Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for sand casting parts
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable sand casting parts can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers across diverse industries. The intricate nature of sand casting, a time-honored technique that transforms molten metal into complex components, requires a deep understanding of the process, material specifications, and supplier capabilities. This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including markets like Vietnam and Germany.
Within these pages, you’ll discover a wealth of information covering various aspects of sand casting, including the types of sand casting methods available, their applications across multiple sectors, and strategic approaches to vetting suppliers. We delve into cost considerations, production timelines, and quality control measures, providing actionable insights to navigate the global market effectively.
By leveraging this guide, buyers can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they select the right sand casting parts that meet their technical requirements and budget constraints. Empowering you with knowledge and practical tools, this resource is designed to enhance your sourcing strategy and foster successful partnerships in the ever-evolving world of metal casting.
Understanding sand casting parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Green Sand Casting | Utilizes a mixture of sand, clay, and water; allows for rapid mold creation. | Automotive parts, construction components | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile; Cons: Lower dimensional accuracy compared to other methods. |
| Resin Sand Casting | Employs resin-coated sand for improved mold strength; suitable for intricate designs. | Aerospace components, precision machinery | Pros: High dimensional accuracy, better surface finish; Cons: Higher costs, longer curing times. |
| Shell Mold Casting | Features thin shells made from sand and resin; ideal for high-volume production. | Large industrial components, heavy machinery | Pros: Excellent surface finish, good dimensional control; Cons: Higher initial setup costs. |
| Lost Foam Casting | Uses foam patterns that vaporize during casting; allows for complex geometries. | Custom parts, art pieces, prototype development | Pros: Complex shapes without cores; Cons: Limited to non-ferrous metals, higher production costs. |
| Permanent Mold Casting | Involves reusable metal molds; offers high production rates and improved surface quality. | High-volume manufacturing, automotive parts | Pros: Excellent dimensional accuracy, reduced waste; Cons: Higher initial investment, limited to simpler shapes. |
What Are the Characteristics and Suitability of Green Sand Casting?
Green sand casting is the most traditional and widely used method in the foundry industry. It utilizes a mixture of sand, clay, and water to form molds, allowing for quick setup and flexibility. This method is particularly suitable for producing large and medium-sized components, primarily in automotive and construction applications. B2B buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and precision, as while green sand casting is economical, it may not meet stringent dimensional tolerances.
How Does Resin Sand Casting Enhance Precision?
Resin sand casting employs a resin-coated sand that enhances the mold’s strength and allows for finer details in the final product. This method is ideal for industries requiring high precision, such as aerospace and specialized machinery. Buyers should weigh the benefits of superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy against the increased costs and longer curing times associated with resin sand casting.
What Makes Shell Mold Casting a Preferred Option for High-Volume Production?
Shell mold casting is characterized by thin shells formed from sand and resin, making it suitable for high-volume production runs. This technique is commonly used for large industrial components and heavy machinery. B2B buyers often prefer shell mold casting for its excellent surface finish and dimensional control, although they should be prepared for higher initial setup costs compared to traditional methods.
Why Choose Lost Foam Casting for Complex Geometries?
Lost foam casting involves creating a mold from a foam pattern that vaporizes during the casting process, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries. This method is suitable for custom parts, art pieces, and prototypes. Buyers should consider the advantages of this innovative approach, such as the elimination of cores, while being aware of its limitations, including its applicability to non-ferrous metals and potentially higher production costs.
What Are the Advantages of Permanent Mold Casting?
Permanent mold casting uses durable metal molds that can be reused multiple times, making it efficient for high-volume manufacturing. This method is particularly advantageous for producing automotive parts and other components that require high dimensional accuracy. Buyers should assess the balance between the initial investment in molds and the long-term benefits of reduced waste and superior quality in finished products.
Key Industrial Applications of sand casting parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of sand casting parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine blocks and transmission housings | High strength and durability in critical components | Material specifications, dimensional accuracy, and lead times |
| Aerospace | Structural components and housings | Lightweight yet strong parts for improved efficiency | Certification standards, quality control, and traceability |
| Construction & Heavy Equipment | Gearboxes and machinery frames | Cost-effective production of large and complex parts | Supplier reliability, production capacity, and material sourcing |
| Oil & Gas | Valve bodies and pump casings | Resistance to harsh environments and pressure | Compliance with industry standards and certifications |
| Electronics | Heat sinks and enclosures | Efficient thermal management and protection | Precision requirements, surface finish specifications, and lead times |
How Are Sand Casting Parts Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, sand casting parts are crucial for manufacturing engine blocks and transmission housings. These components require high strength and durability to withstand extreme conditions. International buyers must focus on sourcing materials that meet specific standards for performance and safety. Additionally, dimensional accuracy and timely delivery are vital to ensure seamless integration into assembly lines.
What Role Do Sand Casting Parts Play in Aerospace Applications?
Aerospace applications utilize sand casting for producing lightweight yet strong structural components and housings. These parts must endure rigorous stress and temperature variations, making sand casting an ideal choice for their production. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers who adhere to strict certification standards and quality control processes to ensure reliability and safety in flight applications.
How Are Sand Casting Parts Beneficial in Construction and Heavy Equipment?
In construction and heavy equipment, sand casting is employed to create gearboxes and machinery frames. This method allows for cost-effective production of large and complex parts, essential for heavy-duty applications. When sourcing, businesses should assess supplier reliability and production capacity, as well as the ability to meet material specifications to ensure durability and performance under demanding conditions.
Why Are Sand Casting Parts Essential for the Oil & Gas Industry?
The oil and gas industry relies on sand casting for producing valve bodies and pump casings, which must resist harsh environmental conditions and high pressures. The ability to create robust components is critical for operational safety and efficiency. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with industry standards and certifications, as this guarantees the quality and reliability of the parts in critical applications.
How Do Sand Casting Parts Enhance Electronic Products?
In the electronics sector, sand casting is used to manufacture heat sinks and enclosures, which are vital for efficient thermal management and protection of sensitive components. Precision in dimensions and surface finishes is crucial to ensure optimal performance. B2B buyers must consider the specific requirements for thermal conductivity and surface treatments when sourcing these parts to meet the high standards of electronic applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘sand casting parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Dimensional Precision in Sand Casting Parts
The Problem: One of the most common issues B2B buyers face when sourcing sand casting parts is the variability in dimensional precision. Buyers often require components that fit into complex assemblies or machinery where tight tolerances are essential. However, due to the inherent limitations of sand casting—such as the settling of sand, the cooling rates of metals, and the skill level of the operators—parts may not meet the required specifications. This can lead to delays in production, increased costs from rework, and ultimately, frustration when parts do not integrate seamlessly into their intended applications.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should prioritize working with suppliers that utilize advanced sand casting techniques, such as automated molding processes or the use of precision-engineered patterns. When sourcing sand casting parts, it’s crucial to ask potential suppliers about their quality control measures, including the use of 3D printing for patterns and advanced inspection techniques like laser scanning. Establishing a clear communication channel for discussing tolerances upfront can help ensure that both parties have aligned expectations. Additionally, investing in prototypes before full production can significantly reduce the risk of dimensional inaccuracies, enabling buyers to verify fit and function prior to committing to larger orders.
Scenario 2: Inconsistent Quality and Surface Finish Issues
The Problem: Buyers often encounter inconsistent quality and surface finish in sand casting parts, which can be particularly problematic for industries where aesthetic appearance and surface integrity are critical, such as automotive or aerospace. Variations in sand quality, mold preparation, and post-casting treatments can lead to defects like rough surfaces, inclusions, or dimensional inconsistencies. These issues not only affect the performance of the parts but can also tarnish a company’s reputation if products do not meet customer expectations.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, B2B buyers should conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers. Requesting samples of previous work, reviewing customer testimonials, and examining the production processes can provide insights into a supplier’s capabilities. Buyers should also consider specifying the use of high-quality sand and advanced surface finishing techniques in their contracts. For example, suppliers can employ shot blasting or chemical treatments to enhance the surface finish of cast parts. Regular quality audits and inspections during production can also help catch potential issues early, ensuring that the final products meet the necessary standards before shipment.
Scenario 3: Long Lead Times and Production Delays
The Problem: Lead times can be a significant pain point for buyers of sand casting parts, especially when unexpected production delays occur. Factors such as the complexity of the design, the availability of raw materials, and the current workload of the casting facility can all contribute to extended lead times. This unpredictability can disrupt supply chains, impact project timelines, and lead to increased costs due to rush orders or alternative sourcing.
The Solution: To combat long lead times, buyers should engage in proactive planning and communication with their suppliers. Establishing a forecast of demand and sharing it with suppliers can help them allocate resources more effectively. Additionally, buyers should seek suppliers that offer flexible production capabilities, such as the ability to scale up operations quickly or utilize multiple facilities. Implementing a Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory strategy can also help mitigate the impact of lead time variability by reducing the amount of inventory held and allowing for more agile responses to changes in demand. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also foster better cooperation, ensuring that buyers are prioritized during peak production periods.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for sand casting parts
What Are the Key Materials Used in Sand Casting Parts?
When selecting materials for sand casting parts, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in sand casting, focusing on their relevance to international B2B buyers.
1. Aluminum Alloys: Versatile and Lightweight
Key Properties: Aluminum alloys are known for their excellent corrosion resistance, lightweight nature, and good thermal and electrical conductivity. They typically have a melting point around 660°C (1220°F), making them suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum alloys is their low density, which reduces shipping costs and makes them ideal for lightweight components. However, they can be more expensive than other metals and may not withstand high-temperature applications as effectively as some ferrous materials. Additionally, the casting process can be complex due to the need for precise temperature control.
Impact on Application: Aluminum alloys are commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications where weight reduction is critical. Their corrosion resistance makes them suitable for marine environments, ensuring longevity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B108 and DIN 1725. In regions like Europe, specific alloy designations (e.g., EN AW-6082) are preferred, while in Africa and South America, availability may vary.
2. Cast Iron: Strength and Durability
Key Properties: Cast iron has excellent wear resistance, high compressive strength, and good castability. Its melting point ranges from 1150°C to 1300°C (2100°F to 2370°F), depending on the specific type of cast iron.
Pros & Cons: The durability and strength of cast iron make it ideal for heavy-duty applications, such as engine blocks and machinery components. However, it is relatively brittle and may not perform well under tensile stress. Additionally, the weight of cast iron can increase shipping costs.
Impact on Application: Cast iron is often used in construction and automotive industries, where strength and durability are paramount. Its ability to withstand high temperatures makes it suitable for engine components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A48 and DIN 1691 is essential. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe may prefer specific grades based on application requirements.
3. Steel Alloys: High Strength and Versatility
Key Properties: Steel alloys offer a combination of high tensile strength, ductility, and toughness. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons: The versatility of steel alloys allows for various applications, from automotive to industrial machinery. However, they can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated, and the manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring additional steps such as heat treatment.
Impact on Application: Steel alloys are used in critical applications, including structural components, automotive parts, and heavy machinery. Their ability to be heat-treated enhances their performance in demanding environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM A536 and JIS G5500. In regions like Germany, specific grades are preferred for different applications, while in Africa, the availability of certain alloys may vary.
4. Bronze Alloys: Corrosion Resistance and Aesthetic Appeal
Key Properties: Bronze alloys are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and wear properties. They typically have a melting point of around 950°C (1742°F) and are often used for parts exposed to harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of bronze is its resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for marine applications. However, bronze can be more expensive than other materials, and its casting process may require more precision to avoid defects.
Impact on Application: Bronze is commonly used in applications such as marine fittings, valves, and decorative components due to its aesthetic appeal and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B505 and DIN 17660 is crucial. Buyers in Europe may have specific preferences for alloy compositions, while in South America, the cost may be a significant factor in material selection.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Sand Casting Parts
| Material | Typical Use Case for sand casting parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost and temperature sensitivity | High |
| Cast Iron | Engine blocks and machinery components | High strength and durability | Brittle and heavier | Medium |
| Steel Alloys | Structural components and machinery | High tensile strength and versatility | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Medium |
| Bronze Alloys | Marine fittings and decorative parts | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and precision required | High |
This strategic material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding sand casting parts, ensuring compliance and suitability for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for sand casting parts
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Sand Casting Parts?
The sand casting process is a vital method in the production of metal parts, offering a blend of flexibility and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the stages involved is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. Here’s a breakdown of the main stages of the manufacturing process.
How Is Material Prepared for Sand Casting?
Material preparation is the first step in the sand casting process, where the quality of the final product begins. The primary material used is sand, which must be mixed with a bonding agent, typically clay, to create a moldable mixture. This step often involves using a sand mixer to ensure a homogeneous blend, which is critical for achieving consistent mold quality.
Additionally, core sand may be prepared separately for parts requiring internal cavities. The composition of the sand mixture can vary based on the specific requirements of the casting, including the type of metal being cast and the desired surface finish. Proper material preparation minimizes defects and enhances the overall quality of the cast parts.
What Are the Forming Techniques in Sand Casting?
The forming stage encompasses several critical steps:
-
Pattern Making: Patterns are created based on the part designs, typically made from wood, metal, or plastic. The choice of material depends on the production volume; wooden patterns are common for one-off pieces, while metal patterns are used for mass production.
-
Molding: The pattern is placed in a flask, and sand is packed around it to form a mold. This step involves careful ramming of the sand to ensure it holds the shape of the pattern. The molding process can be manual or automated, with automation improving efficiency and consistency.
-
Core Making: If the casting design requires internal features, cores made from core sand are produced and placed in the mold. This additional step is essential for creating complex geometries.
-
Gating System Establishment: A gating system is designed to control the flow of molten metal into the mold. Proper gating is crucial to prevent defects such as air pockets and misruns.
What Are the Key Steps in the Assembly and Finishing of Sand Casting Parts?
Once the mold is prepared, the next steps involve melting and pouring the metal:
-
Melting: The chosen metal is melted in a furnace, ensuring it reaches the correct temperature and composition. Electric furnaces are commonly used due to their efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
-
Pouring: The molten metal is carefully poured into the mold. The pouring speed and technique are critical to avoid defects; too fast can cause turbulence, while too slow can lead to premature solidification.
-
Cooling and Removal: After pouring, the metal needs time to cool and solidify. Once cooled, the mold is broken apart, and the casting is removed. This process may involve shaking, hammering, or using automated systems.
-
Finishing: The cast parts may require additional processes such as grinding, machining, or surface treatment to achieve the desired specifications and surface quality. This step ensures that the final product meets the customer’s standards.
How Is Quality Assurance Managed in Sand Casting?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of sand casting, ensuring that the parts produced meet international standards and specific customer requirements.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Sand Casting?
B2B buyers should be aware of the various international standards that govern quality in manufacturing, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE for European markets or API for oil and gas applications may be relevant, depending on the end-use of the cast parts.
These standards not only provide a framework for quality management but also enhance the credibility of suppliers in international markets. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to these standards to ensure consistent quality.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Sand Casting?
Quality control in sand casting typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection ensures that all raw materials, including sand and metal, meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the mold, the melting process, and the pouring technique. This stage is crucial for identifying defects early and implementing corrective actions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the casting is complete, a thorough inspection is performed. This includes visual inspections, dimensional checks, and possibly non-destructive testing (NDT) methods such as X-ray or ultrasonic testing to identify internal flaws.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to mitigate risks associated with poor-quality parts. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of the supplier’s facilities can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. Audits can be performed by the buyer or through third-party inspection agencies.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports offer transparency and can help buyers assess the reliability of the supplier.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the quality of the cast parts. These services can be particularly useful for international buyers who may not have the resources for on-site inspections.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various quality control nuances:
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements for materials and processes. Understanding these requirements is essential for successful international trade.
-
Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices can vary significantly across cultures. Building strong relationships and ensuring clear communication with suppliers can facilitate smoother transactions.
-
Time Zones and Logistics: Coordinating quality control processes across different time zones can be challenging. B2B buyers should establish clear timelines and expectations with suppliers to ensure timely delivery and quality assurance.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with sand casting parts is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and thorough quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers who meet their needs in an increasingly globalized market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘sand casting parts’
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers looking to procure sand casting parts. By following this checklist, you can ensure a smooth procurement process, ultimately leading to high-quality products that meet your specifications.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging suppliers, clearly outline the technical requirements for your sand casting parts. This includes dimensions, tolerances, material specifications, and any specific industry standards that need to be met. Defining these details helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that the final product aligns with your needs.
- Material Type: Specify the metal alloy required (e.g., aluminum, cast iron) based on your application.
- Dimensional Tolerances: Clearly state the acceptable tolerances to ensure precision in the final casting.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in sand casting. Look for companies with a proven track record in your specific industry, as their experience can significantly impact quality and reliability.
- Industry Experience: Prefer suppliers with experience in your sector to ensure they understand your unique requirements.
- Reputation: Check online reviews, testimonials, and case studies to gauge their reputation among other B2B buyers.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that your shortlisted suppliers possess the necessary certifications, such as ISO 9001 or similar quality management standards. Certifications indicate a commitment to quality control and manufacturing excellence.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure suppliers have a robust quality assurance process in place.
- Compliance: Check for compliance with local and international regulations relevant to your industry.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before finalizing any orders, request samples or prototypes of the sand casting parts. This step allows you to assess the quality of the materials and craftsmanship before committing to larger production runs.
- Quality Assessment: Evaluate the physical samples for dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Fit Testing: If applicable, test the samples in your application to ensure compatibility.
Step 5: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Engage in discussions with suppliers regarding their lead times and production capabilities. Understanding these aspects is crucial for planning your supply chain and ensuring timely delivery.
- Production Capacity: Inquire about their capacity to handle your order volume, especially for large or complex parts.
- Flexibility: Assess their ability to accommodate changes in order size or specifications.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a supplier, negotiate the terms and conditions of the contract. This includes pricing, payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty provisions.
- Transparent Pricing: Ensure the pricing structure is clear and includes all potential costs, such as shipping and handling.
- Warranty and Support: Discuss warranty terms and after-sales support to safeguard your investment.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, set up a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Effective communication is vital for addressing any issues that may arise during production and ensuring that your requirements are continuously met.
- Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to monitor progress and address any concerns promptly.
- Point of Contact: Designate a primary contact person on both sides to streamline communication.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement of sand casting parts, ensuring high-quality outcomes that meet their operational needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for sand casting parts Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sand Casting Parts?
When sourcing sand casting parts, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary components that contribute to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The type of metal selected for casting significantly impacts costs. Common metals like aluminum and iron are generally more affordable than specialized alloys like titanium or high-grade stainless steel. Additionally, the quality of the sand and any additives used in the casting process can influence material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and expertise. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring precision in the casting process, particularly for complex designs. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, buyers may see increased pricing compared to regions with lower labor costs, like parts of Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which is beneficial for both suppliers and buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial setup for sand casting involves creating molds and patterns. These tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom parts. The complexity of the design and the number of parts produced can either amortize these costs over a larger volume or escalate them for smaller runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that cast parts meet specified tolerances and quality standards incurs additional costs. Advanced QC processes, such as non-destructive testing and certification, may be necessary for industries with strict regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling are vital components, especially for international transactions. Costs can fluctuate based on Incoterms, shipping methods, and distances involved. Furthermore, tariffs and customs duties can add unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a margin to cover risks and profit. This margin can be influenced by market demand, competition, and the supplier’s positioning in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Sand Casting Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of sand casting parts, making it essential for buyers to understand these elements:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Conversely, low-volume orders may incur higher prices due to the fixed costs associated with tooling and setup.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts typically command higher prices due to the additional labor and material costs involved in designing and producing them. Buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: As mentioned, the choice of materials can greatly influence pricing. Specialty materials with unique properties often come at a premium.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring specific certifications or those intended for high-performance applications may incur additional costs for testing and compliance.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and production capabilities can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with advanced capabilities may charge more, but they often provide better quality and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipment can significantly impact overall costs. Different Incoterms dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and duties, thus influencing the final price you pay.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for Buyers in International Markets?
When negotiating prices for sand casting parts, especially in international markets, consider the following tips:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial prices and consider long-term costs such as maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. This holistic view can inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Leverage Volume: If feasible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs, which can lead to lower per-unit costs. Consider forming purchasing groups with other companies to achieve higher volumes.
-
Be Transparent: Clearly communicate your requirements and constraints to suppliers. Building a trusting relationship can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Research Market Trends: Stay informed about fluctuations in material prices and labor costs in different regions. This knowledge can empower negotiations.
-
Evaluate Multiple Suppliers: Getting quotes from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best value.
Disclaimer on Pricing
It is important to note that the prices and cost components mentioned are indicative and can vary significantly based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always seek multiple quotes and consider a comprehensive approach to cost analysis when sourcing sand casting parts.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing sand casting parts With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Sand Casting Parts
In the realm of manufacturing, sand casting parts have long been a popular method for producing metal components due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. However, as technology evolves, several alternative casting methods have emerged, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. This analysis will compare sand casting with two viable alternatives: die casting and investment casting, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Sand Casting Parts | Die Casting | Investment Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate precision; suitable for complex shapes | High precision and surface finish | Very high precision; excellent surface finish |
| Cost | Low initial setup; economical for low to medium volumes | Higher setup costs; best for high volumes | High initial setup costs; economical for high precision needs |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple process; manual or automated options | Requires specialized machinery | Involves intricate patterns; labor-intensive setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance for equipment; ongoing quality checks needed | Moderate maintenance; specialized equipment needed | High maintenance due to complexity of molds |
| Best Use Case | Custom parts; low-volume production | Mass production of standardized parts | High-precision components with complex geometries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
1. Die Casting
Die casting utilizes a metal mold to create parts with high precision and smooth surfaces. This method is particularly beneficial for large-scale production runs, as it allows for rapid cycle times and consistent quality. However, the initial setup costs for die casting can be significant, making it less viable for low-volume projects. Additionally, while die casting excels in precision, it may not accommodate complex geometries as effectively as sand casting. The best use case for die casting is in industries like automotive and consumer electronics, where uniformity and speed are paramount.
2. Investment Casting
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, involves creating a wax pattern that is coated with a ceramic shell. Once the shell hardens, the wax is melted away, leaving a detailed mold for pouring molten metal. This method is revered for its high precision and ability to produce intricate shapes and fine details. However, the process is labor-intensive and incurs high initial costs due to the complexity of the molds. Investment casting is ideal for applications in aerospace, medical devices, and high-end consumer products where precision and finish are critical.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Needs
When selecting a casting method, B2B buyers must consider various factors, including production volume, required precision, budget constraints, and the complexity of the parts. Sand casting remains an excellent choice for custom, low to medium volume projects due to its cost-effectiveness and adaptability. In contrast, die casting and investment casting shine in high-volume production and precision applications, respectively. By assessing these parameters, buyers can identify the most suitable casting solution that aligns with their operational goals and project specifications.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for sand casting parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Sand Casting Parts?
Understanding the technical properties of sand casting parts is essential for B2B buyers involved in manufacturing and procurement. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal used in sand casting, such as aluminum, iron, or bronze. Each grade has distinct mechanical properties, including tensile strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for ensuring that the final product meets performance requirements and industry standards.
2. Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance indicates the allowable variation in the dimensions of a casting. It is essential for ensuring parts fit together correctly during assembly. In sand casting, tolerances can vary widely; therefore, understanding the required tolerances is key to achieving the desired level of precision, especially in industries such as automotive and aerospace where even minor deviations can lead to significant issues.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of the casting’s surface. It is measured in terms of Ra value (roughness average) and is important for aesthetic and functional reasons. A smoother surface can reduce friction and improve performance, making it a vital specification in applications where parts interact closely.
4. Weight and Volume
Weight and volume specifications are crucial for logistics and cost management in production. Knowing the weight of the casting helps in estimating shipping costs and handling requirements, while the volume can inform mold design and material usage. Accurate weight and volume measurements ensure efficient resource allocation and inventory management.
5. Casting Size
The overall size of the casting, including maximum dimensions, is a fundamental property that affects the mold design and production capabilities. It is important for B2B buyers to communicate their size requirements clearly to ensure that manufacturers can accommodate their needs without compromising quality or leading to excessive costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Sand Casting Parts?
Familiarity with industry terminology is equally important for effective communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are several essential trade terms used in the sand casting sector:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of sand casting, buyers often seek OEMs for custom parts that meet specific requirements. Understanding OEM relationships helps in evaluating quality and reliability in the supply chain.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it affects purchasing decisions, especially for small to medium-sized enterprises that may not require large volumes of cast parts. Knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. In sand casting, an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, lead times, and terms from different manufacturers. This process is essential for making informed purchasing decisions and negotiating contracts.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing sand casting parts from overseas suppliers. They dictate shipping responsibilities, risk, and costs, ensuring clarity in transactions.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes to fulfill an order from the moment it is placed until it is delivered. In the sand casting industry, lead times can vary based on factors such as complexity, material availability, and production capacity. Knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their projects effectively and avoid delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the sand casting procurement process more effectively, ensuring they receive quality parts that meet their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the sand casting parts Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Sand Casting Parts Sector?
The sand casting parts market is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for complex metal components across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery is a significant driver. As manufacturers seek to optimize production processes, the integration of advanced technologies like automation and 3D printing in sand casting is emerging as a key trend. These technologies not only enhance production efficiency but also allow for greater design flexibility and reduced lead times, making them attractive to international B2B buyers.
Emerging markets in Africa and South America present lucrative opportunities for sand casting suppliers. The ongoing industrialization and infrastructure development in these regions are fueling demand for high-quality metal components. Conversely, established markets in Europe, particularly Germany, are focusing on precision and sustainability, pushing suppliers to innovate and improve quality standards.
Additionally, the trend toward digitalization in supply chain management is reshaping how buyers interact with suppliers. B2B platforms and e-commerce solutions are becoming vital for sourcing sand casting parts, allowing buyers from diverse regions to access a wider range of suppliers and products with ease. This digital shift not only enhances procurement efficiency but also fosters competitive pricing.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Transforming the Sand Casting Parts Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the sand casting parts sector, as environmental concerns drive both regulatory and consumer pressures. The casting process traditionally involves significant energy consumption and material waste, prompting a shift toward more sustainable practices. Suppliers are increasingly adopting “green” technologies, such as using electric furnaces for melting metals, which significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to conventional methods.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence among B2B buyers. Companies are now more than ever focused on ensuring their supply chains are transparent and socially responsible. This includes sourcing raw materials from suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and AS9100 for aerospace supply chains are becoming essential for suppliers looking to gain a competitive edge.
Furthermore, the use of recycled materials in sand casting is on the rise. This not only minimizes waste but also appeals to eco-conscious buyers. By prioritizing suppliers who invest in sustainable practices and materials, international buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for environmentally friendly products.
What Is the Historical Context of Sand Casting That Influences Today’s Market?
Sand casting is one of the oldest metal-forming techniques, with roots tracing back to ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Chinese. This rich history informs the current practices and innovations in the industry. Traditionally, sand casting was favored for its low cost and versatility, allowing for the production of various shapes and sizes, from intricate components to large parts.
Over centuries, the technique has evolved, incorporating modern technology to enhance efficiency and precision. Today, it remains a vital process in manufacturing, especially for short runs and custom components. The historical resilience of sand casting has established a strong foundation for its ongoing relevance in the global market, particularly as manufacturers seek reliable, cost-effective solutions for producing complex parts.
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of the sand casting parts market—along with the trends towards sustainability and the historical context—equips B2B buyers with the insights necessary for making informed sourcing decisions. By aligning with suppliers that prioritize innovation, ethical practices, and environmental responsibility, businesses can not only meet their production needs but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of sand casting parts
-
How do I choose the right supplier for sand casting parts?
Choosing the right supplier involves evaluating their experience, capabilities, and reputation in the industry. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in sand casting, particularly those who can provide references from similar projects. It’s essential to assess their manufacturing capabilities, including technology, quality control processes, and certifications. Additionally, consider their ability to meet your specific requirements, such as materials, tolerances, and lead times. Engaging in direct communication and requesting samples can also help gauge their reliability and quality. -
What are the typical lead times for sand casting parts?
Lead times for sand casting parts can vary significantly based on factors such as complexity, order size, and supplier location. Generally, you can expect lead times to range from a few weeks to several months. For simple designs with low volumes, lead times may be shorter, while complex parts or large orders may require more time for mold creation and production. It’s advisable to discuss lead times upfront with potential suppliers and factor in any potential delays related to shipping or customs for international orders. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for sand casting parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for sand casting parts can differ by supplier and depend on the complexity of the part and the production process. Many suppliers establish MOQs to ensure cost-effectiveness and efficient resource allocation. Typically, MOQs can range from as low as 10 pieces for simple designs to several hundred for more complex or custom parts. When sourcing, clarify MOQs with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your production needs and budget. -
How can I ensure the quality of sand casting parts?
To ensure quality in sand casting parts, it is crucial to establish clear specifications before production begins. Request detailed documentation on the supplier’s quality assurance processes, including any certifications like ISO 9001. Conducting regular inspections and audits during the manufacturing process can also help identify potential issues early. Additionally, consider requesting test samples or prototype parts to evaluate quality before committing to larger orders. A solid communication channel with the supplier can facilitate feedback and adjustments as needed. -
What payment terms are typically offered by sand casting suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among sand casting suppliers, but common practices include upfront deposits, progress payments, and net payment terms upon delivery. International buyers often negotiate terms based on order size and relationship with the supplier. Be sure to clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfer, letters of credit) and any potential additional fees. Understanding the supplier’s payment policies can help you manage cash flow effectively while ensuring timely delivery of your parts. -
What are the most common materials used in sand casting?
Sand casting is highly versatile and can accommodate a range of materials, including aluminum, iron, steel, and bronze. The choice of material depends on the desired properties of the final product, such as strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum is often preferred for lightweight applications, while iron and steel are favored for their durability and strength. Consult with your supplier to determine the most suitable material for your specific application, taking into account factors like cost and performance. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for international orders of sand casting parts?
Handling logistics for international orders involves coordinating with your supplier to determine the best shipping method based on cost, speed, and destination. Discuss Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) with your supplier to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties. It’s advisable to work with a freight forwarder experienced in international shipping to navigate customs regulations and ensure compliance. Planning for potential delays and tracking shipments can help maintain visibility throughout the process. -
What are the advantages of using sand casting for my parts?
Sand casting offers several advantages, making it a popular choice for various applications. It can produce complex shapes and large parts with a relatively low initial investment compared to other casting methods. The process is adaptable to different metals and alloys, providing flexibility in material selection. Additionally, sand casting supports both low-volume and large-scale production runs, making it suitable for custom orders. Its simplicity and effectiveness in producing intricate designs make it a reliable option for many industries.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Sand Casting Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sinoway Industry – Sand Casting Solutions
Domain: sinowayindustry.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: The sand casting process is a traditional casting method using sand as the primary modeling material. It is widely used due to its advantages, including no limitations on shape, size, complexity, and alloy type of parts, short production cycles, and low costs. The main steps in the sand casting process are: 1. Sand Preparation: Mixing used sand with clay. 2. Pattern Making: Creating molds and core…
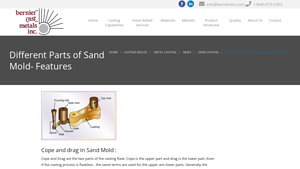
2. Bernier Inc – Cope and Drag Systems
Domain: bernierinc.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Cope and Drag: Upper and lower parts of the casting flask, typically made of wood or metal, containing molding sand. Gating System: Series of channels for molten metal to reach the cavity, including Pouring Basin, Sprue, Sprue Base, Runner, Choke, Skim Bob, Gates, and Ingates. Riser: Also known as feed heads, supply metal to the cavity during solidification shrinkage. Core: Used to create castings…
3. Quaker City Castings – Sand Casting Solutions
Domain: quakercitycastings.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Quaker City Castings specializes in sand casting for iron and steel, utilizing advanced no-bake molding technology. The sand casting process involves creating a pattern, forming a sand mold, pouring molten metal, and breaking away the mold to reveal the cast part. The company produces various types of metal casts including steel, stainless steel, ductile iron, and gray iron castings. The No-Bake p…
4. PreciseCast – Sand Casting Solutions
Domain: precisecast.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Sand Casting is the process of making cast metal parts using sand molds. It utilizes two match plates to form sand mixed with a binder into the desired shape. Key features include:
– Sand Types: Air set sands, primarily silica sand (SiO2), are used for mold creation.
– Surface Finish: Achieves smooth surface finishes of Ra 120-220.
– Wall Thickness: Capable of casting parts with a typical wall thi…
5. IQS Directory – Sand Casting Essentials
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Sand casting is a metal casting process that involves pouring molten metal into a sand mold shaped in the desired form. Key components of sand casting include: 1. **Base Sand**: The backbone of the mold, typically made from silica, olivine, chromite, zircon, or chamotte sand. 2. **Binders**: Substances like clay and water, oil, resin, or sodium silicate that hold sand particles together. 3. **Addi…
6. Impro Precision – Sand Casting & Precision Machining
Domain: improprecision.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Impro Precision specializes in sand casting, investment casting, and precision machining for various industries including automotive, high horsepower engines, construction equipment, agricultural equipment, hydraulic equipment, aerospace, medical, and energy. Typical products made through sand casting include engine blocks, cylinder heads, cylinder pistons, frames, brackets, manifolds for high-hor…
7. TFG USA – Custom Sand Casting Services
Domain: tfgusa.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Custom sand casting services offered by TFG USA, a QMS 9001:2015 certified manufacturer. Sand casting is a cost-effective and efficient metal casting solution suitable for low volume runs. TFG USA serves various industries including industrial manufacturing, energy, and construction, producing durable and precise components such as turbines, pump housings, and custom fittings. The sand casting pro…
8. Cast Technologies – Sand Casting Solutions
Domain: casttechnologies.net
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The sand casting process involves creating a cavity in sand, pouring molten metal into it, and allowing it to cool. Key components include green sand, which is moist and economical, and the use of molds made from sand placed in a flask. The process can involve cope and drag molds, cores for hollow spaces, and sprues for metal introduction. Common metals used include brass, bronze, aluminum, and ca…
9. GW Cast – Sand Casting Solutions
Domain: gwcast.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: The sand casting process is a reliable, cost-effective method for producing complex geometric shapes in aluminium and iron castings. It allows for the creation of parts with thinner walls, higher strength, and complex designs, making it suitable for prototyping and low volume series production. Sand casting is nearly 100% circular in terms of sustainability, as all raw materials (sand and metal) c…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for sand casting parts
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Supply Chain for Sand Casting Parts?
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of sand casting parts is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains. The versatility of sand casting allows for the production of complex components at various scales, making it a valuable manufacturing method for diverse industries. By partnering with skilled suppliers who understand the intricacies of the sand casting process, businesses can ensure high-quality outputs while minimizing costs and lead times.
Investing in strategic sourcing not only enhances product quality but also fosters long-term relationships with manufacturers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. These partnerships can facilitate access to innovative technologies and improve operational efficiencies, crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in today’s market.
As we look ahead, the demand for sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing solutions will continue to grow. B2B buyers are encouraged to actively seek out suppliers who prioritize innovation and quality in their sand casting processes. By doing so, you position your business for success in an ever-evolving landscape. Engage with your suppliers now to explore how strategic sourcing can transform your operations and drive value in your projects.