Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pvd coating service
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing effective physical vapor deposition (PVD) coating services has become paramount for B2B buyers looking to enhance product durability and efficiency. As businesses expand globally, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the challenge of selecting reputable PVD coating service providers is compounded by varying regional standards, technological capabilities, and market conditions. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the diverse types of PVD coatings, their applications across industries, and strategic insights into the supplier vetting process.
Understanding the nuances of PVD coating technology—from its operational mechanics to the specific advantages it offers in enhancing tool life and reducing operational costs—is critical for informed purchasing decisions. The information within this guide will empower international buyers to navigate market complexities strategically, ensuring they select the right coating solutions tailored to their operational needs. By evaluating key factors such as coating types, costs, application requirements, and supplier credentials, businesses can optimize their procurement strategies and ultimately bolster product performance.
Equipped with actionable insights and a clear understanding of the global PVD coating service landscape, B2B buyers can confidently approach their sourcing decisions, driving profitability and operational excellence in their own manufacturing ventures.
Understanding pvd coating service Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium Nitride (TiN) | High hardness, gold-like appearance, excellent wear resistance | Cutting tools, machining, decorative parts | Pros: Corrosion resistant, aesthetic appeal. Cons: Limited effectiveness at very high temperatures. |
| Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Low friction coefficient, high hardness, optimal for sliding applications | Automotive, medical devices, molds | Pros: Excellent lubricity, high wear resistance. Cons: More costly, requires careful handling during application. |
| Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) | Greater thermal stability, ideal for high-speed applications | High-speed cutting tools, forming tools | Pros: Increased tool life, withstands elevated temperatures. Cons: Can be brittle if improperly applied. |
| Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) | Enhanced corrosion resistance, diverse color options | Consumer electronics, automotive parts | Pros: Attractive finish, good thermal conductivity. Cons: Thinner films may not adhere well to all substrates. |
| Chromium Nitride (CrN) | Balanced hardness and toughness, suitable for various environments | Tooling, mechanical components | Pros: Versatile, good adhesion. Cons: Limited performance if exposed to extreme temperatures. |
What Are the Characteristics and B2B Applications of PVD Coating Types?
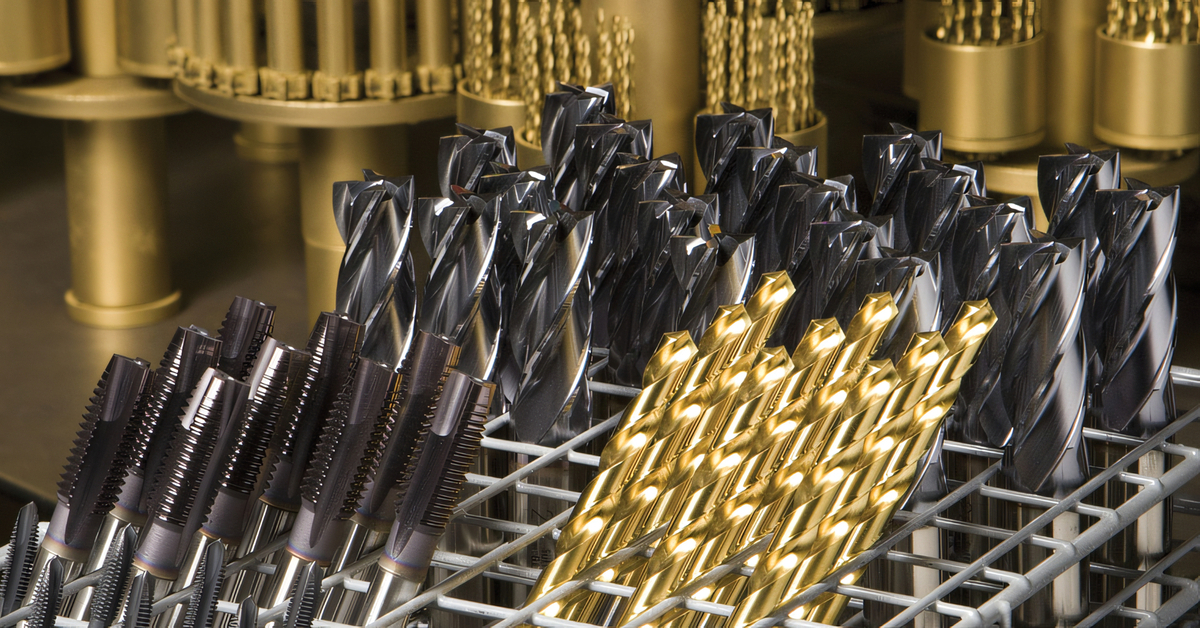
Titanium Nitride (TiN) is widely regarded for its distinctive gold-like finish and remarkable surface hardness, often ranging from 2000 to 3500 HV. It’s particularly suitable for cutting and machining tools, enhancing both tool life and performance. When considering TiN coatings, B2B buyers should analyze the thermal limits of their tools, as TiN is less effective at extremely high temperatures.
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings offer a unique balance of low friction and extreme hardness, making them ideal for applications involving sliding wear, such as automotive components and medical devices. B2B purchasers should note that while DLC coatings deliver superior performance, they come at a higher cost and require precise application schedules to maximize adhesion and functionality.
Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) is particularly noted for its stability under high thermal conditions, making it the preferred choice for high-speed cutting tools. This coating can significantly extend tool life, but buyers should be cautious about the brittleness that may develop if the application isn’t controlled meticulously.
Zirconium Nitride (ZrN) stands out for its excellent corrosion resistance and the variety of aesthetically pleasing colors it offers, which can be particularly advantageous in consumer products. That said, B2B buyers must ensure that the substrate is appropriate for ZrN coating, as thinner films may compromise adhesion.
Chromium Nitride (CrN) provides a solid balance of toughness and hardness, making it versatile enough for various mechanical components and tooling. Buyers looking to utilize CrN coatings should carefully evaluate the expected environmental conditions, as these coatings may not always perform well under extreme temperature variations.
By understanding the distinguishing features and applicable contexts of these PVD coating variations, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, tailored to the specific demands of their industries.
Key Industrial Applications of pvd coating service
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of PVD Coating Service | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Coating of turbine blades | Enhanced performance and resistance to thermal fatigue | Need for strict quality compliance and certification |
| Medical Devices | Coating of surgical instruments | Improved durability and biocompatibility | Understanding regulations (e.g., FDA) for medical use |
| Automotive | PVD coatings on engine components | Increased wear resistance and reduced friction | Supplier capability to cater to automotive industry standards |
| Tool Manufacturing | Coating of cutting and forming tools | Extended tool life and improved machining efficiency | Ability to customize coatings for specific applications |
| Energy | Coating of drilling tools | Enhanced lifespan and productivity in harsh environments | Consideration for the coatings’ performance at varying temperatures |
Aerospace is a critical industry where PVD coatings significantly enhance the performance of turbine blades. These coatings increase the resistance to thermal fatigue and erosion, playing a vital role in the longevity and efficiency of aircraft engines. International B2B buyers, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, must prioritize suppliers who comply with stringent quality standards and certification processes, as any failure in performance can have dire implications.
Medical devices heavily rely on PVD coatings for surgical instruments, ensuring improved durability and biocompatibility. Coatings such as Titanium Nitride (TiN) provide a hard surface that withstands repeated use while resisting corrosion. Organizations sourcing for this application should be well-versed in local regulations like the FDA standards in the U.S. or CE marking in Europe to ensure compliance and marketability.
In the automotive sector, PVD coatings applied to engine components enhance wear resistance and reduce friction, leading to improved fuel efficiency and longer service life. International buyers from Africa and South America should seek suppliers that are capable of meeting industry-specific standards while also providing detailed information on the performance characteristics of the coatings to ensure they align with their application needs.
Manufacturers of cutting and forming tools benefit immensely from PVD coating services, which extend tool life and improve machining efficiency. This is particularly vital in high-volume production environments where downtime for tool replacements is costly. Buyers should focus on suppliers that can customize coatings based on specific machining requirements, ensuring optimal compatibility with their existing production processes.
Lastly, in the energy sector, the use of PVD coatings on drilling tools enhances lifespan and productivity, especially in challenging environments. Given the varying conditions these tools face, it is essential for buyers to confirm that suppliers can provide coatings that withstand extreme temperatures and abrasive materials. Ensuring supplier expertise in these coatings will lead to significant performance benefits for drilling operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pvd coating service’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulties in Selecting the Right Coating Type
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle to determine which type of PVD coating will best meet their specific application needs. With a wide variety of coatings available, each offering different properties such as hardness, chemical composition, and friction coefficients, it can be overwhelming for procurement managers and engineers to choose appropriately. This uncertainty can lead to inappropriate sourcing decisions, resulting in subpar performance and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the different coating options, buyers should conduct a comprehensive needs assessment focusing on the specific application environments and operational demands of their tools or components. Engaging directly with PVD coating service providers early in the procurement process is crucial. Inquire about their experience with similar applications and ask for case studies or examples of previous work. It is also advisable to request expert consultation on the properties and performance of potential coating solutions, ensuring a closer match with your specifications. Establishing a clear communication channel with the provider enables ongoing support and guidance, ultimately leading to more informed and strategic purchase decisions.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Coating Durability and Performance
The Problem: Buyers frequently express concerns regarding the long-term durability and performance attributes of PVD coatings. Many fear that the coatings will wear out too quickly or fail to perform under the specific conditions prevalent in their operational environments, which can lead to costly downtime and increased maintenance expenses.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, it is essential to prioritize a thorough testing phase before full-scale implementation of the PVD coatings. Request trial samples or small-scale coatings to assess how well the chosen PVD material performs under actual operating conditions. Establishing acceptance criteria for performance metrics—such as hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability—during this trial phase will create a structured framework for evaluating the coatings. Additionally, formulating a strong partnership with the PVD service provider can yield insights into their quality control processes. Ask about their testing methodologies and durability testing regimes, which can confirm the long-term reliability of the coating, aligning with the rigorous demands of your production environment.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Lead Times and Turnaround for Coating Services
The Problem: B2B buyers often find themselves dealing with extended lead times and turnaround issues when sourcing PVD coating services. Long delays can disrupt manufacturing schedules, leading to supply chain interruptions and missed deadlines, which are particularly critical for industries where time-to-market is essential.
The Solution: To counteract lead time challenges, it’s important for buyers to establish clear communication and set realistic expectations with PVD coating service providers upfront. Inquire about typical lead times and factors that may affect them, such as the complexity of the coating process required or the cleanliness of the substrates to be coated. Develop a contingency plan that includes multiple suppliers or service providers to create flexibility in the supply chain. Implementing a regular scheduling process or establishing long-term contracts may enhance reliability and predictability in service delivery. Collaborating on forecasting demand with your coating provider can also optimize resource allocation and minimize turnaround times, ensuring that your operations remain unaffected by delays.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pvd coating service
What Are the Key Properties of Steel in PVD Coating Applications?
Steel is one of the most commonly used substrates for PVD coating. Its high temperature rating, typically moving up to 300°C (572°F), ensures it can withstand the PVD deposition process without degrading. Steel exhibits excellent wear resistance, making it suitable for items that experience high mechanical stresses, such as cutting and forming tools. However, while mild steel has minimal corrosion resistance, alloyed steels can significantly enhance this property, thus extending durability in harsh environments.
Pros: Steel’s cost-effectiveness and versatility are significant benefits. It can be easily machined and allows for complex geometries, which means it suits various applications, from automotive to medical devices.
Cons: Steel can be prone to corrosion unless appropriately alloyed or coated, which can limit its application in moisture-rich environments. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity increases with the need for post-coating treatments to ensure optimal performance.
Impact on Application: Steel components need to be compatible with the intended operational environment. When coated, their performance can be enhanced, especially in environments where they are exposed to corrosive media, making proper material selection crucial.
How Does Titanium Function as a Substrate for PVD Coating?
Titanium is another excellent substrate for PVD coating due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and superior corrosion resistance. It maintains structural integrity in extreme temperatures—typically between 200°C (392°F) to 600°C (1112°F) during the coating process.
Pros: Titanium’s inherent properties provide an excellent base for PVD coatings, enhancing characteristics like wear resistance and promoting a long lifespan. Its biocompatibility makes it favored in medical fields, especially for implantable devices.
Cons: The main drawback of titanium is its higher cost compared to steel, along with its manufacturing complexity. Machining can be more challenging due to titanium’s toughness and tendency to work-harden.
Impact on Application: Titanium’s compatibility with hostile environments, along with the ability to create thin, durable coatings, makes it suitable for aerospace components and medical devices, further reinforcing its value in niche markets.
When Should Aerospace Alloys Be Considered for PVD Coating?
Aerospace alloys, such as those composed of aluminum, magnesium, and titanium, represent a significant market for PVD coatings due to their lightweight and high strength properties. Many aerospace applications require robust performance under high-pressure conditions—exceeding 400°C (752°F) with high wear resistance.
Pros: Aerospace alloys are designed to endure the extreme demands of flight, offering excellent fatigue resistance and thermal stability. They can enhance fuel efficiency and reliability.
Cons: The primary downsides include their high cost and specialized machining requirements. Additionally, the susceptibility to certain chemicals can limit their application in some environments.
Impact on Application: PVD coated aerospace components benefit from enhanced performance, particularly in corrosive or high-heat environments, which is critical for establishing compliance with stringent aerospace standards and regulations.
What Role Do Non-Ferrous Metals Play in PVD Coating?
Non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, copper, and brass are increasingly used in PVD coating applications. They display excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, making them suitable for a broad range of applications including electronics and decorative items.
Pros: Non-ferrous metals typically exhibit lower weights, and PVD coatings enhance their mechanical properties while allowing for aesthetic customization.
Cons: Their lower mechanical strength compared to ferrous metals can be a limitation in demanding applications. Treatment processes are often required to improve their surface characteristics before PVD implementation.
Impact on Application: Coating with PVD can significantly enhance the durability and appearance of non-ferrous components, making them more versatile for industries like consumer electronics and automotive.
Summary Table of Material Considerations for PVD Coating
| Material | Typical Use Case for pvd coating service | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Cutting tools, forming tools | Cost-effective, versatile | Corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Titanium | Medical devices, aerospace components | High corrosion resistance, lightweight | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Aerospace Alloys | Aircraft components | Excellent fatigue resistance | High cost, specialized processing | High |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Electronics, decorative components | Aesthetic finish, good conductivity | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
The information here equips international B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, with the insights necessary for making informed decisions related to PVD coating service material selection tailored for specific applications and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pvd coating service
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of PVD Coating Services?
The manufacturing process for PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating services involves several critical stages that are essential for ensuring high-quality outcomes. The typical stages include material preparation, coating application, and rigorous finishing processes.
1. Material Preparation: Ensuring Cleanliness and Suitability
Before any coating can begin, substrates must undergo a thorough cleaning process to remove contaminants, oils, and oxidation that could impair bonding. Cleaning methods such as ultrasonic cleaning, sandblasting, or solvent washing are commonly employed. The decision on which method to use is influenced by the substrate material and intended application, ensuring that the substrate is adequately prepared for effective coating adhesion.
2. Coating Application: Techniques Matter
Once the substrates are cleaned, the actual PVD coating application process begins. The most prevalent methods used include:
- Sputtering: A process where a metal target is bombarded with energetic ions, causing the target material to vaporize and deposit on the substrate.
- Cathodic Arc Deposition: Utilizes high-voltage arcs to evaporate metal, creating a dense and robust coating.
- Laser Ablation: Involves the use of laser energy to vaporize material, allowing for targeted applications in precision components.
Each technique is selected based on the desired coating characteristics—such as thickness, hardness, and adhesion—but typically operates under vacuum conditions to ensure a controlled environment.
3. Finishing: Precision Counts
After coating application, a finishing process may be employed, which includes techniques such as polishing or surface treatment to attain desired aesthetics or functional properties, such as reducing surface roughness or enhancing corrosion resistance.
What Quality Assurance Protocols Are Relevant for PVD Coating Services?
Quality assurance in PVD coating is paramount for ensuring that the final products meet stringent industry standards. Different sectors may demand varied levels of quality compliance, making it crucial for buyers to understand these expectations.
International Standards and Compliance
Many PVD coating service providers adhere to international quality assurance standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, ensuring manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may include CE marking for products intended for the European market or API certifications for materials intended for the oil and gas sector.
Quality Control Checkpoints: What Should Buyers Expect?
Rigorous QC checkpoints are embedded throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage verifies the quality and suitability of raw materials to avoid defects in the finished product. Part of this process includes assessing supplier certificates of compliance and testing raw materials against specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the coating process, various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and coating thickness are monitored to ensure adherence to specifications. Regular checks help address any inconsistencies that may arise during manufacturing.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the PVD coating is completed, the product undergoes final inspection including visual inspections and testing for hardness, thickness, and adhesion qualities. This step is critical for ensuring the final product meets all requested specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Quality Assurance in PVD Coating Services?
For B2B buyers, particularly those in diverse global markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes can be challenging but is essential for risk management.
1. Audits and Inspection Reports
Buyers should perform regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their compliance with quality standards and practices. These audits should examine the supplier’s facilities, equipment, and processes, ensuring that they conform to required industry standards.
Inspection reports detailing compliance with standard operating procedures (SOPs) and quality assessments should be readily available from suppliers. These documents provide insights into the consistency of the supplier’s operations and the quality of the end-products.
2. Third-Party Inspection Services
Employing independent third-party inspection services can further mitigate risks. These entities can conduct unbiased assessments of production processes, testing methodologies, and final product quality. Their reports can facilitate informed decision-making for buyers as well as enhance supplier accountability.
3. Understanding Local and Global Quality Nuances
Given the varying regulatory environments between regions, buyers should have an understanding of local quality assurance requirements alongside international standards. Quality expectations may differ significantly between countries—particularly in sectors such as medical devices or aerospace—that often necessitate comprehensive compliance with both local laws and international benchmarks.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Quality in PVD Coating Services for B2B Success
Purchasing PVD coating services in the international B2B landscape requires a keen understanding of both the manufacturing processes and the quality assurance protocols crucial for achieving operational efficiency and product reliability. By emphasizing stringent quality checks such as IQC, IPQC, and FQC and verifying suppliers through audits, inspection reports, and third-party assessments, businesses can secure superior coatings that enhance the performance of their tools and components. This commitment to quality not only bolsters productivity but also fosters long-term partnerships built on trust and accountability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pvd coating service’
Introduction:
When sourcing PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating services, it’s imperative to follow a structured approach that carefully evaluates potential suppliers and aligns their offerings with your specific needs. This checklist serves as a practical guide to streamline your procurement process, ensuring that you choose the right partner for high-quality coatings that enhance the durability and performance of your tools and components.
-
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Identifying your specific requirements is the first crucial step in sourcing a PVD coating service. Consider the type of materials you need coated, the required hardness, and the intended application of the parts.
– Specify coating properties, such as thickness, color, and chemical composition, to ensure compatibility with your production processes. -
Step 2: Research and Identify Reputable Suppliers
Begin by compiling a list of potential suppliers with a strong reputation in the industry. Look for companies that specialize in PVD coatings and have established a history of successful projects.
– Investigate their online presence, check reviews, and reach out to industry forums for recommendations to build a list of qualified service providers. -
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s critical to thoroughly vet each supplier on your shortlist. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in either your sector or region to assess their experience.
– Pay particular attention to samples of previous work that demonstrate their capability to deliver high-quality coatings appropriate to your specifications. -
Step 4: Verify Technical Capabilities and Equipment
Ensure that the suppliers employ advanced PVD coating technology, including methods that best meet your needs, such as cathodic arc or sputtering. The quality of equipment can significantly impact the coating’s durability and performance.
– Inquire about their manufacturing processes, such as vacuum chamber specifications and temperature ranges, to confirm they can achieve the desired results. -
Step 5: Assess Quality Control Measures
Quality assurance is paramount in PVD coating services due to its impact on product performance and lifespan. Evaluate the supplier’s quality control protocols, including material inspections before and after coating.
– Ask how they measure coating thickness and adhesion, as well as any certifications they hold, to ensure they consistently meet industry standards. -
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Lead Times
Request detailed quotations that break down costs associated with the coating service, including any extra charges for sample runs or expedited services. Align pricing with your budget and operational timelines.
– Clarify lead times for production and any minimum order requirements to ensure that they can meet your delivery deadlines, avoiding potential disruptions in your supply chain. -
Step 7: Establish Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital for a successful partnership. Establish clear lines of communication with your selected supplier to facilitate updates and troubleshoot any potential issues promptly.
– Discuss preferred communication methods and frequency of updates throughout the coating process to ensure alignment and transparency.
By following this checklist, you can approach your procurement of PVD coating services with confidence, knowing you have thoroughly assessed and aligned your needs with your chosen supplier’s capabilities. This approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances the likelihood that your coatings will meet performance expectations and improve your overall product quality.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pvd coating service Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in PVD Coating Services?
When sourcing PVD coating services, it is crucial to understand the cost structure involved. The primary cost components influencing pricing include:
-
Materials: The selection of materials for coatings, such as titanium, chromium, or compounds thereof, directly impacts pricing. High-quality raw materials typically lead to superior coatings that enhance the lifespan and performance of tools and components.
-
Labor: Skilled technicians and engineers are essential for operating PVD coating equipment and ensuring optimal application. Labor costs can vary based on geographical location and the expertise required. Developing regions may experience lower labor costs, while advanced manufacturing nations might charge a premium for skilled labor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. High overhead costs can come from advanced technologies and quality control measures adopted by service providers.
-
Tooling: Setup costs for PVD coating processes include the expenses associated with designing and maintaining customized tooling for specific projects. Depending on the complexity of the coating process, this could represent a significant cost factor.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are necessary to ensure that coatings meet industry standards and client specifications. The costs associated with inspection, testing, and certification can vary but are essential for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation, packaging, and handling costs are also factored into the overall price. International buyers must consider additional logistics costs, including customs duties and insurance, which can influence total expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing to ensure business sustainability. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market positioning and the value-added features of their services.
How Do Price Influencers Affect PVD Coating Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of PVD coating services beyond the basic cost components:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger order volumes often lead to discounted rates per unit. Negotiating with suppliers on MOQs can yield significant savings, particularly for businesses with consistent coating needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: The level of customization required can dramatically impact pricing. Simple, standard coatings are typically less expensive than highly specialized coatings requiring tailored materials or complex application processes.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Coatings that meet industry certifications or specific quality standards generally incur higher prices due to the assurance of performance and reliability. International buyers should inquire about certifications that may be pertinent to their local markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The geographical location, reputation, and production capabilities of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with advanced technology may charge more but offer superior results, potentially lowering the total cost of ownership.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery is vital. Incoterms dictate who bears the costs and risks associated with transport, which can significantly affect the final price. Buyers should clarify these terms to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Negotiating PVD Coating Prices?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engaging suppliers early in the procurement process allows buyers to discuss potential discounts for larger orders or long-term commitments. Building a relationship with suppliers may also lead to better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency Assessment: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and the lifespan of coated components. Investing in higher quality coatings may reduce overall operational costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from diverse regions must factor in currency fluctuations, tariffs, and transportation costs when comparing suppliers. Building in buffers for these variables during negotiations can help secure competitive pricing.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Awareness of industry trends can aid in timing purchases and understanding price fluctuations based on supply and demand. Regular engagement with industry news will give buyers leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer
Prices discussed herein are indicative and can vary substantially based on the specific requirements of each project, the provider’s location, and current market conditions. It is advisable for buyers to obtain detailed quotes tailored to their individual needs from potential suppliers before making decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pvd coating service With Other Solutions
To help international B2B buyers evaluate the options available for surface coatings, it’s essential to explore suitable alternatives to PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating services. By understanding the comparative performance, costs, and applications of different coatings, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | PVD Coating Service | Hard Anodizing | Thermal Spraying |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High hardness (2000-3500Hv), excellent wear resistance, low friction | Good corrosion resistance, moderate wear resistance, durability | Varies widely based on material, provides thick coatings, can improve thermal resistance |
| Cost | Moderate initial cost but lower long-term costs due to durability | Generally lower initial cost but may require more frequent replacement | High initial investment and operational costs due to equipment and materials |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward for standard applications; requires substrate preparation | Simple process, often in-house capable; limited substrates | Complex, requires specialized equipment and skilled operators for application |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; coatings are durable and long-lasting | Moderate maintenance; can wear over time, requiring re-treatment | Moderate to high, depending on application; thick coatings may require periodic maintenance and monitoring |
| Best Use Case | Cutting tools, precise components, decorative applications | Aluminum parts requiring strong corrosion resistance | Components subject to high wear, extreme temperatures, and thermal cycles |
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Hard Anodizing compared to PVD Coating Service?
Hard anodizing involves an electrochemical process that converts the outer surface of aluminum into a wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coating. Its primary advantage is cost-effectiveness, especially for bulk production. However, hard anodizing is limited to aluminum substrates and may not provide the same high hardness and narrow tolerances achievable with PVD coatings. As a result, while it is a reliable choice for specific applications, it may not suit businesses requiring precision or enhanced durability.
How does Thermal Spraying serve as an alternative to PVD Coating Service?
Thermal spraying is a versatile coating method where materials are heated and accelerated towards the surface to form a coating, resulting in thicker applications. It is particularly effective for components exposed to extreme wear, thermal stress, and corrosive environments. Its main advantage lies in the variety of materials that can be used, allowing for tailored performance based on application needs. However, the high operational costs associated with equipment and skilled labor can render it less accessible for smaller businesses or projects with strict budgets.
How should B2B buyers choose the right coating solution?
When selecting a coating service, B2B buyers must carefully assess their operational requirements. Factors such as the type of materials involved, the working environment, desired lifespan, and budget constraints are critical in determining the most suitable option. For applications demanding high precision and performance, PVD coatings may provide the best long-term value, whereas hard anodizing and thermal spraying may be more appropriate for specific material types or conditions. Engaging in a thorough needs analysis and consulting with experienced providers can facilitate optimal decision-making, ensuring that the chosen solution aligns with both technical specifications and financial objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pvd coating service
What Are the Key Technical Properties of PVD Coating Services?
When considering PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating services, understanding the critical technical properties is essential for making informed decisions. Here are some fundamental specifications that define the quality and effectiveness of PVD coatings:
-
Hardness (HV): PVD coatings typically exhibit high hardness values ranging from 2000 to 3500 HV (Vickers Hardness). This hardness significantly contributes to tool longevity and performance, especially in industries requiring precision cutting and forming. For B2B buyers, selecting a coating with the appropriate hardness is crucial to ensure that tools withstand demanding applications and extend their service life.
-
Coating Thickness: The average thickness for PVD coatings ranges from 2 to 5 micrometers, although it can be as thin as a few hundred nanometers or thicker than 15 micrometers depending on specific requirements. The thickness influences durability, performance characteristics, and the potential for increases in manufacturing efficiency. Buyers should consider the application to determine the optimal coating thickness that balances functionality and cost.
-
Friction Coefficient: PVD coatings generally have a low coefficient of friction, typically between 0.1 and 0.35. A lower friction coefficient reduces wear during operation, improving tool performance and enabling higher cutting speeds or feeds. Understanding this property enables businesses to choose PVD coatings that can contribute to more efficient manufacturing processes.
-
Deposition Temperature: PVD processes typically operate within a temperature range of 250 to 450 °C, though some methods allow coating at temperatures as low as 70 °C or as high as 600 °C. This flexibility is important, as it determines the compatibility of various substrate materials. Decision-makers should thoroughly consider the substrate material’s thermal stability to prevent potential damage during the coating process.
-
Adhesion Strength: The bond strength between the coating and the substrate is vital for the performance and longevity of coated products. PVD coatings form strong physical bonds, which reduces the risk of delamination under stress. Selection of a coating with superior adhesion properties ensures that the coated tools or components maintain integrity during use.
What Are Common Terms Used in the PVD Coating Industry?
A grasp of industry-specific vocabulary aids in effective communication and negotiation with service providers. Here are essential terms every B2B buyer should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that manufacture products that are then marketed by another company under its brand name. In the context of PVD coating, understanding whether the coating service aligns with OEM standards can assure product quality and trust in performance.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ signifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This is crucial in understanding pricing structures and potential startup costs. Buyers should assess whether the MOQ aligns with their purchasing strategy and production plans.
-
RFQ (Request for Quote): An RFQ is a standard business process where potential suppliers are invited to provide pricing and terms for specific products or services. Engaging suppliers through RFQs can enhance competitive pricing and provide insights into service capabilities within the PVD coating market.
-
Incoterms: International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers when negotiating shipping and delivery terms, thereby reducing potential misunderstandings or disputes.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time taken from placing an order until it is fulfilled. For PVD services, typical lead times range from 3 to 5 days. Recognizing lead times is crucial for effective inventory management and production scheduling, particularly in fast-moving sectors.
By familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and industry-specific terms, you can make more informed decisions when selecting a PVD coating service, ultimately enhancing your operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pvd coating service Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the PVD Coating Service Sector?
The PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coating service sector is experiencing significant growth driven by several key market dynamics. The increasing demand for high-performance coatings in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and biomedical, is propelling advancements in coating technology. Global buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer advanced solutions—like multi-layered and nano-structured coatings—that provide enhanced durability and performance for their applications.
Emerging technologies such as real-time monitoring and automated PVD systems are reshaping the sourcing landscape. For international B2B buyers, these innovations not only ensure consistent quality but also streamline production processes, reducing lead times. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers with capabilities in customized coating solutions that can meet specific performance parameters, such as reduced friction or increased hardness. Furthermore, sustainability is becoming a key consideration, with buyers favoring suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices and materials.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Important in the PVD Coating Service Sector?
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including PVD coating, is under increasing scrutiny. B2B buyers are now more aware of the importance of selecting suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. They seek out partners who utilize environmentally friendly coatings and materials that minimize ecological footprint while maintaining performance standards. For instance, coatings derived from non-toxic sources and processes that reduce waste are gaining traction.
Moreover, ethical sourcing in the PVD coating sector involves transparency in the supply chain, ensuring that materials are procured responsibly. Certifications that highlight a company’s green practices serve not only to appeal to eco-conscious buyers but also to comply with increasing regulatory pressures in global markets. Buyers from diverse regions, such as Europe and the Middle East, typically value ‘green’ certifications, pushing suppliers to innovate not only in coating technology but also in adopting sustainable and ethical sourcing practices.
How Has the PVD Coating Service Sector Evolved Over Time?
PVD coating services have evolved considerably since their inception. Initially developed for industrial applications, the technology has expanded to serve a wide array of sectors, including consumer goods and medical devices. The introduction of various deposition methods, such as cathodic arc and magnetron sputtering, has allowed for better control over coating properties and improved adhesion.
Over the years, the focus has shifted towards more efficient and sophisticated processes that enable the creation of coatings with complex structures and tailored attributes. This evolution has positioned PVD coatings as crucial for enhancing tool life and performance across numerous applications. As industries seek solutions that combine quality with sustainability, the PVD coating service sector continues to adapt, providing innovative options that meet the evolving needs of international B2B buyers.
Through these developments, international buyers can gain access to superior coating technologies that not only improve their operational efficiency but also align with broader sustainability goals, ensuring long-term value in their sourcing strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pvd coating service
1. How do I select the right PVD coating for my application?
When choosing a PVD coating, consider the specific requirements of your application, including hardness, friction characteristics, chemical resistance, and coating thickness. Different materials and coating combinations can enhance performance in cutting tools, mechanical parts, or decorative applications. Consulting with your supplier about the intended usage and any environmental factors can guide you in selecting the optimal coating. Additionally, reviewing case studies or success stories from the provider may provide insights into the effectiveness of particular coating types in similar applications.
2. What factors should I consider when vetting a PVD coating supplier?
Key factors to consider include the supplier’s industry experience, technological capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Look for certifications such as ISO to ensure adherence to international standards. Additionally, assess their customer service responsiveness, lead times for production, and pricing structures. To further vet their capabilities, ask for references from past clients and review case studies that demonstrate their coating solutions in practice. Attending industry trade shows where the supplier exhibits can also provide firsthand insights into their technology and services.
3. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for PVD coating services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between suppliers and are often influenced by factors such as the complexity of the coating process and the materials involved. Some suppliers may allow small batch runs for initial testing or prototypes, while others may set a more substantial MOQ to justify production setup costs. It’s advisable to communicate your specific needs with potential suppliers early in the negotiation process to ensure alignment on their capabilities and your requirements.
4. How can I ensure the quality of PVD coatings is consistent?
To ensure consistent quality, ask suppliers about their quality assurance processes and the standards they follow during production. Look for detailed inspection protocols, including adhesion tests and thickness measurements, which should be part of their standard operating procedures. Request documentation that proves their coatings pass industry benchmarks for performance, such as hardness or wear resistance. Suppliers may also provide batch testing results upon request, allowing you to monitor quality across multiple orders.
5. What payment terms are common in international PVD coating transactions?
Payment terms can vary according to the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. International B2B contracts typically include options like Letter of Credit, advanced payment, or open account terms after establishing a solid business relationship. It’s vital to negotiate favorable terms that offer protection for both parties, especially regarding currency fluctuations and potential delivery delays. Discuss the payment schedule upfront and ensure it aligns with your budgetary needs and cash flow considerations.
6. What logistics aspects should I consider when sourcing PVD coating services internationally?
Logistics considerations include shipping costs, customs regulations, and potential tariffs on imported goods. It’s essential to work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to avoid delays or complications. Discuss the shipping methods available, estimated delivery times, and the handling of any required documentation. Consider also the supplier’s policies on tracking shipments and resolving any unforeseen issues during transit. Ensuring robust logistics arrangements can prevent disruptions to your supply chain and maintain timely production schedules.
7. Can PVD coatings be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer the ability to customize PVD coatings based on the specific requirements of your application. This can include adjusting the coating material, thickness, and properties such as color or hardness. Collaboration with your supplier is crucial; sharing detailed specifications, expected performance criteria, and any environmental considerations will enable them to develop a coating that meets your precise needs. Prototype testing may also be advisable before full-scale production to ensure the customized coating performs as intended.
8. What is the typical lead time for PVD coating services?
Lead times for PVD coating services generally range from 3 to 5 business days for standard orders, but this can vary based on factors such as order size, complexity of the coating, and the supplier’s current workload. It’s prudent to inquire about specific lead times upfront and factor in any potential delays from logistics, especially for international shipments. Consider building in extra time for tests or adjustments needed to refine the coatings for your particular applications. Regular communication with your supplier can help you stay informed and manage expectations effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
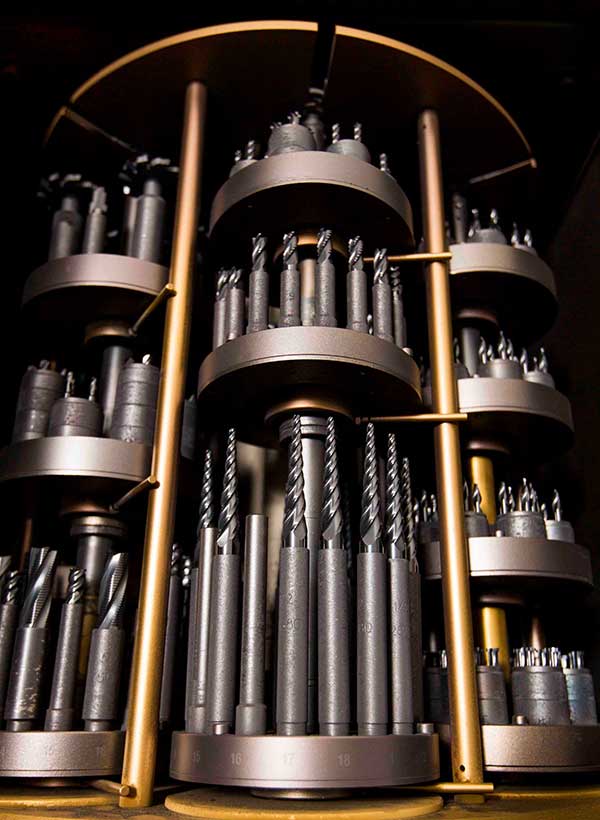
Top 4 Pvd Coating Service Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PVD America – PVD Coatings for Tool Longevity
Domain: pvdamerica.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: PVD (Physical Vapour Deposition) service provider in southern California with 15 years of experience. Offers a wide range of PVD Coatings for cutting tools and forming tools to extend their life. Coatings have hardness levels between 2000 – 3500Hv. Different coatings possess varying properties such as hardness, chemical composition, color, and friction coefficient. Product lines include Alpha Seri…
2. voestalpine – PVD Coatings
Domain: voestalpine.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: PVD coatings from voestalpine High Performance Metals offer enhanced surface properties for tools and components. These coatings provide increased hardness, wear resistance, and reduced friction, extending tool life and improving performance. The coatings are suitable for various materials, including steel, carbide, and ceramics, and can be applied in different thicknesses depending on application…
3. PVD Coatings – Thin Film Coatings
Domain: pvdcoatings.net
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: PVD Coatings offers a variety of decorative and functional thin film coatings including: PVD Brushed Bronze, PVD Carbon, PVD French Gold, PVD Graphite, PVD Mocha Bronze, PVD Polished Black Nickel, PVD Polished Brass, PVD Polished English Brass, PVD Polished Gold, PVD Polished Nickel, PVD Satin Brass, PVD Satin English Brass, PVD Satin Gold, and PVD Satin Nickel. The PVD coating process is environm…
4. RUBIG – PVD Coatings
Domain: rubig.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: RUBIG offers PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) coatings that enhance the functionality of components by providing wear resistance, friction reduction, corrosion protection, and improved optical properties. The coatings can be applied to various materials including metals, glass, ceramics, plastics, and textiles, with a thickness of up to approximately 5 µm. PVD coatings are used in diverse industrie…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pvd coating service
How Can PVD Coating Services Enhance Your Business?
In summary, embracing strategic sourcing for PVD coating services can significantly bolster your operational efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the longevity of your tools and components. As our exploration has shown, the exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and versatility of PVD coatings offer international B2B buyers tailored solutions to meet diverse needs across industries. Choosing the right coating—from titanium nitride to diamond-like carbon—depends on understanding application-specific requirements, making knowledgeable vendor partnerships crucial.
The potential reductions in downtime and maintenance, combined with the enhanced performance and reliability of coated components, provide a compelling case for investing in quality PVD services. Furthermore, the unique properties of these coatings, such as reduced friction and extended tool life, directly correlate to increased productivity and, ultimately, profitability.
As you navigate the landscape of global sourcing, consider engaging with established PVD service providers who can deliver tailored solutions for your specific challenges. By prioritizing quality and expertise, especially in growing markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, you position your business for future success. Start your journey today to leverage the advantages that PVD coatings can bring to your manufacturing processes.