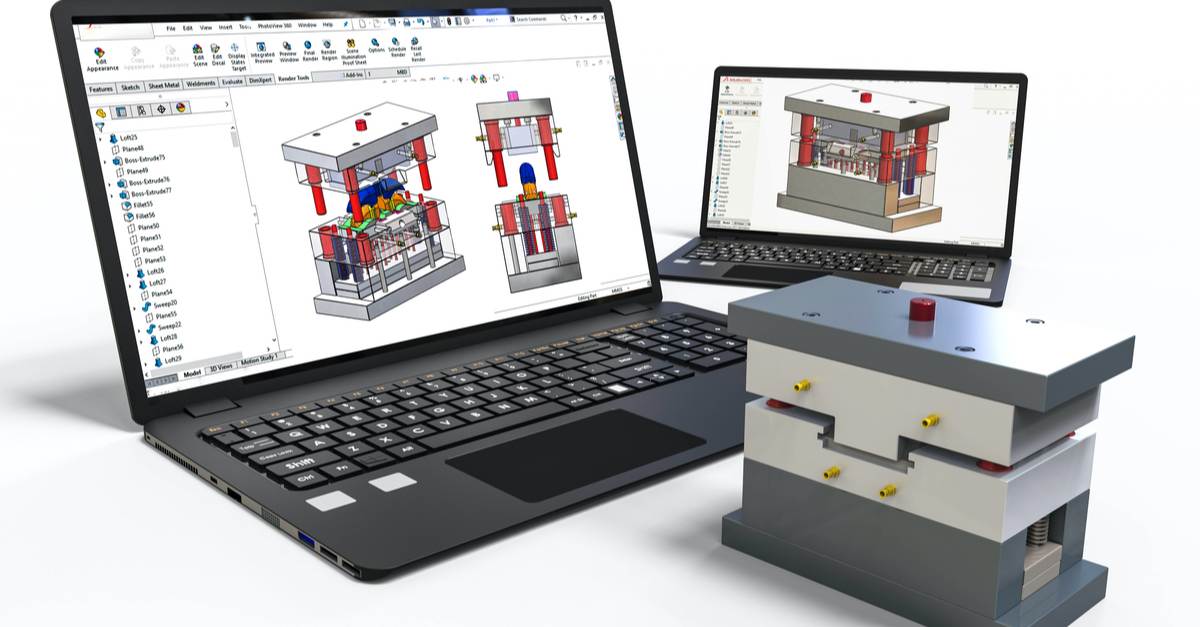
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for rapid prototyping in china
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing rapid prototyping solutions in China presents a formidable challenge for international B2B buyers. The need for high-quality prototypes that can accelerate product development while managing costs is crucial, especially for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria. As companies aim to innovate swiftly, navigating the complexities of the Chinese market—characterized by diverse manufacturing capabilities, varying supplier reliability, and fluctuating costs—can be overwhelming.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower you with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. We will delve into various aspects of rapid prototyping, including the types of services available, common applications across industries, and the critical process of supplier vetting. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost considerations and best practices to ensure your investment yields the highest return. By equipping you with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the landscape, this guide will facilitate your journey toward successful product development, enabling you to harness the full potential of rapid prototyping in China.
With the right information and strategies, your business can not only meet market demands but also thrive in an increasingly globalized economy. Let’s embark on this exploration together to unlock the benefits of rapid prototyping tailored to your unique needs.
Understanding rapid prototyping in china Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | High precision, suited for metals and plastics; scalable | Aerospace, automotive, industrial parts | Pros: High accuracy, versatile materials. Cons: Longer lead times compared to other methods. |
| 3D Printing | Layered additive process; ideal for complex geometries | Prototyping, medical devices, consumer products | Pros: Fast production, design flexibility. Cons: Limited material strength compared to machining. |
| Vacuum Casting | Quick mold-making process; suitable for low-volume production | Electronics, automotive, consumer goods | Pros: Cost-effective for small runs, good surface finish. Cons: Limited to softer materials. |
| Injection Molding | High-speed production with durable plastic parts; requires molds | Mass production in consumer goods, automotive | Pros: Excellent for high volume, consistent quality. Cons: High initial tooling costs. |
| Sheet Metal Fabrication | Involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal sheets | Industrial machinery, automotive, electronics | Pros: Strong and lightweight parts, rapid turnaround. Cons: Limited to flat materials and shapes. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of CNC Machining in China?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machining is a highly precise manufacturing process that uses programmed computer software to control machinery tools. This method is particularly suitable for producing parts made from metals and plastics, making it a go-to for industries such as aerospace and automotive. B2B buyers should consider the high accuracy and versatility of materials when opting for CNC Machining, though they should also be prepared for longer lead times compared to other rapid prototyping methods.
How does 3D Printing stand out in the rapid prototyping landscape?
3D Printing employs an additive manufacturing technique that builds parts layer by layer, enabling the creation of complex geometries. This method is ideal for rapid prototyping in sectors like medical devices and consumer products due to its speed and design flexibility. B2B buyers benefit from the quick turnaround times and the ability to iterate designs rapidly. However, they should be aware that 3D printed parts may not always match the material strength of traditionally machined components.
What advantages does Vacuum Casting offer for low-volume production?
Vacuum Casting is a rapid prototyping technique that involves creating silicone molds for low-volume production runs. It is particularly beneficial for industries such as electronics and automotive, where small batches of parts are often required. This method is cost-effective and provides a good surface finish, making it an attractive option for B2B buyers looking to test products before committing to mass production. However, it is limited to softer materials, which may not suit all applications.
Why is Injection Molding favored for mass production?
Injection Molding is a highly efficient process for producing durable plastic parts, making it ideal for mass production in consumer goods and automotive applications. This method offers consistent quality and can produce large quantities of parts quickly. B2B buyers should consider the long-term cost benefits of Injection Molding, despite the high initial tooling costs. This investment pays off in high-volume production scenarios where uniformity and speed are critical.
What role does Sheet Metal Fabrication play in rapid prototyping?
Sheet Metal Fabrication is a versatile method that involves cutting, bending, and assembling metal sheets to create parts. This technique is widely used in industries such as machinery, automotive, and electronics. B2B buyers appreciate the strength and lightweight nature of fabricated parts, as well as the rapid turnaround times. However, this method is primarily limited to flat materials and shapes, which may restrict design options for certain applications.
Key Industrial Applications of rapid prototyping in china
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Rapid Prototyping in China | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Development of custom components for new models | Accelerates product development and reduces costs | Quality certifications, material options, lead times |
| Aerospace & Aviation | Creation of lightweight prototypes for parts | Enhances performance while minimizing weight | Compliance with aviation standards, precision needs |
| Medical Devices | Prototyping surgical instruments and implants | Ensures functionality and safety before mass production | Regulatory compliance, biocompatibility requirements |
| Consumer Electronics | Rapid testing of new product designs | Speeds up time-to-market and enables market responsiveness | Design flexibility, material durability, cost-effectiveness |
| Robotics | Iterative design for robotic components | Facilitates innovation and competitive advantage | Technical expertise, integration capabilities, scalability |
How is Rapid Prototyping Used in the Automotive Sector in China?
In the automotive sector, rapid prototyping is utilized for the development of custom components, enabling manufacturers to create and test parts for new models quickly. This process allows for iterative design changes based on performance testing, ultimately reducing time and costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. For international buyers, understanding local quality certifications and available material options is crucial, as these factors significantly influence the reliability and compliance of the components produced.
What Role Does Rapid Prototyping Play in Aerospace & Aviation?
Rapid prototyping in the aerospace industry focuses on creating lightweight prototypes for various aircraft parts, which is critical for enhancing performance while minimizing weight. This application helps companies meet stringent safety and performance standards more efficiently. International buyers must consider compliance with aviation regulations and the precision requirements that are essential for aerospace components to ensure safety and reliability in their operations.
How is Rapid Prototyping Transforming Medical Device Development?
In the medical sector, rapid prototyping is instrumental in the design and testing of surgical instruments and implants. It allows for the creation of functional models that can be evaluated for safety and effectiveness prior to mass production. For B2B buyers, navigating regulatory compliance and ensuring that materials meet biocompatibility standards are key considerations in sourcing these prototypes, as they directly impact patient safety and product approval.
How Does Rapid Prototyping Benefit Consumer Electronics?
Rapid prototyping significantly benefits the consumer electronics sector by enabling companies to test new product designs rapidly. This application accelerates the time-to-market for innovative products and allows for quick adjustments based on market feedback. Buyers from diverse regions should prioritize design flexibility and material durability when sourcing prototypes, as these factors are critical for maintaining competitive advantage and meeting consumer expectations.
In What Ways is Rapid Prototyping Impacting Robotics Development?
In the robotics industry, rapid prototyping facilitates the iterative design process for robotic components, allowing for continuous improvement and innovation. This capability helps companies stay ahead of technological advancements and market demands. International buyers should focus on sourcing partners with technical expertise and integration capabilities, as these attributes are essential for scaling production and ensuring that components work seamlessly in complex robotic systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘rapid prototyping in china’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Language Barriers in Communication
The Problem: International B2B buyers often face significant challenges when sourcing rapid prototyping services in China due to language barriers. Miscommunication can lead to misunderstandings regarding project specifications, timelines, and quality standards. For example, a buyer in Nigeria may struggle to articulate specific design requirements for a prototype, leading to errors in the final product and delays in the development process. This not only impacts the buyer’s ability to launch products in a timely manner but can also damage relationships with suppliers.
The Solution: To overcome language barriers, buyers should consider partnering with companies that offer bilingual support or have teams fluent in their preferred language. When submitting design specifications, utilize visual aids such as diagrams, CAD files, or 3D models to convey ideas more clearly. Additionally, engage in regular video calls to ensure real-time clarification of doubts and foster a more collaborative atmosphere. Establishing a clear communication protocol and using project management tools that support multiple languages can also enhance understanding throughout the prototyping process.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Quality Control in Prototyping
The Problem: Another common pain point is the inconsistency in quality control when working with rapid prototyping services in China. Buyers may receive prototypes that do not meet the required specifications, resulting in wasted time and resources. For instance, a company in Saudi Arabia may order a batch of prototypes for a new consumer electronic product, only to find that the dimensions and material properties differ from what was specified. This inconsistency can be detrimental, especially for industries like automotive or medical devices, where precision is critical.
The Solution: To ensure quality control, buyers should implement stringent quality assurance measures from the outset. Request detailed documentation on the supplier’s quality control processes, including certifications such as ISO 9001. It is advisable to conduct a Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review before prototyping begins, allowing both parties to address potential issues early in the process. Additionally, consider using third-party inspection services to verify the quality of prototypes before they are shipped. This proactive approach can help mitigate risks and ensure that the final product meets industry standards.
Scenario 3: Managing Lead Times and Delivery Schedules
The Problem: Buyers often encounter challenges with lead times and delivery schedules when sourcing rapid prototyping services in China. Unpredictable shipping times, customs delays, and inefficient project management can lead to significant delays in product launches. For example, a startup in Europe planning to debut a new product at a major trade show may find that their prototypes do not arrive on time, resulting in missed marketing opportunities and financial losses.
The Solution: To manage lead times effectively, it is crucial for buyers to establish clear timelines and expectations with their Chinese suppliers right from the initial discussions. Utilize project management tools to track progress and set milestones for each phase of the prototyping process. Additionally, consider building a buffer into the timeline to account for potential delays. Engaging with suppliers who have a proven track record of timely deliveries and who offer real-time tracking of shipments can further enhance reliability. Establishing strong relationships with local logistics providers can also streamline the shipping process and reduce unexpected delays.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for rapid prototyping in china
What Are the Key Materials for Rapid Prototyping in China?
In the realm of rapid prototyping, selecting the right material is crucial for ensuring the final product meets performance standards and market requirements. Here, we analyze four common materials utilized in rapid prototyping in China, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does ABS Plastic Perform in Rapid Prototyping?
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a widely used thermoplastic known for its strength and durability. It exhibits good impact resistance, making it suitable for prototypes that require robustness. ABS can withstand temperatures up to approximately 80°C and is resistant to various chemicals, which enhances its application versatility.
Pros: ABS is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, making it a popular choice for prototyping. It offers good surface finish and can be easily painted or glued.
Cons: However, ABS is not as heat-resistant as some other materials, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications. It can also warp during cooling if not managed properly.
Impact on Application: ABS is compatible with a variety of media, including oils and fuels, making it suitable for automotive and consumer product prototypes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that ABS prototypes comply with international standards such as ASTM D638. Additionally, awareness of ABS’s environmental impact and sourcing from compliant suppliers is crucial.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Prototyping?
Aluminum is favored for its lightweight nature and excellent strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand high temperatures and has good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for prototypes intended for outdoor or industrial applications.
Pros: The durability and recyclability of aluminum make it a sustainable choice. Its machinability allows for precise fabrication, which is essential for complex designs.
Cons: The cost of aluminum can be higher than plastics, and the manufacturing process can be more complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly effective in aerospace and automotive applications, where weight savings and strength are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions is essential. Buyers should also consider the sourcing of aluminum to ensure it meets environmental regulations.
Why Choose Stainless Steel for Prototyping?
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It is often used in applications where hygiene is critical, such as medical devices and food processing equipment.
Pros: The longevity and durability of stainless steel make it an excellent investment for prototypes that will undergo rigorous testing.
Cons: The primary drawback is its cost, which is significantly higher than plastics. Additionally, machining stainless steel can be more challenging due to its hardness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel prototypes are compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensuring compliance with standards like ASTM A240 is vital. Buyers from regions with stringent health and safety regulations should prioritize stainless steel for its non-reactive properties.
How Does 3D Printed Resin Compare?
3D printed resin is a versatile material used in rapid prototyping, especially for intricate designs and high-detail applications. It offers excellent surface finish and can be formulated to achieve various mechanical properties.
Pros: Resins can be tailored for specific applications, providing flexibility in design. They also allow for rapid production times, which is beneficial for iterative prototyping.
Cons: However, resins can be brittle and may not withstand high-stress applications. Their sensitivity to UV light can also limit their use in outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: Resins are ideal for detailed prototypes in the consumer electronics and medical fields, where aesthetics and precision are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards for materials used in medical applications is crucial. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of resin disposal and seek suppliers that offer eco-friendly options.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Rapid Prototyping
| Material | Typical Use Case for rapid prototyping in china | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS Plastic | Automotive parts, consumer products | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Limited heat resistance | Low |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive components | Lightweight and strong | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | Excellent durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| 3D Printed Resin | Consumer electronics, detailed prototypes | High detail and rapid production | Brittle and UV sensitivity | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the materials available for rapid prototyping in China, helping them make informed decisions that align with their product development needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for rapid prototyping in china
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Processes for Rapid Prototyping in China?
The manufacturing process for rapid prototyping in China typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product meets the specifications and quality expectations of international B2B buyers.
How is Material Prepared for Rapid Prototyping?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. Depending on the prototyping method used, various materials such as plastics, metals, and composites are selected based on their suitability for the intended application. For instance, CNC machining often utilizes metals like aluminum and stainless steel, while 3D printing may employ thermoplastics like ABS or nylon.
After selecting the materials, they are processed to ensure they meet specific standards. This might include cutting, machining, or treating the materials to enhance their properties. For example, metal components may undergo processes like annealing to improve ductility and strength.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Rapid Prototyping?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired prototypes. Common techniques include:
-
CNC Machining: This subtractive manufacturing method uses computer-controlled tools to remove material and create precise shapes and features. It’s ideal for producing complex geometries with high accuracy.
-
3D Printing: Additive manufacturing techniques like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) build parts layer by layer from digital models. This method is particularly advantageous for rapid iterations and custom designs.
-
Injection Molding: Although typically used for larger production runs, rapid tooling can create molds quickly for low-volume production. This is especially useful when transitioning from prototyping to pilot production.
Each technique has its advantages and is chosen based on factors like cost, material properties, and the required level of detail.
How Does the Assembly Process Work for Prototypes?
After forming, the assembly stage brings together individual components to create the final prototype. This can involve various methods such as:
-
Mechanical Fastening: Using screws, bolts, or clips to join parts securely.
-
Adhesive Bonding: Employing industrial adhesives for a permanent bond, often used in plastic and composite assemblies.
-
Welding: For metal components, welding provides a strong, durable joint.
Quality assurance measures should be integrated into this stage, ensuring that all components fit correctly and function as intended. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly capabilities of their suppliers to ensure they can meet specific design requirements.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied to Prototypes?
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetic and functional qualities of prototypes. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Surface Treatment: Methods such as anodizing or powder coating improve corrosion resistance and surface hardness, particularly for metal parts.
-
Painting: Applying paint can enhance appearance and provide additional protection, with options ranging from matte to high-gloss finishes.
-
Polishing: This technique is used to achieve a smooth, reflective surface, which can be critical for consumer-facing products.
These finishing processes not only improve the product’s look and feel but also ensure durability and compliance with industry standards.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Rapid Prototyping?
Quality control (QC) is a vital aspect of the rapid prototyping process in China, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Manufacturers typically adhere to quality management systems such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for consistent quality improvement.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection occurs when materials arrive at the facility. It ensures that all incoming materials meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, regular checks are performed to verify that production is proceeding according to specifications. This may involve monitoring equipment calibration and inspecting parts for dimensional accuracy.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the manufacturing process is complete, final inspections are conducted to ensure that the finished prototypes meet all quality standards. This may include functional testing and visual inspections.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of prototypes. These can include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools like calipers and gauges to measure the physical dimensions of parts against specifications.
-
Functional Testing: Evaluating the prototype’s performance in real-world conditions to ensure it operates as intended.
-
Material Testing: Assessing material properties through methods such as tensile testing or hardness testing to confirm they meet required standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to mitigate risks. Here are several strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the supplier’s facilities, processes, and quality control measures firsthand. This can provide insights into the manufacturer’s capabilities and adherence to quality standards.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers can provide transparency into their QC processes. These reports should outline inspection results, testing methods, and compliance with relevant standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s processes and products. This is particularly valuable for buyers who may not have the resources to conduct audits themselves.
What Certifications Should B2B Buyers Look for in Suppliers?
When sourcing from Chinese manufacturers, it’s crucial to look for relevant certifications that demonstrate adherence to international quality standards. Certifications such as:
- ISO 9001: Indicates a commitment to quality management systems.
- CE Marking: Ensures compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Relevant for suppliers in industries like oil and gas, confirming compliance with specific industry standards.
These certifications can help B2B buyers assess the reliability of their suppliers and ensure that their products meet necessary regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for rapid prototyping in China is essential for international B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with the stages of manufacturing, key quality control checkpoints, and methods to verify supplier compliance, buyers can make informed decisions and ensure successful partnerships. This knowledge not only enhances product development but also helps mitigate risks associated with sourcing from overseas manufacturers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘rapid prototyping in china’
Introduction
Navigating the landscape of rapid prototyping in China can be daunting for international B2B buyers. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you select the right partners to bring your product ideas to life efficiently and cost-effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before approaching suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements, including materials, dimensions, tolerances, and finish types. This clarity will help in obtaining accurate quotes and ensure that the prototypes meet your design expectations. Consider creating detailed documentation or CAD files to communicate your vision effectively.
Step 2: Conduct Market Research
Investigate the current landscape of rapid prototyping services in China. Look for suppliers that specialize in your industry and have a proven track record. Utilize online platforms, industry forums, and trade shows to gather insights on potential partners and their capabilities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
It’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly before making any commitments. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Look for suppliers with a strong reputation and verified experience in rapid prototyping, ensuring they can handle your specific needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality management and adherence to international manufacturing practices. This step is vital for mitigating risks and ensuring compliance with your own quality standards.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotations
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request detailed quotations that break down costs by materials, labor, tooling, and shipping. This transparency will help you compare offers effectively. Be wary of quotes that seem significantly lower than others, as they may indicate hidden costs or inferior quality.
Step 6: Review Prototyping Technologies Offered
Assess the range of prototyping technologies available from each supplier, such as CNC machining, 3D printing, and injection molding. Each method has its advantages depending on your project’s requirements. Choose a supplier that offers the technology best suited to your product’s complexity and production volume.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Set up regular check-ins and updates throughout the prototyping process. Ensure that the supplier has English-speaking representatives or translators available to facilitate clear discussions, especially if technical terms are involved.
By following these steps, you can confidently navigate the rapid prototyping landscape in China, ensuring that your sourcing decisions lead to successful product development and market entry.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for rapid prototyping in china Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Rapid Prototyping in China?
When sourcing rapid prototyping services in China, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials account for a significant portion of costs, influenced by the type of prototypes being produced—whether they involve metals, plastics, or composites. Prices can vary based on market conditions and the specific materials chosen.
Labor costs are relatively low in China compared to Europe or North America, but they can vary based on the complexity of the work and the skill level required.
Manufacturing overhead includes expenses related to facility maintenance, equipment, utilities, and other operational costs. This can be a hidden cost that impacts the final price.
Tooling costs are particularly relevant for projects that require custom molds or fixtures, which can significantly affect the initial investment.
Quality control processes are essential, especially for industries with stringent standards such as aerospace or medical devices. Investing in QC can increase upfront costs but reduce long-term issues and costs associated with defective products.
Logistics encompasses shipping costs, tariffs, and handling fees, which can vary based on the destination and chosen Incoterms.
Finally, the margin is the profit that suppliers add on top of their costs, which can vary widely based on the supplier’s positioning in the market.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Rapid Prototyping Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of rapid prototyping services in China. One of the most significant is volume or minimum order quantity (MOQ); higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
Specifications and customization also play a critical role. More complex designs or specialized requirements can drive up costs.
The choice of materials is another major influencer; for instance, high-performance materials can significantly increase the price.
Quality and certifications are crucial, particularly for buyers in regulated industries. Suppliers offering ISO or other industry-specific certifications may charge a premium for their services.
Supplier factors, such as reputation, experience, and capabilities, can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more but offer greater reliability.
Lastly, the choice of Incoterms can impact total costs. Understanding terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) is vital for accurately estimating final expenses.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Rapid Prototyping?
For international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, negotiating effectively is key to achieving cost-efficiency. Start by obtaining multiple quotes from different suppliers to understand the market rates and leverage this information during negotiations.
Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial pricing. This includes evaluating long-term implications such as quality assurance, potential rework costs, and logistics.
Be aware of pricing nuances specific to international transactions, such as currency fluctuations, taxes, and duties, which can significantly impact the final cost.
Lastly, maintaining a good relationship with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service in the long run. Suppliers are often more willing to negotiate favorable terms for repeat customers who demonstrate loyalty and volume potential.
Conclusion
In summary, international B2B buyers looking to source rapid prototyping services in China should carefully analyze the various cost components and pricing influencers. By employing strategic negotiation tactics and considering total cost implications, buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions and enhance their overall project success. Always remember that the prices provided by suppliers are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions and specific project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing rapid prototyping in china With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Rapid Prototyping in China
In the competitive landscape of product development, international B2B buyers often seek efficient and cost-effective solutions for rapid prototyping. While rapid prototyping in China offers numerous advantages, it’s essential to explore alternative methods that can also meet specific project requirements. This analysis compares rapid prototyping in China with two viable alternatives: rapid prototyping in Eastern Europe and utilizing local prototyping services in the buyer’s region.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Rapid Prototyping In China | Rapid Prototyping in Eastern Europe | Local Prototyping Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality output with advanced technology | Comparable quality, often with shorter lead times | Variable quality, depends on provider |
| Cost | Generally lower costs due to economies of scale | Moderate costs, slightly higher than China | Potentially higher due to limited options |
| Ease of Implementation | Streamlined processes with online platforms | Efficient communication, usually in English | May vary; local language can be a barrier |
| Maintenance | Minimal, as manufacturers handle issues | Moderate, with local support available | High, as buyers may need to manage issues directly |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production, complex designs | Prototyping with a focus on European standards | Small-scale projects or localized needs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Rapid Prototyping in Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe has emerged as a significant player in the prototyping landscape, offering high-quality services with a focus on advanced technologies like CNC machining and 3D printing. The region benefits from a skilled workforce and a commitment to engineering excellence. One of the main advantages of this alternative is the shorter lead times compared to China, particularly for European clients, which can expedite the development process. However, costs can be slightly higher than in China, and while many firms operate in English, the variability in service quality can be a concern for some buyers.
Local Prototyping Services
Utilizing local prototyping services can provide significant advantages, especially for businesses looking to develop products that cater specifically to their regional markets. This approach often enables better communication and collaboration, as teams can meet face-to-face to discuss project requirements. However, the quality and availability of services can vary widely, and buyers may face higher costs due to a limited number of providers and the absence of economies of scale. This option is best suited for smaller projects or startups that require rapid iterations and local market insights.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Prototyping Solution
When selecting a rapid prototyping solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including project scale, budget, and desired turnaround time. Rapid prototyping in China is an excellent choice for high-volume production and complex designs due to its cost-effectiveness and advanced capabilities. However, for projects requiring closer collaboration or adherence to specific regional standards, exploring Eastern European services or local providers may yield better results. Ultimately, the decision should align with the project’s goals, ensuring that the chosen method enhances both efficiency and product quality.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for rapid prototyping in china
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Rapid Prototyping in China?
When engaging in rapid prototyping in China, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for ensuring product quality and meeting project requirements. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of the materials used in production, which impacts the durability, strength, and suitability for various applications. Common materials include metals (like aluminum and stainless steel) and plastics (such as ABS and nylon). Selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for meeting industry standards and ensuring the final product’s performance. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In rapid prototyping, tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) are often required for intricate parts, while larger tolerances may be acceptable for less complex designs. Understanding tolerance levels is essential for international buyers to ensure that parts will fit and function as intended in their applications. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and quality of the surface of a manufactured part, which can affect aesthetics and functionality. Options range from rough (as-milled) to smooth (anodized or polished). A proper surface finish is not only critical for the visual appeal but also influences the part’s performance, especially in applications involving friction or assembly. -
Dimensional Stability
Dimensional stability is the ability of a material to maintain its shape and size under varying environmental conditions. This property is crucial for parts that will undergo temperature fluctuations or moisture exposure. Ensuring dimensional stability minimizes the risk of warping or deformation, which can lead to production delays or increased costs. -
Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and elasticity provide insights into how a material will perform under stress. These properties are critical for buyers to assess the suitability of a prototype for its intended application, particularly in industries like automotive and aerospace where safety and reliability are paramount.
What Common Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know in Rapid Prototyping?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can enhance communication with suppliers and streamline the procurement process. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help B2B buyers clarify expectations regarding product specifications, quality standards, and lead times. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers understand the scale of their orders and budget accordingly, especially when testing new products in the market. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific quantity of products or services. This process is essential for buyers to compare costs and establish relationships with potential suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms can help buyers navigate shipping logistics and potential costs effectively. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the total time it takes from placing an order to receiving the finished product. Understanding lead times is critical for effective project planning, especially in industries where time-to-market can significantly impact competitiveness. -
Prototyping Methodologies
This term encompasses the various techniques used in rapid prototyping, such as CNC machining, 3D printing, and vacuum casting. Knowledge of these methodologies enables buyers to choose the best approach for their specific project needs, balancing speed, cost, and quality.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with manufacturers in China’s rapid prototyping industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the rapid prototyping in china Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Rapid Prototyping in China?
The rapid prototyping sector in China has experienced robust growth, driven by global demand for faster product development cycles and the increasing complexity of manufacturing processes. Key trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as additive manufacturing, CNC machining, and hybrid manufacturing techniques. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly leveraging China’s capabilities to shorten their time-to-market. The focus has shifted towards low-volume production runs, allowing companies to test market viability without committing to large-scale manufacturing.
Emerging trends also highlight the importance of customization and flexibility. Companies are seeking suppliers that can adapt quickly to changes in design specifications and production requirements. Moreover, the rise of digital platforms for prototyping services is streamlining the sourcing process, enabling buyers to obtain instant quotes and manage orders online. This shift towards digitalization is essential for international buyers looking to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact B2B Relationships in Rapid Prototyping?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor for B2B buyers in the rapid prototyping sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including waste generation and energy consumption, is under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to eco-friendly practices. This includes the use of sustainable materials, such as biodegradable plastics and recycled metals, which can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with prototyping activities.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, particularly for buyers in regions with stringent regulatory standards. Establishing transparent supply chains that adhere to international labor and environmental standards can enhance brand reputation and consumer trust. Many Chinese manufacturers are obtaining green certifications, such as ISO 14001, which signify adherence to environmental management standards. Buyers should seek partners who not only comply with these certifications but also actively engage in practices that promote sustainability throughout their operations.
What Is the Brief History and Evolution of Rapid Prototyping in China?
The evolution of rapid prototyping in China can be traced back to the late 20th century, coinciding with the country’s economic reforms and opening up to international trade. Initially, rapid prototyping technologies were primarily imported from the West, but over the years, Chinese manufacturers have developed their capabilities, leading to significant advancements in both technology and production capacity.
In the early 2000s, the rise of 3D printing technology marked a turning point, enabling faster and more cost-effective prototyping solutions. Today, China stands as a global leader in rapid prototyping, offering a diverse range of services that cater to various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. This historical trajectory underscores China’s adaptability and commitment to innovation, making it an attractive destination for international B2B buyers seeking reliable and cutting-edge prototyping solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of rapid prototyping in china
-
1. How do I choose the right rapid prototyping supplier in China?
When selecting a rapid prototyping supplier in China, prioritize those with a proven track record and extensive experience in your industry. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate a commitment to quality management. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including the technologies they use (CNC machining, 3D printing, etc.) and their ability to handle custom requests. Request samples of previous work to assess quality and responsiveness. Finally, consider suppliers that offer comprehensive support, including design feedback and logistical assistance. -
2. What are the typical lead times for rapid prototyping projects in China?
Lead times for rapid prototyping can vary significantly based on the complexity of the project and the manufacturing methods employed. Generally, projects can be completed in as little as one week for simple designs using 3D printing, while more intricate prototypes, particularly those requiring CNC machining or injection molding, may take two to four weeks. It’s advisable to discuss timelines upfront with your supplier to ensure they can meet your deadlines and to account for potential delays in shipping or customs clearance. -
3. What customization options are available for rapid prototyping in China?
Chinese manufacturers typically offer extensive customization options, allowing you to tailor your prototypes to specific requirements. This includes material selection (plastics, metals, etc.), surface finishes (anodizing, painting, etc.), and design modifications. Discuss your needs in detail with the supplier to explore all available options and ensure that they can accommodate your specific design parameters. Additionally, inquire about their capabilities for low-volume production, should you require further iterations or small batches. -
4. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for rapid prototyping in China?
Minimum order quantities for rapid prototyping can differ widely among suppliers. Many companies offer low MOQs for prototyping services, often allowing single-unit orders for initial samples. However, if you transition to production runs, MOQs may increase significantly, depending on the manufacturing process and materials used. It’s essential to clarify MOQs during your initial discussions to ensure they align with your project scope and budget. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when working with Chinese suppliers?
Payment terms for rapid prototyping projects in China typically include a deposit upfront, often ranging from 30% to 50%, with the balance due upon completion or before shipping. Some suppliers may offer flexible payment options, including letters of credit or payment through secure platforms like PayPal. Always discuss payment terms clearly and ensure they are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings later in the process. -
6. How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my prototypes?
To ensure quality assurance for your prototypes, choose a supplier that has a robust QA process in place. This includes regular inspections during production, adherence to international quality standards, and the use of testing methods such as dimensional verification and material testing. Request a quality control plan before commencing your project, and consider conducting third-party inspections or audits if necessary. Open communication with the supplier throughout the process will also help address any concerns promptly. -
7. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing prototypes from China?
Logistical considerations include understanding shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties that may apply to your order. Work with your supplier to determine the most efficient shipping method—air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Ensure you have all necessary documentation for customs clearance and consider partnering with a freight forwarder who can navigate these complexities on your behalf. Discuss delivery timelines to align with your project requirements. -
8. What are the advantages of rapid prototyping in China compared to other countries?
China offers several advantages for rapid prototyping, including cost-effectiveness due to lower labor and material costs. The country boasts advanced manufacturing technologies and a vast network of suppliers, providing diverse options and faster turnaround times. Additionally, many Chinese firms have significant experience in working with international clients, ensuring they are well-versed in meeting global standards and requirements. This combination of factors can lead to enhanced innovation and efficiency in your product development process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Rapid Prototyping In China Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SuNPe – Rapid Prototyping & Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: sunpe.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: SuNPe is a rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing company based in Zhongshan, China, established in 2005. They offer a range of services including CNC Machining, Vacuum Casting, 3D Printing (SLA/SLS/Metal Printing), Sheet Metal Prototyping, Tooling & Injection Molding, Pressure Die Casting, Extrusion, and Surface Finishing. The company has over 600 skilled staff and operates 5 factories wi…
2. PCBWay – CNC Machining & 3D Printing Services
Domain: pcbway.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining Service: Offers CNC milling, turning, and 3D printing services including SLA, SLS, FDM, and more. Rapid prototyping available in as fast as 1 day. Sheet Metal Fabrication: Customization from prototype to high volume production, capable of producing over 1,000 parts in 10 days. 3D Printing Service: Fast manufacturing of parts within hours, cost-effective compared to machining. Injecti…
3. Star Rapid – Rapid Prototyping & Low-Volume Manufacturing
Domain: starrapid.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Star Rapid offers low-volume manufacturing and prototyping services including: Rapid Prototyping, Rapid Tooling, Injection Molding Services (Plastic Injection Molding, Micro Molding), Production Tooling, CNC Machining, Vacuum Casting, Pressure Die Casting, Finishing Services, and Aluminum Extrusion. They provide 7-day standard lead times on simple parts ranging from 0.5 in. x 0.5 in. to 4 in. x 3 …
4. HLH Prototypes – Rapid Prototype Manufacturing Services
Domain: hlhprototypes.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: HLH Prototypes specializes in Rapid Prototype Manufacturing Services, offering a range of solutions including: 3D Printing (SLA, SLS, FDM, DMLS, Projet MJP), CNC Machining, Rapid Injection Moulding, Carbon Fiber 3D Printing, Sheet Metal Work, Vacuum Casting, Aluminum Forging, and Die Casting. They provide flexible manufacturing solutions for prototypes and low-volume production, with minimum order…
5. RP Proto – Rapid Prototyping & Low-Volume Manufacturing Services
Domain: rpproto.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Rapid Prototyping & Low-Volume Manufacturing Services including CNC Machining, Vacuum Casting, Plastic Injection Molding, 3D Printing, Die Casting, and Sheet Metal Fabrication. Specializes in low-volume manufacturing for industries such as automotive, medical, aerospace, and consumer electronics. Offers services like rapid injection molding (ABS, PC, PEEK), aluminum and plastic CNC machining, surf…
6. Protolis – Rapid Prototyping & Low-Volume Manufacturing
Domain: protolis.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Protolis specializes in rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing of high-quality plastic and metal parts. They offer 8 production methods including CNC Machining, Injection Molding, 3D Printing, Vacuum Casting, Extrusion, Sheet Metal Fabrication, and Compression Molding. Protolis provides over 200 grades of materials including various plastics and metals such as Aluminum, Brass, Stainless St…
7. 3ERP – Rapid Prototyping & Manufacturing Solutions
Domain: 3erp.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Rapid Prototyping Services, Low-Volume Manufacturing, CNC Machining Services (CNC Milling, CNC Turning, 5-Axis CNC Machining, Precision Machining), Injection Molding Services (Mold Tool Making, Rapid Tooling, Plastic Injection Molding, Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding), Sheet Metal Services (Laser Cutting, Metal Bending), 3D Printing, Custom Extrusion, Urethane Casting, Die Casting Solutions, Surfac…
8. Rapid Prototyping – CNC Machining, SLA, Urethane Casting
Domain: boards.core77.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Rapid Prototyping firms in China offer various services including CNC machining, SLA (Stereolithography), and urethane casting. Notable firms mentioned include Sunpe, which is praised for its communication, quality, and competitive pricing; RPWORLD, known for quick turnaround times; and Uidea Rapid Prototype, which specializes in CNC, vacuum casting, rapid tooling, and sheet metal prototyping. Pri…
9. Nice Rapid Tooling – Rapid Aluminium Tooling
Domain: nice-rapidtooling.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Nice Rapid Tooling offers a variety of services including Rapid Aluminium Tooling, SLA Rapid Prototypes, CNC Molding, CNC Milling Services, Injection Moulding, SLA 3D Printing Service, Low Volume Production, FDM 3D Printing Service, CNC Parts Machining, Silicone Compression Molding, Die Casting Mould, and Small Batch CNC Machining. They provide professional service with a focus on quality and inno…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for rapid prototyping in china
In the rapidly evolving landscape of global manufacturing, strategic sourcing for rapid prototyping in China presents a myriad of opportunities for international B2B buyers. By leveraging advanced technologies such as CNC machining, 3D printing, and vacuum casting, companies can significantly reduce lead times and costs, fostering innovation and product development. The robust infrastructure and expertise of Chinese manufacturers enable businesses from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to access high-quality prototypes that align with their specific needs.
Establishing strong partnerships with reliable Chinese suppliers not only enhances operational efficiency but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions. As markets continue to grow and diversify, the importance of adaptable and responsive manufacturing solutions cannot be overstated.
Looking ahead, international buyers are encouraged to embrace the advantages of sourcing from China, ensuring they stay competitive in a global marketplace. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, businesses can unlock their potential for innovation and drive growth in their respective industries. Engage with Chinese manufacturers today to transform your ideas into market-ready products and position your business for success in the future.