Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic price
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing plastic at optimal prices presents a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Fluctuations in plastic prices can impact operational budgets and profitability, making it essential for businesses to stay informed about market dynamics. This guide delves into the complexities of the global plastic price landscape, providing actionable insights on various types of plastics, their applications, and effective strategies for supplier vetting.
Buyers will find comprehensive information on the factors influencing pricing, including production costs, transportation logistics, and market demand trends. Additionally, this guide offers a detailed analysis of how to navigate the ever-changing landscape of plastic procurement, equipping businesses with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions.
By addressing key challenges and providing expert recommendations, this resource empowers B2B buyers to optimize their sourcing strategies, ensuring they remain competitive in their respective markets. Whether you’re looking to understand the nuances of resin pricing or seeking reliable suppliers, this guide is designed to be your go-to resource for navigating the global plastic market effectively.
Understanding plastic price Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commodity Plastics | Standardized, high-volume production, low cost | Packaging, construction, automotive | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited customization, quality may vary. |
| Engineering Plastics | High-performance materials with specific properties | Aerospace, medical devices, electronics | Pros: Superior durability and performance. Cons: Higher cost, often longer lead times. |
| Bioplastics | Derived from renewable resources, biodegradable | Food packaging, consumer goods | Pros: Eco-friendly, growing market demand. Cons: Generally higher prices, limited availability. |
| Specialty Resins | Customized formulations for specific applications | Adhesives, coatings, sealants | Pros: Tailored solutions, high performance. Cons: More expensive, may require longer development times. |
| Recycled Plastics | Reprocessed materials from waste plastics | Consumer products, textiles | Pros: Environmentally sustainable, cost savings on raw materials. Cons: Quality may vary, potential supply chain issues. |
What are the characteristics of Commodity Plastics, and how are they suitable for B2B buyers?
Commodity plastics, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are characterized by their high-volume production and low cost. They are commonly used in applications like packaging, construction, and automotive components due to their availability and affordability. B2B buyers often choose commodity plastics for large-scale projects where cost efficiency is crucial. However, the trade-off for lower prices is often limited customization options and variability in quality, which can impact final product performance.
How do Engineering Plastics meet specific business needs?
Engineering plastics, including polycarbonate and nylon, are designed for high-performance applications requiring enhanced durability and specific mechanical properties. They are extensively used in industries such as aerospace, medical devices, and electronics, where performance is paramount. B2B buyers should consider engineering plastics for projects demanding reliability and precision. While these materials offer superior benefits, they come at a higher cost and may involve longer lead times, necessitating careful budget and timeline planning.
What are the advantages and challenges of using Bioplastics in B2B applications?
Bioplastics are innovative materials made from renewable resources, offering biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint. They are increasingly utilized in food packaging and consumer goods, appealing to environmentally conscious businesses. B2B buyers interested in sustainability may find bioplastics advantageous, especially as consumer demand for eco-friendly products rises. However, the higher production costs and limited availability can be a barrier, requiring buyers to assess whether the benefits align with their business goals.
What role do Specialty Resins play in tailored B2B solutions?
Specialty resins are unique formulations designed for specific applications, such as adhesives, coatings, and sealants. These materials provide tailored solutions that meet stringent performance requirements in various industries. B2B buyers benefit from the customization and high performance of specialty resins, which can enhance product efficacy. The downside includes higher prices and potentially longer development times, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their specific needs and timelines when considering these materials.
How do Recycled Plastics contribute to sustainable B2B practices?
Recycled plastics are derived from post-consumer waste, promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact. They are increasingly used in consumer products and textiles, offering a cost-effective alternative to virgin materials. B2B buyers interested in sustainable practices may find recycled plastics appealing due to their potential for cost savings on raw materials. However, challenges such as variable quality and supply chain reliability must be addressed to ensure that products meet the necessary performance standards.
Key Industrial Applications of plastic price
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plastic price | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior components (dashboards, trims) | Reduces manufacturing costs while ensuring durability | Quality of plastic, compliance with safety standards |
| Packaging | Creation of flexible packaging solutions | Enhances product shelf life and reduces waste | Material type, cost efficiency, and sustainability |
| Construction | Use in insulation materials and piping | Improves energy efficiency and reduces overall costs | Thermal properties, local regulations, and sourcing reliability |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of housings and components | Provides lightweight, durable solutions for devices | Precision requirements, material grades, and lead times |
| Consumer Goods | Production of durable goods (toys, household items) | Offers cost-effective solutions without compromising quality | Supply chain stability, international shipping costs |
How is ‘plastic price’ utilized in the automotive industry, and what are the benefits for B2B buyers?
In the automotive sector, the price of plastics significantly affects the production of interior components such as dashboards and trims. The use of lightweight plastics helps manufacturers reduce vehicle weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and lower emissions. For international buyers, particularly those in Africa and South America, understanding the fluctuations in plastic prices is essential for budget planning and cost control. Buyers must ensure that the plastics sourced meet specific safety and quality standards to comply with regulations in their respective markets.
What role does plastic price play in packaging solutions for B2B buyers?
Plastic price is crucial in the packaging industry, where flexible packaging solutions are in high demand. The right plastic materials enhance product shelf life and reduce waste, making them attractive for businesses aiming to improve sustainability. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, sourcing cost-effective and high-quality packaging materials can significantly impact profit margins. Buyers should consider the type of plastic used, its recyclability, and the overall supply chain dynamics to ensure they get the best value.
How does the construction industry benefit from understanding plastic price?
In construction, plastics are often used in insulation materials and piping systems. The fluctuating prices of these materials can affect project budgets and timelines. By leveraging the advantages of plastics, such as energy efficiency and durability, construction companies can reduce overall costs. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America need to be aware of local regulations regarding building materials and ensure that their suppliers can provide reliable sourcing options that meet these standards.
Why is plastic price important for electronics manufacturing?
The electronics sector relies heavily on plastics for the production of housings and components. The lightweight nature of plastics allows for more efficient designs and improved performance of electronic devices. International buyers, especially from Europe and Asia, must navigate the complexities of sourcing high-quality materials that meet stringent industry standards. Factors such as precision requirements and the specific grades of plastic can significantly influence production costs, making it crucial for buyers to stay informed about market trends.
How does plastic price influence the consumer goods industry?
In the consumer goods sector, plastics are widely used in the production of durable items such as toys and household products. The competitive pricing of plastics allows manufacturers to offer high-quality products at lower prices, enhancing market competitiveness. For B2B buyers in regions like South America and Africa, understanding the implications of plastic pricing on production costs is vital. Buyers should also consider the stability of their supply chains and any potential international shipping costs that may arise due to fluctuating prices.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic price’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Fluctuating Resin Prices Create Budget Uncertainty
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the unpredictable nature of plastic resin prices, which can fluctuate significantly due to various market factors, including raw material costs, geopolitical tensions, and supply chain disruptions. For companies in Africa or South America, where budget constraints are more pronounced, these price variations can lead to significant financial strain and hinder long-term planning. Buyers may find themselves in a position where they cannot secure favorable pricing or risk overcommitting to contracts that become unviable.
The Solution: To navigate fluctuating prices effectively, buyers should adopt a dynamic pricing strategy that includes real-time market intelligence and flexible procurement options. Establishing relationships with multiple suppliers can provide leverage during negotiations, allowing buyers to tap into competitive pricing. Additionally, utilizing platforms like The Plastics Exchange, which offer transparent pricing and market insights, can help buyers make informed decisions. Implementing a hedging strategy by purchasing futures contracts for plastic resins can also protect against price spikes, ensuring budget stability while allowing for timely procurement.
Scenario 2: Supply Chain Disruptions Impacting Availability of Plastic
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges related to supply chain disruptions, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, where political and environmental factors can impact the availability of plastic materials. These disruptions can result in delayed shipments, increased costs, and ultimately, production halts. Buyers may struggle to maintain adequate inventory levels, leading to missed opportunities and dissatisfied customers.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of supply chain issues, buyers should focus on diversifying their sourcing strategies. This includes identifying alternative suppliers across different geographical locations to reduce dependency on a single source. Engaging with suppliers that offer on-demand inventory and just-in-time delivery can also enhance responsiveness. Additionally, investing in supply chain visibility tools can provide real-time insights into inventory levels and shipment statuses, allowing for proactive management of potential disruptions. Establishing contingency plans, including safety stock and emergency suppliers, will further safeguard operations against unforeseen delays.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Understanding Pricing Structures of Plastic Products
The Problem: Many international buyers encounter challenges in understanding the complex pricing structures associated with various types of plastics. This confusion is often exacerbated by the lack of standardized pricing models, differing quality levels, and regional price variations. In markets like Vietnam and Germany, where buyers may lack deep industry knowledge, this can lead to costly purchasing mistakes or suboptimal material choices that affect product quality.
The Solution: To overcome this knowledge gap, B2B buyers should invest time in educating themselves about the different types of plastics and their respective pricing models. Engaging with industry experts through webinars, workshops, or trade shows can provide valuable insights. Utilizing resources such as market intelligence platforms, which offer detailed analysis of price trends and quality metrics, can also be beneficial. Establishing a clear set of specifications for required materials will enable buyers to communicate effectively with suppliers, ensuring they receive accurate quotes. Furthermore, leveraging tools like the Resintel Market Update can keep buyers informed of price fluctuations and market dynamics, empowering them to make more strategic purchasing decisions.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic price
What Are the Key Properties of Common Plastic Materials in B2B Applications?
When selecting materials for plastic applications, understanding the properties of common plastics is crucial for optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness. Here, we analyze four widely used plastics: Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS). Each material has unique characteristics that influence its suitability for various applications.
How Does Polyethylene (PE) Perform in B2B Applications?
Polyethylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance and low moisture absorption, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including packaging and containers. It can withstand temperatures up to 80°C (176°F) and is available in various densities, such as Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
Pros: PE is lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for many industries. Its recyclability also aligns with sustainability goals.
Cons: While PE is durable, it can become brittle at lower temperatures and has limited resistance to UV radiation, which may lead to degradation over time.
Impact on Application: PE is compatible with food products, making it ideal for packaging in the food and beverage sector. However, B2B buyers should consider local regulations regarding food safety standards.
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Polypropylene (PP)?
Polypropylene is notable for its high melting point, around 160°C (320°F), and excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for applications that require repeated bending or flexing, such as automotive parts and textiles.
Pros: PP is lightweight, resistant to many chemicals, and has a good balance of rigidity and flexibility. It is also less expensive than many engineering plastics.
Cons: Its UV resistance is limited, and it can be prone to stress cracking when exposed to certain chemicals.
Impact on Application: PP is widely used in automotive and consumer goods. International buyers must ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ASTM and ISO, to guarantee product quality.
How Does Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Compare in Terms of Performance?
PVC is a versatile plastic available in both rigid and flexible forms. It offers excellent durability and resistance to environmental factors, including moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for construction materials, pipes, and medical devices.
Pros: PVC is cost-effective and can be easily processed. Its mechanical properties make it suitable for a variety of applications.
Cons: The production and disposal of PVC can raise environmental concerns due to the release of harmful chemicals. Additionally, it has a lower temperature resistance compared to other plastics.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in construction and plumbing. B2B buyers in regions with stringent environmental regulations must consider the sustainability of PVC products.
What Makes Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) a Preferred Choice?
ABS is an engineering plastic known for its toughness and impact resistance, making it suitable for applications like consumer electronics and automotive components. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C (212°F).
Pros: ABS is easy to mold and offers a good surface finish, making it aesthetically pleasing for consumer products. It also provides excellent dimensional stability.
Cons: ABS is less resistant to UV light and can degrade over time if exposed to sunlight. Additionally, it can be more expensive than other commodity plastics.
Impact on Application: ABS is widely used in the automotive and electronics industries. Buyers should ensure that products meet international standards, such as DIN or JIS, for quality assurance.
Summary Table of Common Plastic Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic price | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Packaging, containers | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited UV resistance | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Automotive parts, textiles | High melting point | Prone to stress cracking | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Construction materials, pipes | Cost-effective and durable | Environmental concerns | Low |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer electronics, automotive | Toughness and impact resistance | Less UV resistant | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the properties, advantages, and limitations of common plastic materials. By understanding these factors, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic price
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Processes for Plastic Products?
The manufacturing of plastic products involves several critical stages, each designed to optimize the efficiency, quality, and sustainability of the final product. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Processed?
The first stage of plastic manufacturing begins with the preparation of raw materials, typically in the form of resin pellets. These pellets are made from polymers derived from petrochemical sources. During this stage, the pellets may be blended with additives to enhance specific properties like strength, flexibility, or UV resistance. This blending can be achieved through processes such as compounding, where heat and shear are applied to mix the resins thoroughly.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Plastics?
Once the material is prepared, the next step is forming, which encompasses several techniques depending on the desired product. Common methods include:
- Injection Molding: This involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create complex shapes. It is widely used for producing high-volume items like containers and automotive parts.
- Blow Molding: Used primarily for hollow objects like bottles, this method involves inflating a heated plastic tube within a mold.
- Extrusion: In this process, plastic is melted and pushed through a die to create continuous shapes, such as pipes or sheets.
- Thermoforming: This technique uses heat to soften plastic sheets, which are then formed over a mold to create products like trays and packaging.
Each forming method has its own advantages and is selected based on factors such as the complexity of the part, production volume, and material properties.
Assembly: How Are Plastic Products Assembled?
After forming, the next stage is assembly. This may involve joining multiple plastic components using techniques like welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening. For example, automotive plastic parts may require precision assembly to ensure proper fit and function. This stage is crucial for products that require intricate designs or multi-part assemblies.
Finishing: What Processes Enhance Product Quality?
The finishing stage includes surface treatments and coatings that improve the aesthetic appeal and functional performance of the plastic product. Techniques such as painting, printing, and polishing are common, and they can enhance properties like chemical resistance and durability. Additionally, this stage may involve quality checks to ensure that the product meets customer specifications.
What Quality Control Measures Are Essential in Plastic Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is a vital aspect of the plastic manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key quality control (QC) measures include adherence to standards such as ISO 9001, CE marking, and API specifications, which are critical for international B2B transactions.
What International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is a globally recognized standard that outlines criteria for a quality management system. Compliance with this standard indicates that a manufacturer consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. CE marking signifies that a product meets European safety, health, and environmental protection standards, which is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe.
In the context of plastics, API standards may apply for manufacturers producing components for the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products can withstand specific environmental conditions.
What Are the Key QC Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control in plastic manufacturing typically involves several checkpoints, including:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial check assesses the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis (CoA) to validate the material’s specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, IPQC monitors various parameters such as temperature, pressure, and cycle times to ensure that processes remain within specified limits. This proactive approach helps identify potential issues before they affect the final product.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, FQC involves thorough inspections and testing of the finished products. Common testing methods include dimensional checks, mechanical property assessments, and visual inspections to detect defects.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is crucial for ensuring product reliability. Here are several strategies to achieve this:
What Auditing Options Are Available for Suppliers?
Conducting supplier audits is an effective way to evaluate a manufacturer’s quality control processes. Buyers can request audits to assess compliance with international standards and the supplier’s internal quality management systems. Audits can be performed by the buyer’s quality team or outsourced to third-party inspection agencies.
How Can Buyers Access Quality Reports?
Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their QC practices. These reports should include data on production processes, inspection results, and any corrective actions taken in response to quality issues. Transparency in reporting fosters trust and helps buyers make informed decisions.
What Role Do Third-Party Inspections Play?
Engaging third-party inspection services can further enhance confidence in a supplier’s quality control measures. These independent agencies can perform inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specified standards before shipment. This is particularly important when sourcing from regions with varying regulatory environments.
What Are the Specific QC Considerations for International B2B Transactions?
When dealing with international suppliers, B2B buyers should be aware of specific quality control nuances that may arise due to differences in standards, regulations, and manufacturing practices.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Quality Control?
Different regions may have varying standards and regulations governing plastic production. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local requirements in the supplier’s country and ensure that their products comply with both local and international standards. This knowledge can prevent costly delays and ensure smooth importation.
What Should Buyers Know About Cultural and Communication Barriers?
Cultural differences can also impact quality control practices. Establishing clear communication channels and expectations is vital for ensuring that suppliers understand the buyer’s quality standards. Regular follow-ups and open discussions can help bridge any gaps that may arise due to language barriers or differing business practices.
By understanding the intricacies of manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality plastic products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic price’
In today’s competitive market, sourcing plastics effectively is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their supply chain while managing costs. This guide provides a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure plastics at the best prices while ensuring quality and reliability.
1. Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Start by clearly outlining your technical requirements for the plastic materials you need. This includes the type of resin (e.g., LDPE, HDPE, LLDPE), desired properties (e.g., flexibility, durability), and any certifications required for compliance. Precise specifications help in obtaining accurate quotes and ensure you receive the right product for your application.
2. Step 2: Research Market Trends and Pricing
Stay informed about current market conditions by reviewing industry reports and price indices. Utilize resources such as the Producer Price Index for plastics and market intelligence platforms like The Plastics Exchange. Understanding price fluctuations and demand trends can help you make informed purchasing decisions and negotiate better terms.
3. Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, conduct a thorough evaluation. Request detailed company profiles, including their production capabilities, quality assurance processes, and customer references. Look for suppliers with proven track records in your region, as local knowledge can significantly impact logistics and service quality.
4. Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your chosen suppliers possess the necessary certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO standards or compliance with environmental regulations. Certifications are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to quality and sustainability, which can minimize risks associated with product defects or regulatory issues.
5. Step 5: Assess Inventory Levels and Lead Times
Check the supplier’s inventory availability and expected lead times for delivery. Suppliers with extensive stock and efficient logistics can provide faster turnaround times, which is crucial for maintaining your production schedules. Ask about their ability to handle fluctuations in demand and their processes for managing stock levels.
6. Step 6: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you’ve identified potential suppliers, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be clear about your expectations and seek flexible terms that accommodate your purchasing patterns. A well-negotiated agreement can significantly enhance your cash flow and inventory management.
7. Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
After selecting a supplier, establish a clear communication plan to ensure ongoing collaboration. Regular updates about order status, market changes, and potential supply chain disruptions are vital. Open lines of communication foster a stronger partnership and can help address issues proactively as they arise.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing processes for plastics, ensuring they secure competitive prices while maintaining quality and reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic price Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Plastic Price Sourcing?
When sourcing plastics, understanding the cost structure is vital for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The base cost of raw materials, such as resin, significantly influences the total price. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and availability, which are impacted by global supply chain dynamics.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages for workers involved in production, which can vary widely based on the region and the skill level required. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can also affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can reduce overhead, leading to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: For custom plastic parts, tooling costs can be substantial. These are one-time costs related to creating molds and dies necessary for production, and they can be amortized over large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet specified standards incurs costs related to testing and inspection. Investing in quality assurance can prevent costly returns and enhance customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly affect the final price. Factors like distance, mode of transport, and freight rates need to be considered, especially for international transactions.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This can vary based on market conditions and competition.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Plastic Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of plastics, including:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Bulk purchasing often leads to discounts, as suppliers are more inclined to negotiate favorable terms for larger orders. Understanding the MOQ can help buyers optimize their purchasing strategies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs due to the need for specialized tooling and processes. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of custom features against potential cost increases.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality materials typically come at a premium. Certifications for food safety, environmental standards, or other regulatory requirements can also affect pricing.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capacity can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk, impacting the overall cost of sourcing plastics.
What Are Some Essential Buyer Tips for Plastic Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing power by negotiating terms based on volume and long-term commitments. Suppliers may offer better pricing for repeat business or larger orders.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the total cost of ownership, which includes not only the purchase price but also shipping, handling, and potential wastage. This holistic view can lead to better decision-making.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that can affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can sometimes mitigate these risks.
-
Market Research: Regularly monitor market trends and price reports to stay informed about fluctuations in resin prices and other cost factors. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
-
Quality Considerations: While lower prices may be appealing, consider the long-term implications of quality. Investing in higher-quality materials may reduce overall costs by minimizing defects and returns.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of plastic price sourcing requires a deep understanding of cost structures, pricing influencers, and strategic negotiation tactics. By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business goals and ensure cost-effective procurement. Always remember that prices can vary significantly based on market conditions, and it’s prudent to seek multiple quotes before making a final decision.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic price With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Plastic Pricing
In the evolving landscape of materials sourcing, B2B buyers are increasingly seeking alternatives to traditional plastic products. This analysis highlights two viable alternatives—bioplastics and metals—comparing them against conventional plastic pricing. Understanding the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases of these materials will help buyers make informed decisions that align with their sustainability goals and operational needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Plastic Price | Bioplastics | Metals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability and versatility for various applications | Comparable to plastics but may vary by type | Excellent strength and longevity |
| Cost | Generally lower, with prices fluctuating based on resin market | Higher initial costs but decreasing with technology | Higher material costs, plus additional processing costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Established supply chains and manufacturing processes | Growing availability, but still less common | Requires specialized equipment for fabrication |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance in most applications | Similar to traditional plastics | Requires regular maintenance to prevent corrosion |
| Best Use Case | Packaging, automotive parts, consumer goods | Food packaging, disposable cutlery, and biodegradable items | Structural components, high-load applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Bioplastics?
Bioplastics are derived from renewable resources and often designed to be biodegradable. Their primary advantage is the reduced environmental impact compared to conventional plastics. They serve well in applications like food packaging and disposable items, which align with the increasing consumer demand for sustainable options. However, bioplastics can be more expensive upfront and may not perform as well under certain conditions, such as high temperatures. Their availability can also be limited, making sourcing a challenge for some B2B buyers.
How Do Metals Compare as an Alternative to Plastic Pricing?
Metals, such as aluminum and steel, offer exceptional strength and longevity, making them suitable for high-load applications. They are highly recyclable, which can contribute to sustainability goals. However, the cost of metals is typically higher than plastics, and the processing requires specialized equipment that can increase overall production costs. Additionally, metals can be heavier, which might not be ideal for all applications, particularly in sectors like packaging where weight is a critical factor.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
Choosing the right material solution requires a thorough understanding of specific application needs, cost considerations, and environmental impact. B2B buyers should evaluate the performance requirements of their products, the total cost of ownership, and the ease of sourcing and implementing alternatives. By considering these factors and staying informed about market trends, businesses can make strategic decisions that not only optimize their supply chain but also align with their sustainability goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic price
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Plastic Pricing?
Understanding the technical properties of plastics is essential for B2B buyers as they navigate pricing and procurement decisions. Here are some critical specifications that influence plastic prices:
-
Material Grade
Material grades, such as High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) or Polypropylene (PP), dictate the performance characteristics of the plastic. Different grades are suitable for various applications, impacting pricing due to their unique properties. For instance, HDPE is known for its durability and resistance to impact, making it more expensive than lower-grade options. Buyers must select the appropriate material grade based on their end-use requirements to avoid costly mistakes. -
Melt Flow Index (MFI)
The Melt Flow Index measures the viscosity of a plastic material when melted, indicating how easily it can be processed. A lower MFI typically signifies a higher molecular weight and better mechanical properties, while a higher MFI indicates easier processing but potentially lower strength. Understanding MFI is crucial for manufacturers to optimize production processes and minimize waste, directly influencing cost efficiency. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in plastic products. Precise tolerances are vital for components that require tight fits, such as in automotive or aerospace applications. When tolerance levels are not met, it can lead to product failures or increased rework costs. Hence, understanding tolerances helps buyers gauge manufacturing capabilities and ensure product quality. -
Additives and Fillers
The inclusion of additives (like UV stabilizers) or fillers (such as talc or calcium carbonate) can enhance the properties of plastic materials, affecting both performance and cost. Additives improve characteristics like UV resistance or flame retardancy, while fillers can reduce material costs and weight. Buyers should consider how these factors influence overall plastic pricing and product suitability for their applications. -
Impact Resistance
This property measures how well a plastic can withstand sudden shocks or impacts without breaking. Materials with high impact resistance are often more expensive due to the enhanced processing techniques and raw materials involved. Understanding this property is essential for applications where safety and durability are paramount, such as in consumer goods or construction materials.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Plastic Pricing?
Familiarity with industry terminology is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding this term is vital as it impacts pricing structures and supply chain dynamics. Buyers often work with OEMs for custom solutions, requiring clear communication regarding specifications and pricing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for budgeting and inventory management, as suppliers may impose higher prices for lower quantities. Buyers should assess their purchasing needs against MOQs to avoid excess inventory or increased costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better deals. Crafting a precise RFQ can lead to more favorable pricing and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, particularly regarding shipping and delivery. Familiarity with terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) helps buyers understand their cost obligations and risks in cross-border transactions. Properly negotiated Incoterms can significantly impact overall pricing. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. It is an essential factor for inventory planning and production schedules. Understanding lead times can help buyers manage their supply chains effectively and avoid disruptions that may affect pricing and profitability.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure the right materials at competitive prices while maintaining quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic price Sector
What Are the Key Trends Driving the Global Plastic Price Market?
The global plastic price market is influenced by various dynamics, primarily characterized by fluctuating demand and supply chain complexities. Key drivers include economic recovery post-pandemic, rising demand for packaging materials, and significant shifts in consumer behavior towards sustainable products. In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the emphasis on e-commerce has led to increased consumption of plastic for packaging, which in turn affects pricing structures.
Emerging B2B technologies are reshaping sourcing trends. Digital marketplaces like The Plastics Exchange facilitate real-time transactions, making it easier for buyers to access transparent pricing and inventory levels. Furthermore, advanced analytics platforms provide insights into market trends, helping businesses forecast pricing and make informed purchasing decisions. For international buyers, understanding local market conditions and geopolitical factors is crucial, as these can significantly impact freight costs and lead times.
Additionally, the ongoing transition towards circular economies is impacting sourcing strategies. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that offer recycled materials or participate in take-back programs. This trend is particularly pronounced in Europe, where regulatory frameworks encourage sustainable practices. As a result, buyers must remain agile and informed about shifts in production capabilities and material availability to navigate the dynamic landscape effectively.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Plastic Sourcing Decisions in B2B?
Sustainability has emerged as a pivotal factor in shaping sourcing decisions within the plastic price sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and waste is prompting companies to reassess their supply chains and opt for more sustainable practices. International buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and implementing eco-friendly processes.
Ethical sourcing is not merely a trend but a necessity, as businesses face growing scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) are becoming essential criteria for B2B partnerships. These certifications assure buyers that their suppliers adhere to recognized standards for environmental sustainability, which is particularly important in regions with stringent regulations, such as the European Union.
Moreover, the demand for recycled plastics is on the rise. Companies that can provide transparent information about their sourcing practices and the sustainability of their materials are likely to gain a competitive edge. Buyers should seek out suppliers that offer a diverse range of ‘green’ materials, including bio-based plastics and those with verified recycled content. This not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the increasing consumer preference for sustainable products.
What Is the Historical Context of Plastic Pricing Trends?
The history of plastic pricing trends is marked by significant fluctuations influenced by technological advancements and economic factors. Initially, the introduction of synthetic polymers in the early 20th century revolutionized the material landscape, leading to widespread adoption across various industries. However, the global oil crisis in the 1970s caused a sharp increase in resin prices, highlighting the industry’s dependence on petroleum.
In recent decades, the rise of globalization has facilitated the expansion of the plastic market, allowing for lower production costs and increased competition. However, this has also led to volatility in prices due to geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and regulatory changes. The past few years have seen a renewed focus on sustainability, prompting innovations in recycling technologies and the development of bio-based plastics, which are now influencing pricing dynamics.
As international B2B buyers navigate the current market, understanding this historical context can provide valuable insights into future trends and help inform strategic sourcing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic price
-
How do I solve fluctuating plastic prices in my supply chain?
To mitigate the impact of fluctuating plastic prices, consider establishing long-term contracts with suppliers to lock in pricing. Additionally, diversify your supplier base to avoid dependency on a single source, which can expose you to price hikes. Utilize market intelligence tools to monitor trends and forecasts, enabling proactive purchasing decisions. Regularly review your inventory management strategies to optimize stock levels and reduce holding costs. -
What is the best type of plastic for packaging applications?
For packaging applications, polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are commonly preferred due to their excellent flexibility, durability, and resistance to moisture. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is ideal for film applications, while High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is preferred for rigid containers. Consider the specific requirements of your product, such as barrier properties, recyclability, and cost, to determine the best option for your needs. -
What are the key factors to consider when vetting plastic suppliers?
When vetting plastic suppliers, prioritize their industry reputation, production capacity, and compliance with international quality standards. Review their certifications, such as ISO or FDA approvals, to ensure product safety and reliability. Assess their financial stability and customer service responsiveness, as these factors will influence your long-term partnership. Finally, request samples to evaluate the quality of their products before committing to a bulk order. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plastic materials?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plastic materials vary significantly based on the supplier, type of plastic, and specific application. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons. It’s essential to discuss your needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you’re looking for smaller quantities for testing or initial production runs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for new customers to build relationships. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing plastics internationally?
Payment terms for international plastic sourcing can vary widely, but common arrangements include advance payment, letters of credit, and net 30 or 60-day terms. Be prepared to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and the supplier’s policies. It’s advisable to conduct due diligence on the supplier’s financial stability and credit history before committing to terms, as this can mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my plastic products?
To ensure quality assurance for your plastic products, establish clear specifications and quality standards during the procurement process. Request regular quality audits and reports from your supplier, and consider third-party inspections for added assurance. Implement a quality control process within your organization to monitor incoming materials and finished goods. Building a collaborative relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind for international plastic shipments?
When planning international shipments of plastic materials, consider factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling plastics to navigate logistical challenges. Ensure proper documentation, including bills of lading and customs declarations, to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in lead times for production and transportation to align with your supply chain needs. -
How do geopolitical factors influence plastic prices globally?
Geopolitical factors such as trade agreements, tariffs, and political stability can significantly influence global plastic prices. Changes in regulations or trade policies can affect supply chains and costs. It’s essential to stay informed about international news and market trends, as these factors can lead to sudden price volatility. Building strategic relationships with suppliers across various regions can help mitigate risks associated with geopolitical fluctuations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Plastic Price Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. The Plastics Exchange – Key Plastic Resins
Domain: theplasticsexchange.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: HMWPE – Film, HDPE – Inj, HDPE – Blow Mold, LDPE – Film, LDPE – Inj, LLDPE – Film, LLDPE – Inj, PP Homopolymer – Inj, PP Copolymer – Inj. Spot Offers: PP Homopolymer – Inj (Total lbs: 3,644,992, Low: $0.495, High: $0.595), LDPE – Film (Total lbs: 3,279,612, Low: $0.480, High: $0.620), LLDPE – Inj (Total lbs: 1,774,116, Low: $0.490, High: $0.605), HMWPE – Film (Total lbs: 1,671,312, Low: $0.470, Hi…
2. Trading Economics – Polyethylene Pricing
Domain: tradingeconomics.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Polyethylene is a polyolefin resin and the most widely used plastic globally, commonly used in applications such as bottles, bags, toys, and tubes. As of July 11, 2025, the price of Polyethylene is 7,288 CNY/T, having decreased by 0.19% from the previous day. Over the past month, the price has increased by 2.12%, but it remains 14.16% lower than a year ago. The all-time high price was 16,230.00 CN…
3. Plastics Today – Resin Price Reports
Domain: plasticstoday.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Resin Price Reports covering various aspects such as freight costs, global risks, and inventory levels affecting buying decisions. Recent reports indicate rising resin prices due to renewed demand and market fears. Specific reports include: 1. Active trading pushing prices higher (June 22, 2025) 2. A spot of gloom in resin markets (June 14, 2025) 3. Upswing in trading activity amidst multiplying r…
4. IOCL – PP Injection Molding
Domain: plastic4trade.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
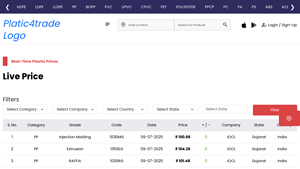
Introduction: 1. PP Injection Molding – Grade: 1030MG, Date: 09-07-2025, Price: ₹ 100.68, Company: IOCL, State: Gujarat, Country: India
2. PP Extrusion – Grade: 1350EG, Date: 09-07-2025, Price: ₹ 104.26, Company: IOCL, State: Gujarat, Country: India
3. PP RAFFIA – Grade: 1030RG, Date: 09-07-2025, Price: ₹ 101.48, Company: IOCL, State: Gujarat, Country: India
4. LLDPE Injection Molding – Grade: 500M24A, Date: 09…
5. PlasticPortal – Polymer Prices
Domain: plasticportal.eu
Introduction: Polymer Prices: Weekly prices of commodity plastics in 2025 for various types including PE-LD, PE-HD, PP, and PS in Central and Eastern Europe. Prices include: HDPE BM – 1,052 € / t (Difference: -42), HDPE film – 1,046 € / t (Difference: -45), HDPE IM – 1,060 € / t (Difference: -31), HDPE pipe (100) – 1,200 € / t (Difference: -29), LDPE film – 1,139 € / t (Difference: -26), rLDPE Film – 864 € / t …
6. Sibur – Superior Quality Butadiene Rubber
Domain: plastic-price.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Sibur SKD Superior Quality Butadiene Rubber (BR)”,”price”:”$1641/MT”,”mooney_viscosity”:”40 – 50 @Temperature 100 °C”,”ash”:”<= 0.30 %”,”tensile_strength_break”:”>= 19.1 MPa”,”tensile_strength_yield”:”>= 6.89 MPa @Strain 300 %”,”elongation_break”:”>= 480 %”},{“name”:”Sibur SKD-ND 3rd Group Butadiene Rubber (BR)”,”price”:”$2363/MT”,”mooney_viscosity”:”50 – 59 @Temperature 100 …
7. BPF – Plastixx Polymer Price Index
Domain: bpf.co.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
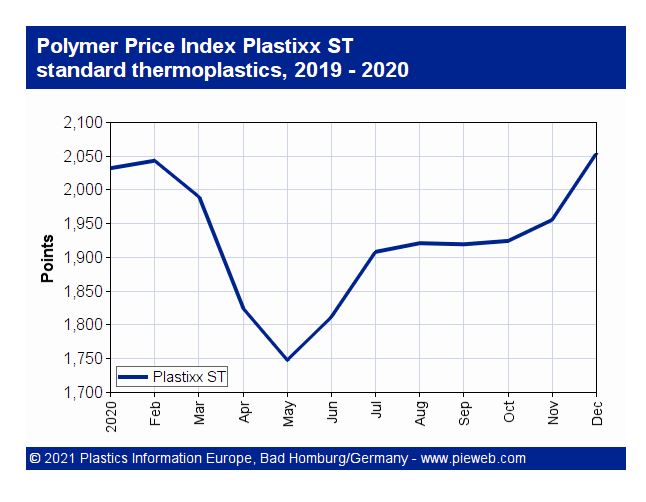
Introduction: Plastixx is the PIE polymer price index introduced in June 2005, reflecting price development of plastics in Western Europe. It is calculated monthly based on market prices for standard thermoplastics and engineering thermoplastics. Plastixx covers major thermoplastics, while Plastixx ST shows price development of standard plastics and Plastixx TT for engineering thermoplastics. The index base is …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic price
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Plastic Procurement Process?
In an increasingly volatile market, strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers navigating the complexities of plastic pricing. Key insights from recent trends indicate a rising Producer Price Index for plastics, reflecting ongoing supply chain challenges, fluctuating demand, and increased freight costs. Buyers must be proactive in their sourcing strategies, leveraging real-time market intelligence to make informed purchasing decisions.
Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can provide stability and access to competitive pricing, essential in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Utilizing online marketplaces and analytics tools can further streamline procurement processes, ensuring that buyers remain agile and responsive to market changes.
Looking ahead, as global demand for plastics continues to evolve, it’s crucial for buyers to stay informed and adaptable. Engage with industry experts and utilize advanced analytics to forecast trends and align your procurement strategies accordingly. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also capitalizes on opportunities within the dynamic landscape of plastic pricing. Embrace strategic sourcing today to secure your supply chain and enhance your competitive advantage.