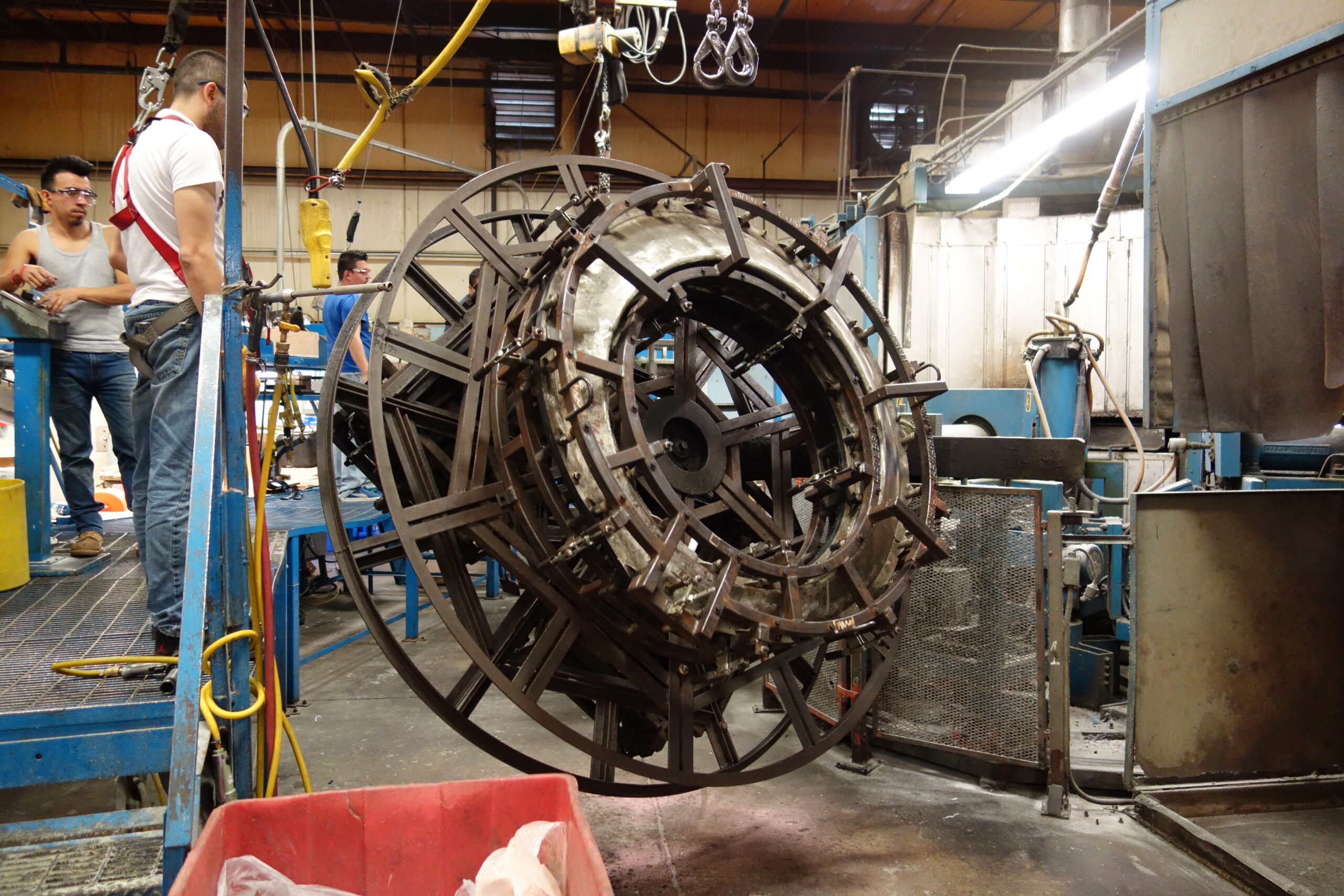
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rotational molding machine
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right rotational molding machine can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers. With various types of machines available—each tailored for specific applications and production needs—understanding which option aligns with your operational goals is crucial. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of the global market for rotational molding machines, providing insights into the different machine types, their applications, and essential factors to consider when making a purchase.
From clamshell and rock and roll machines to carousel and shuttle machines, each category offers unique advantages that can significantly impact production efficiency and product quality. Additionally, this guide will delve into the critical aspects of supplier vetting, cost considerations, and maintenance requirements, ensuring that you are equipped with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
Whether you’re based in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, including markets like Saudi Arabia and Vietnam, understanding the nuances of rotational molding technology will empower you to select the best machinery for your specific needs. By leveraging the insights provided in this comprehensive guide, you can confidently navigate the global market, optimize your production processes, and ultimately enhance your competitive edge in the industry.
Understanding rotational molding machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clamshell Machines | Two halves that form a mold cavity; compact design | Small parts, limited space environments | Pros: Space-efficient, cost-effective for small runs. Cons: Limited to smaller parts. |
| Rock and Roll Machines | Rocks back and forth while rotating; even material distribution | Large, durable parts like tanks and playground equipment | Pros: Excellent for uniform wall thickness, high durability. Cons: Requires more floor space. |
| Carousel Machines | Multiple mold stations on a rotating platform | High-volume production of small to medium parts | Pros: Efficient for mass production, reduced cycle time. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Shuttle Machines | Moves molds between heating and cooling stations | High-volume production of various part sizes | Pros: Versatile and efficient, suitable for different products. Cons: Complexity in operation and maintenance. |
What are Clamshell Machines and Their Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Clamshell machines are characterized by their two-part design that opens and closes to form a mold cavity. This type of machine is particularly suited for facilities with limited space and is ideal for producing small parts. B2B buyers should consider clamshell machines for applications where space is a constraint, and the production of smaller, less complex parts is required. Their cost-effectiveness makes them attractive for companies looking to minimize overhead while maintaining quality.
How Do Rock and Roll Machines Meet the Needs of Larger Parts Production?
Rock and roll machines utilize a unique rocking motion combined with rotation to ensure even coating of the mold. This machine type is particularly beneficial for producing larger, durable parts such as industrial tanks or playground equipment. B2B buyers should focus on the durability and consistent wall thickness provided by rock and roll machines, which can enhance product quality. However, potential buyers need to account for the larger footprint these machines require in their production facilities.
What Advantages Do Carousel Machines Offer for High-Volume Production?
Carousel machines feature multiple mold stations on a rotating carousel, allowing for simultaneous production of several parts. This type is highly efficient for mass production of small to medium-sized components, making it ideal for industries requiring rapid output. Buyers should evaluate the initial investment against the potential for high-volume production and reduced cycle times. While carousel machines can significantly enhance productivity, they may also come with higher costs and require more extensive training for operators.
Why Consider Shuttle Machines for Versatile Production Needs?
Shuttle machines are designed to move molds between heating and cooling stations, enabling the production of various part sizes in a single setup. This versatility makes shuttle machines suitable for companies that require flexibility in their production lines. B2B buyers should consider shuttle machines for their ability to accommodate different product specifications without extensive reconfiguration. However, the complexity of operation and maintenance may present challenges, necessitating skilled personnel for optimal performance.
Key Industrial Applications of rotational molding machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Rotational Molding Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Management | Production of large water storage tanks | Durable and lightweight solutions for water storage | Ensure compliance with local regulations and standards |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of automotive parts (e.g., bumpers) | Cost-effective production of complex, lightweight parts | Consider material compatibility and production volume needs |
| Consumer Products | Creation of outdoor recreational products (e.g., kayaks) | High-quality, durable products with custom designs | Evaluate design flexibility and customization options |
| Construction | Fabrication of site equipment (e.g., concrete forms) | Efficient production with reduced labor costs | Assess machine capabilities for large-scale production |
| Agricultural Equipment | Production of agricultural tanks and containers | Enhanced durability and resistance to harsh conditions | Focus on material selection for UV and chemical resistance |
How Is Rotational Molding Used in Water Management?
In the water management sector, rotational molding machines are employed to create large, robust water storage tanks. These tanks are essential for both residential and industrial applications, requiring materials that can withstand environmental conditions while being lightweight for easy installation. The use of rotational molding ensures uniform wall thickness, enhancing durability and reducing the risk of leaks. International buyers should prioritize sourcing machines that comply with local regulations concerning potable water storage to guarantee safety and reliability.
What Role Does Rotational Molding Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Rotational molding machines are increasingly utilized in the automotive industry for producing parts such as bumpers and interior components. The process allows for the creation of complex shapes with excellent strength-to-weight ratios, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency. Businesses in this sector benefit from the cost-effective production of lightweight parts that meet stringent safety and quality standards. Buyers should consider the machine’s capability to handle specific materials and the production volume needed to ensure efficiency in operations.
How Are Rotational Molding Machines Transforming Consumer Products?
In the consumer products industry, rotational molding is pivotal for crafting outdoor recreational items like kayaks and furniture. This method provides the flexibility to create intricate designs while maintaining the durability required for outdoor use. The seamless construction minimizes the risk of leaks and enhances the product’s lifespan. Buyers from diverse regions should evaluate the customization options available to meet market demands and consider the sustainability of materials used in production.
In What Ways Does Rotational Molding Benefit the Construction Sector?
The construction industry leverages rotational molding machines to manufacture essential site equipment, including concrete forms and barriers. This process allows for efficient production, reducing labor costs and waste materials. The end products are not only lightweight but also strong enough to withstand harsh construction environments. International buyers should focus on sourcing machines that can handle large-scale production to meet project timelines and budget constraints effectively.
Why Is Rotational Molding Important for Agricultural Equipment?
Rotational molding is critical in the agricultural sector for producing tanks and containers that hold chemicals and fertilizers. The durability and resistance to UV rays and harsh chemicals are vital for ensuring the longevity of these products. Manufacturers benefit from the ability to create large, hollow shapes in a single process, minimizing assembly needs. Buyers in this sector should prioritize machines that offer material compatibility with agricultural applications to ensure the resilience of the final products.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rotational molding machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Limited Production Capacity for Complex Parts
The Problem: A manufacturing company in South America is experiencing bottlenecks in production due to the limited capacity of their existing rotational molding machines. They primarily produce complex-shaped parts that require precise dimensions and uniform wall thickness. As demand increases, they find their current equipment insufficient to meet production targets, leading to delays and potential loss of business opportunities. The company struggles with the trade-off between investing in new machinery and the risk of overextending their budget.
The Solution: To address this challenge, the company should conduct a thorough analysis of its production needs and evaluate the specifications of different rotational molding machines available in the market. They should consider investing in a high-capacity carousel or rock and roll machine, which can produce multiple parts simultaneously without sacrificing quality. Engaging with reputable suppliers that offer custom solutions can help ensure that the selected machine aligns with their specific requirements. Additionally, exploring financing options or used machinery can provide a cost-effective pathway to upgrade their production capabilities without straining their budget.
Scenario 2: Quality Control Issues with Finished Products
The Problem: A European company specializing in plastic components faces quality control issues due to inconsistencies in the molded products. Some parts exhibit uneven wall thickness or surface defects, which not only affects performance but also leads to increased waste and rework costs. The production team is frustrated as they cannot pinpoint the root cause of these quality issues, resulting in a lack of confidence in the rotational molding process.
The Solution: The company should implement a systematic approach to quality assurance by investing in advanced monitoring systems that track the molding process in real-time. By equipping their machines with temperature and pressure sensors, they can gain insights into the molding conditions and identify any anomalies during production. Additionally, regular maintenance and calibration of machinery are essential to ensure consistent performance. Training operators on best practices in machine operation and mold preparation can also significantly reduce defects. Collaborating with a machinery supplier that offers ongoing support and training can further enhance the company’s ability to maintain high quality in their production.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Sourcing Spare Parts and Technical Support
The Problem: A rotational molding facility in the Middle East is struggling to source spare parts for their aging machinery, leading to extended downtimes whenever a component fails. The lack of access to technical support from the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) exacerbates the situation, as the team lacks the expertise to troubleshoot and repair issues efficiently. This has led to lost production time and increased operational costs, creating frustration among the management and workforce.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, the facility should establish relationships with multiple suppliers for spare parts, including aftermarket vendors who specialize in rotational molding machinery. Creating a proactive maintenance schedule can help identify wear and tear before it leads to breakdowns, allowing for timely ordering of necessary components. Additionally, investing in a maintenance training program for their team can empower them to handle minor repairs in-house, reducing reliance on external support. Networking with industry peers through associations or trade shows can also provide valuable insights into reliable suppliers and resources for technical assistance. This multi-faceted approach will enhance the facility’s operational resilience and reduce the risk of unplanned downtimes.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rotational molding machine
What Are the Common Materials Used in Rotational Molding?
When selecting materials for rotational molding, it is essential to consider the properties that directly affect product performance, manufacturing complexity, and end-use suitability. Below are analyses of four common materials used in rotational molding, tailored for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Polyethylene in Rotational Molding?
Polyethylene (PE) is one of the most widely used materials in rotational molding due to its excellent balance of properties. It boasts a high resistance to impact and chemicals, making it suitable for various applications, including tanks and containers. PE can withstand temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and has good UV resistance, which is vital for outdoor applications.
Pros: Polyethylene is cost-effective, lightweight, and has good flexibility. It is also easy to process, which simplifies manufacturing.
Cons: However, it has lower temperature resistance compared to other materials and can become brittle at low temperatures. Additionally, its lower rigidity may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: PE is compatible with a wide range of media, including water and chemicals, making it ideal for storage tanks and agricultural applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding food safety and chemical storage, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where standards can be stringent.
How Does Polypropylene Compare as a Rotational Molding Material?
Polypropylene (PP) is another popular choice for rotational molding, known for its excellent chemical resistance and higher temperature tolerance (up to 100°C or 212°F) compared to PE. It also exhibits good fatigue resistance, making it suitable for applications that require repeated stress.
Pros: PP is lightweight, has a high strength-to-weight ratio, and is recyclable, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
Cons: The main drawback is its lower impact resistance compared to PE, making it less suitable for high-impact applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive.
Impact on Application: PP is compatible with various chemicals, making it ideal for containers and automotive parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific recycling regulations in their regions, particularly in Europe, where there is a strong emphasis on sustainability.
What Advantages Does PVC Offer in Rotational Molding?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring chemical resistance, such as piping and tanks. PVC can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F).
Pros: PVC is highly durable, resistant to environmental stress, and can be produced in various colors.
Cons: However, its processing can be more complex, requiring specialized equipment. Additionally, it is less flexible than PE and PP.
Impact on Application: PVC is ideal for applications involving harsh chemicals, such as in the chemical processing industry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local environmental regulations is crucial, especially in Europe, where PVC usage is closely monitored due to its potential environmental impact.
Why Choose Nylon for Rotational Molding Applications?
Nylon is a high-performance engineering plastic known for its strength and thermal stability, with a temperature tolerance of up to 120°C (248°F). It also offers excellent abrasion resistance.
Pros: Nylon provides superior mechanical properties and is suitable for demanding applications, such as automotive and industrial parts.
Cons: The main disadvantage is its higher cost and susceptibility to moisture absorption, which can affect dimensional stability.
Impact on Application: Nylon is suitable for applications requiring high strength and durability, such as gears and structural components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected nylon grade meets specific industry standards, such as ASTM or DIN, particularly in regions with strict compliance requirements.
Summary of Material Selection for Rotational Molding
| Material | Typical Use Case for rotational molding machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene | Tanks, containers | Cost-effective and flexible | Lower temperature resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene | Automotive parts, containers | High strength-to-weight ratio | Lower impact resistance | Medium |
| PVC | Piping, chemical tanks | Highly durable and corrosion-resistant | More complex processing | Medium |
| Nylon | Gears, structural components | Superior mechanical properties | Higher cost and moisture sensitivity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for rotational molding, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rotational molding machine
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Rotational Molding Machines?
The manufacturing process for rotational molding machines consists of several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the final product meets the necessary quality and performance standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Rotational Molding?
The first stage involves preparing the raw materials, primarily thermoplastic resins such as polyethylene or PVC. These materials are often in the form of powdered resin, which is measured and mixed with additives to enhance specific properties like UV resistance or color. The precise measurement and mixing are crucial, as they directly affect the material properties and the final product quality. Manufacturers often utilize automated systems to ensure consistency in material preparation, which minimizes human error and enhances efficiency.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Rotational Molding?
In the forming stage, the prepared resin is placed into a mold, which is then heated while being rotated along two axes. This rotation allows the material to coat the mold evenly, forming a hollow part. The heat causes the resin to melt and adhere to the mold’s interior surface, creating a uniform wall thickness. Common techniques include the use of clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle machines, each suited for different part sizes and production volumes. The choice of machine impacts the efficiency and quality of the molding process, necessitating careful selection based on production needs.
How Is Assembly Conducted for Rotational Molding Machines?
Once the molding process is complete, the next step is assembly. This involves removing the molded parts from the mold and performing any necessary post-processing, such as trimming excess material or adding additional components. This stage may also include the integration of features like inserts or reinforcements, depending on the product requirements. Advanced robotic systems are increasingly utilized in assembly to improve speed and precision, which is particularly beneficial for high-volume production scenarios.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Enhance Quality?
The finishing stage involves various processes to improve the surface quality and functionality of the molded parts. This can include sanding, painting, or applying coatings to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. Additionally, some manufacturers may incorporate quality control techniques at this stage to ensure that the parts meet the required specifications before they are packaged and shipped.
What Are the Quality Assurance Protocols for Rotational Molding Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the rotational molding process to ensure that the final products meet both international standards and specific client requirements. Several protocols and checkpoints are involved throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards like ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for compliance with European health and safety requirements and API standards for oil and gas equipment may be relevant depending on the application of the molded parts. B2B buyers should verify that their suppliers are compliant with these standards to ensure product reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Rotational Molding?
Quality control in rotational molding typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards. This step is crucial as the quality of raw materials directly impacts the final product.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and rotation speed are monitored. Any deviations from established norms can lead to defects, making this checkpoint essential for maintaining quality.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the parts are molded and finished, a final inspection is conducted to verify dimensions, appearance, and functional characteristics. This step often includes destructive and non-destructive testing methods to ensure the parts meet all specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed in quality control, including:
-
Visual Inspections: Assessing surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
-
Mechanical Testing: Evaluating properties like tensile strength and impact resistance through standardized testing methods.
-
Thermal Testing: Ensuring that the materials can withstand operational temperatures without deforming or failing.
These tests help ensure that the products not only comply with quality standards but also perform effectively in their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are several strategies to ensure supplier compliance:
What Are the Best Practices for Conducting Supplier Audits?
Conducting thorough supplier audits is an effective method to verify quality control practices. Buyers should develop a checklist based on relevant standards and their specific requirements, focusing on aspects like equipment calibration, personnel training, and adherence to standard operating procedures. On-site audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturing environment and operational practices directly.
How Can Buyers Request Quality Reports and Documentation?
Buyers should request quality reports and documentation from suppliers, including certificates of compliance, test results, and details of any quality management systems in place. Transparent suppliers will readily provide this information, fostering trust and ensuring accountability.
Should Buyers Consider Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These inspections can help verify compliance with international standards and provide additional assurance of product quality before shipment. This approach is especially beneficial for buyers new to the market or those sourcing from unfamiliar regions.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing rotational molding machines and parts internationally, buyers should be aware of regional differences in quality control standards and practices. For instance, compliance requirements may vary significantly between Europe and the Middle East, necessitating a nuanced understanding of local regulations. Additionally, cultural factors may influence supplier practices, making it essential for buyers to establish clear communication and expectations.
By understanding the intricacies of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols associated with rotational molding machines, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rotational molding machine’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring rotational molding machines, this guide provides a practical checklist to ensure informed decisions. By following these steps, you can streamline the sourcing process and make choices that align with your production needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with suppliers, it’s essential to outline your specific requirements for the rotational molding machine. Consider factors such as the size of parts, production volume, and material types you intend to use. This clarity helps suppliers recommend the most suitable machine configurations, ensuring you don’t overpay or under-specify.
- Types of Machines: Identify whether you need a clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, or shuttle machine based on your production needs.
- Capacity and Size: Determine the dimensions of the parts you plan to manufacture and the expected production rate.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Investigate the current market landscape for rotational molding machines. Analyze various manufacturers and their offerings, focusing on both new and used equipment. This research will provide insight into pricing, technology advancements, and supplier reputation.
- Reputable Brands: Look for established manufacturers known for quality, such as Ferry or Rotoline.
- Industry Trends: Stay informed about innovations in rotational molding that could enhance your production efficiency.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet suppliers before making a commitment. Request comprehensive company profiles, including case studies and references from similar industries or regions. This process helps you gauge their reliability and the quality of their machines.
- Request Documentation: Ask for certifications, warranties, and service agreements.
- Client Testimonials: Seek feedback from other buyers regarding their experiences with the supplier.
Step 4: Assess Machine Features and Capabilities
When evaluating specific machines, focus on their features and capabilities that align with your production needs. Consider aspects such as energy efficiency, ease of operation, and maintenance requirements.
- Control Systems: Look for advanced control systems that offer precision and flexibility in the molding process.
- Material Compatibility: Ensure the machine can handle the specific types of plastics you intend to use.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your chosen suppliers comply with international quality standards and regulations. This step is critical to avoid potential issues related to safety and product quality.
- ISO Certifications: Check for ISO 9001 or other relevant quality management certifications.
- Compliance with Local Regulations: Ensure they meet the standards required in your country or region.
Step 6: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have identified potential suppliers and machines, request detailed quotes. Compare not only the prices but also the terms of service, warranty, and after-sales support.
- Breakdown of Costs: Look for clarity in the pricing structure, including installation and training costs.
- Long-term Value: Consider total cost of ownership rather than just upfront costs, including maintenance and operational expenses.
Step 7: Finalize Your Decision and Plan for Installation
After thorough evaluation and comparison, make your decision and plan for the installation process. Engage with your supplier to discuss installation logistics and training for your staff.
- Installation Support: Confirm that the supplier provides support during the installation phase.
- Training Programs: Ensure your team receives adequate training to operate the machine efficiently.
By following this checklist, you can confidently navigate the procurement of rotational molding machines, ensuring that your investment aligns with your business objectives and production needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rotational molding machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Rotational Molding Machines?
When sourcing rotational molding machines, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The type of plastic resin used in the rotational molding process directly impacts costs. Standard materials like polyethylene are typically less expensive, while specialty resins may incur higher costs due to their enhanced properties.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for both machine operation and maintenance. In regions with a higher labor cost, such as Europe, this can significantly influence overall pricing. Conversely, in developing markets, labor costs may be lower, providing potential savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the facility, utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. A well-optimized manufacturing process can help minimize these overheads.
-
Tooling: Custom molds are necessary for producing specific parts. The complexity of the mold design, along with the materials used, can lead to considerable tooling costs, which should be factored into the total investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous testing and inspection can add to the overall cost. Machines that offer advanced QC features may have a higher upfront price but can reduce long-term costs associated with defects.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary based on the machine’s weight, dimensions, and destination. International buyers should account for potential tariffs and import duties, which can substantially increase the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to the base cost of the machine. This margin can vary significantly based on the supplier’s reputation, market demand, and competition.
What Influences Pricing for Rotational Molding Machines?
Several factors affect the pricing of rotational molding machines, especially for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk often results in discounted prices. Buyers should assess their production needs to determine if they can meet MOQ requirements for better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built machines designed to meet specific production requirements typically come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the necessity of customization against potential cost savings from standard models.
-
Materials Quality and Certifications: Machines constructed from high-quality materials or those that meet international standards and certifications (ISO, CE) may command higher prices. However, these investments often lead to better durability and lower maintenance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and market position can significantly influence pricing. Established suppliers with robust support networks may charge more but can offer additional value through reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (FOB, CIF, DDP) can help buyers gauge the total cost. Each term defines the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Prices?
-
Leverage Negotiation Skills: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if multiple quotes are on the table. Building a relationship can also result in better terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), not just the upfront price. A machine with a higher initial cost may have lower maintenance and operational expenses, leading to overall savings.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances in Different Regions: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing trends and potential hidden costs. For example, logistics and tariffs can vary greatly across regions.
-
Be Informed About Market Conditions: Stay updated on market trends, such as fluctuations in resin prices or technological advancements in machinery, which can impact pricing.
-
Seek Transparency: Ensure that suppliers provide clear breakdowns of costs, including materials, labor, and logistics. This transparency can facilitate better negotiations and informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for rotational molding machines can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they receive the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rotational molding machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Rotational Molding Machines
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, understanding the alternatives to rotational molding machines is crucial for B2B buyers seeking efficient production methods. This analysis compares rotational molding against two viable alternatives: injection molding and blow molding. Each method has unique advantages and drawbacks that can impact production quality, cost, and suitability for specific applications.
| Comparison Aspect | Rotational Molding Machine | Injection Molding | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality, uniform parts; excels in large, hollow shapes | Excellent for high precision; suitable for complex geometries | Ideal for hollow parts; fast production rates |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; cost-effective for large parts | Higher setup costs; economical for mass production | Lower cost for high volume; tooling can be expensive |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized knowledge; moderate complexity in setup | Steeper learning curve; needs precise calibration | Generally easier to implement; less specialized training needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance needs; regular inspections required | High maintenance due to precision components | Lower maintenance; simpler machinery |
| Best Use Case | Large, hollow products like tanks and playground equipment | Small to medium parts with intricate designs | Bottles, containers, and other hollow shapes |
Injection Molding: Pros and Cons
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into a mold. It is renowned for producing high-precision parts with complex geometries, making it suitable for industries like automotive and consumer goods. However, the initial setup costs can be significant due to the need for specialized molds and machinery. While the process is fast for high volumes, it may not be as cost-effective for smaller runs compared to rotational molding.
Blow Molding: Advantages and Disadvantages
Blow molding is a method specifically designed for creating hollow plastic parts, such as bottles and containers. The process is generally quicker and less expensive for high-volume production, making it an attractive option for businesses focused on packaging solutions. However, blow molding is limited in terms of design complexity, as it is primarily suitable for simpler shapes. Additionally, it may not provide the same level of durability and wall thickness uniformity as rotational molding.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the appropriate manufacturing method, B2B buyers should consider several key factors: production volume, part complexity, material requirements, and budget constraints. Rotational molding excels in producing large, durable products with uniform wall thickness, making it ideal for industries requiring robust components. In contrast, injection molding offers precision for intricate designs, while blow molding is best suited for high-volume, simpler hollow products. By carefully analyzing these factors and understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their production goals and financial considerations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rotational molding machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Rotational Molding Machines?
When evaluating rotational molding machines, several technical properties play a crucial role in the decision-making process for B2B buyers. Understanding these specifications can help ensure that the selected machine meets production requirements efficiently and cost-effectively.
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of plastic resin used in the rotational molding process. Common materials include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Each material has unique properties, such as durability, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals, which influence the final product’s quality. Choosing the right material grade is essential for achieving the desired performance characteristics, impacting everything from product lifespan to compliance with industry standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in dimensions of the molded part. In rotational molding, typical tolerances range from ±0.5% to ±1% depending on the complexity of the part. Understanding tolerances is crucial for ensuring that parts fit together correctly in assemblies and function as intended. For buyers, this specification can affect production costs and timelines if adjustments are needed to meet stringent engineering standards.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time refers to the total time required to complete one full molding cycle, including heating, cooling, and unloading. Efficient cycle times can significantly impact production output and operational efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding cycle time helps in estimating production capacity and aligning it with market demand. A shorter cycle time can lead to increased profitability, especially in high-volume manufacturing scenarios.
4. Heating Method
Different machines utilize various heating methods, such as convection, conduction, or infrared. The heating method affects how uniformly the resin melts and coats the mold. For instance, convection heating may offer better uniformity but can be slower than conduction methods. Buyers should consider the heating method’s implications on energy consumption, production speed, and the quality of the final product.
5. Machine Size and Configuration
Rotational molding machines come in various sizes and configurations (e.g., clamshell, rock and roll, carousel). The machine’s size and design will determine the types and sizes of parts that can be produced. Understanding machine configuration is vital for buyers to ensure that it aligns with their specific production needs and available floor space. Selecting the right configuration can optimize production efficiency and reduce operational costs.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Rotational Molding Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation within the rotational molding sector.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of rotational molding, understanding OEM relationships can clarify sourcing options for parts and equipment. Buyers often look for reputable OEMs to ensure quality and reliability in their production processes.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant for B2B buyers when negotiating bulk orders of molded parts. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses assess their purchasing strategies and manage inventory effectively.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the rotational molding industry, issuing an RFQ can help buyers compare pricing and terms from various manufacturers, ensuring they secure the best deal for their production needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms can help B2B buyers navigate logistics and shipping arrangements more effectively, minimizing misunderstandings related to costs and responsibilities.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from placing an order to its fulfillment. In rotational molding, this can include manufacturing, shipping, and delivery times. Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory management and meeting customer demands, enabling buyers to plan their production schedules accordingly.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in rotational molding machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and market competitiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rotational molding machine Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Rotational Molding Machine Sector?
The rotational molding machine market is experiencing significant growth, driven by various global factors. As industries such as automotive, consumer goods, and packaging increasingly adopt rotational molding due to its ability to produce complex, durable, and lightweight parts, the demand for these machines is on the rise. Additionally, the versatility of rotational molding machines allows for the production of a wide range of products—from tanks and containers to toys and industrial components—making them an attractive option for manufacturers across multiple sectors.
Emerging B2B technology trends include the integration of automation and Industry 4.0 principles into the rotational molding process. Smart machines equipped with IoT capabilities enable real-time monitoring and data collection, enhancing production efficiency and reducing downtime. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce and digital platforms is changing how international buyers source machines, with an increasing number of suppliers offering online catalogs and virtual consultations, streamlining the purchasing process.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on cost-effective solutions that do not compromise quality. As these markets grow, sourcing strategies are evolving. Companies are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not just machines but also comprehensive support services, including maintenance, training, and customization options. This shift underscores the importance of strategic partnerships in navigating the complexities of global supply chains.
How Does Sustainability Influence B2B Sourcing in the Rotational Molding Machine Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the rotational molding sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly plastic production, has prompted many companies to seek ways to reduce their carbon footprint. Rotational molding is inherently more sustainable than other molding methods, as it generates less waste and uses fewer materials, making it an attractive option for eco-conscious buyers.
Furthermore, the importance of ethical sourcing practices is gaining traction. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. This includes sourcing raw materials from responsible suppliers, utilizing recyclable or biodegradable materials, and ensuring that production processes minimize energy consumption and waste generation. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of recycled materials are becoming key factors in supplier selection.
By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, companies can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing demand for environmentally responsible products. This trend not only supports global sustainability goals but also resonates with consumers who are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on ethical considerations.
What Is the Historical Context of Rotational Molding?
Rotational molding, a process with roots dating back over a century, has evolved significantly to meet the changing demands of various industries. Initially developed for the production of simple hollow shapes, advancements in technology have transformed rotational molding into a sophisticated manufacturing method capable of producing complex and high-quality products. The introduction of modern materials and machine designs has expanded its application across diverse sectors, including automotive, agriculture, and consumer goods.
The historical progression of rotational molding reflects broader trends in manufacturing, such as the shift towards automation and the increasing emphasis on sustainability. As global markets continue to evolve, the rotational molding sector is poised to adapt further, driven by innovation and the pressing need for environmentally friendly production methods. This evolution highlights the importance of staying informed about historical developments to understand current market dynamics and future opportunities in the rotational molding machine sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rotational molding machine
-
How do I select the right rotational molding machine for my production needs?
Selecting the right rotational molding machine involves assessing your production requirements, including the size, volume, and complexity of the parts you wish to manufacture. Consider the types of machines available, such as clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle machines, each suited for different applications. Additionally, evaluate factors such as space availability, budget constraints, and the desired level of automation. Engaging with suppliers to discuss your specific needs can also provide valuable insights into the best machine options for your business. -
What is the best type of rotational molding machine for high-volume production?
For high-volume production, carousel machines are typically the best choice. They consist of multiple mold stations arranged in a rotating carousel, allowing for simultaneous production of several parts. This design enhances efficiency and reduces cycle times, making it ideal for manufacturers needing to meet large demand. Alternatively, shuttle machines can also be effective, as they enable multiple molds to be processed in sequence, further optimizing production efficiency. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting suppliers of rotational molding machines?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, customer reviews, and reputation for quality. Check if they offer post-purchase support, including maintenance and technical assistance. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities and whether they provide customization options to suit your specific needs. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with international standards and certifications, as this can affect the reliability and safety of the equipment you invest in. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for rotational molding machines?
The MOQ for rotational molding machines can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the specific machine type. Generally, many manufacturers offer machines as single units, especially for custom or specialized equipment. However, if you are purchasing multiple machines or additional components, suppliers may set a higher MOQ to optimize production and reduce costs. Always clarify these terms before proceeding with your order to avoid unexpected charges. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a rotational molding machine?
Payment terms for rotational molding machines can differ based on the supplier and the transaction size. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%) and the balance due before shipping or upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment plans for larger orders. It is essential to negotiate favorable terms that align with your cash flow and financial planning, ensuring both parties are clear on the payment schedule. -
How can I ensure quality assurance during the procurement of a rotational molding machine?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications from the supplier that outline the machine’s compliance with industry standards. Schedule factory visits or audits to observe the manufacturing process and quality control measures in place. Additionally, consider asking for trial runs or demonstrations of the machine to assess its performance before finalizing the purchase. A robust warranty and after-sales support can also provide added security regarding the machine’s reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing a rotational molding machine?
When importing a rotational molding machine, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that could impact overall costs. Choose reliable logistics partners experienced in handling heavy machinery to ensure safe transport. Be aware of the lead times for manufacturing and shipping, and plan accordingly to minimize production downtime. Finally, ensure you have all necessary documentation, including import permits and compliance certificates, to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process. -
How can I customize a rotational molding machine to fit my specific production needs?
Customization options for rotational molding machines often include modifications to mold sizes, heating methods, and automation levels. Discuss your production requirements with potential suppliers to explore available customization options. Some manufacturers may offer bespoke solutions tailored to unique applications, while others might provide modular systems that allow for future upgrades. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can help ensure that the machine aligns perfectly with your operational goals and product specifications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Rotational Molding Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rotodynamics – Rotational Molding Machines
Domain: rotodynamics.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Rotational molding machines come in different types: Clamshell Machines, Rock and Roll Machines, Carousel Machines, and Shuttle Machines. Clamshell Machines are suitable for smaller parts and limited space. Rock and Roll Machines are ideal for larger, durable parts. Carousel Machines allow for high volume production of small to medium-sized parts. Shuttle Machines enable simultaneous production of…
2. KDCapital – Independent Arm Roto Molders
Domain: kdcapital.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: 1. 2018 Rotoline CR 2.60 Independent Arm Carousel – Ref # 8076889
2. 1997 Ferry RotoSpeed RS3-200 Independent Arm Machine – Ref # 8076764
3. 1993 Ferry RS4-220 Rotational Molder – Ref # 8074689
4. 1989 REI 96 Multi-Arm Roto Molder – Ref # 8076047
5. 1985 REI 110 Multi-Arm Roto Molder – Ref # 8076046
3. Ferry Industries – RotoSpeed Independent Arm Machines
Domain: ferryindustries.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: RotoSpeed Independent Arm Machines are designed for the rotational molding industry, featuring a four-arm, five-station independent-arm carousel machine. Key details include:
– Multiple-station arrangement for heating, cooling, and servicing
– Each arm on a separate cart that indexes about a center pivot post
– Five process stations: Oven, Pre-cool or Intermediate Cooling, Unload, Load
– Purch…
4. Ferry – RS4-3000HD
Domain: meadoworks.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Rotational Molding Machinery available for purchase includes the following models:
1. Ferry – RS4-3000HD
– Item No.: 5513
– Year: 2006
2. Ferry – RS5-3000SHD
– Item No.: 5625
– Year: 2016
3. Persico – Leonardo Super LM-0-20/20
– Item No.: 4767
– Year: 2012
4. Persico – Leonardo Smart 2.4
– Item No.: 5494
– Year: 2017
5. Rotoline – DC 4.00 XT
– Item No.: 341…
5. PSI Brand – Miniature Roto Moulder
Domain: psibrand.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Miniature Roto Moulder – PSI Brand
– World’s smallest operating rotational moulder
– Demonstrated at the Rotoplas exposition in Chicago, September 2017
– Designed for demo graphics at exhibitions
– Features a unique multi-axis moulder
– Utilizes a high temperature glass mould and polyethylene
– Moulding process involves heat generated by two radiant electric bars
– Moulding time: approximately 8 m…
6. OREX – Rotational Molding Machines
Domain: orex-rotomoulding.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: OREX ROTOMOULDING offers a range of rotational molding machines including Carousel, Shuttle, and Rock and Roll types. The Carousel machine is designed for high production capacity and continuous operation, ideal for mass production. The Shuttle machines have customizable heating chamber diameters ranging from 2000 mm to 5000 mm, catering to unique production needs. The Rock and Roll machines are s…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rotational molding machine
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers of Rotational Molding Machines?
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, leveraging rotational molding technology provides a distinct advantage in producing high-quality, durable parts with design flexibility. The diverse range of machines—clamshell, rock and roll, carousel, and shuttle—caters to various production needs, enabling businesses to optimize operations based on specific requirements. As strategic sourcing becomes increasingly vital, understanding the nuances of these machines allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Why Is Strategic Sourcing Essential in the Rotational Molding Sector?
Strategic sourcing not only ensures cost-effectiveness but also enhances supply chain efficiency. By engaging with reputable suppliers and considering both new and used machines, international buyers can secure the best technology tailored to their production scale and budget. This approach minimizes risk and maximizes return on investment, vital for companies looking to expand in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
How Can International Buyers Prepare for Future Opportunities?
As the demand for sustainable and innovative manufacturing solutions grows, B2B buyers are encouraged to stay ahead of industry trends and technological advancements. Engaging with suppliers who understand local market dynamics and can offer customized solutions will be crucial. By prioritizing strategic sourcing today, businesses can position themselves for success in tomorrow’s manufacturing landscape. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your production capabilities and drive growth in your market.