Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for polish galvanized steel
Navigating the complexities of sourcing polished galvanized steel can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Germany and Brazil. The challenge lies not only in identifying quality suppliers but also in understanding the nuances of polishing galvanized steel, which is vital for maintaining its protective properties while enhancing its aesthetic appeal. This guide delves into the multifaceted world of polished galvanized steel, covering essential aspects such as types, applications, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights, this comprehensive resource empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions. It addresses common concerns regarding the risks of polishing, alternative surface treatments, and the importance of maintaining the integrity of the zinc coating. Furthermore, it highlights best practices for selecting suppliers who can deliver not just quality materials but also valuable expertise in handling galvanized steel products.
In a competitive global market, understanding these key factors can significantly enhance procurement strategies, ensuring that businesses not only meet their immediate needs but also foster long-term relationships with reliable suppliers. Whether you are looking to enhance the visual appeal of your products or seeking durable solutions for challenging environments, this guide is your roadmap to success in the polished galvanized steel market.
Understanding polish galvanized steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Polished Galvanized | Typical zinc coating with a polished finish | Automotive parts, construction materials | Pros: Improved aesthetics; Cons: Risk of coating damage, requires maintenance. |
| Bright Galvanized Steel | Enhanced reflective surface, smoother finish | Decorative applications, architectural uses | Pros: High reflectivity; Cons: More expensive, potential for reduced corrosion resistance. |
| Powder-Coated Galvanized | Galvanized steel with a powder coating for added durability | Outdoor furniture, industrial equipment | Pros: Enhanced durability and color options; Cons: Higher initial cost, requires careful surface preparation. |
| Pre-Finished Galvanized Steel | Factory-applied finishes with varied aesthetics | Pre-fabricated structures, appliances | Pros: Consistent quality; Cons: Limited customization options, dependent on supplier stock. |
| Galvanized Steel with Clear Coating | Polished and sealed with a transparent protective layer | Machinery, outdoor installations | Pros: Extended lifespan, maintains appearance; Cons: Requires reapplication, potential for yellowing over time. |
What Are the Characteristics of Standard Polished Galvanized Steel?
Standard polished galvanized steel features a typical zinc coating that is polished to enhance its appearance. This type is commonly used in automotive parts and construction materials. Buyers should consider the trade-off between aesthetics and the risk of compromising the zinc layer, which can lead to increased maintenance needs over time.
How Does Bright Galvanized Steel Differ from Other Types?
Bright galvanized steel is recognized for its enhanced reflective surface and smoother finish, making it ideal for decorative applications and architectural uses. While it offers superior aesthetics, buyers must weigh the higher cost and potential reduction in corrosion resistance compared to standard options.
What Benefits Does Powder-Coated Galvanized Steel Provide?
Powder-coated galvanized steel combines the protective benefits of galvanization with a durable powder coating, making it suitable for outdoor furniture and industrial equipment. This type offers a variety of color options and enhanced durability, though it comes with a higher initial cost and necessitates careful surface preparation to ensure adhesion.
Why Choose Pre-Finished Galvanized Steel?
Pre-finished galvanized steel is produced with factory-applied finishes, providing consistent quality and aesthetic appeal. It is commonly used in pre-fabricated structures and appliances. While it streamlines the procurement process, buyers should note that customization options may be limited and dependent on supplier inventory.
How Does Galvanized Steel with Clear Coating Extend Lifespan?
This variation involves polishing the galvanized steel and applying a transparent protective coating to enhance longevity while maintaining appearance. It is suitable for machinery and outdoor installations. Buyers should consider the need for periodic reapplication of the clear coat and the potential for discoloration over time, which could affect aesthetics.
Key Industrial Applications of polish galvanized steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Polish Galvanized Steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural Components for Buildings | Enhanced aesthetic appeal and durability | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards. |
| Automotive | Vehicle Body Panels and Components | Improved corrosion resistance and surface finish | Select suppliers with expertise in automotive-grade galvanized steel. |
| Agricultural Equipment | Farm Machinery and Equipment | Increased lifespan and reduced maintenance costs | Look for suppliers who provide customized solutions for specific machinery needs. |
| Renewable Energy | Solar Panel Mounting Structures | Long-term durability in harsh environments | Assess the zinc coating thickness suitable for specific climates. |
| Infrastructure | Fencing and Guardrails | Aesthetic enhancement with protective qualities | Verify the compatibility of coatings with local environmental conditions. |
How Is Polish Galvanized Steel Used in Construction Applications?
In the construction sector, polish galvanized steel is commonly used for structural components such as beams, columns, and trusses. The polished finish not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of buildings but also provides added protection against corrosion, which is crucial in both urban and rural settings. International buyers, particularly from regions with high humidity or extreme weather, should ensure that the galvanized steel meets local building codes and standards for durability and safety.
What Are the Benefits of Polish Galvanized Steel in the Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry utilizes polished galvanized steel for vehicle body panels and components, where both appearance and performance are essential. The polished surface improves the vehicle’s visual appeal while offering superior corrosion resistance, which is vital for maintaining the vehicle’s longevity. Buyers from Europe and South America should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in automotive-grade materials to ensure compliance with stringent industry regulations.
How Does Polish Galvanized Steel Enhance Agricultural Equipment?
In agriculture, polished galvanized steel is utilized in various farm machinery and equipment, such as tractors and harvesters. The polished finish not only provides a clean, professional look but also extends the lifespan of equipment by protecting it from rust and corrosion. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing from suppliers who offer customized solutions tailored to specific agricultural needs can significantly reduce maintenance costs and improve operational efficiency.
Why Is Polish Galvanized Steel Important for Renewable Energy Applications?
In the renewable energy sector, particularly for solar panel mounting structures, polished galvanized steel is favored for its durability and corrosion resistance. The polished finish can withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-term performance and reliability. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider the thickness of the zinc coating based on local climatic conditions to optimize the lifespan of their installations.
How Is Polish Galvanized Steel Used in Infrastructure Projects?
Polished galvanized steel is widely used in infrastructure applications such as fencing and guardrails. The aesthetic enhancement offered by the polished finish, combined with the protective qualities of galvanization, makes it ideal for public spaces and roadways. International buyers should verify that the coatings used are compatible with local environmental conditions, ensuring that the infrastructure remains visually appealing and structurally sound over time.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘polish galvanized steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: The Risk of Compromised Coating Integrity
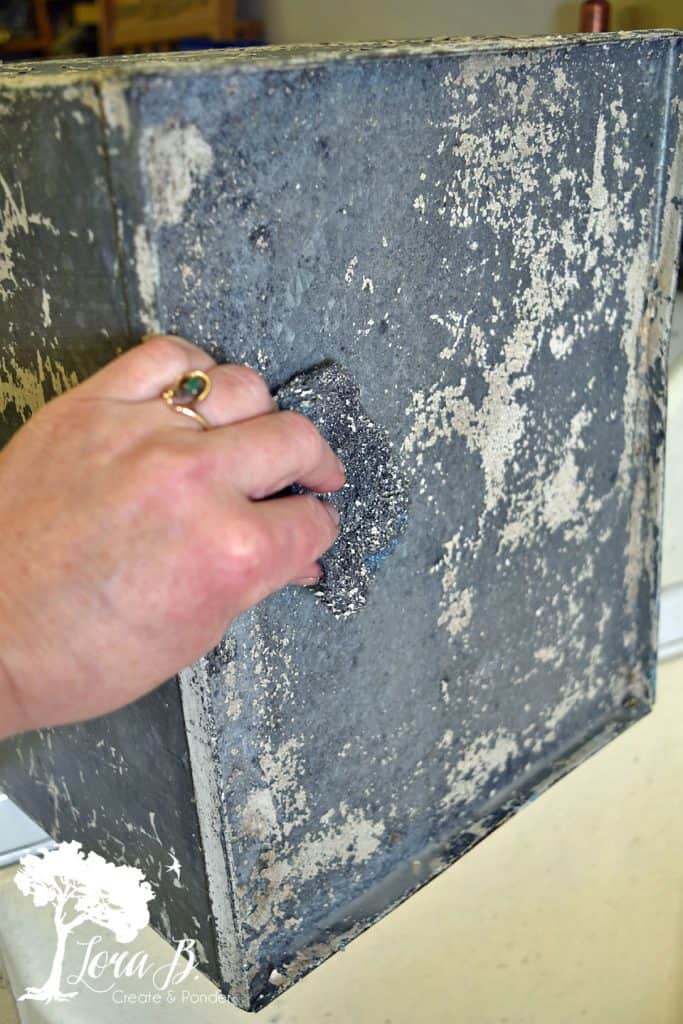
The Problem: When B2B buyers seek to enhance the appearance of polish galvanized steel, they often underestimate the risks involved in the polishing process. The zinc coating, which provides essential corrosion resistance, can be severely compromised if polishing is not executed with care. This can lead to rust and deterioration, especially in humid or corrosive environments, ultimately impacting the longevity and structural integrity of the steel. Buyers may find themselves facing unexpected maintenance costs and operational disruptions due to this oversight.
The Solution: To mitigate the risk of compromising the zinc coating, it’s crucial to choose appropriate polishing methods and materials. Buyers should prioritize non-abrasive polishing agents designed specifically for galvanized steel. A thorough cleaning process using a mild detergent or vinegar solution can prepare the surface effectively without damaging the protective layer. If polishing is deemed necessary for aesthetic reasons, employing fine-grit pads and polishing compounds that are gentle on zinc is advisable. Regular inspections after polishing can help identify any signs of wear early, allowing for timely intervention before corrosion sets in.
Scenario 2: Increased Maintenance Due to Polishing
The Problem: International buyers often select polished galvanized steel for its aesthetic appeal, only to find that frequent maintenance is required due to the damage inflicted during the polishing process. Without the protective zinc layer, the steel is exposed to environmental factors that accelerate rust formation. This situation is particularly problematic for businesses operating in regions with high humidity or corrosive atmospheres, where the costs and labor associated with increased maintenance can quickly add up.
The Solution: To avoid this pitfall, businesses should consider alternatives to traditional polishing that maintain the integrity of the galvanized coating. One effective method is to apply clear protective coatings after the initial polishing to shield the exposed areas from moisture and oxidation. Additionally, opting for pre-finished galvanized products can provide the desired aesthetic without compromising corrosion resistance. When maintenance is necessary, using specialized cleaning agents formulated for galvanized surfaces can help preserve the finish while minimizing wear on the protective layer.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Surface Finish Post-Polishing
The Problem: Buyers of polished galvanized steel often face the issue of achieving a consistent surface finish. Polishing can lead to an uneven or blotchy appearance, which may not only detract from the product’s visual appeal but also undermine its perceived value. This inconsistency can be particularly frustrating for companies that pride themselves on quality and aesthetics, especially in competitive markets where presentation matters.
The Solution: To ensure a uniform finish, it is essential for buyers to implement a systematic approach to polishing. This involves using high-quality polishing tools and ensuring that the same technique is applied consistently across the entire surface. Utilizing specialized polishing pastes designed for galvanized steel can enhance the overall appearance without risking damage to the zinc layer. Furthermore, conducting a thorough assessment of the galvanized steel’s texture before polishing can help establish a baseline, allowing for better control over the final look. For those who are concerned about the potential for uneven results, exploring advanced surface treatments like passivation or galvanic brightening may provide a viable alternative that enhances reflectivity and consistency without compromising the protective qualities of the galvanized coating.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for polish galvanized steel
What Are the Key Materials for Polishing Galvanized Steel?
When considering the polishing of galvanized steel, various materials and methods can be employed, each with distinct properties and implications for performance. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the polishing process, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and their relevance to international B2B buyers.
1. Fine-Grit Sanding Pads
Key Properties: Fine-grit sanding pads are designed to provide a smooth finish without excessively removing the zinc coating. They typically range from 220 to 600 grit, allowing for controlled abrasion.
Pros & Cons: These pads are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them suitable for DIY applications. However, they require careful handling to avoid over-polishing, which can compromise the protective layer. The risk of uneven surfaces increases if not used correctly.
Impact on Application: Fine-grit sanding pads are effective for light surface restoration and can be used on various shapes and sizes of galvanized steel. However, they may not be suitable for intricate designs where precision is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Europe and South America should ensure that the sanding pads comply with local safety standards, such as EN or ANSI certifications. Additionally, understanding the availability of specific grit sizes in local markets is essential for efficient procurement.
2. Non-Abrasive Polishing Cloths
Key Properties: Non-abrasive polishing cloths are soft materials that do not scratch the surface of galvanized steel. They are often made from microfiber or cotton and are designed for gentle polishing.
Pros & Cons: These cloths are excellent for maintaining the integrity of the zinc coating while providing a shine. They are low-cost and reusable, making them environmentally friendly. However, they may not effectively remove heavy oxidation or stains, limiting their use to light cleaning.
Impact on Application: Ideal for routine maintenance, non-abrasive cloths can enhance the aesthetic appeal of galvanized steel without risking corrosion. They are particularly useful in environments where the steel is exposed to moisture.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that the cloths are free from harmful chemicals, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations. Sourcing from reputable manufacturers that comply with international quality standards is advisable.
3. Mild Polishing Paste
Key Properties: Mild polishing pastes are formulated specifically for use on zinc-coated surfaces. They typically contain non-abrasive compounds that enhance shine without damaging the protective layer.
Pros & Cons: These pastes are effective in restoring the appearance of galvanized steel while preserving its corrosion resistance. However, they can be more expensive than other options and may require additional cleaning steps to remove residue.
Impact on Application: Suitable for both decorative and functional applications, polishing pastes can significantly improve the visual quality of galvanized steel products. They are particularly beneficial for items exposed to public view.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the polishing pastes comply with local regulations regarding chemical safety and environmental impact. Understanding the compatibility of these products with local materials is also crucial.
4. Clear Protective Coatings
Key Properties: Clear protective coatings, such as polyurethane or acrylic, are designed to seal and protect polished surfaces. They enhance gloss while providing a barrier against moisture and contaminants.
Pros & Cons: These coatings extend the life of polished finishes and can significantly improve corrosion resistance. However, they add an extra step to the finishing process and may require specific application techniques.
Impact on Application: Clear coatings are particularly valuable in humid environments, where they can prevent rust formation. They are also beneficial for outdoor applications where galvanized steel is exposed to the elements.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for coatings. Understanding the climatic conditions of the application area can help in selecting the right type of coating for optimal performance.
Summary Table of Materials for Polishing Galvanized Steel
| Material | Typical Use Case for polish galvanized steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-Grit Sanding Pads | Light surface restoration | Cost-effective and easy to use | Risk of over-polishing | Low |
| Non-Abrasive Polishing Cloths | Routine maintenance | Preserves zinc coating and environmentally friendly | Limited effectiveness on heavy oxidation | Low |
| Mild Polishing Paste | Decorative and functional applications | Restores appearance while maintaining corrosion resistance | Higher cost and requires additional cleaning steps | Medium |
| Clear Protective Coatings | Outdoor and humid environments | Extends life of polished finish | Adds complexity to the finishing process | Medium to High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of materials suitable for polishing galvanized steel, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for polish galvanized steel
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Polish Galvanized Steel?
The manufacturing of polished galvanized steel involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets both aesthetic and functional requirements. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers who need high-quality materials for their projects.
Material Preparation: How Is Galvanized Steel Readied for Polishing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of the raw materials. This involves selecting high-quality steel sheets that will undergo the galvanization process. The steel is then thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants such as oil, dirt, or rust. Common cleaning methods include chemical baths or abrasive cleaning techniques.
Once the steel is cleaned, it is subjected to surface treatments that may enhance its adherence to the zinc coating. These treatments can include pickling, which uses acids to remove surface oxides, and passivation, which helps improve corrosion resistance. This preparation is crucial as it directly impacts the effectiveness of the galvanization and the quality of the polished surface.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Galvanized Steel?
The forming stage is where the prepared steel is shaped into the desired configurations. This can involve various techniques such as:
- Stamping: Utilizing a die to cut and shape steel sheets into specific forms.
- Bending: Applying force to create angles or curves in the steel.
- Welding: Joining multiple pieces of steel together to create assemblies.
Each method must be executed with precision to ensure the structural integrity of the product. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that employ advanced forming technologies, as this can significantly enhance the quality and consistency of the final product.
Assembly: How Are Components Joined in the Manufacturing Process?
After forming, components may require assembly. This step often involves welding, riveting, or using adhesives to create a complete product. The assembly process is critical, as it determines the overall strength and durability of the galvanized steel structure.
Quality assurance measures during assembly are vital. Suppliers should employ trained technicians and utilize jigs or fixtures to ensure that components align correctly, minimizing the risk of defects. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques used by suppliers to ensure they meet the required standards for their specific applications.
Finishing: What Are the Techniques for Polishing Galvanized Steel?
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the appearance and surface quality of galvanized steel. While polishing is a common method, it poses risks to the zinc coating that protects against corrosion. Therefore, alternative finishing techniques may be recommended, such as:
- Mechanical Polishing: Utilizing non-abrasive pads or specialized tools to enhance the surface finish without damaging the zinc layer.
- Chemical Treatments: Applying solutions that clean and brighten the galvanized surface without removing the protective coating.
- Coating: Applying clear coatings or paints that enhance aesthetics while providing additional protection.
B2B buyers should discuss finishing options with suppliers to ensure that the selected method aligns with their quality and durability expectations.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Polish Galvanized Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, particularly for products intended for international markets. For B2B buyers, understanding the QA protocols can help ensure that they receive high-quality materials that meet their specifications.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Manufacturers of polished galvanized steel should adhere to international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific standards like CE marking for products sold within Europe or API standards for oil and gas applications may also apply. Compliance with these standards not only ensures product quality but also facilitates easier trade across borders.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints should be established at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing the quality of raw materials before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive testing and inspections of the finished product before shipment.
These checkpoints help maintain a high standard of quality throughout production, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring that the final product meets customer expectations.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods employed in the QA process for polished galvanized steel include:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, uniformity, and adherence to specifications.
- Coating Thickness Measurement: Using tools like micrometers to ensure that the zinc coating meets required thickness standards.
- Adhesion Testing: Assessing the bond strength of coatings applied to galvanized surfaces.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Subjecting samples to accelerated corrosion tests to evaluate durability.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on these testing methods from their suppliers to verify compliance with industry standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for B2B buyers seeking reliable partners. Here are some methods to ensure that suppliers adhere to stringent QC measures:
What Steps Should Buyers Take to Audit Suppliers?
Conducting audits is an effective way to assess a supplier’s manufacturing and quality assurance processes. Buyers should consider performing:
- On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility to evaluate processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to conduct thorough assessments of the supplier’s quality practices.
What Documentation Should Buyers Request?
Buyers should request the following documentation from suppliers:
- Quality Management System Certifications: Proof of compliance with ISO standards and other relevant certifications.
- Inspection Reports: Detailed records of inspections and tests performed during manufacturing.
- Traceability Records: Documentation that allows for tracking materials from raw inputs through to finished products.
These steps can provide valuable insights into a supplier’s commitment to quality and their ability to meet international standards.
How Do Quality Control Nuances Differ for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control. Factors such as regulatory compliance, shipping practices, and local standards can significantly impact procurement decisions.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Local Regulations?
Each region may have specific regulations governing the use of galvanized steel products. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to ensure that their purchases comply with local laws and standards. This knowledge can help avoid costly delays and compliance issues.
How Can Buyers Leverage International Standards to Their Advantage?
By understanding and leveraging international standards, B2B buyers can facilitate smoother transactions and reduce risks associated with non-compliance. Suppliers that adhere to recognized standards are often more reliable and can provide assurances regarding product quality and safety.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for polished galvanized steel is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and quality expectations.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘polish galvanized steel’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure polished galvanized steel. Understanding the nuances of sourcing this material is crucial to ensure that you receive a product that meets your technical specifications while maintaining its durability and aesthetic appeal. The following steps will help you navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your sourcing process, clearly outline your technical requirements for polished galvanized steel. This includes dimensions, thickness, surface finish, and any specific performance criteria relevant to your industry.
– Why it Matters: Precise specifications ensure that suppliers understand your needs, reducing the risk of miscommunication and product returns.
– What to Look For: Include details such as the intended application, environmental conditions, and any regulatory standards that must be met.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in polished galvanized steel. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list of candidates.
– Why it Matters: A well-researched supplier list helps you find reliable partners who can deliver quality products and services.
– What to Look For: Focus on suppliers with a proven track record in your specific market, especially those with experience in international trade if you are sourcing from different continents.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management or other industry-specific certifications.
– Why it Matters: Certifications indicate a commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards, which is essential for ensuring the integrity of your materials.
– What to Look For: Request copies of certifications and check their validity with the issuing organizations.
Step 4: Request Samples for Testing
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of polished galvanized steel from shortlisted suppliers.
– Why it Matters: Testing samples allows you to assess the quality and suitability of the material for your specific applications.
– What to Look For: Evaluate the samples for surface finish, corrosion resistance, and any other performance characteristics that are critical for your use case.
Step 5: Understand Pricing and Payment Terms
Engage with suppliers to obtain detailed pricing information, including any potential hidden costs such as shipping, tariffs, and taxes.
– Why it Matters: A clear understanding of the total cost will help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses later in the procurement process.
– What to Look For: Negotiate payment terms that align with your cash flow needs, considering options like net payment terms or early payment discounts.
Step 6: Assess Logistics and Delivery Options
Evaluate the logistics capabilities of your suppliers, including lead times, shipping methods, and handling of customs clearance if importing.
– Why it Matters: Timely delivery is crucial for maintaining project schedules, especially in international sourcing.
– What to Look For: Confirm the supplier’s experience with logistics in your region, and inquire about their ability to meet your delivery timelines consistently.
Step 7: Establish a Quality Assurance Process
Implement a quality assurance process to monitor the quality of polished galvanized steel upon delivery and throughout its lifecycle.
– Why it Matters: Regular quality checks help mitigate risks associated with defects or corrosion, ensuring that the material performs as expected.
– What to Look For: Set clear criteria for quality assessment and establish a communication channel with suppliers for addressing any quality issues that arise.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your procurement process for polished galvanized steel and ensure that you make informed decisions that align with your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for polish galvanized steel Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Polish Galvanized Steel?
When sourcing polish galvanized steel, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of zinc-coated steel is influenced by the price of raw steel and zinc. Fluctuations in these commodities can significantly impact overall costs. Additionally, if specialized finishes or treatments are required for polishing, this will further increase material expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages for workers involved in the polishing process. This includes skilled labor for polishing and unskilled labor for preparation and cleaning. Labor rates vary widely by region, making it essential to consider local wage standards, especially for buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs consist of utilities, rent, equipment depreciation, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help keep these costs down, which is particularly relevant for suppliers in competitive markets like Europe and South America.
-
Tooling: The investment in specialized tools for polishing galvanized steel can be substantial. This includes polishing wheels, pads, and various cleaning agents. Suppliers who own advanced machinery may pass on these costs to buyers, so it’s important to assess the quality of the equipment used.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that the polished galvanized steel meets quality standards incurs additional costs. QC processes, including testing and inspections, are vital for maintaining product integrity, especially for buyers requiring specific certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the chosen shipping method. Incoterms will dictate who bears these costs, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Polish Galvanized Steel Pricing?
Several factors influence the pricing of polished galvanized steel, particularly in the international B2B market:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often come with discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize their purchasing power.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom orders, such as specific dimensions or finishes, can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The quality of the materials used for polishing and any relevant certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) can affect pricing. Premium materials command higher prices but may offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they often offer better service and assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is critical, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and liability. This can significantly impact the total cost.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Negotiate Better Pricing for Polish Galvanized Steel?
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially if you are ordering in bulk. Don’t hesitate to seek competitive quotes to leverage better deals.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): When evaluating offers, consider not just the purchase price but also the long-term costs associated with maintenance, logistics, and potential downtime. A lower initial cost may not always equate to a better value.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Each region has unique pricing dynamics. For example, European suppliers may have different cost structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to labor laws, tariffs, and supply chain logistics.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keep abreast of fluctuations in raw material prices and industry trends. This knowledge can empower buyers to negotiate better and anticipate changes in pricing.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Please note that prices for polished galvanized steel can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough research and engage directly with suppliers to obtain precise pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing polish galvanized steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Polishing Galvanized Steel
In the quest for maintaining the aesthetic appeal and longevity of galvanized steel, many buyers consider polishing as an option. However, this method can compromise the protective zinc coating, leading to increased susceptibility to corrosion and higher maintenance costs. Fortunately, there are several alternative solutions that can enhance the appearance of galvanized steel without sacrificing its protective qualities. This analysis compares polishing galvanized steel with two viable alternatives: applying a clear protective coating and powder coating.
| Comparison Aspect | Polish Galvanized Steel | Clear Protective Coating | Powder Coating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Moderate; may reduce corrosion resistance | High; maintains zinc protection | Very high; durable and resistant |
| Cost | Low initial cost, but higher long-term maintenance | Moderate; depends on the quality of the coating | Higher; includes application costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Moderate; requires careful technique to avoid damage | Easy; requires minimal preparation | Moderate; requires surface preparation and equipment |
| Maintenance | High; frequent upkeep needed post-polishing | Low; periodic cleaning required | Very low; resistant to wear and tear |
| Best Use Case | Decorative applications with minimal exposure to elements | Environments needing corrosion protection with enhanced aesthetics | High-performance applications requiring durability |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Clear Protective Coatings?
Clear protective coatings, such as polyurethane or acrylic, provide a transparent barrier over galvanized steel. This method enhances the appearance by creating a glossy finish while preserving the zinc layer underneath. The application process is straightforward, requiring only cleaning and a simple application of the coating. However, while the upfront cost is moderate, it may vary based on the quality of the coating and application. Maintenance is minimal, as these coatings typically only require periodic cleaning. The main drawback is that if the coating wears off over time, the underlying steel may be exposed to corrosion, necessitating timely reapplication to maintain protection.
How Does Powder Coating Compare to Polishing Galvanized Steel?
Powder coating offers a robust alternative that combines aesthetics with exceptional durability. This method involves applying a dry powder that is then cured under heat, creating a hard, protective layer that is highly resistant to scratches, UV rays, and corrosion. While the initial cost is higher than polishing or clear coatings due to the required equipment and expertise, the longevity and low maintenance of powder-coated surfaces make it a cost-effective option in the long run. The preparation for powder coating requires thorough cleaning of the galvanized surface to ensure proper adhesion, which can be seen as a drawback. Nevertheless, powder coating is ideal for applications in harsh environments where durability is paramount.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting the best solution for galvanized steel, B2B buyers should consider their specific requirements, including the intended use, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. For projects where aesthetics are important but exposure to harsh conditions is limited, a clear protective coating may suffice. Conversely, for applications that demand high durability and resistance to wear, powder coating is the superior choice. Ultimately, the right solution balances performance, cost, and maintenance to ensure the longevity and effectiveness of galvanized steel in various applications. By carefully evaluating these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and enhance the value of their investments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for polish galvanized steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Polish Galvanized Steel?
When considering polished galvanized steel for your projects, understanding its technical properties is crucial. Here are some essential specifications that influence purchasing decisions:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of galvanized steel typically refers to its composition and the thickness of the zinc coating applied. Common grades include ASTM A653 for hot-dip galvanized steel. The grade impacts corrosion resistance, strength, and suitability for specific applications. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is vital for ensuring the longevity and durability of the product in various environments. -
Zinc Coating Thickness
Measured in microns, the thickness of the zinc coating directly affects the corrosion resistance of the steel. A standard range is between 40 to 85 microns, depending on the intended use. For international buyers, especially in humid or corrosive environments, understanding the zinc coating thickness is essential to ensure that the galvanized steel will perform adequately over time without excessive maintenance. -
Tensile Strength
This property indicates the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that the material can withstand before failure. For galvanized steel, tensile strength is typically measured in megapascals (MPa). Knowing the tensile strength is critical for applications that require specific load-bearing capacities, ensuring that the steel can support the intended use without risk of structural failure. -
Yield Strength
Yield strength is the stress at which a material begins to deform permanently. For galvanized steel, yield strength is also measured in MPa and is crucial for determining how much load the steel can handle before it begins to bend or warp. This property is particularly important for structural applications in construction and manufacturing, where safety and integrity are paramount. -
Corrosion Resistance
The corrosion resistance of polished galvanized steel is a key consideration, especially in industries such as construction and automotive. It is influenced by the quality of the galvanization process and the environment in which the steel is used. B2B buyers should assess the expected lifespan and maintenance requirements based on the corrosion resistance to make informed purchasing decisions. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of polished galvanized steel not only affects aesthetics but also influences its performance in terms of adhesion for coatings and resistance to dirt accumulation. A smooth finish may be preferred for certain applications, while a textured finish may provide better grip and less visibility of surface imperfections. Understanding the surface finish can guide buyers in selecting the right product for their specific needs.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Polish Galvanized Steel?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of polished galvanized steel, OEMs may require specific grades and finishes for their components, necessitating clear communication about specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for buyers, especially smaller businesses, as it affects inventory management and overall costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that potential buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. When sourcing polished galvanized steel, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to receive detailed proposals and compare offers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping agreements. Knowledge of relevant Incoterms is essential for international B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and liability during transportation. -
Galvanization
This term refers to the process of applying a protective zinc coating to steel or iron to prevent rusting. Understanding the galvanization process is vital for buyers to assess the quality and durability of the steel they are purchasing. -
Passivation
Passivation involves treating the surface of galvanized steel to enhance its corrosion resistance without removing the zinc layer. This process is important for buyers looking for additional protection and longevity in their steel products.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing polished galvanized steel, ensuring that they select the right materials for their specific applications and requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the polish galvanized steel Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Polish Galvanized Steel?
The global market for galvanized steel is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors such as construction, automotive, and infrastructure. The rise of urbanization, particularly in developing regions like Africa and South America, is pushing the demand for durable and corrosion-resistant materials. Polish galvanized steel, known for its aesthetic appeal and protective qualities, is particularly favored in architectural applications. In Europe, especially Germany, there is a marked trend toward sourcing high-quality, pre-finished galvanized products, which streamline the supply chain and enhance project timelines.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies in the galvanized steel sector. Digital platforms for procurement are gaining traction, enabling international buyers to efficiently compare suppliers, track inventory, and manage logistics. Blockchain technology is also making inroads, providing transparency in the supply chain, which is crucial for buyers concerned about ethical sourcing and product authenticity. Furthermore, automation in manufacturing processes is enhancing the quality and consistency of galvanized steel products, meeting the rising expectations of B2B buyers.
How Is Sustainability Influencing the Sourcing of Polish Galvanized Steel?
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the sourcing of polish galvanized steel. The environmental impact of steel production, particularly regarding carbon emissions and resource depletion, has led to a shift towards more sustainable practices. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate commitment to reducing their ecological footprint. This includes the use of recycled materials in the galvanization process and implementing energy-efficient production methods.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining prominence. Buyers are looking for suppliers that adhere to stringent environmental regulations and provide transparency about their sourcing practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for green building materials are becoming essential for suppliers aiming to capture international markets. These certifications not only reassure buyers of the sustainability of their purchases but also enhance their corporate social responsibility profile.
What Is the Evolution of Polish Galvanized Steel in the Market?
The evolution of polish galvanized steel can be traced back to the early 20th century when galvanization processes were first introduced to enhance the durability of steel against corrosion. Initially, the focus was primarily on functionality, but as industries evolved, aesthetic considerations became equally important. The introduction of innovative surface treatment technologies allowed for the production of galvanized steel with varied finishes, catering to the design-oriented construction market.
In recent years, the demand for polish galvanized steel has surged due to its versatility and the growing emphasis on sustainability. Manufacturers have responded by developing advanced coating techniques that not only improve the visual appeal but also enhance the material’s longevity. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the steel industry, where quality and appearance are increasingly influencing procurement decisions among international B2B buyers.
Through understanding these dynamics, buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing polish galvanized steel, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of polish galvanized steel
-
How do I maintain the appearance of polished galvanized steel?
To maintain the appearance of polished galvanized steel, it is crucial to avoid abrasive cleaning methods that can strip the protective zinc layer. Instead, use mild cleaning agents specifically designed for galvanized surfaces. Regularly wipe the surface with a soft cloth to remove dust and grime, and consider applying a clear protective coating, such as polyurethane, to enhance shine and provide additional corrosion resistance. Regular maintenance helps preserve the aesthetic and functional qualities of the steel over time. -
What is the best method to polish galvanized steel without damaging it?
The best method to polish galvanized steel involves using non-abrasive materials and gentle techniques. Start with a thorough cleaning using a mild soap solution to remove impurities. Next, apply a fine-grit polishing pad or a soft cloth with a mild polishing paste designed for zinc-coated materials. Avoid excessive pressure and inspect the surface frequently to ensure you do not compromise the zinc coating, which is essential for corrosion resistance. -
What are the risks associated with polishing galvanized steel?
Polishing galvanized steel can compromise the protective zinc coating, leading to increased susceptibility to rust and corrosion. Removing parts of the zinc layer exposes the underlying steel to moisture and environmental factors, which can degrade its structural integrity. Additionally, polishing may result in an inconsistent surface finish, negating the intended aesthetic improvements. It is often recommended to explore alternatives to polishing that maintain the protective qualities of the galvanized surface. -
How can I source high-quality polished galvanized steel from international suppliers?
When sourcing polished galvanized steel internationally, start by identifying reputable suppliers with a strong track record in the industry. Look for suppliers who provide detailed product specifications, quality certifications, and customer reviews. Attend trade shows and industry conferences to network and assess potential partners. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources, and ensure to conduct thorough due diligence, including verifying business licenses and requesting samples before making significant orders. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for polished galvanized steel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) for polished galvanized steel can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific product requirements. Generally, MOQs can range from as low as 500 kg to several tons for larger manufacturers. It is advisable to discuss your project needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your purchasing capacity. Smaller orders may incur higher prices, so consider consolidating orders with other materials to achieve better pricing. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing polished galvanized steel?
Payment terms for polished galvanized steel can differ by supplier and region. Common arrangements include partial upfront payments (30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services to mitigate risk. Always clarify payment conditions before finalizing contracts, and consider negotiating terms that provide flexibility while ensuring security for both parties. -
How can I ensure the quality of polished galvanized steel during shipping?
To ensure the quality of polished galvanized steel during shipping, work with suppliers who provide proper packaging and handling methods to prevent damage. Request that products be wrapped in protective materials to avoid scratches or dents. Additionally, consider arranging for quality inspections at the point of origin or before shipment. Using trusted logistics partners with experience in handling metal products can also help mitigate risks associated with transportation. -
What are the key factors to consider when customizing polished galvanized steel products?
When customizing polished galvanized steel products, key factors include the specific applications and environmental conditions the steel will face. Consider the required dimensions, finishes, and any additional protective coatings that might enhance durability. Discuss your customization needs with suppliers to explore available options, including surface treatments or specialized coatings. Understanding local regulations and standards for construction materials in your target market is also crucial for compliance and quality assurance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Polish Galvanized Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Comet – Galvanized Metal Cleaner
Domain: lovetoknow.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Cleaners approved for cleaning galvanized metal include Comet, bleach, Simple Green, The Rust for Must, and Stainless Steel Cleaner. Vinegar and ammonia can affect the appearance of the coating. For cleaning, materials needed are dish soap, water, a bucket, a soft-bristle brush, a cloth, and metal polish. To remove rust, materials include a wire brush, white vinegar, sandpaper, a broom, zinc-rich …
2. The Combine Forum – Essential Cleaning Solutions
Domain: thecombineforum.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: 1. SOS soap pads (steel wool with soap) – used for cleaning grime and surface rust stains on galvanized steel. 2. Wax paper – recommended for putting a shine back and providing wax protection after cleaning. 3. Oxalic acid solution (0.03 to 0.05 percent) – suggested for cleaning galvanized steel, with a preference for oxalic over acetic acid. 4. Ammonia solution – mentioned as less corrosive than …
3. Smart Wheels – Alloy Wheel Cleaner
Domain: mig-welding.co.uk
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. Alloy Wheel Cleaner from Smart Wheels – recommended for use on alloy bodies, but should be diluted. 2. Metal Polish like Autosol – can clean and reduce dullness, but won’t restore shine completely. 3. Strong Ammonia Solution – suggested for dissolving surface oxides. 4. WD40 – recommended for adding sheen after light wire brushing. 5. Pressure Washing – suggested as a method to clean before app…
4. Sherwood Steel – Cleaning Solutions
Domain: sherwoodsteelinc.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Vinegar solution, Car wash fluid, Dish-washing liquid, Wax or metal polish, Milk solution and baby powder, Hose, Bucket of warm water, Toothbrush, Soft-bristled brush, Lint-free cloths.
5. Yesterday’s Tractors – Galvanized Steel Care
Domain: forums.yesterdaystractors.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: 1. Linseed Oil: Recommended for polishing galvanized steel; helps remove oxidation and enhances appearance. 2. Vinegar and Steel Wool: Suggested method for achieving a shiny finish on galvanized steel. 3. Steelite Coating: Used in new Gleaners to maintain shine, particularly in the food industry.
6. Instagram – Scraping Services
Domain: instagram.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Contact for Instagram scraping services, inquire about the number of pages to scrape per month.
7. Lora Bloomquist – Essential Cleaning & Sealing Products
Domain: lorabloomquist.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: 1. Cleaning Products:
– S.O.S. pads (blue-foaming)
– Brillo pads
– Degreaser spray
2. Sealing Products:
– Water-based polyurethane (clear satin finish)
– Spray can version of polyurethane
– Poly sprayer
3. Additional Supplies:
– Modge Podge for sealing vintage labels
– Mild soap for cleaning
– Steel wool cleaning pad
4. Vintage Items to Clean:
– Galvan…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for polish galvanized steel
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Polish Galvanized Steel?
In the evolving landscape of polish galvanized steel, strategic sourcing remains paramount for international buyers. The unique properties of galvanized steel, including its corrosion resistance and aesthetic versatility, make it a preferred choice across various industries. However, the risks associated with polishing—such as compromising the protective zinc coating—should not be overlooked. Buyers must weigh the benefits of polishing against potential maintenance challenges and consider alternative surface treatments that enhance appearance without sacrificing durability.
How Can Buyers Ensure Value and Quality in Their Sourcing Decisions?
To maximize value, it is crucial for buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to engage with reputable suppliers who understand the nuances of galvanized steel. Prioritizing quality sourcing will help mitigate risks and ensure that products meet both aesthetic and functional requirements. Buyers should also explore pre-finished options or specialized coatings that provide a polished look while maintaining the integrity of the material.
What Does the Future Hold for Polish Galvanized Steel in Global Markets?
As global demand for high-quality materials continues to rise, the outlook for polish galvanized steel remains positive. Companies that embrace innovative surface treatments and sustainable sourcing practices will be well-positioned to capitalize on market opportunities. We encourage international buyers to actively seek partnerships that foster quality and sustainability in their sourcing strategies, ensuring they remain competitive in an ever-evolving market.