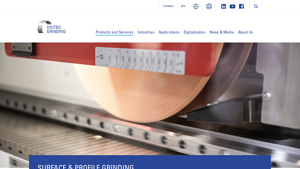
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for precision surface grinding
In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing precision surface grinding services presents a unique set of challenges for B2B buyers. As companies strive to enhance product quality while maintaining competitive pricing, understanding the nuances of precision surface grinding becomes essential. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, delving into various types of precision grinding processes, their applications across industries, and best practices for supplier vetting. By providing insights into cost structures and key considerations, we aim to empower international buyers—particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Germany and Saudi Arabia—to make informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the complexities of precision surface grinding requires not only technical knowledge but also an awareness of market trends and supplier capabilities. Buyers must consider factors such as tolerances, material specifications, and production volumes to ensure optimal outcomes. This guide will equip you with the necessary tools to evaluate potential suppliers, compare service offerings, and ultimately select the right partners for your precision grinding needs. By the end of this guide, you will be well-positioned to tackle the challenges of sourcing precision grinding services, ensuring your projects achieve the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
Understanding precision surface grinding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Spindle Surface Grinding | Utilizes a horizontally mounted abrasive wheel; ideal for flat surfaces. | Aerospace components, automotive parts, molds, and dies. | Pros: High precision, good for large parts. Cons: Limited to flat surfaces. |
| Vertical Spindle Surface Grinding | Features a vertically oriented wheel; effective for intricate shapes. | Electronics, medical devices, and small precision parts. | Pros: Versatile for complex geometries. Cons: Generally slower than horizontal grinding. |
| Rotary Surface Grinding | Employs a rotating table; suitable for larger workpieces. | Tool and die production, heavy machinery components. | Pros: Efficient for high-volume production. Cons: Can be less precise than other methods. |
| Creep-Feed Grinding | Involves slower feed rates with deeper cuts; excellent for contours. | Aerospace, automotive, and custom tooling. | Pros: Ideal for complex shapes and high material removal. Cons: Longer cycle times. |
| Precision Blanchard Grinding | Uses a magnetic chuck to hold workpieces; effective for flat surfaces. | Large castings, plates, and heavy components. | Pros: High stock removal rates, cost-effective for large batches. Cons: Limited to specific shapes and sizes. |
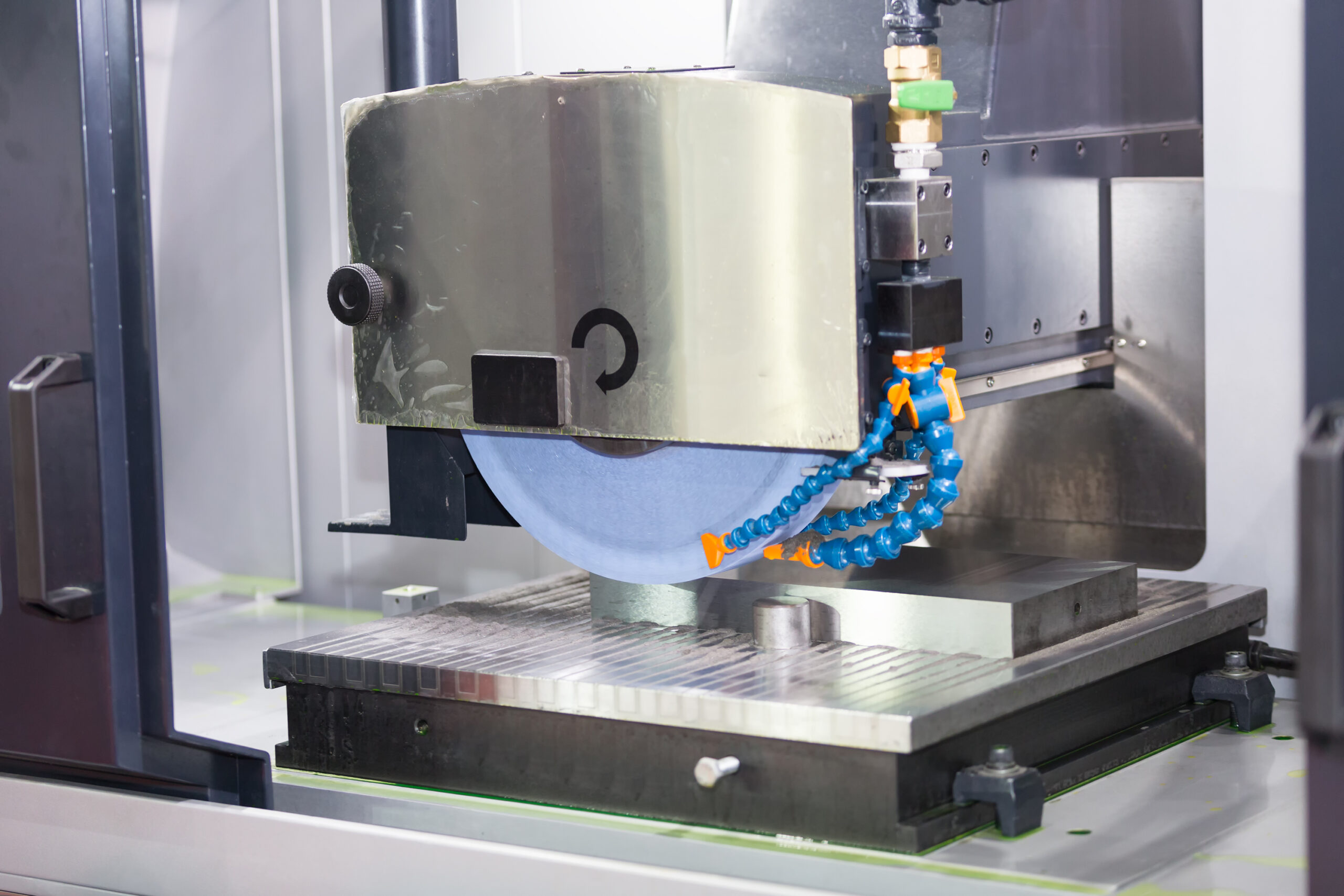
What Are the Key Characteristics of Horizontal Spindle Surface Grinding?
Horizontal spindle surface grinding is characterized by its use of a horizontally mounted abrasive wheel that rotates at high speeds. This method excels in achieving high precision on flat surfaces, making it ideal for applications in aerospace components, automotive parts, and molds. B2B buyers should consider this option when they require parts with tight tolerances and a smooth finish. However, its limitation to flat surfaces may necessitate additional processes for complex geometries.
How Does Vertical Spindle Surface Grinding Differ from Other Types?
Vertical spindle surface grinding features a vertically oriented wheel, making it particularly effective for intricate shapes and small precision parts. This method is commonly used in the electronics and medical device industries, where precision is paramount. While it offers versatility for complex geometries, buyers should note that it may operate at slower speeds compared to horizontal grinding, impacting production timelines.
What Advantages Does Rotary Surface Grinding Offer?
Rotary surface grinding utilizes a rotating table to accommodate larger workpieces, making it suitable for applications in tool and die production and heavy machinery components. This method is efficient for high-volume production runs, allowing for consistent results across multiple pieces. However, buyers should be aware that while it offers efficiency, it may sacrifice some precision compared to more specialized grinding methods.
When Should Creep-Feed Grinding Be Considered?
Creep-feed grinding is distinguished by its slower feed rates and deeper cuts, making it ideal for complex contours and shapes. It is often used in industries like aerospace and automotive, where intricate designs are necessary. While it allows for high material removal, buyers should consider the longer cycle times associated with this method, which may affect overall production speed.
What Is the Role of Precision Blanchard Grinding in Industrial Applications?
Precision Blanchard grinding employs a magnetic chuck to hold workpieces, making it particularly effective for large castings and heavy components. This method is known for its high stock removal rates and cost-effectiveness in large batch production. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific shapes and sizes of their parts, as Blanchard grinding may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring extreme precision.
Key Industrial Applications of precision surface grinding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Precision Surface Grinding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Grinding of turbine components and engine parts | Ensures high precision and reliability in critical applications | Need for ISO certifications and adherence to aerospace standards |
| Medical Devices | Finishing of surgical instruments and implants | Guarantees safety and performance in life-critical devices | Compliance with FDA regulations and biocompatibility standards |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of micro-components for devices | Achieves tight tolerances essential for device functionality | Ability to handle small batch sizes with quick turnaround times |
| Automotive | Surface grinding of engine blocks and transmission parts | Enhances durability and performance of automotive components | Consideration for high-volume production capabilities |
| Tool and Die Manufacturing | Precision grinding of molds and dies | Improves the accuracy and quality of produced parts | Availability of advanced grinding technologies and expertise |
How is Precision Surface Grinding Applied in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace sector, precision surface grinding is critical for the fabrication of turbine components and engine parts. These components must meet stringent tolerances to ensure safety and performance under extreme conditions. Buyers in this sector should look for suppliers with ISO certifications and a proven track record of compliance with aerospace standards. This ensures that the grinding processes utilized can withstand rigorous testing and regulatory scrutiny.
What Role Does Precision Surface Grinding Play in Medical Device Production?
Precision surface grinding is vital for the finishing of surgical instruments and implants in the medical device industry. The requirement for high precision is paramount, as even minor deviations can compromise patient safety. Buyers should seek suppliers that are compliant with FDA regulations and can demonstrate biocompatibility. This will ensure that the finished products are safe for use in medical applications and meet the necessary health standards.
How is Precision Surface Grinding Beneficial in Electronics Manufacturing?
In the electronics industry, precision surface grinding is employed to manufacture micro-components essential for devices like smartphones and computers. The ability to achieve tight tolerances is crucial for the functionality of these devices, as they often incorporate intricate parts. International buyers should prioritize suppliers that can handle small batch sizes efficiently while maintaining quick turnaround times, which is essential for keeping pace with rapid technological advancements.
Why is Precision Surface Grinding Important for the Automotive Industry?
Precision surface grinding is extensively used in the automotive sector for the surface treatment of engine blocks and transmission parts. By enhancing the durability and performance of these components, manufacturers can ensure the reliability of their vehicles. When sourcing grinding services, businesses should consider suppliers capable of high-volume production to meet the demands of automotive manufacturing while ensuring consistent quality.
How Does Precision Surface Grinding Improve Tool and Die Manufacturing?
In tool and die manufacturing, precision grinding is crucial for producing molds and dies that require high accuracy. This process improves the quality and precision of the parts produced, which is essential for maintaining competitive advantage in manufacturing. Buyers in this sector should look for suppliers with advanced grinding technologies and specialized expertise to ensure optimal outcomes in their production processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘precision surface grinding’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Challenge of Achieving Tight Tolerances in Precision Surface Grinding
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with achieving the tight tolerances required for high-precision components, especially in industries like aerospace and medical devices where specifications can be as tight as +/- 0.0001 inches. Buyers often find that even minor deviations can lead to significant performance issues or increased production costs due to rework or scrap. This challenge is compounded when working with complex geometries or materials that are difficult to grind, leaving buyers frustrated and uncertain about how to ensure quality and compliance.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing suppliers that specialize in precision surface grinding with a proven track record of meeting stringent tolerances. When evaluating potential suppliers, it’s essential to review their certifications (such as ISO 9001) and request examples of past projects similar to your requirements. Additionally, communicate your specific tolerances and material specifications upfront. Consider engaging in collaborative engineering sessions with your supplier to discuss optimal grinding methods and techniques tailored to your parts. This proactive approach can help establish a clear understanding of expectations and ensure that the grinding process aligns with your quality standards.
Scenario 2: Dealing with Surface Finish Quality Issues
The Problem: Another common pain point is achieving the desired surface finish quality. Buyers often receive components that, while dimensionally accurate, have surface finishes that do not meet their aesthetic or functional requirements. This issue is particularly pronounced in industries where surface roughness is critical, such as in the manufacturing of molds or components in consumer electronics. Poor surface finish can lead to performance problems, increased friction, and even product failure, causing delays in production schedules and dissatisfaction among end customers.
The Solution: To address surface finish quality issues, buyers should clearly specify their requirements in terms of roughness average (Ra) values and any relevant industry standards during the initial discussions with suppliers. Moreover, it’s beneficial to ask for surface finish samples from potential vendors, allowing you to assess their capabilities directly. Implementing a pre-production sample approval process can also mitigate this issue; by evaluating a sample part before full production, you can ensure that the surface finish meets your expectations. Additionally, consider suppliers that utilize advanced grinding technologies, such as creep-feed grinding, which can enhance surface finishes while maintaining tight tolerances.
Scenario 3: Managing Costs and Lead Times Effectively
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges related to managing costs and lead times associated with precision surface grinding. Rapid changes in market demand can lead to pressure for quicker turnaround times, while unexpected cost increases can strain budgets. Buyers often find themselves at a crossroads, needing to balance quality, speed, and cost, which can be particularly challenging when working with specialized components or materials.
The Solution: To effectively manage costs and lead times, buyers should engage in strategic partnerships with their suppliers. Building a long-term relationship can lead to better pricing, priority scheduling, and improved communication, all of which can help mitigate cost and time pressures. When sourcing, consider suppliers that offer a range of services—such as in-house engineering support or integrated supply chain solutions—that can help streamline the production process. Additionally, implementing lean manufacturing principles can assist in reducing waste and optimizing processes. Regularly reviewing your supplier’s performance against agreed-upon metrics will also ensure that you maintain control over cost and lead time expectations while fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
By addressing these common pain points with actionable solutions, B2B buyers can enhance their precision surface grinding operations, ensuring they meet the demanding requirements of their industries while maintaining competitive advantages.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for precision surface grinding
What Are the Key Materials Used in Precision Surface Grinding?
In precision surface grinding, selecting the right material is crucial for achieving optimal performance and durability. Below, we analyze four common materials used in this process, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel: A Versatile Choice
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,600°F (870°C) and offers good mechanical properties, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, especially in environments prone to corrosion. However, it can be more expensive than other metals, and the grinding process requires specialized abrasives to achieve the desired finish. The manufacturing complexity may also increase due to the need for specific tooling.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in medical devices, aerospace components, and food processing equipment, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or DIN 1.4401 is essential. Buyers from regions like Europe or the Middle East should ensure that their suppliers meet these standards to maintain quality and reliability.
2. Aluminum: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good thermal conductivity, and is resistant to corrosion. It can handle temperatures up to 1,220°F (660°C) and is often alloyed to enhance its mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low cost and ease of machining. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not perform well in high-stress applications. Its softness can lead to faster wear on grinding tools, increasing operational costs.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in automotive parts, consumer electronics, and packaging materials, where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the common standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions and ensure that their suppliers adhere to these specifications.
3. Tool Steel: High Performance for Tough Applications
Key Properties: Tool steel is designed for high wear resistance and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It typically has a hardness rating of 58-65 HRC and can endure extreme conditions.
Pros & Cons: The durability and performance of tool steel are unmatched, making it ideal for precision components. However, it is relatively expensive and can be challenging to grind, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application: Tool steel is frequently used in manufacturing molds, dies, and cutting tools, where precision and longevity are crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A681 or JIS G4404 is vital. Buyers from regions like South America and Africa should verify that their suppliers meet these quality benchmarks to ensure product integrity.
4. Composite Materials: Innovative Solutions
Key Properties: Composite materials, often made from a combination of metals and polymers, offer unique properties such as reduced weight and enhanced strength. They can be engineered to withstand various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of composites is their tailored properties, which can be optimized for specific applications. However, they can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized grinding techniques.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in aerospace and automotive industries, where weight reduction and performance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards applicable to composites, such as ASTM D3039 for tensile properties. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to these standards is crucial for maintaining quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Precision Surface Grinding
| Material | Typical Use Case for Precision Surface Grinding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, aerospace components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, specialized tooling | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive parts, consumer electronics | Lightweight, cost-effective | Less durable, faster tool wear | Medium |
| Tool Steel | Molds, dies, cutting tools | High wear resistance | Expensive, challenging to grind | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, automotive applications | Tailored properties | Higher production cost | Medium to High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating the complexities of precision surface grinding. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can lead to better decision-making and enhanced product performance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for precision surface grinding
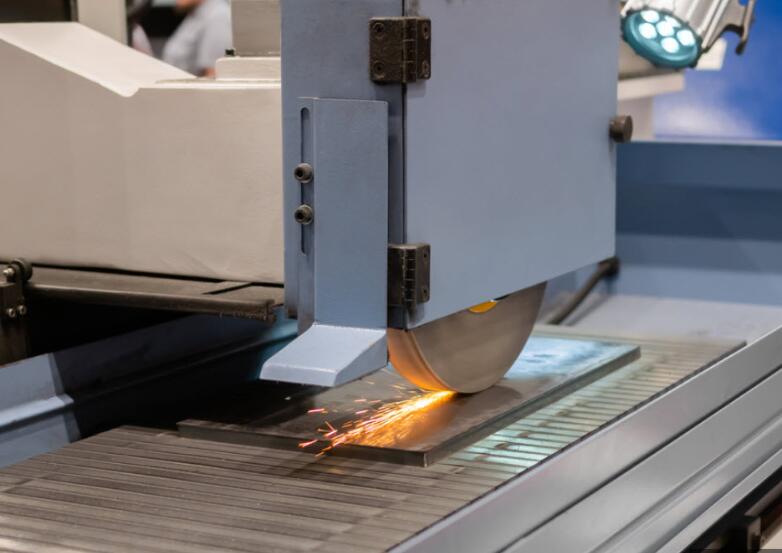
What Are the Key Manufacturing Processes for Precision Surface Grinding?
Precision surface grinding is a meticulous process that transforms raw materials into finely finished components with tight tolerances. The manufacturing stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage is crucial in ensuring that the final product meets the exact specifications required by various industries.
How Does Material Preparation Influence Precision Surface Grinding?
The first step in precision surface grinding is material preparation. This involves selecting the right materials, which can include ferrous and non-ferrous metals, as well as exotic materials. The selected materials are then cut to approximate sizes, ensuring they are free from contaminants that could affect the grinding process.
Proper material preparation is essential for achieving the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy. This stage often includes processes like machining or sawing to remove excess material, followed by thorough cleaning to eliminate oils, dust, and other particles that could interfere with grinding.
What Forming Techniques Are Used in Precision Surface Grinding?
Once materials are prepared, they undergo forming techniques that set the stage for precision grinding. The primary method used in this phase is horizontal spindle surface grinding. In this process, an abrasive wheel rotates at high speeds and is brought into contact with the workpiece. The friction created removes material, shaping the part while also achieving the necessary surface finish.
For parts that require cylindrical grinding, different work-holding devices are utilized. The type of abrasives selected—such as zirconia alumina, silicon carbide, or aluminum oxide—depends on the material being ground and the specific requirements of the project.
How Is Finishing Achieved in Precision Surface Grinding?
Finishing is the final stage in the precision surface grinding process. This stage focuses on achieving the required tolerances and surface finishes. Depending on the application, precision grinding can achieve tolerances as tight as +/- 0.0001 inches and surface finishes around 10 RMS.
During this stage, additional grinding techniques, such as creep-feed grinding or centerless grinding, may be employed to enhance the surface quality. The choice of technique will depend on the specific requirements of the project, including the complexity of the part and the materials involved.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Precision Surface Grinding?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of precision surface grinding, ensuring that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations. To maintain high-quality output, manufacturers typically adhere to various international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Are Relevant to Precision Surface Grinding?
One of the most recognized quality management standards is ISO 9001. This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable across various industries, including precision machining. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement.
For specific industries, additional certifications such as CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards or API standards for oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications not only enhance credibility but also facilitate smoother trade across international borders.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Precision Surface Grinding?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically integrated throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, incoming materials are inspected for defects and compliance with specifications. This initial step ensures that only high-quality materials are processed.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the grinding process, periodic checks are conducted to monitor dimensional accuracy and surface quality. This real-time assessment allows for immediate adjustments to the grinding parameters, minimizing the risk of defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the grinding process is complete, the final products undergo rigorous testing. This may include dimensional inspections, surface roughness measurements, and visual inspections to ensure compliance with specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Precision Surface Grinding?
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the quality of precision ground components. Common methods include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Tools such as calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are used to verify that the components meet specified dimensions.
-
Surface Roughness Testing: Instruments like surface roughness testers assess the surface finish, ensuring it falls within the acceptable range for the intended application.
-
Visual Inspections: These are performed to detect any visible defects, such as cracks or surface irregularities.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in international markets, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes. This provides insights into their operational capabilities and quality management systems.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports and compliance certificates. This transparency can help build trust and inform purchasing decisions.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to perform independent assessments of the supplier’s products. This step can provide an additional layer of assurance regarding product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
When sourcing precision surface grinding services internationally, buyers must be aware of regional differences in quality standards and practices. For instance, European buyers may place a higher emphasis on compliance with CE marking, while companies in the Middle East may prioritize adherence to local industry standards.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences can impact communication regarding quality expectations. Therefore, establishing clear specifications and maintaining open lines of communication with suppliers is crucial for successful international partnerships.
By understanding these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select suppliers capable of meeting their precise needs in the competitive global market.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘precision surface grinding’
Introduction
Sourcing precision surface grinding services requires careful consideration and a strategic approach to ensure that your specific needs are met effectively. This guide provides a clear checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process, ensuring you select a supplier capable of delivering high-quality results that meet your technical specifications and industry standards.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, tolerances, surface finish quality, and material types. Having precise specifications helps streamline the sourcing process and ensures suppliers understand your needs, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings later on.
- Tolerances: Specify the acceptable tolerances, such as +/- 0.0001”, to ensure precision.
- Surface Finish: Indicate the desired surface finish (e.g., 10 RMS) to guide the grinding process.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers. Look for companies with a strong reputation in precision grinding, particularly those with experience in your industry.
- Industry Experience: Focus on suppliers who have successfully completed projects similar to yours.
- Geographic Considerations: Consider suppliers in regions that can easily ship to your location, particularly if you’re sourcing from Africa, South America, or the Middle East.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications and Standards
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. This step is crucial as it reflects the supplier’s commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- Quality Assurance: Ensure they have robust quality control processes in place.
- Compliance: Confirm compliance with any industry-specific standards that may apply to your project.
Step 4: Request Samples and Case Studies
Before making a decision, request samples of previous work and case studies to assess the supplier’s capabilities. This allows you to evaluate their work quality and the precision of their grinding processes.
- Sample Evaluation: Analyze the samples for dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Case Studies: Review case studies that demonstrate successful outcomes for similar projects.
Step 5: Discuss Production Capabilities and Turnaround Times
Engage in discussions with potential suppliers about their production capabilities, including their equipment and technology. Understanding their capacity to handle both small and large orders is essential for long-term planning.
- Capacity: Ask about their ability to meet tight deadlines and manage fluctuating order volumes.
- Technology: Inquire about the types of grinders and technologies used, as advanced equipment can lead to better precision.
Step 6: Assess Customer Support and Communication
Evaluate the supplier’s customer service and communication practices. A supplier who is responsive and easy to communicate with can make the procurement process smoother and more efficient.
- Responsiveness: Gauge how quickly they respond to inquiries and provide information.
- Support: Assess the level of technical support they offer during the project.
Step 7: Compare Pricing and Terms of Service
Finally, compare pricing models and terms of service among the shortlisted suppliers. While cost is important, it should be balanced with quality and service levels.
- Detailed Quotations: Request comprehensive quotes that outline all costs involved.
- Payment Terms: Understand the payment terms and conditions, including any penalties for late payments or discounts for early payments.
By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions when sourcing precision surface grinding services, ensuring that you partner with a supplier that meets your needs and expectations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for precision surface grinding Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Precision Surface Grinding?
When sourcing precision surface grinding services, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials like ferrous and non-ferrous metals may have different costs based on market conditions. Exotic metals, while often required for specialized applications, can substantially increase material costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in precision grinding, where expertise is needed to maintain accuracy and quality. Labor costs can vary based on geographic location, skill level, and the complexity of the grinding operations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Advanced facilities with modern equipment may have higher overheads but can offer better efficiency and quality.
-
Tooling: The type and quality of grinding tools used directly affect the cost. Specialized tooling for intricate designs or higher tolerances can lead to increased expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous quality control measures ensures that products meet specified tolerances. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the level of certification required, such as ISO standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are also a factor, particularly for international buyers. Distance, shipping methods, and customs duties can add to overall expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include their profit margin in the pricing, which can vary based on their market position, reputation, and the services they offer.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Precision Surface Grinding Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of precision surface grinding services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often qualify for bulk discounts, significantly reducing the per-unit cost. However, buyers should balance volume with their immediate needs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized grinding services that require unique tooling or processes will typically incur higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The material selection not only affects the base price but also influences the tooling and labor costs. High-performance materials may require specialized processes that can increase overall pricing.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers with higher quality standards or certifications often charge more. However, this investment can lead to better product reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and technology level can affect pricing. Well-established suppliers may command higher prices due to their experience and track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international transactions. They determine who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect the total cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Precision Surface Grinding Prices?
When negotiating prices for precision surface grinding, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Conduct Comprehensive Market Research: Understanding the market rates for precision grinding services in different regions can empower buyers during negotiations. This knowledge helps identify fair pricing and potential suppliers.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on upfront costs, consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, quality assurance, and potential rework costs. This approach ensures long-term value.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If planning to place large orders, discuss potential discounts upfront. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to better pricing.
-
Clarify Specifications Early: Clearly define your project requirements and specifications to avoid additional costs later in the process. Miscommunications can lead to costly adjustments.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and simplify communication. This is particularly advantageous in regions like Africa and South America, where transportation can be a significant expense.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for precision surface grinding services are subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct due diligence when selecting a supplier to ensure competitive pricing and quality.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing precision surface grinding With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Precision Surface Grinding
In the realm of precision manufacturing, surface grinding is a critical process that ensures high accuracy and superior surface finishes. However, various alternative methods can also achieve similar outcomes. This section examines these alternatives, providing B2B buyers with insights to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and operational contexts.
Comparison Table of Precision Surface Grinding and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Precision Surface Grinding | CNC Machining | Lapping |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High accuracy (+/- 0.0001″) and excellent surface finish (10 RMS) | Very high precision and versatility across various materials | Achieves ultra-smooth finishes, excellent for flat surfaces |
| Cost | Moderate to high depending on complexity and material | Variable; often higher initial setup costs | Generally lower costs for materials, but requires skilled operators |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific equipment and skilled operators | Requires CNC programming knowledge and setup time | Involves fewer machines but requires expertise in the lapping process |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance of grinding machines needed | CNC machines require both software and hardware maintenance | Low maintenance for lapping machines, but tooling needs regular replacement |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for tight tolerances in aerospace, automotive, and medical applications | Best for complex geometries and large production runs | Suited for final finishing of flat surfaces in high-precision industries |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a versatile alternative that allows for the precise cutting, shaping, and finishing of materials. It excels in producing complex parts with intricate designs. The primary advantage of CNC machining lies in its flexibility; it can accommodate various materials, from metals to plastics, and is suitable for both small and large production runs. However, the initial setup costs can be high, and it requires skilled operators familiar with programming and machine operation. For B2B buyers looking for adaptability and the capability to produce complex geometries, CNC machining is a strong contender.
Lapping
Lapping is a finishing process that uses abrasive slurry to achieve extremely smooth surfaces. It is particularly effective for flat surfaces and can produce finishes that surpass those achieved by grinding. The process is less intensive in terms of machinery compared to precision surface grinding, making it more cost-effective for certain applications. However, lapping typically requires skilled operators to ensure that the desired surface finish is consistently achieved. This method is best suited for applications in industries such as optics and semiconductor manufacturing, where surface finish is critical. For buyers prioritizing ultra-smooth finishes, lapping offers a compelling option.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate manufacturing solution, B2B buyers should carefully consider their specific requirements, including tolerance levels, production volumes, and material types. Precision surface grinding remains a premier choice for high-precision applications, particularly in sectors like aerospace and medical devices. However, alternatives like CNC machining and lapping can provide unique advantages in terms of flexibility and surface finish, respectively. By weighing the pros and cons of each method, buyers can align their choices with their operational goals and achieve optimal results in their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for precision surface grinding
What Are the Critical Technical Properties in Precision Surface Grinding?
When engaging in precision surface grinding, understanding the key specifications is essential for B2B buyers seeking quality and efficiency. Here are some of the most important technical properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type and quality of the metal or alloy being processed. Common materials include ferrous metals (like stainless steel) and non-ferrous metals (such as aluminum). The choice of material grade significantly impacts the grinding process, as different materials have varying hardness and thermal properties. Selecting the right grade ensures optimal grinding performance and longevity of tooling.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In precision surface grinding, tolerances can be as tight as ±0.0001 inches, which is critical for applications in aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers assess whether a supplier can meet their specific manufacturing requirements, ensuring compatibility and performance in final applications.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish measures the texture of the ground surface, often quantified in microinches or RMS (Root Mean Square). Achieving a high-quality surface finish is vital for reducing friction and wear in mechanical components. A smooth finish can also enhance the aesthetic appearance of parts, which may be crucial for consumer-facing products. Buyers should inquire about the expected surface finish to align with their operational needs.
4. Grinding Wheel Specifications
The type and specification of grinding wheels used in the process are pivotal. Wheels can vary in material composition, grit size, and bonding agent, influencing the efficiency and quality of grinding. For instance, wheels made from aluminum oxide are suitable for ferrous materials, while silicon carbide is better for non-ferrous metals. Familiarity with grinding wheel specs allows buyers to match the right wheel to their specific application, optimizing performance.
5. Feed Rate
The feed rate is the speed at which the workpiece is fed into the grinding wheel. It affects the material removal rate and the heat generated during grinding. A well-calibrated feed rate can enhance productivity while maintaining precision. Buyers should understand the implications of feed rate adjustments on both the grinding process and the final product quality.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Precision Surface Grinding?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communications and negotiations with suppliers. Here are some essential trade terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts that are used in another company’s end product. In precision surface grinding, OEMs often require high-quality components with specific tolerances and finishes. Understanding OEM requirements helps buyers ensure that their suppliers can meet industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell in a single order. This term is crucial for buyers to understand their purchasing commitments and to manage inventory effectively. Knowing the MOQ can also influence supplier selection based on production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. Submitting a detailed RFQ can streamline the procurement process, ensuring that suppliers provide competitive and accurate pricing based on the buyer’s specific needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They specify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly impact overall costs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers involved in cross-border transactions to avoid misunderstandings.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automation of machine tools through computer programming. In precision surface grinding, CNC technology enhances the accuracy and consistency of the grinding process. Buyers should seek suppliers with advanced CNC capabilities to ensure high precision and repeatability in their production runs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster productive relationships with suppliers in the precision surface grinding industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the precision surface grinding Sector
What Are the Global Drivers Influencing the Precision Surface Grinding Market?
The precision surface grinding market is experiencing notable growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and the increasing demand for high-precision components across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Globalization is also playing a significant role, with international buyers seeking reliable suppliers capable of meeting strict quality standards and tight tolerances, often required for components in high-stakes industries. Furthermore, the rise of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is transforming traditional grinding practices, allowing for more efficient production processes, reduced lead times, and enhanced product quality.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards digital solutions, such as machine learning and IoT integration, which facilitate predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring of grinding processes. These technologies not only improve operational efficiency but also allow manufacturers to optimize resource allocation. For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions. Markets in Germany and Saudi Arabia are particularly focused on innovation, with buyers increasingly looking for suppliers that can offer advanced technologies and sustainable practices.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Precision Surface Grinding Sector?
Sustainability has become a key consideration for B2B buyers in the precision surface grinding sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is increasingly important, as buyers prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to responsible sourcing of materials and adherence to environmental regulations.
In this context, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems and the use of ‘green’ materials are becoming essential for suppliers looking to enhance their market appeal. Buyers are seeking out precision grinding services that utilize eco-friendly abrasives and lubricants, which not only reduce environmental footprints but also improve workplace safety. By partnering with suppliers who prioritize sustainability, international buyers can not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles, which is increasingly important in today’s global market.
What Is the Evolution of Precision Surface Grinding and Its Impact on B2B Buyers?
The evolution of precision surface grinding can be traced back to the industrial revolution, where early grinding techniques were labor-intensive and less precise. Over time, technological advancements have revolutionized the sector, leading to the development of automated and CNC grinding machines that offer superior accuracy and efficiency. The introduction of advanced abrasives and grinding fluids has further enhanced the capabilities of precision grinding, allowing for tighter tolerances and improved surface finishes.
As precision surface grinding continues to evolve, B2B buyers are presented with a broader range of options and capabilities. This evolution has also led to increased competition among suppliers, resulting in better pricing and improved service offerings for international buyers. Understanding this historical context helps buyers appreciate the technological advancements that have shaped the current market landscape and informs their sourcing strategies when selecting suppliers for precision grinding services.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of precision surface grinding
-
1. How do I choose the right precision surface grinding supplier?
Selecting the right supplier for precision surface grinding involves assessing their experience, certifications, and technological capabilities. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications, as this indicates adherence to quality standards. Additionally, examine their portfolio for past projects similar to your requirements. Request references and conduct site visits if possible, to evaluate their operations and ensure they can meet your specifications in terms of precision, volume, and delivery timelines. -
2. What materials can be processed using precision surface grinding?
Precision surface grinding can handle a wide variety of materials, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, exotic materials, and even certain plastics. Common materials processed include stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. Depending on your project, it’s essential to communicate the specific material requirements to your supplier to ensure they have the right equipment and expertise to achieve the desired tolerances and surface finishes. -
3. What are the common tolerances achievable with precision surface grinding?
Precision surface grinding can achieve remarkably tight tolerances, often within ±0.0001 inches. The exact tolerance achievable may depend on the material being processed, the grinding technique used, and the equipment capabilities. It’s crucial to discuss your specific tolerances with your supplier to ensure they can meet your project’s requirements, especially in industries like aerospace and medical devices where precision is critical. -
4. How can I ensure quality assurance in precision surface grinding?
To ensure quality assurance, request that your supplier implements a robust quality control process, including in-process inspections and final audits. Ask about their measurement techniques, such as the use of coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or surface roughness testers, to validate the dimensions and finish of your parts. Additionally, check if they offer documentation, such as certificates of compliance, to confirm that the finished products meet your specifications. -
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for precision surface grinding services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers based on their production capabilities and business model. Some suppliers may accept small batch orders, while others might have higher MOQs to justify setup costs. It’s advisable to clarify MOQs upfront to avoid any misunderstandings and to assess if the supplier’s capabilities align with your production needs, especially for international orders where logistics can add complexity. -
6. What payment terms are typically offered by precision surface grinding suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely, often depending on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the order. Common options include upfront payments, net 30 or 60 terms, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider discussing options like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risk. Always negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow while ensuring the supplier has the assurance needed to begin work. -
7. How does international shipping impact my precision surface grinding orders?
International shipping can significantly affect lead times and costs for precision surface grinding orders. Factors such as customs clearance, shipping methods, and freight forwarding services can introduce delays. It’s essential to work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics and can provide transparent timelines and costs. Clarify shipping terms, including Incoterms, to understand responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. -
8. What customization options are available for precision surface grinding projects?
Many precision surface grinding suppliers offer customization options tailored to specific project requirements. This can include varying tolerances, surface finishes, and material specifications. Discuss your needs in detail with potential suppliers to see how they can accommodate your requirements, whether it’s through specialized grinding techniques, custom tooling, or adjustments in production processes to deliver the desired outcome for your application.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Precision Surface Grinding Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SPR Tool – Precision Grinding Solutions
Domain: sprtool.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Precision grinding is a machining process used to achieve high degrees of flatness and surface finish on materials with small surfaces. It is capable of tolerances up to +/- 0.0001″ and surface finishes around 10 RMS. Common applications include tiny metal parts in electronic devices, aerospace instruments, medical devices, and scientific instruments. Types of precision grinding include horizontal…
2. Erie Precision Grinding – Precision Grinding Services
Domain: erieprecisiongrinding.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Erie Precision Grinding offers precision grinding services including CNC Grinding, Surface Grinding, Cylindrical Grinding, and Internal Diameter Grinding. Key equipment includes the Chevalier Dual-Column Surface Grinder with a capacity of 50″ x 120″ x 40″ and a grinding wheel size of 20″ on a 30-HP spindle, capable of achieving parallelism of .0002 inches. The company is located in Erie, Pennsylva…
3. AT Machining – Precision Grinding Solutions
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Precision Grinding is a machining process that involves abrasive particles for material removal, suitable for achieving tight tolerances and finishing problems in metal and non-metal parts. Types of precision grinding include: 1. Cylindrical Grinding – Uses a cylindrical grinder for circular workpieces, controlled by CNC or manual methods. 2. Surface Grinding – Reshapes and refines surfaces using …
4. Chevalier – Grinding Machines
Domain: chevalierusa.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Chevalier Machinery offers a variety of grinding machines including: Surface Grinders (manual, semi-automatic, fully automatic), Rotary Surface Grinders, Double Column Grinders, Surface & Profile CNC Grinders, Precision CNC Surface Grinders, Heavy Duty CNC Surface Grinders, Conversational CNC Surface & Profile Grinders (SMART-IV Series), Traveling Column Grinders, Automatic Surface Grinders, Semi-…
5. Penn Tool Co. – Metal Surface Grinders
Domain: penntoolco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Metal surface grinders are essential for metalworking shops, designed to produce smooth, flat finishes on metal. They are available in various sizes for rough or precision grinding. Penn Tool Co. offers reliable, durable, and efficient surface grinders, including models from trusted brands like Kent, GMC, and Baileigh. Notable products include the Birmingham Precision Manual Surface Grinder with a…
6. UNITED GRINDING – CNC Surface & Profile Grinding Machines
Domain: grinding.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Surface & Profile Grinding Solutions from UNITED GRINDING include advanced CNC surface and profile grinding machines from brands such as MÄGERLE, BLOHM, and JUNG. Key offerings include 5/6-axis grinding centers, rotary table grinding machines, vertical grinding machines, and special grinding machines. Applications cover a wide range including creep feed grinding, multi-tasking operations, superabr…
7. OpenWA – Surface Grinders
Domain: openwa.pressbooks.pub
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Surface grinders are machine tools that remove material from a workpiece using an abrasive grinding wheel. They are essential for achieving high precision, surface finish, and overall shape that cannot be accomplished through other machining processes like turning, milling, or drilling. The main types of surface grinders include Horizontal, Vertical, and Cylindrical grinders. Horizontal spindle su…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for precision surface grinding
What Are the Key Benefits of Strategic Sourcing in Precision Surface Grinding?
In the competitive landscape of precision surface grinding, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial element for international B2B buyers. By leveraging high-quality services tailored to specific needs, businesses can achieve tighter tolerances and superior surface finishes, essential for applications across industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics. Sourcing from experienced providers ensures not only quality but also compliance with international standards like ISO 9001:2008, which is vital for maintaining operational excellence.
How Can B2B Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Strategies?
Buyers should prioritize partnerships with companies that offer versatile grinding capabilities, including handling various materials and accommodating both large and small orders. Engaging with suppliers who utilize advanced technologies and maintain a focus on customer satisfaction can lead to enhanced productivity and cost-effectiveness. Furthermore, understanding the specific grinding processes—such as horizontal spindle and cylindrical grinding—can significantly inform purchasing decisions.
What’s Next for International Buyers in Precision Surface Grinding?
As industries evolve, the demand for precision grinding services will only intensify. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must remain agile and informed about market trends and technological advancements. By proactively seeking out innovative suppliers, you can ensure your operations remain competitive. Now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies and capitalize on the opportunities within the precision surface grinding sector. Embrace the future of manufacturing with confidence and precision.