Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for proto machine
Navigating the global market for proto machines presents unique challenges, particularly for B2B buyers striving to source high-quality automated screwdriving systems that enhance operational efficiency. As international demand grows, understanding the diverse applications, types, and supplier vetting processes is essential. This guide offers a comprehensive overview of proto machines, including insights into their design features, such as compactness and reliability, and the advantages they bring to various industries, from automotive to aerospace.
In this resource, we delve into critical factors that influence purchasing decisions, including cost considerations, delivery timelines, and after-sales support. By examining testimonials from existing customers, we illuminate the value of selecting a trusted supplier that prioritizes creativity, responsibility, and customer satisfaction.
Tailored for B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets such as Germany and Brazil—this guide empowers you to make informed choices. With actionable insights and strategic recommendations, it serves as an essential tool for organizations looking to optimize their procurement process and leverage the capabilities of proto machines to drive growth and innovation in their operations.
Understanding proto machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Screwdriving Systems | Fully automated, compact design, plug-and-play setup | Automotive, Electronics Assembly | Pros: High reliability, fast cycle time. Cons: Initial investment may be high. |
| Precision Turn and Mill Machines | High precision, capable of complex geometries | Aerospace, Oil & Gas, Government | Pros: Exceptional accuracy, versatile applications. Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Customized Parts Production | Tailored production capabilities, long and short runs | Manufacturing, Prototyping | Pros: Meets specific needs, flexible production. Cons: Longer lead times for custom designs. |
| Holographic Communication Devices | AI-enabled, lifelike holographic displays | Marketing, Training, Remote Work | Pros: Engaging user experience, innovative solutions. Cons: High technology cost, may require training. |
| Small Assembly Machines | Compact, efficient for small-scale production | Consumer Electronics, Appliance Assembly | Pros: Space-saving, cost-effective for small runs. Cons: Limited scalability for larger operations. |
What Are the Characteristics of Automated Screwdriving Systems?
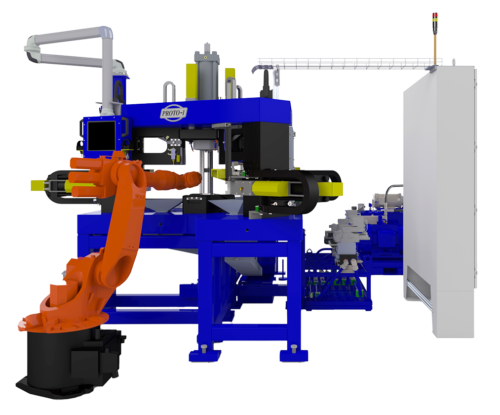
Automated screwdriving systems are designed for high-speed assembly processes, particularly in sectors like automotive and electronics. These machines feature a compact design and a plug-and-play setup, allowing for rapid deployment and integration into existing workflows. They significantly enhance productivity by reducing cycle times and minimizing manual errors. B2B buyers should consider their operational scale and the initial investment required, as these systems can offer substantial long-term savings and efficiency gains.
How Do Precision Turn and Mill Machines Operate?
Precision turn and mill machines are critical in industries requiring high tolerances, such as aerospace and oil and gas. These machines excel in producing complex geometries with exceptional accuracy. They are suitable for both small and large production runs, making them versatile for various applications. However, buyers need to be aware of the skill level required to operate these machines effectively, as well as the potential maintenance costs associated with high-precision equipment.
Why Opt for Customized Parts Production?
Customized parts production caters to businesses that require specific components tailored to their unique specifications. This type of proto machine allows for both long and short production runs, providing flexibility in manufacturing. It is particularly valuable in prototyping and specialized manufacturing sectors. Buyers should weigh the benefits of tailored solutions against potential longer lead times and the need for close collaboration with manufacturers during the design phase.
What Advantages Do Holographic Communication Devices Offer?
Holographic communication devices represent a cutting-edge solution for businesses looking to enhance engagement and collaboration. These AI-enabled displays provide lifelike interactions, making them ideal for marketing, training, and remote communications. While they offer innovative solutions that can transform user experiences, potential buyers must consider the initial investment and the need for staff training to maximize the technology’s benefits.
When Should You Choose Small Assembly Machines?
Small assembly machines are ideal for businesses with limited space or those focusing on small-scale production. These machines are efficient and cost-effective, making them suitable for sectors like consumer electronics. However, they may not be the best choice for operations expecting to scale significantly, as their limited capacity can hinder growth. B2B buyers should evaluate their production needs and future growth plans when considering these machines.
Key Industrial Applications of proto machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of proto machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Automated Screwdriving Systems | Enhances assembly line efficiency and reduces labor costs | Reliability, speed of delivery, and customization options are critical. |
| Aerospace | Precision Machining for Components | Ensures high-quality, durable parts for safety compliance | Certifications, material quality, and precision capabilities are essential. |
| Oil & Gas | Customized Parts Production | Streamlines operations and minimizes downtime | Supplier reliability, on-time delivery, and quality assurance processes are vital. |
| Electronics | Small Assembly of Complex Devices | Reduces time-to-market and enhances product quality | Flexibility in production runs and ability to handle diverse specifications are key. |
| Healthcare | Medical Device Manufacturing | Improves patient safety and device reliability | Compliance with regulatory standards and quick turnaround times are crucial. |
How is Proto Machine Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, proto machines are primarily utilized for automated screwdriving systems. These systems allow for the simultaneous driving and feeding of screws, significantly reducing cycle times on assembly lines. By incorporating such technology, manufacturers can enhance operational efficiency, lower labor costs, and ensure consistent quality. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should consider the reliability and speed of delivery when sourcing these systems to meet production demands.
What Role Does Proto Machine Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, proto machines are integral for precision machining of critical components. The high standards for safety and durability in this industry necessitate exceptional quality in parts production. Proto machines provide tailored solutions that adhere to stringent aerospace regulations. Buyers in Europe, especially Germany, should focus on suppliers with the necessary certifications and proven track records in precision capabilities to ensure compliance and reliability in their supply chain.
How Can Proto Machines Enhance Operations in the Oil & Gas Sector?
The oil and gas industry benefits from proto machines through customized parts production that streamlines operations. These machines can produce specific components required for various applications, minimizing downtime and enhancing productivity. For international buyers, particularly in the Middle East, it is essential to evaluate supplier reliability and quality assurance processes, ensuring that parts are delivered on time and meet industry standards.
In What Ways are Proto Machines Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics sector, proto machines facilitate the small assembly of complex devices, which is crucial for reducing time-to-market and enhancing product quality. These machines can handle diverse specifications and production runs, allowing manufacturers to adapt to market demands swiftly. Buyers from regions like South America should prioritize suppliers that offer flexibility and quick turnaround times to remain competitive in a fast-paced industry.
How Do Proto Machines Contribute to Healthcare Device Manufacturing?
Proto machines play a vital role in the manufacturing of medical devices, where precision and reliability are paramount. They ensure that devices meet rigorous safety standards, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Buyers, particularly from Europe, must consider suppliers that comply with regulatory standards and can deliver high-quality products in a timely manner to support critical healthcare applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘proto machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter significant challenges when integrating proto machines into their existing production lines. These machines often require specific configurations to work seamlessly with legacy systems. Buyers may face compatibility issues, leading to increased downtime and operational inefficiencies. This struggle can be particularly acute for companies in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision and reliability are paramount.
The Solution: To overcome integration challenges, buyers should engage with proto machine suppliers early in the purchasing process. Conducting a thorough needs assessment will help identify the specific requirements of existing systems. It is crucial to request detailed specifications from the supplier regarding compatibility and integration capabilities. Additionally, consider opting for systems that offer a “plug and play” setup, as these designs are typically more user-friendly and can significantly reduce installation time. Collaborating closely with the supplier’s technical team during the installation phase can also facilitate a smoother integration, ensuring that any potential issues are addressed promptly.
Scenario 2: Concerns About Maintenance and Downtime
The Problem: Buyers often worry about the long-term maintenance and reliability of proto machines. In industries with high production demands, unexpected machine downtime can result in substantial financial losses and affect delivery schedules. This concern is magnified in regions with less access to immediate technical support or spare parts, where delays in maintenance can lead to prolonged operational halts.
The Solution: To mitigate maintenance concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing machines from suppliers that offer comprehensive service agreements, including proactive maintenance schedules and quick-response support. Before finalizing a purchase, inquire about the supplier’s parts availability and the average lead time for replacement components. Establishing a partnership with a local technician or service provider can also be beneficial, ensuring that on-site support is available when needed. Moreover, investing in training for in-house staff on basic troubleshooting and maintenance can empower teams to address minor issues before they escalate into larger problems.
Scenario 3: Inadequate Customization Options
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with finding proto machines that meet their specific operational needs. Off-the-shelf machines may not accommodate unique product specifications, leading to inefficiencies or the need for additional modifications. This lack of customization can be particularly problematic for businesses in niche markets or those producing specialized products that require tailored manufacturing processes.
The Solution: To address customization challenges, buyers should engage with proto machine manufacturers that emphasize flexible design and production capabilities. When initiating discussions, clearly outline your operational requirements and the specific features you need. Many suppliers offer options for custom jaws or vision-based alignment, which can be tailored to fit unique applications. It is advisable to request prototypes or pilot runs to validate that the machine meets your specifications before full-scale production. Building a strong collaborative relationship with the manufacturer can also facilitate ongoing customization and improvements as your business evolves, ensuring that your proto machine continues to meet your changing needs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for proto machine
When selecting materials for proto machines, it is crucial to consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. This selection process not only impacts the performance and longevity of the machines but also influences manufacturing costs and compliance with international standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in proto machines, focusing on their characteristics and implications for international B2B buyers.
What are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Proto Machines?
Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal widely used in the construction of proto machines. Its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity makes it suitable for components that require efficient heat dissipation. Aluminum also has a high strength-to-weight ratio, which is beneficial for applications where reducing weight is critical.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is durable and easy to machine, which simplifies manufacturing processes. However, it can be more expensive than other metals like steel and may not withstand high temperatures as effectively, limiting its use in high-heat applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and air, making it a versatile choice for many proto machine components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Europe and South America should ensure compliance with standards such as EN 573 for aluminum alloys. Understanding local preferences for aluminum grades can also enhance product acceptance.
Why is Stainless Steel a Preferred Material for Proto Machines?
Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments. Its ability to maintain structural integrity under high temperatures and pressures further enhances its suitability for proto machines.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is highly durable and offers excellent resistance to various chemicals, it is heavier than aluminum and can be more challenging to machine, which may increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly effective in applications involving aggressive media, such as chemicals or high-pressure systems, where other materials might fail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM A240 standards is essential for buyers in North America, while European buyers may refer to EN 10088. Understanding the specific grades of stainless steel preferred in different markets can aid in meeting buyer expectations.
How Does Plastic Compare as a Material for Proto Machines?
Plastics, particularly engineering plastics like polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly being used in proto machines due to their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. These materials can be molded into complex shapes, allowing for innovative designs.
Pros & Cons: Plastics are generally cost-effective and offer good insulation properties. However, they may not withstand extreme temperatures or heavy loads as effectively as metals, which can limit their application scope.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for non-structural components or applications where weight reduction is crucial. They are compatible with various fluids but may degrade in the presence of certain chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, which is crucial for ensuring product reliability across different markets.
What Role Does Carbon Steel Play in Proto Machines?
Carbon steel is a widely used material in the manufacturing of proto machines due to its strength and versatility. It is particularly favored for structural components that require high durability.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and easy to machine, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, it is prone to rust and corrosion, requiring protective coatings or treatments, which can add to the overall cost.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications where strength is a priority, but its susceptibility to corrosion may limit its use in wet or corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Understanding compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for carbon steel can help buyers ensure they meet local regulations and quality expectations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Proto Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for proto machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight components | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Limited high-temperature performance | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | High-pressure applications | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Heavier and harder to machine | High |
| Plastic | Non-structural parts | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited high-temperature performance | Low |
| Carbon Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Prone to rust, requires coatings | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for proto machine
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Proto Machines?
The manufacturing process of proto machines typically encompasses several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each of these stages plays a critical role in ensuring the final product meets both performance and quality standards.
How Is Material Prepared for Proto Machines?
Material preparation begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials, often sourced from reputable suppliers. Common materials include metals such as aluminum and steel, which are chosen for their durability and strength. The preparation phase involves cutting, machining, and treating these materials to ensure they meet the specifications required for the next manufacturing steps. Advanced techniques such as CNC machining are frequently employed to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into components that will be used in the proto machine. Techniques such as stamping, bending, and welding are commonly utilized. For example, automated screwdriving systems may incorporate parts that are stamped from sheet metal and then welded together to create robust assemblies. The use of automated systems not only enhances efficiency but also reduces the risk of human error, which is crucial for maintaining quality.
How Is Assembly Performed in Proto Machine Manufacturing?
Once components are formed, the assembly stage takes place. This may include integrating mechanical, electrical, and software components to create a fully functional proto machine. In many cases, assembly is performed in a cleanroom environment to prevent contamination and ensure precision. The assembly process often utilizes modular designs, allowing for easier maintenance and upgrades. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly methods used, as these can impact the machine’s longevity and reliability.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Used?
Finishing processes are vital for enhancing the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of proto machines. Techniques such as painting, anodizing, and surface treatment are employed to protect against corrosion and wear. Additionally, finishing processes can improve the machine’s operational efficiency by reducing friction between moving parts. For international buyers, understanding the specific finishing processes used can provide insights into the machine’s suitability for various operational environments.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Proto Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. For proto machines, adhering to standards like ISO 9001 is crucial for maintaining quality and consistency.
What International Standards Apply to Proto Machines?
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized quality management standard that outlines requirements for an effective quality management system (QMS). Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a company’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for the oil and gas sector may also apply. These certifications can significantly influence the purchasing decisions of B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, including Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
- IQC focuses on the quality of incoming materials, ensuring they meet specified criteria before production begins.
- IPQC monitors the manufacturing process itself, allowing for real-time adjustments to maintain quality standards.
- FQC assesses the finished product before it is shipped to customers, verifying that all specifications have been met.
These checkpoints are essential for identifying defects early and ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods include dimensional inspections, functional testing, and stress testing. Dimensional inspections verify that components meet specified tolerances, while functional testing ensures that the proto machine operates as intended. Stress testing simulates operational conditions to assess durability and performance under load. B2B buyers should inquire about the specific testing methods employed by suppliers to ensure they align with their quality expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing from international markets. Buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers adhere to high-quality standards.
What Role Do Audits and Reports Play in Quality Verification?
Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into a supplier’s adherence to quality standards. Buyers should request audit reports and certifications to assess the supplier’s compliance with international standards like ISO 9001. This documentation can also highlight the supplier’s commitment to continuous improvement.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Quality Assurance?
Engaging third-party inspection services adds an additional layer of assurance. These independent entities can conduct inspections and testing at various stages of the manufacturing process, providing unbiased evaluations of product quality. B2B buyers should consider incorporating third-party inspections into their procurement strategy, particularly for high-value or critical components.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances, particularly when sourcing from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Each region may have different regulatory requirements and quality standards, which can affect product quality and compliance.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Assurance?
Understanding the regional standards applicable to a supplier’s location is essential for B2B buyers. For example, European buyers may prioritize CE certification, while those in the Middle East may focus on local compliance standards. Buyers should conduct thorough research on these regional differences to ensure that their procurement strategies align with local regulations.
What Should Buyers Look for in Supplier Communication?
Effective communication with suppliers is vital for ensuring clarity on quality expectations. B2B buyers should establish clear lines of communication regarding quality standards, testing methods, and certification requirements. Regular updates and transparency from suppliers can help mitigate risks and foster a collaborative partnership focused on quality assurance.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for proto machines is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on the stages of manufacturing, relevant standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their quality and performance expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘proto machine’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in navigating the procurement process for proto machines. By following this step-by-step checklist, you will ensure that you make informed decisions, select the right suppliers, and ultimately acquire machines that meet your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for the proto machine. This includes factors such as size, capacity, automation level, and specific functionalities required for your operations.
– Importance: A well-defined specification helps suppliers understand your needs, resulting in more accurate quotes and product recommendations.
– Tip: Consider consulting with your engineering team to identify critical specifications that may affect performance and compatibility.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers specializing in proto machines. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to gather a list of candidates.
– Importance: A diverse supplier pool increases your chances of finding the best fit in terms of technology, pricing, and service.
– Tip: Look for suppliers with experience in your industry or similar applications to ensure they understand your specific requirements.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Credentials
Before proceeding, it’s crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Assess their certifications, quality control processes, and industry reputation.
– Importance: Verification of credentials ensures you are dealing with legitimate suppliers who adhere to industry standards and regulations.
– Tip: Request copies of certifications such as ISO or other relevant quality management systems to assess their commitment to quality.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
Contact your shortlisted suppliers to request detailed quotes for the proto machines that meet your specifications. Ensure that the quotes include pricing, lead times, warranty information, and after-sales service.
– Importance: Comparing quotes allows you to evaluate the value offered by each supplier, beyond just the price.
– Tip: Be wary of quotes that are significantly lower than others, as they may indicate compromised quality or hidden costs.
Step 5: Assess After-Sales Support and Service
Evaluate the level of after-sales support each supplier offers, including installation, training, and maintenance services.
– Importance: Reliable after-sales service is critical to minimizing downtime and ensuring the longevity of your equipment.
– Tip: Inquire about the supplier’s response times for service requests and the availability of spare parts.
Step 6: Check References and Client Testimonials
Request references from previous clients, especially those who have procured similar machines. Reach out to these clients to understand their experiences with the supplier.
– Importance: Hearing directly from other buyers can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s reliability, product quality, and customer service.
– Tip: Look for testimonials from clients in your geographical region or industry to gauge the supplier’s compatibility with your business context.
Step 7: Finalize the Contract and Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, carefully review and finalize the contract terms, including payment conditions, delivery schedules, and warranties.
– Importance: A well-defined contract protects both parties and ensures that expectations are clear.
– Tip: Consider involving legal counsel to review the contract to safeguard your interests, especially regarding liability and support terms.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline the sourcing process for proto machines, ensuring that they make well-informed decisions that align with their business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for proto machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Proto Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing proto machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary components of cost include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials significantly impacts the overall price. This includes the type and quality of metals, plastics, or composites used in production. Higher-grade materials will typically increase costs but may enhance durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for skilled machinists and technicians involved in the manufacturing process. In regions like Europe or North America, labor may be more expensive than in parts of Africa or South America, affecting pricing strategies.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can reduce overhead costs, allowing for more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are incurred for the creation of molds, dies, and other equipment required for production. Custom tooling for specific designs can add to initial costs but may be necessary for high-volume runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability and adherence to specifications. While this incurs additional costs, it is essential for maintaining customer trust and satisfaction, especially in industries like automotive or aerospace.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on geographic location, shipping methods, and Incoterms. International buyers need to factor in customs duties and potential tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s operational efficiency.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect Proto Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the final pricing of proto machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate volume commitments for better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs or features may increase costs. Buyers should clearly communicate requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Choices: The selection of materials can drastically affect price. Buyers should assess the trade-off between cost and quality to determine the best fit for their needs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that meet specific industry standards or certifications may come at a premium but can ensure compliance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence costs. Established suppliers may charge more for their proven track record, while new entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Different terms can shift costs and responsibilities between buyers and sellers, impacting the total landed cost.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Negotiate Better Prices for Proto Machines?
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Leveraging relationships can yield favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime in your assessment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Additionally, consider the costs of compliance with local regulations when importing machinery.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand average pricing in your region. This knowledge can empower you during negotiations.
-
Explore Alternative Suppliers: Don’t hesitate to seek multiple quotes from different suppliers. This can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best value proposition.
Conclusion
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of proto machine sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers. By analyzing cost components, recognizing pricing influencers, and employing strategic negotiation techniques, buyers can optimize their procurement processes, ensuring they secure quality machinery at competitive prices. Remember, indicative prices can vary significantly based on specific requirements and market conditions, so always seek tailored quotes from suppliers.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing proto machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Proto Machine: What Are Your Options?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of automated solutions, businesses often seek alternatives to enhance operational efficiency and productivity. When considering automated screwdriving systems, it’s essential to evaluate not only the Proto Machine but also other viable technologies that can meet diverse industrial needs. This comparison will help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Proto Machine | Alternative 1: Automated Screw Feeder System | Alternative 2: Manual Screwdriver with Power Assist |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High reliability, fast cycle time | Moderate reliability, slower than automation | Variable performance, dependent on operator skill |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment | Lower initial cost, but higher labor costs | Low initial investment, ongoing labor costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Plug-and-play, easy to set up | Requires some training, moderate complexity | Simple setup, minimal training needed |
| Maintenance | Full-service tech response | Regular maintenance needed, moderate support | Minimal maintenance, but dependent on tool quality |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production | Low to medium volume, flexible tasks | Small scale or intricate work requiring precision |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Each Alternative?
Alternative 1: Automated Screw Feeder System
Automated screw feeder systems are designed to streamline the assembly process but come with trade-offs. While they have a lower initial cost compared to Proto Machine, they typically offer moderate reliability and a slower speed of operation. These systems often require some training for operators, which can add to the implementation timeline. They are best suited for low to medium volume production, where flexibility in handling different tasks is essential. However, businesses should be aware that ongoing labor costs can accumulate, impacting overall cost-effectiveness.
Alternative 2: Manual Screwdriver with Power Assist
Manual screwdrivers equipped with power assist technology provide a cost-effective solution for smaller operations. They require a low initial investment and are easy to set up, making them accessible for businesses with limited budgets. The performance of these tools, however, is highly dependent on the skill of the operator, which can lead to variability in output quality. While they are ideal for intricate work that demands precision, the ongoing labor costs and potential inefficiencies in high-volume scenarios make them less suitable for larger production lines.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When evaluating the right automated solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including production volume, budget constraints, and the complexity of tasks. For high-volume production environments where reliability and speed are critical, the Proto Machine stands out as an optimal choice. In contrast, businesses with lower production needs or those requiring flexibility may find automated screw feeder systems or manual screwdrivers with power assist more aligned with their operational goals. Ultimately, understanding the specific needs and constraints of your business will guide you to the most suitable solution.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for proto machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Proto Machines?
When considering the procurement of proto machines, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring that they meet operational needs and quality standards. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the specific classification of the raw materials used in the machine’s construction, which can include metals, plastics, or composites.
– B2B Importance: The choice of material affects durability, resistance to wear, and overall performance. Buyers must select machines made from materials that can withstand their specific operational conditions, ensuring longevity and reducing maintenance costs. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: Tolerance levels indicate the acceptable limits of variation in dimensions and specifications of machine parts.
– B2B Importance: High precision in tolerances is essential for applications requiring exact fits and finishes, such as in aerospace or automotive sectors. Specifying tolerances helps prevent costly errors and rework, enhancing efficiency and product quality. -
Cycle Time
– Definition: Cycle time is the total time taken to complete one full operation cycle, including loading, processing, and unloading.
– B2B Importance: Faster cycle times lead to increased productivity, allowing businesses to meet high demand and improve throughput. Understanding cycle times helps buyers assess the efficiency of proto machines relative to their production schedules. -
Power Consumption
– Definition: This refers to the amount of energy required for the machine to operate effectively.
– B2B Importance: Machines with lower power consumption can significantly reduce operational costs, particularly in energy-intensive industries. Buyers need to consider energy efficiency as part of their total cost of ownership. -
Safety Features
– Definition: Safety features include mechanisms designed to protect operators and equipment, such as emergency stop buttons, guards, and automatic shut-offs.
– B2B Importance: Compliance with safety standards is critical to avoid accidents and potential liabilities. Investing in machines with robust safety features not only protects staff but can also lead to lower insurance premiums. -
Modularity
– Definition: Modularity refers to the design of machines that allows for easy upgrades or changes in configuration.
– B2B Importance: A modular design enables businesses to adapt to changing production needs without extensive re-investment. This flexibility can be a significant advantage in dynamic markets.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Proto Machines?
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms to familiarize yourself with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Knowing the OEM can help buyers assess the quality and reliability of the machine components. It also aids in understanding warranty and support structures. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. It ensures that buyers can meet their operational needs without overstocking. -
RFQ (Request for Quote)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare pricing and services from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making and cost savings. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps clarify shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, which is particularly important for international buyers in regions like Africa and South America. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the time between placing an order and receiving the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for planning and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The warranty period is the duration during which the manufacturer guarantees the product against defects.
– Importance: Knowing the warranty terms helps buyers assess the level of risk involved in their investment, influencing purchasing decisions based on expected machine performance and longevity.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting proto machines, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the proto machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Proto Machine Sector?
The proto machine sector is experiencing a robust transformation driven by advancements in automation, increased demand for precision manufacturing, and the rapid evolution of digital technologies. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Germany and Brazil), are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer integrated solutions to enhance operational efficiency. Key trends include the growing adoption of automated screwdriving systems, which streamline assembly processes and significantly reduce cycle times. These systems are characterized by their compact designs, improved safety features, and plug-and-play capabilities, making them particularly appealing to businesses aiming to optimize their production lines.
Furthermore, the rise of Industry 4.0 is pushing companies to integrate IoT (Internet of Things) technologies into their manufacturing processes. This trend enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, providing buyers with greater control over their supply chains. Another emerging trend is the customization of machinery to meet specific client needs, which is vital for companies in diverse sectors like automotive and aerospace. With an increasing emphasis on rapid prototyping and short-run production, B2B buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers that can offer flexible manufacturing solutions and fast turnaround times.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Proto Machine Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become pivotal considerations in the proto machine sector, particularly as global awareness of environmental issues grows. B2B buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains for environmental impacts, leading to a demand for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This encompasses not only the use of eco-friendly materials but also the implementation of processes that reduce waste and energy consumption. For instance, incorporating renewable energy sources and optimizing logistics can significantly lower a company’s carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing is equally crucial, as buyers are keen to ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as benchmarks for suppliers aiming to prove their commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, the trend towards using recycled materials in the production of proto machines can enhance a company’s marketability while aligning with the values of environmentally conscious consumers and businesses. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international B2B buyers can not only mitigate risks but also enhance their brand reputation in a competitive market.
What Is the Evolution and Historical Context of the Proto Machine Sector?
The proto machine sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from traditional machining techniques to advanced automated systems. Initially, the industry relied heavily on manual processes, which limited production efficiency and scalability. However, the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in the late 20th century marked a turning point, enabling manufacturers to achieve higher precision and repeatability in their machining processes.
As industries began to embrace automation, companies recognized the need for integrated solutions that combined various machining capabilities. This led to the development of automated screwdriving systems and other specialized machinery that streamlined assembly operations. Today, the focus has shifted toward smart manufacturing practices, where data-driven insights and advanced robotics play a crucial role in enhancing productivity and quality. This historical context underscores the importance of innovation and adaptation in the proto machine sector, offering B2B buyers valuable insights into the capabilities and potential of modern suppliers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of proto machine
-
How do I solve production bottlenecks in my assembly line?
To effectively resolve production bottlenecks, consider implementing automated screwdriving systems like those offered by Proto Machine. These systems are designed for easy setup and operation, allowing for simultaneous driving and feeding, which significantly reduces cycle times. Additionally, integrating vision-based alignment can enhance precision in assembly. Assess your current workflow to identify specific pain points and consult with Proto Machine for tailored solutions that fit your operational needs. -
What is the best automated screwdriving system for high-volume production?
The best automated screwdriving system for high-volume production is one that offers reliability, speed, and ease of integration. Proto Machine’s fully automated screwgun and feeder systems are ideal, featuring a compact design and plug-and-play functionality. These systems enable efficient operation with minimal downtime, ensuring that your production line can maintain high output levels. When selecting a system, consider your specific production requirements, such as cycle time and part compatibility. -
How can I ensure the quality of my custom parts from suppliers?
To ensure the quality of custom parts from suppliers, establish clear quality assurance (QA) protocols. Begin by outlining your specifications and expectations in detail. It’s beneficial to request samples before placing bulk orders to evaluate quality firsthand. Additionally, engage in regular communication with your supplier to discuss any concerns and improvements. Proto Machine emphasizes customer collaboration, ensuring that production results meet or exceed expectations, which is critical for maintaining high-quality standards. -
What are the common payment terms for international B2B transactions?
International B2B transactions often involve diverse payment terms, which can include advance payment, letters of credit, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30 or net 60). It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect both parties and ensure timely payments. Be aware of currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees. Establishing a mutually agreeable payment method can enhance trust and facilitate smoother transactions. Always consult with your financial advisor to select the best option for your business context. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for custom machinery?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for custom machinery can vary significantly among suppliers, including Proto Machine. Typically, MOQs are determined by production costs and material availability. For specialized orders, MOQs may be higher due to setup and tooling expenses. Discuss your specific needs with the supplier to understand their MOQ policies and explore options for smaller initial orders or pilot runs. This approach can help mitigate risk while assessing the supplier’s capabilities. -
How can I vet suppliers for my international procurement?
Vetting suppliers for international procurement involves several steps. Start by researching potential suppliers’ backgrounds, including their reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Request references and case studies to evaluate their previous work. Conduct site visits if possible or utilize third-party inspection services for quality assurance. Additionally, consider suppliers who demonstrate compliance with international standards and certifications, which can indicate reliability and commitment to quality. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing from abroad?
When sourcing machinery from abroad, logistics considerations are crucial for successful delivery. Assess shipping methods, transit times, and costs, as these can significantly affect your overall budget and timeline. Factor in customs regulations and potential tariffs that may apply to your imports. Collaborate with a reputable logistics partner to navigate these complexities, ensuring that your shipments arrive on time and in compliance with local laws. Clear communication with your supplier about shipping terms is also essential. -
How do I manage communication effectively with international suppliers?
Effective communication with international suppliers is vital for successful collaboration. Utilize clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or cultural references that may lead to misunderstandings. Schedule regular meetings to discuss project updates and address any concerns promptly. Use technology tools such as video conferencing and project management software to facilitate real-time communication. Establishing a dedicated point of contact can also streamline communication and ensure that all inquiries are handled efficiently.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Proto Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Proto Machine & Mfg. – Precision Turn and Mill Services
Domain: theprotoway.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Proto Machine & Mfg., Inc. offers precision turn and mill services, small assembly for long and short product runs, and customized parts production. They emphasize personal service, exceptional quality, competitive pricing, and on-time delivery. Their customer base includes commercial, aerospace, oil industry, and government sectors. They have a successful track record of completing and delivering…
2. PROTO – Industrial Tools & Equipment
Domain: protoindustrial.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: PROTO offers a wide range of industrial tools including:
– Power Tools: Automotive Tools, Compressors, Drills, Grinders & Polishers, Impact Drivers & Wrenches, Routers, Planers & Joiners, Screwdrivers & Screwguns, Specialty & Other Tools.
– Hand Tools: Automotive Tools, Chisels, Punches & Files, Clamps & Vises, Hammers, Knives & Blades, Mixed Tool Sets, Painting & Decorating Tools, Pliers & Snip…
3. Protomachines – LED8 & RADIUM
Domain: protomachines.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: LED8: Wide range of adjustments and features for tackling various situations with one tool. RADIUM: Designed for lighting interior spaces and small-to-medium sized projects effortlessly.
4. Protolabs – CNC Machining Services
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Online CNC Machining Service offering cost-efficient machined parts at any quantity. Capabilities include CNC Milling (3-axis and 5-axis indexed milling) and CNC Turning (with live tooling for cylindrical features). Machined prototypes and production parts can be delivered in as fast as 1 day. Materials available include various metals (Aluminum, Brass, Copper, Stainless Steel, Steel Alloy, Mild L…
5. Protomachine – Custom Car Building
Domain: stanceworks.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Protomachine is a custom car building shop founded by Mike, Riley Stair, and Nic Foster. They specialize in complete custom cars, custom suspension installs, chassis builds, headers, and exhaust systems. The shop is located in Orange County, California, and aims to bring automotive dreams to reality. They have a presence on Instagram (@protomachine) and a website (www.protomachine.com) for further…
6. Proto Machine & Mfg – Precision Turning & Milling
Domain: facebook.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: This company, Proto Machine & Mfg – Precision Turning & Milling, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for proto machine
Why is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for International B2B Buyers of Proto Machines?
Strategic sourcing in the procurement of proto machines offers a multitude of advantages, particularly for international buyers. By prioritizing reliable suppliers like Proto Machine Works, companies can ensure high-quality products that enhance operational efficiency. The focus on fully automated screwdriving systems and customized production capabilities allows for seamless integration into existing workflows, driving productivity and minimizing downtime.
Moreover, the emphasis on customer-centric service, as evidenced by positive testimonials, reinforces the importance of choosing partners who prioritize innovation and responsiveness. By leveraging advanced technology and robust support systems, businesses can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What’s Next for B2B Buyers in the Proto Machine Market?
Looking ahead, the landscape of automated manufacturing is rapidly evolving. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage proactively with suppliers to explore tailored solutions that meet their unique operational needs. As the demand for precision and reliability grows, so does the opportunity to forge strategic partnerships that yield long-term benefits.
Investing in proto machines today not only enhances current capabilities but also positions businesses favorably for future growth. Take the next step in your sourcing journey by connecting with trusted suppliers who can support your ambitions and drive innovation in your operations.