Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rms finishing
Navigating the complexities of sourcing RMS finishing services can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The intricacies involved in selecting the right surface finishing technique—whether it be electropolishing, mechanical polishing, or others—demand a comprehensive understanding of the various methods and their applications. This guide is designed to equip you with essential knowledge about RMS finishing, covering everything from types and applications to supplier vetting and cost considerations.
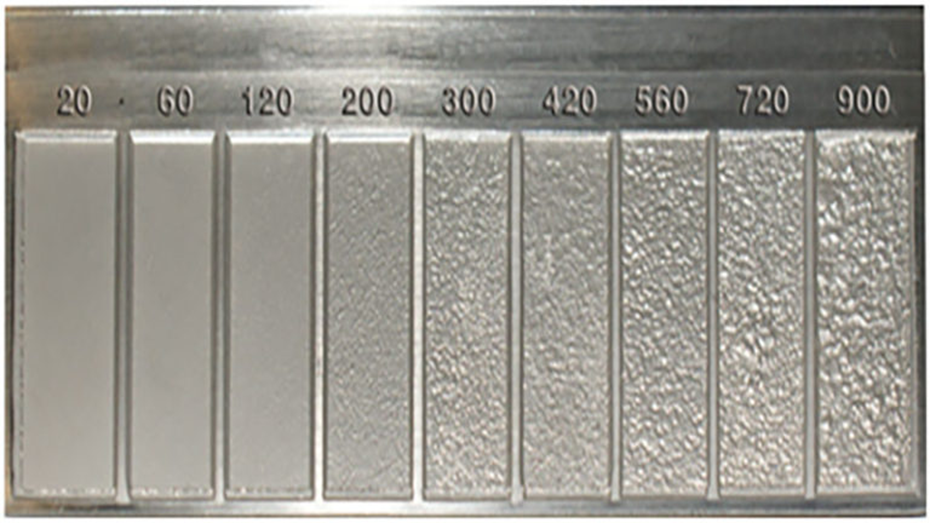
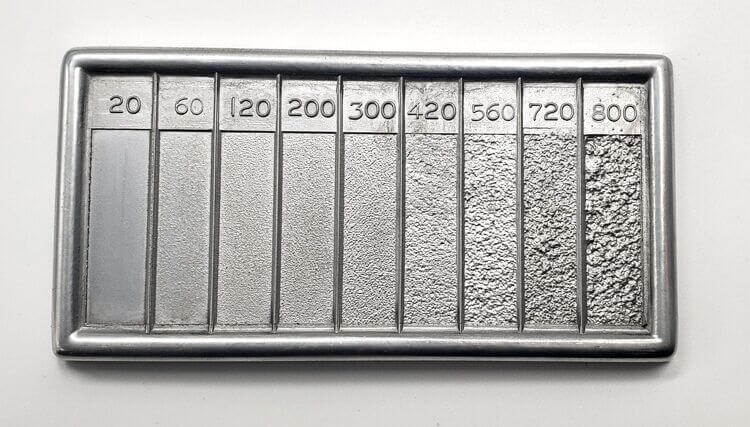
As global supply chains become increasingly interconnected, making informed purchasing decisions is crucial for maintaining competitive advantage. This guide empowers B2B buyers by elucidating the key factors to consider when sourcing RMS finishing services, including how to evaluate surface roughness metrics like Ra and RMS, which can significantly impact product performance and longevity.
In particular, buyers from regions such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia will benefit from insights tailored to their unique market dynamics, ensuring they can effectively navigate local and international suppliers. By leveraging the actionable insights within this guide, you will be better positioned to select the right partners and techniques, thereby enhancing your product offerings and achieving operational excellence.
Understanding rms finishing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Polishing | Removes macroscopic imperfections | Automotive, Aerospace, Medical | Pros: Effective for visible finishes; Cons: Limited effect on micro-level roughness. |
| Electropolishing | Enhances surface finish by removing material | Food Processing, Pharmaceutical | Pros: Significant reduction in surface roughness; Cons: May not be suitable for all materials. |
| Chemical Finishing | Uses chemical processes to alter surface properties | Electronics, Precision Engineering | Pros: Can achieve very smooth finishes; Cons: Process control can be complex. |
| Abrasive Finishing | Involves grinding or sanding to achieve desired finish | Metal Fabrication, Construction | Pros: Versatile for various materials; Cons: Potential for material removal inaccuracies. |
| Laser Finishing | Employs laser technology for precision finishing | Aerospace, High-tech Industries | Pros: Highly precise and customizable; Cons: High initial investment and operational costs. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Mechanical Polishing?
Mechanical polishing is a widely used method that focuses on removing macroscopic imperfections to enhance the surface finish of metals. This technique is particularly suitable for industries such as automotive and aerospace, where aesthetics and surface integrity are crucial. Buyers should consider the material type and desired finish, as mechanical polishing may not significantly improve micro-level roughness. Additionally, while it provides a visually appealing result, the process can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
How Does Electropolishing Improve Surface Quality?
Electropolishing is a specialized process that enhances surface quality by removing a thin layer of material, resulting in a smoother finish. It is particularly beneficial in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and surface integrity are paramount. Buyers should evaluate the compatibility of the material with electropolishing, as not all materials respond equally well. The process can lead to a substantial reduction in surface roughness, making it an excellent choice for applications requiring stringent cleanliness standards.
What are the Key Features of Chemical Finishing?
Chemical finishing involves the use of chemical agents to alter the surface properties of materials, often resulting in a very smooth finish. This method is commonly employed in electronics and precision engineering sectors where high tolerances and surface quality are critical. Buyers must consider the complexity of the process and the need for precise control over chemical reactions. While chemical finishing can achieve exceptional smoothness, it requires careful monitoring to avoid adverse effects on the material properties.
How Does Abrasive Finishing Differ from Other Methods?
Abrasive finishing utilizes grinding or sanding techniques to achieve the desired surface finish. It is a versatile method suitable for various materials and is commonly used in metal fabrication and construction industries. Buyers should be mindful of the potential for inaccuracies in material removal, which could affect dimensional tolerances. While abrasive finishing can be effective for achieving specific finishes, it may require additional steps to ensure surface quality meets industry standards.
What Advantages Does Laser Finishing Offer?
Laser finishing employs advanced laser technology to achieve precise surface finishes, making it ideal for high-tech industries such as aerospace. This method allows for a high degree of customization and precision, catering to specific application requirements. Buyers should weigh the benefits of precision against the high initial investment and operational costs associated with laser systems. While laser finishing can deliver superior results, the economic viability depends on the scale of production and specific project needs.
Key Industrial Applications of rms finishing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rms finishing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Component surface preparation | Enhanced performance and reliability of critical components | Compliance with strict aerospace standards; sourcing certified suppliers |
| Medical Devices | Surgical instruments and implants | Improved biocompatibility and reduced risk of infection | Need for precision and adherence to regulatory requirements |
| Automotive | Engine and transmission parts | Increased efficiency and longevity of components | Demand for cost-effective solutions without compromising quality |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline and valve finishing | Enhanced corrosion resistance and longevity in harsh environments | Focus on suppliers with experience in extreme conditions |
| Electronics | Circuit board and component finishing | Improved conductivity and reliability of electronic devices | Preference for suppliers with advanced technology and certifications |
How is rms finishing utilized in the aerospace industry?
In the aerospace sector, rms finishing is critical for preparing the surfaces of components such as turbine blades and structural parts. The precise surface finish achieved through rms techniques enhances the aerodynamic properties and fatigue resistance of these components, directly impacting performance and safety. International buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with stringent aerospace standards like AS9100, emphasizing the need for certified processes and traceability in materials used.
What role does rms finishing play in medical device manufacturing?
Rms finishing is vital in the medical device industry, particularly for surgical instruments and implants, where surface quality directly influences biocompatibility. A smooth finish minimizes the risk of bacterial adhesion and enhances patient safety. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers who meet ISO 13485 standards and can demonstrate expertise in producing high-quality finishes that comply with regulatory requirements, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East.
How does rms finishing benefit the automotive sector?
In the automotive industry, rms finishing is applied to engine components and transmission parts to improve their performance and durability. A refined surface finish reduces friction and wear, leading to greater efficiency and longer service life of parts. B2B buyers should seek suppliers who offer competitive pricing while maintaining high-quality standards, as the automotive market is highly cost-sensitive, particularly in emerging markets like South America and Africa.
Why is rms finishing important for the oil and gas industry?
Rms finishing is essential for components in the oil and gas sector, such as pipelines and valves, where enhanced corrosion resistance is crucial due to exposure to harsh environments. The finishing process ensures that surfaces can withstand extreme conditions, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Buyers should consider suppliers with proven experience in handling materials suited for such applications, along with certifications that attest to their capabilities in extreme conditions.
How does rms finishing improve electronics manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, rms finishing is employed to enhance the surface quality of circuit boards and components, which is essential for ensuring optimal conductivity and reliability. A precise finish can significantly reduce the risk of failures in electronic devices. International buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers who utilize advanced finishing technologies and have the ability to meet specific industry standards, ensuring that the components perform reliably in diverse applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rms finishing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Achieving Consistent Surface Quality Across Multiple Batches
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of ensuring consistent surface finish quality across different production batches. Variations in surface roughness can lead to product failures, increased rejection rates, and ultimately, damage to the company’s reputation. This issue is particularly prevalent when sourcing materials from different suppliers or when switching between various production methods. Buyers may struggle to meet specified surface roughness requirements, such as those expressed in RMS or Ra metrics, which can result in costly delays and rework.
The Solution: To achieve consistent surface quality, buyers should implement a robust quality assurance process that includes standardized testing methods for surface finish. This involves regularly using profilometers to measure surface roughness in line with industry standards, such as ASME B46.1. Additionally, it is crucial to establish clear specifications with suppliers, detailing acceptable roughness values and tolerances. Consider investing in training for production staff on the importance of surface finish and the impact of different finishing processes. Regular audits of supplier capabilities and quality control measures can also help maintain high standards across batches. Finally, collaborating with suppliers to develop a mutually beneficial quality improvement plan can enhance consistency and reliability in surface finishing.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complex International Standards and Regulations
The Problem: For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigating the myriad of surface finish standards and regulations can be overwhelming. Different countries and industries may have specific requirements regarding surface roughness metrics, which can complicate procurement and compliance. Buyers may find it challenging to determine the right specifications and face the risk of costly penalties or product recalls if their products fail to meet local standards.
The Solution: To effectively navigate international standards, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific requirements relevant to their target markets. This includes familiarizing themselves with local regulations regarding surface finishes and identifying the most commonly accepted standards, such as ISO or ASTM specifications. Establishing partnerships with local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into regional compliance issues. Furthermore, buyers should ensure that their suppliers are certified and familiar with the standards applicable to the products they are supplying. Regular training sessions and updates on changes in regulations can help keep teams informed and compliant, reducing the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
Scenario 3: Reducing Production Downtime Due to Surface Finish Issues
The Problem: Production downtime is a significant concern for B2B buyers, especially when issues related to surface finish arise. Problems such as excessive roughness, which can lead to poor adhesion in coatings or finishes, can halt production lines and delay delivery schedules. These interruptions not only affect profitability but also strain relationships with customers who expect timely deliveries of high-quality products.
The Solution: To minimize production downtime related to surface finishing, buyers should adopt a proactive maintenance strategy for their finishing equipment. Regularly scheduled maintenance and calibration of machines used in the finishing process can prevent unexpected failures that contribute to poor surface quality. Implementing a feedback loop where production teams can report surface finish issues immediately will allow for faster response times and resolution. Additionally, conducting root cause analysis on any surface finish-related downtime incidents can help identify recurring issues and lead to the development of preventative measures. Investing in advanced finishing technologies, such as automated polishing or electropolishing, can also enhance efficiency and product quality, thereby reducing the likelihood of production halts.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rms finishing
What Are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel in rms Finishing?
Stainless steel is a widely used material for rms finishing due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. It typically exhibits high strength, making it suitable for applications that require durability under stress. Stainless steel can withstand a range of temperatures and pressures, which is crucial for industries such as oil and gas, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. The material’s non-reactive nature also makes it ideal for environments where hygiene is paramount.
Pros and Cons of Stainless Steel for rms Finishing
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its long-lasting performance, especially in corrosive environments. It is relatively easy to machine and can achieve a high-quality surface finish, which is essential for rms applications. However, the cost can be a significant drawback, as stainless steel tends to be more expensive than other materials. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can increase due to the need for specialized tooling and processes.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For applications involving food or pharmaceuticals, stainless steel’s compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is critical. Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure that their suppliers can meet these standards to avoid regulatory issues. The material’s compatibility with various cleaning agents and sterilization processes is also a consideration for these markets.
How Does Aluminum Perform in rms Finishing Applications?
Aluminum is another popular choice for rms finishing, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive. Its lightweight nature combined with good corrosion resistance makes it an attractive option for applications where weight savings are crucial. Aluminum can also be anodized to enhance its surface properties further.
Pros and Cons of Aluminum for rms Finishing
The key advantage of aluminum is its low density, which allows for lightweight designs without sacrificing strength. It is generally less expensive than stainless steel, making it a cost-effective option for many applications. However, aluminum is softer and may not perform as well under high-stress conditions, which can limit its use in heavy-duty applications. Additionally, achieving a high-quality surface finish can be more challenging compared to stainless steel.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers should be aware of the specific grades of aluminum that comply with local standards, such as DIN or JIS. For instance, certain aluminum alloys may be more suitable for specific environmental conditions prevalent in regions like South America or Europe. Understanding the local market’s preferences for aluminum grades can help buyers make informed decisions.
What Are the Advantages of Titanium in rms Finishing?
Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, making it an ideal choice for high-performance applications. It is often used in aerospace, marine, and medical applications where durability is paramount.
Pros and Cons of Titanium for rms Finishing
The primary advantage of titanium is its ability to withstand extreme environments, including high temperatures and corrosive substances. However, the cost of titanium is significantly higher than that of stainless steel and aluminum, which can be a limiting factor for some buyers. Additionally, the machining of titanium is more complex and requires specialized equipment, increasing manufacturing costs and lead times.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
For B2B buyers in regions like the Middle East and Europe, understanding the specific certifications required for titanium in aerospace or medical applications is crucial. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO can impact procurement decisions. Buyers should also consider the availability of titanium alloys that meet their specific application needs.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in rms Finishing?
Carbon steel is widely used in various industries due to its high strength and affordability. It is commonly used in construction and manufacturing applications where high tensile strength is required.
Pros and Cons of Carbon Steel for rms Finishing
The main advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness and strength. It is easier to machine compared to stainless steel and titanium, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, carbon steel is prone to rust and corrosion, which can limit its use in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. This necessitates additional surface treatments, which can add to the overall cost.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Buyers from regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, like parts of Africa, should consider the need for protective coatings or treatments for carbon steel. Understanding local regulations regarding material specifications is also essential, as compliance with ASTM or other standards can affect the procurement process.
| Material | Typical Use Case for rms finishing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and cost-effective | Softer, may not handle high stress | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical | Outstanding strength and durability | Very high cost and complex machining | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, manufacturing | Cost-effective and strong | Prone to rust, requires treatment | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rms finishing
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing for RMS Finishing?
The manufacturing process for RMS (Root Mean Square) finishing involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required surface quality and dimensional specifications. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation: How Do You Ensure the Right Starting Material?
The first step in the RMS finishing process is selecting high-quality raw materials. This typically involves sourcing metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, or other alloys that are compatible with the desired application. Material preparation may include cleaning to remove contaminants and ensuring the material is free from defects that could affect the final finish. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s material sourcing practices and whether they adhere to international standards like ISO 9001, which ensures quality management systems are in place.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape the Material?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, which can involve various techniques such as machining, stamping, or casting. Machining is particularly relevant in RMS finishing as it allows for precise control over the dimensions of the part. During this phase, it is crucial to monitor tolerances closely to ensure that the components will achieve the desired surface finish later on. B2B buyers should ask potential suppliers about their machining capabilities and how they manage tolerances during this stage.
Assembly: How Is Quality Maintained During Assembly?
In cases where the RMS finishing applies to assembled products, the assembly stage is critical. This phase often includes welding, fastening, or other joining methods. Quality assurance during assembly is vital to ensure that no defects are introduced. Buyers should seek suppliers who implement robust assembly protocols and conduct inspections at this stage to catch any potential issues early.
Finishing: What Techniques Improve Surface Quality?
The finishing stage is where RMS finishing truly comes into play. Techniques such as electropolishing and mechanical polishing are commonly used. Electropolishing, for instance, can improve surface roughness significantly, enhancing both aesthetics and performance. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific finishing techniques used and their impact on the RMS values of the final product. It’s essential to understand how these processes can affect the product’s functionality, particularly in industries where surface quality is critical, such as aerospace or medical devices.
How Is Quality Control Implemented in RMS Finishing?
Quality control (QC) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for RMS finishing, ensuring that products meet specified standards and regulations. Understanding how QC is implemented can help B2B buyers assess the reliability of potential suppliers.
What Are the Key International Standards for Quality Control?
International standards such as ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015 are essential for manufacturers, as they provide a framework for quality management and environmental responsibility. Suppliers should be able to demonstrate compliance with these standards, which can be verified through documentation and certifications. Industry-specific standards, such as CE marking in Europe or API standards for the oil and gas industry, are also critical. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to these standards to mitigate risks associated with product quality and safety.
What Are the Checkpoints in the Quality Control Process?
Quality control typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection stage ensures that raw materials meet specified requirements before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, regular inspections are conducted to monitor processes and detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection stage verifies that the finished product meets all specifications before it is shipped to the customer.
B2B buyers should inquire about the QC processes implemented by suppliers and how frequently these checkpoints are conducted to ensure ongoing compliance.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in RMS Finishing?
Various testing methods are employed to assess surface quality and ensure products meet RMS specifications. Common techniques include:
- Profilometry: This method measures the surface roughness using a profilometer, providing precise Ra and RMS values.
- Visual Inspections: Trained personnel perform visual checks to identify defects or inconsistencies in surface finish.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or dye penetrant testing can be used to detect subsurface defects without damaging the product.
Buyers should ask suppliers about the testing methods they use and request access to testing reports to validate the quality of their products.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Here are some actionable steps to ensure the reliability of potential partners.
What Audit Procedures Should Buyers Consider?
Conducting audits is one of the most effective ways to verify a supplier’s quality control processes. Buyers can perform on-site audits or request third-party audits to ensure compliance with international standards and industry-specific requirements. These audits can reveal insights into the supplier’s operational capabilities, quality management systems, and adherence to best practices.
How Can Buyers Access Quality Control Reports?
Requesting quality control documentation is another vital step. Buyers should ask suppliers for quality management system reports, inspection records, and testing results. These documents provide transparency and reassurance that the supplier maintains high-quality standards throughout the manufacturing process.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of potential challenges in quality control. Language barriers, cultural differences, and varying regulatory standards can complicate supplier relationships. It is essential for buyers to establish clear communication channels and set explicit expectations regarding quality standards and certifications. Building a relationship of trust and transparency can significantly enhance the quality assurance process.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for RMS finishing is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing stages, alongside robust QC measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers that meet their specific needs and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rms finishing’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring RMS finishing services effectively, this guide outlines critical steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. Understanding the nuances of RMS finishing and evaluating suppliers on various parameters can lead to better quality products and long-term partnerships.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements for your RMS finishing needs. This includes the desired surface roughness levels, such as Ra and RMS values, material types, and specific industry standards your products must meet. Providing detailed specifications helps suppliers understand your expectations and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in RMS finishing. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of qualified candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before proceeding, verify the certifications and compliance of your shortlisted suppliers. Check for ISO certifications relevant to quality management (ISO 9001) and environmental management (ISO 14001). These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to international standards and practices, which is crucial for maintaining product quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Case Studies
Request product samples and case studies from potential suppliers to assess their capabilities. Evaluating samples will give you firsthand insight into the quality of their RMS finishing work. Case studies can illustrate their experience with similar projects, showcasing their ability to meet specific requirements and deadlines.
Step 5: Assess Technical Capabilities
Understand the technical capabilities of your suppliers, including the equipment and processes they use for RMS finishing. Inquire about their use of advanced technologies like electropolishing and mechanical polishing, as these can significantly impact surface quality. Suppliers should demonstrate expertise in producing finishes that meet your precise specifications.
Step 6: Analyze Pricing and Terms
Request detailed quotations from multiple suppliers to compare pricing structures. Ensure that you understand what is included in the quoted prices, such as material costs, labor, and any additional services like post-processing. Also, review payment terms and delivery timelines to ensure they align with your project requirements.
Step 7: Establish Communication Protocols
Once you’ve selected a supplier, establish clear communication protocols to facilitate ongoing collaboration. Define points of contact, preferred communication channels, and regular check-in schedules to discuss progress and any issues that may arise. Effective communication is essential to maintaining a strong supplier relationship and ensuring that project milestones are met.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing RMS finishing services with confidence, ensuring they find reliable suppliers capable of delivering high-quality results.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rms finishing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in RMS Finishing Sourcing?
When engaging in RMS finishing sourcing, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences costs. High-quality metals or specialized alloys may carry a premium, but they can enhance the final product’s durability and performance. It’s crucial to balance material quality with budget constraints.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is often required for RMS finishing processes, which can include electropolishing or mechanical polishing. Labor costs vary depending on the region; for instance, labor may be more expensive in Europe compared to South America or Africa.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, equipment depreciation, and facility costs. Efficient operations can help minimize these overheads, allowing for competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Investment in specialized tooling for RMS finishing can be substantial. The type of tooling required will depend on the specific finishing techniques employed and the complexity of the components being processed.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure that the finished products meet the required specifications and standards. This can include inspection, testing, and certification, which add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the destination and the chosen Incoterms. International shipping may introduce additional fees, including tariffs and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect RMS Finishing Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in RMS finishing sourcing:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchasing to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications often lead to increased costs. Standardized products may be cheaper, but they might not meet all performance requirements.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of premium materials and obtaining certifications (such as ISO or ASME) can drive up costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these certifications based on their application.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their quality assurance processes, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects logistics costs. CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) pricing may seem higher, but it could cover potential risks, making it a safer option for international buyers.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating RMS Finishing Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, and the Middle East, effective negotiation and understanding pricing nuances are crucial:
-
Conduct Thorough Research: Understand market rates and typical pricing structures for RMS finishing services. This knowledge arms buyers with leverage during negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial costs but also the long-term implications of sourcing decisions. This includes maintenance costs, durability, and potential operational efficiencies gained from higher quality finishes.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate not only on price but also on payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Flexible terms can provide significant value.
-
Utilize Local Networks: Engage with local industry groups or trade associations to gain insights and potentially find suppliers who are more aligned with your budget and quality needs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for RMS finishing services can vary widely based on numerous factors, including the specifics of the project, geographic location, and supplier dynamics. Buyers should approach pricing discussions with an understanding that costs can fluctuate based on market conditions and operational requirements. Always request detailed quotes and clarify all components involved in the pricing structure.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rms finishing With Other Solutions
When evaluating surface finishing options for industrial applications, it is essential to consider various alternatives that can achieve similar outcomes to RMS finishing. Each method has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making it crucial for B2B buyers to understand these differences to make informed purchasing decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | RMS Finishing | Mechanical Polishing | Electropolishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, effective in reducing surface roughness | Effective for macroscopic blemishes, less effective on microscopic level | Can improve surface finish by up to 50%, excellent for fine finishes |
| Cost | Moderate investment | Generally lower cost | Higher initial investment but cost-effective for large batches |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators, specific machinery | Easier to implement, less specialized equipment needed | More complex setup, requires specific chemical processes |
| Maintenance | Moderate maintenance | Low maintenance | Regular monitoring of chemical baths required |
| Best Use Case | Precision components in aerospace and medical industries | General manufacturing where visual appearance is key | Applications requiring corrosion resistance and cleanliness, like food and pharmaceutical industries |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Mechanical Polishing Compared to RMS Finishing?
Mechanical polishing utilizes abrasive materials to enhance surface quality. This method is well-suited for removing visible surface defects and achieving a smoother finish. One of its primary advantages is its lower cost and ease of implementation, which makes it accessible for various manufacturing environments. However, it may not effectively address microscopic surface roughness, which is where RMS finishing excels. Mechanical polishing often requires additional treatments for specific applications, limiting its versatility compared to RMS.
How Does Electropolishing Stand Against RMS Finishing in Terms of Effectiveness?
Electropolishing is a chemical process that removes a thin layer of material from a metal surface, resulting in a smoother finish. This method is particularly effective in achieving high levels of cleanliness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. While electropolishing can provide substantial improvements in surface quality—up to 50%—it requires a more complex setup and higher initial costs. Additionally, regular maintenance of the chemical baths used in this process can add to operational overhead. For applications where surface cleanliness is paramount, electropolishing may be the preferred choice over RMS finishing.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Surface Finishing Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting a surface finishing solution, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific application requirements, including the desired surface quality, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. For precision applications in highly regulated industries, RMS finishing may be the best choice due to its ability to achieve precise surface roughness. Conversely, for general manufacturing needs or aesthetic improvements, mechanical polishing could be more cost-effective. Electropolishing is ideal for applications that demand high levels of cleanliness and corrosion resistance. By weighing the pros and cons of each method against their unique needs, buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their production processes and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rms finishing
What Are the Key Technical Properties for RMS Finishing?
When considering RMS (Root Mean Square) finishing, several critical technical properties are essential for ensuring product quality and performance. Understanding these specifications can significantly affect procurement and manufacturing processes.
1. Surface Roughness (Ra and RMS)
Surface roughness is a crucial property measured in micrometers (µm) or micro-inches (µin). Ra, or Roughness Average, calculates the average height of surface peaks and valleys, while RMS focuses on the square root of the average of squared deviations. For B2B buyers, knowing the required surface roughness can impact product performance, especially in applications involving sealing, friction, and aesthetic appeal.
2. Material Grade
Material grade specifies the composition and mechanical properties of the material used in manufacturing. Common grades for metals include stainless steel grades like 304 and 316. Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital, as it influences the durability, corrosion resistance, and overall functionality of the finished product. Buyers must ensure that the material aligns with industry standards and application requirements.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable deviation from a specified dimension, which can be critical in precision engineering. For RMS finishing, typical tolerances can range from ±0.01 mm to ±0.5 mm, depending on the application. Precise tolerances are necessary to guarantee that components fit correctly and function as intended. Inaccuracies can lead to costly reworks or product failures, making tolerance a key consideration in procurement decisions.
4. Finish Grade
Finish grade refers to the standard of the surface finish, which can include various classifications like 2B, No. 4, or No. 8 for stainless steel. These grades denote the level of polishing and finishing applied. Understanding finish grades is essential for B2B buyers as they affect both aesthetic qualities and functional performance, particularly in sanitary and high-visibility applications.
5. Coating and Treatment Specifications
Different coatings and treatments, such as passivation or electropolishing, can enhance surface properties like corrosion resistance and cleanliness. Buyers need to evaluate the benefits of these treatments based on their industry requirements. Coatings can also affect the surface roughness measurements, making it essential to specify them during the finishing process.
What Are Common Trade Terms in RMS Finishing?
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms relevant to RMS finishing.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape is critical for buyers to identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory effectively and minimize costs, particularly when dealing with specialized RMS finishing services.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. It is a crucial step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of predefined rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for buyers to understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, ensuring smooth transactions across borders.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and inventory management, particularly in industries where timely delivery is critical to operational efficiency.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize procurement processes, and enhance overall operational success in RMS finishing projects.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rms finishing Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the RMS Finishing Sector?
The global landscape for RMS (Root Mean Square) finishing is shaped by several key drivers and trends that international B2B buyers need to understand. The demand for high-quality surface finishes continues to rise across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. This is particularly true for emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where industrial growth is accelerating. Notably, advancements in technology, such as automation and precision measurement tools, are transforming sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for supplier selection, enabling them to access global markets with ease.
Emerging trends also include a growing emphasis on customization and rapid prototyping, which necessitate suppliers who can deliver tailored RMS finishing solutions. As industries increasingly adopt lean manufacturing principles, the need for efficient and cost-effective finishing processes has become paramount. Additionally, sustainability is now a significant factor influencing sourcing decisions; buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide environmentally friendly finishing solutions without compromising quality.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Decisions in the RMS Finishing Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical components in the B2B marketplace, particularly in the RMS finishing sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and businesses are expected to adopt more sustainable practices. This shift is not merely a trend but a necessity, driven by regulatory pressures and consumer demand for greener products.
International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. The use of eco-friendly materials, such as water-based solvents and recycled substrates, is gaining traction. Furthermore, companies are focusing on ethical supply chains to ensure that their sourcing practices do not contribute to environmental degradation or social injustice. As a result, buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers’ environmental practices and certifications, ensuring that they align with their sustainability goals.
What Is the Historical Context of RMS Finishing That Influences Current Practices?
The RMS finishing sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Historically, surface finish standards were primarily defined by the automotive and aerospace industries, where precision was paramount. As technology advanced, so did the methods for achieving desired surface finishes, with RMS and Ra (Roughness Average) becoming the standard metrics for quality assessment.
The introduction of digital profilometers and sophisticated machining techniques allowed for more accurate measurements of surface roughness, leading to improved quality control in manufacturing processes. Today, RMS finishing is not only about achieving specific measurements but also about enhancing the performance and durability of materials. This historical evolution informs current practices, as buyers now seek suppliers who understand both the technical aspects of finishing and the broader implications of their processes on quality, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
By understanding these dynamics, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals while ensuring they are sourcing from responsible and innovative suppliers in the RMS finishing sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rms finishing
-
How do I solve surface roughness issues in my products?
To address surface roughness issues, first assess the specific requirements for your application. Determine whether you need a smoother finish for aesthetic reasons or functional purposes, such as reducing friction or improving adhesion. Depending on the material, techniques like electropolishing or mechanical polishing can be effective. Electropolishing can enhance surface smoothness by up to 50%, while mechanical polishing is suitable for removing larger imperfections. Collaborate closely with your finishing supplier to select the best process and ensure that they can meet your desired roughness specifications. -
What is the best surface finish for stainless steel components?
The optimal surface finish for stainless steel components typically depends on the intended application. For general use, a No. 4 finish offers a good balance between aesthetics and functionality. For applications requiring high corrosion resistance and cleanliness, a No. 8 mirror finish may be preferred. If you’re in the food or pharmaceutical industries, consider electropolishing, which not only enhances aesthetics but also provides superior cleanliness. Always consult with your supplier to ensure the chosen finish meets industry standards and your specific requirements. -
How can I verify the quality of a supplier for rms finishing?
To verify the quality of a supplier for rms finishing, start by assessing their certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Request samples of their previous work and check client references to gauge satisfaction levels. It’s beneficial to conduct an on-site visit, if possible, to inspect their facilities and processes. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance protocols, including the use of profilometers for measuring surface roughness. A reputable supplier will be transparent about their processes and willing to provide documentation of their quality control measures. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rms finishing services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rms finishing services can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the finishing process. Many suppliers establish MOQs to cover production costs and ensure efficiency. For smaller businesses or new projects, it’s advisable to discuss flexibility with the supplier; some may accommodate lower MOQs for trial runs or prototype work. Always clarify MOQs before placing an order to avoid unexpected costs or delays, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing rms finishing internationally?
Payment terms when sourcing rms finishing internationally can vary based on the supplier’s policies and the buyer’s location. Common terms include net 30 or net 60 days, where payment is due within that timeframe after the invoice date. Some suppliers may require a deposit upfront, especially for larger orders or custom work. It’s crucial to establish clear payment terms before finalizing any agreements, and consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit for larger transactions to mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
How do I ensure compliance with international trade regulations for rms finishing?
To ensure compliance with international trade regulations for rms finishing, familiarize yourself with both your home country’s import/export laws and the regulations of the supplier’s country. This includes understanding tariffs, customs duties, and any specific certifications required for your products. Engage with a customs broker or trade compliance expert who can guide you through the complexities of international shipping. Additionally, ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as certificates of origin and compliance with international standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing rms finishing?
When sourcing rms finishing, logistics considerations are critical for timely delivery and cost management. Assess shipping options, including air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Evaluate the supplier’s location in relation to major shipping routes to minimize transit times. Ensure that the supplier has reliable packaging methods to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, factor in customs clearance times and potential delays, and consider working with logistics providers who specialize in international shipping to streamline the process. -
How can I customize rms finishing to meet specific project needs?
Customizing rms finishing to meet specific project needs involves clear communication with your supplier regarding your requirements. Discuss the desired surface roughness, aesthetics, and functional properties you aim to achieve. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions, such as varying the finishing process or combining multiple techniques to meet complex specifications. Request samples and prototypes to evaluate the results before committing to larger orders. Collaborative development with your supplier can lead to innovative solutions that enhance product performance and market competitiveness.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Rms Finishing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Engineers Edge – Surface Finish Insights
Domain: engineersedge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the surface finish of a 1/2” thick aluminum plate that is being sent out for a vertical brush finish. The key focus is on the RMS (Root Mean Square) values that indicate surface roughness. RMS values mentioned include: RMS 63 (smooth surface finish), RMS 125 (average manufacturing surface), and RMS 25 (very clean smooth surface finish). The text also clarifies that …
2. Harrison EP – Electropolishing Services
Domain: harrisonep.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Electropolishing services for various materials including stainless steel, nickel, Hastelloy, and aluminum. Benefits include improved cleanability, corrosion resistance, surface finish, reduced product adhesion, and restoration of polished surfaces. Applications span industries such as marine, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and aerospace. Surface roughness calculations for Ra and RMS are provided,…
3. Next Gen Tooling – Surface Roughness Measurement
Domain: nextgentooling.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: RMS and Ra are methods of calculating surface roughness using a profilometer. Ra (Roughness Average) is the arithmetic average of surface heights, while RMS (Root Mean Square) is calculated by taking the square root of the average of the squared height deviations. Ra is more commonly used today, especially in metric measurements, while RMS was more popular in the past when US industry primarily us…
4. LJ Star – Surface Finish Solutions
Domain: ljstar.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: LJ Star offers surface finish charts detailing mechanical polishing and electropolishing processes. Electropolishing is highlighted as the most effective method for removing surface abnormalities, providing superior surfaces for cleaning and sterilization, enhancing corrosion resistance, and reducing surface friction. The text discusses various surface finish standards, emphasizing the importance …
5. Integrate Technologies – RMS Finish Specifications
Domain: integratechnologies.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: RMS Finish is a surface finish specification for flanges, typically ranging from 125 to 250 RMS, commonly used with spiral wound gaskets. For higher-pressure flanges, a finer finish of RMS 60 is utilized for RTJ gaskets. The process involves ensuring the machine is level and centered to achieve the best finish, adhering to ASME codes. Quality assurance checks are performed to ensure the finish mee…
6. Vapor Honing Technologies – Essential Surface Finishing Guide
Domain: vaporhoningtechnologies.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The Only Surface Finishing Chart (and Guide) You’ll Ever Need provides essential information on surface finishes, including definitions, measurement methods, and key parameters. It explains the importance of surface finishes in equipment performance, how to measure them using contact and non-contact methods, and details various measurement units such as Maximum Roughness Depth (Rmax), Mean Roughne…
7. NE Electropolishing – Surface Roughness Measurement Solutions
Domain: neelectropolishing.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: RMS and RA are tools for measuring metal surface roughness. RMS (Root Mean Square) measures surface roughness of irregular surfaces using a professional-grade profilometer, calculating the vertical distance between peaks and valleys. RA (Roughness Average) measures the average of absolute values of surface roughness, also using a profilometer to determine deviations from the mean line. Both method…
8. GD&T Basics – Surface Finish Essentials
Domain: gdandtbasics.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Surface finish refers to the texture of a surface, often specified in technical drawings for mechanical parts. It consists of three elements: roughness, lay, and waviness. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) has published standards Y14.36M and B41.6 for surface texture symbols and definitions. Roughness is the most commonly specified aspect, measured using a profilometer, with para…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rms finishing
In the realm of rms finishing, understanding surface roughness measurements—specifically Ra and RMS—is crucial for ensuring optimal product performance. Both metrics provide insights into surface quality, yet they cater to different industry needs; Ra offers a straightforward average, while RMS emphasizes the impact of surface imperfections. For international B2B buyers, this distinction can guide material selection and processing choices, directly influencing product durability and functionality.
Strategic sourcing in rms finishing not only enhances supply chain efficiency but also fosters partnerships with reliable suppliers capable of meeting stringent surface finish standards. As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe evolve, the demand for high-quality finishes will continue to rise, necessitating a proactive approach to sourcing.
Looking ahead, international buyers should leverage advancements in finishing technologies and supplier capabilities to stay competitive. Embracing strategic sourcing will not only optimize operational efficiency but also position businesses to meet the growing demands of diverse markets. Engage with suppliers today to explore innovative finishing solutions that can elevate your product offerings and drive success in the global marketplace.