Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for platinum 3d printing
The growing demand for platinum 3D printing presents a unique challenge for international B2B buyers: how to effectively source and implement this advanced technology within their operations. As businesses in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Nigeria and Germany) seek to innovate, the need for reliable information on platinum 3D printing becomes paramount. This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of the various types of platinum used in additive manufacturing, their applications in industries like jewelry and aerospace, and essential strategies for vetting suppliers.
Buyers will gain insights into the cost implications associated with platinum 3D printing, alongside a detailed analysis of the technology’s benefits, such as reduced material waste and the ability to create intricate designs that traditional methods cannot achieve. By addressing these critical factors, this guide empowers B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
In an era where technological advancements can dictate competitive advantage, understanding the nuances of platinum 3D printing is essential for businesses looking to thrive in a global marketplace. This guide is designed to be a valuable resource, equipping buyers with the knowledge they need to navigate the complexities of sourcing and implementing platinum 3D printing solutions effectively.
Understanding platinum 3d printing Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wax Casting | Utilizes wax models for intricate designs; high detail fidelity | Jewelry, luxury items | Pros: Excellent detail; Cons: Higher production costs |
| Metal Binder Jetting | Allows complex shapes; less material waste; no physical manipulation | Jewelry, industrial parts | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited finishing options |
| Direct Energy Deposition | Adds material layer by layer; suitable for repairs and prototypes | Aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Versatile applications; Cons: Slower production speed |
| Powder Bed Fusion | Melts powdered platinum layer by layer; high precision | Custom jewelry, dental applications | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Longer lead times |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Uses light to cure resin; creates detailed prototypes | Product development, concept models | Pros: Excellent surface finish; Cons: Limited material types |
What are the Key Characteristics of Wax Casting in Platinum 3D Printing?
Wax casting is a traditional yet effective method for creating intricate platinum designs. This process involves creating a wax model that is coated with a ceramic shell, which is then heated to remove the wax and cast platinum into the mold. It is especially suitable for high-end jewelry where detail and finish are paramount. B2B buyers should consider the higher costs associated with this method, particularly for complex designs, but the resulting products often justify the investment due to their superior quality.
How Does Metal Binder Jetting Revolutionize Platinum 3D Printing?
Metal Binder Jetting is a cutting-edge technique that significantly enhances the production of platinum components. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries without the need for extensive post-processing. It is particularly advantageous for producing intricate jewelry designs and industrial components with minimal material waste. Buyers should weigh the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of this method against the potential limitations in surface finishing, as additional steps may be necessary to achieve the desired look.
What are the Advantages of Direct Energy Deposition?
Direct Energy Deposition (DED) is a highly versatile 3D printing method that is suitable for both manufacturing new parts and repairing existing ones. This process works by melting powdered platinum and depositing it layer by layer, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications where precision is critical. While DED can be slower than other methods, its adaptability for various applications makes it a valuable option for B2B buyers looking for customized solutions.
Why Choose Powder Bed Fusion for Platinum Applications?
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) is known for its ability to create highly accurate and complex platinum parts. This method involves melting layers of powdered platinum using a laser, resulting in a finely detailed finish. It is widely used in custom jewelry and dental applications where precision is essential. However, buyers should be prepared for longer lead times and potentially higher costs associated with this method, which can impact project timelines.
How Does Stereolithography (SLA) Benefit Prototyping in Platinum 3D Printing?
Stereolithography (SLA) is a process that utilizes light to cure resin, enabling the creation of highly detailed prototypes. While SLA is not a direct method for printing platinum, it serves as a valuable tool for developing precise models before committing to metal printing. This approach is particularly useful in product development and concept modeling. B2B buyers should consider the advantages of SLA in terms of surface finish and accuracy, although the limited material options may restrict its use in final production.
Key Industrial Applications of platinum 3d printing
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Platinum 3D Printing | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jewelry and Fashion | Custom jewelry design and production | Enables intricate designs, reduces material waste | Look for suppliers with expertise in luxury 3D printing |
| Aerospace | High-performance components for aircraft | Lightweight and durable parts enhance fuel efficiency | Ensure compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Production of surgical instruments and implants | High biocompatibility and durability for patient safety | Verify quality control processes and material certifications |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of connectors and heat sinks | Excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability | Seek suppliers with advanced printing technologies |
| Automotive | Creation of custom parts and prototypes | Accelerates design iterations and reduces lead times | Assess the supplier’s ability to handle complex geometries |
How is Platinum 3D Printing Transforming the Jewelry and Fashion Industry?
In the jewelry and fashion sector, platinum 3D printing allows for the creation of bespoke pieces that showcase intricate designs and textures. Traditional methods often limit the complexity of designs due to the challenges of working with platinum’s high melting point. By utilizing 3D printing, jewelers can produce unique, lightweight designs while minimizing material waste. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with a strong portfolio in luxury applications and the ability to deliver high-quality finishes, particularly those serving markets in Africa and Europe, where craftsmanship is highly valued.
What Advantages Does Platinum 3D Printing Offer in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, platinum 3D printing is utilized to manufacture high-performance components that require both lightweight properties and exceptional durability. Parts created through this method can contribute to enhanced fuel efficiency and overall aircraft performance. Buyers in this sector must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent aerospace standards and possess the necessary certifications to guarantee the reliability and safety of the components produced.
How is Platinum 3D Printing Enhancing Medical Device Manufacturing?
The medical device industry benefits significantly from platinum 3D printing, particularly in the production of surgical instruments and implants. Platinum’s biocompatibility makes it an ideal choice for devices that come into contact with the human body. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve, thereby improving the functionality of medical devices. International buyers should focus on sourcing from manufacturers with rigorous quality control processes and relevant material certifications to ensure safety and efficacy.
Why is Platinum 3D Printing Important for the Electronics Sector?
In the electronics industry, platinum 3D printing is employed to create connectors and heat sinks that require excellent electrical conductivity and thermal stability. The ability to produce intricate designs with high precision helps manufacturers optimize their products’ performance. When sourcing platinum 3D printed components, businesses should look for suppliers that leverage advanced printing technologies and have a proven track record in producing reliable electronic parts.
How Does Platinum 3D Printing Facilitate Automotive Customization?
The automotive sector is increasingly adopting platinum 3D printing for creating custom parts and prototypes. This technology allows for rapid design iterations, significantly reducing lead times and enabling manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their capacity to handle complex geometries and ensure that they can meet the specific requirements of automotive applications, especially in regions like South America and the Middle East where customization trends are rising.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘platinum 3d printing’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the High Costs of Platinum 3D Printing
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant cost challenges when considering platinum 3D printing for their manufacturing needs. The high price of platinum, coupled with the specialized technology and tools required for processing, makes it a daunting investment, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Additionally, the need for durable and expensive tools to handle platinum can further escalate costs, leading to concerns about whether the return on investment will justify the initial outlay.
The Solution:
To mitigate these cost issues, buyers should explore partnerships with established 3D printing service providers that specialize in platinum. By outsourcing the manufacturing process, companies can leverage the expertise and existing infrastructure of these providers, which often have the necessary tools and technology to handle platinum efficiently. Additionally, negotiating bulk orders or long-term contracts can yield cost savings. It is also advisable to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that includes potential savings from reduced material waste and labor costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods. This approach allows companies to make informed decisions about their investments in platinum 3D printing while minimizing financial risk.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Design Limitations in Platinum 3D Printing
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter limitations when it comes to designing intricate or complex shapes with platinum due to traditional manufacturing constraints. This can be particularly challenging in industries like jewelry and high-end watchmaking, where unique designs are crucial for differentiation in the market. Buyers often find that the intricacies they envision cannot be realized with standard manufacturing processes, leading to frustration and missed opportunities in product innovation.
The Solution:
To address these design challenges, companies should invest in advanced 3D modeling software that facilitates the creation of complex geometries specifically tailored for platinum 3D printing. Collaborating with skilled designers who understand the unique properties of platinum and the capabilities of 3D printing technology can also help unlock new design possibilities. Additionally, leveraging techniques such as lattice structures and hollow designs can reduce material usage and enhance the aesthetic appeal of the final product. Engaging in continuous dialogue with 3D printing service providers about design feasibility and best practices will ensure that the final output meets both functional and artistic expectations.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality and Precision in Platinum 3D Printed Products
The Problem:
Quality assurance is a critical concern for B2B buyers of platinum 3D printed products, especially in sectors where precision is non-negotiable, such as aerospace and luxury goods. The potential for dimensional inaccuracies or surface finish inconsistencies can lead to rejected parts, increased rework costs, and ultimately, client dissatisfaction. Buyers may struggle to find reliable quality control measures that ensure their platinum products meet the necessary standards.
The Solution:
To enhance quality assurance in platinum 3D printing, buyers should establish a comprehensive quality management system that includes detailed specifications for tolerances, surface finishes, and post-processing requirements. Partnering with suppliers that implement rigorous testing and inspection protocols, such as 3D scanning and metallurgical analysis, will help ensure that products meet predefined standards. Additionally, adopting iterative prototyping can help identify potential issues early in the design process, allowing for adjustments before full-scale production. Training staff on the specific requirements for handling and post-processing platinum will further enhance product quality and reliability. By prioritizing quality control at every stage, businesses can build trust with clients and ensure the success of their platinum 3D printing initiatives.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for platinum 3d printing
What Are the Key Properties of Platinum Alloys for 3D Printing?
When considering materials for platinum 3D printing, platinum alloys, particularly those containing ruthenium, are prominent. Platinum 950‰ is a common alloy used, consisting of 95% platinum and 5% ruthenium. This alloy boasts excellent corrosion resistance, high melting points (around 1900°C), and superior mechanical properties. These attributes make it suitable for intricate designs and applications in luxury jewelry and high-end watchmaking. The high-temperature tolerance is crucial for applications that may involve extreme conditions, while its corrosion resistance ensures longevity and aesthetic appeal.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Platinum in 3D Printing?
The primary advantage of using platinum in 3D printing is its ability to produce intricate designs that are often unattainable through traditional manufacturing methods. The additive nature of 3D printing minimizes material waste and allows for the creation of complex geometries, such as lattices and hollow structures. However, the challenges of working with platinum include high costs associated with both the material and the specialized equipment required for processing. The manufacturing complexity can also lead to longer lead times, which may not align with fast-paced market demands.
How Does Platinum’s Performance Impact Specific Applications?
In jewelry design, the unique properties of platinum allow for the creation of pieces that are not only visually striking but also durable. The material’s hypoallergenic properties make it suitable for sensitive skin, a significant consideration in the luxury market. However, the high density and weight of platinum may limit its use in certain applications, such as lightweight jewelry or intricate components that require lower mass. International buyers should also consider the compatibility of platinum with other materials, particularly when designing multi-material pieces.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Platinum for 3D Printing?
For B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with international standards like ASTM, DIN, and JIS is crucial. Buyers must ensure that the platinum alloys used meet local regulations and quality standards to avoid complications in manufacturing and sales. Additionally, understanding the market dynamics, including the demand for luxury goods and the cost implications of using platinum, can help in making informed purchasing decisions. Buyers should also be aware of the logistical challenges associated with sourcing high-quality platinum, which may vary by region.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Platinum 3D Printing
| Material | Typical Use Case for platinum 3d printing | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Platinum 950‰ | Luxury jewelry, high-end watches | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Platinum Alloy | Aerospace components, medical devices | High melting point, suitable for extreme conditions | Limited availability and high sourcing costs | High |
| Ruthenium-Platinum | Jewelry with intricate designs | Allows for complex geometries and reduced waste | Requires specialized equipment for processing | High |
| Platinum Powder | Prototyping and custom jewelry | Versatile for various applications | Potential for high material costs and lead times | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the strategic material selection for platinum 3D printing, emphasizing the importance of understanding material properties, advantages, and limitations in the context of international B2B purchasing.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for platinum 3d printing
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Platinum 3D Printing?
The manufacturing process of platinum 3D printing involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring high-quality outputs. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Platinum 3D Printing?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-quality platinum alloy, typically consisting of 95% platinum and 5% ruthenium, to enhance its properties for 3D printing. The alloy is finely powdered to facilitate the additive manufacturing process. Ensuring a consistent grain size is vital for achieving uniformity in the final product, as irregularities can lead to defects during printing.
Moreover, the powder undergoes rigorous quality checks to confirm its chemical composition and purity. This is crucial because the performance characteristics of the final product, such as mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, are directly influenced by the quality of the raw materials.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Platinum Objects?
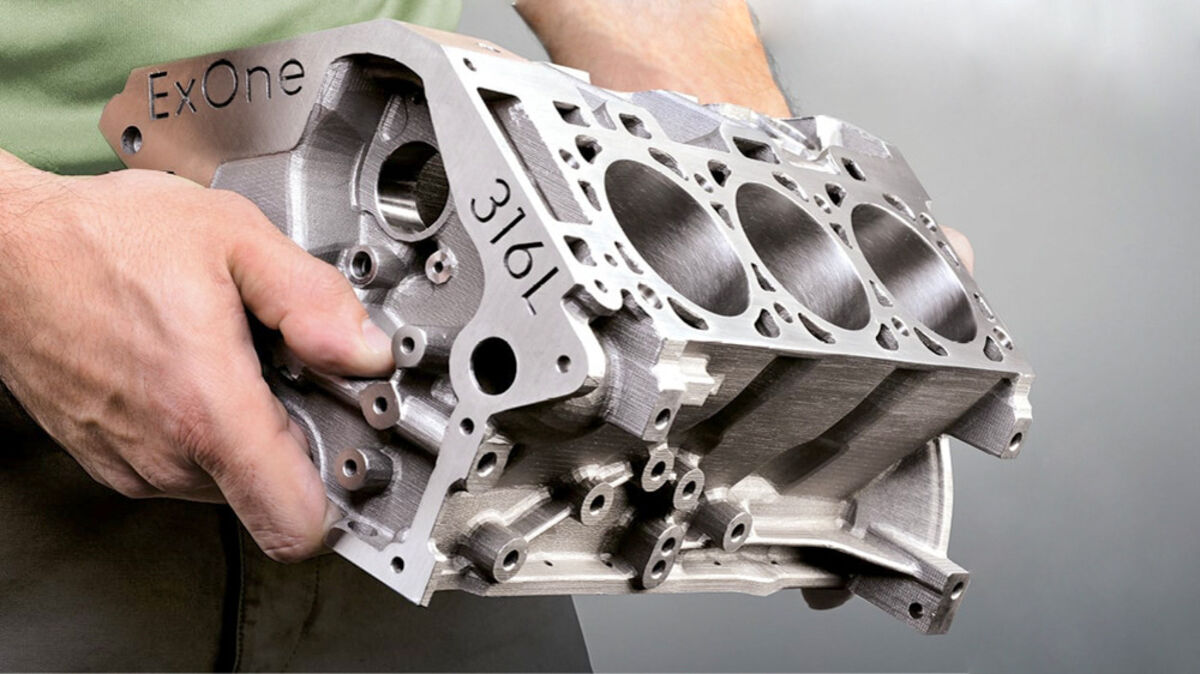
The primary technique for forming platinum objects in 3D printing is the Metal Binder Jetting (MBJ) technology. This innovative process enables manufacturers to create complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve. Unlike conventional techniques that require physical manipulation of the metal, MBJ utilizes a binder to selectively adhere the powdered platinum particles layer by layer.
This method significantly reduces material waste and allows for intricate designs, including hollow structures and detailed textures. However, due to the high melting point of platinum (around 1900°C), specialized equipment is necessary to handle the metal effectively, which can increase production costs.
How Are Platinum Products Assembled and Finished?
Once the forming process is complete, the next step is assembly, which may involve combining multiple printed parts. This is especially relevant for jewelry applications, where intricate designs often require the joining of different components. The assembly must ensure structural integrity, particularly for pieces that will undergo wear.
Finishing is the final stage, encompassing processes such as polishing and surface treatment. These steps enhance the aesthetic appeal of the product while ensuring that all surfaces meet the required specifications. It is crucial to note that internal details may not be polished, leading to potential quality issues if not properly accounted for in the design phase.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Platinum 3D Printing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of platinum 3D printed products, especially for international B2B buyers. Compliance with international standards like ISO 9001 ensures that manufacturers adhere to a quality management system that consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements.
Industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold within the European Economic Area, and API standards for specific applications, also play a significant role in assuring product quality. These certifications not only enhance trust but also facilitate smoother cross-border transactions.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Platinum 3D Printing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining product integrity throughout the manufacturing process. The typical QC stages include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of incoming raw materials, ensuring they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, real-time monitoring ensures adherence to established parameters. This includes checks on layer adhesion, dimensional accuracy, and adherence to design specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After finishing, a thorough inspection is conducted to confirm that the final product meets all quality and aesthetic standards. This may involve visual inspections, dimensional checks, and material testing.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Platinum 3D Printed Products?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and performance of platinum 3D printed products. These include:
-
Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measuring tools, manufacturers verify that the dimensions of the printed parts align with design specifications.
-
Mechanical Testing: This involves assessing the strength, ductility, and hardness of the finished products to ensure they can withstand intended usage conditions.
-
Surface Roughness Measurement: Surface quality is critical, especially for jewelry applications. Testing for surface roughness helps ensure that products will meet consumer expectations.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. Key strategies include:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. This helps in building a trustworthy supplier relationship.
-
Requesting QC Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide detailed QC reports that outline their testing methods, results, and compliance with relevant standards. This documentation is essential for transparency.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes and the integrity of their products.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control nuances. These include variations in local regulations, differing standards of quality, and potential logistical challenges in sourcing materials and transporting products.
Understanding the regulatory landscape in the buyer’s region is critical. For instance, compliance with local environmental regulations may impact material sourcing and manufacturing processes. Additionally, the quality perception can vary across markets; thus, establishing clear communication with suppliers about quality expectations is essential.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in platinum 3D printing are complex yet crucial for delivering high-quality products. By understanding these processes and implementing effective quality control strategies, B2B buyers can ensure they receive products that meet their specifications and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘platinum 3d printing’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed for B2B buyers seeking to procure platinum 3D printing services. With the growing demand for intricate and high-quality designs in sectors such as jewelry and luxury goods, understanding the procurement process is essential. This checklist outlines critical steps to ensure you select the right supplier and materials for your platinum 3D printing needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by establishing clear technical requirements for your project. This includes the desired dimensions, tolerances, and design complexities that the platinum 3D printing process must accommodate.
– Considerations: Ensure you account for the limitations of 3D printing technology, such as wall thickness and detail requirements, to avoid issues during production.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers specializing in platinum 3D printing. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry.
– Key Factors: Review their portfolio, focus on past projects similar to your needs, and assess their technological capabilities, particularly their use of advanced methods like Metal Binder Jet technology.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with industry standards. This step is crucial to ensure quality and reliability in their processes.
– Look For: ISO certifications, adherence to safety and environmental regulations, and any industry-specific accolades that demonstrate their commitment to quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Prototypes
Request samples or prototypes of previous work to evaluate the quality and craftsmanship of the supplier’s products. This can provide insight into their ability to deliver intricate designs.
– Important Notes: Pay attention to detail, finish quality, and material properties. Assess whether their output meets your specifications and design expectations.
Step 5: Discuss Production Capabilities and Lead Times
Engage with suppliers to understand their production capabilities, including the technology they use and their capacity to meet your volume requirements.
– Key Questions: Inquire about their typical lead times, scalability for larger orders, and how they handle rush requests. This will help you align your project timelines with their capabilities.
Step 6: Understand Pricing Structures and Terms
Clarify the pricing models used by potential suppliers to avoid unexpected costs. Different suppliers may have varying pricing structures based on factors like material, design complexity, and production volume.
– Considerations: Ensure that all costs, including setup fees and post-processing, are transparent. Look for suppliers who offer flexible payment terms that suit your budget.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Develop a clear communication strategy with your chosen supplier to facilitate smooth collaboration. Effective communication is essential for addressing any issues that may arise during the design and production phases.
– Best Practices: Set regular check-ins, define points of contact, and establish protocols for feedback and revisions. This proactive approach will help ensure that your project stays on track and meets your expectations.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for platinum 3D printing, ensuring they select the right suppliers and achieve their design objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for platinum 3d printing Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Platinum 3D Printing?
In the realm of platinum 3D printing, the cost structure is multifaceted, comprising several critical components. Material costs are the most significant, particularly as platinum is one of the most expensive metals used in manufacturing. Typically, the alloy consists of 95% platinum and 5% ruthenium, both of which contribute to higher costs due to their market prices.
Labor costs also play a pivotal role, especially given the specialized skills required for handling and processing platinum. Skilled labor is essential for ensuring precision in design and execution, which further adds to the overall expenditure. Manufacturing overhead encompasses the costs of equipment, maintenance, and utilities, particularly since platinum requires high-temperature processing techniques that demand advanced machinery and tools.
Tooling costs are another crucial element, as the high melting point of platinum (around 1900°C) necessitates the use of specialized, durable tools that can withstand extreme conditions. This leads to a higher upfront investment in tooling compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Additionally, quality control (QC) processes must be stringent, given the high stakes involved in producing luxury items such as jewelry, which may incur extra costs for testing and certification.
Finally, logistics costs should not be overlooked. The transportation of platinum materials and finished products often involves significant expenses due to the value and weight of the materials, as well as compliance with international shipping regulations. Lastly, suppliers typically add a margin that reflects their operational costs and desired profit levels.
How Do Pricing Influencers Impact Platinum 3D Printing Costs?
Several key factors influence the pricing of platinum 3D printing services. Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQ) are critical; higher volumes can lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Specifications and customization also affect pricing—complex designs requiring intricate detailing will typically incur higher costs due to increased material and labor requirements.
The choice of materials significantly impacts costs, especially if premium grades or specialized finishes are desired. Quality certifications can further influence pricing; suppliers with recognized certifications may charge a premium due to their commitment to high standards and reliability.
Additionally, supplier factors such as location, reputation, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Suppliers with extensive experience in platinum 3D printing may offer better quality and service, justifying higher costs. Incoterms also play a role in the final pricing, as they dictate shipping responsibilities and risks, impacting overall logistics costs.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use to Optimize Costs?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of platinum 3D printing pricing is essential for cost efficiency. Buyers should focus on negotiation strategies that leverage their purchasing power, especially when ordering in bulk.
Exploring Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is crucial; this involves assessing not just the upfront costs but also long-term expenses, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential waste. Buyers should also be aware of pricing nuances associated with different regions. For instance, factors such as tariffs, import duties, and local market conditions can significantly affect the final price.
Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service agreements, as suppliers may be more willing to offer discounts or favorable terms to repeat customers. Additionally, being open to alternative specifications or materials that meet the necessary quality standards can also lead to cost savings.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While this analysis provides a framework for understanding the costs and pricing of platinum 3D printing, it is essential to note that prices can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their unique needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing platinum 3d printing With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Platinum 3D Printing
In the realm of advanced manufacturing, particularly in the jewelry and luxury sectors, platinum 3D printing stands out due to its unique properties and capabilities. However, businesses often seek alternative solutions that may better align with their specific needs, budget constraints, or production requirements. This section compares platinum 3D printing against two viable alternatives: traditional platinum casting and 3D printing using alternative metals, such as titanium.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Platinum 3D Printing | Traditional Platinum Casting | 3D Printing with Alternative Metals (e.g., Titanium) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, complex designs possible | Good for traditional designs, less complex | Good precision, varies with metal quality |
| Cost | Higher initial setup and material costs | Generally lower initial costs but higher labor costs | Generally lower material costs than platinum |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized equipment and skills | Established processes, easier for traditional jewelers | Easier to implement; widely available technology |
| Maintenance | Requires specific maintenance for printers | Low maintenance, but labor-intensive | Low maintenance, depending on the metal used |
| Best Use Case | Complex, custom designs in luxury items | High-volume, traditional pieces | Prototyping and lower-cost custom items |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Traditional Platinum Casting
Traditional platinum casting is a well-established method that has been used for decades in jewelry manufacturing. The process involves creating a mold and pouring molten platinum into it. One of its main advantages is the lower initial investment compared to 3D printing technologies. However, this method is less suited for intricate designs due to limitations in mold complexity. Additionally, the labor-intensive nature of casting can lead to higher long-term costs, especially in low-volume production scenarios.
3D Printing with Alternative Metals (e.g., Titanium)
Using alternative metals like titanium for 3D printing presents an attractive option for businesses looking for cost-effective solutions. Titanium offers good strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications. The 3D printing process for titanium is more accessible and generally incurs lower material costs than platinum. However, the downside includes the potential compromise on the luxury appeal that platinum offers, as well as the need for post-processing to achieve desired finishes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
For B2B buyers in the jewelry and luxury sectors, the choice between platinum 3D printing and its alternatives hinges on several factors, including the desired complexity of designs, cost considerations, and production methods. If intricate, high-value pieces are the goal, platinum 3D printing may justify its higher costs through enhanced design possibilities. Conversely, for businesses focused on more traditional designs or lower-cost production, traditional casting or alternative metals may be more appropriate. Ultimately, aligning the choice with the specific requirements of the project, including budget and design intent, will lead to the best outcomes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for platinum 3d printing
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Platinum 3D Printing?
Understanding the essential technical properties of platinum 3D printing is crucial for businesses looking to leverage this advanced manufacturing process. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: Platinum used in 3D printing is often alloyed with ruthenium, resulting in a composition commonly referred to as Platinum 950 (95% platinum and 5% ruthenium). This grade is essential for ensuring the durability and aesthetic quality of the final product, especially in high-end jewelry applications.
-
Tolerance: Tolerances in platinum 3D printing typically range from ±0.1 to 0.15 mm for precision parts. Understanding tolerance levels is vital for ensuring that components fit together as intended, particularly in intricate designs where precision is key.
-
Bounding Box Dimensions: The maximum and minimum bounding box dimensions dictate the size of the models that can be printed. For platinum, the maximum dimensions may reach up to 89 × 89 × 100 mm, while the minimum is 2.4 × 2.4 × 0.6 mm. Being aware of these limits helps manufacturers design parts that can be effectively produced without resizing or compromising detail.
-
Wall Thickness: Supported walls must be at least 0.8 mm thick to withstand the printing and cleaning processes. Unsupported walls should also meet this minimum requirement. This specification is crucial for ensuring the structural integrity of the printed item, especially when dealing with complex geometries.
-
Detailing Capabilities: The ability to achieve embossed details of at least 0.4 mm high and engraved details of 0.35 mm is significant for creating intricate designs. This property allows for the production of highly detailed jewelry and components that stand out in the market.
-
Shrinkage Rate: After casting and finishing, platinum parts can shrink by approximately 2.5%, plus an additional 0.25 mm. Understanding this shrinkage is important for designers to account for dimensional accuracy in the final product, especially in applications where fit is critical.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know About Platinum 3D Printing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can significantly streamline communication and decision-making processes. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of platinum 3D printing, an OEM might utilize 3D printing technology to create intricate components for luxury goods.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory costs and procurement strategies, especially when dealing with high-value materials like platinum.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing businesses to compare options and negotiate costs for platinum 3D printing services.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping logistics, risk management, and cost allocation in transactions involving platinum 3D printing.
-
Additive Manufacturing: This term refers to the process of creating objects layer by layer, often using 3D printing technology. Understanding additive manufacturing is crucial for businesses, as it presents unique advantages in terms of design flexibility and material efficiency, particularly with complex materials like platinum.
-
3D Metal Binder Jet Technology: This is a specific method of 3D printing that utilizes a binding agent to create metal parts. This technology is particularly relevant for platinum, as it allows for the production of intricate designs that traditional methods cannot achieve, thus broadening the scope of applications in luxury goods.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding platinum 3D printing, ensuring they meet their business needs effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the platinum 3d printing Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Platinum 3D Printing?
The platinum 3D printing sector is experiencing robust growth driven by several global factors. The demand for luxury and high-end jewelry continues to rise, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America, where there is a growing affluent consumer base. Additionally, the Middle East’s luxury market is expanding, with a keen interest in bespoke jewelry pieces. In Europe, particularly Germany, the focus is on innovative design and technology, pushing manufacturers to adopt advanced 3D printing techniques.
Emerging technologies, such as 3D metal binder jetting, are revolutionizing the way platinum is processed. This method allows for the creation of complex designs that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques, thereby reducing production costs and time. The ability to create intricate designs with less material waste is particularly appealing to B2B buyers looking to optimize their supply chains. Furthermore, as sustainability becomes a priority, companies are increasingly adopting additive manufacturing methods that promote more efficient resource use.
Another significant trend is the integration of digital tools in the design and manufacturing process. B2B buyers are now leveraging software that enhances design capabilities, enabling them to visualize and customize products before production. This trend is particularly beneficial in sectors like jewelry, where personalization is key to attracting customers.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Addressed in Platinum 3D Printing?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the platinum 3D printing industry. Traditional platinum sourcing often involves environmentally destructive mining practices. In contrast, 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the necessary amount of material, making it a more eco-friendly option. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing practices.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially as consumers become more conscious of the origins of their purchases. Companies that provide transparency in their sourcing processes and adhere to ethical standards are more likely to attract discerning B2B buyers. Certifications for ‘green’ materials and processes can serve as a significant differentiator in the marketplace.
Moreover, the industry is witnessing an uptick in collaborations aimed at developing sustainable practices. For instance, initiatives that focus on recycling platinum and other precious metals are gaining traction, presenting opportunities for B2B buyers to engage with suppliers who contribute to a circular economy.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Platinum 3D Printing?
The evolution of platinum 3D printing has been marked by significant technological advancements. Initially, platinum was predominantly utilized in traditional jewelry-making processes, which were labor-intensive and limited in design flexibility. However, the introduction of 3D printing technologies, particularly in the last decade, has transformed the landscape.
Early experiments in 3D printing with platinum faced challenges due to the metal’s high melting point and unique properties. As technologies like 3D metal binder jetting emerged, manufacturers began to unlock the potential of platinum, allowing for intricate designs and reducing production costs. This evolution has not only expanded the range of products available but has also paved the way for innovative applications in sectors beyond jewelry, including luxury watches and high-end decorative items.
Today, platinum 3D printing stands at the intersection of art and technology, offering endless possibilities for customization and design that cater to the sophisticated tastes of global consumers. As this sector continues to mature, it presents a wealth of opportunities for international B2B buyers looking to differentiate their offerings in a competitive market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of platinum 3d printing
-
How do I choose the right supplier for platinum 3D printing?
Selecting a reliable supplier for platinum 3D printing involves several key considerations. First, evaluate the supplier’s experience and expertise in working with platinum, particularly their use of advanced technologies like 3D Metal Binder Jetting. Request case studies or references to assess their past projects. Additionally, check certifications and compliance with international quality standards. Engaging in direct communication about your specific requirements will also help gauge their responsiveness and customer service. Lastly, consider their geographic location and logistics capabilities, especially if you’re sourcing from regions like Africa or South America. -
What are the typical lead times for platinum 3D printing projects?
Lead times for platinum 3D printing can vary significantly based on the complexity of the design, the supplier’s capacity, and the production method employed. Generally, you can expect a timeframe ranging from two to six weeks for initial prototypes. For larger production runs, lead times may extend to several months, especially if custom tooling or extensive quality assurance processes are required. It’s advisable to discuss timelines upfront with your supplier to align expectations and ensure timely delivery of your products. -
What customization options are available for platinum 3D printing?
Platinum 3D printing offers extensive customization possibilities, including intricate designs, unique textures, and personalized engravings. You can specify dimensions, shapes, and finishes based on your project requirements. The additive manufacturing process allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional methods cannot achieve, making it ideal for bespoke jewelry or specialized industrial components. Always provide detailed specifications and collaborate closely with your supplier to ensure that your vision is accurately translated into the final product. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for platinum 3D printing?
Minimum order quantities for platinum 3D printing can vary by supplier and project specifications. Generally, MOQs may range from a single prototype to several dozen pieces, depending on the complexity of the designs and the production capabilities of the manufacturer. For custom or specialized designs, suppliers may be more flexible with MOQs, especially if you’re establishing a long-term partnership. It’s beneficial to negotiate these terms early in the conversation to align your production needs with the supplier’s capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect for platinum 3D printing services?
Payment terms for platinum 3D printing services can differ widely among suppliers and may be influenced by your relationship with them. Common arrangements include partial upfront payments followed by the balance upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, allowing you to pay within a specified period after receipt of goods. It’s crucial to discuss and agree on payment structures upfront to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place for platinum 3D printing?
Quality assurance in platinum 3D printing is vital to ensure that the final products meet your specifications and industry standards. Look for suppliers that implement rigorous QA processes, including dimensional inspections, surface finish evaluations, and material composition testing. Additionally, inquire about their certification to quality management systems, such as ISO 9001. A transparent QA process should include the ability to provide documentation and reports, allowing you to verify the quality of the products before acceptance. -
How does international shipping work for platinum 3D printed products?
International shipping for platinum 3D printed products involves several logistical considerations, including customs regulations, tariffs, and shipping methods. Choose suppliers that have experience with international logistics to ensure compliance with local laws and efficient delivery. Discuss shipping options—air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is more economical but slower. Additionally, confirm the packaging methods used to protect your products during transit and inquire about insurance options for high-value shipments. -
What are the environmental impacts of platinum 3D printing?
Platinum 3D printing can offer environmental benefits compared to traditional manufacturing methods. The additive nature of 3D printing reduces material waste, as only the necessary amount of platinum powder is used in the process. Moreover, advances in technology minimize energy consumption during production. However, it’s essential to consider the sourcing of platinum, as ethical mining practices are crucial. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and responsible sourcing can further enhance the environmental credentials of your platinum 3D printing projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Platinum 3D Printing Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Shapeways – Platinum 3D Printing Material
Domain: shapeways.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: Platinum 3D Printing Material Information:
– Material Composition: 95% Platinum, 5% Ruthenium
– Technology: Wax Casting
– Highlights: High quality & professional finishing, capable of intricate details
– Handling and Care: Skin-friendly, good electrical conductance
– Design Guidelines:
– Maximum Bounding Box: 89 × 89 × 100 mm
– Minimum Bounding Box: 2.4 × 2.4 × 0.6 mm
– Supported Wal…
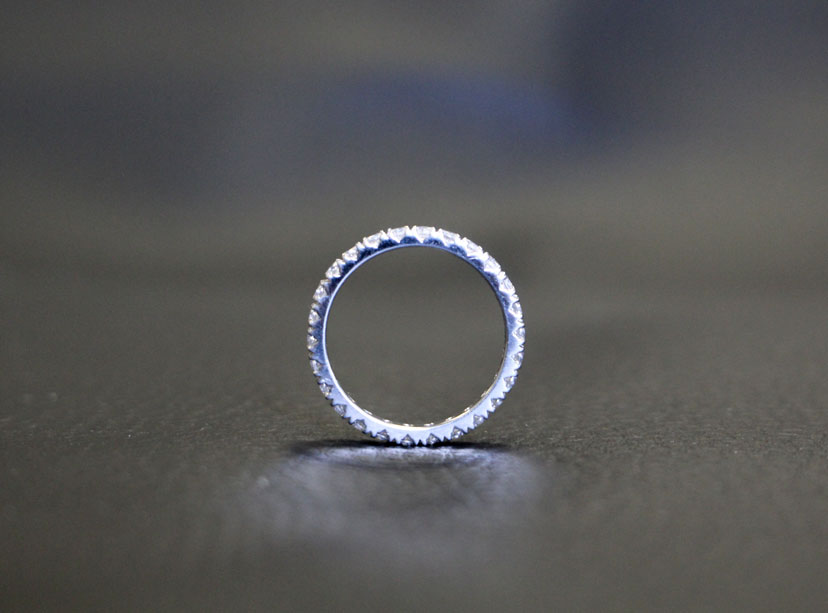
2. Reddit – 3D Printed Platinum Ring with Diamond
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 3D printed ring in platinum, specifically 950 platinum, weighing approximately 10 grams. The ring features a high-quality princess cut diamond of 0.35 carats with an HRD certificate. The estimated cost of the ring is around 1,000 USD.
3. Platinum Investment – Tùsaire Collection
Domain: platinuminvestment.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: The Tùsaire Collection is a 30-piece innovative platinum jewellery range launched through a collaboration between Platinum Guild International (PGI) and designer Maeve Gillies. It features platinum and titanium torc necklaces with interchangeable elements such as cuffs, rings, and earrings. The centerpiece is a platinum necklace set with Scottish Renfrewshire quartz, named ‘King of the Mountains.’…
4. Progol3D – Advanced Direct Metal 3D Printing
Domain: progol3d.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Direct Metal 3D Printing in 18k Gold, Platinum, and Titanium; Selective Laser Melting technology; Integrated Business Model; Internal R&D Department; Six Metals; Mechanical and physical properties of metals; Printing Area and Resolution; Casting capabilities including hollow objects, tailored weight, density benchmarks, roughness benchmarks, thickness and surface benchmarks; Green Technology; Supp…
5. Formfutura – Platinum LCD Resin
Domain: formfutura.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Platinum LCD Resin – General Purpose”, “sku”: “PTLCDGP-CLEA-00500”, “ean”: “8719956553134”, “price”: “€ 35,12”, “weight”: “500 grams”, “colors”: [“Clear”, “Solid Black”, “Solid Light Grey”, “Solid White”, “Translucent Aquamarine”, “Translucent Black”, “Translucent Blue”, “Translucent Orange”, “Translucent Red”, “Translucent Yellow”], “features”: [“Almost no odour”, “UV & weather resistan…
6. All3DP – Platinum Necklace
Domain: all3dp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: This stunning platinum necklace represents the apex of 3D printed jewelry today.
7. Polar Filament – Retro Platinum PLA
Domain: polarfilament.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Retro Platinum PLA”, “weight”: “1kg”, “diameter”: “1.75mm”, “material_type”: “PLA”, “color”: “Platinum”, “features”: [“High-quality filament”, “Easy to print”, “Low warping”, “Compatible with most 3D printers”], “applications”: [“Prototyping”, “Hobby projects”, “Artistic prints”]}
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for platinum 3d printing
What Are the Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers in Platinum 3D Printing?
The strategic sourcing of platinum 3D printing offers unparalleled advantages in the luxury and jewelry sectors. With its capability for intricate designs and high-quality finishes, platinum 3D printing stands out as a transformative technology. The introduction of advanced methods like 3D Metal Binder Jet technology has made it feasible to overcome traditional manufacturing challenges, significantly reducing costs and enhancing design possibilities. As global demand for platinum jewelry continues to rise, particularly in emerging markets, businesses that adopt these innovative techniques will likely gain a competitive edge.
How Can International Buyers Capitalize on Platinum 3D Printing?
For B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, engaging with suppliers who specialize in platinum 3D printing can unlock new avenues for product development and market expansion. By leveraging the unique attributes of 3D printing, companies can produce bespoke items that cater to evolving consumer preferences while minimizing material waste.
What’s Next for Your Business in Platinum 3D Printing?
As we look toward the future, the potential for platinum 3D printing remains robust. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to explore partnerships with innovative manufacturers and invest in cutting-edge technologies. Embrace the opportunities that platinum 3D printing presents, and position your business at the forefront of this exciting evolution in the jewelry industry.