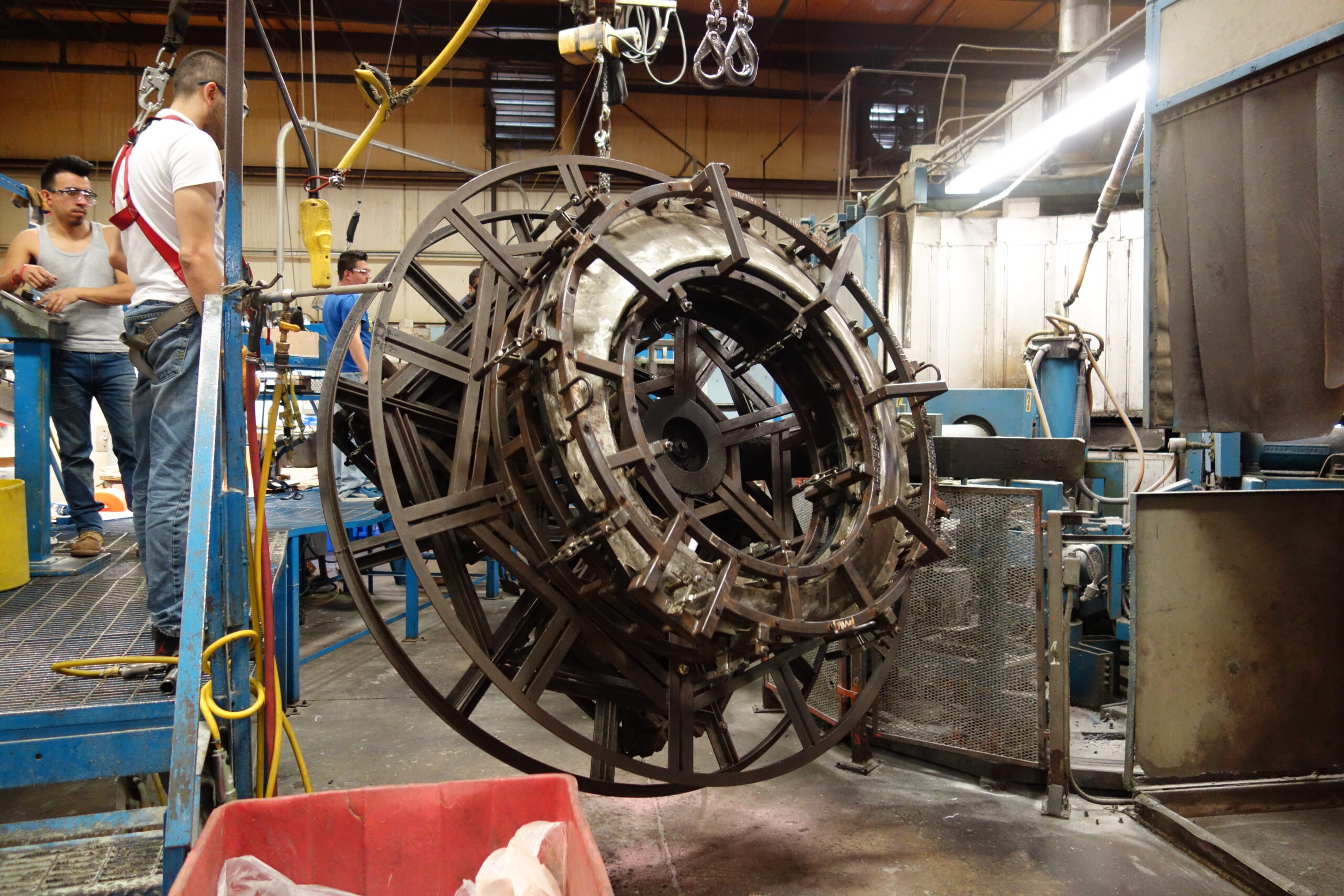
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rotational molding machines
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right rotational molding machines can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse options available, from clamshell to rock and roll machines, understanding which type best suits your production needs is crucial for optimizing manufacturing efficiency and product quality. This comprehensive guide addresses essential topics such as machine types, applications across various industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations, providing a holistic view of the rotational molding market.
For businesses in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, making informed purchasing decisions can significantly impact operational success. This guide empowers buyers by offering insights into the latest advancements in technology, best practices for machine maintenance, and strategic approaches to supplier selection. By equipping decision-makers with the necessary knowledge, it aims to streamline the procurement process, reduce risk, and enhance the overall value derived from investing in rotational molding machines.
Whether you are a seasoned manufacturer or venturing into rotational molding for the first time, this guide serves as a valuable resource. It not only helps demystify the complexities of the market but also assists in navigating the nuances of international trade, ensuring that you can confidently select the right machinery to meet your production goals.
Understanding rotational molding machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clamshell Machines | Two halves that open/close; suitable for small parts | Toys, containers, small components | Pros: Space-efficient, cost-effective for small runs. Cons: Limited to smaller parts. |
| Rock and Roll Machines | Back-and-forth rocking motion; ideal for larger items | Industrial tanks, playground equipment | Pros: Excellent material distribution, strong parts. Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Carousel Machines | Multiple mold stations on a rotating carousel | High-volume production of medium parts | Pros: Efficient for mass production, reduced cycle time. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Shuttle Machines | Molds shuttle between heating and cooling stations | Smaller to medium-sized parts, rapid cycles | Pros: Fast production, versatile mold options. Cons: Requires more floor space. |
| Independent Arm Machines | Modular design with multiple arms for flexibility | Custom parts, specialized applications | Pros: Highly customizable, scalable production. Cons: Complexity may require specialized training. |
What Are Clamshell Machines and Their B2B Suitability?
Clamshell machines are characterized by their two-part design that opens and closes, resembling a clamshell. This type is particularly suitable for producing small parts in facilities with limited space. B2B buyers should consider clamshell machines for applications in industries like toys and small containers, where cost-effectiveness and space efficiency are essential. However, their limitation to smaller parts may necessitate additional machinery for larger components.
How Do Rock and Roll Machines Operate?
Rock and roll machines utilize a unique rocking motion combined with rotation to ensure even coating of the mold. They are particularly effective for producing larger and more durable items, such as industrial tanks and playground equipment. Buyers in sectors requiring robust products should weigh the benefits of strong material distribution against the higher energy consumption associated with this machine type.
Why Choose Carousel Machines for High-Volume Production?
Carousel machines feature a rotating carousel with multiple mold stations, making them ideal for high-volume production of small to medium-sized parts. Their ability to significantly reduce cycle times appeals to businesses focusing on efficiency and scalability. However, the initial investment can be substantial, making it crucial for buyers to analyze their production needs and budget before proceeding.
What Advantages Do Shuttle Machines Offer?
Shuttle machines operate by moving molds back and forth between heating and cooling stations, which allows for rapid production cycles. They are well-suited for producing smaller to medium-sized parts and are favored for their versatility in accommodating various mold designs. Buyers should consider the need for adequate floor space, as shuttle machines may require more room than other types.
How Do Independent Arm Machines Enhance Customization?
Independent arm machines stand out with their modular design, allowing for up to four independent arms that can be added without mechanical modifications. This flexibility makes them ideal for custom parts and specialized applications across various industries. While they offer significant advantages in scalability and customization, potential buyers should be prepared for the complexity of operation, which may necessitate specialized training for staff.
Key Industrial Applications of rotational molding machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Rotational Molding Machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of fuel tanks and interior components | High durability and lightweight parts reduce overall vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency. | Consider machine capacity for large parts and material compatibility for fuel resistance. |
| Consumer Products | Manufacturing of storage containers and toys | Customizable designs meet specific market demands, enhancing brand differentiation. | Look for machines that offer design flexibility and precision molding capabilities. |
| Construction | Creation of large water tanks and drainage systems | Cost-effective production of complex shapes helps reduce construction costs and time. | Evaluate the machine’s ability to handle large mold sizes and its cooling efficiency. |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of medical storage and transport solutions | Ensures compliance with safety standards while providing durable, easy-to-clean products. | Focus on sourcing machines that allow for precise control and high-quality surface finishes. |
| Agriculture | Production of large agricultural equipment parts | Provides strong, lightweight components that improve equipment efficiency and longevity. | Assess the machine’s adaptability to different materials and its production speed for high-volume needs. |
How Are Rotational Molding Machines Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, rotational molding machines are utilized for producing components such as fuel tanks and interior parts. The process allows for the creation of lightweight yet durable parts, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. International buyers should consider the machine’s capacity to produce large parts and ensure compatibility with materials that can withstand fuel exposure.
What Are the Benefits of Rotational Molding in Consumer Products?
Rotational molding machines are essential for manufacturing consumer products like storage containers and toys. This method enables the production of customized designs that can meet specific market demands, enhancing brand differentiation. When sourcing machinery, companies should prioritize machines that offer design flexibility and precision to ensure high-quality output that aligns with consumer expectations.
How Do Rotational Molding Machines Benefit the Construction Industry?
In construction, rotational molding machines are used to create large water tanks and drainage systems. The ability to produce complex shapes cost-effectively can significantly reduce construction costs and timelines. Buyers in this sector should evaluate the machine’s capacity to handle large molds and its cooling efficiency to ensure optimal production rates.
Why Are Rotational Molding Machines Important for Medical Devices?
The medical industry relies on rotational molding machines for fabricating storage and transport solutions for medical equipment. These machines help ensure compliance with stringent safety standards while delivering durable and easy-to-clean products. Buyers should focus on sourcing machines that provide precise control and high-quality surface finishes to meet regulatory requirements.
What Role Do Rotational Molding Machines Play in Agriculture?
In agriculture, rotational molding machines are critical for producing large equipment parts, providing strong yet lightweight components that enhance operational efficiency. This application helps improve the longevity of agricultural equipment. Buyers should assess the machine’s adaptability to various materials and its production speed to meet high-volume demands effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rotational molding machines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Product Quality Due to Machine Calibration Issues
The Problem: One of the most pressing challenges B2B buyers face when using rotational molding machines is achieving consistent product quality. Variations in wall thickness, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy can arise from improper machine calibration. This inconsistency can lead to increased scrap rates, dissatisfied customers, and ultimately financial losses. For manufacturers in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, maintaining a high standard of quality is crucial for securing contracts and retaining clients.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, it is essential to invest in proper training for operators on machine calibration and maintenance. Regularly scheduled maintenance checks should be instituted, focusing on critical components such as heating elements, mold alignment, and rotation speeds. Additionally, utilizing advanced monitoring systems, like infrared thermometry, can provide real-time data on mold temperatures, allowing for immediate adjustments. Establishing a robust quality assurance protocol that includes routine inspections of finished products can help identify issues early, ensuring that corrective actions are taken before products reach the market.
Scenario 2: High Operating Costs from Inefficient Machine Usage
The Problem: B2B buyers often experience high operational costs due to inefficient usage of rotational molding machines. Factors such as excessive energy consumption, unnecessary downtime, and poor material utilization can significantly impact overall production costs. This is especially relevant for companies in regions with fluctuating energy prices or those looking to maximize profits in a competitive landscape.
The Solution: To address these challenges, buyers should consider implementing a comprehensive efficiency audit of their rotational molding operations. This audit can identify areas where energy consumption can be reduced, such as optimizing heating cycles and implementing better cooling practices. Additionally, investing in programmable control systems that allow for precise adjustments during the molding process can help minimize waste. Adopting lean manufacturing principles can also streamline operations, reducing downtime by ensuring that all machines are operating at peak efficiency. Collaborating with machine manufacturers to explore energy-efficient models or retrofitting existing machines with energy-saving technologies can yield significant long-term cost savings.
Scenario 3: Limited Flexibility in Production Capabilities
The Problem: Many manufacturers struggle with the limitation of their rotational molding machines, which can hinder their ability to adapt to changing market demands. For example, a company may find that its current machinery is not equipped to handle new product lines or varying order sizes, leading to missed opportunities and potential revenue loss. This challenge is particularly relevant in dynamic markets where customer preferences can shift rapidly.
The Solution: To enhance flexibility, buyers should evaluate machines that offer modular designs or multi-station configurations. Machines like independent-arm carousel systems allow for quick changeovers and can accommodate various mold sizes and shapes without significant downtime. Additionally, considering the purchase of used rotational molding machines that are still in good condition can provide cost-effective options for expanding production capabilities without the financial burden of new equipment. Establishing strong relationships with mold manufacturers can also facilitate rapid prototyping and development of new products, enabling manufacturers to stay ahead of market trends and satisfy customer demands swiftly.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rotational molding machines
What Are the Key Materials Used in Rotational Molding Machines?
When it comes to rotational molding, the choice of material significantly impacts the performance, durability, and overall cost-effectiveness of the end products. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the rotational molding process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Polyethylene (PE)
Key Properties: Polyethylene is known for its excellent impact resistance and flexibility. It has a temperature range of -100°F to 180°F (-73°C to 82°C) and exhibits good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PE is its low cost and ease of processing, which makes it ideal for high-volume production. However, it has lower UV resistance and can degrade over time when exposed to sunlight, limiting its outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: PE is often used in products like storage tanks, toys, and outdoor furniture. Its compatibility with various media, especially water and chemicals, makes it a popular choice in industries such as agriculture and construction.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that the PE used complies with local environmental regulations. Familiarity with standards such as ASTM D4976 can be beneficial.
2. Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties: Polypropylene offers a higher temperature resistance than PE, with a range of -40°F to 250°F (-40°C to 121°C). It is also resistant to fatigue and has good chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of PP is its higher strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for applications requiring durability. However, it can be more expensive than PE and may require more complex processing techniques.
Impact on Application: PP is commonly used in automotive parts, industrial containers, and medical products due to its robustness and lightweight nature. Its compatibility with a wide range of chemicals enhances its utility in various sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of compliance with standards such as DIN EN ISO 1183 for density and ASTM D638 for tensile properties.
3. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is known for its excellent chemical resistance and flame retardancy. It can withstand temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) and is often used in applications requiring high durability.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of PVC is its resistance to environmental degradation, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it can be more expensive to process and may release harmful chemicals during production.
Impact on Application: PVC is widely used in plumbing, electrical insulation, and construction materials. Its compatibility with various chemicals makes it suitable for industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with strict environmental regulations, such as Europe, should ensure that the PVC used meets compliance standards like REACH and RoHS.
4. Nylon (Polyamide)
Key Properties: Nylon is known for its high tensile strength and resistance to wear and abrasion. It can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°F to 300°F (-40°C to 149°C).
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of nylon is its exceptional mechanical properties, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may absorb moisture, affecting its dimensional stability.
Impact on Application: Nylon is often used in automotive components, industrial machinery, and consumer goods that require high strength and durability. Its compatibility with various lubricants and chemicals enhances its application range.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in South America and Africa should be aware of the need for compliance with ASTM D4066 and other relevant standards, as well as the potential for moisture-related issues in humid environments.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rotational Molding Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for Rotational Molding Machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Storage tanks, toys, outdoor furniture | Low cost and ease of processing | Poor UV resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene | Automotive parts, industrial containers | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and complex processing | Medium |
| PVC | Plumbing, electrical insulation | Excellent chemical resistance | Higher processing costs | Medium |
| Nylon | Automotive components, industrial machinery | Exceptional mechanical properties | Expensive and moisture absorption issues | High |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding the materials used in rotational molding machines, ensuring compliance with regional standards and optimizing product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rotational molding machines
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Rotational Molding Machines?
The manufacturing process for rotational molding machines is a complex yet structured operation that involves several key stages. Understanding these stages can assist B2B buyers in evaluating potential suppliers and ensuring they receive high-quality machinery tailored to their production needs.
1. Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Processed?
The first step in manufacturing rotational molding machines involves the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. High-quality steel or aluminum is commonly used for the machine frame, while molds are often crafted from durable materials like fiberglass or aluminum. The materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards.
Once selected, materials are cut, shaped, and treated to enhance their durability and performance. For instance, steel components might be coated to resist corrosion, while mold surfaces are polished to facilitate easy release of the molded products. This stage is critical, as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the machine’s longevity and effectiveness.
2. Forming: What Techniques Are Used in Machine Fabrication?
The forming stage involves the assembly of machine components into a cohesive unit. This process can include welding, machining, and assembly of various parts, such as the heating elements, arms, and control systems. Advanced techniques like CNC machining are often employed to ensure precision and consistency.
Each machine type—be it clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, or shuttle—requires specific forming techniques tailored to its unique design and function. For instance, clamshell machines necessitate precise alignment of the two halves of the mold, whereas shuttle machines focus on the efficient movement of multiple molds between stations.
3. Assembly: How Are Rotational Molding Machines Put Together?
Once individual components are formed, the next phase is assembly. This process involves integrating various parts into a complete system. Technicians follow detailed schematics to ensure that all components fit and function correctly. Special attention is given to the alignment of rotating arms and the calibration of heating elements, as these directly affect the molding process’s efficiency.
During assembly, manufacturers often implement modular designs, allowing for future upgrades or expansions. This flexibility can be particularly advantageous for B2B buyers looking to scale operations over time.
4. Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied to the Machines?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments, painting, and quality inspections. This phase is crucial for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and longevity of the machines. Finishing techniques may involve powder coating for durability and resistance to environmental factors.
Quality checks are integral during this stage, ensuring that the machine meets the specifications outlined during the design phase. This is also when manufacturers may conduct initial tests to evaluate the machine’s functionality before it is packaged and shipped to clients.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Rotational Molding Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is a vital aspect of the manufacturing process for rotational molding machines. It ensures that the machines meet both international standards and specific industry requirements.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
For B2B buyers, it is essential to be aware of international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. Adherence to these standards assures buyers that the manufacturer has established processes for consistent quality control.
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for European markets or API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications can also be critical. These certifications indicate compliance with safety and quality regulations specific to the respective industries.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control checkpoints are systematically integrated throughout the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials as they arrive at the manufacturing facility. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s IQC procedures to ensure that only high-quality materials are used.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing stages, continuous monitoring is conducted to ensure that production processes adhere to quality standards. This includes regular inspections and testing of components.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the machine is shipped, a comprehensive assessment is performed to verify that it meets all specifications and performance criteria. This final check is crucial for ensuring the machine’s reliability in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take a proactive approach to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers. This can involve:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality control measures. This is particularly important for international buyers, as it allows them to assess compliance with local regulations and standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and inspection reports. These documents can help buyers understand how quality is maintained throughout the production cycle.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s practices. This is especially beneficial for buyers in regions where local regulations may differ from international standards.
What Unique Considerations Exist for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the complexities of international manufacturing and quality assurance can present unique challenges.
How Do Cultural and Regulatory Differences Affect Quality Assurance?
Understanding the cultural and regulatory landscape of the supplier’s country is crucial. Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality standards, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. B2B buyers should conduct thorough research and potentially engage local consultants to navigate these differences effectively.
What Should Buyers Look for in Terms of Compliance?
Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with both international standards and local regulations. This may involve verifying that the supplier holds the necessary certifications for exporting machinery to specific markets. Additionally, understanding the warranty and service agreements offered by the supplier can provide further assurance regarding product quality and reliability.
Conclusion: Why Quality Assurance in Rotational Molding Machines Is Non-Negotiable
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for rotational molding machines are critical factors for B2B buyers. By understanding the stages of manufacturing and the importance of quality control, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Investing in high-quality machinery not only enhances production efficiency but also contributes to long-term business success.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rotational molding machines’
To facilitate a successful procurement process for rotational molding machines, this guide offers a step-by-step checklist tailored for B2B buyers. It is designed to streamline your decision-making process and ensure that you select the most suitable machinery for your production needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes specifications such as part size, material type, production volume, and desired features (e.g., automation capabilities). Defining these parameters helps in narrowing down suitable machine options and aids suppliers in providing accurate quotes.
Step 2: Research Different Machine Types
Familiarize yourself with the various types of rotational molding machines available, such as clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle machines. Each type serves specific production needs; for example, clamshell machines are ideal for smaller parts, while carousel machines excel in high-volume production. Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting a machine that aligns with your production goals.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making a commitment. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from other buyers in similar industries or regions. This evaluation process not only assesses their reliability and experience but also provides insights into the quality of their machines and customer service.
- Check Certifications: Ensure that suppliers have relevant certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate compliance with international quality management systems.
- Assess After-Sales Support: Investigate the level of after-sales service offered, including warranty terms, availability of spare parts, and technical support.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request detailed quotes that include not just the machine cost but also shipping, installation, and training fees. Comparing these quotes helps in understanding the total cost of ownership, allowing for a more informed decision. Be wary of prices that seem too low, as they may reflect compromised quality or hidden costs.
Step 5: Conduct a Site Visit or Virtual Tour
If feasible, arrange for a site visit to the supplier’s facility or request a virtual tour. This allows you to see the machines in operation and assess the supplier’s manufacturing capabilities firsthand. Observing the production process can provide valuable insights into the machine’s performance and the overall professionalism of the supplier.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing your order, engage in negotiations to clarify payment terms, delivery timelines, and installation support. Clear communication of expectations can prevent misunderstandings later. Ensure that all agreements are documented to protect your interests.
Step 7: Finalize Purchase and Plan for Installation
Once all terms are agreed upon, finalize the purchase and coordinate the logistics for delivery and installation. Plan for training sessions for your operators to ensure they are familiar with the new machinery and its operational protocols. A well-executed installation and training process is crucial for maximizing the productivity of your new rotational molding machine.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring that they select the right rotational molding machines to meet their specific production requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rotational molding machines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Rotational Molding Machines Sourcing?
When sourcing rotational molding machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary components include:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials used for machine components significantly affect costs. High-grade steel and specialized alloys can increase the upfront investment but may offer better durability and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct manufacturing labor and skilled technicians required for assembly and maintenance. In regions with lower labor costs, such as certain parts of Africa or South America, this can be a cost-saving factor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead includes costs associated with the manufacturing facility, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for molds can represent a substantial portion of the initial investment. The complexity and size of the molds dictate the tooling costs, which are vital for ensuring high-quality production.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that the final products meet industry standards, which may involve additional costs but can prevent expensive recalls or failures.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs for shipping machines can vary based on distance and mode of transport. International shipping may involve customs duties and insurance, impacting the overall cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market demand and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rotational Molding Machine Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of rotational molding machines, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Higher volumes often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating MOQ can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machines tailored to specific production needs can drive up costs. Standard models are usually more cost-effective.
-
Materials Used: The choice of materials not only affects initial costs but also impacts maintenance and operational longevity. Investing in high-quality materials can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Quality Certifications: Machines with industry certifications may carry a premium price tag. However, these certifications can assure buyers of reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and production capacity of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but offer better after-sales support and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital. They define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, affecting the overall cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Rotational Molding Machine Sourcing?
International B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms. Suppliers may offer discounts for upfront payments or larger orders.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Investigate Used Equipment: Consider the purchase of quality used rotational molding machines. This can significantly reduce initial costs while still providing reliable performance.
-
Conduct Market Research: Understanding the market landscape in your region (such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe) can provide insights into competitive pricing and available options.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times, providing additional savings and operational flexibility.
-
Understand Regional Regulations: Be aware of any import tariffs, duties, or compliance costs that may apply when sourcing from international suppliers, as these can impact the final cost.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for rotational molding machines can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is essential for buyers to conduct thorough due diligence, obtain multiple quotes, and consider all associated costs to ensure they make informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rotational molding machines With Other Solutions
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, B2B buyers often explore various production methods to meet their specific needs. Rotational molding machines are a popular choice for producing large, hollow parts, but alternative solutions may also provide suitable results depending on the project requirements. This analysis compares rotational molding with two viable alternatives: injection molding and blow molding, highlighting key aspects that can influence a buyer’s decision.
| Comparison Aspect | Rotational Molding Machines | Injection Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent for large, hollow parts with uniform thickness. | High precision for complex shapes and smaller parts. | Ideal for producing hollow containers quickly. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; cost-effective for large production runs. | High initial costs; suitable for high volumes to offset setup costs. | Lower setup costs; cost-effective for mid-volume production. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized training; setup can be time-consuming. | Streamlined for mass production; easier to implement with standard molds. | Generally straightforward; requires less training for operation. |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs; requires skilled personnel. | Low maintenance if well-maintained; requires expertise for troubleshooting. | Minimal maintenance; machines are generally user-friendly. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for large, durable products like tanks and playground equipment. | Best for high-precision parts in automotive and consumer goods. | Perfect for bottles and containers in the packaging industry. |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that excels in producing high-precision parts, particularly for complex geometries. The primary advantage of injection molding is its ability to create intricate designs with tight tolerances, making it ideal for industries such as automotive and electronics. However, the initial investment can be substantial due to mold costs, making it less appealing for low-volume production. Additionally, while injection molding offers quick cycle times, the setup and changeover times can be lengthy, impacting overall efficiency for smaller runs.
How Does Blow Molding Compare?
Blow molding is a method specifically designed for creating hollow plastic parts, such as bottles and containers. Its primary advantage lies in the speed of production, allowing manufacturers to produce large quantities in a short time. The setup costs for blow molding are generally lower than those for injection molding, making it suitable for mid-volume production. However, blow molding is limited to simpler shapes and may not provide the same level of design complexity as rotational or injection molding. Consequently, while it is efficient for packaging, it may not meet the demands of more intricate applications.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting between rotational molding machines and alternative manufacturing methods like injection or blow molding, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific production requirements. Factors such as part complexity, production volume, budget constraints, and product durability will significantly influence the decision. Rotational molding machines excel in producing large, durable parts with uniform wall thickness, while injection molding is optimal for precision components, and blow molding offers rapid production for hollow containers. By aligning the chosen method with project goals and operational capabilities, buyers can ensure that they make an informed choice that maximizes efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rotational molding machines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rotational Molding Machines?
In the realm of rotational molding, understanding the essential technical properties of machines is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several key specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of plastic used in the rotational molding process, such as polyethylene (PE), polyvinyl chloride (PVC), or nylon. Different materials offer varying levels of durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors. For instance, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is known for its strength and chemical resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Selecting the right material grade ensures the final product meets specific performance requirements, influencing both quality and customer satisfaction. -
Mold Size and Configuration
The size and configuration of the mold significantly impact the dimensions and complexity of the parts produced. Rotational molding machines are available in various mold sizes, ranging from small components to large, complex shapes. Understanding the mold size helps manufacturers determine their production capabilities and whether the machine can accommodate their specific product requirements, ultimately affecting lead times and production efficiency. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the duration required to complete one full production cycle, including heating, cooling, and unloading. Shorter cycle times can lead to increased production rates, which is crucial for meeting market demands and optimizing operational efficiency. B2B buyers should assess the cycle time relative to their production volume needs to ensure the machine aligns with their business goals. -
Temperature Control Range
The temperature control range indicates the machine’s ability to maintain specific temperatures during the molding process. Precise temperature control is vital for achieving consistent material properties and preventing defects. Machines with a wide temperature range offer greater flexibility in processing various materials, making them suitable for diverse applications. -
Production Capacity
Production capacity refers to the number of parts a machine can produce within a specific timeframe. This capacity is influenced by the type of machine (e.g., carousel vs. shuttle) and the complexity of the parts being molded. Understanding production capacity helps buyers estimate operational costs and align their investments with anticipated demand. -
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is increasingly becoming a priority in manufacturing. Machines designed with energy-saving features can significantly reduce operational costs and environmental impact. B2B buyers should look for machines that offer energy-efficient heating systems or lower energy consumption rates, as these can lead to substantial long-term savings.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Rotational Molding?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication in the B2B landscape. Here are several common terms related to rotational molding machines:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In rotational molding, OEMs often provide specialized machinery or components tailored to specific industry needs, allowing buyers to source high-quality equipment that meets their production standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of goods that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Manufacturers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production schedules and market demands. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the context of rotational molding, submitting an RFQ can help buyers compare costs and identify the best suppliers for their needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping goods. Understanding these terms helps B2B buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, ensuring smoother transactions and reducing potential disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods. It is a critical factor in production planning and inventory management. B2B buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of machines and components. -
Tolerances
Tolerances refer to the allowable variations in dimensions of the molded parts. Tight tolerances are crucial for applications requiring precise fits and functionality. Buyers should specify their tolerance requirements during the procurement process to ensure that the final products meet their specifications.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding rotational molding machines, optimizing their production capabilities and enhancing overall business performance.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rotational molding machines Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics Influencing Rotational Molding Machines?
The global market for rotational molding machines is shaped by a variety of factors, including increasing demand for customized plastic products and a shift towards lightweight materials across industries. Regions like Africa and South America are witnessing a surge in manufacturing capabilities, driven by investments in infrastructure and an expanding consumer base. In Europe and the Middle East, sustainability initiatives are prompting manufacturers to seek advanced molding technologies that minimize waste and enhance energy efficiency.
Emerging technologies such as automation and smart manufacturing are revolutionizing the operational landscape. Companies are increasingly adopting Industry 4.0 principles, integrating IoT-enabled machines that provide real-time data on production efficiency and machine performance. This trend is particularly appealing to international buyers, as it allows for optimized production schedules and reduced operational costs. Additionally, advancements in materials science are leading to the development of new polymers that enhance the durability and functionality of molded products, further expanding market opportunities.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Sourcing of Rotational Molding Machines?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers of rotational molding machines. As manufacturers aim to reduce their environmental footprint, the demand for machines that utilize eco-friendly processes and materials is on the rise. Ethical sourcing practices are increasingly important, with companies seeking suppliers that prioritize responsible manufacturing methods and sustainable raw materials.
Certification in environmental standards, such as ISO 14001, is a key factor for buyers when selecting machinery suppliers. These certifications assure buyers that the products are manufactured with minimal environmental impact. Furthermore, the use of recyclable materials in the production of rotational molding machines is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the availability of ‘green’ materials and the sustainability measures implemented by machine manufacturers. This focus on sustainability not only meets regulatory requirements but also enhances brand reputation in a market that values corporate responsibility.
What Is the Historical Context of Rotational Molding Machines?
The evolution of rotational molding machines can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the need for efficient production of hollow plastic parts emerged. Initially, the technology was limited to basic applications, but over the years, it has evolved significantly with advancements in machinery design and materials. The introduction of computer-controlled systems in the 1980s marked a turning point, allowing for greater precision and flexibility in the molding process.
Today, the market offers a wide array of machines, including clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle types, each tailored to specific production needs. This diversification has enabled manufacturers to produce complex shapes and larger volumes while maintaining high quality and consistency. As the industry continues to innovate, international B2B buyers can leverage these advancements to enhance their production capabilities and meet the growing demands of their respective markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rotational molding machines
-
How do I choose the right rotational molding machine for my production needs?
Choosing the right rotational molding machine involves assessing your specific production requirements, such as part size, volume, and complexity. Consider the different types of machines available—clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle machines. Evaluate their production capacities, space requirements, and the materials you plan to use. Additionally, consult with suppliers to understand their expertise and customization options that could meet your unique needs. -
What are the advantages of using custom rotational molding solutions?
Custom rotational molding solutions offer several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and durability. This process allows for the creation of complex shapes and uniform wall thickness, which enhances the strength and longevity of the parts. Furthermore, custom solutions can be tailored to specific industry requirements, ensuring that the final products meet quality standards while minimizing waste and production costs. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for rotational molding machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, customer reviews, and the quality of their machines. Request references and case studies that demonstrate their capability in handling projects similar to yours. Additionally, inquire about after-sales support, warranty terms, and spare parts availability. It’s also beneficial to assess their compliance with international standards, particularly if you’re sourcing from regions like Africa or South America. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rotational molding machines?
Minimum order quantities for rotational molding machines can vary significantly based on the supplier and the machine type. Some manufacturers may offer machines for single-unit purchases, while others might require larger orders for specific models. It’s crucial to discuss your production needs and budget with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your business strategy, especially if you are a startup or entering a new market. -
What payment terms are typically offered for international purchases of rotational molding machines?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include upfront payments, partial payments during production, and final payments upon delivery. Some suppliers may also offer financing options or payment through letters of credit to mitigate risk. Always clarify these terms before finalizing your purchase to ensure they align with your cash flow and financial strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) in the rotational molding process?
To ensure quality assurance in the rotational molding process, implement a robust QA program that includes regular inspections at various production stages. Collaborate with your supplier to understand their QA protocols and request documentation of their testing methods. Consider third-party quality audits to verify compliance with industry standards. Moreover, establish clear specifications and tolerances for your products to guide the manufacturing process effectively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing rotational molding machines?
When importing rotational molding machines, logistics considerations include shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. Ensure that you have a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling heavy machinery. Familiarize yourself with the import duties and taxes applicable in your country. Additionally, plan for the installation and commissioning of the machines, which may require specialized personnel or equipment. -
What types of materials are suitable for rotational molding?
Rotational molding is compatible with a variety of materials, primarily thermoplastics such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and PVC. These materials are favored for their durability, impact resistance, and flexibility. Depending on your product requirements, discuss with suppliers about the best material choices that meet your performance, regulatory, and sustainability goals. Some suppliers may also offer options for environmentally friendly materials or recycled plastics.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Rotational Molding Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rotodynamics – Rotational Molding Machines
Domain: rotodynamics.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Rotational molding machines are versatile manufacturing tools used to produce high-quality parts through a process that involves heating a mold while rotating it around two perpendicular axes. The main types of rotational molding machines include: 1. Clamshell Machines: Best for smaller parts, suitable for limited space, opens and closes like a clamshell. 2. Rock and Roll Machines: Ideal for large…
2. Ferry Industries – RotoSpeed Independent Arm Machines
Domain: ferryindustries.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: RotoSpeed Independent Arm Machines are pioneering four-arm, five-station carousel machines for the rotational molding industry. Key features include:
– Multiple-station arrangement for heating, cooling, and servicing.
– Each arm operates on a separate cart, indexing around a center pivot post on a common load-bearing track.
– Five process stations: Oven, Pre-cool or Intermediate Cooling, Unload…
3. PlastiWin – Used Rotational Molding Machines
Domain: plastiwin.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: PlastiWin offers quality used rotational molding machines for sale in various sizes and models. Brands include Ferry, FSP, Rotoline, Caccia, McNeil, Persico, Polivini, Rei Automation, Rising Sun, and STP. Types of machines available include Rock and Roll, Shuttle, Clam Shell, and Rotating Arm. The company provides expert guidance to help find the right machinery for specific applications and budge…
4. Rotoline – Rotomolding Machines
Domain: rotoline.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Rotoline offers a range of Rotomolding Machines including: 1. Sphere Oven – for rotational molding. 2. Shuttle Machine – designed for multiple application technology. 3. Carrossel – enables sequential production in large quantities. 4. Lab Machine – ideal for laboratories and universities. 5. Rock And Roll – high productivity for large parts. Additionally, Rotoline provides various accessories suc…
5. KDCapital – Independent Arm & Multi-Arm Roto Molders
Domain: kdcapital.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: 1. 2018 Rotoline CR 2.60 Independent Arm Carousel – Ref # 8076889
2. 1997 Ferry RotoSpeed RS3-200 Independent Arm Machine – Ref # 8076764
3. 1993 Ferry RS4-220 Rotational Molder – Ref # 8074689
4. 1989 REI 96 Multi-Arm Roto Molder – Ref # 8076047
5. 1985 REI 110 Multi-Arm Roto Molder – Ref # 8076046
6. Rotomachinery Group – Machines with Independent Arms
Domain: rotomachinery.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: Rotomachinery Group specializes in the design and installation of machines and accessories for rotational molding, with over 50 years of experience and more than 1,600 plants installed in 100 countries. Key products include: 1. Machines with Independent Arms – for simultaneous production of items with different cycle durations or multilayer. 2. Fixed Arms Machines – reliable and robust for rapid p…
7. Orex – Rotomoulding Machines
Domain: orex-rotomoulding.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Orex offers a wide range of rotomoulding machines for the rotational moulding of plastics, including Carousel, Shuttle, and Rock and Roll machines. The Carousel machine has a high production capacity. Shuttle-type machines are available with heating chamber diameters of 2000 mm to 5000 mm. Rock and Roll machines are designed for producing oblong and narrow products like canoes and tanks. Orex prov…
8. API Plastics – Custom Rotational Molding Services
Domain: api-plastics.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Custom Rotational Molding services provided by API include:
– High-quality custom rotational molding and comprehensive manufacturing services.
– Collaborative product design assistance from experienced engineers.
– State-of-the-art machinery with a spherical swing of up to 160 inches.
– Hand-trimming and advanced CNC trimming capabilities for precision.
– Qualified assembly team dedicated to quali…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rotational molding machines
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Rotational Molding Operations?
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing of rotational molding machines is essential for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. By understanding the diverse machine options—such as clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle machines—buyers can select the equipment that best aligns with their specific production needs. Emphasizing cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and sustainability, rotational molding presents a unique opportunity to create durable and complex parts while minimizing material waste.
As international markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, continue to expand, the demand for high-quality rotomolding solutions is on the rise. Engaging with reputable suppliers who offer customized solutions and robust after-sales support will not only enhance your operational capabilities but also foster long-term partnerships.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for B2B buyers to leverage technological advancements and industry innovations in their sourcing strategies. Embrace the future of manufacturing by investing in the right rotational molding technology today. Explore your options, assess your specific requirements, and take the first step towards transforming your production capabilities.