Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sandblast vs bead blast
In today’s competitive global market, sourcing the right surface finishing method, such as sandblasting or bead blasting, can significantly influence the quality and longevity of metal components. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenge lies not only in understanding the distinct applications of each technique but also in navigating the complexities of supplier selection and cost considerations. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of sandblast vs bead blast, providing detailed insights into their respective processes, advantages, and best use cases.
Throughout this guide, you will find an in-depth analysis of the types of abrasive materials used, the specific applications suited for each method, and strategic tips for vetting suppliers to ensure you partner with industry leaders. Additionally, we will explore cost implications and provide actionable strategies to maximize your investment. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational goals, enhance product performance, and ultimately drive business success. Whether you are a manufacturer seeking to optimize production efficiency or a procurement specialist aiming to deliver value, this guide will serve as an essential resource in navigating the intricate landscape of surface finishing techniques.
Understanding sandblast vs bead blast Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sandblasting | Uses coarse abrasive materials like sand or aluminum oxide. | Heavy rust removal, paint stripping, concrete prep. | Pros: Fast and efficient; effective on tough surfaces. Cons: Can damage delicate surfaces; leaves a rough finish. |
| Glass Bead Blasting | Utilizes fine glass beads, resulting in a smoother finish. | Polishing metals, cleaning delicate components. | Pros: Gentle on surfaces; ideal for a polished look. Cons: Slower process; less effective on heavy contaminants. |
| Steel Grit Blasting | Employs steel grit for aggressive cleaning and surface profiling. | Heavy-duty applications, industrial equipment. | Pros: Highly effective for tough materials; good for surface preparation. Cons: Can be abrasive and cause wear on softer materials. |
| Aluminum Oxide Blasting | Involves sharp aluminum oxide particles for precision. | Automotive parts, aerospace components. | Pros: Offers precision; versatile for various surfaces. Cons: More expensive; can create a rough texture. |
| Soda Blasting | Uses sodium bicarbonate for a non-destructive clean. | Restoring vintage cars, delicate surfaces. | Pros: Gentle and eco-friendly; effective on soft coatings. Cons: Limited to light cleaning; less effective on heavy rust. |
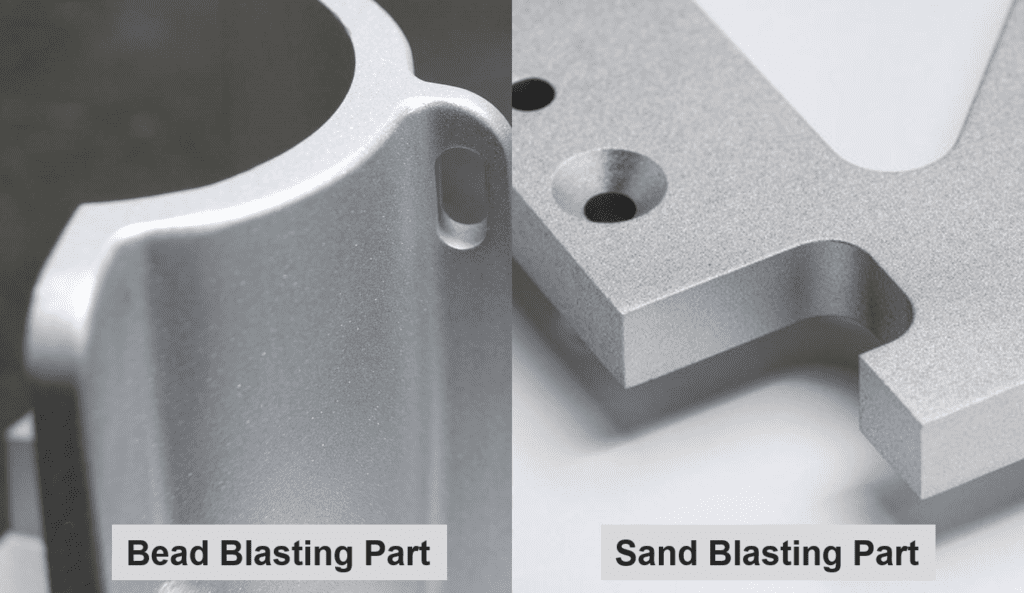
What Are the Characteristics of Sandblasting?
Sandblasting is a widely recognized abrasive blasting technique that utilizes coarse materials like sand or aluminum oxide. This method is particularly effective for removing heavy rust, old paint, and surface contaminants from tough materials. B2B buyers should consider sandblasting for applications requiring aggressive surface preparation, such as concrete work or heavy machinery restoration. However, it’s crucial to note that sandblasting can lead to surface damage on more delicate materials, necessitating careful selection based on the specific application.
How Does Glass Bead Blasting Differ in Suitability?
Glass bead blasting employs fine glass beads, making it a gentler alternative to sandblasting. This method is ideal for polishing and cleaning delicate surfaces, such as stainless steel or aluminum, without causing damage. B2B buyers in industries like aerospace or automotive may find glass bead blasting invaluable for achieving a smooth, polished finish on intricate components. However, the process is slower and less effective for removing heavy coatings, making it less suitable for more aggressive cleaning tasks.
What Advantages Does Steel Grit Blasting Offer for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Steel grit blasting is characterized by its use of steel grit, which provides an aggressive cleaning and surface profiling capability. This method is particularly beneficial for heavy-duty applications, such as industrial equipment and structural components. B2B buyers should consider steel grit blasting for its effectiveness in preparing surfaces for coatings and treatments. However, it can also be abrasive, potentially damaging softer materials, so it is essential to evaluate the substrate before proceeding.
Why Choose Aluminum Oxide Blasting for Precision?
Aluminum oxide blasting uses sharp particles for precision applications, making it suitable for automotive and aerospace components. This technique allows for versatile surface preparation, achieving various finishes depending on the particle size used. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of aluminum oxide blasting for its ability to provide a precise finish, although it tends to be more expensive than other methods and may leave a rougher texture.
When Is Soda Blasting the Best Choice?
Soda blasting utilizes sodium bicarbonate as an abrasive medium, offering a non-destructive cleaning solution. This technique is particularly favored for restoring vintage cars and cleaning delicate surfaces without damaging the substrate. B2B buyers looking for an eco-friendly option for light cleaning will find soda blasting appealing. However, its effectiveness is limited against heavy rust or thick coatings, which may require more aggressive methods for complete removal.
Key Industrial Applications of sandblast vs bead blast
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sandblast vs bead blast | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Sandblasting for paint removal and surface preparation | Enhances adhesion for new coatings, reduces rework | Quality of abrasive media, environmental regulations, cost-effectiveness |
| Aerospace | Glass bead blasting for surface finishing of turbine blades | Improves fatigue resistance, enhances performance | Precision of bead size, adherence to aerospace standards, supplier certifications |
| Construction | Sandblasting for cleaning concrete surfaces | Prepares surfaces for coatings, improves durability | Availability of specialized equipment, safety measures, local regulations |
| Oil & Gas | Glass bead blasting for cleaning and preparing pipeline parts | Ensures integrity and reliability of components | Material compatibility, environmental impact, sourcing of specific bead types |
| Metal Fabrication | Sandblasting for rust and paint removal on metal parts | Increases longevity of components, reduces downtime | Abrasive effectiveness, equipment maintenance, operational costs |
In the automotive manufacturing sector, sandblasting is often employed to remove old paint and prepare surfaces for new coatings. This process enhances the adhesion of paint, significantly reducing the likelihood of peeling and rework. Buyers in this sector should consider the quality of abrasive media and compliance with environmental regulations, especially in regions with stringent guidelines.
Within the aerospace industry, glass bead blasting is utilized for finishing turbine blades and other critical components. This method improves fatigue resistance and overall performance without damaging the base material. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to rigorous aerospace standards and provide precision in bead size to achieve the desired finish.
In construction, sandblasting is a common practice for cleaning concrete surfaces before applying protective coatings. This process not only prepares the surface for better adhesion but also enhances the overall durability of the structure. Buyers should focus on sourcing specialized equipment that meets local safety regulations and can handle large-scale projects efficiently.
The oil and gas industry benefits from glass bead blasting to clean and prepare pipeline parts. This method is crucial for ensuring the integrity and reliability of components, which are often exposed to harsh environments. Buyers need to prioritize material compatibility and consider the environmental impact of their blasting processes, particularly in ecologically sensitive areas.
Finally, in metal fabrication, sandblasting is extensively used for the removal of rust and paint from metal parts. This application increases the longevity of components and minimizes downtime for repairs. When sourcing services, businesses should evaluate the effectiveness of the abrasives used, the maintenance of blasting equipment, and overall operational costs to ensure a cost-effective solution.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sandblast vs bead blast’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Choosing the Right Abrasive for Complex Projects
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Brazil is faced with a dilemma when preparing a range of intricate metal parts for a new product line. The components require a delicate balance of surface cleaning and texture without compromising their structural integrity. The buyer is unsure whether sandblasting or glass bead blasting would best meet their needs, leading to confusion and potential delays in production timelines.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this challenge, the buyer should first assess the specific requirements of their components, including the type of surface contaminants, desired finish, and material sensitivity. A practical approach would be to conduct a small-scale test with both methods on a sample piece. This allows for a direct comparison of results and helps determine which method achieves the best finish without damaging the part. Additionally, consulting with experienced suppliers who can provide tailored advice based on their expertise in both sandblasting and glass bead blasting can further aid in making an informed decision. Engaging with vendors that offer comprehensive testing services can be particularly beneficial, as they can simulate the different blasting techniques on similar materials and provide detailed feedback on potential outcomes.
Scenario 2: Managing Cost Efficiency in Surface Preparation
The Problem: An industrial equipment supplier in Germany is under pressure to reduce costs while maintaining high-quality surface finishes on their products. With rising operational expenses, the procurement manager is evaluating the cost-effectiveness of sandblasting versus glass bead blasting. They are struggling to justify the potential higher costs associated with glass bead blasting without clear evidence of its benefits over sandblasting.
The Solution: To address this pain point, the procurement manager should undertake a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that includes not only the direct costs of abrasive materials but also the long-term implications on product quality and customer satisfaction. They can collect data on the lifecycle of products finished with each method, factoring in aspects such as durability, maintenance needs, and customer feedback. It may also be beneficial to reach out to suppliers for bulk pricing on glass beads, as well as to inquire about the potential for reduced labor costs associated with faster processing times. Additionally, establishing a pilot project using both methods on a limited product range can yield valuable insights into the true costs versus benefits, ultimately aiding in a more informed decision-making process.
Scenario 3: Quality Control and Surface Finish Consistency
The Problem: A metal fabrication company in South Africa is experiencing variability in surface finish quality across different batches of products. This inconsistency has led to increased rework and dissatisfaction among clients. The operations manager is uncertain whether the issue stems from the choice between sandblasting and glass bead blasting or from variations in the blasting process itself.
The Solution: To resolve this issue, the operations manager should implement a standardized operating procedure (SOP) for the blasting process, clearly defining parameters such as pressure, distance, and duration for both sandblasting and glass bead blasting. Training staff on these SOPs is crucial to ensure consistency. Additionally, investing in advanced monitoring equipment that tracks the blasting process in real time can help identify any deviations from the established parameters. Regular quality checks post-blasting should be instituted, utilizing surface measurement tools to ensure the desired finish is consistently achieved. Engaging with a specialized consultant can provide further insights into optimizing the blasting process, ensuring that the company maintains high standards of quality while leveraging the appropriate blasting technique for their specific applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sandblast vs bead blast
What Are the Key Materials for Sandblast and Bead Blast Applications?
When selecting materials for sandblasting and bead blasting, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of common abrasive media is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we analyze four widely used materials: silica sand, aluminum oxide, glass beads, and steel grit. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its effectiveness in different applications, particularly for international buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Silica Sand
Key Properties: Silica sand is composed primarily of silicon dioxide (SiO2) and is known for its hardness and angular shape. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silica sand is its cost-effectiveness, as it is one of the most affordable abrasive materials available. However, it poses health risks due to silica dust, which can lead to respiratory issues. Additionally, it can leave a rough surface finish, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Silica sand is effective for removing heavy rust and old paint but may not be ideal for delicate surfaces. Its angular particles can cause pitting on softer materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with health and safety regulations is critical, especially in regions with strict occupational health standards. Buyers should check local regulations regarding silica use, as some countries may have restrictions.
2. Aluminum Oxide
Key Properties: Aluminum oxide is a synthetic abrasive known for its durability and sharpness. It can withstand high temperatures and is resistant to chemical corrosion.
Pros & Cons: Its key advantage is its versatility; it can be used for both aggressive and fine finishing applications. However, aluminum oxide is more expensive than silica sand and can be less effective on softer materials.
Impact on Application: Aluminum oxide is suitable for a wide range of applications, from removing heavy coatings to polishing delicate surfaces. It provides a smoother finish compared to silica sand.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the aluminum oxide meets international standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance. The higher cost may be justified for applications requiring precision.
3. Glass Beads
Key Properties: Made from soda-lime glass, glass beads are spherical and non-angular, providing a gentler blasting action. They are effective at achieving a smooth finish and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of glass beads is their ability to clean and polish surfaces without damaging them, making them ideal for delicate applications. However, they are less effective for heavy rust removal compared to more aggressive abrasives.
Impact on Application: Glass beads are particularly effective for cleaning complex geometries and providing a satin finish on metals like stainless steel and aluminum. They can also remove light coatings without affecting the base material.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of glass beads available, as they can vary in size and hardness. Compliance with safety standards is also essential, as glass dust can pose health risks.
4. Steel Grit
Key Properties: Steel grit is a hard, angular abrasive made from recycled steel. It is known for its high durability and ability to withstand repeated use.
Pros & Cons: Steel grit is highly effective for aggressive cleaning and surface preparation, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it can be more expensive than silica sand and may cause surface damage on softer materials.
Impact on Application: Steel grit is ideal for removing heavy coatings, rust, and preparing surfaces for painting. Its sharp edges can create a rough texture, which may be desirable in some applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of steel grit in their region and ensure it meets relevant international standards for quality and safety. The higher cost may be offset by its effectiveness in demanding applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for sandblast vs bead blast | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica Sand | Heavy rust and paint removal | Cost-effective | Health risks due to silica dust | Low |
| Aluminum Oxide | Aggressive and fine finishing | Versatile for various applications | Higher cost, less effective on softer materials | Medium |
| Glass Beads | Cleaning and polishing delicate surfaces | Gentle on surfaces, smooth finish | Less effective for heavy rust removal | Medium |
| Steel Grit | Heavy-duty cleaning and surface preparation | Highly effective for aggressive applications | Can damage softer materials | High |
This analysis provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their projects and the properties of each abrasive material.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sandblast vs bead blast
What are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Sandblasting and Bead Blasting?
The manufacturing processes for sandblasting and bead blasting involve several critical stages that ensure optimal surface finishing. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers to make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
How is Material Prepared for Sandblasting and Bead Blasting?
Material Preparation is the foundational step in both sandblasting and bead blasting. It involves cleaning the surfaces of the components to remove any contaminants such as oils, dust, or rust. This initial cleaning can be performed using solvents or ultrasonic cleaning. For sandblasting, the materials often include metals like steel or aluminum, which may require different pre-treatment methods depending on their condition. Bead blasting, on the other hand, is typically used on smoother surfaces and might not require extensive pre-cleaning.
What Techniques are Used in the Forming Stage?
Forming primarily refers to the shaping of the material before it undergoes blasting. This may include machining or welding processes that create the final part geometry. For components destined for sandblasting, the forming technique may be more aggressive, as the subsequent blasting process is designed to remove surface imperfections. Conversely, for bead blasting, forming techniques may focus on creating a smoother finish since the bead blasting process aims to enhance the surface rather than reshape it.
How is Assembly Conducted in the Manufacturing Process?
Assembly is another significant stage where various components are brought together. This stage may involve fastening, welding, or otherwise joining parts to create a complete assembly. For both sandblasting and bead blasting, it’s critical to ensure that the assembly is structurally sound before proceeding to the finishing stage. This is particularly important in industries where precision is paramount, such as aerospace or automotive manufacturing.
What Finishing Techniques are Employed in Sandblasting and Bead Blasting?
Finishing is where the primary differences between sandblasting and bead blasting become evident. Sandblasting employs a more aggressive abrasive material, such as aluminum oxide or silica sand, which is propelled at high velocity to strip away surface layers. This technique is effective for heavy-duty applications but can leave a rough surface.
Bead blasting utilizes fine glass beads that gently polish the surface. This method is less aggressive, making it ideal for applications requiring a smooth, satin finish without damaging the substrate. The choice between these techniques depends on the desired surface finish and the specific requirements of the application.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing processes of sandblasting and bead blasting. Adhering to relevant international standards ensures that the finished products meet specific quality criteria, which is particularly crucial for B2B buyers operating across diverse markets.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Quality Assurance?
Manufacturers typically follow ISO 9001 standards, which outline the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures consistency in product quality and enhances customer satisfaction. Additionally, depending on the industry, other standards may apply, such as CE marking for European markets, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are crucial for ensuring product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they are used in production to ensure they meet predefined specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the process and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the manufacturing process is complete, the final product undergoes thorough testing to verify its conformance to specifications.
What Common Testing Methods are Used in Quality Assurance?
Several testing methods are commonly employed in QA for sandblasting and bead blasting. These include:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, dimensional accuracy, and overall finish.
- Adhesion Testing: Ensuring that coatings adhere properly to the blasted surfaces.
- Surface Roughness Testing: Measuring the texture of the surface to ensure it meets the specified requirements.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. This can be achieved through:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturer’s processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Requesting QC Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control measures, including inspection reports and compliance certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality practices.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control. Different markets may have varying standards, and it’s essential to ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international regulations. Additionally, understanding the logistics of shipping and compliance with import/export regulations is crucial for maintaining quality throughout the supply chain.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for sandblasting and bead blasting is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the details of each stage—from material preparation to finishing—and ensuring robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sandblast vs bead blast’
This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure sandblasting or bead blasting services. Understanding the differences between these two methods is essential for making informed decisions that align with your specific project requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Project Requirements
Clearly outline what you need from the blasting process. Determine the type of material you are working with, the desired surface finish, and whether you need to remove heavy coatings or just clean and polish. This step is crucial as it directly influences your choice between sandblasting and bead blasting.
- Material Type: Consider the hardness and composition of the material.
- Surface Finish: Decide if you require a rough or smooth finish for the application.
Step 2: Research Abrasive Media Options
Understand the types of abrasive media used in both processes. Sandblasting typically employs harsher materials like sand or aluminum oxide, while bead blasting uses gentler glass beads. Knowing the properties of each media helps you assess which method will meet your needs without damaging your parts.
- Sandblasting Media: Suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Bead Blasting Media: Ideal for delicate surfaces and achieving a refined finish.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing to a supplier, evaluate their capabilities and experience in both sandblasting and bead blasting. Request detailed information about their equipment, processes, and previous projects to ensure they can meet your specifications.
- Equipment Quality: Check for modern, well-maintained machinery.
- Project History: Look for case studies relevant to your industry.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Solicit detailed quotes from multiple suppliers. This will help you understand the pricing structure and any additional costs that may arise, such as setup fees or minimum order requirements. Comparing quotes allows for more informed budget planning.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure the quote includes all potential costs.
- Volume Discounts: Ask about pricing for larger orders.
Step 5: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers adhere to industry standards and regulations. Certifications such as ISO or specific regional compliance can be indicators of quality and reliability. This step is critical for avoiding risks associated with subpar work or materials.
- Quality Assurance: Look for suppliers with robust quality management systems.
- Safety Standards: Confirm compliance with local and international safety regulations.
Step 6: Assess Turnaround Times
Discuss and understand the expected turnaround time for your project. This is vital for planning your production schedule and ensuring that you can meet your deadlines. Different processes may have varying timelines based on their complexity and the volume of work.
- Production Capacity: Inquire about the supplier’s ability to handle your order size.
- Lead Times: Factor in potential delays due to material availability or equipment issues.
Step 7: Review Customer References
Ask for references from previous clients who have used similar services. This provides insights into the supplier’s reliability, quality of work, and customer service. Engaging with past clients can help you gauge the supplier’s overall performance.
- Client Feedback: Look for testimonials that reflect the supplier’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Industry Reputation: Consider the supplier’s standing within the industry.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when selecting between sandblasting and bead blasting services, ensuring that their project requirements are met efficiently and effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sandblast vs bead blast Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing nuances between sandblasting and bead blasting is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. Both methods serve distinct purposes and come with varying cost implications, influenced by multiple factors.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sandblasting and Bead Blasting?
-
Materials: The choice of abrasive media significantly impacts costs. Sandblasting typically utilizes less expensive materials like sand, aluminum oxide, or steel grit, resulting in lower material costs. In contrast, glass bead blasting requires more costly soda-lime glass beads, which can increase the overall expenditure.
-
Labor: Labor costs depend on the complexity of the blasting process and the skill level required. Sandblasting often demands more skilled labor due to its aggressive nature and the need for precision, leading to higher labor costs. Bead blasting, being less intensive, may require less specialized labor, potentially lowering costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs, including equipment maintenance and facility expenses, can vary. Sandblasting equipment is generally more robust and may incur higher maintenance costs compared to the less intensive setup for bead blasting.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can also differ. Sandblasting may require more robust tooling capable of handling harsher conditions, while bead blasting tools can be simpler and less costly.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring quality in both processes is essential but can vary in cost. The need for stringent quality checks in sandblasting due to the risk of damage can add to the overall cost, whereas bead blasting may have lower QC costs due to its gentler approach.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can differ based on the weight and volume of materials. Bead blasting’s materials are generally lighter, which can reduce shipping costs compared to bulkier sandblasting materials.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can fluctuate based on the demand for each service. Sandblasting often has a broader application base, allowing suppliers to maintain competitive margins, while bead blasting may have narrower profit margins due to its specialized application.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sandblasting and Bead Blasting Costs?
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often provide discounts for higher volumes or minimum order quantities (MOQs). Buyers looking for bulk orders can negotiate better pricing, especially for sandblasting, which tends to be more cost-effective at scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom requirements, such as specific abrasive sizes or surface finishes, can drive up costs. Sandblasting may be more adaptable to rougher specifications, while bead blasting is better for precise finishes, influencing the pricing structure.
-
Quality and Certifications: Certifications and quality standards, especially in regulated industries, can increase costs. Suppliers with recognized certifications may charge a premium, so it’s essential for buyers to assess the need for such qualifications.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices, but their reliability could justify the expense.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is critical for international buyers. Incoterms can influence overall costs and should be clarified to avoid unexpected charges.
What Are the Best Tips for B2B Buyers in Negotiating Costs?
-
Negotiate Terms: Establishing clear communication about volume, delivery timelines, and payment terms can facilitate better pricing. Leverage competition among suppliers to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of just the upfront costs, consider the long-term implications of each method, including maintenance, labor, and material costs over time.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing locally can reduce logistics costs and tariffs, making the overall process more cost-efficient.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Nuances: Be aware of market trends and price fluctuations in your region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, to make informed purchasing decisions.
Conclusion
While indicative prices for sandblasting and bead blasting can vary widely based on the factors discussed, understanding the cost structure and pricing influences can empower B2B buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions. By carefully evaluating materials, labor, and supplier capabilities, businesses can optimize their expenditure and achieve better value from their chosen surface finishing methods.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sandblast vs bead blast With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Sandblast vs Bead Blast: Understanding Other Solutions
In the realm of surface preparation and finishing, businesses often face the challenge of choosing the most effective method for their specific applications. While sandblasting and bead blasting are popular choices, there are alternative solutions that may better meet the unique needs of different industries. This section compares sandblast and bead blast with other viable methods, providing B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Sandblast Vs Bead Blast | Ultrasonic Cleaning | Chemical Etching |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Aggressive, effective for heavy rust and paint removal; can shape surfaces. | Gentle, ideal for intricate parts; removes contaminants without surface damage. | Precise, controls material removal; effective for fine details. |
| Cost | Generally lower due to inexpensive abrasive materials. | Higher initial investment; operational costs can vary based on the solution used. | Moderate; costs can escalate with complex applications and chemical disposal. |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively easy to set up; requires appropriate safety measures. | Requires specialized equipment and training; more complex setup. | Requires handling of hazardous materials; regulatory compliance is essential. |
| Maintenance | Equipment needs regular maintenance; abrasive media needs replenishing. | Minimal maintenance; equipment requires periodic checks for functionality. | Maintenance can be labor-intensive; chemical handling requires safety protocols. |
| Best Use Case | Heavy-duty applications, rough surfaces, and rapid paint removal. | Delicate parts, intricate geometries, and sensitive materials. | Applications needing precision, such as electronics and aerospace components. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Ultrasonic Cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaning utilizes high-frequency sound waves in a liquid solution to remove contaminants from surfaces. This method is particularly effective for intricate parts and delicate components. The primary advantage of ultrasonic cleaning is its ability to reach complex geometries and remove contaminants without damaging the surface. However, the initial investment in equipment can be higher, and operational costs depend on the cleaning solution used.
Chemical Etching
Chemical etching involves applying chemical solutions to remove material from a surface, allowing for precise control over the etching depth and texture. This method is ideal for applications that require high precision, such as the electronics and aerospace industries. While it offers excellent detail and control, the use of hazardous chemicals necessitates strict adherence to safety regulations, which can complicate implementation. The cost can also increase significantly if complex applications require specialized chemicals.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Surface Finishing Solution
Selecting the appropriate surface finishing method involves evaluating the specific requirements of your project. For heavy-duty applications where speed and effectiveness are crucial, sandblasting may be the preferred choice. Conversely, if the project involves delicate components that require precision, alternatives like ultrasonic cleaning or chemical etching may be more suitable. B2B buyers should consider factors such as performance, cost, ease of implementation, and maintenance when making their decision. Understanding the nuances of each method ensures that companies can achieve optimal results tailored to their unique operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sandblast vs bead blast
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Sandblasting and Bead Blasting?
When deciding between sandblasting and bead blasting, understanding their critical technical specifications is essential for making informed B2B decisions. Here are several key properties to consider:
-
Abrasive Material Type
Sandblasting typically utilizes harder, sharper materials such as aluminum oxide or silicon carbide. In contrast, bead blasting employs softer glass beads. The type of abrasive impacts the surface finish achieved and the degree of material removal. For B2B buyers, selecting the right abrasive material is crucial, as it influences both the efficiency of the cleaning process and the integrity of the substrate. -
Surface Roughness Profile
The resulting surface roughness varies significantly between the two methods. Sandblasting often leaves a more textured surface, while bead blasting achieves a smoother, polished finish. Buyers need to consider the end-use of the parts being treated; for instance, a smoother finish may be required for aesthetic applications or for improved adhesion in coatings. -
Blast Pressure and Speed
Sandblasting operates at higher pressures, allowing for faster material removal. Bead blasting, however, uses lower pressures to minimize damage to sensitive surfaces. Understanding the required pressure settings is vital for achieving the desired surface quality without compromising the integrity of the component, making it an essential factor in the procurement process. -
Cleaning Effectiveness
Sandblasting is generally more effective for removing heavy rust, old paint, or stubborn coatings, while bead blasting excels in cleaning delicate surfaces and removing thin coatings. B2B buyers should assess the specific cleaning needs of their applications to choose the appropriate method, ensuring optimal results and reducing costs associated with rework. -
Process Efficiency
Sandblasting tends to be faster than bead blasting, making it a more cost-effective option for larger or more robust components. Understanding the efficiency of each process helps buyers optimize production timelines and cost management, particularly in high-volume manufacturing environments.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know in Sandblast vs Bead Blast?
Navigating the technical landscape of sandblasting and bead blasting involves familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are marketed by another company under its brand name. Understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility and quality in the components being treated. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for buyers as it affects inventory management and overall procurement costs, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. B2B buyers should be prepared to provide detailed specifications when issuing RFQs to ensure accurate pricing and service offerings. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standard trade terms used in international contracts to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, especially when dealing with international suppliers, as it impacts the overall cost and liability of shipping processes. -
Surface Finish Specification
This term encompasses the requirements for the final texture and quality of a surface after processing. Buyers must specify surface finish standards (e.g., Ra values) to ensure that the final product meets functional and aesthetic needs. -
Technical Data Sheet (TDS)
A TDS provides detailed information about a product’s properties, usage, and handling instructions. Reviewing TDS documents is essential for buyers to understand the capabilities and limitations of the blasting processes involved.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting between sandblasting and bead blasting, ultimately enhancing their procurement strategies and operational efficiencies.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sandblast vs bead blast Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting Sandblast and Bead Blast Techniques?
The global market for sandblasting and bead blasting is experiencing significant growth, driven by a surge in demand across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and metal fabrication. Key trends include the increasing adoption of advanced technologies such as automated blasting systems and robotics, which enhance efficiency and precision. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on customization, as manufacturers seek tailored solutions that meet specific surface finishing requirements.
International B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are witnessing a shift towards more sophisticated abrasive blasting methods. This trend is influenced by the need for higher quality finishes and faster turnaround times, leading to the integration of digital technologies for better monitoring and control of blasting processes. Moreover, as global supply chains become more interconnected, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that can offer reliable service and consistent quality across different geographical markets.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Sandblast and Bead Blast Industry?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the sandblast and bead blast sectors. The environmental impact of abrasive materials and the blasting process itself necessitates a shift towards greener practices. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who utilize eco-friendly abrasives, such as recycled glass beads, which reduce waste and lower carbon footprints.
Furthermore, ethical sourcing is gaining traction as companies prioritize transparent supply chains. Buyers are encouraged to assess their suppliers’ adherence to environmental regulations and their commitment to sustainable practices. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) are becoming essential criteria for evaluating potential partners. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only enhance their brand image but also meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for responsible manufacturing practices.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Sandblast and Bead Blast Technologies?
The origins of abrasive blasting date back to the late 19th century, when the first sandblasting machines were developed. Initially used primarily for cleaning and surface preparation, these techniques have evolved significantly. The introduction of different abrasive materials, such as glass beads and aluminum oxide, has expanded the applications of blasting processes, enabling more specialized surface finishes.
Over the decades, advancements in technology, including the automation of blasting systems and the development of more efficient abrasives, have transformed the industry. Today, both sandblasting and bead blasting are integral to modern manufacturing processes, providing essential solutions for surface treatment across various sectors. As the industry continues to evolve, it remains crucial for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest innovations and trends that could impact their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sandblast vs bead blast
-
How do I determine whether to use sandblasting or glass bead blasting for my project?
Choosing between sandblasting and glass bead blasting depends on your project’s specific requirements. Sandblasting is ideal for heavy-duty applications, effectively removing thick coatings, rust, and surface contaminants. In contrast, glass bead blasting is better suited for cleaning and polishing delicate surfaces without causing damage. Consider the material type, the desired finish, and whether you need aggressive cleaning or a gentle touch. Consulting with experienced suppliers can help tailor the best approach for your needs. -
What are the key benefits of sandblasting compared to bead blasting?
Sandblasting offers several advantages, including faster cleaning and the ability to remove stubborn coatings and contaminants effectively. It is more cost-effective due to the lower price of abrasive materials used, making it suitable for large-scale projects. Sandblasting is particularly beneficial for rough surfaces or when preparing surfaces for painting, as it creates a matte finish that enhances adhesion. However, its aggressive nature may not be suitable for all materials, particularly delicate ones. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for sandblasting and bead blasting services internationally?
To find trustworthy suppliers, start by researching companies with a strong reputation in the industry. Look for certifications, client testimonials, and case studies. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or ThomasNet for vetted suppliers, and consider attending trade shows or industry conferences to network. Conduct due diligence by asking for samples of their work, verifying their production capabilities, and checking for compliance with international quality standards to ensure they meet your specific needs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for sandblasting and bead blasting services?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the service. Some suppliers may have low MOQs for standard services, while custom orders or specialized applications might require higher quantities. It’s essential to communicate your needs upfront and inquire about flexibility in order sizes. Many suppliers are willing to accommodate smaller orders, especially for new clients or trial projects. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing sandblasting and bead blasting services?
Payment terms can vary widely based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront, followed by the balance upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established customers or larger orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, credit card) and ensure that the terms are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for sandblasting and bead blasting projects?
To maintain quality assurance, it’s crucial to establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier. Request detailed documentation of their QA processes, including inspections, testing, and certifications. Consider implementing a third-party quality check to verify that the finished products meet your requirements. Regular communication and progress updates during the project can also help address any issues promptly and maintain quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing sandblasting or bead blasting services?
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of services. Ensure that your supplier has experience in international shipping and understands customs regulations in your region. Discuss packaging, shipping methods, and delivery timelines upfront to avoid delays. It’s also wise to factor in potential tariffs or duties, as these can impact overall costs. Establishing a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the process and minimize risks. -
Are there any environmental considerations when choosing between sandblasting and bead blasting?
Yes, environmental considerations are increasingly important. Sandblasting can produce silica dust, which poses health risks and may require specific environmental controls. Glass bead blasting, on the other hand, is generally considered more environmentally friendly due to the non-toxic nature of glass media. When sourcing services, inquire about the supplier’s compliance with environmental regulations and their commitment to sustainable practices to ensure alignment with your corporate responsibility goals.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Sandblast Vs Bead Blast Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Enviro-Tech Coatings – Coating and Metal Finishing Services
Domain: enviro-tech-coatings.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Enviro-Tech Coatings offers a wide range of coating, painting, and metal finishing services for various industries. Their services include: 1. Painting OEM parts 2. Metal finishing 3. Metal cleaning with glass beads, walnut shells, and ceramic media 4. Painting for steel and pipe fabricators 5. Fusion bonded epoxy for underground piping. They provide full surface reconditioning services on industr…
2. Glass Bead Blasting vs. Sandblasting – Key Differences for Anodised Aluminium
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the comparison between glass bead blasting and sandblasting for anodised aluminium. Key points include: 1. Glass bead blasting provides a smoother, shinier finish that is easier to clean, while sandblasting results in a rougher, matte texture that is difficult to clean. 2. The user is interested in achieving an emerald green anodised aluminium color with a bumpy surf…
3. RIE Coatings – Sandblasting & Bead Blasting Services
Domain: riecoatings.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: RIE Coatings offers sandblasting and bead blasting services for surface preparation on aluminum and steel. Sandblasting is an aggressive technique used for heavy-duty applications like rust removal, while bead blasting is a precision cleaning method that avoids damaging the substrate. Sandblasting specifications include SS-PC-SP-SXX 9906020 and MIL-A-21380. The sandblasting process involves propel…
4. Orchid – Sand vs. Beads in Metal Removal
Domain: orchid.ganoksin.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Orchid – Sand vs. Beads in Metal Removal, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Eziil – Bead Blasting Solutions
Domain: eziil.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Bead blasting is a surface finishing technique that uses small, spherical media (typically glass beads) to clean, deburr, and finish a workpiece. The process involves propelling the media at high velocity against the surface, removing contaminants, smoothing rough edges, and creating a uniform matte finish. Common bead-blasting media include: 1. Glass Bead Blasting Media: Made from lead-free, soda…
6. Wayken – Bead Blast Finishing
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Bead blast finish is a surface finishing technique that involves the release of fine glass or steel beads at high pressure to achieve a shiny, smooth, and clean surface on components. It is suitable for metals, plastics, rubber, and glass materials. The process uses spherical glass or steel media, with glass beads being more environmentally friendly and softer on surfaces, while steel beads are co…
7. Chris Reeve Knives – Knife Handle Finishes
Domain: chrisreeve.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Chris Reeve Knives offers two finishes for knife handles: Glass Blast and Sandblast. The Glass Blast finish uses crushed glass to create a finer, tighter grain, resulting in a super scratch-resistant, smooth finish that maintains grip. This finish is available as an upgrade for all knives with plain titanium or micarta handles. The Sandblast finish uses sand to create an extra grippy texture that …
8. Tuofa – Bead Blasting Services
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Bead Blasting: A surface treatment process using spherical beads made of glass, plastic, or ceramic at high pressure. Characteristics include a gentler approach, fine surface finish, and versatility across materials. Applications include surface cleaning, preparation, and finishing, particularly in industries like aerospace and electronics. Advantages are its gentleness on delicate surfaces, unifo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sandblast vs bead blast
As B2B buyers navigate the decision between sandblasting and bead blasting, understanding the distinct advantages of each method is crucial. Sandblasting excels in aggressive surface preparation, effectively removing heavy rust and paint, making it ideal for robust applications. Conversely, glass bead blasting offers a gentler touch, perfect for achieving a polished finish on delicate surfaces without causing damage.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in maximizing value from these processes. By aligning the choice of blasting technique with specific project requirements, companies can enhance operational efficiency and product quality. This understanding not only facilitates better procurement decisions but also fosters long-term relationships with suppliers who can meet diverse needs.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage these insights to inform their sourcing strategies. Emphasizing collaboration with experienced suppliers and exploring innovative solutions will be key to staying competitive. Engage with trusted partners today to ensure your projects benefit from the most suitable surface finishing methods, ultimately driving your business success forward.