhances the saw’s cutting efficiency and longevity. In this phase, suppliers may also conduct chemical analyses to ensure the materials meet specific alloy compositions required for different cutting applications.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This process typically involves several techniques, including forging, casting, or machining. Forging is commonly used for blades, as it enhances the material’s strength and toughness. For instance, the blade’s teeth might be precision-machined to create sharp edges capable of cutting through various metals without undue wear. Advanced techniques, such as laser cutting, may also be utilized for more intricate designs.
Assembly Process
Following the forming stage, the assembly process begins. This involves integrating various components of the saw, including the motor, blade, and housing. Manufacturers must ensure that all parts fit seamlessly to prevent vibrations and misalignments during operation. This stage may also include the installation of safety features, such as blade guards and automatic shut-off mechanisms, which are crucial for user safety.
Finishing Touches
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing. This may involve surface treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and durability, such as anodizing or applying protective coatings. Additionally, blades may undergo sharpening processes to ensure they are ready for immediate use. Quality control checks are essential at this stage to ensure that the finished product meets specified performance standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Metal Cutting Saws?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of metal cutting saws, as it directly impacts performance, safety, and customer satisfaction. Various international and industry-specific standards guide manufacturers in establishing effective QA processes.
International Standards for Quality Control
One of the most widely recognized international standards is ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Manufacturers seeking ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to quality through consistent processes and continuous improvement. This certification is crucial for B2B buyers, as it indicates a supplier’s dedication to producing reliable products.
Additionally, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, ensuring compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards. Buyers from Europe, in particular, should look for CE certification as a mark of quality assurance.
Industry-Specific Standards
For specialized applications, industry-specific certifications may also be relevant. For instance, the American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards for tools used in the oil and gas industry. Understanding these certifications can help buyers ensure that the saws they procure are suitable for their specific applications and environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Effective quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints are designed to catch defects early and ensure that the final product meets the required specifications.
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
The first checkpoint is Incoming Quality Control (IQC), where raw materials and components are inspected upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. This step is crucial for verifying that materials meet the specified quality and safety standards before they are used in production. Suppliers often employ chemical and physical testing methods to assess material integrity.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) occurs during the manufacturing process. This involves regular inspections and testing at various stages, ensuring that any deviations from specifications are addressed immediately. Techniques such as visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance tests are commonly used to maintain quality during production.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
The final checkpoint is Final Quality Control (FQC), where the finished products undergo rigorous testing before they are packaged and shipped. This stage often includes performance testing to ensure that the saws can cut through specified materials effectively. B2B buyers should inquire about the testing methods used in this phase to understand the reliability of the products they are purchasing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensure product reliability.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One effective method is to conduct supplier audits. These audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards. Regular audits can help build trust and foster long-term relationships between buyers and suppliers.
Requesting Quality Control Reports
Buyers should also request detailed quality control reports that outline the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports provide insight into the supplier’s commitment to quality and can help buyers make informed purchasing decisions.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspection Services
Engaging third-party inspection services is another way to verify supplier quality. Independent inspectors can provide unbiased assessments of the manufacturing processes and product quality. This is particularly valuable for international buyers who may not have the resources to conduct on-site inspections.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control can help international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing metal cutting saws from different regions.
Regional Standards and Compliance
Different countries may have varying regulations and standards for manufacturing and product safety. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations in their regions, such as those enforced by the National Standards Authority in Nigeria or the Brazilian National Institute of Metrology. This knowledge will help ensure that purchased products comply with local laws.
Language and Communication Barriers
Language barriers can also pose challenges in quality assurance processes. Buyers should ensure that they have clear communication with suppliers regarding quality standards and expectations. It may be beneficial to work with suppliers who have experience in international trade and can communicate effectively in multiple languages.
Cultural Differences in Business Practices
Cultural differences may influence business practices and perceptions of quality. Buyers should be aware of these differences and adapt their approach accordingly. Building strong relationships with suppliers through regular communication and visits can help bridge any gaps in understanding.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance standards, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing metal cutting saws, ensuring that they procure high-quality tools that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘saw to cut through metal’
In the competitive landscape of metal fabrication, selecting the right saw for cutting metal is critical for operational efficiency and product quality. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure saws designed for metal cutting. By following these actionable steps, buyers can ensure they make informed purchasing decisions that align with their specific needs.
1. Identify Your Cutting Requirements
Understanding the specific types of metal you will be cutting is essential. Different metals such as mild steel, stainless steel, or aluminum require different cutting tools and blades. Additionally, consider the thickness and volume of material, as this will dictate the power and type of saw needed.
- Blade Type: Choose blades designed for the specific metal to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
- Cutting Capacity: Ensure the saw can handle the maximum thickness and width of the materials you plan to cut.
2. Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing precise technical specifications will guide your procurement process. Consider factors such as power requirements (corded vs. cordless), cutting speed, and the type of cuts you need (straight, miter, etc.).
- Motor Power: A higher motor power typically equates to better cutting performance, especially for thicker materials.
- Cutting Speed: Look for saws that offer adjustable speeds for versatility across different applications.
3. Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a purchase, thoroughly vet potential suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and customer testimonials to assess their credibility and product quality.
- Supplier Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the metal cutting industry.
- Customer References: Contact previous buyers to gauge their satisfaction and the supplier’s reliability.
4. Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that suppliers meet industry standards and certifications. This is particularly important for international transactions where compliance with local regulations is necessary.
- Quality Assurance: Check for ISO certifications or similar quality standards that reflect a commitment to excellence.
- Safety Standards: Verify that tools meet safety regulations specific to your region, which is crucial for worker safety.
5. Request Samples or Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request samples or demonstrations of the saws you are considering. This allows you to evaluate the performance and ease of use before making a commitment.
- Testing Performance: Assess the saw’s cutting speed, precision, and ease of handling during the demonstration.
- User Feedback: Gather input from your team to ensure the tool meets their operational needs.
6. Compare Pricing and Warranty Options
Conduct a thorough comparison of pricing across different suppliers while also taking warranty options into account. A competitive price is important, but the warranty can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
- Total Cost Analysis: Consider not just the purchase price, but also potential maintenance and operational costs.
- Warranty Coverage: A longer warranty period can provide peace of mind and reduce the risk of unexpected expenses.
7. Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, ensure that you finalize the purchase agreement with clear terms. This should include delivery timelines, payment terms, and after-sales support.
- Clear Communication: Ensure that all terms are clearly stated to avoid misunderstandings later.
- After-Sales Support: Confirm the availability of technical support and spare parts to maintain the saw’s performance over time.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the procurement process for metal cutting saws, ensuring they choose the right tools that align with their business needs and operational goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for saw to cut through metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Metal Cutting Saws?
When sourcing saws for cutting metal, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials used, such as high-grade carbide for blades or heavy-duty steel for the body, significantly influences the cost. Premium materials enhance durability and cutting efficiency, justifying higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary depending on the region and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Skilled labor is essential for producing high-quality tools, and this may be reflected in the pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs, impacting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for cutting saw production can be substantial. Custom tooling for unique designs or specifications will increase costs but may be necessary for specific applications.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that tools meet industry standards. The costs associated with testing and certification can add to the overall price but are essential for maintaining product quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are particularly important for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and destination ports influence these logistics costs significantly.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary widely based on market positioning and competition. Buyers should be aware that established brands may charge a premium due to perceived quality and brand reputation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Cutting Saw Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of metal cutting saws, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically attract lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their needs to maximize cost efficiency.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized tools tailored to specific applications often come with a higher price tag. It’s essential to evaluate whether the customization adds significant value to the operation.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Tools made from superior materials or those with recognized certifications (e.g., ISO) can command higher prices. Buyers should balance the need for certification with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms used in international shipping can help buyers anticipate additional costs such as tariffs, insurance, and freight. This knowledge is critical for budgeting the total landed cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs for Metal Cutting Saws?
B2B buyers should consider several strategies to ensure cost efficiency when sourcing metal cutting saws:
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms. Building a relationship with suppliers may also yield volume discounts or favorable payment terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational efficiency, and lifespan of the tool. Investing in higher-quality saws may result in lower long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be mindful of regional pricing differences influenced by local market conditions, currency fluctuations, and import duties. Conducting thorough market research can help identify competitive pricing.
-
Comparative Analysis: Assess multiple suppliers to understand the market range for similar products. This can provide leverage during negotiations and ensure that you are getting a fair deal.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on factors such as supplier, region, and market conditions. Always request quotes from multiple suppliers to get the most accurate pricing for your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing saw to cut through metal With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Metal Cutting Saws
When selecting tools for cutting metal, it’s essential to consider various alternatives to saws. Different methods can cater to specific needs, whether it’s for precision, cost-effectiveness, or ease of use. This analysis compares the effectiveness of metal cutting saws against other viable solutions, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison of Metal Cutting Methods
| Comparison Aspect | Saw To Cut Through Metal | Angle Grinder | Metal Snips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, clean cuts | Versatile, good for rough cuts | Good for thin materials, less precision |
| Cost | Moderate ($200 – $900) | Low ($50 – $150) | Very low ($20 – $50) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires some setup | Easy to use, portable | Very easy, no setup needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate, blade replacement needed | Low, occasional wheel change | Low, minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Structural metal, pipes | Sheet metal, weld cuts | Thin sheet metal, curves |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
How Does an Angle Grinder Compare to Metal Cutting Saws?
Angle grinders are highly versatile tools that can cut, grind, and polish metal surfaces. They excel in situations requiring rough cuts or when working with various metal types, such as sheets or tubes. The main advantage of an angle grinder is its portability and ease of use, making it suitable for both shop and field applications. However, while they are cost-effective, they may not provide the same level of precision as saws, potentially leading to rough edges that require additional finishing.
What Are the Advantages of Using Metal Snips Instead of Saws?
Metal snips are ideal for cutting thin sheets of metal and are particularly useful for intricate work, including curves and tight spaces. They are inexpensive and require no power source, making them a practical choice for small projects or DIY applications. However, their limitations include the inability to cut through thicker materials and the potential for jagged edges, which may necessitate further finishing. This makes them less suitable for industrial or high-volume production environments where precision and speed are critical.
Conclusion: Which Metal Cutting Solution Should You Choose?
When deciding between a saw for cutting metal and its alternatives, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs. If precision and clean cuts are paramount, a metal cutting saw is likely the best choice, especially for structural applications. However, for lighter tasks or when working with thinner materials, angle grinders or metal snips may offer adequate performance at a lower cost. Ultimately, the right solution depends on the type of metal being cut, the required precision, and the available budget. Consider these factors carefully to optimize your operations and ensure efficient metal cutting in your projects.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for saw to cut through metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Saws for Cutting Metal?
When considering a saw for cutting metal, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Understanding these specifications can guide B2B buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
Blade Material Grade
The blade material significantly influences the saw’s cutting efficiency and durability. Common materials include high-speed steel (HSS), carbide-tipped, and bi-metal blades. HSS blades are affordable and suitable for softer metals, while carbide-tipped blades are designed for tougher materials, offering longer life and reduced wear. For B2B buyers, selecting the right blade material can result in lower operational costs and improved productivity.
Tooth Count (Teeth Per Inch – TPI)
The number of teeth on a blade affects the quality of the cut and the cutting speed. Blades with a higher TPI produce smoother cuts but may cut slower, while those with fewer teeth cut faster but can leave rough edges. Understanding the application—whether precision cutting or rapid removal—is vital for buyers to choose the appropriate blade for their needs.
Cutting Capacity
Cutting capacity refers to the maximum size of the material that can be cut by the saw. This includes the thickness and width of the metal. For B2B operations, ensuring that the saw can handle the sizes of materials commonly used is critical to avoid downtime and inefficiency.
Power Rating
The power rating, typically measured in watts or horsepower, indicates the strength of the saw’s motor. A higher power rating can facilitate cutting through thicker or harder metals more effectively. Buyers should assess their cutting requirements and select a saw that can maintain performance without overloading.
Speed Settings
Variable speed settings allow operators to adjust the cutting speed based on the material being worked on. This flexibility can enhance cutting efficiency and reduce the risk of damaging the material. For B2B buyers, investing in saws with adjustable speed settings can cater to diverse project requirements.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for navigating the B2B landscape effectively. Here are some key terms relevant to purchasing metal-cutting saws.
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of saws, purchasing from OEMs ensures that buyers receive high-quality, compatible parts and tools designed specifically for their equipment.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects inventory management and cost efficiency. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their specific needs to avoid excess inventory or stockouts.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers, issuing an RFQ can help compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal and terms for their metal-cutting needs.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs associated with their purchases, ensuring smoother transactions.
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. For businesses relying on timely deliveries for production schedules, understanding lead times is essential for effective planning and maintaining workflow.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing saws for cutting metal, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the saw to cut through metal Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Saw to Cut Through Metal Sector?
The global market for metal cutting saws is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand from sectors such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. Emerging economies in Africa and South America, particularly Nigeria and Brazil, are witnessing rapid industrialization, which fuels the need for efficient metal cutting tools. Additionally, technological advancements in power tools, such as improved blade materials and cutting technologies, are reshaping the landscape. Innovations like high-torque motors and enhanced carbide blades are enabling faster, cleaner cuts with reduced operational costs.
B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing tools that offer versatility and efficiency. For instance, saws designed for multiple metal types—ferrous and non-ferrous—are becoming essential in diverse applications. The rise of e-commerce platforms for sourcing tools is also noteworthy, enabling international buyers to access a broader range of products and competitive pricing. Furthermore, smart technologies are making their way into the sector, with features such as IoT connectivity that allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, thus optimizing tool usage and reducing downtime.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Saw to Cut Through Metal Market?
Sustainability has become a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the saw to cut through metal market. The environmental impact of metal cutting processes—often involving energy-intensive operations and waste generation—has prompted companies to seek solutions that minimize their carbon footprint. Manufacturers are now focusing on developing tools that not only perform efficiently but also adhere to stringent environmental regulations.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers are increasingly aware of the supply chain’s social implications, pushing for transparency and responsible sourcing practices. This includes selecting suppliers who prioritize fair labor practices and environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. Additionally, the demand for ‘green’ certifications and materials is rising. Buyers are encouraged to look for tools made with recycled materials or those that have undergone environmentally responsible production methods.
What Is the Historical Context of Saw Technology in B2B Applications?
The evolution of saw technology for cutting metal has progressed significantly over the decades. Initially, hand tools like hacksaws and metal snips dominated the market, offering limited efficiency and requiring considerable manual effort. With the advent of electric power tools in the mid-20th century, the industry saw a transformation. Power saws, such as band saws and chop saws, revolutionized metal cutting, allowing for faster and more precise cuts.
As industrial demands grew, so did the complexity of saw designs. Modern advancements have led to the introduction of high-performance blades made from advanced materials, enabling manufacturers to produce tools that are not only more durable but also capable of handling diverse metal types. Today, the market continues to innovate, with trends leaning towards automation and smart technologies, ensuring that metal cutting remains efficient, sustainable, and adaptable to the evolving needs of the industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of saw to cut through metal
1. How do I choose the right saw for cutting through metal?
Selecting the appropriate saw for cutting metal depends on the type of metal, thickness, and the desired finish. For heavy-duty applications, a mitering chop saw or a circular saw with a TCT blade is recommended for precision and efficiency. For lighter tasks, a handheld angle grinder may suffice. Consider factors such as power source (corded vs. battery), cutting capacity, and blade compatibility. Additionally, evaluate the saw’s ergonomic design and safety features to ensure operator comfort and safety during use.
2. What is the best type of saw for cutting stainless steel?
When cutting stainless steel, a chop saw equipped with a high-tooth-count TCT blade is often the best choice. These saws deliver clean cuts with minimal burrs and heat generation. Alternatively, a band saw may be used for thicker stainless steel materials, providing versatility and precision. It’s crucial to select blades specifically designed for stainless steel, as they will enhance cutting efficiency and prolong blade life. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications for optimal blade selection.
3. What factors should I consider when sourcing metal cutting saws internationally?
When sourcing metal cutting saws internationally, consider the supplier’s reputation, product quality, and compliance with international standards. Verify certifications and customer reviews to assess reliability. Evaluate shipping options, delivery times, and customs regulations specific to your country. It’s also essential to understand payment terms and currency exchange rates, as these can impact overall costs. Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can help address any concerns before finalizing your purchase.
4. How can I ensure the quality of the saws I purchase for my business?
To ensure the quality of saws, request samples or conduct a factory visit if feasible. Check for certifications such as ISO or CE, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Implement a thorough inspection process upon receipt, including testing the saw’s cutting performance and durability. Establish a clear return policy with the supplier to address any defects or non-conformities. Regularly review supplier performance to ensure ongoing quality assurance.
5. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal cutting saws?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal cutting saws can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and type of saw. Generally, MOQs may range from 10 to 100 units. It’s advisable to negotiate MOQs with suppliers, especially if you are a smaller business or new to the market. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or bulk orders, allowing you to test the product quality before committing to larger quantities.
6. What payment terms are commonly offered by international suppliers of metal cutting saws?
Payment terms for international suppliers of metal cutting saws typically include options like Letter of Credit (LC), advance payment, or payment upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 terms for established relationships. It’s essential to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, PayPal) and any additional fees. Ensure to discuss the terms before finalizing orders to avoid any misunderstandings regarding payment timelines and conditions.
7. How do I handle logistics and shipping for saws purchased from overseas suppliers?
Managing logistics for overseas purchases involves choosing a reliable freight forwarder familiar with international shipping regulations. Determine the best shipping method (air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness) based on your timeline and budget. Be aware of customs duties, taxes, and potential tariffs on imported goods, as these can affect overall costs. Ensure that the supplier provides necessary documentation, such as a bill of lading and commercial invoice, to facilitate smooth customs clearance.
8. Can I customize the saws I order to meet specific business needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for metal cutting saws, allowing you to tailor features such as blade type, size, and additional functionalities to suit your specific applications. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities and any associated costs. Customization may also extend to branding, such as logo placements. Ensure to obtain written confirmation of the specifications and any additional lead times that may apply to customized orders.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Saw To Cut Through Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Evolution – 14 in. TCT Blade
Domain: store.evolutionpowertools.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Evolution 14BLADEST”,”size”:”14 in.”,”teeth”:”66T”,”arbor”:”1 in.”,”material”:”Mild Steel and Ferrous Metal TCT Blade”,”price”:”$95.00″},{“name”:”Evolution S355MCS”,”type”:”Mitering Chop Saw”,”blade_size”:”14 in.”,”warranty”:”3 Years”,”power”:”Corded”,”max_miter”:”46°”,”price”:”$900.00″},{“name”:”Evolution S355CPSL”,”type”:”Metal Cutting Chop Saw”,”blade_size”:”14 in.”,”warra…
2. Woodsmith – Essential Cutting Tools
Domain: woodsmith.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Hacksaws: Handheld tools with fine-toothed blades for cutting metal; require secure clamping and patience. Angle Grinders: Versatile power tools for cutting, grinding, and polishing; use abrasive cutting discs; safety gear essential. Plasma Cutters: Machines for precision cutting using high-velocity ionized gas; suitable for various metals; requires protective equipment. Circular Saws: Adaptable f…
3. Diablo – Framing Saws for Metal Cutting
Domain: forum.millerwelds.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Framing saws with Diablo steel blades are mentioned as suitable for cutting metal. Specific models discussed include Homedepot’s Ridgid 6 1/2″ and Harbor Freight 7 1/4″ Chicago Electric. Users recommend metal cutting saws for better performance and longevity. A Milwaukee 6370-21 13 Amp 8-Inch Metal Cutting Circular Saw is noted for cutting 1/2″ mild steel. Other tools mentioned include a Skill Mag…
4. Evolution – S380CPS
Domain: garagejournal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Evolution S380CPS, DeWalt DW872, Milwaukee metal saw, Klutch bench top band saw, HEM saw 782XL
5. Fine Homebuilding – Cable Saw Solutions
Domain: finehomebuilding.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cable saw (hand-pulled type) that can potentially cut through metal, such as an iron bar. Suggestions include using a saw coated with abrasive grit or a flexible rod to dislodge the bar. The discussion also mentions alternative methods for dealing with the obstruction in a chimney.
6. HowStuffWorks – Circular Saw Metal Cutting Blades
Domain: home.howstuffworks.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: To cut metal using a circular saw, you need a carbide-tipped abrasive cutoff wheel specifically designed for metal. These blades differ from wood-cutting blades in material and design to handle the hardness and characteristics of metal. The choice of blade depends on the type of metal being cut, with different blades required for non-ferrous metals like brass, aluminum, copper, or lead. Carbide-ti…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for saw to cut through metal
In conclusion, strategic sourcing for metal-cutting saws is pivotal for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency and maintain competitive advantage. By understanding the diverse range of cutting tools available—from heavy-duty chop saws to versatile circular saws—buyers can select equipment that meets specific project needs while optimizing costs. Prioritizing suppliers that offer high-quality blades and robust warranties can significantly impact performance and longevity, essential for industries in fast-paced markets.
As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate sourcing decisions, it is crucial to consider local supplier capabilities, shipping logistics, and after-sales support. Engaging with reputable manufacturers ensures access to the latest technologies and innovations in metal cutting, which can lead to improved productivity and reduced downtime.
Looking ahead, the demand for efficient, high-performance metal cutting solutions is set to rise. By proactively investing in strategic sourcing initiatives, businesses can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Take the first step today to explore partnerships with leading suppliers and elevate your operations to new heights.