Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for saw that cuts through metal
In the dynamic landscape of industrial manufacturing, sourcing the right saw that cuts through metal is a critical challenge for B2B buyers across the globe. With the increasing complexity of projects and diverse material requirements, choosing the appropriate metal-cutting saw can significantly impact productivity and operational costs. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the various types of metal-cutting saws, including circular saws, chop saws, and cold saws, tailored for specific applications and materials.
Buyers will gain insights into the key specifications to consider, such as blade types, cutting capacities, and operational efficiencies, enabling them to make informed decisions. Additionally, the guide delves into effective supplier vetting strategies, helping businesses identify reputable manufacturers and distributors that can meet their unique needs. Cost considerations are also addressed, providing a holistic view of budgeting for equipment that delivers both performance and longevity.
This resource is designed specifically for international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging markets such as Brazil and Vietnam. By empowering buyers with actionable insights and essential knowledge, this guide facilitates smarter purchasing decisions, ultimately enhancing project outcomes and driving business growth. Whether you’re a seasoned procurement professional or new to the metalworking industry, understanding these nuances will equip you to navigate the global market confidently.
Understanding saw that cuts through metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hack Saw | Manual operation, thin blade, C-shaped frame | Maintenance, small-scale metalwork | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Labor-intensive, less suitable for large projects. |
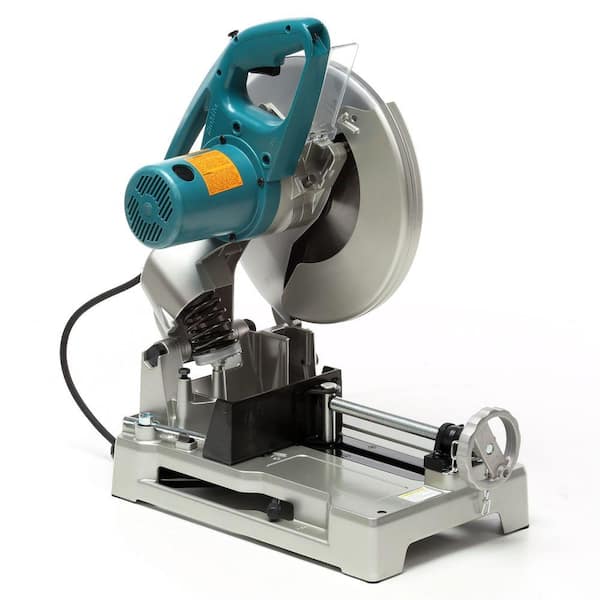
| Circular Saw | Electric, portable, various blade types | Construction, fabrication, metalworking | Pros: Fast cutting, versatile blade options. Cons: Requires skill for accuracy, can generate heat. |
| Cold Saw | Toothed blade for heat dissipation, slower cutting speed | Industrial metal cutting, precision applications | Pros: Produces clean cuts, minimizes heat damage. Cons: Higher initial cost, slower than other saws. |
| Chop Saw | Fixed base, mitering capability, abrasive or TCT blades | Heavy-duty cutting, structural steel fabrication | Pros: Accurate angles, efficient for bulk cutting. Cons: Less portable, noise during operation. |
| Magnetic Drill | Portable, uses magnetic adhesion for stability | Construction, site drilling | Pros: Highly portable, precise drilling. Cons: Limited to drilling applications, requires power source. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of a Hack Saw?
The hack saw is a manually operated tool best suited for smaller metal cutting tasks. It features a thin blade mounted on a C-shaped frame, allowing for precision cuts in various metals. While cost-effective, its labor-intensive nature and potential for uneven cuts make it less suitable for large-scale projects. B2B buyers should consider the intended volume of work and the skill level of operators when selecting this tool.
How Does a Circular Saw Enhance Metal Cutting Efficiency?
A circular saw is a versatile electric tool that can handle various metal types using different blade configurations. Its portability and ability to make straight and angled cuts make it ideal for construction and fabrication tasks. However, users must be skilled to ensure accuracy, as the saw can generate significant heat during operation. B2B buyers should evaluate their cutting needs and consider investing in models with adjustable speed settings for improved performance.
Why Choose a Cold Saw for Precision Applications?
Cold saws are designed for industrial applications where precision is paramount. Their toothed blades dissipate heat during cutting, resulting in cleaner edges and less thermal distortion. While these saws are typically more expensive and operate at slower speeds, they are ideal for tasks requiring high accuracy, such as aerospace or automotive components. B2B buyers should assess the long-term benefits of clean cuts against the initial investment.
What Advantages Does a Chop Saw Offer in Heavy-Duty Cutting?
Chop saws are specifically designed for heavy-duty metal cutting with fixed bases and mitering capabilities. They can utilize abrasive or TCT blades, making them suitable for structural steel fabrication and other industrial applications. While they provide accurate angles and efficient bulk cutting, their lack of portability and noise during operation can be drawbacks. Buyers should consider their workspace and noise regulations when selecting this equipment.
How Do Magnetic Drills Improve Site Drilling Operations?
Magnetic drills are portable tools that use magnetic adhesion to stabilize the drilling process on metal surfaces. They are ideal for construction sites where precision drilling is needed without the bulk of traditional drilling machines. Although they require a power source and are limited to drilling tasks, their portability and accuracy make them highly valuable in B2B applications. Buyers should assess their drilling needs and power availability when considering this tool.
Key Industrial Applications of saw that cuts through metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of saw that cuts through metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Cutting structural steel beams and reinforcements | Ensures precise cuts for structural integrity and safety | Durability, blade compatibility, and cutting capacity |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Fabricating metal components for vehicles | Enhances production efficiency and reduces material waste | Speed, precision, and adaptability to various metal types |
| Metal Fabrication | Custom metal design and fabrication for various applications | Facilitates innovative designs and rapid prototyping | Versatility in cutting different metal thicknesses and types |
| Aerospace | Precision cutting of aircraft components and parts | Reduces weight and increases fuel efficiency | Tolerance levels, heat resistance, and compliance with industry standards |
| Shipbuilding | Cutting large metal sheets and components for vessel construction | Improves build quality and reduces turnaround time | Size and weight of equipment, portability, and power requirements |
How is ‘saw that cuts through metal’ utilized in the construction industry?
In the construction sector, saws that cut through metal are essential for processing structural steel beams and reinforcements. These saws provide precise cuts that are crucial for maintaining structural integrity and safety in building projects. Buyers in this sector need to consider the durability of the saws, compatibility with various blade types, and maximum cutting capacity to handle different steel thicknesses. Efficient cutting reduces project timelines and minimizes waste, translating to significant cost savings.
What role do metal cutting saws play in automotive manufacturing?
In automotive manufacturing, these saws are used to fabricate metal components, such as frames and engine parts. The efficiency and precision offered by advanced saws lead to higher production rates and reduced material waste, which are critical in a competitive market. B2B buyers should prioritize saws that can handle various metals and thicknesses while ensuring that they meet speed and precision requirements. This adaptability is vital for manufacturers looking to innovate and remain competitive.
Why are saws important in the metal fabrication industry?
Saws that cut through metal are indispensable in metal fabrication for creating custom designs and prototypes. They allow fabricators to execute complex cuts with high precision, enabling innovative solutions for clients. Buyers must focus on the saw’s versatility to handle different metal types and thicknesses, as well as its ability to provide clean cuts without excessive heat generation. This capability not only enhances the quality of the final product but also streamlines the fabrication process.
How do aerospace manufacturers benefit from metal cutting saws?
In the aerospace industry, precision cutting of aircraft components is paramount for performance and safety. Saws that cut through metal are utilized to create lightweight yet strong parts, contributing to improved fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the saws meet stringent tolerance levels and heat resistance standards, as well as compliance with industry regulations. Investing in high-quality cutting tools can lead to significant advantages in production efficiency and product reliability.
What advantages do shipbuilders gain from using metal cutting saws?
Shipbuilding requires cutting large metal sheets and components, where saws that cut through metal play a critical role. These saws enhance build quality and reduce turnaround times, allowing shipbuilders to meet tight deadlines. When sourcing saws for this application, considerations should include the size and weight of the equipment, portability for on-site use, and power requirements to handle heavy-duty tasks. Efficient cutting tools can significantly improve operational productivity in this demanding industry.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘saw that cuts through metal’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Precision Cuts
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges with achieving precise cuts when working with metal. This issue often arises in industries such as manufacturing and construction, where accuracy is paramount. Inadequate tools or improper techniques can lead to misaligned cuts, resulting in wasted materials, increased costs, and delays in project timelines. For instance, a construction company may find that using a standard circular saw for cutting steel beams doesn’t yield the necessary precision, leading to rework and frustration.
The Solution: To overcome precision issues, buyers should invest in high-quality metal cutting saws specifically designed for the type of metal being worked with. For example, choosing a cold saw or a metal chop saw can significantly enhance cutting accuracy. Cold saws operate at lower speeds and utilize toothed blades that minimize heat buildup, leading to cleaner cuts and less distortion. Additionally, implementing proper techniques—such as securing the workpiece with clamps and using a guide for straight cuts—can further improve accuracy. When sourcing equipment, look for saws with adjustable settings to accommodate different metal thicknesses, and consider conducting trial cuts to ensure that the chosen saw meets precision requirements.
Scenario 2: Safety Concerns During Metal Cutting
The Problem: Safety is a critical concern for businesses that utilize metal cutting saws. Many buyers worry about the risks associated with operating heavy machinery, such as potential accidents or injuries from sparks, sharp blades, and noise. For instance, a metal fabrication shop may face challenges in ensuring that all employees adhere to safety protocols, leading to incidents that can disrupt operations and result in costly downtime.
The Solution: To enhance safety, it is essential for businesses to prioritize the selection of saws equipped with advanced safety features. Look for models that come with blade guards, emergency stop buttons, and ergonomic handles to reduce strain during operation. Additionally, implementing comprehensive training programs for employees on the safe use of metal cutting saws can mitigate risks. This training should include proper personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, such as gloves, goggles, and hearing protection. Regular safety audits can also help identify potential hazards and reinforce a culture of safety within the workplace.
Scenario 3: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficiency
The Problem: B2B buyers often face high operational costs stemming from inefficient metal cutting processes. Ineffective equipment can lead to increased energy consumption, frequent blade replacements, and longer cutting times. For example, a construction company that relies on outdated equipment may find that their saws struggle to cut through thicker metals, resulting in slower project completion and higher labor costs.
The Solution: To combat inefficiency, businesses should evaluate and upgrade their metal cutting tools to more advanced models that offer better performance and energy efficiency. Investing in saws with improved blade technology—such as carbide-tipped blades—can extend the life of the blades and reduce the frequency of replacements. Additionally, consider using saws that incorporate features like variable speed settings, which allow for adjustments based on the type of metal and thickness being cut. Regular maintenance of the saws can also enhance their longevity and efficiency. By tracking operational metrics, such as cutting speed and energy consumption, buyers can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize their processes, ultimately reducing operational costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for saw that cuts through metal
What Are the Key Materials for Saws That Cut Through Metal?
When selecting a saw that cuts through metal, understanding the materials used in the construction of the saw and its blades is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring durability. Here, we analyze four common materials: high-speed steel (HSS), carbide-tipped, bi-metal, and diamond blades, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
High-Speed Steel (HSS): What Makes It a Common Choice?
High-speed steel is a popular material for saw blades due to its ability to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness. HSS blades can cut through various metals, including mild steel and aluminum, making them versatile for different applications.
Pros: HSS blades are relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making them a cost-effective choice for many businesses. They also offer good toughness and wear resistance.
Cons: However, HSS blades may not be as durable as other materials when cutting harder metals, and they can require frequent sharpening, leading to increased downtime.
Impact on Application: HSS is suitable for general metal cutting tasks but may not be the best choice for heavy-duty applications involving high-strength materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM for quality assurance. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is high, HSS can be an attractive option.
Carbide-Tipped Blades: Are They Worth the Investment?
Carbide-tipped blades are designed with tips made from tungsten carbide, which significantly enhances cutting performance and longevity. These blades are ideal for cutting through harder metals, including stainless steel and high-strength alloys.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbide-tipped blades is their durability; they can maintain sharpness longer than HSS blades, resulting in less frequent replacements. They also provide smoother cuts and reduced heat generation.
Cons: The initial cost of carbide-tipped blades is higher than HSS, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, they can be more complex to manufacture, impacting lead times.
Impact on Application: These blades are particularly effective in industrial settings where precision and durability are paramount, making them suitable for heavy-duty metalworking tasks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may prefer carbide-tipped blades due to their performance advantages, but they should be aware of the higher costs and ensure compliance with relevant manufacturing standards.
Bi-Metal Blades: How Do They Compare?
Bi-metal blades combine the toughness of HSS with the wear resistance of carbide, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. They typically feature an HSS cutting edge welded to a flexible steel back.
Pros: Bi-metal blades are highly versatile and can cut through various materials, including soft and hard metals. They offer excellent durability and resistance to breakage.
Cons: While they provide a good balance of performance and cost, bi-metal blades may not achieve the same level of precision as carbide-tipped blades in specialized applications.
Impact on Application: These blades are ideal for general metal cutting and are often used in both industrial and construction settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Bi-metal blades are widely accepted in global markets, but buyers should verify compliance with local standards, especially in regions with stringent manufacturing regulations.
Diamond Blades: When Are They Necessary?
Diamond blades are primarily used for cutting hard materials, including concrete and ceramics, but they can also be effective for certain metals when precision is required.
Pros: Diamond blades offer exceptional cutting speed and longevity, making them suitable for high-volume applications. They produce minimal heat, reducing the risk of material warping.
Cons: The cost of diamond blades is significantly higher than other options, which may not be justifiable for all applications. Additionally, they are typically less versatile for general metal cutting tasks.
Impact on Application: Diamond blades are most beneficial in specialized applications where precision and speed are critical, such as in construction or metal fabrication.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific applications and ensure compliance with international standards, as the high cost may limit their use in price-sensitive markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Saws That Cut Through Metal
| Material | Typical Use Case for saw that cuts through metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel | General metal cutting, mild steel | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Requires frequent sharpening | Low |
| Carbide-Tipped | Cutting harder metals, stainless steel | Durable and maintains sharpness longer | Higher initial cost | High |
| Bi-Metal | Versatile applications, soft and hard metals | Excellent durability and flexibility | May lack precision in specialized tasks | Medium |
| Diamond | Specialized cutting of hard materials | Exceptional cutting speed and longevity | High cost and less versatility | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for saws that cut through metal, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for saw that cuts through metal
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing a Saw That Cuts Through Metal?
The manufacturing process for saws designed to cut through metal typically involves several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is essential for producing high-quality, durable saws that meet the demands of industrial applications.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing journey begins with sourcing high-grade materials, often including carbon steel, high-speed steel (HSS), or tungsten carbide for the blades. These materials are selected based on their hardness, durability, and ability to maintain sharpness. The raw materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specified standards before moving to the next stage.
Forming Techniques
The forming stage involves shaping the saw components. For blade manufacturing, techniques such as stamping, laser cutting, and CNC machining are commonly employed. These methods allow for precise cuts and shapes, ensuring that the blades fit correctly onto the saw’s body. The teeth of the blades are often ground to specific angles to optimize cutting efficiency, with additional processes like heat treatment applied to enhance hardness and wear resistance.
Assembly Process
Once the components are formed, the assembly process begins. This includes attaching the blade to the saw body, installing the motor (for powered saws), and ensuring all moving parts are securely fitted. Assembly techniques can vary, with some manufacturers opting for automated assembly lines while others may utilize manual assembly for more complex saws. Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout this stage to ensure that each saw meets performance standards.
Finishing Touches
The final stage, finishing, includes processes such as coating, polishing, and packaging. Coatings may include anti-corrosion treatments or protective layers to enhance durability. Polishing ensures a smooth finish, which can reduce friction during cutting. Proper packaging is also vital to prevent damage during shipping, especially for international buyers.
How is Quality Assurance Implemented in Metal Cutting Saws Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of metal cutting saws, ensuring that each product meets international and industry-specific standards. Buyers must be aware of the quality assurance processes in place to ensure they receive reliable and effective tools.
International Standards and Certifications
Manufacturers often adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with ISO standards indicates that the manufacturer has established processes for consistent quality in their products. Additionally, certifications like CE mark (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply, particularly for saws intended for specific industries.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks the quality of raw materials before they enter the production line. It ensures that only materials meeting specified standards are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC monitors the assembly and forming processes. This includes checking dimensions, tolerances, and any critical features that could affect performance.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly and finishing, FQC involves comprehensive testing of the finished product. This may include functional tests, durability tests, and performance evaluations to ensure the saw operates as intended.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to evaluate the quality of metal cutting saws. These can include:
-
Cutting Performance Tests: Assessing the saw’s ability to cut through different types of metal, measuring parameters such as speed and precision.
-
Durability Testing: Simulating extended use to evaluate how the saw withstands wear and tear over time.
-
Vibration and Noise Level Testing: Ensuring that the saw operates within acceptable limits for user safety and comfort.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures employed by suppliers, particularly when sourcing from international manufacturers.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One of the most effective ways to verify a supplier’s QC processes is through audits. These audits can be conducted on-site or through third-party firms that specialize in quality assessments. During an audit, buyers can examine the manufacturer’s processes, quality control documentation, and compliance with international standards.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request quality reports and documentation from suppliers, which outline the QC processes, test results, and compliance certifications. This documentation can provide insights into the manufacturer’s commitment to quality and reliability.
Engaging Third-Party Inspection Services
For buyers operating in regions with language barriers or different regulatory standards, engaging third-party inspection services can offer an added layer of assurance. These services can conduct independent inspections and provide unbiased reports on the quality of the products before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control when sourcing metal cutting saws.
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations that affect the quality and safety of metal cutting tools. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that suppliers comply with these standards. For example, the CE mark is mandatory for products sold in the European Union, while other regions may have different certification requirements.
Navigating Import Regulations
Import regulations can also impact the quality assurance process. Buyers must ensure that the products meet not only the manufacturer’s quality standards but also the import requirements of their home country. This may involve additional testing, certifications, or documentation.
Building Long-Term Relationships
Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can enhance trust and facilitate better communication regarding quality control. Regular engagement and feedback can help suppliers improve their processes, ultimately benefiting both parties.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in the production of metal cutting saws, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure they acquire reliable, high-quality tools for their operations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘saw that cuts through metal’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure saws designed for cutting through metal. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right equipment tailored to your specific needs, thereby optimizing performance, reducing costs, and enhancing productivity in your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, it’s essential to outline your specific requirements. Consider the type of metal you will be cutting (e.g., mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum) and the thickness of the material. Defining these specifications helps narrow down the suitable saw types and blades necessary for optimal performance.
- Blade Type: Decide whether you need a circular saw, cold saw, or chop saw based on the materials and cut quality required.
- Power Source: Determine if a corded or cordless model best suits your work environment and mobility needs.
Step 2: Research Available Saw Types
Understanding the various types of saws available will assist in making an informed decision. Each type of saw has unique features and advantages suited for different applications.
- Manual vs. Power Saws: Identify whether you need a manual saw for lighter tasks or a heavy-duty power saw for industrial applications.
- Cutting Mechanism: Familiarize yourself with options like abrasive blades, TCT (tungsten carbide-tipped) blades, and cold saws, each offering distinct cutting capabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Once you have a clear understanding of your requirements, the next step is to assess potential suppliers. A thorough evaluation ensures that you partner with a reliable and competent vendor.
- Supplier Background: Investigate the supplier’s history, industry experience, and reputation among other businesses in your sector.
- Certifications: Ensure suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO or industry-specific endorsements, which demonstrate compliance with international quality standards.
Step 4: Request and Analyze Quotes
After identifying potential suppliers, request detailed quotations. Comparing multiple quotes allows for better negotiation and ensures you receive competitive pricing.
- Cost Breakdown: Look for transparency in pricing, including costs for the saw, blades, accessories, and warranties.
- Lead Times: Inquire about delivery timelines, as prompt availability is crucial for maintaining your project schedules.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support
Reliable after-sales support is vital for maintaining the performance of your saw. Ensure that the supplier offers comprehensive support services.
- Warranty Terms: Check the warranty duration and what it covers, as this can safeguard against future issues.
- Technical Support: Determine the availability of technical assistance, training, and parts replacement services.
Step 6: Conduct a Trial or Demonstration
If possible, arrange for a demonstration or trial period with the chosen saw. This allows you to assess the equipment’s performance in a real-world setting.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the saw’s cutting speed, precision, and ease of use to ensure it meets your operational standards.
- User Feedback: Gather input from your team members who will be operating the saw to identify any potential concerns or preferences.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Establish Terms
Once satisfied with the equipment and supplier, finalize the purchase agreement. Ensure that all terms are clearly defined to avoid misunderstandings later.
- Payment Terms: Agree on payment methods and timelines to align with your budget and cash flow needs.
- Delivery and Installation: Confirm delivery schedules and whether the supplier will assist with installation or setup.
By adhering to this sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can confidently select a saw that cuts through metal, ensuring both efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for saw that cuts through metal Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Metal-Cutting Saws?
When analyzing the cost structure of saws designed for cutting metal, several components come into play. The primary cost factors include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the overall cost. High-grade carbide or specialized alloys used in blades can raise the price but offer superior performance and durability. For instance, a TCT (Tungsten Carbide Tipped) blade may cost more upfront but provide lower long-term costs due to reduced wear and tear.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing high-quality saws. Labor costs vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and the skill level required. In regions like Europe, labor costs may be higher compared to South America or Africa, affecting the final pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient production processes can help mitigate these costs, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for manufacturing saws can be significant. Custom tooling for specialized saws may lead to higher costs, which could be passed on to the buyer.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that products meet quality standards requires investment in QC processes. Suppliers who implement rigorous QC may charge more, but this can result in fewer defects and lower total cost of ownership for buyers.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary greatly, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can all influence the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure business sustainability. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position and competitive landscape.
What Influences Pricing for Metal-Cutting Saws?
Several factors can influence the pricing of metal-cutting saws, which are crucial for B2B buyers to understand.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often offer discounts for bulk purchases. Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can affect pricing, so negotiating larger orders may yield cost savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs due to the need for specialized materials or tooling. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential increase in price.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can justify higher prices. Buyers should assess the long-term value of investing in higher-quality saws.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and historical performance can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium, but the assurance of quality and service can offset higher costs.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international buyers. These terms dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can significantly affect total costs.
What Are the Best Practices for Buyers When Negotiating Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation and cost management are key.
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, MOQs, and payment terms. Building a relationship can lead to better deals over time.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership: While initial pricing is important, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, durability, and efficiency. A higher upfront cost may lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of pricing variations that can arise from currency fluctuations, import tariffs, and local market conditions. This knowledge can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Regional Insights: Buyers in emerging markets should leverage local supplier networks and insights to enhance negotiation power and potentially lower costs.
In summary, understanding the cost structure and pricing influencers for metal-cutting saws is crucial for B2B buyers. By considering these factors and employing strategic negotiation techniques, businesses can secure the best value for their investments.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing saw that cuts through metal With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Metal Cutting Saws
When it comes to cutting metal, the traditional saw that cuts through metal is a popular choice due to its efficiency and precision. However, there are several alternative solutions available that may better suit specific applications, budgets, or operational requirements. Below, we compare these alternatives to help B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Saw That Cuts Through Metal | Plasma Cutter | Water Jet Cutter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with minimal heat generation, ideal for various metal types | Excellent for thick metals, fast cutting speed | Extremely precise cuts, no heat-affected zone |
| Cost | Moderate ($200 – $900) | Higher initial investment ($1,500 – $5,000) | Highest initial cost ($5,000 – $100,000) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires basic training for operators | Requires specialized training and safety precautions | Requires skilled operators and setup time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy blade changes | Regular maintenance needed for consumables | High maintenance due to pump and nozzle upkeep |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for construction, fabrication, and repair shops | Best for heavy-duty cutting in industrial applications | Suitable for intricate designs and materials that cannot withstand heat |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Plasma Cutters?
Plasma cutters are a popular alternative for metal cutting, particularly when speed is of the essence. They utilize a high-velocity jet of ionized gas to cut through metals, making them highly effective for thicker materials. However, they require a higher initial investment and specialized training for operators, which may not be feasible for smaller businesses. Additionally, while they offer speed, the cut quality may not match that of traditional saws, particularly for thinner materials.
How Does a Water Jet Cutter Compare to Metal Saws?
Water jet cutters use a high-pressure jet of water, often mixed with abrasives, to cut through metal. This method is renowned for its ability to produce intricate shapes with a high degree of accuracy while avoiding heat-affected zones. The primary disadvantage is the significant initial cost and the need for skilled operators to handle the technology. Furthermore, the setup and maintenance can be more complex compared to traditional saws, making it less accessible for smaller operations.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Metal Cutting?
Selecting the right metal cutting solution depends on several factors, including the type of metal, thickness, desired cut quality, and budget. For businesses focused on high precision and lower operational costs, the traditional saw that cuts through metal may be the best option. However, for those needing to cut thicker materials quickly or achieve complex designs, plasma or water jet cutters might be more suitable despite the higher initial costs. Ultimately, assessing the specific requirements of each project will guide B2B buyers to the most effective and economical choice for their metal cutting needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for saw that cuts through metal
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Saws That Cut Through Metal?
When considering saws for metal cutting, understanding the technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to evaluate:
-
Blade Material Grade: The blade material significantly affects cutting performance and durability. Common materials include high-speed steel (HSS), carbide-tipped, and bi-metal. HSS blades are suitable for lighter applications, while carbide-tipped blades offer superior longevity and performance for tougher materials. Choosing the right blade material can reduce operational costs by minimizing replacement frequency and maintenance needs.
-
Blade Size and Teeth Count: The size of the blade and the number of teeth directly influence the cutting speed and finish quality. Larger blades with more teeth provide smoother cuts but may require slower feeding rates. Conversely, blades with fewer teeth cut faster but can leave a rougher finish. Understanding these dynamics helps businesses balance speed and quality based on project requirements.
-
Kerf Width: The kerf is the width of the cut made by the blade. A thinner kerf means less material waste and faster cutting speeds, which is particularly valuable in high-volume production settings. Selecting a saw with the appropriate kerf width can enhance efficiency and cost-effectiveness in metalworking operations.
-
Cutting Capacity: This refers to the maximum dimensions of the material that can be effectively cut by the saw. It is crucial for businesses to match the saw’s cutting capacity with their project specifications to avoid downtime or operational delays. A saw with adequate cutting capacity ensures that larger materials can be processed without needing additional equipment.
-
Power Source: Saws can be powered by electricity, battery, or manual operation. Electric saws typically offer greater cutting power and efficiency, while battery-operated saws provide portability. Understanding the power requirements and the operational environment will help businesses choose the right saw for their specific needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Metal Cutting Saws?
Familiarizing yourself with industry terminology is critical for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is important for buyers seeking quality and reliability in the saws and components they purchase.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their purchasing strategies and manage inventory efficiently, ensuring they do not overstock or understock essential equipment.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. This process is vital for obtaining competitive bids and ensuring that buyers can evaluate options based on cost, quality, and delivery timelines.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for managing shipping costs, risks, and logistics, particularly for international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
-
TCT (Tungsten Carbide Tipped): This term refers to saw blades that have tips made from tungsten carbide, which significantly enhance cutting performance and durability. Buyers should look for TCT blades when cutting hard metals to ensure longevity and efficiency.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting metal-cutting saws, ultimately leading to improved productivity and cost savings in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the saw that cuts through metal Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Affecting the Metal Cutting Saw Sector?
The global market for metal cutting saws is experiencing a significant transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer demands. Key trends include the increasing adoption of automated and precision cutting solutions, which enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs for businesses. As industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe expand, there’s a growing emphasis on machinery that can deliver consistent performance across various metal types, including ferrous and non-ferrous materials.
Emerging B2B technologies, such as IoT-enabled devices, are being integrated into metal cutting saws to provide real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. This trend is particularly beneficial for international buyers who seek to minimize downtime and optimize production processes. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and compare products more efficiently.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional factors. For instance, in developing markets like Brazil and Vietnam, the demand for cost-effective yet high-performance cutting solutions is increasing as local manufacturing industries grow. Conversely, European markets are leaning towards higher-end products that offer advanced features and greater energy efficiency.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Metal Cutting Saw Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the metal cutting saw sector. As environmental regulations tighten globally, manufacturers are increasingly under pressure to adopt sustainable practices. This includes reducing waste, minimizing energy consumption, and sourcing materials responsibly. Buyers are encouraged to look for suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly manufacturing processes and utilize recyclable or sustainably sourced materials in their products.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses recognize the value of transparency in their supply chains. Buyers should seek suppliers who comply with environmental certifications such as ISO 14001 or those who demonstrate commitment to corporate social responsibility. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the values of a growing segment of consumers who prefer to engage with environmentally conscious companies.
Moreover, the market is witnessing an increase in products that incorporate “green” technologies, such as saws designed to operate with lower emissions or those that utilize biodegradable lubricants. These innovations appeal to international buyers who are not only looking for high-quality tools but also want to contribute to a sustainable future.
What Is the Historical Context of Metal Cutting Saws in B2B Transactions?
The evolution of metal cutting saws dates back to the industrial revolution when the need for efficient metal processing became paramount. Initially, manual hacksaws dominated the market, but the introduction of powered saws revolutionized the industry, allowing for faster and more precise cuts. Over the decades, advancements in blade technology, such as the development of carbide-tipped blades, have significantly improved cutting efficiency and durability.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards high-tech solutions, with the incorporation of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology and automation in saw design. This shift not only enhances precision but also allows for greater flexibility in cutting various materials. As the market continues to evolve, the historical context highlights the ongoing demand for innovation and efficiency in metal cutting technologies, which remains a priority for B2B buyers worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of saw that cuts through metal
-
1. How do I choose the right saw for cutting metal?
Selecting the right saw for metal cutting depends on various factors, including the type of metal, thickness, and the desired cut quality. For precision and clean cuts on thicker materials, consider using a cold saw or a metal cutting circular saw, as these minimize heat generation and burrs. For lighter metals or smaller jobs, a handheld circular saw or a hack saw may suffice. Always evaluate the saw’s specifications, such as blade type and size, to ensure compatibility with your cutting needs. -
2. What is the best type of saw for cutting stainless steel?
For cutting stainless steel, a cold saw is often the best choice due to its ability to produce clean cuts with minimal heat distortion. These saws utilize toothed blades that dissipate heat, reducing the risk of warping the material. If a cold saw is not available, a metal cutting circular saw with a carbide-tipped blade designed specifically for stainless steel can also be effective. Always verify the blade’s specifications to ensure it is suitable for stainless steel cutting. -
3. What are the key features to look for in a metal cutting saw?
When selecting a metal cutting saw, consider essential features such as blade material (carbide-tipped for durability), power source (cordless or corded), cutting capacity (maximum thickness and width), and the saw’s weight for portability. Additionally, look for advanced features like adjustable miter angles, cooling systems for heat management, and integrated chip collectors for cleaner work environments. These features enhance performance and efficiency, making them vital for industrial applications. -
4. How do I vet suppliers when sourcing metal cutting saws internationally?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by checking their certifications and industry experience. Look for ISO certifications or compliance with local standards. Request references from previous clients and assess their reputation through online reviews or industry forums. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if possible, and inquire about their quality control processes. This thorough vetting ensures you partner with reliable suppliers who can meet your quality and delivery expectations. -
5. What are the typical payment terms for purchasing metal cutting saws?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the transaction size. Common arrangements include a 30% deposit upfront, with the remaining balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment via escrow services for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing the contract and ensure they align with your financial capabilities and risk management strategies. -
6. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for metal cutting saws?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for metal cutting saws often depends on the manufacturer and the specific model. Typically, MOQs can range from a few units for standard models to larger quantities for specialized or customized saws. When negotiating with suppliers, it’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront to ensure they fit your purchasing needs and budget. Some suppliers may be flexible on MOQs for first-time buyers or long-term partnerships. -
7. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my metal cutting saws?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed product specifications and certifications from your supplier. Implement a quality control plan that includes pre-shipment inspections and testing of the saws for performance and safety standards. Establish clear communication regarding your quality expectations and consider employing a third-party inspection service for added assurance. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks associated with defective products. -
8. What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing metal cutting saws?
When importing metal cutting saws, it’s crucial to understand shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose between air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness, depending on your timeline. Ensure all necessary documentation, such as import permits and invoices, is in order to prevent delays at customs. Additionally, consider the supplier’s ability to handle logistics and provide support for any potential issues during transit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Saw That Cuts Through Metal Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Evolution – 14BLADEST 14 Blade
Domain: store.evolutionpowertools.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Evolution 14BLADEST”,”blade_size”:”14 in.”,”number_of_teeth”:66,”bore”:”1 in.”,”kerf”:”0.094 in.”,”compatible_with”:”Evolution Chop Saws”,”price”:”$95.00″},{“name”:”Evolution S355MCS”,”blade_size”:”14 in.”,”warranty”:”3 Years”,”power”:”Corded”,”max_miter_left”:”46°”,”max_miter_right”:”46°”,”price”:”$900.00″},{“name”:”Evolution S355CPSL”,”blade_size”:”14 in.”,”warranty”:”3 Yea…
2. Trick Tools – Slugger 9 Inch Metal Cutting Saw
Domain: trick-tools.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: This company, Trick Tools – Slugger 9 Inch Metal Cutting Saw, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Evolution – S380CPS Dry Cut Saw
Domain: garagejournal.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Evolution S380CPS, dry cut saw, suitable for cutting flat bar (A36) 3/8 and 1/2 inch, and up to 3 inch round solid mild steel. Known for fast, square cuts and repeatable angles. Users report it is loud, produces hot chips, and requires careful handling to avoid damaging the blade. Price mentioned: $2795 for HEM saw, $329 for Northern Tools Klutch bench top band saw. Users suggest using a face shie…
4. Original Saw Company – Metal Cutting Radial Arm Saws
Domain: originalsaw.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Metal Cutting Radial Arm Saws by Original Saw Company are designed for industrial applications, featuring durability, precision, and versatility. Key specifications include:
– Construction: Cast and ductile iron, heavy-duty, 900+ pounds for vibration-free cutting.
– Cutting capabilities: Handles materials like steel, aluminum, brass, plastics, and fiberglass.
– Max Depth of Cut: Options for 5″,…
5. Milwaukee Tool – M18 FUEL™ Metal Cutting Circular Saw
Domain: milwaukeetool.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: M18 FUEL™ Metal Cutting Circular Saw (Tool Only) | Model: 2782-20 | Blade Size: 5-3/8″ – 5-7/8″ | Cutting Speed: 3,900 RPM | Cuts: Up to 370 cuts in ¾” EMT | Motor: POWERSTATE™ Brushless Motor | Technology: REDLINK PLUS™ Intelligence | Battery: M18™ REDLITHIUM™ XC5.0 Battery Pack | Features: Fastest cuts, longest tool life, compact and lightweight design.
6. Fine Homebuilding – Cable Saw
Domain: finehomebuilding.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Cable saw (hand-pulled type) that can cut through metal, such as an iron bar; potentially carbide impregnated; used for accessing difficult areas like a chimney.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for saw that cuts through metal
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of metal cutting saws is pivotal for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. Understanding the diverse range of saws—such as circular saws, cold saws, and chop saws—enables companies to select the right tool for their specific metal cutting needs. Factors such as blade material, cutting speed, and machine durability should guide purchasing decisions, ensuring that investments yield high performance and longevity.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for reliable and efficient metal cutting solutions is expected to grow. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, businesses can not only optimize their supply chains but also foster partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand the unique challenges of their regions.
Looking ahead, it is essential for buyers to remain proactive in their sourcing strategies, continually assessing market trends and technological advancements. Engaging with suppliers that offer innovative solutions will be key to staying competitive. Begin your journey towards a more efficient metal cutting operation today by exploring reliable suppliers and cutting-edge technologies that can elevate your business performance.