Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for riveting process
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing, sourcing effective riveting processes can be a daunting challenge for B2B buyers. The riveting process stands out as a critical method for joining metal parts, offering unmatched strength and durability. However, navigating the complexities of rivet types, applications, and supplier capabilities requires a keen understanding of the market. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing various riveting techniques, including solid, blind, and self-piercing rivets, alongside their specific applications across industries such as automotive, construction, and electronics.
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, will find valuable insights into the intricacies of selecting the right riveting solutions. Our guide also addresses essential considerations such as supplier vetting processes, cost analysis, and quality assurance measures. By leveraging this information, you can make informed purchasing decisions that not only meet your operational needs but also align with global standards and practices.
Ultimately, this guide empowers you to streamline your sourcing strategies, ensuring that you select the most suitable riveting processes and partners for your business. With a focus on actionable insights and best practices, you can confidently navigate the global market, enhancing your competitive edge and driving successful project outcomes.
Understanding riveting process Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Riveting | Involves solid rivets deformed using a hammer or rivet gun | Structural applications (bridges, buildings) | Pros: High strength, reliable; Cons: Requires access to both sides |
| Blind Riveting | Can be installed from one side; uses a mandrel | Automotive, furniture, and HVAC systems | Pros: Easy installation in tight spaces; Cons: Limited strength compared to solid rivets |
| Press Riveting | Uses external pressure for deformation; mass production | Electronics, automotive assemblies | Pros: Fast and consistent; Cons: Equipment cost can be high |
| Pull Riveting | Deformation occurs under tension; suitable for thin materials | Aerospace and lightweight structures | Pros: Strong connection with minimal access; Cons: Requires specialized tools |
| Self-Piercing Riveting | Does not require pre-drilled holes; fastened by pressure | Automotive and metalworking industries | Pros: Quick installation, no pre-punching; Cons: May not be suitable for all materials |
What are the characteristics of Solid Riveting for B2B applications?
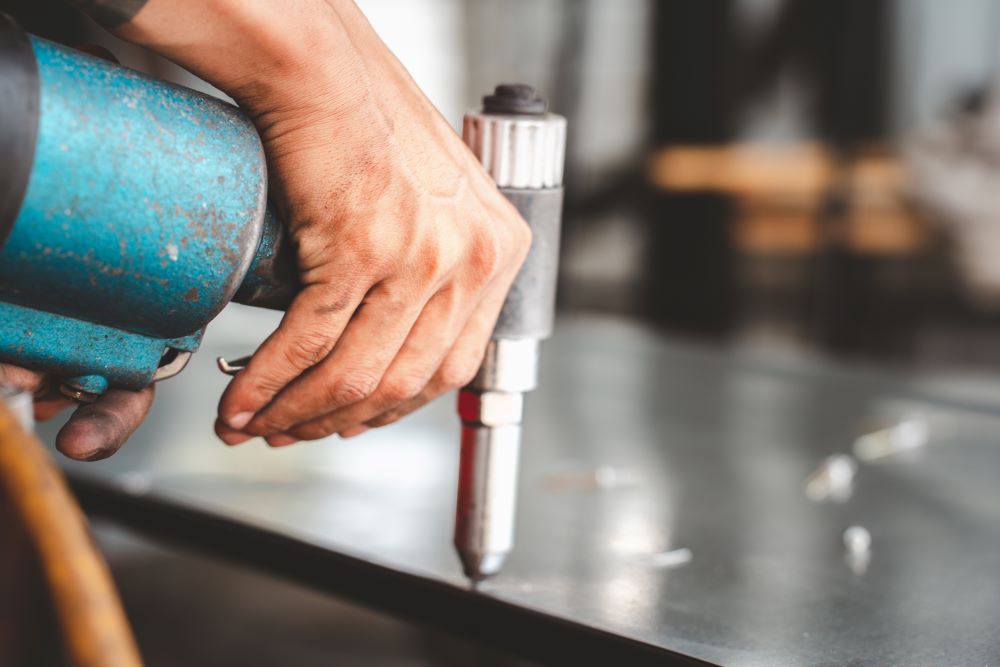
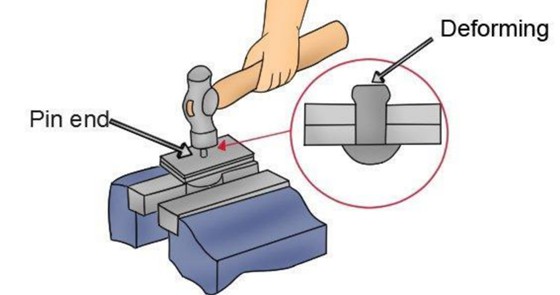
Solid riveting is characterized by the use of solid rivets that are deformed to create a secure joint. This process is highly regarded for applications requiring significant strength, such as in the construction of bridges and high-rise buildings. B2B buyers should consider the need for access to both sides of the joint since solid riveting typically requires this. While it provides a reliable and durable connection, the installation may be more labor-intensive compared to other methods.
How does Blind Riveting cater to specific industry needs?
Blind riveting, often referred to as pop riveting, allows for one-sided access during installation, making it ideal for applications in automotive assembly, HVAC systems, and furniture manufacturing. The use of a mandrel to deform the rivet tail ensures a secure fit without needing access to the rear side of the joint. Buyers should evaluate the strength requirements of their application, as blind rivets may not provide the same load-bearing capacity as solid rivets, but they excel in situations where space is limited.
What are the benefits of Press Riveting in mass production?
Press riveting employs external pressure to deform rivets, making it an efficient choice for mass production environments such as electronics and automotive sectors. This method ensures uniformity and speed, which can significantly reduce production times. B2B buyers should weigh the initial investment in press riveting equipment against the potential for increased throughput and reduced labor costs. However, the equipment costs can be a barrier for smaller operations.
In what scenarios is Pull Riveting the best option for buyers?
Pull riveting is particularly effective for applications involving thin materials, such as in aerospace and lightweight structural components. This method allows for strong connections even when access is limited, as it utilizes tension to create a secure joint. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their projects, as pull riveting may necessitate specialized tools. While it offers excellent strength, the choice of materials and thickness must be compatible with this riveting method.
Why choose Self-Piercing Riveting for fast-paced industries?
Self-piercing riveting is distinguished by its ability to join materials without the need for pre-drilled holes, making it a favorite in fast-paced environments like automotive and metalworking industries. This method streamlines the assembly process, reducing labor time and costs. B2B buyers should consider the types of materials they are working with, as self-piercing rivets may not be suitable for all applications. The rapid installation process, however, can lead to significant efficiency gains in high-volume production settings.
Key Industrial Applications of riveting process
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of riveting process | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft fuselage assembly | Provides lightweight, strong, and vibration-resistant joints | Compliance with aviation standards and material certifications |
| Automotive | Body panel assembly | Enhances structural integrity and reduces manufacturing time | Availability of specialized rivets for varied materials |
| Construction | Steel structure fabrication | Offers durable connections for high-load applications | Sourcing high-strength rivets suitable for environmental conditions |
| Electronics | Assembly of electronic enclosures | Ensures secure connections that withstand thermal expansion | Precision in rivet size and type to match component specifications |
| Marine | Shipbuilding and repair | Delivers corrosion-resistant joints crucial for durability | Consideration of marine-grade materials and environmental factors |
How is the riveting process utilized in the aerospace industry?
In the aerospace sector, the riveting process is critical for assembling aircraft fuselages. Rivets provide a lightweight yet robust connection that can withstand the high stresses and vibrations experienced during flight. The use of solid rivets ensures structural integrity, while blind rivets facilitate assembly in hard-to-reach areas. For international buyers, understanding compliance with strict aviation standards and sourcing certified materials is essential to ensure safety and reliability.
What are the applications of riveting in the automotive industry?
Automotive manufacturers utilize riveting for body panel assembly, where it enhances structural integrity while streamlining the production process. The ability to join different materials, such as aluminum and steel, is crucial for modern vehicle designs that prioritize weight reduction and fuel efficiency. Buyers must consider the availability of specialized rivets that can accommodate various material types and thicknesses, as well as the need for quick assembly to meet production timelines.
How does riveting support construction projects?
In construction, the riveting process is employed to fabricate steel structures, such as bridges and high-rise buildings. Riveting offers durable connections capable of supporting heavy loads, making it suitable for critical structural components. International buyers should focus on sourcing high-strength rivets that can withstand specific environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosion, to ensure long-lasting performance in their projects.
What role does riveting play in electronics manufacturing?
Riveting is commonly used in the assembly of electronic enclosures, where it ensures secure connections that can endure thermal expansion and vibrations. The process allows for the quick and efficient joining of components, which is vital in high-volume production environments. Buyers in this sector should pay close attention to the precision of rivet sizing and type, as mismatched specifications can lead to assembly issues and product failures.
How is riveting applied in the marine industry?
In marine applications, riveting is essential for shipbuilding and repair, where it provides corrosion-resistant joints that are crucial for durability in harsh marine environments. The riveting process allows for the quick assembly of components while maintaining the structural integrity of the vessel. Buyers should consider sourcing marine-grade rivets that meet industry standards for corrosion resistance and strength to ensure the longevity of their marine projects.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘riveting process’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Rivet Type for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with the diverse range of rivet types available, leading to confusion about which rivet is best suited for their specific application. This can result in using inappropriate rivets that fail to meet strength or durability requirements, causing costly rework or product failures. For instance, an automotive manufacturer may need to choose between solid rivets for structural integrity or blind rivets for hard-to-reach areas, but lack the expertise to make an informed decision.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their project requirements, including material types, load-bearing needs, and accessibility. It’s essential to collaborate with suppliers who can provide detailed technical specifications and guidance on rivet selection. Additionally, investing in training for the engineering team on the various rivet types and their applications can enhance decision-making. Utilizing a comprehensive rivet catalog that outlines the properties, advantages, and ideal use cases of each rivet type can streamline the selection process and ensure that the right rivet is used for each specific application.
Scenario 2: Inefficiencies in the Riveting Process Leading to Increased Production Time
The Problem: Buyers often face inefficiencies during the riveting process, such as misalignment of parts, improper hole sizing, or inadequate riveting tools. These issues not only prolong production time but also affect the quality of the final product. For example, a furniture manufacturer might experience delays due to recurring adjustments required for aligning metal sheets before riveting, ultimately leading to missed deadlines and increased labor costs.
The Solution: To address these inefficiencies, companies should implement a standardized riveting procedure that includes precise design specifications and thorough pre-production checks. This involves investing in high-quality riveting tools that ensure consistent performance and accuracy. Additionally, utilizing jigs or fixtures can help maintain alignment during the riveting process. Conducting regular training sessions for operators on best practices and new riveting technologies can also enhance efficiency. Moreover, adopting a digital inventory management system can help track tool maintenance and availability, ensuring that production runs smoothly without unnecessary downtime.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Ensuring Rivet Joint Integrity and Quality Control
The Problem: Ensuring the integrity of riveted joints is a critical concern for B2B buyers, particularly in industries like aerospace or construction where safety is paramount. Inadequate inspection processes can lead to undetected defects, resulting in compromised product safety and increased liability. A construction firm, for example, may find that their quality control measures do not adequately address the potential for rivet failure under stress, putting their projects at risk.
The Solution: To mitigate risks associated with rivet joint integrity, companies should implement a robust quality control program that includes rigorous inspection protocols. This can involve the use of non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray imaging, to detect internal defects in riveted joints. Establishing a clear set of criteria for acceptable rivet installation, including head formation and tail deformation, can enhance quality assurance. Additionally, investing in quality certifications and supplier audits ensures that materials and rivets used meet industry standards. Regularly reviewing and updating quality control processes to incorporate the latest advancements in riveting technology will help maintain high safety and performance standards.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for riveting process
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in the Riveting Process?
When selecting materials for the riveting process, understanding their properties and how they align with application requirements is crucial. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and copper. Each material has unique characteristics that influence its performance in various applications.
How Does Aluminum Perform as a Riveting Material?
Aluminum is lightweight and exhibits excellent corrosion resistance, making it a popular choice in industries such as aerospace and automotive. Its temperature rating typically ranges from -200°C to 300°C, depending on the alloy.
Pros: Aluminum rivets are easy to work with, cost-effective, and provide good strength-to-weight ratios. They are particularly suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aircraft manufacturing.
Cons: However, aluminum can be less durable than steel, particularly under high-stress conditions. It is also more susceptible to fatigue failure over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum rivets are ideal for joining materials in environments where corrosion resistance is essential. They are often used in outdoor applications or in industries that require lightweight components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia and Brazil should consider local climatic conditions that may affect aluminum’s performance. Compliance with standards such as ASTM and JIS is essential for ensuring quality.
What Are the Advantages of Using Steel in Riveting?
Steel rivets are known for their high strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as construction and shipbuilding. They typically have a temperature rating up to 600°C, depending on the specific alloy used.
Pros: Steel rivets provide excellent tensile strength and are resistant to deformation under load. They are cost-effective for large-scale projects due to their availability and manufacturing processes.
Cons: The primary drawback of steel is its susceptibility to corrosion unless treated or coated. Additionally, steel rivets can be heavier, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Steel rivets are commonly used in structural applications where strength is paramount. They are less suitable for environments prone to moisture unless protective coatings are applied.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as DIN for steel products. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of Africa, corrosion-resistant coatings may be necessary.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Riveting Applications?
Stainless steel offers an excellent combination of strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including food processing and marine environments. Its temperature rating can exceed 800°C, depending on the alloy.
Pros: Stainless steel rivets are highly durable and resistant to rust and corrosion, making them ideal for harsh environments. They maintain structural integrity over time, even under extreme conditions.
Cons: The primary drawback is the higher cost compared to aluminum and standard steel rivets. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to work with due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel rivets are perfect for applications requiring high hygiene standards, such as in the food and beverage industry. They are also suitable for marine applications due to their resistance to saltwater corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial, especially for buyers in Europe. Understanding the specific grade of stainless steel required for an application is also essential.
What Role Does Copper Play in Riveting?
Copper rivets are known for their excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for electrical applications. They typically have a temperature rating of up to 200°C.
Pros: Copper rivets are easy to work with and provide strong, reliable connections. They are particularly effective in applications requiring electrical conductivity, such as in electronics and electrical wiring.
Cons: However, copper is softer than other metals, which can limit its use in high-stress applications. It is also more expensive than aluminum and steel.
Impact on Application: Copper rivets are primarily used in electrical applications and situations where conductivity is essential. They may not be suitable for structural applications requiring high strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with electrical standards in their respective regions. For example, in South America, adherence to local electrical codes is critical.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Riveting
| Material | Typical Use Case for riveting process | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less durable under high stress | Low |
| Steel | Construction, shipbuilding | High strength and cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Med |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and harder to work with | High |
| Copper | Electrical applications | Excellent conductivity | Softer and limited in high-stress applications | Med |
This guide provides a strategic overview for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and compliance considerations across different regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for riveting process
What Are the Key Stages in the Riveting Manufacturing Process?
The riveting manufacturing process is a systematic approach that ensures the effective joining of materials, typically metals, through mechanical fasteners known as rivets. The process can be broken down into several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Riveting?
Material preparation is the foundation of a successful riveting process. This stage involves selecting the appropriate materials based on the application’s strength and durability requirements. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and copper alloys. Before riveting, surfaces must be cleaned to remove any contaminants such as oils, dust, or oxidation, which can affect the integrity of the joint. Additionally, components must be designed and aligned correctly to ensure accurate riveting, as misalignment can lead to weak connections.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Riveting?
The forming stage involves creating the rivet heads and ensuring proper deformation of the rivet tail. There are several techniques used in this process, including:
-
Press Riveting: This method utilizes a hydraulic or mechanical press to deform the rivet, allowing for consistent and repeatable results. It is particularly effective for mass production.
-
Pull Riveting: This technique involves pulling the mandrel of a blind rivet to deform the tail. It is advantageous in applications where access is limited, as it can be performed from one side only.
-
Swage Riveting: In this method, the rivet is deformed by applying radial pressure, which is useful for creating a secure joint in specific applications like automotive manufacturing.
Each of these techniques requires specialized equipment and skilled operators to ensure precision and quality.
How Does the Assembly Stage Work in Riveting?
During the assembly stage, the prepared components are brought together for the riveting process. This involves inserting the rivet into the pre-drilled holes of the materials to be joined. Proper alignment is crucial, and clamps or fixtures may be employed to hold the components in place. Once positioned, the riveting tool is used to form the rivet head on the opposite side, ensuring a tight fit. This stage is critical, as any misalignment can compromise the joint’s strength.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Riveted Products?
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of riveted assemblies. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Surface Treatment: This may involve painting, anodizing, or applying coatings to protect against corrosion and improve appearance.
-
Deburring and Polishing: Removing sharp edges and smoothing surfaces ensures safety and improves the overall quality of the finished product.
-
Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to verify that all rivets are correctly formed and that the assembly meets specified standards.
What Are the Quality Assurance Practices for Riveting?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the riveting process to ensure that joints are robust and meet international standards. Several QA practices are commonly implemented:
Which International Standards Apply to Riveting Quality Assurance?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that organizations consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for products in Europe and API standards for the oil and gas sector ensure compliance with safety and performance benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Riveting Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the riveting process to identify defects early:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the riveting process helps catch issues related to alignment, rivet deformation, and overall assembly integrity.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After completion, a comprehensive inspection is conducted to verify that the finished product meets all quality standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Riveting Quality Control?
Testing methods vary depending on the application and required strength of the joint. Common methods include:
-
Tensile Testing: Measures the strength of the riveted joint under tension.
-
Shear Testing: Evaluates the joint’s ability to withstand shear forces.
-
Visual Inspection: A thorough examination of the rivet heads and joint integrity to identify any visible defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential. Here are effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand.
-
Reviewing Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports provides insights into the supplier’s compliance with international standards and their internal quality metrics.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices and product performance.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
When engaging with suppliers from different regions, B2B buyers should be aware of specific quality control and certification nuances. For example, certification requirements may vary by country or industry, and understanding local regulations can help avoid compliance issues. Additionally, cultural differences in quality assurance practices may exist, making it crucial for buyers to establish clear communication and expectations.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the riveting manufacturing process and its quality assurance practices can significantly impact the success of B2B partnerships. By focusing on rigorous quality control measures and adhering to international standards, businesses can ensure that they receive reliable and durable riveted products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘riveting process’
To assist B2B buyers in the process of procuring riveting services and products, this guide outlines essential steps that ensure a smooth and effective sourcing experience. Riveting plays a crucial role in various industries, and understanding how to navigate the sourcing process can significantly impact project outcomes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is vital for ensuring that the riveting solutions you procure meet your project’s specific requirements. This includes detailing the materials to be joined, the type of rivets required (e.g., solid, blind, or split rivets), and the anticipated load or stress the joint will endure. Precise specifications help suppliers understand your needs and provide accurate solutions.
Step 2: Identify Your Application Needs
Understanding where and how the riveted components will be used is crucial for selecting the right riveting process. Consider factors such as environmental conditions (e.g., exposure to moisture or chemicals), the degree of vibration, and aesthetic requirements. This knowledge will guide you in choosing the most suitable riveting methods and materials.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s essential to conduct a thorough evaluation. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers who have experience with your specific application and can demonstrate a track record of quality and reliability.
- Key Considerations:
- Supplier certifications (ISO, etc.)
- Customer feedback and reviews
- Capabilities in both manual and automated riveting processes
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
To ensure the rivets and processes meet your standards, request samples or prototypes before placing a large order. This step allows you to assess the quality of the rivets and the effectiveness of the riveting process in real-world applications. Testing samples can help identify any potential issues early on.
Step 5: Review Pricing and Terms
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, review their pricing structures and terms of service. Ensure that you understand the cost implications of different riveting methods and materials. Look for transparency in pricing, including any potential additional costs for tooling, shipping, or customizations.
- Important Aspects:
- Bulk purchase discounts
- Payment terms
- Warranty and return policies
Step 6: Verify Compliance with Industry Standards
Ensure that the riveting solutions comply with relevant industry standards and regulations. This is particularly important for applications in sectors like aerospace, automotive, or construction, where safety and durability are paramount. Confirm that the supplier adheres to these standards and can provide the necessary documentation.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Finally, set up a clear communication plan with your chosen supplier. Define points of contact, preferred communication channels, and regular check-in schedules to discuss project progress and any issues that may arise. Effective communication is key to a successful partnership and can help mitigate misunderstandings during the riveting process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing of riveting processes, ensuring that they select the best suppliers and solutions for their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for riveting process Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Riveting Process Sourcing?
When analyzing the cost structure for riveting processes, several components contribute to the total expense incurred by businesses. Understanding these elements is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
-
Materials: The primary materials used in riveting include various types of rivets, such as solid, blind, and self-piercing rivets, which can vary in cost based on the material (e.g., aluminum, steel, copper). The choice of rivet type directly influences the cost, particularly when specific materials or grades are required for strength or corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled workers who operate riveting machinery and perform quality checks. In regions with varying labor costs, such as Africa or South America, sourcing from different locations can significantly impact the overall price.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, thereby lowering costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary based on the complexity of the riveting process and the need for specialized equipment. Investment in high-quality tooling can lead to increased efficiency and reduced waste, impacting the overall cost positively.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the riveting process meets industry standards requires robust QC measures, which may involve testing and inspections. These processes can add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product integrity and compliance with certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling of materials and finished products significantly influence the total cost. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties must be considered, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and relationship dynamics with buyers.
What Price Influencers Should Buyers Consider When Sourcing Riveting Processes?
Several factors can influence the pricing of riveting processes, and understanding these can aid buyers in negotiating better terms.
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower unit prices. Suppliers are more willing to offer discounts for bulk orders, which can significantly affect overall costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized rivets or unique specifications can increase costs. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential for cost savings with standardized products.
-
Materials: The type of materials selected for riveting will impact pricing. Premium materials or those requiring special certifications can elevate costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Rivets that meet stringent quality standards or certifications may come at a premium. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of such certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can all influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their experience and quality assurance processes.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding these terms can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively.
How Can Buyers Negotiate for Better Pricing in Riveting Process Sourcing?
To achieve cost efficiency in sourcing riveting processes, buyers can employ several strategies:
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Long-term partnerships often yield discounts and improved service.
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider maintenance, logistics, and quality assurance costs. A lower upfront cost may not always be the best option if it leads to higher TCO.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and bulk discounts. Suppliers may be willing to adjust terms to secure a deal.
-
Research Market Prices: Understanding current market prices and trends can empower buyers during negotiations, ensuring they are not overpaying.
-
Consider Regional Differences: Pricing can vary significantly by region. Buyers should explore sourcing from different locations to identify the best value, particularly when considering markets in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for riveting processes can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. It is recommended that buyers conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing and informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing riveting process With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to the Riveting Process in Metal Joining
When considering metal joining processes, it’s essential to evaluate various alternatives to riveting. Each method offers distinct advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific application, materials, and operational requirements. This analysis provides insights into how riveting compares to other popular solutions, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Riveting Process | Welding Process | Adhesive Bonding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength, durable joints; excellent for fatigue resistance. | Strong, permanent bonds; ideal for high-stress applications. | Good for various materials; flexibility in joint design. |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; tools and rivets can be costly. | Generally lower material costs but high labor and equipment costs. | Low material costs; potential for higher labor costs depending on application. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific tools and training; relatively straightforward. | Complex setup; requires skilled labor and safety precautions. | Simple application; may require curing time and surface preparation. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance after installation; joints are stable. | May need periodic inspection and re-welding under extreme conditions. | Potential for degradation over time; requires periodic inspection. |
| Best Use Case | Aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery where strength is crucial. | Construction and heavy industries where structural integrity is paramount. | Electronics, automotive interiors, and applications where aesthetics matter. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Welding as an Alternative?
Welding is a widely used metal joining process that creates strong bonds through the fusion of materials. It is particularly advantageous for applications requiring high structural integrity, such as in construction and heavy machinery. However, the complexity of welding setups and the need for skilled labor can increase operational costs and time. Additionally, safety precautions must be taken to manage heat and fumes, making it less appealing for some operations.
How Does Adhesive Bonding Compare to Riveting?
Adhesive bonding involves using chemical adhesives to join materials, offering flexibility in joint design and the ability to bond dissimilar materials. This method is particularly effective in applications where weight reduction is crucial or where aesthetic considerations are paramount, such as in automotive interiors. However, adhesive bonds may not provide the same level of strength as riveting or welding, especially under extreme stress or temperature conditions. Additionally, adhesives can require curing time, which can impact production timelines.
Conclusion: Which Joining Solution Should B2B Buyers Choose?
When selecting a metal joining solution, B2B buyers must carefully consider their specific needs, including the materials involved, desired strength, cost constraints, and production timelines. Riveting offers unique advantages in terms of durability and performance, particularly in high-stress applications. However, welding and adhesive bonding may be more suitable for certain projects based on their operational efficiencies and material compatibility. By evaluating each option against their project’s requirements, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for riveting process
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the Riveting Process?
In the riveting process, understanding the technical properties is crucial for ensuring the integrity and reliability of the final assembly. Here are some essential specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of rivets plays a significant role in determining their strength and suitability for specific applications. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and copper, each offering different tensile strengths and corrosion resistance. For instance, aluminum rivets are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for aerospace applications, while steel rivets provide higher strength for structural applications. Selecting the right material grade ensures durability and performance in the intended environment.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, which is critical in riveting to ensure that rivets fit correctly into pre-drilled holes. Proper tolerance helps maintain joint integrity and prevents failures due to misalignment or excessive stress. In a B2B context, specifying tight tolerances can reduce rework and improve product quality, which is essential for maintaining competitive advantage.
3. Rivet Size
Rivet size, including diameter and length, directly influences the strength of the joint. Larger diameters typically provide greater holding power, while length must be chosen based on the thickness of the materials being joined. In B2B transactions, understanding the implications of rivet size on load-bearing capacity can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their project requirements.
4. Shear Strength
Shear strength is the maximum load a rivet can withstand before it fails due to lateral forces. This property is particularly important in applications subjected to dynamic loads or vibrations, such as in automotive and aerospace industries. By evaluating shear strength, buyers can ensure that their riveting solutions meet safety and performance standards, thereby minimizing the risk of assembly failure.
5. Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance is critical for rivets used in harsh environments, such as marine or industrial settings. Coatings or material selection (e.g., stainless steel or coated aluminum) can enhance this property. For international buyers, particularly in regions with high humidity or salt exposure, understanding corrosion resistance is vital to ensure long-term performance and reduce maintenance costs.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Riveting?
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are key terms related to the riveting process:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of riveting, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers ascertain the quality and reliability of the rivets they intend to purchase, as OEMs typically adhere to stringent manufacturing standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is particularly relevant in the riveting industry, where bulk purchasing can lead to cost savings. B2B buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs to avoid excess inventory or increased costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to invite them to submit price quotes for specific products or services. In riveting, an RFQ can include detailed specifications, such as material grade, size, and quantity, ensuring that suppliers provide accurate pricing tailored to the buyer’s requirements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers engaged in international trade, as they clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery points, which can significantly affect the total cost of procurement.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the riveting process, lead time can vary based on factors like manufacturing capabilities and supply chain logistics. Buyers should consider lead times when planning production schedules to ensure timely project completion.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring that they procure the right riveting solutions for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the riveting process Sector
What Are the Key Market Trends Influencing the Riveting Process Sector?
The riveting process sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by various global factors. One of the primary market drivers is the increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. This shift is prompting manufacturers to adopt advanced riveting techniques that enhance joint strength while minimizing weight. Emerging technologies, such as automated riveting systems and smart rivet guns, are also gaining traction, enabling higher precision and efficiency in production.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly focused on sourcing innovative solutions that can improve operational efficiency and reduce costs. The adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, including IoT and AI, is facilitating real-time monitoring of riveting processes, allowing for predictive maintenance and quality control. Moreover, the rise of e-commerce platforms is making it easier for buyers to access a broader range of riveting products and services, simplifying procurement processes.
In addition to technological advancements, buyers are also influenced by geopolitical dynamics and trade agreements, which can affect material availability and pricing. As a result, B2B buyers must remain vigilant in navigating these market dynamics to identify reliable suppliers that align with their production needs and sustainability goals.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Riveting Process Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become critical considerations for B2B buyers in the riveting process sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing practices is under scrutiny, pushing companies to adopt greener processes. Riveting, as a mechanical joining method, can contribute to sustainability when coupled with eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
Ethical supply chains are equally important, particularly for international buyers who prioritize transparency and corporate social responsibility. This includes sourcing materials from suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and certifications for sustainable materials can guide B2B buyers in making responsible sourcing decisions.
Moreover, the use of recyclable rivets and coatings that minimize environmental impact can enhance a company’s green credentials. As customers increasingly demand sustainable products, buyers who prioritize eco-friendly sourcing may gain a competitive edge in their respective markets. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also resonates with end-users who are increasingly making purchasing decisions based on ethical considerations.
What Is the Historical Context of the Riveting Process and Its Evolution for B2B Buyers?
The riveting process has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations, where it was used to create durable structures and tools. Initially, rivets were crafted from wrought iron and employed in shipbuilding and bridge construction. As industrialization progressed in the 19th century, the introduction of steam-powered machinery revolutionized riveting techniques, allowing for the mass production of riveted components.
The 20th century saw further advancements with the development of various types of rivets, including blind rivets and self-piercing rivets, which enhanced the versatility and application of riveting in diverse industries. Today, the riveting process continues to evolve, integrating modern technologies such as robotics and automation. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers, as it highlights the longevity and reliability of riveting as a joining technique, reinforcing its relevance in contemporary manufacturing environments. Understanding this evolution can help buyers make informed decisions when selecting riveting solutions that meet their operational and strategic objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of riveting process
-
1. How do I choose the right riveting process for my project?
Choosing the right riveting process depends on various factors such as material type, joint design, and production volume. For high-strength requirements, solid rivets are typically preferred, while blind rivets are ideal for applications with limited access. Additionally, consider the environment where the product will be used; for example, self-piercing rivets work well in automotive applications due to their speed and efficiency. Consulting with a supplier who understands your specific needs can help tailor the solution for optimal performance. -
2. What are the advantages of using riveting over other joining methods?
Riveting offers several advantages, including the ability to create strong, permanent joints that resist vibrations better than screws or bolts. Unlike welding, riveting does not require high temperatures, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials. Furthermore, rivets can be installed from one side of a joint, simplifying assembly in tight spaces. Overall, riveting is a versatile and efficient choice for many industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. -
3. What should I consider when vetting international suppliers for riveting services?
When vetting international suppliers, prioritize their experience and expertise in the riveting process relevant to your industry. Check for certifications that demonstrate quality assurance, such as ISO standards. It’s also vital to assess their production capabilities, lead times, and past customer reviews. Establishing clear communication channels and understanding their logistics capabilities, especially for international shipping, will help ensure a smooth partnership. -
4. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for riveting products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may have flexible MOQs for prototypes or small-scale projects, while others may require larger orders to justify production costs. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to determine if they can accommodate your order size. Additionally, inquire about pricing tiers, as larger orders often come with discounts. -
5. How can I customize riveting solutions for my specific applications?
Customization in riveting solutions can involve selecting specific rivet types, sizes, and materials to meet your application needs. Work closely with your supplier to discuss your design requirements, including joint strength, aesthetics, and environmental conditions. Many suppliers offer bespoke manufacturing services, allowing you to create unique solutions that align with your project specifications. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing riveting products internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and location. Common practices include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and net payment terms after delivery. Using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services can mitigate risks. Always clarify payment expectations upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction. -
7. What quality assurance measures should I expect in the riveting process?
Quality assurance is crucial in the riveting process to ensure strong and reliable joints. Expect suppliers to implement rigorous testing procedures, including visual inspections, tensile strength tests, and non-destructive testing methods. Request documentation of these QA processes and any relevant certifications to confirm that they adhere to industry standards. Regular audits and feedback loops can also help maintain quality throughout the production run. -
8. How do logistics and shipping impact my riveting project timelines?
Logistics and shipping play a significant role in project timelines, particularly for international sourcing. Discuss shipping methods and expected delivery times with your supplier early in the negotiation process. Factors such as customs clearance, freight forwarding, and local regulations can affect lead times. Establishing a clear timeline with milestones for production and shipping will help manage expectations and ensure timely project completion.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Riveting Process Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tameson – Rivets
Domain: tameson.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: A rivet is a mechanical fastener used to join two or more materials permanently, consisting of a head at one end and a cylindrical body (shaft) at the other, with a tapered end called the tail. Rivets are designed for permanent joints, similar to welding, and are effective in resisting vibrations. Different types of rivets include: 1. Solid rivet: A solid shaft with a head, deformed using a rivet …
2. Wayken RM – Rivets
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Rivets are mechanical fasteners used to hold metal sheets together, consisting of a head and a tail. They are made from materials like brass, copper, steel, and aluminum. The working process involves drilling a hole, inserting the rivet, and deforming the tail to create a secure joint. Key materials include:
– Aluminum: Lightweight, malleable, resistant to deterioration.
– Stainless Steel: Strong,…
3. ScienceDirect – Self-Piercing Riveting Insights
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Self-piercing riveting is a cold forming technique used to fasten together two or more sheets of materials mechanically with a rivet. The focus is on aluminum alloys, specifically Alclad 2024-T3. Key parameters affecting fatigue life include load transfer, secondary bending, material type, protective systems, fasteners (solid and blind rivets), hole preparation, grain direction, and loading condit…
4. CJME – Self-Piercing Riveting Solutions
Domain: cjme.springeropen.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Self-piercing riveting (SPR) is a cold forming technique used to fasten together two or more sheets of materials with a rivet without the need to predrill a hole. It is increasingly popular in the automotive sector due to the use of lightweight materials. SPR is preferred over resistance spot welding (RSW) for joining aluminium components, as RSW is not suitable for aluminium due to its high therm…
5. Reddit – Hot Riveting Process
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hot riveting process involves heating rivets to expand them, then inserting them into pre-drilled holes in materials. As the rivet cools, it contracts, creating a tight joint through compression. The strength of the joint relies on the tensile strength of the materials and the friction between them.
6. Making – Riveting Technique
Domain: making.unsw.edu.au
Introduction: Riveting is a mechanical connection method used in jewellery making to join parts without heat, utilizing flared heads of rivets. The simplest type is the basic rivet, made from round wire inserted into a hole of the same diameter (e.g., 1.5mm wire into a 1.5mm hole). Rivets are suitable for materials that cannot withstand soldering heat, such as wood, plastic, bone, and glass. Common rivet types …
7. TWI Global – Rivets
Domain: twi-global.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: A rivet is a mechanical fastener with a head on one end and a cylindrical stem (tail) on the other, resembling a metal pin. Rivets are installed by drilling, placing, or punching into a hole, and the tail is deformed to hold the rivet in place, typically expanding to about one and a half times the original diameter. Riveting can create lap or butt joints with various configurations, including sing…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for riveting process
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial manufacturing, strategic sourcing for riveting processes emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse types of rivets—such as solid, blind, and split rivets—along with their specific applications can significantly enhance the quality and durability of product designs. By leveraging advanced riveting techniques like press and pull riveting, businesses can achieve efficient production rates while ensuring robust connections, essential for sectors ranging from automotive to construction.
Investing in a strategic sourcing approach not only reduces costs but also fosters long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers, ensuring access to high-quality materials and innovative technologies. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this is a unique opportunity to harness local market insights while expanding into global supply chains.
As the demand for sustainable and resilient manufacturing practices continues to grow, now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies. Embrace the potential of riveting technologies to streamline operations and enhance product offerings. Engage with trusted suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that align with your business objectives, positioning your organization for future success in a competitive global market.