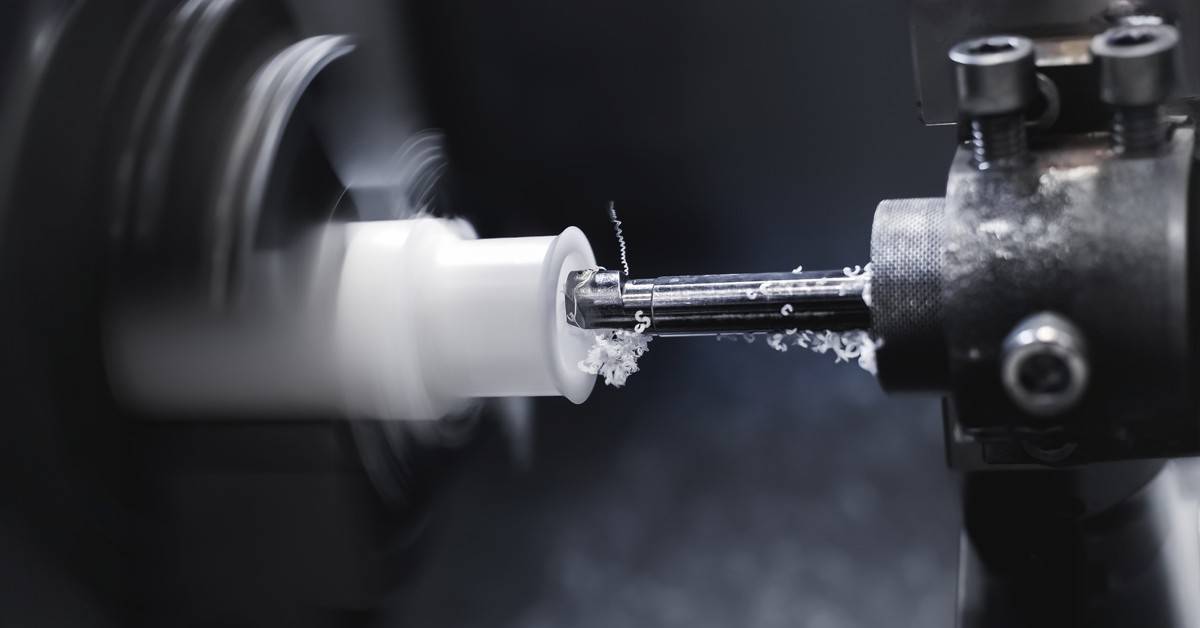
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pvc machining
Navigating the complexities of sourcing high-quality PVC machining components can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially when balancing cost, quality, and supplier reliability. With PVC’s unique properties, such as excellent chemical resistance and durability, it has become an essential material across various industries, including medical, construction, and consumer goods. This guide provides a thorough exploration of PVC machining, covering essential aspects such as types of machining processes, application areas, and key considerations for selecting the right suppliers.
Understanding the nuances of PVC machining is vital for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where specific regional challenges may arise. From identifying suitable machining methods to evaluating the quality of components, this guide empowers buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. It delves into critical factors such as material properties, cost implications, and best practices for supplier vetting, ensuring that businesses can confidently navigate the global market for PVC machining.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and expert recommendations, this comprehensive resource aims to streamline the procurement process, mitigate risks, and enhance overall project outcomes. Whether you’re looking to source components for industrial applications or consumer products, this guide is designed to be your go-to reference for all things related to PVC machining.
Understanding pvc machining Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | High precision, programmable control | Medical devices, industrial components | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability. Cons: Higher setup costs, longer lead times for complex designs. |
| Injection Molding | Mass production capability, complex shapes | Packaging, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes, excellent surface finish. Cons: High initial mold costs, limited flexibility. |
| Extrusion | Continuous production, versatile profiles | Pipes, window frames, construction materials | Pros: Efficient for long shapes, customizable profiles. Cons: Limited to specific shapes, slower for small runs. |
| Thermoforming | Quick prototyping, thin-walled structures | Consumer goods, medical packaging | Pros: Fast production cycles, low tooling costs. Cons: Limited to simple geometries, less durable than other methods. |
| 3D Printing | Additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping | Custom parts, small-scale production | Pros: Design flexibility, short lead times. Cons: Slower than traditional methods for large volumes, surface finish may require post-processing. |
What are the key characteristics of CNC Machining for PVC?
CNC machining is a highly precise method for machining PVC, utilizing computer-controlled tools to achieve intricate designs. This technique is particularly suitable for applications requiring tight tolerances, such as medical devices and industrial components. B2B buyers should consider the higher setup costs and the time required to program complex parts, but the trade-off is a level of accuracy and repeatability that can significantly enhance product quality.
How does Injection Molding serve the PVC market?
Injection molding is ideal for mass production of PVC items, capable of creating complex shapes with high efficiency. Common applications include packaging and automotive components. While the initial investment for molds can be substantial, the cost per unit decreases significantly with larger production runs. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits against initial costs, especially for projects with high volume demands.
What are the advantages of Extrusion in PVC machining?
Extrusion is a continuous process that allows for the production of long, uniform shapes such as pipes and window frames. This method is versatile and can be customized to meet specific profile requirements. B2B buyers benefit from the efficiency of this process, but should note that it is less suitable for short production runs or intricate designs, which may limit its applicability in some projects.
What makes Thermoforming a viable option for PVC applications?
Thermoforming involves heating PVC sheets until pliable and then forming them into desired shapes using molds. This method is particularly advantageous for quick prototyping and producing thin-walled structures, making it a popular choice in consumer goods and medical packaging. While tooling costs are lower than injection molding, buyers should consider that this method is limited to simpler geometries and may not provide the durability of other machining techniques.
How can 3D Printing enhance PVC machining for businesses?
3D printing is an innovative additive manufacturing technique that allows for rapid prototyping and the production of custom parts. It offers unparalleled design flexibility, making it suitable for low-volume production and unique applications. However, B2B buyers should be aware that while 3D printing enables quick iterations, it may not match the speed of traditional methods for larger production quantities, and surface finishes may require additional finishing processes.
Key Industrial Applications of pvc machining
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of PVC Machining | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical | Manufacturing of medical tubing and connectors | Ensures high safety standards and compliance with regulations | Quality certifications (e.g., ISO, UL), material purity |
| Construction | Production of piping and window frames | Offers durability, resistance to corrosion, and low maintenance | Material specifications, supplier reliability, local regulations |
| Electrical & Electronics | Fabrication of insulation for wiring and components | Enhances safety and performance of electrical systems | Compliance with electrical standards, thermal properties |
| Packaging | Creating protective packaging and containers | Provides lightweight yet durable solutions for product safety | Customization options, sustainability practices, lead times |
| Automotive | Production of interior trim and protective seals | Improves vehicle aesthetics and functionality | Material grades, resistance to environmental factors, cost efficiency |
How is PVC Machining Utilized in the Medical Sector?
In the medical industry, PVC machining plays a critical role in the production of medical tubing, connectors, and various components essential for patient care. The high chemical resistance and biocompatibility of PVC make it ideal for applications such as blood transfusion bags and intravenous lines. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, ensuring that suppliers meet stringent quality certifications, such as ISO and UL, is essential to guarantee safety and compliance with health regulations.
What are the Benefits of PVC Machining in Construction?
PVC machining is widely used in the construction industry for producing durable components like piping systems and window frames. The inherent properties of PVC, such as its resistance to corrosion and low maintenance requirements, contribute to the longevity of structures. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing suppliers who can meet specific material standards and local building regulations, ensuring that the products can withstand environmental challenges.
Why is PVC Machining Important for Electrical Applications?
In the electrical and electronics sector, PVC machining is crucial for fabricating insulation for wires, connectors, and various components. The excellent dielectric strength and flame-retardant properties of PVC enhance the safety and performance of electrical systems. For B2B buyers in Europe and Africa, it is vital to consider suppliers that comply with electrical safety standards and offer materials with appropriate thermal properties to ensure reliable performance.
How Does PVC Machining Enhance Packaging Solutions?
PVC machining is instrumental in creating protective packaging solutions, including containers and blister packs. The lightweight yet sturdy nature of PVC helps safeguard products during transportation and storage. Buyers in South America and Africa should focus on suppliers that offer customization options and adhere to sustainability practices, ensuring that their packaging solutions meet both safety and environmental standards.
What Role Does PVC Machining Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive industry, PVC machining is utilized to produce interior trim components and protective seals. The material’s durability and aesthetic flexibility enhance vehicle design while providing functional benefits like noise reduction and weather resistance. For international buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria and Brazil, it is essential to evaluate material grades and the supplier’s ability to deliver cost-effective solutions that meet performance expectations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘pvc machining’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Burrs and Surface Finish in PVC Machining
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges with burrs and poor surface finishes when machining PVC. The material’s abrasive nature can lead to rapid tool wear, especially when using improper cutting tools or techniques. Burrs not only affect the aesthetic quality of the product but can also complicate further processing steps, leading to increased production costs and time delays. This issue is particularly prevalent in high-volume production runs where consistency is crucial.
The Solution:
To mitigate burr formation and achieve a superior surface finish, buyers should prioritize the selection of sharp, high-quality carbide cutters specifically designed for machining plastics. Utilizing tools with a high number of flutes can help reduce the cutting forces and minimize the heat generated during the machining process. Additionally, implementing mist coolant systems can effectively reduce tool temperature and improve surface quality. It’s crucial to conduct a trial run with varying feed rates and spindle speeds to identify the optimal settings for your specific PVC grade. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of cutting tools will also help maintain quality and efficiency throughout the machining process.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Challenges with Tool Degradation from PVC
The Problem:
Another common pain point is the degradation of tools used in machining PVC. Buyers often report that standard cutting tools wear out quickly, leading to increased costs and downtime. This degradation is exacerbated by the release of hydrochloric acid when PVC is heated, which can corrode tooling materials. As a result, manufacturers struggle to maintain consistent production levels and may face difficulties in meeting customer deadlines.
The Solution:
To combat tool degradation, buyers should invest in specialized cutting tools made from high-quality materials, such as carbide or even coated carbide options designed specifically for plastics. These tools are engineered to withstand the chemical and thermal stresses associated with PVC machining. Additionally, implementing a systematic tool management program that includes regular inspections and replacements can significantly enhance tool longevity. Employing a coolant system that uses non-aromatic, water-soluble coolants will also help to maintain tool performance and extend their lifespan. Educating machinists on the proper speeds and feeds for PVC will further minimize wear and enhance productivity.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Compliance with Industry Standards in PVC Machining
The Problem:
Compliance with industry standards, such as UL94-V0 fire ratings, is a significant concern for buyers machining PVC for specific applications like electrical components or medical devices. Failing to meet these standards can lead to product recalls, legal issues, and damage to reputation. Buyers may find it challenging to source PVC materials that meet specific compliance requirements, especially in regions with varying regulatory landscapes.
The Solution:
To ensure compliance, buyers should establish strong relationships with reputable suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and certifications for their PVC materials. Conducting thorough research to identify materials that meet industry standards before commencing machining is essential. Buyers should also consider partnering with manufacturers that have experience in compliance testing and can assist in material selection. Regular audits and quality checks throughout the machining process will help to ensure that the final products meet necessary standards. Additionally, educating the production team about the implications of non-compliance will foster a culture of quality and diligence, ultimately protecting the business from potential setbacks.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pvc machining
What Are the Key Properties of PVC for Machining?
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is a widely used thermoplastic known for its unique combination of properties. It exhibits high corrosion resistance, excellent dielectric strength, and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for various applications across industries such as construction, medical devices, and consumer products. PVC is available in both rigid and flexible forms, allowing for versatility in manufacturing processes. The material’s durability and flame retardant nature further enhance its appeal, particularly in environments where safety and longevity are paramount.
What Are the Pros and Cons of PVC in Machining Applications?
When considering PVC for machining, there are several advantages and disadvantages to weigh.
Pros:
– Durability: PVC is highly resistant to chemicals and weathering, making it ideal for long-lasting applications.
– Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to metals and other plastics, PVC is generally more economical, which is crucial for budget-conscious projects.
– Ease of Machining: PVC can be CNC machined effectively, allowing for precise component fabrication.
Cons:
– Abrasiveness: PVC can be abrasive to cutting tools, leading to increased wear and tear, which may raise manufacturing costs over time.
– Thermal Sensitivity: The material can deform under high temperatures, necessitating careful control of machining parameters to avoid defects.
– Limited High-Temperature Applications: PVC is not suitable for applications involving extreme heat, which can limit its use in certain sectors.
How Does PVC Impact Specific Applications?
The compatibility of PVC with various media is a significant factor in its application. For instance, its resistance to diluted acids and bases makes it suitable for chemical processing environments. However, it is vulnerable to certain solvents, such as ketones and chlorinated hydrocarbons, which can limit its use in specific scenarios. Understanding these compatibility issues is essential for international B2B buyers who may operate in diverse industrial sectors.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting PVC?
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local and international standards is crucial. Common standards like ASTM, DIN, and JIS govern the quality and safety of materials. Buyers should also consider the availability of PVC grades that meet specific regulatory requirements, such as UL94 for flame retardancy. Understanding local market preferences and the availability of skilled machining services can also impact the successful implementation of PVC in manufacturing processes.
Summary Table of Material Selection for PVC Machining
| Material | Typical Use Case for PVC Machining | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rigid PVC | Construction components, pipes | High durability and chemical resistance | Limited high-temperature applications | Low |
| Flexible PVC | Electrical insulation, medical tubing | Excellent flexibility and insulation | Vulnerable to certain solvents | Medium |
| PVC Composites | Industrial applications, automotive parts | Enhanced mechanical properties | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| PVC Foam | Packaging, signage | Lightweight and easy to fabricate | Lower durability compared to rigid PVC | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of PVC machining, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pvc machining
What Are the Main Stages in the PVC Machining Manufacturing Process?
PVC machining involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality and performance. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers appreciate the complexity involved and the importance of choosing the right supplier.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the PVC machining process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate grade of PVC, which can be rigid or flexible, depending on the application. Suppliers should maintain detailed records of material properties, including tensile strength, elongation, and chemical resistance. This data is vital for ensuring the selected material meets the specific requirements of the end product.
Once the material is selected, it may undergo processes like annealing to relieve internal stresses. This step is crucial as it helps prevent cracking and crazing during machining. Suppliers often use controlled heating and cooling methods in annealing ovens to achieve the desired results.
2. Forming Techniques: What Methods Are Used in PVC Machining?
Various techniques are employed in the forming stage of PVC machining, with the most common being CNC machining. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining allows for high precision and consistency in producing complex components. The key techniques include:
- CNC Milling: This method is essential for creating intricate shapes and designs. It utilizes sharp carbide cutters and low RPM settings to minimize heat generation and tool degradation.
- Injection Molding: For high-volume production, injection molding is often employed. This method allows for rapid production of parts but may require an initial investment in molds.
- Thermoforming: This technique is suitable for creating larger parts and involves heating the PVC until it becomes pliable, then shaping it over a mold.
Choosing the right technique depends on the project requirements, including volume, complexity, and cost.
3. Assembly: How Is PVC Machined and Assembled?
After forming, the next stage is assembly. This process may involve joining multiple PVC components using adhesives or mechanical fasteners. It is crucial to select adhesives that are compatible with PVC to ensure a strong bond. During assembly, it’s vital to maintain clean working conditions to avoid contamination, which can compromise the quality of the final product.
B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly methods used by suppliers, as this can impact the durability and performance of the finished products.
4. Finishing: What Are the Key Finishing Techniques for PVC Products?
Finishing processes are critical in enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of PVC products. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: This may involve sanding, polishing, or coating to improve surface quality and appearance.
- Machining: Additional machining may be required to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. This step often involves using specialized tools designed for cutting plastics.
- Quality Checks: After finishing, products undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specified standards.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is a fundamental aspect of PVC machining, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. B2B buyers should be familiar with the following standards:
1. International Standards: How Do ISO Certifications Impact Quality?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized international standard for quality management systems. Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement. This certification is particularly important for international buyers, as it assures that the supplier adheres to global best practices.
2. Industry-Specific Certifications: What Additional Certifications Should Buyers Consider?
Depending on the application, additional industry-specific certifications may be relevant. For instance:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Important for products used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific performance criteria.
Understanding these certifications can help buyers make informed decisions about their suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in PVC Machining?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the PVC machining process, with various checkpoints established to ensure compliance with quality standards. The primary QC checkpoints include:
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt. Buyers should verify that the materials meet specified criteria and certifications before they enter the production process. This step is crucial for preventing defects in the final product.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During production, ongoing quality checks should be conducted at various stages. This includes monitoring machining parameters such as temperature, cutting speed, and feed rate. IPQC helps identify any deviations from the established standards, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
3. Final Quality Control (FQC)
After production, a thorough inspection of the finished products is essential. FQC may include dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional testing to ensure that the products meet the required specifications and performance standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers should consider the following verification methods:
1. Supplier Audits
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality control processes and adherence to standards. Buyers should assess the supplier’s facilities, equipment, and quality management practices during these audits.
2. Quality Reports
Requesting quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their performance over time. These reports should detail the results of IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes, highlighting any issues and corrective actions taken.
3. Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This is particularly beneficial for international buyers who may face challenges in verifying supplier practices remotely.
What Are the Unique Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control nuances:
- Local Regulations: Understanding local regulations and standards is crucial, as they may differ significantly from international norms.
- Supply Chain Risks: International logistics can introduce risks related to material handling and transportation. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust processes to mitigate these risks.
- Cultural Differences: Awareness of cultural differences in business practices can help facilitate smoother communication and collaboration with suppliers.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for PVC machining, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure high-quality products for their applications.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘pvc machining’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers interested in procuring PVC machining services. As PVC is a widely used thermoplastic with unique properties, understanding the nuances of sourcing machining services is crucial for ensuring high-quality, durable products that meet your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical specifications of the PVC components you require. This includes dimensions, tolerances, and material grades. Precise specifications help potential suppliers understand your requirements and ensure that the final product meets your standards, avoiding costly mistakes and delays.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers that specialize in PVC machining. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry, particularly those with experience in your specific application area. Pay attention to their machining capabilities, equipment, and any certifications they hold, such as ISO or UL approvals.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Experience and Expertise
Before committing, assess the experience and expertise of potential suppliers. Inquire about their history in machining PVC and the types of projects they have completed. Focus on suppliers who have worked with similar industries or applications to ensure they understand the unique challenges associated with PVC machining.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your selected suppliers possess the necessary certifications relevant to your industry. Certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management or UL94 for flammability standards are crucial for ensuring that suppliers adhere to industry best practices. This verification process safeguards your investment and mitigates risks.
Step 5: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the machined PVC components. This step allows you to evaluate the supplier’s machining quality, surface finish, and adherence to your specifications. Testing samples can save you from larger issues in mass production and ensure the supplier can meet your quality expectations.
Step 6: Discuss Machining Techniques and Tooling
Engage in a conversation with potential suppliers about their machining techniques and tooling options. PVC is abrasive, so it’s essential to understand the tools they use and their strategies for minimizing wear on cutters. Ask about their cooling methods, such as the use of non-aromatic, water-soluble coolants, to ensure optimal machining performance.
Step 7: Evaluate Pricing and Lead Times
Finally, assess the pricing structures and lead times offered by each supplier. While cost is a significant factor, consider the balance between price, quality, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the supplier can meet your deadlines without compromising on quality, as delays can impact your overall project timelines.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing PVC machining services, ultimately leading to successful project outcomes and lasting partnerships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pvc machining Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in PVC Machining?
When analyzing the cost structure for PVC machining, several components must be considered to provide a comprehensive overview. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of PVC itself can vary significantly based on the grade and specifications required for the project. Different forms, such as rigid or flexible PVC, will influence pricing. Additionally, any additives used to enhance properties will add to material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for machining PVC effectively. The complexity of the machining process and the expertise required can influence labor costs. For instance, workers trained in using specialized equipment for PVC machining may command higher wages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. As PVC machining often requires specific machinery and tools, overhead can be substantial. Companies must also consider costs associated with safety and compliance regulations, particularly in international markets.
-
Tooling: The selection of tools is critical in PVC machining. High-speed steel (HSS) tools may be less expensive initially, but carbide cutters, known for their durability and effectiveness, might be more cost-efficient in the long run despite a higher upfront cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining high-quality standards is vital in PVC machining, especially for applications in sensitive industries like medical devices. Implementing rigorous QC processes incurs additional costs but ensures product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs to deliver finished products to buyers can vary, particularly in international trade. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and import/export duties must be factored into the overall cost structure.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin on top of their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s strategic positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Impact PVC Machining Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of PVC machining, making it essential for buyers to understand these variables:
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it economically advantageous for businesses with high demand.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized parts typically incur higher costs due to the need for specialized tools and processes. Buyers should clarify their specifications upfront to receive accurate quotes.
-
Materials: As mentioned earlier, the type and grade of PVC selected will significantly impact pricing. Buyers should consider the balance between cost and the required performance characteristics.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications (e.g., UL94-V0 for flame retardancy) may come at a premium. Suppliers specializing in certified materials often charge more due to the stringent processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, location, and capacity of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer reliability and better service, while newer entrants may provide competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affect logistics costs and responsibilities. Buyers should be clear on these terms to avoid unexpected charges.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for PVC Machining Sourcing?
To optimize the sourcing process for PVC machining, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially for large orders. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate to secure long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes considering maintenance costs, tool longevity, and the potential need for replacements.
-
Understanding Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local economic conditions that can affect pricing. Understanding regional market dynamics can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and potential collaboration on future projects. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and loyalty.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for PVC machining can vary widely based on the factors outlined above. It is advisable for buyers to request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers and conduct thorough market research to ensure they receive competitive and fair pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing pvc machining With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to PVC Machining
In the realm of manufacturing, selecting the appropriate material and machining method is crucial for achieving optimal performance and cost efficiency. While PVC machining is a popular choice due to its favorable properties, it is essential to explore alternative solutions to determine the best fit for specific applications. This analysis compares PVC machining with other viable methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | PVC Machining | Injection Molding | 3D Printing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, good insulation | Excellent for high volume | Flexible design capabilities |
| Cost | Moderate material and machining cost | High initial setup cost | Variable, often lower for small runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment | Complex setup and tooling | User-friendly, minimal setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate, tool wear can be high | Low, but requires mold maintenance | Low, but material may require calibration |
| Best Use Case | Customized parts, low to medium volume | Mass production, complex shapes | Prototyping, intricate designs |
Pros and Cons of Alternatives
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create parts. The primary advantage of this method is its efficiency for large-scale production. Once the initial setup is completed, parts can be produced rapidly, resulting in lower per-unit costs for high-volume orders. However, the initial tooling costs are significant, making it less economical for smaller batches. Additionally, the process may limit design flexibility due to mold constraints.
3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, has revolutionized how parts are produced. This method allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized designs without the need for expensive molds. It is particularly advantageous for prototyping and small production runs where flexibility and rapid iteration are essential. However, the material costs can vary significantly, and the mechanical properties of printed parts may not always match those produced by traditional methods. Additionally, the speed of production can be slower for large quantities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When choosing between PVC machining and its alternatives, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including production volume, required part complexity, and budget constraints. PVC machining is ideal for projects that require durability and customization without the overhead of mold costs. In contrast, injection molding is suited for high-volume production where cost per unit is critical. Meanwhile, 3D printing offers unparalleled design flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, making it a preferred option for innovation-driven projects.
Ultimately, the decision should align with the specific needs of the project, weighing the advantages and limitations of each method to achieve the best results. By thoroughly evaluating these alternatives, buyers can optimize their manufacturing processes and enhance their product offerings.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pvc machining
What Are the Key Technical Properties of PVC Machining?
When considering PVC machining for your business needs, understanding the material’s properties is critical. Here are several essential specifications that impact machining processes and final product performance:
1. Material Grade
PVC is available in various grades, including rigid and flexible forms. The grade selected can significantly influence the machining process, durability, and application suitability. For instance, rigid PVC is often used for construction components, while flexible PVC is ideal for applications requiring elasticity, such as cable insulation. Choosing the correct grade ensures that the end product meets functional requirements and regulatory standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions during machining. In PVC machining, maintaining tight tolerances is vital for ensuring component fit and functionality. High-precision applications, such as in the medical or automotive industries, may require tolerances of ±0.001 inches or tighter. Understanding tolerance requirements upfront can minimize waste and reduce the need for rework.
3. Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT)
The HDT of PVC indicates the temperature at which the material deforms under a specified load. For PVC, the HDT is typically around 169°F (76°C). This property is crucial for applications exposed to elevated temperatures, as it helps determine whether the material can maintain its structural integrity. Knowing the HDT can aid in selecting the right PVC grade for heat-sensitive applications, ultimately ensuring product longevity.
4. Tensile Strength
Tensile strength measures a material’s resistance to being pulled apart. For PVC, the tensile strength is approximately 7,300 psi (yield), which makes it suitable for various applications where strength is necessary. Understanding tensile strength is essential for B2B buyers to ensure that the PVC components can withstand operational stresses without failure.
5. Chemical Resistance
PVC exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, making it suitable for applications in environments where exposure to acids or other corrosive substances is likely. This property is particularly important for industries such as construction and healthcare. B2B buyers should assess the chemical compatibility of PVC with the intended application to prevent premature degradation of the material.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in PVC Machining?
Navigating the terminology in PVC machining is essential for effective communication and procurement. Here are some common trade terms that every B2B buyer should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of PVC machining, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can deliver quality components that meet specific standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ for PVC components is crucial for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure that they order sufficient quantities to meet production needs without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. In PVC machining, submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and understand the costs associated with different machining options, including materials and labor.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in international trade, as it clarifies shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery timelines.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools via computer programming. In PVC machining, CNC technology enhances precision and repeatability, making it ideal for producing complex components. Understanding CNC capabilities can help buyers evaluate potential suppliers and their machining processes.
By familiarizing yourself with these properties and terms, you will be better equipped to make informed decisions in the PVC machining landscape, ensuring that your procurement aligns with your business objectives and quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the pvc machining Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in PVC Machining?
The PVC machining sector is experiencing significant growth driven by the material’s versatile applications across various industries, including construction, medical devices, and consumer goods. The global demand for PVC is being propelled by urbanization, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where infrastructure development is a priority. Moreover, the shift towards lightweight materials in automotive and construction applications is enhancing PVC’s appeal due to its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing trends in PVC machining. Automation and CNC machining are becoming increasingly prevalent, enabling manufacturers to produce high-precision components at lower costs. This technological evolution is particularly beneficial for international buyers who seek consistency and quality in their supply chain. Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 concepts, such as IoT and data analytics, is allowing companies to optimize their operations, reduce waste, and improve lead times.
Sourcing PVC from regions with established manufacturing capabilities is becoming essential for B2B buyers. For instance, suppliers in Europe and the Middle East are recognized for their adherence to stringent quality standards, making them attractive options for businesses in developing markets. Furthermore, international buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide value-added services, such as material selection expertise and customized machining capabilities.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing PVC Machining?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the PVC machining sector. The environmental impact of PVC production and its lifecycle is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. This includes minimizing waste during machining processes and utilizing energy-efficient equipment. Additionally, the PVC industry is making strides towards using recycled materials, which not only lessens environmental impact but also appeals to eco-conscious buyers.
Ethical sourcing is another vital aspect that B2B buyers must consider. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and maintain transparency in their supply chains is increasingly important. Buyers are more likely to favor suppliers who possess recognized ‘green’ certifications, indicating their commitment to sustainable practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as benchmarks for potential partners in the PVC machining sector.
Moreover, buyers should evaluate the lifecycle impact of the materials they source. PVC can be manufactured with additives that enhance its properties, but not all additives are environmentally friendly. Therefore, international buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer ‘green’ alternatives that comply with environmental regulations and standards.
What Is the Historical Context of PVC Machining in B2B Markets?
The evolution of PVC machining dates back to the mid-20th century when PVC was first introduced as a commercial product. Initially, its usage was limited due to its rigidity and processing challenges. However, advancements in machining technologies, such as CNC and improved cutting tools, have made it possible to effectively machine PVC into complex shapes and components.
By the 1980s, PVC’s popularity surged due to its favorable cost-performance ratio and versatility, leading to its widespread adoption across various sectors. Today, PVC machining is a well-established industry, characterized by continuous innovation in processing techniques and materials. As a result, it has become an essential material for international B2B buyers looking for reliable and cost-effective solutions in their manufacturing processes. The ongoing development of PVC formulations, including those with enhanced sustainability features, signals a promising future for the sector, making it a key area for investment and sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pvc machining
-
How do I choose the right supplier for PVC machining?
Selecting the right supplier for PVC machining involves evaluating their experience, capabilities, and quality control processes. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in machining PVC and other thermoplastics. Request samples of their work to assess quality, and inquire about their certifications and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider their capacity to handle your specific project needs, including customization options and adherence to deadlines. Establishing clear communication and understanding their logistics capabilities can also help ensure a smooth partnership. -
What are the most important properties of PVC for machining applications?
PVC is known for its durability, chemical resistance, and excellent dielectric strength, making it suitable for various applications. When machining PVC, its abrasion resistance and low moisture absorption are critical properties to consider. These characteristics ensure that the final products maintain integrity and performance over time. Additionally, understanding the differences between rigid and flexible PVC can aid in selecting the right material for specific applications, such as construction components or medical devices. -
What is the typical lead time for PVC machining projects?
Lead times for PVC machining projects can vary based on factors such as the complexity of the design, the size of the order, and the supplier’s current workload. Typically, you can expect lead times ranging from 2 to 8 weeks. It’s essential to discuss your project timelines with potential suppliers upfront and ensure they can meet your deadlines. Additionally, consider seasonal demand fluctuations that might affect production schedules when planning your orders. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for PVC machining?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can differ significantly among suppliers. Some may have low MOQs for custom machined parts, while others might require larger orders to offset production costs. It’s advisable to clarify MOQs during your initial discussions with potential suppliers to ensure they align with your project requirements. Understanding the MOQ can help you budget effectively and decide whether to consolidate orders for better pricing. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing PVC machining services?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier’s policies and the nature of your agreement. Common practices include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., 30 or 60 days). It’s crucial to negotiate payment terms that are mutually beneficial and provide you with adequate cash flow. Additionally, consider discussing any potential discounts for early payment or bulk orders, which can improve your overall procurement strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in PVC machining?
To ensure quality assurance in PVC machining, ask suppliers about their quality control processes, including inspection methods and equipment used. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 that indicate a commitment to maintaining high standards. Request samples or prototypes before committing to larger orders, allowing you to evaluate the quality firsthand. Establishing clear specifications and tolerances in your contract can also help maintain quality throughout the production process. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing PVC machined parts?
When importing PVC machined parts, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. It’s vital to work with suppliers familiar with international shipping to ensure compliance with import/export regulations. Discuss packaging requirements to prevent damage during transit and confirm the logistics provider’s reliability. Additionally, consider insurance options for high-value shipments to mitigate risks associated with transportation. -
What are the common applications of PVC in various industries?
PVC is widely used across several industries due to its versatility and favorable properties. Common applications include construction (window frames, pipes), medical (tubing, bags), and consumer products (packaging, flooring). Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for industrial components, while its dielectric strength serves well in electrical applications. Understanding these applications can help you identify the right PVC products for your specific industry needs and facilitate informed procurement decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Pvc Machining Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. AIP Precision – PVC Solutions
Domain: aipprecision.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a rigid thermoplastic material known for its high corrosion resistance, high chemical resistance, low moisture absorption, and excellent dielectric strength. Key properties include good insulation, durability, flame retardance, low maintenance, long lifespan, abrasion resistance, and lightweight characteristics. PVC is available in rigid and flexible forms and is common…
2. Practical Machinist – PVC Machining Solutions
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Material: PVC (UL94-V0 approved)\nMachining Tools: HSS 2-flute end mills, carbide cutters\nCutting Techniques: Low RPM, high feed, mist lubricant or plain air\nIssues: Burr formation, cutter degradation due to heat and chlorine release from PVC\nAlternatives: Noryl (meets UL94-V0, halogen-free, similar machining properties to acetal)\nCost Considerations: Material cost approximately $10, tool cost…
3. AT Machining – PVC Solutions
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a widely used synthetic plastic known for its excellent strength, durability, and chemical resistance. It is available in two forms: flexible (plasticized) and rigid (unplasticized). Key properties include good insulation, affordability, low water absorption, and resistance to environmental elements. Common types of PVC used in CNC machining include Plasticized PVC, UPV…
4. Cox Manufacturing – PVC Machined Parts
Domain: coxmanufacturing.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: PVC Machining & Machined Parts from Cox Manufacturing Company. PVC is a low-cost plastic ideal for parts requiring strength while remaining lightweight. It is highly machinable to close tolerances and has excellent corrosion, flame, and water resistance. Key characteristics include high strength, impact resistance, and toughness. Machining cost factor of PVC is 1.1 compared to steel 12L14. Common …
5. CNC-Step – CNC Machines for Machining Plastic
Domain: cnc-step.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: CNC Machines for Machining Plastic: 1. CNC Router High-Z T-Series: up to 2100x1050mm 2. CNC Mill T-Rex: steel frame, up to 12000x4000mm 3. Router with Servo Motors: up to 12000x4000mm 4. CNC Milling Machine RaptorX-SL: up to 12000x3000mm 5. Industrial Milling Machine AcerDURO: up to 2000x1000mm 6. Water Jet Cutter: up to 3800 bar high-pressure pump 7. Engraving Machine High-Z S-Serie: up to 1000×6…
6. eMachineShop – Custom PVC Parts
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom PVC Parts from eMachineShop, molded and machined for over 15 years. Design and order using free CAD software or upload CAD files for fast quotes. Features include: FREE Shipping in the USA, No Minimum Order Quantity, 100% Quality Guaranteed. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a thermoplastic known for being fire retardant, electrically insulative, and easily machined, making it suitable for high i…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pvc machining
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance PVC Machining Success?
In the ever-evolving landscape of PVC machining, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement processes. Understanding the unique properties of PVC, including its high corrosion resistance and versatility, allows businesses to make informed decisions that align with their specific application requirements. This not only improves product quality but also enhances operational efficiency and reduces long-term costs.
As buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe explore sourcing options, it is essential to partner with suppliers who possess deep expertise in machining thermoplastics. Leveraging advanced machining techniques, such as CNC machining and the use of specialized cutting tools, can significantly mitigate challenges associated with machining PVC, such as tool degradation and material waste.
Looking ahead, the demand for high-quality PVC components is set to rise, driven by advancements in sectors such as medical devices and construction. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to engage with suppliers who prioritize innovation and quality assurance in their machining processes. By doing so, they can secure a competitive edge in their respective markets and ensure the successful execution of their projects.