Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polishing method
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right polishing method can be a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. The quest for high-quality polished surfaces, essential for functionality and aesthetics across various industries, requires a deep understanding of the available techniques and their applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of polishing methods, covering everything from mechanical and chemical polishing to the latest advancements in diamond slurry techniques. By exploring the diverse types and applications of polishing, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific requirements, whether it be for high-pressure seals in the Middle East or reflective finishes for luxury products in Europe.
Navigating the global market for polishing methods also involves critical factors such as supplier vetting, cost considerations, and regional compliance standards. This guide empowers B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—by equipping them with actionable insights and strategies to streamline their purchasing process. With a focus on optimizing supplier relationships and ensuring quality outcomes, this resource aims to enhance the decision-making capabilities of businesses looking to invest in polishing technology. Ultimately, informed choices in polishing methods can lead to improved product quality, enhanced customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Understanding polishing method Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Polishing | Utilizes abrasive materials and mechanical force | Automotive, Aerospace, Medical Devices | Pros: High precision, suitable for complex geometries. Cons: Can cause surface damage if improperly executed. |
| Chemical Polishing | Employs chemical agents to dissolve surface imperfections | Metal Fabrication, Electronics | Pros: Effective for uniform finishes, less physical wear. Cons: Environmental concerns with chemical use. |
| Electrolytic Polishing | Uses electrochemical processes for smoothing surfaces | Semiconductor Manufacturing, Jewelry | Pros: Produces high-quality finishes, minimal material removal. Cons: Requires specialized equipment and safety measures. |
| Diamond Polishing | Involves diamond abrasives for ultra-fine finishes | Optics, Aerospace, High-End Manufacturing | Pros: Achieves superior surface finish, high durability. Cons: Higher cost of materials and equipment. |
| Fixed-Abrasive Polishing | Utilizes captured abrasives for consistent results | Precision Engineering, Tool Manufacturing | Pros: Consistent quality, reduced abrasive waste. Cons: Limited to specific applications and setups. |
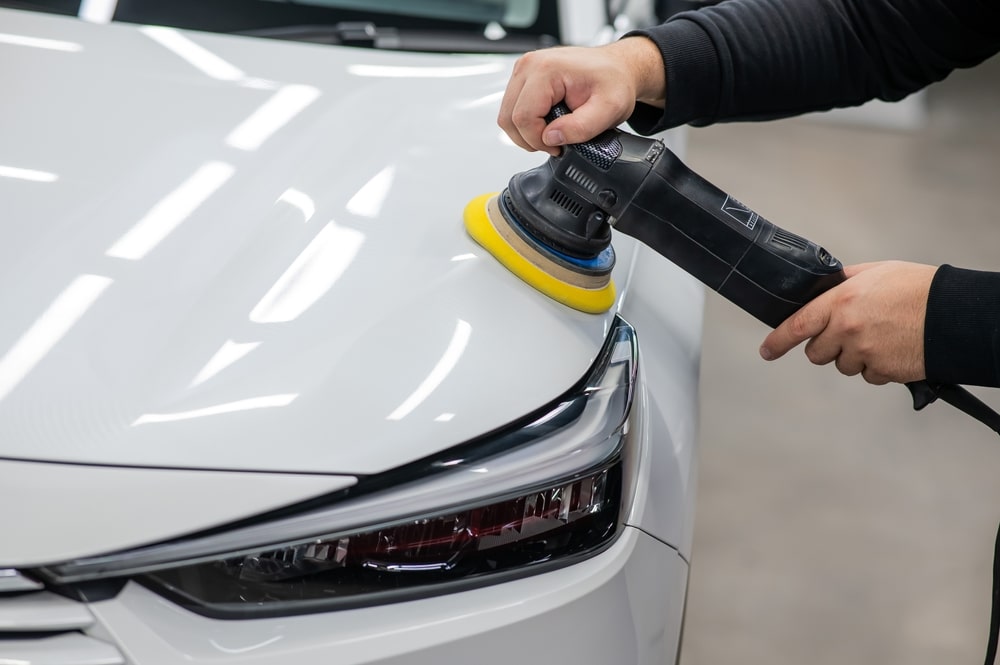
What Are the Characteristics of Mechanical Polishing and Its Suitability for B2B Buyers?
Mechanical polishing is a widely-used method that involves the application of abrasive materials, such as polishing wheels or pads, combined with mechanical force to refine surfaces. This technique is particularly suitable for industries requiring high precision, such as automotive and aerospace manufacturing. B2B buyers should consider the type of material being polished and the desired finish, as improper application can lead to surface damage or deformation, impacting product performance and quality.
How Does Chemical Polishing Work and What Should Buyers Know?
Chemical polishing, or pickling, involves the use of acidic or alkaline solutions to dissolve surface irregularities, making it ideal for metal fabrication and electronics sectors. This method provides a uniform finish with minimal physical wear on the material. However, buyers must be aware of environmental regulations regarding chemical use and potential hazards associated with handling these agents. Additionally, the choice of chemical agents can impact the overall cost and effectiveness of the polishing process.
What Advantages Does Electrolytic Polishing Offer for B2B Applications?
Electrolytic polishing leverages electrochemical processes to achieve smooth surfaces, making it a preferred choice in semiconductor manufacturing and jewelry production. This method produces high-quality finishes with minimal material removal, which is critical in applications where precision is paramount. Buyers should consider the initial investment in specialized equipment and the necessary safety measures, as the process involves handling electrical currents and corrosive solutions.
What Makes Diamond Polishing a Premium Choice for Certain Industries?
Diamond polishing utilizes diamond abrasives to deliver ultra-fine finishes, making it highly effective in optics, aerospace, and high-end manufacturing sectors. This method is valued for its ability to achieve superior surface quality and durability. However, B2B buyers should weigh the higher costs associated with diamond abrasives and equipment against the long-term benefits of enhanced product performance and longevity. It is essential to assess whether the investment aligns with the quality requirements of the intended application.
How Does Fixed-Abrasive Polishing Differ and What Are Its Key Considerations?
Fixed-abrasive polishing employs captured abrasives to ensure consistent results, making it suitable for precision engineering and tool manufacturing. This method reduces abrasive waste and offers a uniform finish, which is advantageous for high-volume production environments. However, buyers should consider the limitations regarding the types of materials and applications that can utilize this method. The setup may also require specific machinery, which can impact initial investment costs.
Key Industrial Applications of polishing method
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Polishing Method | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Polishing of turbine blades and components | Enhances performance and longevity of parts, reduces drag, and increases fuel efficiency. | Seek suppliers with expertise in high-precision polishing and adherence to aerospace standards. |
| Medical Devices | Polishing of surgical instruments and implants | Ensures biocompatibility and reduces the risk of infection; improves aesthetic appeal. | Look for manufacturers with ISO certifications and experience in medical-grade materials. |
| Automotive | Polishing of engine components and body panels | Improves surface finish for better aerodynamics and visual appeal, enhancing brand value. | Prioritize suppliers who can provide rapid prototyping and meet stringent automotive regulations. |
| Electronics | Polishing of semiconductor wafers and components | Achieves superior surface quality for better conductivity and performance in electronic devices. | Focus on suppliers with advanced polishing technology and cleanroom capabilities to avoid contamination. |
| Jewelry and Luxury Goods | Polishing of precious metals and gemstones | Enhances visual appeal and market value; essential for maintaining quality standards. | Engage with suppliers who specialize in custom polishing solutions and have a track record in luxury markets. |
How is the Polishing Method Applied in Aerospace Manufacturing?
In the aerospace sector, polishing is crucial for turbine blades and other components, where a smooth surface finish is necessary to minimize drag and enhance performance. Polishing not only improves the aerodynamic properties of these parts but also extends their lifespan by reducing the likelihood of fatigue and failure. International buyers, particularly from regions like the Middle East and Europe, should prioritize suppliers with proven expertise in high-precision polishing, as adherence to aerospace standards is critical for safety and compliance.
What Role Does Polishing Play in Medical Device Production?
Medical devices, including surgical instruments and implants, require meticulous polishing to ensure they are biocompatible and free from contaminants. A polished surface helps reduce the risk of infection and enhances the overall aesthetic appeal of medical devices. Buyers in Africa and South America should look for manufacturers with ISO certifications and a solid understanding of medical-grade materials, as this ensures compliance with health regulations and quality standards.
How is Polishing Beneficial in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, polishing is employed to refine engine components and enhance body panels. This process not only improves the surface finish but also contributes to better aerodynamics, which can lead to increased fuel efficiency. Additionally, a polished surface can significantly boost the visual appeal of vehicles, enhancing brand value. Buyers should consider suppliers that offer rapid prototyping and can meet the stringent regulations associated with automotive manufacturing.
Why is Polishing Important in Electronics Manufacturing?
Polishing plays a vital role in the electronics industry, particularly for semiconductor wafers and components. A high-quality polish is essential for achieving superior surface characteristics that enhance conductivity and overall performance in electronic devices. International B2B buyers, especially those from Europe and the Middle East, should focus on suppliers that utilize advanced polishing technologies and maintain cleanroom environments to prevent contamination during the polishing process.
How Does Polishing Affect Jewelry and Luxury Goods?
In the jewelry and luxury goods sector, polishing is essential for enhancing the visual appeal of precious metals and gemstones. A high-quality polish not only improves the aesthetic value but also plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall quality standards expected in luxury markets. Buyers should engage with suppliers who specialize in custom polishing solutions and have a proven track record in delivering high-quality finishes, ensuring that their products meet the expectations of discerning customers.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polishing method’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty Achieving Consistent Surface Finish
The Problem: Many B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace and automotive often face challenges in achieving a consistent surface finish across multiple parts. Variations in polishing techniques, equipment, or operator skill can lead to discrepancies in quality, which in turn may affect product performance and customer satisfaction. This inconsistency can result in increased rework, delays in production timelines, and higher operational costs.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should invest in automated polishing systems equipped with advanced sensors and feedback mechanisms. These systems can monitor surface quality in real-time, adjusting parameters such as pressure and speed to ensure uniformity across all parts. Additionally, developing a standardized training program for operators can help minimize variability. Documentation of best practices and regular audits of the polishing process will further reinforce quality control, ensuring that every batch meets the required specifications.
Scenario 2: Equipment Downtime Due to Maintenance Issues
The Problem: Polishing equipment can often suffer from unexpected downtime due to wear and tear or improper maintenance. For manufacturers relying on polishing for critical components, this can lead to significant production halts, missed deadlines, and financial losses. Buyers may struggle to find reliable maintenance services or spare parts, which exacerbates the situation.
The Solution: To mitigate equipment downtime, B2B buyers should establish a proactive maintenance schedule that includes routine inspections and preventive measures. Partnering with equipment suppliers for regular maintenance support can ensure that machines are kept in optimal condition. Additionally, buyers should consider investing in equipment with predictive maintenance capabilities that utilize IoT technology to anticipate failures before they occur. This foresight can help maintain continuous operation, ultimately reducing the risk of unexpected production interruptions.
Scenario 3: Environmental and Safety Compliance Challenges
The Problem: B2B buyers in regions with stringent environmental regulations may face difficulties in ensuring that their polishing processes comply with local laws. The use of hazardous chemicals in polishing slurries, as well as the disposal of waste materials, can pose significant compliance risks. Failure to adhere to regulations can lead to hefty fines, legal issues, and damage to the company’s reputation.
The Solution: To navigate these compliance challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing eco-friendly polishing materials and slurries that meet environmental standards. Engaging with suppliers who specialize in sustainable polishing solutions can provide access to safer alternatives that do not compromise on quality. Additionally, implementing a robust waste management program that includes recycling and proper disposal methods will ensure compliance with environmental regulations. Regular training for employees on safety protocols and compliance requirements will further enhance the company’s commitment to environmental stewardship and workplace safety.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for polishing method
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Polishing Methods?
When selecting materials for polishing methods, understanding the properties and applications of various materials is crucial for achieving optimal results. Here, we analyze four common materials used in polishing processes: stainless steel, aluminum, glass, and ceramics.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Polishing Applications?
Stainless steel is widely used in polishing applications due to its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for various industrial environments. The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability; it maintains structural integrity even under rigorous polishing conditions. However, the cost can be relatively high compared to other metals, and its manufacturing complexity can be a hurdle, especially in regions with less advanced manufacturing capabilities. For international buyers, particularly in Africa and the Middle East, compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 is essential to ensure quality and performance.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Aluminum in Polishing?
Aluminum is another popular material for polishing, known for its lightweight and malleability. It offers good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized, and can achieve a mirror-like finish, making it ideal for cosmetic applications. The primary disadvantage of aluminum is its lower durability compared to stainless steel, which may lead to quicker wear in high-friction environments. Additionally, its cost is generally moderate, making it accessible for many manufacturers. Buyers from South America and Europe should be aware of regional standards such as EN 573 for aluminum alloys to ensure compliance and quality.
Why Is Glass a Preferred Material for Polishing in Certain Industries?
Glass is often polished to achieve high optical clarity and aesthetic appeal, particularly in the optics and automotive industries. Its smooth surface allows for excellent light transmission and minimal distortion. However, glass is brittle, making it more susceptible to breakage during handling and processing. The cost of polished glass can also be high, particularly for specialty applications. For international buyers, especially in Europe, adherence to standards like ISO 10110 for optical elements is crucial to maintain quality and performance.
How Do Ceramics Stand Out in Polishing Applications?
Ceramics are increasingly used in polishing due to their hardness and resistance to wear and corrosion. They perform exceptionally well in high-temperature applications, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive industries. The main drawback is that ceramics can be brittle, leading to breakage during processing. Additionally, the manufacturing complexity can drive costs up, making them a high-cost option. Buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM C1161 to guarantee product quality.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Polishing Methods
| Material | Typical Use Case for polishing method | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Industrial machinery, automotive parts | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive trim, consumer electronics | Lightweight and good finish capability | Lower durability compared to steel | Medium |
| Glass | Optical components, automotive glass | High optical clarity and aesthetic appeal | Brittle and prone to breakage | High |
| Ceramics | Aerospace components, cutting tools | High hardness and wear resistance | Brittle and higher manufacturing costs | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials used in polishing methods. By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polishing method
What Are the Main Stages of the Polishing Manufacturing Process?
The polishing process is critical for achieving high-quality finishes on a variety of materials. The manufacturing workflow can typically be broken down into four key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Polishing?
Material preparation is the first and crucial step. This involves selecting the right base material, which can range from metals like stainless steel and aluminum to ceramics and glass. The initial condition of the material is paramount; it should be free from significant defects such as deep scratches or cracks. This stage often includes cutting, grinding, or lapping to create a suitable surface that can be polished effectively. The aim is to ensure that the surface is smooth enough to allow the polishing process to achieve the desired finish without excessive material removal.
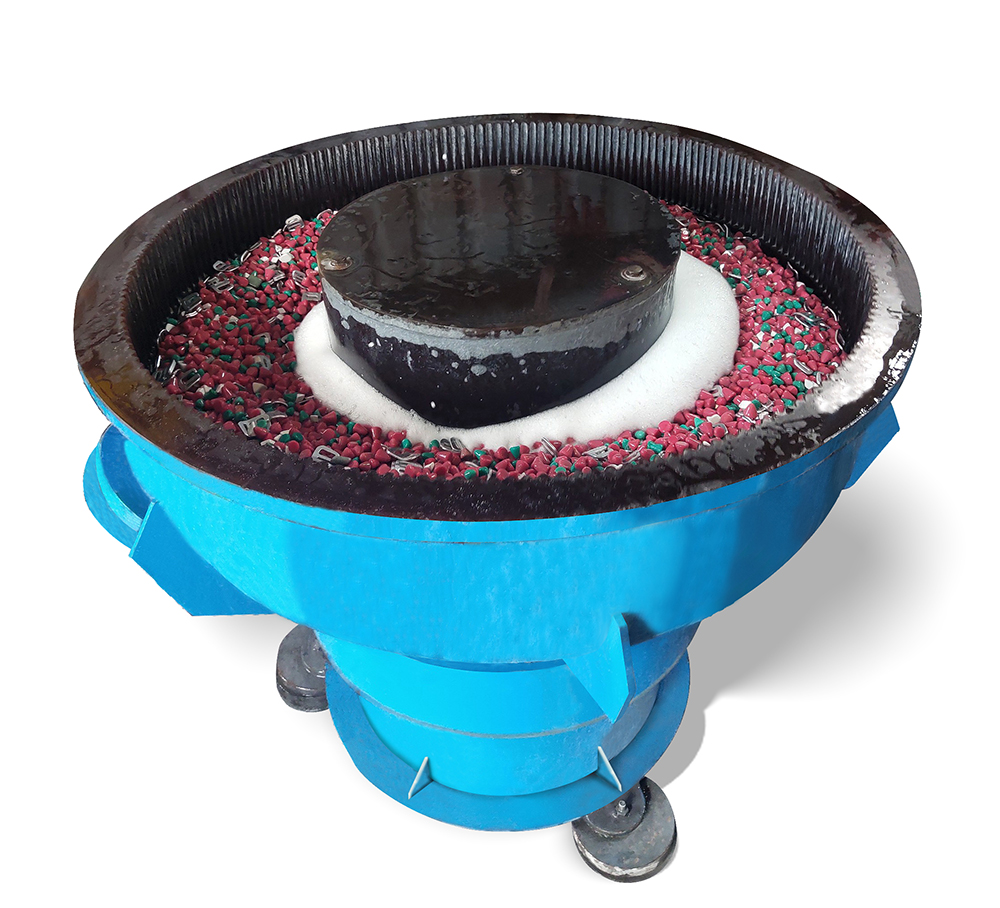
What Techniques Are Employed in the Polishing Process?
In the forming stage, the material may undergo various processes, including mechanical or chemical polishing. Mechanical polishing uses abrasive materials to refine the surface through friction, while chemical polishing employs solutions to remove surface irregularities. The choice of technique often depends on the material and the required finish. For instance, mechanical polishing is ideal for achieving a mirror finish on metals, while chemical polishing may be more suited for intricate geometries where mechanical methods could cause damage.
How Does Assembly Play a Role in Polishing?
Although polishing is often seen as a standalone process, assembly can be relevant in certain applications. For example, in the production of optical devices, multiple components may need to be polished and then assembled to ensure that the final product meets stringent optical clarity requirements. During assembly, care must be taken to avoid introducing new defects that could compromise the polished finish.
What Finishing Techniques Are Used After Polishing?
Finishing is the final stage of the polishing process. After polishing, additional treatments such as passivation or coating may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance or improve the aesthetic quality of the surface. This step is essential for ensuring the longevity and performance of the polished parts, particularly in harsh environments.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Critical in Polishing?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the polishing process, ensuring that the final product meets both functional and aesthetic standards. Adhering to international standards such as ISO 9001 is essential for manufacturers seeking to establish credibility in the global market. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE and API can further enhance a manufacturer’s reputation, particularly in sectors such as aerospace and automotive.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Polishing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical for maintaining the integrity of the polishing process. The main checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials for quality and suitability before they enter the production process.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the polishing process, samples may be taken at various stages to ensure that the surface finish is progressing as required. This may involve measuring surface roughness or performing visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After polishing, the finished products undergo thorough inspection and testing to verify that they meet the specified standards and customer requirements.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Polishing?
Common testing methods for polished surfaces include:
- Surface Roughness Testing: Utilizing instruments like profilometers to quantify the smoothness of a polished surface.
- Visual Inspection: Employing trained personnel to assess the aesthetic quality of the polished finish, looking for defects like scratches or discoloration.
- Functional Testing: Depending on the application, functional tests may be performed to ensure that the polished parts meet performance specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC is crucial. Here are some strategies:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Look for compliance with international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation of their quality control processes, including test results and certification of standards.
- Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging third-party services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of QC and certifications is particularly important for international buyers. Different regions may have varying standards and expectations. For example, the CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, while API certification is essential for oil and gas industries. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with the relevant standards for their target markets.
Furthermore, it’s important to recognize that cultural differences may impact quality perceptions. For instance, buyers from regions with stringent quality expectations may require more detailed documentation and testing than suppliers are accustomed to providing. Establishing clear communication and setting expectations upfront can mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that quality standards are met.
Conclusion
The polishing method encompasses a detailed manufacturing process and rigorous quality assurance measures. B2B buyers must be well-informed about these aspects to make educated decisions when selecting suppliers. By understanding the stages of polishing, the importance of quality control, and the verification methods available, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their specifications and industry standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polishing method’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist B2B buyers in procuring effective polishing methods. Polishing is crucial for achieving high-quality finishes that enhance both the aesthetic and functional properties of products. By following this checklist, buyers can ensure they select the right techniques and suppliers to meet their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Determine the desired surface finish, material type, and any specific requirements such as thickness or tolerances. This clarity helps you identify suitable polishing methods and communicate effectively with potential suppliers.
- Surface Finish Types: Consider whether you require rough polishing, semi-polishing, or mirror polishing based on the application.
- Material Considerations: Different materials may require specific polishing techniques (e.g., mechanical vs. chemical polishing).
Step 2: Research Available Polishing Techniques
Understanding the various polishing techniques is essential to making an informed choice. Techniques such as mechanical, chemical, and electrolytic polishing each have unique benefits and applications.
- Mechanical Polishing: Suitable for high surface quality requirements; ideal for metals and glass.
- Chemical Polishing: Effective for metals, offering smooth finishes by dissolving surface irregularities.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. This helps ensure that the supplier has the expertise and reliability you need.
- Certifications: Verify any relevant certifications, such as ISO standards, that demonstrate quality assurance.
- Experience: Look for suppliers with experience in your specific industry to ensure they understand your unique requirements.
Step 4: Request Samples and Perform Testing
Once you’ve shortlisted potential suppliers, request samples of their polishing work. This step is vital to assess the quality of their finishes and ensure they meet your specifications.
- Quality Assessment: Examine the samples for defects, surface roughness, and overall appearance.
- Test Applications: If possible, conduct tests on your actual materials to evaluate compatibility and performance.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
After selecting a supplier, engage in discussions to negotiate terms and conditions. This includes pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about bulk purchasing options to reduce costs.
- Service Agreements: Ensure that service agreements cover aspects like warranties and support for any issues post-delivery.
Step 6: Establish a Quality Control Process
Implement a quality control process to monitor the polishing work throughout the production cycle. This helps maintain the desired standards and ensures any issues are addressed promptly.
- Inspection Protocols: Develop clear inspection protocols based on your technical specifications.
- Feedback Mechanism: Establish a system for providing feedback to the supplier to enhance future collaborations.
Conclusion
By following this sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement of polishing methods and ensure they select the most suitable suppliers for their needs. This strategic approach not only enhances product quality but also strengthens supplier relationships.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polishing method Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Polishing Method Sourcing?
When sourcing polishing methods, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: This encompasses the cost of abrasives, polishing pads, and chemical solutions. The type of material significantly impacts pricing; for instance, diamond abrasives are more expensive than traditional ones, but they offer superior performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for high-quality polishing, particularly for complex or precision tasks. Labor costs can vary widely depending on geographical location and the expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to equipment maintenance, facility expenses, and utilities. Efficient production processes can help minimize these costs, providing better pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools for polishing can be a significant investment. Custom tooling may be necessary for specific applications, influencing overall costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures that the polished surfaces meet industry standards. This may add to the cost but is essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, particularly for international buyers, can vary based on distance, mode of transport, and freight terms. Understanding Incoterms can help buyers anticipate these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the uniqueness of the polishing service offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Polishing Method Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of polishing methods, which buyers should consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions tailored to specific needs may incur additional costs. Clear communication regarding specifications can help manage expectations and budget.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects pricing. High-quality materials may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to long-term savings through reduced wear and tear.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers offering certified materials or processes may charge a premium. However, these certifications can provide assurance regarding compliance and performance, particularly in regulated industries.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence costs. Partnering with established suppliers may offer better reliability but could come at a higher price.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping can significantly affect total costs. Different Incoterms dictate who bears the responsibility for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, influencing the overall budget.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Polishing Method Sourcing?
International B2B buyers can employ several strategies to enhance cost efficiency:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Building a strong relationship with suppliers can lead to better negotiation outcomes. Discussing long-term partnerships may yield favorable pricing and terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on initial costs, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A higher-quality polishing service may result in lower TCO over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Sourcing: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of potential hidden costs, such as tariffs and taxes, which can significantly affect overall expenditure.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure suppliers provide comprehensive quotes that break down costs. This transparency can help identify areas where savings can be made.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilizing software for procurement and supply chain management can help streamline sourcing processes and provide insights into cost-saving opportunities.
Conclusion
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, price influencers, and effective negotiation strategies is vital for international B2B buyers sourcing polishing methods. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can optimize their sourcing strategies, ensuring quality while managing costs effectively. Please note that prices can vary widely based on specific circumstances, and it is advisable to request quotes tailored to individual needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polishing method With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternative Solutions for Polishing
In the realm of surface finishing, polishing methods play a crucial role in achieving high-quality, reflective surfaces. However, there are various alternative solutions that can also meet specific requirements for different applications. Understanding these alternatives helps B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs, budget, and desired outcomes.
Comparison Table: Polishing Method vs. Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Polishing Method | Mechanical Polishing | Chemical Polishing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality, reflective finish | Good surface quality, but may leave micro-scratches | Excellent smoothness, can achieve sub-micron finishes |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Lower initial investment | Moderate, depending on chemicals used |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment | Relatively straightforward | Requires chemical handling protocols |
| Maintenance | High (pads and slurries need regular replacement) | Moderate (equipment upkeep) | Low (once setup, minimal intervention) |
| Best Use Case | Optical components, jewelry, high-precision parts | General metal components, automotive | Stainless steel, semiconductor applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Mechanical Polishing?
Mechanical polishing employs abrasive materials to refine surfaces through physical action. This method is particularly effective for general metal components and automotive parts, where a good surface finish is required without the need for extreme precision. The main advantage of mechanical polishing is its relatively low cost and ease of implementation; however, it may leave micro-scratches on the surface, which could be undesirable for applications requiring a flawless finish. Additionally, it does not achieve the same level of smoothness as polishing methods or chemical polishing, limiting its use in high-end applications.
How Does Chemical Polishing Compare to Other Methods?
Chemical polishing utilizes acidic or alkaline solutions to dissolve surface irregularities, making it ideal for metals like stainless steel and in semiconductor manufacturing. This method can achieve superior smoothness, often down to sub-micron levels, making it highly effective for applications requiring optical clarity. However, the primary drawbacks are the potential hazards associated with handling chemicals and the need for strict safety protocols. Additionally, while the setup cost can be moderate, ongoing expenses may vary based on chemical consumption and waste management.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a surface finishing method, B2B buyers must carefully consider their specific application requirements, including the desired surface quality, cost constraints, and operational feasibility. Polishing methods excel in applications that demand high precision and aesthetic appeal, while mechanical polishing may suffice for less critical finishes. Conversely, chemical polishing offers unmatched smoothness for specialized applications but requires a more complex handling approach. By evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and ensure optimal performance in their respective industries.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polishing method
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Polishing Methods?
Understanding the essential technical properties of polishing methods is critical for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions. Here are some of the most relevant specifications:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of materials used for polishing, including abrasives and pads. High-quality materials, such as diamond abrasives, are essential for achieving superior finishes and durability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the polishing process, influencing the final product’s performance and longevity.
2. Surface Roughness (Ra)
Surface roughness, often measured in micrometers (µm), indicates the smoothness of the polished surface. Various polishing methods can achieve different roughness levels, such as Ra 0.008 µm for ultra-fine polishing. For manufacturers, understanding the required surface roughness is vital for meeting product specifications and ensuring compatibility with downstream processes, such as coating or sealing.
3. Polishing Pad Hardness
The hardness of polishing pads affects the final finish and the material removal rate. Soft pads are typically used for delicate surfaces, while hard pads are suitable for more robust materials. Choosing the appropriate pad hardness is crucial for achieving the desired finish without compromising the workpiece’s integrity, making it a significant consideration for B2B buyers.
4. Abrasive Particle Size
The size of abrasive particles used in the polishing slurry is another critical property. Finer particles yield smoother finishes, while coarser particles are effective for initial material removal. This property is important for buyers as it directly influences production timelines and the quality of the finished product.
5. Processing Time
Processing time refers to the duration required to achieve the desired polishing results. Shorter processing times can lead to increased productivity and lower operational costs. For B2B buyers, understanding processing time is essential for efficient production scheduling and cost management.
6. Chemical Resistance
Polishing methods can involve chemical agents, especially in chemical polishing techniques. The resistance of materials to these chemicals can affect the longevity and effectiveness of the polishing process. Buyers need to consider chemical resistance to ensure that the selected materials will withstand the processes without degradation.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Polishing Methods?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the B2B space. Here are some common terms related to polishing methods:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the polishing industry, OEMs often provide specialized machinery or components critical for specific polishing applications. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality equipment tailored to their needs.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers as it can affect inventory management and overall procurement costs. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases effectively and avoid excess inventory.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. In the polishing sector, submitting an RFQ can help buyers obtain competitive pricing and evaluate potential suppliers based on their capabilities and offerings.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, risk, and costs. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B transactions, especially when dealing with international suppliers, as they clarify the logistics and financial responsibilities involved in the polishing process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. In the polishing industry, knowing the lead time is essential for planning production schedules and ensuring timely delivery of finished goods.
6. Surface Finish Specification
This term encompasses the required quality and characteristics of a polished surface, including roughness, gloss, and texture. Buyers must specify surface finish requirements to ensure that the final products meet industry standards and customer expectations.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operations and ensure the quality of their products in various markets.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polishing method Sector
What Are the Current Trends Influencing the Polishing Method Market?
The polishing method sector is experiencing dynamic changes driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for high-quality finishes across various industries. One of the key global drivers is the rapid growth in manufacturing and automotive industries, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East. These regions are investing heavily in infrastructure and industrialization, leading to an increased requirement for precision polishing solutions that enhance product durability and aesthetic appeal.
Emerging B2B technologies such as automation and robotics are transforming the polishing process, enabling higher efficiency and consistency in results. Automated polishing systems reduce labor costs and minimize human error, making them attractive to manufacturers aiming for scalability. Additionally, the integration of AI and machine learning into polishing systems is paving the way for predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, allowing businesses to optimize their operations and reduce downtime.
International buyers from Europe, including countries like Germany and Italy, are also pushing for innovations that enhance sustainability. This trend is prompting suppliers to adopt advanced materials and methods that not only improve performance but also reduce environmental impact. For instance, the use of eco-friendly polishing agents and water-based slurries is gaining traction, appealing to businesses focused on sustainability and compliance with stringent regulations.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Polishing Method Sector?
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration for B2B buyers in the polishing method sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including polishing, necessitates a shift towards more sustainable practices. Polishing operations often involve the use of chemicals and abrasives that can be harmful if not managed properly. As such, ethical sourcing of materials has become critical, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers who prioritize responsible practices.
The importance of establishing ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can demonstrate transparency in their sourcing processes, ensuring that materials are procured responsibly and with minimal environmental impact. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Ecolabels for eco-friendly products are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to attract conscientious buyers.
Moreover, the push for “green” certifications is influencing the types of materials used in polishing. Water-based polishing slurries and biodegradable abrasives are gaining popularity, aligning with the global trend towards sustainability. By adopting these materials, businesses not only comply with regulatory standards but also enhance their brand reputation among eco-conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Polishing Method Sector?
The polishing method has evolved significantly over the years, transitioning from rudimentary techniques to sophisticated processes that leverage advanced technology. Historically, polishing was a manual task, relying on basic tools and abrasives to achieve desired finishes. However, as industries grew and the demand for high-quality products surged, the need for precision and consistency in polishing became paramount.
The introduction of mechanical polishing methods in the mid-20th century marked a turning point, enabling manufacturers to achieve finer finishes more efficiently. Subsequently, chemical and electrolytic polishing techniques emerged, offering solutions for complex geometries and materials that were challenging to polish mechanically. Today, the sector continues to innovate, focusing on automation and sustainability, which are essential for meeting the needs of modern B2B buyers in a competitive global market.
As the polishing method sector progresses, understanding these historical shifts can provide valuable insights for international buyers seeking to navigate current market dynamics and sourcing trends effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polishing method
-
1. How do I solve issues with surface imperfections during polishing?
To effectively address surface imperfections, it’s crucial to understand the type of polishing method best suited for your material. Mechanical polishing is ideal for removing larger defects, while chemical polishing can smooth out finer irregularities. Ensure your pre-polishing surface is adequately prepared, as a high-quality base will yield better results. Additionally, consider the use of specialized polishing slurries and pads to enhance the process. Regularly inspecting the polished surface for defects and adjusting your technique accordingly will help achieve the desired finish. -
2. What is the best polishing method for stainless steel?
For stainless steel, a combination of mechanical and chemical polishing is often the most effective approach. Mechanical polishing utilizes abrasives to remove surface imperfections, while chemical polishing helps achieve a high-gloss finish by leveling the surface at a microscopic level. This two-step process not only enhances aesthetics but also improves corrosion resistance. Selecting the right abrasives and polishing compounds is essential to avoid scratching and maintain the integrity of the material during the process. -
3. How can I ensure quality assurance in my polishing processes?
Implementing a robust quality assurance (QA) system is vital for maintaining high polishing standards. Establish clear specifications for surface finish and perform regular inspections at various stages of the polishing process. Utilize advanced measurement tools to evaluate surface roughness and visual quality. Additionally, partner with suppliers who have a proven track record in quality management and can provide documentation for their processes. Regular audits and feedback loops can further enhance quality control. -
4. What should I consider when vetting suppliers for polishing services?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience in the specific polishing methods you require, such as mechanical, chemical, or electrolytic polishing. Check for certifications that demonstrate compliance with industry standards and regulations. Request samples of their previous work to evaluate the quality of their finishes. Additionally, inquire about their production capacity, lead times, and their ability to handle custom requirements. Building a relationship with your supplier can also provide insights into their reliability and customer service. -
5. Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for polishing services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly among polishing service providers. Some may have MOQs based on the type of material, complexity of the polishing process, or the equipment used. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs upfront to ensure the supplier can accommodate smaller orders if necessary. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate MOQs for long-term partnerships or bulk orders, so clarifying this aspect can help in budgeting and planning your procurement strategy. -
6. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing polishing services internationally?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s location and policies. Common terms include advance payments, net 30, or net 60 days upon receipt of goods. For international transactions, consider using letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. It’s also important to clarify currency conversion and transaction fees associated with international payments. Establishing clear payment terms in your contract can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
7. How do logistics impact the sourcing of polishing services?
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of polished products. When sourcing internationally, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential delays at ports. Work with suppliers who have a reliable logistics network and can provide tracking information for shipments. Additionally, factor in lead times for both production and shipping when planning your project timelines to ensure you meet your delivery deadlines. -
8. Can polishing methods be customized for specific applications?
Yes, polishing methods can often be customized to meet specific application requirements. Discuss your project needs with potential suppliers, including desired surface finish, material type, and any unique operational constraints. Many suppliers offer tailored solutions, such as specialized polishing compounds, equipment adjustments, or modified processes to achieve specific outcomes. Collaboration with your supplier can lead to innovative solutions that enhance product performance and meet your exact specifications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Polishing Method Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Precision Surface – Polishing Solutions
Domain: precision-surface.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Polishing is a process to generate a reflective surface using fine-micron or sub-micron abrasive particles combined with a liquid, typically in a “wet” process. It often utilizes a polishing pad that contains the abrasive, which is softer than the part being polished. The material removal during polishing is minimal, usually measured in microns. A high-quality surface finish is required prior to p…
2. Neway Precision – Polishing Techniques
Domain: newayprecision.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Polishing Techniques: Mechanical Polishing, Chemical Polishing, Electrolytic Polishing. Commonly Polished Materials: Metals (stainless steel, brass, aluminum), Gemstones (diamonds, rubies, emeralds), Glass, Plastics (acrylic, polycarbonate). Surface Finish Classification: Rough Polishing, Semi-Polishing, Mirror Polishing. Functions of Polishing: Aesthetic Purposes (enhancing visual appeal), Functi…
3. Wayken – Metal Polishing Benefits
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: 1. Benefits of Metal Polishing:
– Product Aesthetics: Smoothens rough surfaces, removes scratches, and ensures a glossy finish.
– Provides a Protective Layer: Resists contamination and oxidation, reducing wear and tear.
– Improved Light Reflection: Enhances shine and vibrancy, beneficial for architectural elements and jewelry.
– Better Functionality: Reduces friction, improving…
4. ScienceDirect – Polishing Process in Semiconductor Manufacturing
Domain: sciencedirect.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The polishing process is primarily used in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly for ULSI chips. It involves mechanical polishing techniques, including Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP), which is essential for achieving defect-free, mirror-like surfaces on semiconductor wafers. CMP utilizes a workpiece, typically a semiconductor substrate, pressed against a rotating platen covered by a polis…
5. DMSmiles – Tooth Polishing
Domain: dmsmiles.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Tooth polishing is a painless dental procedure that makes teeth look stain-free, smooth, and glossy. It is often part of a standard routine cleaning and can improve aesthetics while preventing dental problems. The procedure involves inspecting teeth for decay, scaling to remove tartar and plaque, buffing and polishing to remove stains, flossing, and applying a protective fluoride coat. Benefits in…
6. Keyence – 4K Digital Microscope
Domain: keyence.eu
Introduction: 4K Digital Microscope; Application in Automotive and Aerospace Industries; Used for observation and inspection of the polishing process; Enables visualization of polishing techniques and abrasive materials; Features include automatic area measurement, 3D measurement, Optical Shadow Effect Mode; Observations at various magnifications (e.g., 1000x, 200x, 4000x); Suitable for analyzing surfaces, abra…
7. Reddit – Dice Polishing Techniques
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Polishing method for dice making involves using zona polishing papers and Plastx polish. The user is seeking advice on achieving a clear finish to highlight the details in the dice without needing frequent polishing. A suggested method includes using 600-800 grit sandpaper for shaping and applying a plastic restorer, with a mention of specific brands (C4 and P4) that can be found through Google.
8. News Medical – Tooth Polishing Procedure
Domain: news-medical.net
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Tooth polishing is a dental procedure aimed at preventing teeth problems and enhancing their appearance by making them whiter, stain-free, and glistening. It improves dental health and aesthetics. The procedure has evolved, with dentists now recommending careful case selection due to potential erosion of the tooth structure and loss of the protective fluoride layer. Advantages include painless tre…
9. MDPI – Metallurgical Surface Polishing Insights
Domain: mdpi.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: This company, MDPI – Metallurgical Surface Polishing Insights, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polishing method
As the polishing industry continues to evolve, strategic sourcing remains a critical element for international B2B buyers seeking quality and efficiency in their operations. The diverse polishing methods—ranging from mechanical to chemical techniques—offer distinct advantages depending on the material and desired finish. Understanding these nuances allows businesses to select the most effective processes, ultimately enhancing product quality and operational productivity.
Investing in high-quality polishing solutions not only improves the aesthetic appeal of products but also plays a vital role in functional applications, such as corrosion resistance and surface integrity. For companies in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, aligning with reputable suppliers can provide access to advanced technologies and materials that meet international standards.
Looking ahead, the demand for polished surfaces will likely grow across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. To stay competitive, international buyers should prioritize strategic sourcing partnerships that leverage innovation and expertise. By doing so, they can ensure that their polishing processes remain efficient and effective, ultimately driving success in an increasingly global marketplace. Embrace the opportunity to refine your sourcing strategies today and position your business for a polished future.