Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic machine shop
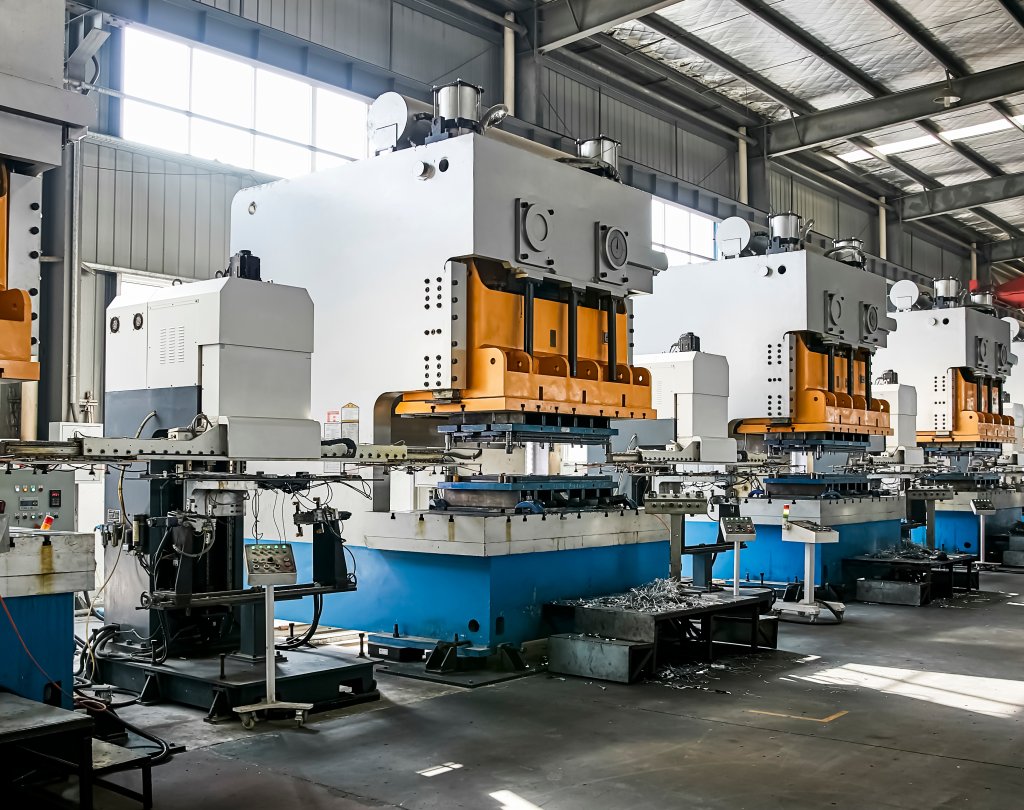
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing high-quality components from a reliable plastic machine shop presents a critical challenge for B2B buyers. As businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive to meet their production needs, understanding the nuances of plastic machining becomes essential. This guide aims to illuminate the complexities of the plastic machine shop market, offering insights into various machining techniques, material selections, and the diverse applications that plastics serve across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical.
Navigating this multifaceted market requires a thorough vetting process for suppliers, ensuring they possess the necessary expertise, quality assurance practices, and quick turnaround capabilities to meet project specifications. This guide provides actionable strategies for assessing potential partners, evaluating cost structures, and understanding the implications of material choices on production efficiency.
By arming international B2B buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions, this resource empowers them to effectively engage with plastic machine shops and leverage their capabilities to enhance product offerings. Whether you’re in Nigeria, Vietnam, or any other global market, the insights shared here will streamline your sourcing process and support your operational success in an increasingly complex supply chain.
Understanding plastic machine shop Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Plastic Machining | Offers tailored solutions with advanced CNC tech | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices | Pros: High precision, tailored designs. Cons: Longer lead times for custom jobs. |
| High-Volume Production | Focuses on mass production with optimized processes | Consumer goods, packaging, electronics | Pros: Cost-effective, quick turnaround. Cons: Less flexibility for design changes. |
| Prototype Development | Specializes in rapid prototyping and small runs | Product development, testing, design validation | Pros: Fast iterations, low risk. Cons: Higher per-unit costs. |
| Specialty Plastic Machining | Uses advanced materials for specific industries | Chemical processing, aerospace, defense | Pros: High-performance materials, tailored properties. Cons: Limited availability and higher costs. |
| Educational and Training | Provides hands-on learning and skills development | Educational institutions, training programs | Pros: Builds industry skills, practical experience. Cons: Limited production capacity. |
What Are the Characteristics of Custom Plastic Machining?
Custom plastic machining is characterized by its ability to create bespoke components using advanced CNC technology. This type of shop is ideal for industries requiring high precision, such as aerospace and medical devices. Buyers should consider the shop’s expertise in translating specific project requirements into tangible products, as well as their material selection capabilities. While custom solutions offer unparalleled precision and adaptability, they often come with longer lead times and potentially higher costs.
How Does High-Volume Production Differ from Other Types?
High-volume production shops focus on efficiently manufacturing large quantities of identical components, making them suitable for consumer goods and packaging industries. These shops utilize streamlined processes and automation to minimize costs and maximize output. Buyers should prioritize shops with proven track records in mass production and quality assurance processes. While this method offers significant cost savings and quick turnaround times, it may lack flexibility for design modifications once production is underway.
Why Choose Prototype Development Services?
Prototype development services specialize in creating models and small runs to test concepts before full-scale production. This type of shop is crucial for product development, allowing businesses to validate designs and functionality without committing to large orders. Key considerations for buyers include the speed of iteration and the shop’s experience with various materials. Although the initial costs per unit may be higher, the reduced risk of errors and the ability to refine designs make this option appealing for innovative projects.
What Makes Specialty Plastic Machining Unique?
Specialty plastic machining shops focus on using advanced materials tailored for specific applications, such as those in the chemical processing or aerospace sectors. These shops often employ unique machining techniques to handle high-performance plastics that can withstand extreme conditions. Buyers should evaluate the shop’s expertise in working with specialized materials and their ability to meet stringent industry standards. While these services provide unmatched quality and performance, they may come at a higher price and with limited material availability.
How Do Educational and Training Shops Contribute to the Industry?
Educational and training plastic machine shops focus on developing skills and knowledge within the industry. They provide hands-on experience for students and professionals looking to enhance their technical abilities. These shops are ideal for educational institutions and training programs aiming to bridge the gap between theory and practice. While they play a vital role in workforce development, their production capacity may be limited compared to commercial shops, making them less suited for large-scale manufacturing needs.
Key Industrial Applications of plastic machine shop
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plastic machine shop | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft systems | Enhanced safety and performance | Expertise in tight tolerances and material selection |
| Medical Devices | Custom surgical instruments and implants | Improved patient outcomes and compliance | Certifications, biocompatibility, and quick turnarounds |
| Automotive | Lightweight structural components | Increased fuel efficiency and reduced costs | Material properties, durability, and supply chain reliability |
| Food and Beverage | Custom parts for processing equipment | Compliance with safety standards | FDA approval, material certifications, and hygiene standards |
| Electronics | Insulators and housings for electronic devices | Enhanced performance and durability | Electrical properties, quick prototyping, and scalability |
How is Plastic Machining Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, plastic machining is critical for producing precision components used in aircraft systems, such as cockpit displays, control panels, and lightweight structural elements. The ability to create intricate designs with tight tolerances ensures that parts meet stringent safety and performance standards. International buyers must consider the shop’s expertise in aerospace-grade materials and their ability to deliver components that comply with industry regulations, particularly regarding weight and durability.
What Role Does Plastic Machining Play in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Medical device manufacturing heavily relies on plastic machining for custom surgical instruments and implants. The precision of machined plastic parts is vital for ensuring proper functionality and patient safety. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that offer certified materials with biocompatibility and quick turnaround times to meet the fast-paced demands of healthcare. Additionally, compliance with medical regulations and standards is a crucial factor in sourcing decisions.
Why is Plastic Machining Important for Automotive Industries?
The automotive industry benefits from plastic machining by utilizing lightweight structural components that contribute to fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle weight. Machined plastics can replace traditional metal parts, leading to significant cost savings in manufacturing and material expenses. When sourcing for automotive applications, buyers should focus on suppliers that understand the specific material properties required for durability and performance under varying conditions, as well as those who can ensure timely delivery to align with production schedules.
How is Plastic Machining Applied in Food and Beverage Industries?
In the food and beverage industry, plastic machining is essential for creating custom parts used in processing equipment, such as conveyor systems and packaging machinery. These components must comply with strict safety and hygiene standards, making material selection and certification critical. International buyers should look for machine shops that can provide FDA-approved materials and demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance, ensuring that the parts meet regulatory requirements and operate efficiently in food processing environments.
What Benefits Does Plastic Machining Offer to the Electronics Sector?
Plastic machining is widely utilized in the electronics sector for producing insulators and housings that protect sensitive components from environmental factors. The durability and electrical properties of machined plastics contribute to the overall performance and longevity of electronic devices. Buyers in this sector should seek suppliers capable of rapid prototyping and scaling production while ensuring that materials meet the necessary electrical and thermal specifications to enhance product reliability.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic machine shop’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Material Selection for Custom Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate materials for their custom plastic components. The vast array of plastics available—such as ABS, Nylon, and PEEK—can be overwhelming, especially when considering factors like mechanical properties, environmental exposure, and cost. This indecision can lead to delays in production and increased costs if the wrong material is chosen, resulting in parts that do not meet performance requirements or even failure in application.
The Solution: To navigate this challenge, buyers should engage in a collaborative dialogue with potential plastic machine shops early in the project. Inquire about their material expertise and ask for recommendations based on specific application requirements. Additionally, provide detailed project specifications, including expected load, temperature variations, and environmental conditions. A reputable plastic machine shop should offer material samples and insights into the performance characteristics of various plastics. By leveraging their expertise, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project goals, ultimately minimizing delays and ensuring part quality.
Scenario 2: Ensuring Precision in High-Volume Production
The Problem: When scaling up production for high-volume orders, maintaining precision across all components becomes a critical issue. Buyers often face inconsistencies in dimensions and tolerances, which can lead to product defects, increased rework, and unhappy customers. This is particularly crucial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where precision is non-negotiable, and even minor deviations can have serious consequences.
The Solution: Implementing a robust quality assurance process is key to overcoming this pain point. Buyers should prioritize working with plastic machine shops that utilize advanced CNC machining technologies, such as 5-axis machining, which allows for greater precision in creating complex geometries. It’s advisable to request detailed documentation on the shop’s quality control measures, including calibration protocols and inspection methods. Additionally, conducting regular audits and establishing clear communication regarding tolerances and expectations can help ensure that each batch meets the required specifications. This proactive approach not only safeguards the quality of the final products but also fosters a stronger partnership with the machine shop.
Scenario 3: Slow Response Times and Communication Gaps
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter frustration with slow response times and communication gaps when sourcing parts from plastic machine shops. This can lead to missed deadlines, stalled projects, and a lack of transparency in the production process. Buyers often find themselves chasing updates on quotes or production timelines, which can strain relationships and hinder project momentum.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should establish clear lines of communication and set expectations upfront. When initiating a partnership, discuss response time expectations for quotes and updates, ensuring both parties are aligned. Look for plastic machine shops that offer online tools for self-service quoting and tracking orders, which can significantly enhance transparency and speed. Additionally, consider selecting shops with dedicated account managers who can provide personalized service and quick responses to inquiries. By fostering a communicative relationship and utilizing technology, buyers can streamline the sourcing process and enhance overall project efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic machine shop
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Plastic Machine Shops?
When selecting materials for plastic machining, understanding their properties is crucial to ensuring product performance and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in plastic machine shops, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, application impacts, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Key Properties:
ABS is known for its outstanding impact resistance, toughness, and ease of machining. It has a temperature rating of around 80°C and exhibits good chemical resistance, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
The advantages of ABS include its low cost and excellent machinability, which allows for quick production cycles. However, it has limited temperature resistance compared to other engineering plastics, which may restrict its use in high-heat applications.
Impact on Application:
ABS is commonly used in consumer products, automotive parts, and electronic housings due to its aesthetic qualities and durability. It is not recommended for applications exposed to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM for material specifications. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing ABS from local suppliers can reduce shipping costs and lead times.
2. Nylon (Polyamide)
Key Properties:
Nylon offers excellent wear resistance, high tensile strength, and good thermal stability, with a temperature rating of up to 120°C. It is also resistant to abrasion and has low friction properties.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of Nylon is its durability and versatility, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including gears and bearings. However, it can absorb moisture, which may affect its mechanical properties over time, particularly in humid environments.
Impact on Application:
Nylon is ideal for applications requiring high strength and wear resistance, such as automotive and industrial components. Its moisture sensitivity may necessitate careful consideration in humid climates.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should verify that their suppliers provide Nylon that meets relevant standards. Local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact should also be considered.
3. PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Key Properties:
PEEK is a high-performance polymer that can withstand temperatures up to 260°C and offers exceptional chemical resistance. It is also known for its mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
Pros & Cons:
PEEK’s key advantage is its ability to perform in extreme conditions, making it suitable for aerospace and medical applications. However, it comes with a high price tag, which may limit its use to specialized applications.
Impact on Application:
In applications where high temperature and chemical resistance are critical, such as in the aerospace and medical sectors, PEEK is often the material of choice. Its high cost can be justified by the performance benefits it provides.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should be aware of the stringent compliance requirements for PEEK in regulated industries. Understanding local certification processes in Europe and the Middle East can facilitate smoother procurement.
4. Polycarbonate
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is a transparent thermoplastic known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity. It has a temperature rating of around 135°C and offers good UV resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of polycarbonate is its strength combined with lightweight properties, making it ideal for applications where visibility and durability are essential. However, it can be prone to scratching and may require protective coatings.
Impact on Application:
Polycarbonate is widely used in applications such as safety goggles, automotive components, and electronic housings where clarity and strength are paramount. Its susceptibility to scratches may necessitate additional treatments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions with stringent safety regulations, like Europe, should ensure that polycarbonate materials comply with safety standards. Understanding local market preferences for clarity and durability can also influence material selection.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Plastic Machine Shops
| Material | Typical Use Case for Plastic Machine Shop | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Consumer products, automotive parts | Low cost and excellent machinability | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Nylon | Gears, bearings, industrial components | High strength and wear resistance | Moisture absorption affects properties | Medium |
| PEEK | Aerospace, medical applications | Performs well in extreme conditions | High cost | High |
| Polycarbonate | Safety goggles, automotive components | High impact resistance and clarity | Prone to scratching | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into common materials used in plastic machining, aiding in informed decision-making tailored to specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic machine shop
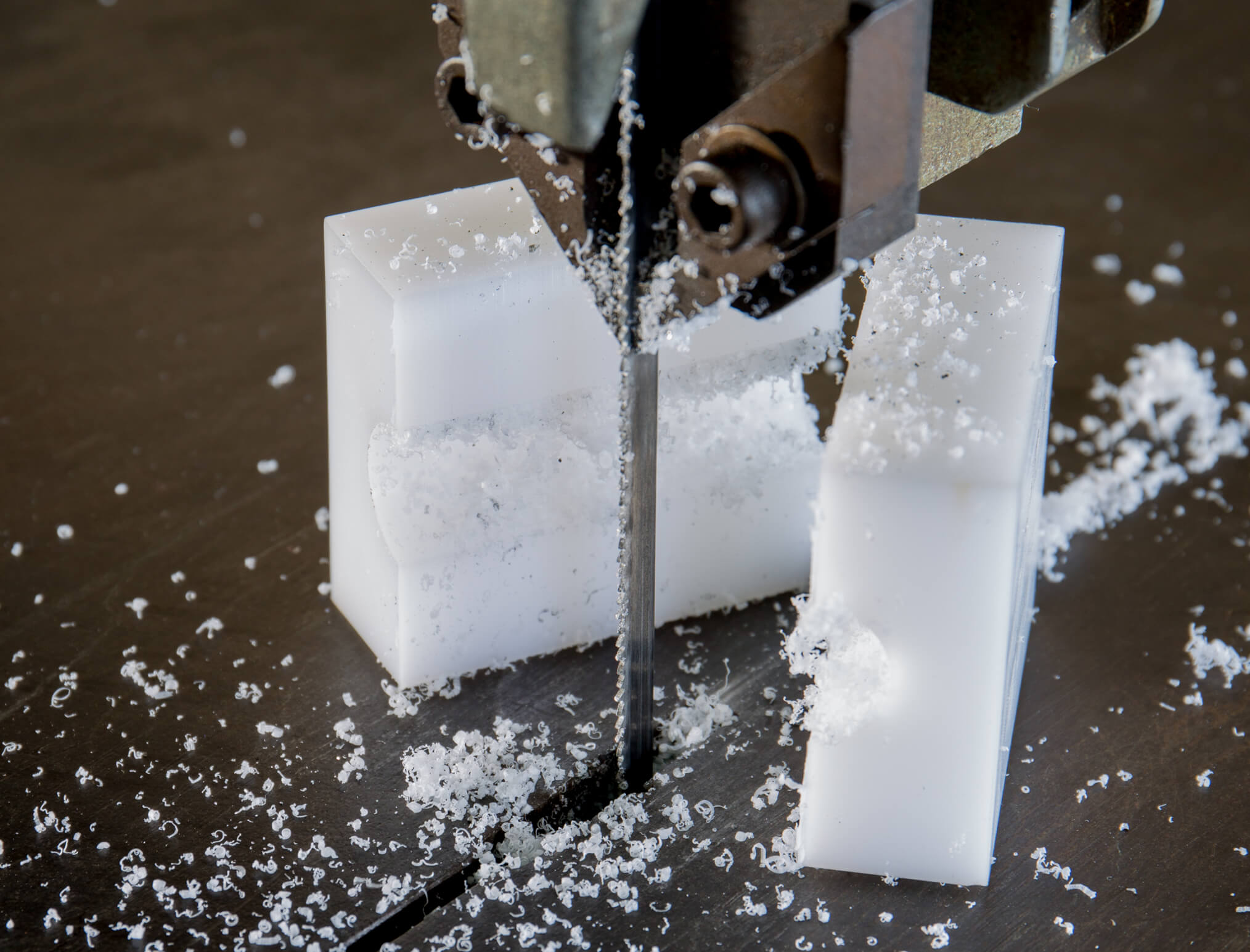
What Are the Key Stages of Manufacturing in a Plastic Machine Shop?
The manufacturing process in a plastic machine shop involves several critical stages, each essential for producing high-quality components that meet specific client requirements. The main stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Plastic Machining?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting the appropriate plastic type based on the application and the specific properties needed, such as strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals or temperature. Common materials used include ABS, Nylon, PEEK, and Polycarbonate.
Once the material is selected, it undergoes a series of preparatory steps, such as cutting into manageable sizes and ensuring they are free from defects. This stage may also involve drying or conditioning the material to remove moisture, which can affect machining quality.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Plastic Machining?
The forming stage includes various techniques that convert raw materials into the desired shapes. Key processes in this stage are:
-
CNC Machining: This is the backbone of modern plastic machining, allowing for high precision and customization. Techniques such as turning, milling, and drilling are employed to achieve intricate designs and tight tolerances.
-
Injection Molding: For high-volume production, injection molding is often utilized. It involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to create complex shapes, making it efficient for large runs.
-
3D Printing: Rapid prototyping and small-batch production can benefit from additive manufacturing techniques, which allow for quick adjustments and flexibility in design.
Each technique has its advantages and is selected based on project specifications, volume, and complexity.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Plastic Manufacturing?
Assembly in plastic machining may involve joining multiple components, which can be achieved through various methods such as adhesive bonding, mechanical fastening, or welding, depending on the materials used.
A critical aspect of assembly is ensuring that components fit together accurately and function as intended. This stage may also include additional processes like surface treatment to enhance adhesion or aesthetic qualities.
What Finishing Processes Are Important for Plastic Components?
Finishing processes are essential to enhance the functionality and appearance of the final product. Common finishing techniques include:
-
Grinding and Lapping: These processes are used to achieve smoother surfaces and tighter tolerances, which are especially important in applications such as aerospace and medical devices.
-
Polishing: This step improves surface aesthetics and can enhance properties such as light transmission in optical applications.
-
Coating: Applying protective coatings can improve chemical resistance and durability, which is crucial for components exposed to harsh environments.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Expect from Plastic Machine Shops?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specified standards and client expectations. International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems that enhance customer satisfaction through consistent quality.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented?
Quality control (QC) in plastic machining typically involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria before they are used in production.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring during production is crucial. This stage includes regular inspections and measurements to catch any deviations from standards in real-time.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After the manufacturing process, a thorough inspection of finished products is conducted. This includes dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional tests to ensure that the product meets all specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of plastic components, including:
-
Mechanical Testing: This assesses properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and flexibility, ensuring that components can withstand their intended applications.
-
Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing tools like calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify that components meet precise specifications.
-
Environmental Testing: Evaluating how materials perform under different conditions, such as temperature fluctuations or exposure to chemicals, to ensure reliability in real-world applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of a plastic machine shop is crucial. Here are key strategies:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits can provide insights into the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and adherence to standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation such as quality assurance reports, material certifications, and compliance records can help verify a supplier’s commitment to quality.
-
Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and the final products.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Certification for International B2B Buyers?
Quality certification can vary significantly by region and industry. For example, certifications like CE mark may be vital for products exported to Europe, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Similarly, API certification may be essential for components used in the oil and gas industry.
B2B buyers should be aware of these nuances and ensure that their suppliers possess the appropriate certifications relevant to their specific markets. This diligence not only guarantees compliance but also enhances trust and reliability in the supplier relationship.
Conclusion
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols within a plastic machine shop are multifaceted and critical for producing high-quality components. By understanding the stages of manufacturing, quality control checkpoints, testing methods, and certification nuances, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting a supplier. This knowledge is particularly vital for international buyers who must navigate different standards and practices across regions.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic machine shop’
In the competitive landscape of manufacturing, sourcing the right plastic machine shop is essential for achieving precision and quality in your projects. This guide provides a step-by-step checklist to assist B2B buyers in identifying and selecting the most suitable plastic machining partner for their specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before reaching out to potential suppliers, clearly outline your project requirements. This includes dimensional tolerances, material specifications, and any special features necessary for your components. A well-defined scope helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that they can meet your expectations.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of plastic machine shops that specialize in the services you need. Look for suppliers with proven expertise in your industry and the capability to handle the specific materials you require. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather recommendations and insights.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities and Technologies
Assess the machining technologies and capabilities of each potential supplier. Key areas to consider include:
– CNC Machining Options: Verify if they offer advanced CNC capabilities, such as 5-axis machining, which allows for greater precision and complexity in designs.
– Material Handling: Ensure they have experience with the specific plastic materials you plan to use, such as ABS, Nylon, or PEEK, and can assist with material selection.
Step 4: Verify Quality Assurance Processes
Quality is paramount in plastic machining. Inquire about the supplier’s quality assurance protocols, including certifications like ISO 9001, and their approach to maintaining quality throughout the machining process. Ask for details on their inspection methods and the tools they use to ensure that parts meet specified tolerances.
Step 5: Request Samples and Case Studies
To gauge a supplier’s capabilities, request samples of previous work or case studies relevant to your project. This will allow you to assess the quality and precision of their products firsthand. Look for examples that demonstrate their ability to meet similar specifications and industry standards.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Flexibility
Understand the supplier’s typical lead times and their ability to accommodate changes in order volume or specifications. Quick turnaround times are crucial for keeping your projects on schedule, especially if you require prototypes or production runs. Discuss their capacity for scaling production as your needs evolve.
Step 7: Evaluate Cost Structures and Terms
Finally, review the pricing models and payment terms offered by potential suppliers. Ensure that you understand all associated costs, including tooling, setup, and shipping. A transparent pricing structure helps you avoid unexpected expenses and facilitates better budgeting for your projects.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process and select a plastic machine shop that aligns with their technical needs and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic machine shop Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Plastic Machine Shop Sourcing?
Understanding the cost structure of plastic machine shop services is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their sourcing strategies. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of plastic material significantly influences costs. Common options like ABS, Nylon, and PEEK vary in price and machinability. High-performance plastics often come at a premium but can reduce long-term costs due to their durability and resistance to wear and temperature.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial for precision machining. Labor costs can fluctuate based on location, expertise, and the complexity of the machining required. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but the availability of skilled workers can impact project timelines and quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Efficient operations can help lower overhead, but international buyers should consider potential tariffs and import duties that may affect overall expenses.
-
Tooling: The need for specialized tools or dies can add to the initial cost. Custom tooling is often necessary for unique specifications, impacting both the lead time and the price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet required specifications necessitates investment in quality assurance processes. Certifications and traceability documents may also add to costs, but they are critical for industries like aerospace and medical where compliance is mandatory.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly, especially for international shipments. Factors such as Incoterms can affect who bears the costs and risks during transport, influencing the total cost of ownership.
-
Margin: Finally, suppliers will factor in their desired profit margin, which can vary based on competition and market demand.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Plastic Machining Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in the plastic machining sector, impacting both the initial quote and the final invoice.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Understanding the MOQ of suppliers can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts often involve additional costs for design and tooling. Clearly defining project specifications upfront can prevent unexpected expenses later.
-
Material Selection: The type of plastic selected can significantly affect price. Higher-quality materials may be more expensive initially but can offer cost savings over time through increased longevity and reduced maintenance needs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Parts requiring specific industry certifications may incur additional costs. Buyers should assess the importance of certifications relative to their industry to make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and operational efficiency can all influence pricing. Partnering with a supplier that has a reliable track record can mitigate risks associated with delays and quality issues.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk, thereby affecting overall pricing.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Sourcing Costs?
To ensure cost-efficiency in sourcing plastic machining services, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Flexibility in terms can lead to better rates.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Look beyond initial pricing to assess the total cost of ownership. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and replacement costs associated with the materials used.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Different regions may have varied pricing structures due to local economic conditions and labor costs. Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as tariffs or import duties, that can arise when sourcing from overseas.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online catalogs and self-service options to gather quotes and compare prices efficiently. This can save time and help identify competitive pricing without the need for lengthy negotiations.
By understanding these components and leveraging strategic insights, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing from plastic machine shops while ensuring they achieve the best possible value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic machine shop With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Plastic Machining
When considering a plastic machine shop for component manufacturing, it’s essential to evaluate alternative solutions that may offer similar capabilities. This analysis helps B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs, cost constraints, and performance expectations. Below, we compare plastic machine shops to two viable alternatives: 3D Printing and Metal Machining.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Plastic Machine Shop | 3D Printing | Metal Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and customization for complex parts | Good for rapid prototyping; less precision than machining | Excellent precision; suited for high-strength components |
| Cost | Generally lower for high-volume production; material-dependent | Lower initial costs, but material costs can add up | Higher upfront costs due to tooling and setup |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators and setup time | User-friendly for CAD designs; less setup time | Requires specialized machinery and skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular maintenance of CNC machines needed | Minimal; maintenance mainly on printers | High; ongoing maintenance for machines and tools |
| Best Use Case | Custom, high-precision parts for various industries | Rapid prototyping and low-volume production | High-strength, durable components in demanding applications |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
3D Printing: Pros and Cons
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is an increasingly popular alternative for producing plastic components. One significant advantage is its ability to create complex geometries without the need for extensive tooling, making it ideal for rapid prototyping. However, while 3D printing excels in flexibility and speed, it often falls short in precision compared to traditional machining methods. The material costs for high-performance plastics can also be higher, which may not be cost-effective for large production runs.
Metal Machining: Pros and Cons
Metal machining involves the use of CNC technology to shape and cut metal components, offering exceptional strength and durability. This method is highly effective for producing parts that require high tolerances and superior mechanical properties. However, the initial setup and tooling costs can be significant, making it less ideal for low-volume production. Additionally, metal machining typically requires longer lead times compared to plastic machining, which can be a drawback for businesses needing quick turnarounds.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right manufacturing solution depends on various factors, including the specific requirements of your project, budget, and production volume. A plastic machine shop may be the best option for high-precision, custom plastic components, especially when cost-effectiveness and quick turnarounds are essential. In contrast, 3D printing can be advantageous for rapid prototyping and design flexibility, while metal machining is ideal for applications demanding high strength and durability. By thoroughly assessing these alternatives, B2B buyers can align their choices with their operational goals, ensuring they invest in the most suitable manufacturing method for their needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic machine shop
What Are the Key Technical Properties Relevant to Plastic Machine Shops?
Understanding the critical technical properties involved in plastic machining is essential for B2B buyers seeking high-quality components. Here are some of the most important specifications:
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific type of plastic used in machining, which influences the part’s performance, durability, and application suitability. Common grades include ABS, Nylon, and PEEK. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the final product meets the required mechanical and thermal properties, impacting the longevity and functionality of the components, especially in demanding industries like aerospace and medical.
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in the dimensions of a machined part. It is crucial for ensuring parts fit together correctly in assemblies. High precision tolerances are vital in applications such as medical devices and automotive components, where even minor deviations can lead to failures or malfunctions. Understanding tolerance requirements can help buyers negotiate better with machine shops and ensure their specifications are accurately met.
Surface Finish
Surface finish describes the texture and smoothness of a machined part’s surface. It is critical for both aesthetic and functional reasons, particularly in applications where friction, wear, or contamination are concerns. A smoother finish can enhance the performance of parts in mechanical assemblies, thereby extending their lifespan. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure the end products are not only functional but also meet regulatory standards.
Machinability
Machinability refers to how easily a material can be machined into a desired shape. Different plastics have varying machinability ratings based on their properties, which affect cutting speeds, tool wear, and overall production efficiency. Understanding machinability helps buyers select the right materials and processes, ensuring quicker turnaround times and reduced costs in production.
Chemical Resistance
Chemical resistance is the ability of a material to withstand exposure to various chemicals without degrading. This property is particularly important in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing. Buyers must assess the chemical exposure risks their components will face to choose materials that will maintain integrity and safety over time.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in the Plastic Machining Industry?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiation processes. Here are some common terms relevant to B2B buyers:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify the right suppliers for their specific needs, especially when sourcing components for larger assemblies.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand, as it can impact inventory management and budget allocation. Knowing the MOQ can help in planning purchases and negotiating favorable terms with suppliers.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific quantities of goods or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and services from different vendors to make informed purchasing decisions.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B buyers to clarify shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, thereby minimizing risks associated with cross-border transactions.
CAD-CAM (Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing)
CAD-CAM refers to the use of software to design products (CAD) and control manufacturing processes (CAM). This technology enhances precision and efficiency in plastic machining, allowing for complex designs and optimizing production workflows. Familiarity with CAD-CAM capabilities can aid buyers in selecting machine shops that utilize advanced technologies for better outcomes.
By grasping these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when engaging with plastic machine shops, ensuring their projects meet quality, cost, and timeline expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic machine shop Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Plastic Machine Shop Sector?
The plastic machine shop sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide high-quality, customized plastic components with quick turnaround times. Key trends include the adoption of advanced CNC machining technologies, such as 5-axis machining, which enhances precision and allows for the production of complex geometries. This technology not only improves part quality but also reduces the time and cost associated with multiple setups.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on materials with superior mechanical properties, such as PEEK and Ultem, which cater to high-performance applications in industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices. The trend towards just-in-time manufacturing is also reshaping sourcing strategies, compelling plastic machine shops to maintain large inventories and ensure swift response to requests for quotes (RFQs). For buyers, understanding these dynamics is crucial to leveraging the capabilities of machine shops effectively, thus ensuring their projects are completed on time and within budget.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting B2B Relationships in Plastic Machine Shops?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical concern for B2B buyers in the plastic machine shop sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and machining processes prompts buyers to seek suppliers committed to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. Suppliers are increasingly adopting green certifications and sourcing recyclable or biodegradable materials to align with global sustainability goals. This shift not only helps mitigate environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation among eco-conscious consumers.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are becoming a focal point for buyers who prioritize transparency and traceability in their sourcing processes. Suppliers that can demonstrate compliance with environmental regulations and provide documentation on material origins are more likely to attract discerning clients. As the demand for sustainable practices continues to rise, plastic machine shops that invest in green technologies and materials will not only meet regulatory requirements but also position themselves favorably in the competitive B2B landscape.
What Is the Historical Evolution of Plastic Machining and Its Relevance Today?
The evolution of plastic machining dates back to the early 20th century when synthetic polymers began to replace traditional materials in manufacturing. Initially, plastic machining was rudimentary, with limited techniques available. However, advancements in technology, particularly the introduction of CNC machining in the late 20th century, revolutionized the sector. This technology enabled manufacturers to produce highly intricate designs with greater accuracy and efficiency.
Today, the relevance of this evolution is evident in the diverse applications of plastic components across various industries. From aerospace to medical devices, the demand for precision-crafted plastic parts continues to grow, driven by the need for lightweight, durable materials that meet stringent performance standards. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that have shaped the plastic machine shop sector, enabling them to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic machine shop
-
1. How do I choose the right plastic machine shop for my project?
Selecting the right plastic machine shop involves evaluating several critical factors. First, assess their expertise in the specific type of machining you require, such as CNC machining or injection molding. Check their portfolio to ensure they have experience with similar projects and industries. Additionally, consider their material offerings and whether they can source the plastics you need. Quality assurance processes, certifications, and customer reviews are also vital indicators of reliability. Finally, inquire about their lead times and capacity to handle your project’s scale. -
2. What materials are commonly used in plastic machining?
Plastic machining utilizes a variety of materials depending on the application. Commonly used plastics include ABS for its impact resistance and ease of machining, Nylon for strong and stiff components, and PEEK for high-performance applications in extreme conditions. Other materials like Polycarbonate, HDPE, and Acrylic offer specific benefits such as clarity, durability, and chemical resistance. Understanding the properties of each material is crucial to ensure it meets your project’s mechanical and thermal requirements. -
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plastic machining services?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely among plastic machine shops, often influenced by the complexity of the parts, material costs, and production capabilities. Some shops may accept low MOQs for prototyping or custom orders, while others may require larger quantities for cost-effectiveness in high-volume production. It’s essential to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your budget and production timeline. -
4. What payment terms should I expect when working with a plastic machine shop?
Payment terms can differ significantly based on the supplier and your business relationship. Common practices include upfront deposits, net 30 or net 60 terms, or payment upon delivery. For international buyers, it’s advisable to discuss payment methods that minimize risk, such as letters of credit or escrow services. Always ensure that terms are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
5. How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing from a plastic machine shop?
To ensure quality assurance, inquire about the machine shop’s quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO standards. Request documentation for material traceability and inspection reports for previous projects. Additionally, consider conducting an on-site visit or arranging a third-party inspection to evaluate their operations firsthand. Establishing clear specifications and quality benchmarks in your contract will also help maintain high standards throughout the production process. -
6. What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing plastic components internationally?
When sourcing plastic components internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and delivery timelines. It’s crucial to work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics and can provide reliable shipping options. Ensure that all necessary paperwork, including customs documentation and import/export permits, is in order to avoid delays. Additionally, evaluate the potential impact of tariffs and duties on your overall budget to make informed financial decisions. -
7. What customization options are typically available from plastic machine shops?
Most plastic machine shops offer a range of customization options to meet specific project requirements. This can include variations in size, shape, and features, as well as the ability to work with different materials. Shops may also provide services such as surface finishing, color matching, and assembly. Discuss your design specifications in detail with potential suppliers to explore all available customization capabilities and ensure they can meet your expectations. -
8. How do I vet a plastic machine shop before placing an order?
Vetting a plastic machine shop is essential to ensure they can meet your project needs. Start by researching their industry reputation through reviews and case studies. Request references from previous clients to gain insights into their reliability and quality. Evaluate their technical capabilities by asking about their machinery, expertise, and experience with your specific materials and processes. Finally, assess their communication and responsiveness, as these factors are crucial for a successful partnership.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Plastic Machine Shop Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Atlas Fibre – Precision Plastic Machine Shop Services
Domain: atlasfibre.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Plastic Machine Shop Services: Precision Crafted Components
Materials:
– Glass Epoxy
– Glass Silicone
– Glass Melamine
– Glass Polyester
– Phenolic
– Custom Materials
– Engineering Thermoplastics
Shapes:
– Sheets
– Rods
– Tubes
– Precision Blanks
– Prepreg Composite
– Springs and Vibratory Vacuum Pumps and Vanes
Top Materials:
– FR4
– G10
– G11
– G7
– G3
Capabilities:
– CNC Machining (CNC Lath…
2. Curbell Plastics – Key Plastic Materials
Domain: curbellplastics.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Curbell Plastics offers a large inventory of plastic materials suitable for machine shops, including: 1. ABS – Outstanding impact resistant, low cost, easy to machine and thermoform. 2. Acetal – High strength, stiff, low friction with good wear properties. 3. Acrylic – Strong, stiff, clear plastic available in various colors and finishes. 4. CE Canvas Phenolic – Electrical grade with cotton canvas…
3. Professional Plastics – Plastic Sheets & Rods
Domain: professionalplastics.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Machine Shops – Plastic Supplier with 22 Locations in USA, Singapore & Taiwan. Leader in Plastic Sheets, Rods, Tubing, Profiles, & Parts since 1984. Top materials include Plexiglass Sheet, PEEK Sheets & Rod, Cast Acrylic Sheet, Polycarbonate Sheets, HDPE Sheets, Acetal Sheet & Rod, UHMW Sheet & Rod, Nylon Sheet & Rod, Vespel SP-1. Other materials include ABS, Acetal/Delrin®, Acrylic/Plexiglass, Bo…
4. Polymer Shapes – Key Products for Machine Shops
Domain: polymershapes.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Key products for machine shops include: PPSU (Polyphenylsulfone), PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene), PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide), Phenolic/Thermoset Plastics, PI (Polyimide), Polyester (PET), Polyurethane (PU), PAI (Polyamide-imide), PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), PEI (Polyetherimide, ULTEM™), Nylon (Polyamide, PA), Ultra High Molecular Weight Polyethylene (UHMW), Industrial PVC/CPVC, LEXAN™ Polycarbon…
5. Port Plastics – Cut to Size Services
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: 1. Port Plastics – Location: Phoenix, Arizona; Services: Cut to size, direct shipping for larger orders; Reliability: Great reliable company.
2. Professional Plastics – Offers a range of plastic materials; Recommended for larger orders.
3. McMaster Carr – Suitable for one or two pieces; Offers a variety of materials.
4. Boedeker Plastics – Location: Shiner, Texas; Services: Huge stocking supplier,…
6. IPMI – Precision Plastic Machining
Domain: ipmiengineering.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: IPMI specializes in machining plastics, offering precision plastic components for various industries. Types of plastics machined include Delrin, Nylon, Glass Filled Nylon, Acrylic, UHMW, and PEEK (High Temperature Plastic). The company provides CNC plastic machining services, capable of high or low volume production. IPMI utilizes modern, high-speed machines and automation for quality parts at com…
7. Piedmont Plastics – Plastic Materials for Machining
Domain: piedmontplastics.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Piedmont Plastics provides a wide range of plastic materials suitable for machine shops, including acrylic, polycarbonate, PVC, and more. These materials are used for various applications such as machining, fabrication, and manufacturing processes. The company emphasizes the importance of high-quality materials to enhance productivity and efficiency in machine shop operations.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic machine shop
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, strategic sourcing for plastic machining services is not merely a procurement task; it is a vital component of operational success. International B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can leverage the advantages of precision machining to enhance product quality while managing costs effectively.
Key takeaways include the importance of selecting a plastic machine shop that offers expertise in advanced machining techniques, such as CNC and 5-axis machining, which are crucial for producing high-precision components across diverse industries. Additionally, the availability of a wide range of materials tailored to specific applications ensures that companies can meet stringent performance standards while maintaining competitiveness.
As you consider partnerships with plastic machine shops, prioritize those that demonstrate a commitment to quality assurance, quick turnaround times, and comprehensive material support. The future of manufacturing lies in collaborative relationships that drive innovation and efficiency.
Take action today—explore potential suppliers who can meet your unique needs and contribute to your success in an increasingly global market. Together, we can navigate the complexities of plastic machining to achieve remarkable results.