Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rms finish
In an increasingly competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the pressing challenge of sourcing high-quality rms finish solutions that meet their specific operational needs. Understanding the nuances between various surface finish measurements—such as Ra and RMS—can significantly impact product performance and quality. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, exploring the different types of rms finishes, their applications across industries, and the critical factors to consider when vetting suppliers.
By delving into the intricacies of surface roughness calculations and industry standards, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Nigeria and Germany, will be equipped with actionable insights. This guide not only outlines how to assess costs effectively but also highlights best practices for supplier engagement, ensuring that purchasing decisions are both informed and strategic.
With a focus on empowering B2B buyers, this resource aims to demystify the complexities of rms finishes and provide the tools needed to navigate the global market confidently. Whether you are looking to enhance product quality or streamline procurement processes, understanding rms finishes is essential for achieving operational excellence and maintaining a competitive edge in today’s marketplace.
Understanding rms finish Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electropolished | Achieves a smooth, shiny finish by removing material via electrolysis | Medical devices, food processing | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, improved hygiene. Cons: Higher cost, limited dimensional tolerance. |
| Mechanical | Involves physical polishing or grinding to reduce surface roughness | Aerospace, automotive components | Pros: Effective for large surface areas, customizable finishes. Cons: May not achieve as fine a finish as electropolishing. |
| Anodized | Electrochemical process that thickens the natural oxide layer on metals | Electronics, architectural finishes | Pros: Enhanced durability, corrosion resistance. Cons: Limited color options, not suitable for all metals. |
| Blasted | Uses abrasive materials to create a textured finish | Construction, industrial parts | Pros: Increases surface area for coatings, good adhesion. Cons: Can create micro-cracks, not suited for precision applications. |
| Passivated | Chemical treatment that enhances corrosion resistance | Chemical processing equipment | Pros: Improves durability, reduces maintenance needs. Cons: May not improve aesthetics significantly. |
What Are the Characteristics of Electropolished Finishes?
Electropolished finishes are characterized by their exceptionally smooth and shiny appearance, achieved through an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material from the surface. This type of finish is particularly suitable for industries requiring high hygiene standards, such as medical devices and food processing. When considering electropolishing, B2B buyers should evaluate the cost against the significant benefits of corrosion resistance and cleanliness, as well as the need for precise dimensional tolerances.
How Do Mechanical Finishes Differ in Application?
Mechanical finishes involve traditional methods such as grinding, polishing, or sanding to achieve the desired surface roughness. These finishes are widely used in the aerospace and automotive sectors, where large surface areas require effective treatment. Buyers should consider the versatility of mechanical finishes, as they can be tailored to specific requirements, though they may not reach the fine surface smoothness provided by electropolishing.
What Makes Anodized Finishes a Popular Choice?
Anodized finishes are created through an electrochemical process that enhances the natural oxide layer on metals, primarily aluminum. This process increases durability and corrosion resistance, making anodized finishes ideal for applications in electronics and architectural elements. However, B2B buyers should note that while anodizing enhances performance, it may limit aesthetic options in terms of color and is not applicable to all metal types.
Why Choose Blasted Finishes for Industrial Applications?
Blasted finishes utilize abrasive materials to create a textured surface, which is beneficial for improving the adhesion of paints and coatings in construction and industrial settings. While this type of finish increases surface area, it can also introduce micro-cracks that may compromise structural integrity. Buyers should weigh the advantages of enhanced coating adhesion against the potential drawbacks when considering blasted finishes for their products.
What Are the Benefits of Passivated Finishes?
Passivated finishes involve a chemical treatment process that significantly enhances the corrosion resistance of metals, making them ideal for chemical processing equipment. This finish type is advantageous for B2B buyers looking to reduce maintenance needs and prolong the lifespan of their equipment. However, it is essential to note that passivation may not significantly improve the aesthetic qualities of the surface, which could be a consideration for certain applications.
Key Industrial Applications of rms finish
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of rms finish | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine Components | Enhanced durability and performance under extreme conditions | Certification compliance, precision tolerances, and material grade |
| Pharmaceutical | Medical Devices | Reduced risk of contamination and improved hygiene | Regulatory standards, biocompatibility, and surface finish consistency |
| Food Processing | Equipment for Food Production | Improved sanitation and reduced product adhesion | Food safety certifications, material resistance to corrosion, and ease of cleaning |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline and Valve Manufacturing | Enhanced flow efficiency and reduced maintenance costs | Material specifications, resistance to harsh environments, and dimensional accuracy |
| Automotive | Fuel Injection Systems | Improved fuel efficiency and engine performance | Supplier reliability, quality assurance processes, and adherence to industry standards |
How is ‘rms finish’ Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, components such as engine parts and turbine blades benefit significantly from an rms finish. This surface finish enhances durability, enabling parts to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. The precision required in these applications demands strict adherence to certification standards, making it essential for buyers to source materials that meet specific tolerances and performance criteria. International buyers, particularly from regions like Europe and the Middle East, should ensure that suppliers provide documentation confirming compliance with aerospace standards.
Why is ‘rms finish’ Critical in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
The pharmaceutical sector relies heavily on rms finishes for medical devices and production equipment. A smooth surface reduces the risk of contamination, which is critical in maintaining product integrity and safety. Buyers in this sector must consider regulatory requirements, including biocompatibility and cleanliness standards, when sourcing materials. Additionally, consistent surface finishes are crucial for ensuring reliable product performance, making supplier quality assurance processes a vital consideration for international buyers.
What Role Does ‘rms finish’ Play in Food Processing Equipment?
In food processing, rms finishes are essential for equipment that requires high levels of sanitation. A smoother surface reduces product adhesion, making cleaning easier and enhancing hygiene. Buyers must focus on food safety certifications and material resistance to corrosion when sourcing equipment. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local regulations regarding food safety and equipment standards is critical to ensure compliance and operational efficiency.
How Does ‘rms finish’ Improve Efficiency in Oil & Gas?
In the oil and gas sector, rms finishes are applied to pipelines and valves to enhance flow efficiency and reduce maintenance needs. A well-finished surface minimizes turbulence and friction, leading to better performance and lower operational costs. Buyers should prioritize sourcing materials that can withstand harsh environments and meet stringent dimensional accuracy requirements. For international buyers, particularly in areas with emerging markets, it is essential to assess supplier capabilities in delivering high-quality finishes that adhere to industry standards.
Why is ‘rms finish’ Important for Automotive Fuel Systems?
Automotive manufacturers utilize rms finishes in fuel injection systems to improve fuel efficiency and engine performance. A smooth surface allows for better fuel atomization and reduces wear on components. Buyers in this sector need to consider supplier reliability and quality assurance processes to ensure consistent performance. International buyers, particularly from Europe and South America, should also be aware of regional automotive standards that influence material choices and surface finish requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rms finish’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of RMS Finish Across Suppliers
The Problem:
B2B buyers often struggle with sourcing components that meet their specific surface finish requirements, particularly when working with multiple suppliers. The inconsistency in the RMS finish can lead to significant issues, such as product failures or increased wear in machinery, ultimately affecting performance and reliability. This variability can be particularly challenging for manufacturers in sectors such as aerospace and automotive, where precise tolerances are critical. Buyers may find themselves receiving parts with roughness levels that do not align with their stringent standards, leading to costly delays and rework.
The Solution:
To mitigate this problem, buyers should establish a clear set of specifications for the RMS finish they require. This should include detailed metrics, such as acceptable RMS values, surface texture profiles, and any relevant industry standards. It is advisable to request certification or test results for the surface finishes from suppliers to ensure compliance with these specifications. Additionally, developing long-term partnerships with a select group of suppliers who have proven track records can help maintain consistency. Regular audits and quality checks can further ensure that the surface finish remains within acceptable limits, reducing the risk of receiving non-compliant products.
Scenario 2: Misunderstanding Between Ra and RMS Measurements
The Problem:
A common pain point for B2B buyers is the confusion between Ra (Roughness Average) and RMS (Root Mean Square) measurements. This misunderstanding can lead to miscommunication with suppliers and ultimately result in sourcing parts that do not meet the intended performance criteria. For example, if a buyer specifies a surface finish in Ra without clarifying the RMS equivalent, they may receive components with a surface texture that is too rough, impacting their application. Such discrepancies can also lead to increased friction, wear, and failure in mechanical assemblies.
The Solution:
To address this issue, it is essential for buyers to educate themselves and their teams about the differences between Ra and RMS measurements. Buyers should take the initiative to include both specifications in their purchasing documents, clarifying the acceptable ranges for each. When discussing surface finishes with suppliers, asking for both Ra and RMS values can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the surface quality. Furthermore, utilizing profilometers to measure surface finishes before accepting deliveries can help ensure compliance with the required specifications, reducing the risk of operational failures.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Achieving Desired Surface Finish for Complex Geometries
The Problem:
Manufacturers often face challenges in achieving the desired RMS finish on complex geometries, such as intricate molds or components with tight tolerances. The difficulty arises from the limitations of standard finishing techniques, which may not adequately reach all surface areas or may alter the dimensions of the parts during the finishing process. This can lead to a surface that is either too rough or uneven, compromising the functionality of the final product. Buyers in industries like medical devices or precision engineering are particularly affected, where surface finish is critical for performance and regulatory compliance.
The Solution:
To overcome these challenges, buyers should explore advanced finishing techniques tailored for complex geometries. Techniques such as precision electropolishing or abrasive flow machining can provide uniform RMS finishes on intricate shapes without compromising dimensional integrity. When sourcing these services, it is vital to communicate the specific requirements and geometry of the components to the finishing provider. Additionally, conducting small-scale trials with potential suppliers can help assess their capability to achieve the desired surface finish before committing to larger production runs. Implementing a robust feedback loop with the finishing vendor can also ensure continuous improvement and adaptation of processes to meet evolving requirements.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rms finish
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for rms Finish?
When selecting materials for achieving an optimal rms finish, several factors come into play, including the material’s inherent properties, its suitability for specific applications, and regional compliance standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in achieving an rms finish: stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and carbon steel.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in rms Finish Applications?
Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications exposed to moisture and harsh chemicals. It typically has a high-temperature rating, allowing it to maintain structural integrity under elevated conditions.
Pros: Its durability and aesthetic appeal make stainless steel a popular choice. It also offers good machinability and can be easily polished to achieve a high-quality finish.
Cons: However, stainless steel can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized machining tools, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including food and pharmaceuticals, making it suitable for industries that require stringent hygiene standards.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or DIN 17440 is crucial. Buyers from regions like Germany may prioritize materials that meet European Union regulations, while those in Africa and South America may consider local certifications.
What Are the Benefits of Aluminum for rms Finish?
Aluminum is lightweight and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where weight savings are critical. It also has good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros: The material is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, allowing for efficient manufacturing processes. Its ability to be anodized enhances its surface finish further.
Cons: Aluminum’s lower strength compared to stainless steel and susceptibility to scratching can be limiting factors in high-wear applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used in automotive and aerospace applications, where weight reduction is essential. Its compatibility with various media makes it versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that their aluminum selections comply with standards such as ASTM B221 or JIS H4000, especially when dealing with aerospace or automotive components.
Why Choose Titanium for rms Finish Applications?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, particularly in aggressive environments.
Pros: Its durability makes it suitable for demanding applications, including aerospace and medical devices. Titanium can achieve a high-quality finish, enhancing both performance and aesthetics.
Cons: The primary drawback is its high cost and the complexity involved in machining, which can lead to increased production times.
Impact on Application: Titanium is often used in applications requiring biocompatibility, such as implants. Its resistance to corrosion also makes it suitable for marine environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM F136 or ISO 5832-2 is essential for medical applications. Buyers should also be aware of the availability of titanium in their local markets.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Achieving rms Finish?
Carbon steel is a versatile material widely used in various industrial applications due to its strength and availability.
Pros: It is relatively inexpensive and can be easily machined to achieve a desirable finish. Its strength makes it suitable for structural applications.
Cons: However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can limit its use in certain environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in construction and manufacturing, but its compatibility with certain media must be assessed to prevent corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that carbon steel complies with standards such as ASTM A36 or JIS G3101, particularly in construction projects.
Summary Table of Material Selection for rms Finish
| Material | Typical Use Case for rms finish | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength, scratches easily | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength and durability | High cost and machining complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction, manufacturing | Versatile and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion without treatment | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for achieving an optimal rms finish, catering specifically to the needs of international B2B buyers in diverse regions. Understanding these materials’ properties, advantages, and limitations will aid in making informed procurement decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rms finish
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Achieving an RMS Finish?
Achieving a high-quality RMS (Root Mean Square) finish involves a series of meticulous manufacturing processes. For B2B buyers, understanding these stages is crucial for selecting the right suppliers and ensuring product quality.
How Is Material Prepared for RMS Finish?
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate raw materials, which can vary based on the desired finish and application. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and various alloys.
Before any processing begins, materials undergo inspections for defects or inconsistencies. This includes visual inspections and dimensional checks to ensure they meet specifications. After this, the materials are cut or shaped to the required dimensions, often using precision machining techniques.
What Forming Techniques Are Used to Achieve RMS Finish?
Once the materials are prepared, they move to the forming stage. This can involve several techniques, including:
-
CNC Machining: Utilizing computer numerical control machines allows for high precision in shaping materials. CNC machines can create complex geometries while maintaining consistent surface quality.
-
Casting and Forging: These methods can be employed for bulk material shaping. However, they usually require further finishing to meet RMS standards.
-
Bending and Stamping: These processes are useful for creating specific shapes and are often used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Each technique has implications for the final surface finish, making it essential to choose the right method based on the application and desired RMS value.
What Are the Finishing Techniques That Improve Surface Quality?
The finishing stage is critical for achieving the desired RMS finish. Techniques include:
-
Electropolishing: This electrochemical process removes material from the surface, improving smoothness and corrosion resistance. It can enhance surface finish by up to 50%, making it a popular choice for achieving low RMS values.
-
Mechanical Polishing: This method uses abrasives to smooth the surface at a macroscopic level, removing visible blemishes and enhancing the overall appearance.
-
Passivation: Typically applied to stainless steel, passivation improves corrosion resistance and can enhance surface smoothness.
Selecting the right finishing technique often depends on the specific application requirements, including aesthetic considerations and performance metrics.
How Is Quality Assurance Ensured in RMS Finish Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring that products meet the stringent requirements associated with RMS finishes. International and industry-specific standards guide this process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for RMS Finish?
ISO 9001:2015 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems that applies to various industries, including manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that processes are standardized, and quality is consistently monitored.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industries may require adherence to other certifications, such as:
-
CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety and health standards.
-
API Standards: Relevant for the oil and gas industry, ensuring that equipment meets specific performance and safety benchmarks.
Understanding these standards helps B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers based on their compliance and quality management practices.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in RMS Finish Production?
Quality control (QC) is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This is the initial inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. It ensures that the materials meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, continuous monitoring is conducted to identify any deviations from established parameters. This may involve periodic sampling and testing to ensure that the RMS finish is being achieved consistently.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products are shipped, a final inspection is conducted to verify that all specifications, including surface finish, are met. This may involve using profilometers to measure surface roughness accurately.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance.
What Methods Can Buyers Use to Verify QC Processes?
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits is a practical way to assess the effectiveness of a supplier’s quality management system. Audits can be done by the buyer’s quality assurance team or through third-party services.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC processes, including the frequency of inspections and the results of any tests conducted.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing processes can provide an unbiased view of the supplier’s capabilities. This is particularly valuable for buyers in regions with different regulatory environments.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
B2B buyers need to be aware of the nuances in QC and certification requirements that may vary by region. For example, European standards may differ significantly from those in Africa or South America. Understanding these differences helps buyers make informed decisions and avoid potential compliance issues.
Furthermore, buyers should consider the supplier’s experience in international trade, as this often correlates with their understanding of various certifications and quality standards. Collaborating with suppliers who have a proven track record in international markets can reduce risks and enhance supply chain reliability.
Conclusion
In summary, achieving an RMS finish involves a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and rigorous quality assurance practices. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, finishing methods, and robust QC protocols, B2B buyers can ensure they select suppliers capable of delivering high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rms finish’
To assist international B2B buyers in sourcing RMS finish products effectively, this guide provides a clear checklist to streamline the procurement process. Understanding the nuances of surface finishes, particularly RMS, is essential for ensuring that the materials meet specific performance requirements.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by establishing clear technical specifications for the RMS finish you require. This includes determining the acceptable roughness levels, typically measured in micrometers (µm), and any particular standards applicable to your industry, such as ISO or ASME guidelines. Clearly articulated specifications will help you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers who specialize in RMS finish products. Look for companies that have a proven track record in your industry and check their certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Engaging with suppliers who understand your market—be it in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—can greatly enhance the quality of your sourcing process.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Pay particular attention to their capabilities in achieving the desired RMS finish, including their technology, machinery, and any unique processes they may employ, such as electropolishing.
Step 4: Request Samples for Quality Assessment
Always request samples of products that demonstrate the RMS finish you require. This step allows you to assess the quality firsthand, ensuring that the surface finish meets your specifications. Evaluate the samples for consistency in roughness and overall surface quality, as well as any imperfections that could affect performance.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the products you are considering comply with relevant industry standards. This may include checking for compliance with ASTM, ASME, or ISO standards related to surface finishes. Compliance not only assures quality but also minimizes risks associated with non-conformance in international markets.
Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations with selected suppliers regarding pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Be clear about your expectations and ensure that the terms reflect the quality of the RMS finish required. A well-negotiated contract can prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Plan
Once you have selected a supplier, establish a quality assurance plan that includes periodic reviews of the RMS finish quality. Regular audits and inspections can help maintain the desired surface finish levels and ensure ongoing compliance with your specifications. This proactive approach is essential for long-term supplier relationships.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the complexities of sourcing RMS finish products, ensuring that they meet their technical requirements and industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rms finish Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing RMS Finish?
Understanding the cost structure associated with sourcing an RMS finish is critical for B2B buyers. The primary components that contribute to the overall cost include:
-
Materials: The type of material significantly influences cost. Stainless steel, for instance, is commonly used for finishes, but variations in grade and alloy can lead to price fluctuations. Buyers should assess the specific material requirements to gauge potential costs accurately.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on the complexity of the finishing process. Techniques such as electropolishing or mechanical polishing require skilled technicians, which can increase labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative expenses. High-quality suppliers often have robust quality management systems in place, which can lead to higher overhead but also better product outcomes.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific finishes can be a significant cost driver. The need for specialized equipment or modifications to existing tools for unique specifications can increase initial investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the RMS finish meets specific standards. The costs associated with testing and certification are essential to factor in, especially for industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs should not be underestimated. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can all contribute to the total logistics cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a profit margin based on their operational costs, market demand, and competition. Understanding the market dynamics can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact RMS Finish Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of RMS finishes:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) and order volume can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized finishes or specific tolerances can increase costs. Clear communication of requirements can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and associated certifications (e.g., ISO, ASME) can impact pricing. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality materials and certifications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence prices. Established suppliers may charge more due to their expertise, while newer entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of trade (Incoterms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms can prevent unexpected costs and liabilities, particularly in logistics and customs.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in RMS Finish Sourcing?
B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing RMS finishes:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to discuss pricing structures, especially for larger orders. Building a rapport can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and potential operational costs that can arise from using lower-quality finishes.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers must be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local suppliers or distributors can mitigate some of these risks.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to benchmark prices against competitors. This can provide insights into fair pricing and help in negotiations.
-
Supplier Diversification: Consider multiple suppliers to reduce dependency on a single source. This approach can lead to better pricing and ensure continuity of supply.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rms finish With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to RMS Finish
In the realm of surface finishing, businesses often seek the most effective methods to achieve desired surface quality and performance. While RMS finish provides a reliable measurement of surface roughness, alternative solutions may offer distinct advantages depending on specific operational needs. Below is a comparative analysis of RMS finish against two prominent alternatives: electropolishing and mechanical polishing.
| Comparison Aspect | RMS Finish | Electropolishing | Mechanical Polishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Good for uniform surfaces | Excellent for micro-level finish | Effective for macroscopic blemishes |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial investment | Generally lower cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precise measurement | Needs specialized equipment | Easier to set up and operate |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate maintenance | High maintenance due to wear |
| Best Use Case | General applications in manufacturing | Medical devices, food industry | Automotive parts, decorative finishes |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Electropolishing Compared to RMS Finish?
Electropolishing is a widely recognized alternative that enhances surface finish at a microscopic level by removing material from the surface. The primary advantage of electropolishing is its ability to improve corrosion resistance and reduce surface roughness by up to 50%. This method is particularly beneficial in industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, where hygiene is paramount. However, the process can be costly and requires specific equipment, making it less accessible for smaller manufacturers.
How Does Mechanical Polishing Compare to RMS Finish?
Mechanical polishing stands out for its effectiveness in eliminating larger surface imperfections and achieving a smooth finish. This method is often more affordable and simpler to implement than electropolishing, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers. However, it may not achieve the same level of micro-smoothness as RMS finish or electropolishing, which could be a drawback for applications requiring high precision. Additionally, mechanical polishing can lead to increased maintenance costs due to the wear and tear on the equipment.
Conclusion: Which Surface Finishing Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting a surface finishing solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific application requirements, budget constraints, and operational capabilities. RMS finish offers a balanced approach for general manufacturing needs, while electropolishing is ideal for sectors requiring stringent cleanliness and surface quality standards. Mechanical polishing, on the other hand, serves well for applications where cost efficiency and ease of use are paramount. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on the unique demands of the buyer’s industry and the specific performance characteristics they aim to achieve.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rms finish
What Are the Key Technical Properties of RMS Finish?
When evaluating RMS (Root Mean Square) finish, several critical specifications come into play. Understanding these properties is vital for B2B buyers to ensure product quality and performance.
-
Surface Roughness (RMS Value)
The RMS value quantifies the average height deviations of a surface from its mean line, calculated through the root mean square method. This specification is crucial in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where surface integrity can impact product performance and longevity. A lower RMS value indicates a smoother surface, which is often necessary for reducing friction and wear in mechanical applications. -
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific classification of the material used in production, such as stainless steel or aluminum. Different grades have varying properties that influence corrosion resistance, strength, and machinability. Understanding material grades helps buyers select the right material for their applications, ensuring compliance with industry standards and performance requirements. -
Dimensional Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable variation in a part’s dimensions, which is critical in manufacturing processes. This specification ensures that components fit together correctly in assemblies. Inconsistent tolerances can lead to functionality issues, increased wear, and higher maintenance costs, making it essential for buyers to verify tolerance specifications before procurement. -
Finish Type
The finish type indicates the method used to achieve the surface quality, such as electropolishing or mechanical polishing. Each method has different effects on surface roughness and material properties. Selecting the appropriate finish type can improve the performance of parts in their intended applications, especially in environments subject to corrosion or wear. -
Evaluation Length
This refers to the length over which the surface roughness is measured. It is significant because variations in roughness can occur over different lengths, impacting the overall assessment of surface quality. Understanding the evaluation length helps buyers ensure that they are getting an accurate representation of the surface finish. -
Equivalent Ra Values
Ra (Roughness Average) values are often used interchangeably with RMS in some contexts. These values provide a simpler measure of surface roughness and can be essential for historical comparisons or regulatory compliance. Buyers should be aware of how these values correlate and their implications for product performance.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to RMS Finish?
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms related to RMS finish:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers as it often affects pricing, quality assurance, and supply chain reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers as it impacts inventory management and production planning. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses manage costs and avoid excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal request sent to suppliers to obtain pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is an essential part of the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare offerings and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping contracts. Familiarity with these terms is important for B2B transactions, especially in international trade, as they dictate who bears the risk and cost at various stages of the shipping process. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is critical for planning and inventory management, allowing businesses to align production schedules with market demand. -
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment encompasses various processes applied to a surface to enhance its properties, such as corrosion resistance or aesthetic appeal. Buyers must consider surface treatments when specifying products to ensure they meet the performance needs of their applications.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions regarding RMS finish, ensuring they select the right products for their specific needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rms finish Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing the RMS Finish Sector?
The global RMS finish market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for precision-engineered components across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Key trends include the adoption of automation and digitalization in manufacturing processes. Technologies such as CNC machining and advanced surface finishing techniques, including electropolishing, are becoming more prevalent. These innovations not only enhance the quality of surface finishes but also improve production efficiency and reduce lead times, making them attractive to international B2B buyers.
Furthermore, as sustainability becomes a priority, manufacturers are increasingly focusing on reducing waste and energy consumption during the finishing processes. This shift is particularly relevant for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where cost-effectiveness and environmental responsibility are paramount. The rise of Industry 4.0 is also influencing sourcing strategies, as real-time data analytics and IoT integration allow companies to optimize their supply chains and enhance decision-making capabilities.
In Europe, stringent regulations regarding product quality and environmental impact are pushing suppliers to adopt higher standards, such as ISO certifications. This trend is essential for buyers in Germany and other European nations who prioritize compliance and quality assurance in their sourcing processes. Ultimately, understanding these market dynamics will enable B2B buyers to make informed decisions and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affect the RMS Finish Sector?
In today’s marketplace, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the RMS finish sector. Companies are increasingly recognizing the environmental impact of their supply chains, prompting a shift towards more sustainable practices. This includes sourcing materials that have a lower carbon footprint and employing processes that minimize waste and energy usage.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to corporate social responsibility. This includes obtaining certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and utilizing green materials in their finishing processes. For instance, suppliers that employ eco-friendly chemicals or recyclable materials in their RMS finishing techniques can provide a competitive edge, appealing to buyers who prioritize sustainability.
Additionally, as global consumers become more environmentally conscious, the demand for products with verified sustainability credentials is rising. This trend is evident in markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that align with their ethical values. By focusing on sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can not only enhance their brand reputation but also tap into a growing market segment that values responsible production practices.
What Is the Historical Context of RMS Finishing Techniques?
The evolution of RMS finishing techniques can be traced back to the early days of industrial manufacturing, where surface finish was often an afterthought. Initially, mechanical polishing was the primary method employed to enhance surface quality. However, as industries advanced, the need for higher precision and improved surface integrity became apparent.
The introduction of more sophisticated techniques, such as electropolishing, revolutionized the RMS finish sector by providing a means to achieve superior surface finishes with enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Over the decades, the development of profiling technology has enabled manufacturers to measure and analyze surface roughness more accurately, leading to standardized metrics like Ra and RMS.
Today, the focus has shifted towards integrating advanced technologies such as automation and real-time data analytics into the finishing process. This historical context highlights the ongoing importance of innovation in meeting the evolving demands of international B2B buyers, ensuring that they have access to high-quality, precision-engineered products that meet modern standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rms finish
-
How do I determine the right surface finish specification for my application?
When selecting a surface finish, consider the functional requirements of your application. Analyze factors such as friction, wear resistance, aesthetic appeal, and regulatory compliance. For instance, certain industries like pharmaceuticals may require smoother finishes to prevent contamination, while aerospace components may prioritize durability. Collaborate with your suppliers to assess the technical specifications, including Ra and RMS values, that meet your performance criteria. Consulting industry standards can also guide you in making informed decisions. -
What is the difference between Ra and RMS surface finish measurements?
Ra (Roughness Average) and RMS (Root Mean Square) are both metrics for measuring surface roughness but are calculated differently. Ra provides an arithmetic average of surface heights, while RMS accounts for the square of height deviations, making it more sensitive to large peaks. In practice, Ra is more commonly used today, especially in metric specifications, due to its straightforward interpretation. Understanding these differences helps you choose the appropriate measurement for your specific requirements. -
What factors influence the cost of rms finish services?
Several factors can affect the cost of rms finish services, including the complexity of the required finish, the volume of materials, and the chosen finishing process (e.g., electropolishing vs. mechanical polishing). Additionally, geographical location can impact shipping and logistics costs. For B2B buyers, obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers and discussing your specific needs can help you find a competitive price while ensuring quality standards are met. -
What minimum order quantities (MOQ) should I expect when sourcing rms finishes?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among suppliers, often depending on the finishing process and the material type. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as 50 units, while others may require orders of 500 or more for custom finishes. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly and negotiate terms that align with your business requirements. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can sometimes lead to more flexible MOQ arrangements. -
How can I vet suppliers for rms finish services?
To ensure you select a reliable supplier for rms finishes, conduct thorough research. Look for suppliers with certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Request samples of their work and check references from previous clients. Additionally, assess their production capabilities and turnaround times to ensure they align with your project timelines. A site visit can also provide valuable insights into their operational standards. -
What payment terms are typically offered by rms finish suppliers?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments before delivery, or net terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). For international transactions, consider currency fluctuations and payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth procurement process. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from rms finish providers?
Reputable rms finish providers should implement stringent quality assurance (QA) measures to ensure product consistency and compliance with specifications. This includes regular inspections, in-process testing, and final quality checks before shipment. Request documentation of QA processes, such as inspection reports and compliance certifications. Understanding these measures will help you gauge the supplier’s commitment to quality and reliability. -
How do logistics and shipping impact the sourcing of rms finishes?
Logistics play a crucial role in the sourcing of rms finishes, particularly for international buyers. Consider factors such as shipping times, customs clearance, and freight costs. Partnering with suppliers who have robust logistics capabilities can streamline the delivery process. Additionally, understanding local regulations and import duties in your region will help you anticipate costs and avoid delays. Collaborating closely with your supplier can enhance transparency and efficiency in the logistics process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Rms Finish Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Harrison EP – Electropolishing Services
Domain: harrisonep.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: Electropolishing services for various materials including stainless steel, nickel, Hastelloy, and aluminum. Benefits include improved cleanability, corrosion resistance, surface finish, reduced product adhesion, and restoration of polished surfaces. Applications span industries such as marine, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and aerospace. The process can improve surface finish by up to 50%, with r…
2. NextGen Tooling – Surface Roughness Measurement Solutions
Domain: nextgentooling.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: RMS and Ra are methods for calculating surface roughness using a profilometer. Ra (Roughness Average) is the arithmetic average of surface heights, while RMS (Root Mean Square) is calculated as the square root of the average of the squared height deviations. Ra is more commonly used today, especially in metric measurements, while RMS was more popular in the past when US industry primarily used inc…
3. LJ Star – Sight Glasses and Sanitary Fittings
Domain: ljstar.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: LJ Star offers sight glasses, sanitary fittings, and visual flow indicators with a variety of surface finishes including mechanical polishing and electropolishing. Electropolishing is highlighted as the most effective method for removing burrs, folds, inclusions, and other surface abnormalities, resulting in a smoother, easier-to-clean surface. The surface finish is measured using roughness averag…
4. L&S Machine Company – CNC Machining & Waterjet Cutting
Domain: lsmachineco.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: L&S Machine Company offers CNC machining and waterjet cutting services with a focus on understanding surface finishes. They emphasize the importance of specifying the correct surface finish to avoid increased production time and costs. The company can achieve surface finishes ranging from 4 microinches (mirror-like finish) to 320 microinches (visible machining marks). They work closely with custom…
5. Engineers Edge – Aluminum Plate with Vertical Brush Finish
Domain: engineersedge.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
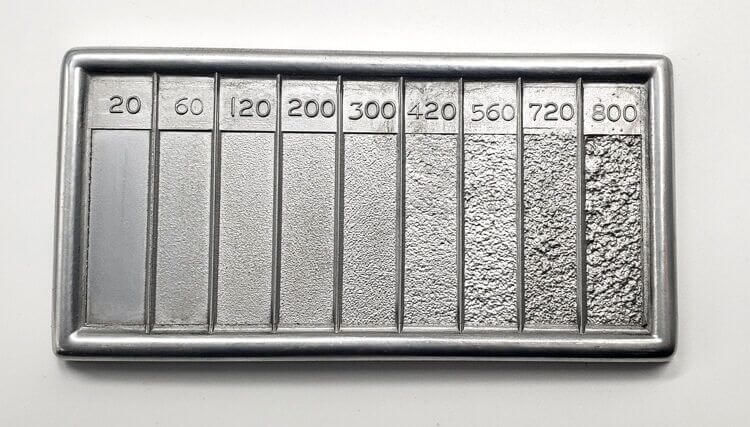
Introduction: 1/2” thick aluminum plate with a vertical brush finish; RMS values discussed include RMS 63 (smooth surface), RMS 125 (average manufacturing surface), and RMS 25 (very clean smooth surface finish). RMS (Root Mean Square) is used to measure surface roughness, with RMS values typically 11% higher than Ra (Roughness Average). Common RMS values mentioned include 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 125, 250, and 500.
6. Integrate Technologies – RMS Finish Specifications
Domain: integratechnologies.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: RMS Finish is a surface finish specification for flanges used with different types of gaskets. The typical RMS finish range is between 125 to 250, which is commonly utilized for spiral wound gaskets. For higher-pressure flanges, an RMS finish of 60 is recommended for RTJ gaskets to ensure a better seal. The process involves leveling the machine and ensuring it is centered to achieve the desired fi…
7. GD&T Basics – Surface Finish Essentials
Domain: gdandtbasics.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Surface finish refers to the texture of a surface, often specified in technical drawings for mechanical parts. It consists of three elements: roughness, lay, and waviness. Roughness is the most commonly specified aspect, measured using a profilometer, and represented by parameters Ra (average roughness) and Rz (mean roughness depth). Ra is typically used in the U.S., while Rz is more common intern…
8. Vapor Honing Technologies – Surface Finish Solutions
Domain: vaporhoningtechnologies.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: The text provides information about surface finishes, their importance, and measurement methods. Key details include: 1. Surface finishes determine the physical appearance and functionality of equipment. 2. Important parameters include surface lay, roughness, and waviness. 3. Measurement methods include contact (stylus) and non-contact (3D metrology). 4. Common surface finish units discussed are: …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rms finish
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers Regarding RMS Finish?
In navigating the complexities of surface finishes, particularly RMS (Root Mean Square), international B2B buyers must prioritize understanding the fundamental differences between RMS and Ra measurements. RMS is more sensitive to surface irregularities, making it crucial for applications where precision is paramount. This knowledge enables buyers to make informed decisions that enhance product performance and longevity, especially in industries like aerospace, automotive, and pharmaceuticals.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business Operations?
Strategic sourcing of materials with the appropriate surface finish not only reduces operational costs but also improves product quality. By selecting suppliers who adhere to stringent surface finish standards, buyers can ensure that their products meet international quality benchmarks. This is particularly vital for companies operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where regulatory compliance and quality assurance are non-negotiable.
What Should Buyers Consider Moving Forward?
As the demand for precision-engineered components continues to rise, the outlook for RMS finish remains promising. Buyers should actively seek partnerships with suppliers who offer advanced surface finishing technologies, such as electropolishing, to achieve superior surface quality. Engaging with manufacturers who understand the nuances of surface roughness can provide a competitive edge in the global marketplace. Embrace these insights to refine your sourcing strategy and drive your business forward.