Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for price for laser cutting machine
Sourcing competitive prices for laser cutting machines poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers across diverse markets. As industries increasingly adopt advanced manufacturing technologies, understanding the nuances in pricing, specifications, and supplier reliability is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide comprehensively explores various types of laser cutting machines—including CO2 and fiber lasers—along with their applications, performance metrics, and operational capabilities.
Additionally, it delves into crucial aspects of supplier vetting, ensuring that buyers select reliable manufacturers that align with their project needs and budget constraints. Through sector-specific insights tailored for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including Brazil and Germany—this guide empowers organizations to navigate the intricacies of the global market.
Price variability, influenced by factors such as technology advancements and regional market dynamics, can be overwhelming. However, by utilizing this resource, B2B buyers will gain a clear understanding of the cost landscape, enabling them to make better purchasing decisions and ultimately boost their operational efficiency. With specialized knowledge at your fingertips, you can confidently procure the ideal laser cutting machine that meets your business goals while optimizing your investment.
Understanding price for laser cutting machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser Cutters | Ideal for non-metal materials, precision cutting, and engraving. | Signage, art, textiles, and wood products. | Pros: Versatile for various materials. Cons: Slower for metals compared to fiber lasers. |
| Fiber Laser Cutters | High power for metal cutting, efficient and fast. | Metal fabrication, automotive, and heavy industries. | Pros: Suitable for thick metals, less maintenance. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Desktop Laser Cutters | Compact and user-friendly, designed for smaller workspaces. | Prototyping, crafts, and small businesses. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to operate. Cons: Limited cutting area and material range. |
| Industrial Laser Systems | High-speed and large cutting areas, robust machinery. | Mass production, heavy-duty applications. | Pros: High productivity, durability. Cons: Significant space and investment required. |
| Hybrid Laser Machines | Combines CO2 and fiber laser technologies for broad applications. | Diverse sectors from crafts to industrial cutting. | Pros: Multi-functional, adaptable. Cons: Complexity may lead to higher maintenance. |
What Are the Characteristics of CO2 Laser Cutters for B2B Buyers?
CO2 laser cutters emit a laser beam that is particularly effective on non-metal materials such as wood, plastics, and fabric. They offer high precision, making them suitable for applications like signage production and detailed engraving. B2B buyers should note their versatility in handling various materials and their relatively lower purchase price compared to fiber lasers. However, users looking to cut metals might find CO2 lasers slower and less efficient than fiber options.
How Do Fiber Laser Cutters Serve the Metal Fabrication Industry?
Fiber laser cutters operate at a wavelength that efficiently cuts through metals, making them ideal for industries that require high-speed and high-precision metal fabrication. These machines can handle materials like stainless steel and titanium, producing clean and accurate cuts with minimal thermal distortion. B2B buyers considering fiber lasers should weigh the initial investment against their long-term productivity gains and lower maintenance needs due to their robust design.
Why Should Small Businesses Consider Desktop Laser Cutters?
Desktop laser cutters are designed for users who need efficiency in limited spaces, making them popular among small or home-based businesses. Their lightweight and compact design allows for easy portability, and they are generally user-friendly. Suitable for prototyping and art projects, B2B buyers will appreciate their lower cost and ease of operation. However, the trade-off often includes a smaller cutting area and material limitations.
What Are the Advantages of Industrial Laser Systems for Large Production?
Industrial laser systems are engineered for mass production and often feature high-speed capabilities and large cutting areas. These machines are ideal for heavy-duty applications and can increase overall productivity for businesses in manufacturing sectors. For B2B buyers, the advantage lies in their ability to handle large volumes and varied materials, though the initial investment is significantly higher, and they require more floor space.
How Do Hybrid Laser Machines Enhance Versatility for Various Industries?
Hybrid laser machines combine the functionalities of CO2 and fiber lasers, offering businesses a versatile solution suitable for a broader range of applications. They can cut both metal and non-metal materials effectively, thus appealing to diverse sectors from artisanal crafts to heavy industrial cutting. For B2B buyers, the value lies in having one machine that can adapt to various tasks; however, the complexity in operation and potential maintenance costs can be a consideration when investing.
Key Industrial Applications of price for laser cutting machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of price for laser cutting machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision metal fabrication for automotive parts | Enhanced production efficiency and reduced waste | Equipment power, cutting thickness range, and automation features |
| Construction | Custom metal signage and decorative elements | Improved aesthetics and brand visibility | Material compatibility, design complexity, and lead time |
| Electronics | Manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and components | Increased precision and reduced assembly costs | Required accuracy, software integration, and component types |
| Textile and Fashion | Cutting intricate patterns in fabrics for apparel | Faster production cycles and unique product offerings | Versatility with materials and tools, speed, and cost-effectiveness |
| Arts and Crafts | Creating personalized gifts and unique art pieces | Expanded creative potential and customer engagement | Machine versatility for diverse materials and design capabilities |
How Does a Laser Cutting Machine Benefit Manufacturers in Precision Metal Fabrication?
In the manufacturing sector, laser cutting machines are vital for precision metal fabrication, especially for creating automotive parts. They allow manufacturers to cut intricate shapes with exceptional accuracy, minimizing material waste. For B2B buyers, this means investing in machines that can handle specific metals and thicknesses. Considerations should include the machine’s wattage to ensure it can cut the required materials effectively and the potential for automation to streamline operations.
What Are the Applications of Laser Cutting Machines in Construction Industries?
In construction, laser cutting machines are used for creating custom metal signage and decorative elements. Their ability to precisely cut various materials aligns with the growing demand for personalized and unique designs. This provides businesses with enhanced aesthetic appeal, making their projects stand out. Buyers should focus on sourcing equipment that accommodates diverse materials and intricate design capabilities to meet customer expectations effectively.
How Does Laser Cutting Enhance Electronics Manufacturing?
The electronics industry benefits significantly from laser cutting technology, especially in the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other components. Laser cutting allows for high levels of precision and speed, which are essential in meeting the stringent quality standards required in electronics manufacturing. Buyers must prioritize lasers that integrate seamlessly with CAD software used in design, ensuring that they can produce components efficiently and at a lower cost.
What Role Do Laser Cutting Machines Play in the Textile and Fashion Sector?
In the textile and fashion sector, laser cutting machines facilitate the cutting of intricate patterns in fabrics, essential for apparel manufacturing. This automation not only speeds up production cycles but also enables designers to create unique product offerings that captivate consumers. When sourcing, companies should consider the machine’s versatility in handling various fabric types, as well as its operational speed to maintain a competitive edge in the fast-paced fashion industry.
How Are Laser Cutting Machines Transforming the Arts and Crafts Industry?
Laser cutting machines have transformed the arts and crafts industry by enabling creators to produce personalized gifts and unique art pieces. This technology enhances creative potential, allowing artists to experiment with various designs and materials, thereby increasing customer engagement. For B2B buyers in this sector, it’s crucial to choose machines that offer versatility to handle a wide range of materials and design capabilities, ensuring they can cater to various customer demands.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘price for laser cutting machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Budget Constraints with High-Quality Options
The Problem: For many businesses, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, a laser cutting machine represents a significant investment. Interest in high-quality machines quickly confronts financial constraints, making it challenging for buyers to balance cost with quality. The fear of purchasing a machine that might not meet operational needs can lead to prolonged decision-making or even lost business opportunities due to inadequate solutions.
The Solution: To successfully negotiate the price and quality of a laser cutting machine, conduct thorough market research to understand the variability in pricing based on features, specifications, and brand reputation. Create a detailed list of your operational needs, such as the types of materials you will cut, desired speed, and precision. Use this criteria when exploring options from multiple suppliers to compare not just the sticker price, but the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance and expected lifespan. Engaging with suppliers who offer financing options or leasing arrangements can also ease budget concerns. Consider joining user forums or networks to gain insights from other businesses that have navigated similar challenges.
Scenario 2: Understanding the Hidden Costs of Ownership
The Problem: B2B buyers often focus solely on the machine’s purchase price, neglecting potential hidden costs that can significantly impact overall expenses. These costs may include installation fees, maintenance, consumables like lenses and gases, and training for staff. For companies new to laser cutting, these additional costs can lead to budget mismanagement and operational disruptions.
The Solution: When planning a purchase, request a complete breakdown of both upfront and ongoing costs from potential vendors. A well-regarded supplier should provide a transparent quote that includes installation, training, and a rough estimate of replacement parts within the first few years. To further minimize future expenses, consider investing in a machine that offers comprehensive after-sales support and a warranty that covers routine wear and tear. Also, factor in the price of any necessary software updates or subscriptions. Educate your team about the machine’s operation to avoid misuse, which can lead to premature repairs or replacements, ultimately adding to your costs.
Scenario 3: The Challenge of Selecting the Right Machine for Your Operations
The Problem: With a multitude of laser cutting machines available on the market, choosing the right machine tailored to specific operational needs can feel daunting. Industrial manufacturers often face conflicting information regarding the capabilities of CO2 versus fiber laser machines, and the wide disparity in pricing can cloud judgment—leading to concerns about making a costly mistake.
The Solution: Begin the selection process by clarifying your primary objectives. Identify the materials you will cut most frequently and the thicknesses involved, as these factors will significantly influence the machine type you should consider. When comparing CO2 and fiber lasers, know that CO2 lasers are typically better for non-metal materials, while fiber lasers excel in cutting metals efficiently. Request demonstrations from suppliers or look for exhibitions where you can see machines in action. Additionally, do not hesitate to ask for case studies or testimonials to better understand how particular models perform in real business settings. This knowledge will empower you to make a well-informed purchase decision that aligns with your operational goals and long-term business strategy.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for price for laser cutting machine
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Laser Cutting Machines?
When selecting materials for laser cutting machines, it’s imperative to consider various attributes that influence performance and suitability for specific applications. This analysis will discuss four common materials: acrylic, wood, stainless steel, and aluminum, offering insights that are particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Acrylic: A Versatile Non-Metal Option
Acrylic is known for its excellent optical clarity and versatility. It has strong impact resistance, making it less prone to breakage. Acrylic can withstand temperatures up to 80°C but can warp when exposed to high heat for prolonged periods.
Pros: Acrylic is lightweight, easy to fabricate, and can be cut into intricate designs, making it suitable for signage and display purposes. Its low cost makes it accessible for small businesses.
Cons: While durable, acrylic can scratch easily and may not have the same long-term UV resistance as other materials. It can also be more flammable.
Impact on Application: Often used for signage, display cases, and decorative items, acrylic is best processed with lower wattage CO2 lasers to avoid melting.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local material standards (like ASTM) is essential. Additionally, buyers should be wary of the availability and import regulations concerning acrylic in their regions.
Wood: A Traditional Material with Unique Qualities
Wood has long been a favored material in laser cutting due to its aesthetic appeal and workability. Different types have varying hardness levels, which affects cutting parameters.
Pros: Wood is renewable, cost-effective, and yields excellent detail when laser cut. It supports a range of finishes, making it ideal for furniture, crafts, and decor.
Cons: Absorption of moisture may warp or degrade wood over time, and it varies significantly in density, necessitating adjustments in the cutting process.
Impact on Application: Typically used for furniture, crafts, and prototypes, wood can exhibit smoke and residue when burnt during cutting, requiring proper ventilation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Ensure compliance with environmental regulations regarding sourcing and waste disposal, particularly in regions focused on sustainability.
Stainless Steel: The Go-To for Industrial Applications
Stainless steel combines strength with corrosion resistance, making it suitable for harsh environments, including outdoor applications.
Pros: High durability and corrosion resistance make stainless steel ideal for structural components, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Cons: It has higher cutting costs and manufacturing complexity due to its density. Additionally, thicker gauges may demand higher-powered lasers, influencing initial investment.
Impact on Application: Common in industrial applications, when cutting stainless steel, precision is essential for promoting quality finishes and maintaining structural integrity.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards, such as DIN or ASTM for metallurgical properties, is crucial for industries that undergo certification and inspections.
Aluminum: Lightweight with Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Aluminum’s unique strength-to-weight ratio lends itself to various applications in aerospace, automotive, and even consumer goods.
Pros: Lightweight yet strong, aluminum is corrosion resistant and has excellent thermal properties, making it suitable for heat exchangers and lightweight frames.
Cons: It is trickier to cut compared to other materials; it may reflect laser energy, causing efficiency losses. Proper setup is critical to avoid issues during the cutting process.
Impact on Application: Widely used in aerospace and advanced engineering applications where precision cuts are necessary, particularly in welded structures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Different grades of aluminum may require differing preparations and specifications, so alignment with local industry standards is necessary.
Material Selection Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for price for laser cutting machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic | Signage, displays, decorative items | Excellent clarity and low cost | Prone to scratching and flammable | Low |
| Wood | Furniture, crafts, prototypes | Renewable and detail-friendly | Varies in density, sensitive to moisture | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Industrial parts and medical devices | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cutting costs and complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight with good strength | Challenging to cut; may reflect laser | Medium |
This guide aims to empower B2B buyers with actionable insights into material selection for laser cutting machines, enabling informed decisions that align with specific applications and regulatory environments.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for price for laser cutting machine
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Laser Cutting Machines?
The manufacturing process for laser cutting machines typically involves several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is vital in ensuring that the final product meets the high standards expected in industrial applications.
Material Preparation: The first stage involves selecting high-quality raw materials, which may include metals such as stainless steel and aluminum, as well as non-metal materials like acrylic and wood. Suppliers often employ rigorous incoming quality checks (IQC) to ensure that all materials meet the necessary specifications. This can include testing for thickness, density, and purity using various methods such as spectrometry for metals and laser thickness gauge inspections for non-metals.
Forming: During the forming stage, the raw materials undergo processes like cutting and shaping. Advanced techniques, such as CNC machining and laser cutting, are employed to achieve precise dimensions and contours. Laser cutting machines equipped with hybrid servo motors can achieve exceptional speeds and accuracy, which is essential for producing intricate designs that often characterize modern applications.
Assembly: The assembly stage combines all components of the machine, including the laser source, mirrors, lenses, and the robotic arm if applicable. Emphasis is placed on ensuring that all elements are aligned correctly to maintain optimal cutting performance. The use of fixtures and jigs is common to achieve consistent results. It’s also at this stage that initial quality control checks take place (In-Process Quality Control or IPQC), ensuring that each assembly meets predetermined specifications before moving on to further testing.
Finishing: After assembly, the finishing stage encompasses the final touches that prepare the laser cutting machine for operation. This may include surface finishes, painting, or assembling user interfaces. Robust testing of machine functionality occurs at this point, including safety tests by Health and Safety Compliance boards.
How Are International Quality Standards Integrated into Laser Cutting Machine Production?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the quality assurance processes is as crucial as the manufacturing processes themselves. The integration of international standards ensures that laser cutting machines are competitive globally.
Relevant International Standards: Many laser cutting machine manufacturers strive for compliance with ISO 9001, which outlines criteria for a quality management system. Certification to this standard indicates that a manufacturer follows best practice in their design, production, and distribution processes. In Europe, CE marking ensures that products meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards, while API certification might apply for specific applications in oil and gas sectors.
Quality Control Checkpoints: Throughout the manufacturing process, several QQC checkpoints are critical. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This occurs at the materials stage to ensure all incoming materials conform to quality standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the assembly phase, this check ensures all components fit and function as required.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This is the last check before shipping and includes functional tests on the assembled machine, ensuring it meets operational requirements and safety standards.
What Common Testing Methods Are Employed in the Quality Assurance of Laser Cutting Machines?
Testing methods employed by manufacturers of laser cutting machines are rigorous and designed to guarantee performance and safety. They include:
- Laser Beam Quality Tests: Using M² factor analysis, manufacturers evaluate the consistency and focus of the laser beam, which is critical for achieving cutting precision.
- Functional Performance Testing: Machines are run through real-world cutting scenarios to evaluate cutting speed, accuracy, and material versatility. This testing often replicates customer workflows to ensure machine performance aligns with buyer expectations.
- Durability Tests: Machines undergo stress tests to evaluate their resilience under continuous use conditions. This might include extended operational cycles that simulate long-term use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for international B2B buyers who seek to ensure that they receive high-quality products. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting comprehensive audits of potential suppliers can provide deep insights into their manufacturing practices, adherence to standards, and overall efficiency. This might include reviewing their quality management systems and certifications.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should not hesitate to ask manufacturers for detailed QC documentation. This can include reports demonstrating compliance with international standards, including performance testing results and certificates of conformity.
-
3rd-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to review suppliers’ operations can add an additional layer of security. These agencies can offer unbiased assessments of the supplier’s practices, materials, and finished products.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers from Emerging Markets?
For buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, an understanding of local regulatory nuances and certifications is vital. Manufacturers may need to obtain specific certifications based on regional compliance regulations, particularly when exporting machines to comply with local safety or environmental laws.
-
Local Standards Compliance: Understanding local standards is necessary, as they could differ significantly from international ones. Compliance with local regulations can facilitate smoother market entry and mitigate risks related to customs or legal complications.
-
Cultural Compatibility: Effective communication regarding specifications and quality expectations often vary across cultures. Therefore, B2B buyers should ensure clarity of requirements, including how quality expectations align with local operational practices.
By paying careful attention to these factors in both the manufacturing process and the quality assurance of laser cutting machines, international buyers can make informed purchasing decisions that ensure not just the acquisition of high-quality equipment, but also long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘price for laser cutting machine’
When considering the procurement of a laser cutting machine, it’s essential to follow a structured approach to ensure the machine meets your operational needs and offers long-term value. This guide outlines the critical steps for B2B buyers, helping you navigate the landscape of laser cutting technology effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider the materials you plan to cut (e.g., metals, plastics, wood) and their thickness. Additionally, define required features such as work area size, cutting speed, and power capacity to ensure the machine fits your production needs.
Step 2: Set Your Budget Constraints
Understanding your budget is critical when sourcing a laser cutting machine. Prices can vary widely based on specifications, brand, and additional features. Research industry standards and compare prices from multiple suppliers to define a realistic budget and identify various options available within that range, ensuring you don’t overspend or compromise on quality.
Step 3: Research and Shortlist Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable manufacturers and suppliers. Look for those that specialize in laser cutting technology, as well as customer reviews and testimonials. A well-established supplier will not only offer quality machines but also reliable support and service.
- Key considerations include:
- Years in business and market reputation.
- Customer satisfaction ratings and feedback from previous buyers.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Before finalizing suppliers, check for relevant certifications that assure compliance with international standards. Certifications such as CE, ISO, or specific industry standards can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and safety. This step helps mitigate risks related to machine performance and operational safety.
Step 5: Request Product Demonstrations or Samples
To ensure that a machine meets your expectations, request live demonstrations or samples of work completed with the machines you are considering. This will provide practical insight into the machine’s capabilities and performance. Pay attention to details like cutting quality, speed, and ease of operation, which can greatly impact productivity.
Step 6: Inquire About After-Sales Support and Maintenance
It’s essential to understand what type of after-sales support, warranty, and maintenance options are available. A good supplier should offer training, spare parts availability, and a responsive customer support team. This will be invaluable as your team acclimates to the new machine and as maintenance needs arise over time.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize the Purchase
Finally, once you’ve settled on a supplier and machine, enter negotiations regarding price, delivery timelines, and payment terms. Ensure that all agreements are documented, including warranties and support commitments. A strong contract can protect your investment and clarify responsibilities on both sides.
By adhering to this checklist, you will be better equipped to make an informed decision on procuring a laser cutting machine that meets your operational needs while also providing value and reliability for your business operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for price for laser cutting machine Sourcing
When sourcing laser cutting machines, understanding the intricate cost structure and pricing landscape is pivotal for international B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis delves into the primary cost components involved, the factors influencing pricing, and actionable insights that can foster successful negotiations.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Laser Cutting Machine Pricing?
The cost structure of laser cutting machines comprises several critical components:
-
Materials: The selection of base materials significantly impacts the price. For instance, CO2 lasers generally utilize less expensive components compared to high-power fiber lasers, which require advanced materials to handle high-energy outputs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both manufacturing and maintenance. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region; manufacturers in countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to production facilities, utilities, and administrative costs. Suppliers with advanced automation may have lower overhead costs, allowing for better pricing.
-
Tooling and Fixtures: The initial investment in tooling can affect the machine’s price, particularly for customized solutions tailored to specific industries.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that machines meet international standards, adding to the cost but enhancing reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the destination, weight, and mode of transport. International buyers often need to factor in additional fees such as customs duties and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically incorporate a profit margin that reflects their position, market demand, and service level.
Which Pricing Influencers Should Buyers Consider?
Several factors influence the final pricing of laser cutting machines:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders may attract substantial discounts, making it more economical for companies with significant production needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Tailored configurations or specialized features can elevate the cost. Buyers should clearly define specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines certified to international standards (e.g., ISO) may come at a premium. However, they provide assurance of quality and potentially lower maintenance costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers may offer warranties, support services, and parts availability at a higher initial cost, providing long-term savings and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial as they delineate responsibilities and costs associated with transportation, indicating who bears the costs and risks at various stages.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Sourcing Laser Cutting Machines?
International B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies through these practical tips:
-
Negotiation: Always be prepared to negotiate price and terms. Leverage volume orders and potential long-term partnerships to secure favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess not only the purchase price but also ancillary costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. A machine with a lower initial cost may incur higher operational costs over time.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Calculate TCO by evaluating all costs associated with the lifecycle of the machine. This includes initial purchase price, operational costs, maintenance, and disposal.
-
Pricing Nuances: Different regions may include local taxes, duties, and tariffs that can significantly affect the overall cost. Buyers in Africa and South America, for example, may face import challenges, while those in Europe may benefit from streamlined logistics within the EU.
Conclusion: Navigating the Cost Landscape with Insight
When sourcing laser cutting machines, a comprehensive understanding of cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic buying tips is essential. By meticulously analyzing these aspects, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and ultimately strengthen their competitive advantage in their respective markets. Always remember that while indicative prices may serve as a guideline, the final quote can differ based on specific negotiations and market conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing price for laser cutting machine With Other Solutions
As industries continue to evolve, businesses often face decisions concerning the best tools and technologies to meet their manufacturing needs. Laser cutting machines are a popular choice for their precision and versatility; however, exploring alternative solutions can unveil additional options that may better suit specific requirements. This analysis compares laser cutting machines against two viable alternatives: waterjet cutting machines and plasma cutting machines, helping B2B buyers understand which approach can best serve their operational goals.
| Comparison Aspect | Price For Laser Cutting Machine | Waterjet Cutting Machine | Plasma Cutting Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, suitable for both metals and non-metals with intricate designs | Excellent for thicker materials but slower; versatile but less precise | Fast cutting speed, effective for thicker metals but less intricate |
| Cost | Ranges from $4,497 to $86,997 depending on specifications | Mid-range cost, generally starting from $10,000 to $50,000 | Generally more affordable, from $2,000 to $15,000 based on equipment size |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; software integration necessary | Requires skilled personnel for operation, setup can be complex | Simpler setup, but still needs operator training |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for optics and gas systems | Low maintenance but requires periodic checks on water quality and pressure | Generally lower maintenance, though consumable parts may wear out quickly |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for detailed engraving and cutting on a variety of materials | Best suited for thick metals (up to 12″ thick); widely used in industries that need cut intricate shapes | Suitable for industrial metal fabrication, especially for thicker plates |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Waterjet Cutting Machines?
Waterjet cutting machines utilize a high-pressure stream of water, often mixed with abrasive materials, to cut through various materials, making them highly versatile. The primary advantage of waterjet technology is its ability to cut through materials that may be damaged by heat, such as certain plastics and metals without thermal distortion. However, the setup costs can be higher than those for laser machines, and while they offer great versatility, the cutting speed is generally slower compared to laser cutting. Furthermore, they may require more floor space and the need for water management systems adds complexity.
How Do Plasma Cutting Machines Compare?
Plasma cutting machines employ an electric arc to melt and cut through metals, making them one of the fastest methods available for thick metal cutting. Their lower purchase price makes plasma cutters appealing for small to medium-sized operations focused primarily on metal fabrication. However, their speed comes at the cost of precision, as the kerf (width of the cut) is generally wider than that produced by laser cutting and they can struggle with thinner materials. Furthermore, plasma cutting generates significant heat, which can affect heat-sensitive applications.
Conclusion
When selecting the right cutting technology, B2B buyers should assess their specific operational needs, considering factors such as material types, thickness, and required precision. While laser cutting machines offer unparalleled precision and versatility for a wide range of applications, alternatives like waterjet and plasma cutting machines can provide compelling advantages in certain use cases, particularly in terms of cost and performance capabilities with thicker materials. Thoughtful evaluation of these aspects can help businesses invest in the most appropriate solution for their manufacturing environment, ensuring long-term efficiency and effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for price for laser cutting machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Laser Cutting Machines Relevant to Price?
When evaluating laser cutting machines, several technical specifications influence their performance, quality, and ultimately, price. Understanding these properties is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Compatibility
Laser cutting machines can work with diverse materials, including metals, plastics, and wood. Understanding the machine’s capability to cut specific materials—like stainless steel or acrylic—directly impacts its cost. Machines designed for higher versatility typically come at a premium, but provide greater flexibility for businesses with varied manufacturing needs.
2. Cutting Speed
Measured in inches per minute (IPM), cutting speed indicates how quickly a machine can operate. Faster machines enhance production efficiency, making them crucial for high-volume applications. For instance, CO₂ lasers often achieve cutting speeds ranging from 30 to 100 IPM depending on material thickness. Businesses must weigh the cost of faster machines against potential increases in productivity.
3. Laser Power
Power is a crucial specification, expressed in watts. Higher wattage allows for cutting thicker materials and increasing speed, but generally raises the machine’s price. For example, fiber lasers can range from 1,500 watts to 60,000 watts, affecting operational capabilities significantly. Companies must assess their actual material cutting requirements to avoid overspending on unnecessary power.
4. Precision and Tolerance
Precision impacts the quality of the cut and the final product standards. Tolerance is the allowable variation in dimensions, often specified in millimeters. Higher precision and tighter tolerances are essential for industries requiring exact specifications, such as aerospace and medical devices. However, machines that offer enhanced precision may command higher prices, making it important for buyers to consider their specific application needs.
5. Control System
The type of control system—CNC vs. DSP—can affect both ease of use and machine price. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems typically offer greater flexibility and capability for complex designs, while DSP (Digital Signal Processing) systems can be easier for beginners. The choice of control technology may influence not only the initial investment but also ongoing operational efficiency.
6. Maintenance Requirements
The long-term costs associated with maintenance can significantly influence the total cost of ownership. Machines requiring frequent service or specialized components will increase operational expenses, impacting overall budget. Investigating the maintenance schedules, accessibility of parts, and support from manufacturers is crucial for assessing the total cost of a laser cutting machine.
What Are Common Trade Terminologies in the Laser Cutting Machine Market?
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for B2B buyers to navigate negotiations and contracts effectively.
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces components or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser cutting machines, buying from established OEMs can ensure reliability and compatibility with other industrial machinery, influencing decision-makers when selecting suppliers.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the least amount of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for businesses planning to make bulk purchases, as higher volume orders often lead to better pricing. Understanding MOQs helps buyers align their procurement strategies with production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process used to invite suppliers to bid on specific products or services. For laser cutting machines, submitting a detailed RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and supplier capabilities directly, ensuring competitive offers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential when importing laser cutting machines, as they govern shipping costs, risk, and insurance—key components that can affect overall pricing.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the duration from order placement to delivery. Shorter lead times are often desired but may come at increased costs. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning, especially in industries where timing is critical.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can engage more effectively in negotiations, ensuring they secure the best laser cutting machines suited to their operational requirements and budgets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the price for laser cutting machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Influencing Laser Cutting Machine Prices?
The laser cutting machine sector is experiencing dynamic shifts fueled by technological advancements, changing industry demands, and global economic factors. A notable driver in the market is the increasing adoption of automation and Industry 4.0 concepts, compelling manufacturers to invest in precision cutting solutions that enhance productivity and quality. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards miniaturization and versatility in machine design, making laser cutting accessible for various applications—from small workshops to large-scale industrial setups.
Emerging technologies such as fiber laser and hybrid machines have significantly expanded the range of materials being processed and improved cutting speeds. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these innovations can be crucial for selecting machines that meet specific operational needs. The rising demand for eco-friendly and energy-efficient solutions also drives manufacturers to refine their products to comply with sustainability standards, thus influencing pricing strategies.
The global market is currently leaning towards competitive pricing structures, driven by increased competition and the proliferation of entry-level models. In regions such as Brazil and Germany, buyers have varying preferences based on local manufacturing capabilities and material availability, necessitating suppliers to tailor their offerings. As businesses navigate these dynamics, focus on sourcing high-quality machines that deliver a strong ROI becomes paramount.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Laser Cutting Machine Market?
Sustainability is no longer just a corporate responsibility but a strategic imperative that affects purchasing decisions in the B2B sector. Laser cutting machines, often seen as energy-intensive equipment, are evolving with increasing emphasis on reducing environmental impacts. Manufacturers are now integrating energy-efficient designs and waste-reduction technologies to appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
Ethical sourcing and transparent supply chains are critical for B2B buyers. Companies are keen to partner with manufacturers who prioritize responsible sourcing of materials and adhere to environmental regulations. Green certifications, such as ISO 14001, are becoming important factors in the procurement process, as they reflect a commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, innovative materials like biodegradable plastics and recyclable metals are increasingly being utilized in applications that involve laser cutting. Suppliers that provide such materials and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability often find favor in the eyes of international buyers looking to bolster their environmental credentials while investing in laser cutting solutions. Adopting a green approach not only benefits the planet but also enhances brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Historical Context of Laser Cutting Technology?
The history of laser cutting technology traces back to the early 1960s, when the first functional laser was developed. Initially limited to research and highly specialized applications, the technology gained traction in manufacturing sectors by the late 1970s. The introduction of CO2 laser systems revolutionized metal processing, allowing for high precision and versatility in cutting various materials.
As electronics advanced, the costs associated with laser machinery decreased, leading to widespread adoption beyond heavy industries. Today, with the integration of CNC technology, laser cutting machines are not only common in large manufacturing plants but are increasingly utilized by small businesses and hobbyists. This democratization of laser technology has expanded its application across sectors, from automotive to textiles, and has driven a diverse range of products to meet varying consumer needs. Understanding this historical backdrop helps B2B buyers appreciate the trajectory of the sector and make informed decisions regarding investments in laser cutting technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of price for laser cutting machine
1. How can I determine the appropriate type of laser cutting machine for my needs?
To choose the right laser cutting machine, assess your specific applications and materials. Consider whether you need a CO2 laser for non-metals like wood and acrylic, or a fiber laser suitable for cutting metals and harsher materials. Review the work area size that fits your projects, the thickness and type of materials you’ll cut, and desired cutting speed. Supplier consultation can aid in identifying features that match your operational goals and budget constraints.
2. What considerations should I keep in mind when comparing prices for laser cutting machines?
When comparing laser cutting machines, analyze total cost ownership rather than just initial price. Include operational expenses like maintenance, energy consumption, and potential training costs. Compare features such as cutting speed, precision, and material versatility. Make sure to account for warranty terms and support services included in the purchase. Obtaining quotes from multiple suppliers can provide leverage in negotiations and a better understanding of market rates.
3. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for laser cutting machines?
Most manufacturers and suppliers have MOQs, especially for custom or bulk orders. Generally, MOQs may vary based on the type of machine and customization required. It is essential to communicate your needs clearly to suppliers to ensure that they can accommodate your order size. Builders may offer flexible terms for first-time buyers or smaller enterprises, allowing room for negotiation.
4. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a laser cutting machine?
Payment terms can vary significantly by supplier, but common arrangements might include full payment upfront, deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance paid before shipping, or installment plans. It’s advisable to clarify all terms in writing and understand what methods of payment are acceptable. Be cautious of suppliers that request full payment without providing security, such as a purchase agreement or other guarantees.
5. How can I verify the credibility of a laser cutting machine supplier?
To vet a supplier, conduct thorough research online, including reviews and testimonials from previous buyers. Check for industry certifications, such as ISO standards, and ensure they have proper licensing. Engage in direct communication to assess their response time and willingness to answer your queries. Visiting their facility, if feasible, can offer additional assurance about their operational capability and transparency.
6. What quality assurance practices are essential when sourcing laser cutting machines?
Quality assurance (QA) practices are crucial to ensure that machines meet both safety and performance standards. Verify if the supplier offers warranty protections, routine quality checks, or certifications. Request detailed specifications and performance guarantees. Additionally, understand the return policy or procedures for any potential defects. You may consider third-party inspections, especially for large investments.
7. How do logistics and shipping affect the total cost of purchasing a laser cutting machine?
Logistics and shipping can significantly impact the overall cost of a laser cutting machine purchase. Factors such as freight costs, customs duties, and insurance should be factored in. Evaluate suppliers that provide shipping options and their associated costs upfront. If sourcing internationally, additional considerations may include transportation timeframes and handling fees, which can affect your operations timeline.
8. Can I customize my laser cutting machine after purchase?
Yes, many suppliers allow for customization of laser cutting machines to better fit your specific needs. This can include modifications to the software, hardware upgrades, or adjusting operational parameters. Discuss potential customization options with your supplier before purchase to ensure that they can meet your requirements. Be mindful of any additional costs or lead times associated with these changes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
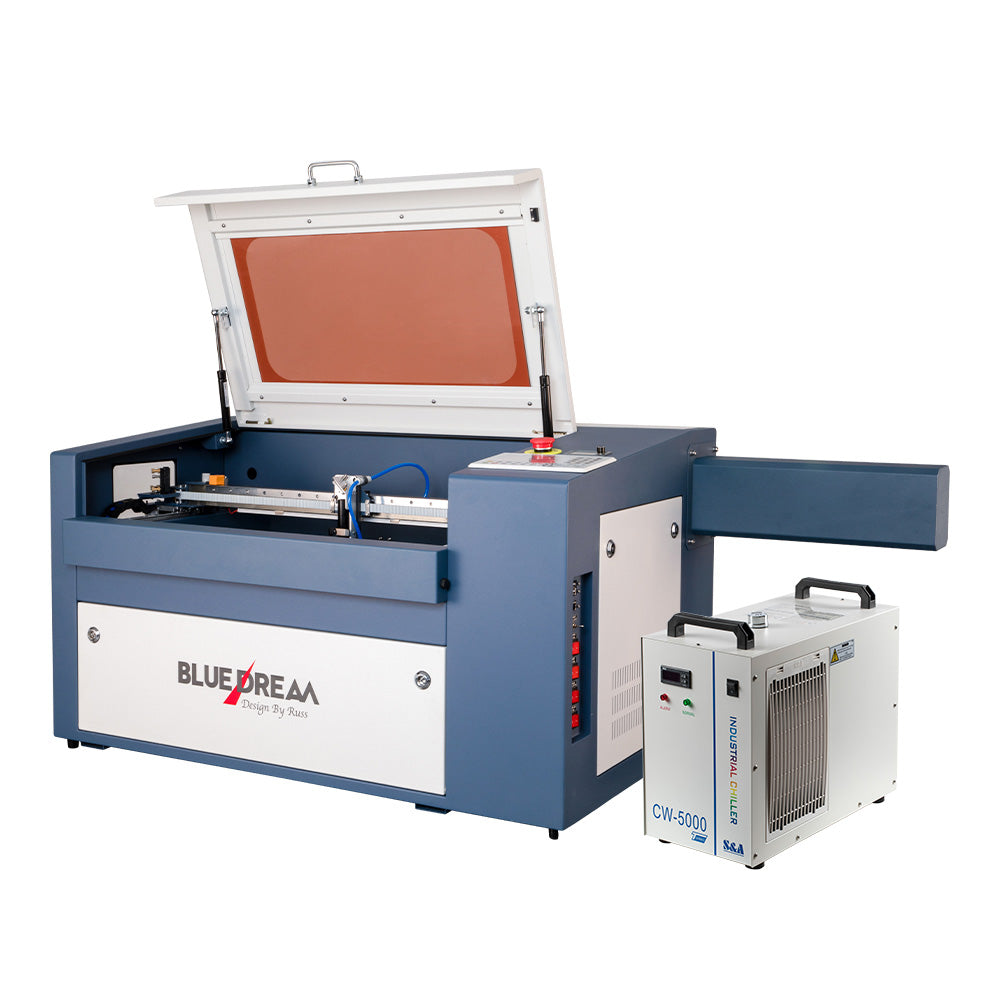
Top 8 Price For Laser Cutting Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Style CNC – Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: {‘description’: ‘A laser cutting machine is an automatic slitting tool that uses a DSP or CNC controller kit in conjunction with CAM software to instruct a CO2 or FIBER laser beam to cut through metals, metalloids and nonmetals along tool paths created by CAD software, as well as cut custom shapes, contours, and holes out of sheets, tubes and profiles to create precision parts, signs, tags, decora…
2. OMTech – Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machines
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: OMTech Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machines include:
1. FC22 1500W Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine – Monthly payment option starting at *$828/MO (Price Match Guarantee).
2. FC22-C 1500W Open Metal Laser Cutting Machine – Monthly payment option starting at *$767/MO (Price Match Guarantee).
3. FC-105 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine – Monthly payment option starting at *$1,081/MO (Price Match Guarante…
3. FSL Muse – Hobby Laser Cutter
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Hobby grade laser cutter, investment of $5,000 – $6,000, brands considered include FSL Muse (not Glowforge), potential to pay for itself in 6 months or less, interest in making and selling through Etsy and local craft shows, goal to transition to part-time or full-time business.
4. CNC Machines – Used Laser Cutters
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Used CNC Laser Cutters available from various brands including AMADA, MITSUBISHI, MAZAK, TRUMPF, BYSTRONIC, AP LAZER, BOSS LASER, LASERPRO, LVD STRIPPIT, TROTEC, BODOR, CINCINNATI, COHERENT, HK LASER & SYSTEMS, HYPERUSA, IPG PHOTONICS, NUKON, ROBOTEC, ROFIN. Types of CNC laser cutters include gas laser cutting, crystal laser cutting, and fiber laser cutting. Key models offered include ENSIS 3015, …
5. SA Lasers – Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: salasers.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Laser cutting machines are tools that use laser beams to cut through materials such as wood, acrylic, fabric, glass, leather, plastic, and metal. The main types of laser cutting machines include CO2 lasers, Fiber lasers, and YAG lasers. CO2 lasers are the most common and cost around $2000; Fiber lasers are faster and cut through thicker materials, costing up to $100,000; YAG lasers are the most ex…
6. Wattsan – Laser Machines
Domain: wattsan.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Wattsan – Laser Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. MatterHackers – xTool F1 Laser Engraver
Domain: matterhackers.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Laser Cutters & Engravers offer versatile capabilities such as high precision, speed for quick engraving, and non-contact cutting. Featured brands include Glowforge, xTool, Laguna Tools, WAZER, FLUX, and FSL. Key products include xTool F1 Laser Engraver in several configurations (Start-Up Bundle, Deluxe Bundle, Slide Extension Bundle, etc.), FLUX Ador Color Printing Laser Cutter in 10w and 20w opt…
8. LightBurn Software – Cenoz Laser Engraver
Domain: forum.lightburnsoftware.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Cenoz Laser Engraver
Price: $79 (currently $75)
Order Date: August 9, 2022
Received Date: August 12, 2022
Construction: All metal
Extrusion: 2040 (vs 2020)
Wiring: Uses cable chains
Gantry screws: Four M5 screws for the gantry, a couple of M3 screws for the end of the gantry cable chain
Working Area: Approximately 220mm x 290mm
Laser Power: 3W (claimed)
Controller Board: JL1 Mainboard
User Softwar…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for price for laser cutting machine
In navigating the landscape of laser cutting machine pricing, companies must strategically assess their specific needs, manufacturing capabilities, and budget constraints. Key insights reveal that prices for laser cutting machines vary significantly, influenced by factors such as technology type (CO2 vs. fiber), machine capabilities, and brand reputation. Understanding the versatility across different models can empower buyers, allowing them to select machines that not only fit immediate projects but also support future expansion into diverse material processing.
Moreover, strategic sourcing proves essential in maximizing value and minimizing risk. By engaging in thorough market research, negotiating with suppliers, and exploring various purchasing options—whether new, refurbished, or direct-from-manufacturers—businesses can secure advantageous deals that foster sustainability and growth.
Looking ahead, as global industrial demands evolve, investing in the right laser cutting technology will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this knowledge to make informed procurement decisions. Don’t hesitate to initiate conversations with suppliers to explore tailored solutions that meet your operational needs today and set the stage for success tomorrow.