Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic injection mold cost
In an increasingly competitive global landscape, understanding the nuances of plastic injection mold cost is essential for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their manufacturing processes. One of the key challenges international businesses face, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, is navigating the diverse pricing structures and complexities associated with sourcing molds. This guide aims to demystify the costs involved in plastic injection molding, providing a comprehensive overview that includes various types of molds, their applications, and critical factors influencing pricing.
From the initial design and material selection to operational costs and supplier vetting, this resource equips decision-makers with actionable insights to facilitate informed purchasing choices. Whether you’re a startup in Nigeria aiming to scale production or a seasoned manufacturer in Brazil looking to reduce overhead, understanding the breakdown of costs—from tooling to production volume—will empower you to make strategic investments.
Moreover, we delve into the importance of choosing the right supplier and the impact of technological advancements on mold manufacturing. By the end of this guide, you will have a clearer perspective on how to effectively manage your injection molding projects, ensuring that your organization remains competitive while maximizing return on investment.
Understanding plastic injection mold cost Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low-Volume Injection Molds | Cost-effective, typically made from 3D printing or aluminum; suitable for small production runs. | Prototyping, small batch production | Pros: Lower initial investment; faster turnaround. Cons: Limited durability; not ideal for high-volume production. |
| Single-Cavity Injection Molds | Designed to produce one part per cycle; simpler and less costly than multi-cavity molds. | Small to medium production runs | Pros: Lower mold cost; easier to design. Cons: Slower production rate; higher per-unit cost for larger runs. |
| Multi-Cavity Injection Molds | Capable of producing multiple parts per cycle; designed for high-volume production. | Mass production of identical parts | Pros: Reduced cost per part; efficient for large orders. Cons: Higher upfront costs; complex design requirements. |
| Family Molds | Mold that produces different parts in a single cycle; designed for related components. | Automotive, consumer electronics | Pros: Versatile; saves time and costs on multiple molds. Cons: Complicated design; potential quality trade-offs. |
| Hot Runner Systems | Utilizes heated channels to keep plastic molten; minimizes waste and cycle time. | High-volume production of complex parts | Pros: Reduced material waste; faster cycle times. Cons: Higher initial investment; requires specialized maintenance. |
What are the Characteristics of Low-Volume Injection Molds?
Low-volume injection molds are typically constructed using 3D printing or aluminum, making them an economical choice for businesses looking to produce small quantities of parts. These molds are ideal for prototyping and testing designs before committing to larger production runs. B2B buyers should consider this option when they need quick iterations or are testing market viability without significant financial risk. However, the durability of these molds is limited, making them unsuitable for extensive production.
When to Use Single-Cavity Injection Molds?
Single-cavity injection molds are designed to manufacture one part per cycle, making them a straightforward solution for small to medium production runs. Their simplicity often translates to lower costs, making them attractive for B2B buyers with limited budgets. However, while they are easier to design, the slower production rate can lead to higher costs per unit for larger orders. Companies should weigh the volume of production against the mold investment to determine suitability.
How Do Multi-Cavity Injection Molds Benefit Mass Production?
Multi-cavity injection molds are engineered to produce several parts in a single cycle, making them essential for mass production. This design significantly reduces the cost per part, making it a preferred choice for businesses that anticipate large order quantities. However, the complexity of these molds can lead to higher initial costs and require more intricate design processes. B2B buyers should ensure that their production volumes justify the investment in multi-cavity molds.
What are the Advantages of Family Molds?
Family molds can produce various related parts in one cycle, offering versatility for applications such as automotive or consumer electronics. This approach saves time and reduces costs by eliminating the need for multiple molds for different components. However, the design of family molds can be complicated, and there may be trade-offs in quality among the produced parts. B2B buyers should consider the overall efficiency of family molds against the potential challenges in design and production.
Why Consider Hot Runner Systems for High-Volume Production?
Hot runner systems maintain the plastic in a molten state as it travels through the mold, minimizing waste and reducing cycle times. These systems are particularly beneficial for high-volume production of complex parts, allowing for greater efficiency. However, they come with a higher initial investment and require specialized maintenance, which could be a barrier for some businesses. B2B buyers must assess their production scale and capabilities to determine if hot runner systems align with their operational needs.
Key Industrial Applications of plastic injection mold cost
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of plastic injection mold cost | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of dashboard components and interior trims | Reduces manufacturing costs while ensuring high precision and repeatability | Sourcing durable materials and experienced mold makers to handle complex designs |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing housings for devices like smartphones | Enhances product aesthetics and durability at scale | Consideration for rapid prototyping and low-volume options for testing before large runs |
| Medical Devices | Creation of syringes and surgical instruments | Ensures compliance with stringent regulations and high quality standards | Need for specialized molds that can handle biocompatible materials and meet regulatory certifications |
| Packaging | Development of custom containers and closures | Increases shelf appeal and functionality of products | Evaluate material compatibility with the contents and design flexibility for different sizes |
| Home Appliances | Molding parts for kitchen gadgets and appliances | Lowers production costs and improves product lifecycle | Focus on mold durability and the ability to withstand high-volume production cycles |
How is Plastic Injection Mold Cost Applied in the Automotive Sector?
In the automotive industry, plastic injection molding is crucial for producing dashboard components and interior trims. The high initial costs of molds are offset by the ability to produce large volumes of parts with tight tolerances. International buyers must consider sourcing from experienced mold makers who can provide durable materials capable of withstanding the rigors of automotive use. Ensuring compliance with industry standards while balancing cost efficiency is essential for maintaining competitive pricing in the market.
What Role Does Plastic Injection Mold Cost Play in Consumer Electronics?
For consumer electronics, plastic injection molding is employed to create housings for devices like smartphones and tablets. This process not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of the products but also ensures durability at scale. B2B buyers, especially from emerging markets, should look for suppliers that offer rapid prototyping services, allowing for adjustments before committing to large production runs. Cost-effective mold solutions that maintain high quality are critical in this fast-paced industry.
Why is Plastic Injection Mold Cost Important in Medical Devices?
In the medical device sector, precision and compliance are paramount. Injection molding is used to manufacture items such as syringes and surgical instruments, where the cost of molds can be significant. However, the value lies in the ability to produce high-quality, sterile products that meet stringent regulatory requirements. Buyers must focus on sourcing molds that can handle biocompatible materials and ensure that their suppliers have the necessary certifications to comply with health regulations.
How Does Plastic Injection Mold Cost Affect Packaging Solutions?
Packaging applications benefit from plastic injection molding through the development of custom containers and closures that enhance product appeal and functionality. The initial mold investment is justified by the ability to create unique designs that stand out in the market. B2B buyers should prioritize material compatibility with the product contents and ensure flexibility in mold designs to accommodate various sizes and shapes, thus maximizing their packaging solutions.
What Benefits Does Plastic Injection Mold Cost Provide for Home Appliances?
In the home appliance industry, plastic injection molding is utilized for creating parts for kitchen gadgets and appliances, significantly lowering production costs while improving product durability. International buyers should focus on sourcing molds that can withstand high-volume production cycles and are made from durable materials. Understanding the balance between upfront costs and long-term savings through efficient manufacturing processes is vital for optimizing overall production costs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘plastic injection mold cost’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating the High Initial Investment for Molds
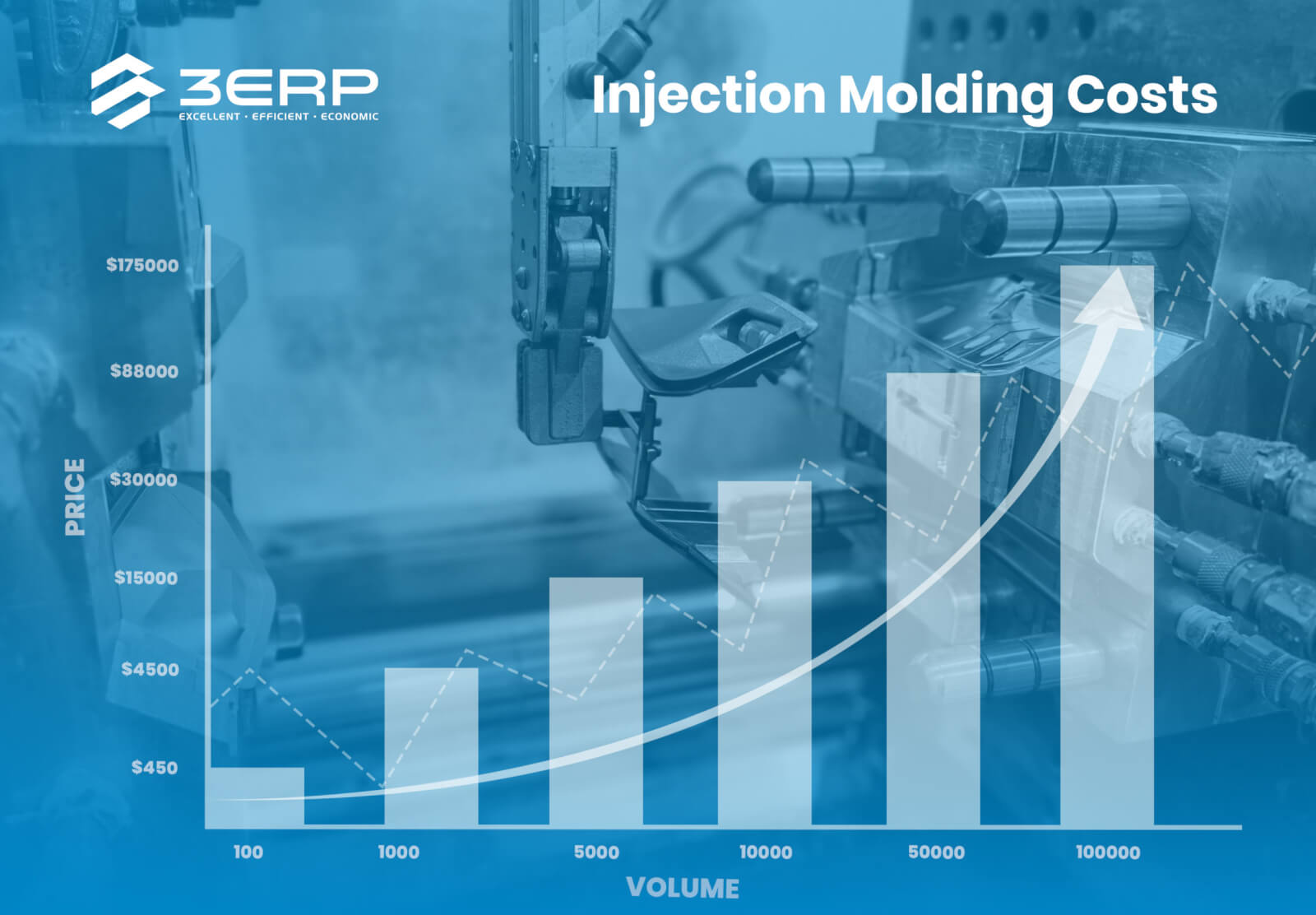
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Africa and South America, face the daunting challenge of high initial costs associated with plastic injection molds. The price can range from $1,000 for simple molds to over $100,000 for complex, multi-cavity designs. For small to mid-sized businesses, this steep investment can significantly strain budgets, making it difficult to justify the expense without guaranteed high production volumes.
The Solution: To alleviate this pain point, buyers should consider utilizing low-cost alternatives initially, such as 3D printed molds or CNC machined aluminum molds for low-volume production. These options allow businesses to test the market and refine their designs without committing to expensive tooling. Furthermore, engaging with a reputable contract manufacturer can provide insights into mold cost structures and help negotiate better terms based on projected volume. By starting with a smaller, less expensive mold, companies can gauge demand and scale up production as needed, thus spreading the higher costs over a larger number of units later.
Scenario 2: Understanding Cost Variability Across Different Projects
The Problem: Buyers often struggle with the unpredictable nature of injection mold costs, which can vary significantly based on part complexity, material choice, and production volume. This inconsistency can lead to budgeting challenges, where the final costs exceed initial estimates, causing project delays and financial strain.
The Solution: To combat this issue, businesses should adopt a comprehensive approach to project planning. Begin by clearly defining project specifications, including part design and material requirements, before consulting with mold makers. Creating a detailed request for quotation (RFQ) that outlines all parameters will enable suppliers to provide more accurate estimates. Additionally, consider running pilot projects with simpler designs to establish a baseline cost, which can be scaled up for more complex designs in the future. This proactive planning helps set realistic expectations and allows for better financial forecasting.
Scenario 3: Managing Ongoing Costs Beyond Initial Mold Investment
The Problem: After the initial investment in molds, many buyers overlook the ongoing operational costs associated with injection molding, such as maintenance, material sourcing, and labor. This can lead to unexpected expenses that impact overall profitability, particularly in regions where skilled labor is scarce or material costs fluctuate significantly.
The Solution: To manage ongoing costs effectively, buyers should implement a holistic cost analysis framework that accounts for all aspects of the injection molding process. Regular maintenance schedules for molds can prevent costly breakdowns, while establishing relationships with multiple material suppliers can help mitigate risks associated with price volatility. Additionally, investing in training for local staff can enhance operational efficiency and reduce dependency on external labor. By actively managing these ongoing costs, companies can improve their overall profitability and ensure a more sustainable production process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic injection mold cost
What Are the Key Materials for Plastic Injection Molds?
When considering the cost of plastic injection molds, the choice of material is critical. Different materials offer unique properties that can significantly influence the mold’s performance, durability, and overall cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in plastic injection molding, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Steel Affect Plastic Injection Mold Costs?
Key Properties: Steel molds, particularly those made from hardened tool steel, exhibit high durability and excellent thermal conductivity. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for a variety of thermoplastic materials.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel molds is their longevity; they can produce millions of parts before showing signs of wear. However, they come with a high initial cost, often exceeding $50,000 for complex designs. Manufacturing steel molds is also labor-intensive, requiring skilled machinists and advanced machinery.
Impact on Application: Steel molds are ideal for high-volume production runs, especially for parts that require precision and durability. They are compatible with a wide range of plastics, including those that are fiberglass-filled, which can be abrasive to less durable materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local material availability and compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN. The high cost of steel molds may also necessitate a thorough ROI analysis, particularly for smaller production runs.
What Role Does Aluminum Play in Injection Mold Cost?
Key Properties: Aluminum molds are lighter than steel and offer good thermal conductivity, which can reduce cycle times. They are generally easier to machine, allowing for quicker turnaround times in mold production.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum molds is their lower cost—typically ranging from $5,000 to $30,000—making them suitable for low to medium production volumes. However, they are less durable than steel and may only be viable for a few thousand cycles before needing replacement.
Impact on Application: Aluminum molds are often used for prototyping or short production runs. They are suitable for less abrasive materials and can be a cost-effective solution for companies testing new products.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications and whether aluminum molds meet local manufacturing standards. In regions with stringent regulations, ensuring compliance with material specifications is essential.
How Do 3D Printed Molds Influence Costs?
Key Properties: 3D printed molds can be made from various materials, including plastics and metals. They allow for complex geometries and rapid prototyping, which can significantly shorten the development cycle.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of 3D printed molds is their low initial cost, often starting at around $100. They are ideal for low-volume production and can be produced quickly. However, they typically lack the durability of traditional molds and may not withstand high production volumes.
Impact on Application: 3D printed molds are best suited for low-volume applications or testing new designs. They can be used with less demanding materials but may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Companies in emerging markets may find 3D printing a cost-effective entry point into injection molding. However, they should ensure that the materials used meet local standards and regulations.
What Are the Benefits of Composite Materials in Injection Molding?
Key Properties: Composite materials, often reinforced with fiberglass or carbon fiber, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent thermal stability. They can be tailored for specific applications, enhancing performance.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of composite molds is their ability to produce lightweight, durable parts. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Composite molds are particularly effective in industries requiring lightweight components, such as automotive and aerospace. They can handle high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for advanced thermoplastics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the availability of composite materials in their region and consider compliance with international standards. The higher costs associated with composites may necessitate a careful analysis of production volumes and expected ROI.
Summary of Material Selection for Plastic Injection Molds
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic injection mold cost | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | High-volume production runs | Exceptional durability | High initial cost | High |
| Aluminum | Prototyping and low to medium production | Lower cost and quicker production | Limited durability | Medium |
| 3D Printed | Low-volume production and prototyping | Low initial investment | Not suitable for high volumes | Low |
| Composite | Lightweight, high-performance applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers navigating the complexities of plastic injection mold costs. Understanding the properties and implications of each material can help in making informed decisions that align with production goals and budget constraints.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic injection mold cost
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Plastic Injection Molds?
The manufacturing process for plastic injection molds consists of several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and cost-effectiveness of the mold. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers looking to optimize their investment in injection molding.
How Is Material Prepared for Injection Molding?
Material preparation is the initial stage where the raw materials, typically thermoplastics, are selected based on the intended application. Common materials include ABS, PP, and PS, among others. The selected material must be dried to eliminate moisture, which can negatively impact the quality of the final product. The drying process often involves using specialized ovens or dehumidifiers. Proper material preparation ensures that the subsequent stages of the injection molding process yield high-quality parts with minimal defects.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Injection Molding?
The forming stage involves the actual injection of the molten plastic into the mold. This process is typically executed using a hydraulic or electric injection molding machine. The key techniques employed during this stage include:
- Injection Phase: The heated plastic is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, which ensures that the material fills every part of the mold.
- Holding Phase: Once the mold is filled, pressure is maintained for a short duration to compensate for material shrinkage as it cools.
- Cooling Phase: The mold is cooled, allowing the plastic to solidify and take the shape of the mold cavity.
The efficiency of these techniques significantly affects cycle times and, consequently, production costs. B2B buyers should consider suppliers with advanced machinery that can optimize these phases for better throughput.
How Does the Assembly and Finishing Process Work?
After the cooling phase, the molded parts are ejected from the mold. Depending on the complexity of the design, some parts may require additional assembly or finishing processes. These can include:
- Trimming: Removing excess material or flash that may have formed during the injection process.
- Assembly: For multi-part products, assembly may involve joining different components that were molded separately.
- Surface Treatment: Finishing techniques such as painting, coating, or polishing may be applied to enhance the aesthetic and functional properties of the final product.
Understanding these processes helps B2B buyers gauge the total cost and quality of their injection-molded products.
What Are the Key Quality Assurance Standards for Injection Molding?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the injection molding process to ensure that the final products meet both regulatory and customer specifications. Various international and industry-specific standards govern this aspect.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized international standards for quality management systems. Adhering to ISO 9001 ensures that the manufacturing process is consistently evaluated and improved, leading to higher quality products. Other relevant standards include:
- ISO 13485: Pertaining to medical devices, ensuring compliance with stringent safety and efficacy requirements.
- CE Marking: A certification indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
B2B buyers should seek suppliers who are certified under these standards to ensure reliable quality assurance practices.
What Are the Common Quality Control Checkpoints in Injection Molding?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical throughout the injection molding process. Commonly employed QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the injection molding process in real-time to catch any deviations early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished product to ensure it meets design specifications and quality standards.
These checkpoints help mitigate risks and ensure that defects are identified and addressed promptly, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can implement several verification methods:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality management systems can provide insights into their adherence to established standards.
- Reports: Requesting quality control reports, including defect rates and corrective actions taken, can help buyers assess supplier performance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes.
For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, ensuring that suppliers meet these quality standards is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and compliance in their respective markets.
What Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider Regarding Quality Control?
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances in quality control that can vary by region. For instance, regulatory requirements in Europe may differ significantly from those in Africa or South America. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with the regulations applicable to their target markets.
Additionally, language barriers and cultural differences may affect communication regarding quality standards and expectations. Establishing clear and consistent communication channels can help mitigate misunderstandings and enhance collaboration.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for plastic injection molds is vital for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their investments, and ensure high-quality outcomes in their injection molding projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘plastic injection mold cost’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure plastic injection molds efficiently and cost-effectively. Understanding the various factors that influence mold costs will empower you to make informed decisions, ensuring that your investment aligns with your production needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial for accurate cost estimation. This includes the part dimensions, complexity, and material requirements. A well-defined project scope helps suppliers provide precise quotes and reduces the risk of unexpected costs later on.
- Consider part size: Larger parts typically require more material and complex molds.
- Assess design complexity: Intricate designs may necessitate advanced machining techniques, impacting mold costs.
Step 2: Determine Production Volume
Understanding your production volume needs will influence the type of mold you require. For low-volume projects, a simple single-cavity mold may suffice, while high-volume production often necessitates multi-cavity molds to optimize efficiency and reduce per-unit costs.
- Evaluate your demand: Estimate the number of units you need monthly or annually.
- Choose the right mold type: Single-cavity molds are ideal for lower quantities, whereas multi-cavity molds are essential for large-scale production.
Step 3: Research Material Requirements
The choice of material for both the product and the mold affects costs significantly. Different plastics and composites can vary in price, and some require specialized molds made from durable materials to withstand wear and tear.
- Identify suitable materials: Consider the properties required for your final product.
- Assess mold material: Hardened steel molds are often necessary for abrasive materials, which can increase initial costs but provide longevity.
Step 4: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vetting suppliers is essential to ensure quality and reliability. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar projects. This step helps you gauge their capability and reputation within the industry.
- Check for certifications: Ensure suppliers adhere to international quality standards.
- Review past work: Look for examples of similar molds they have successfully produced.
Step 5: Request Detailed Quotes
Once you have narrowed down potential suppliers, request detailed quotes that outline all costs involved. This should include mold design, production, and any additional fees for material or delivery.
- Compare total costs: Look beyond initial mold pricing to include setup, maintenance, and operational costs.
- Negotiate terms: Use the information gathered to negotiate better terms or discounts based on your volume commitments.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Production Schedules
Understanding lead times for mold production and delivery is critical, especially if you are working against tight deadlines. Different suppliers may have varying production capacities, which can impact your overall project timeline.
- Inquire about timelines: Ask for estimated production and delivery times to align with your project schedule.
- Plan for contingencies: Factor in potential delays and have backup plans in place to avoid production interruptions.
Step 7: Establish After-Sales Support and Maintenance Plans
After securing your mold, ensure that the supplier provides adequate support and maintenance options. This is vital for long-term production efficiency and addressing any issues that may arise post-purchase.
- Review warranty options: Understand what warranties are available for the molds.
- Discuss maintenance services: Inquire if the supplier offers ongoing support for repairs or modifications as your production needs evolve.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic injection mold cost Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Plastic Injection Mold Sourcing?
When sourcing plastic injection molds, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and decision-making. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials for both the molds and the injected products significantly affects costs. Molds are typically made from steel or aluminum, with steel being more expensive but more durable, especially for high-volume production. The raw materials for the plastic itself also contribute to costs, with thermoplastics like ABS or polypropylene being common choices.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass skilled workers needed for designing, building, and operating the injection molding machines. For businesses outsourcing production, these costs are included in the service provider’s pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production environment, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. These overheads can vary significantly based on the location of the manufacturing facility.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often the most significant upfront investment in injection molding. The complexity of the mold design, the type of manufacturing process (CNC machining, EDM, or 3D printing), and the number of cavities in the mold directly influence these costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality control processes ensures that the produced parts meet the required specifications and standards. This may involve additional testing and inspection phases, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight and customs duties, should not be overlooked, especially for international transactions. These costs can vary based on the Incoterms agreed upon and the distance between the manufacturer and the buyer.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin is typically factored into the pricing structure. This margin can vary widely based on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the complexity of the services offered.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Plastic Injection Mold Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of plastic injection molds:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher production volumes generally lead to lower costs per unit due to economies of scale. Suppliers often have different pricing tiers based on the quantity ordered.
-
Specifications and Customization: Highly customized molds or products with intricate designs may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly communicate their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials for both the mold and the final product can significantly impact pricing. Specialized materials may lead to higher tooling costs.
-
Quality and Certifications: Molds that require compliance with specific industry standards or certifications (e.g., ISO) may carry higher costs due to the additional quality assurance processes involved.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s experience, location, and production capabilities can also influence pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge premium prices.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping and delivery can affect the overall cost structure. Different Incoterms can shift the responsibility for shipping and customs duties between the buyer and seller, impacting the total cost.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for B2B Buyers in Plastic Injection Mold Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency and ensure a favorable deal, B2B buyers should consider the following tips:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the long-term costs associated with the molds, including maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime. This holistic view will help in assessing the true value of a supplier’s offer.
-
Leverage Volume Commitments: If possible, negotiate for better pricing by committing to larger orders or long-term contracts. This can provide leverage for discounts.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Obtain comprehensive quotes that break down all cost components, allowing for better comparison between suppliers and understanding of pricing structures.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For international buyers, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and improve lead times. Local suppliers may also have better knowledge of regional compliance standards.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand that pricing may vary significantly based on regional factors, including currency fluctuations, economic conditions, and local market competition.
Final Thoughts on Plastic Injection Mold Costs
While the costs associated with plastic injection molding can be substantial, particularly for complex molds, the efficiency and scalability of the process often lead to lower per-unit costs in high-volume production. Buyers should approach sourcing with a clear understanding of the cost components and pricing influencers, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their business objectives. Always remember that indicative prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so regular market assessments and supplier evaluations are essential for long-term success.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing plastic injection mold cost With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Plastic Injection Mold Cost
In the landscape of manufacturing, businesses frequently seek cost-effective and efficient methods to produce plastic parts. While plastic injection molding is a dominant choice due to its high precision and scalability, alternative solutions exist that may better suit specific project requirements. This analysis compares plastic injection mold costs with other viable manufacturing methods, including 3D printing and blow molding, providing insights for B2B buyers to make informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Plastic Injection Mold Cost | 3D Printing | Blow Molding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, repeatable | Varies by printer; good for prototypes | High-volume production, less precision |
| Cost | $1,000 – $100,000+ | $100 – $20,000+ (varies by scale) | $10,000 – $50,000+ |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor, tooling | User-friendly, low barrier to entry | Moderate; specialized equipment needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate; molds require upkeep | Low; minimal maintenance needed | Moderate; equipment maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of complex parts | Prototyping and low-volume runs | Hollow parts, large volumes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
3D Printing: A Flexible Solution for Prototyping and Low-Volume Production
3D printing stands out as an innovative alternative to plastic injection molding, particularly for prototyping and small production runs. This method allows for rapid design iterations and customization without the significant upfront costs associated with molds. The initial investment in a 3D printer can be relatively low, making it accessible for startups and smaller businesses. However, the performance can vary based on the type of printer used, and the speed of production may not match that of injection molding for large quantities. Additionally, the surface finish and mechanical properties of 3D-printed parts may not always meet the stringent requirements of certain applications.
Blow Molding: Ideal for High-Volume Production of Hollow Parts
Blow molding is another effective manufacturing method, primarily used for creating hollow plastic parts such as bottles and containers. This technique offers high-speed production rates and is cost-effective for large volumes, with lower per-unit costs as production scales. However, the initial setup costs can still be significant, particularly for custom molds. Blow molding is less suited for complex geometries compared to injection molding, making it essential for buyers to assess their specific part requirements. The maintenance of blow molding equipment can also be moderate, requiring skilled personnel to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Manufacturing Solution for Your Business
When deciding between plastic injection molding and its alternatives, B2B buyers must carefully evaluate their specific needs, including production volume, part complexity, and budget constraints. Plastic injection molding excels in high-volume applications requiring precision and durability, while 3D printing offers flexibility for prototyping and low-volume production. Blow molding serves as an efficient solution for mass-producing hollow components. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, businesses can select the most appropriate manufacturing solution that aligns with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic injection mold cost
What Are the Key Technical Properties Influencing Plastic Injection Mold Costs?
Understanding the technical properties of plastic injection molds is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize costs and ensure quality in their manufacturing processes. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
Material Grade
The material used for mold construction significantly impacts its durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum, which is cost-effective for low-volume production, and hardened tool steel, ideal for high-volume runs due to its strength and wear resistance. Choosing the right material grade not only affects the initial cost but also the lifespan of the mold, influencing long-term ROI.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation in the mold’s dimensions and is critical for ensuring that the final product meets quality standards. Tight tolerances are necessary for parts that require high precision, whereas looser tolerances can reduce manufacturing costs. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers align their mold specifications with product functionality and market expectations.
Cavity Count
Cavity count indicates how many identical parts a mold can produce in a single cycle. Single-cavity molds are suitable for low-volume projects, while multi-cavity molds are essential for mass production. The choice of cavity count directly affects the mold’s initial cost and production efficiency; thus, selecting the right configuration is vital for balancing upfront investment with operational efficiency.
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the duration it takes to complete one production cycle, from injection to ejection of the molded part. Shorter cycle times result in higher productivity and lower cost per unit, making this a key factor in cost estimation. Buyers should consider the impact of cycle time on their overall production capacity and timelines when evaluating different mold options.
Surface Finish
The surface finish of the molded part affects not only its aesthetic appeal but also its functionality. Different finishes may require additional processing or specialized molds, which can increase costs. Understanding the desired surface finish helps buyers negotiate mold specifications that align with both budgetary constraints and product quality.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know About Injection Molding?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiations in the injection molding sector. Here are several essential terms to know:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of injection molding, buyers often work with OEMs to create custom parts that fit specific applications. Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers navigate partnerships and sourcing strategies effectively.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For injection molding, MOQs can vary significantly based on mold complexity and production capabilities. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess feasibility and manage inventory costs, especially when planning new product launches.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services. In the injection molding industry, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to gather multiple quotes, enabling them to compare costs and make informed decisions. Crafting a detailed RFQ can facilitate better responses from suppliers.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for buyers involved in cross-border procurement, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, ultimately affecting the total cost of the mold.
T1 and T2 (Tooling Levels)
T1 and T2 refer to different tooling levels that indicate the complexity and durability of the molds. T1 molds are typically used for prototyping or low-volume production, while T2 molds are designed for high-volume manufacturing and longevity. Recognizing these distinctions can guide buyers in selecting the appropriate tooling for their production needs.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions that align with their operational goals and budgetary constraints.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the plastic injection mold cost Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in the Plastic Injection Mold Cost Sector?
The plastic injection mold cost sector is influenced by a variety of global drivers, particularly as international B2B buyers navigate a rapidly evolving landscape. One key trend is the increasing demand for low-cost, high-quality production methods, particularly in developing regions such as Africa and South America. Countries like Nigeria and Brazil are witnessing a surge in manufacturing as local businesses seek to capitalize on lower labor costs and proximity to raw materials. This trend is further fueled by advancements in technology, such as automation and the use of artificial intelligence in the design and production processes, which enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing are also reshaping the market, allowing for rapid prototyping and lower upfront costs for mold production. This is particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require flexibility without the burden of significant capital investment. Additionally, the shift towards Industry 4.0, characterized by smart manufacturing and interconnected systems, is enabling companies to optimize their supply chains and reduce lead times.
International B2B buyers must also consider geopolitical factors that influence sourcing decisions. Tariffs, trade agreements, and political stability can significantly affect mold costs and availability. As companies look to diversify their supply chains, sourcing from regions like Eastern Europe or Southeast Asia may become more attractive, offering competitive pricing while mitigating risks associated with over-reliance on a single market.
How Is Sustainability Reshaping the Plastic Injection Mold Cost Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for B2B buyers in the plastic injection mold sector. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes, including high energy consumption and waste generation, has led to an increased demand for sustainable practices. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and implementing eco-friendly production methods.
Ethical sourcing has gained prominence as businesses recognize the importance of transparent supply chains. Suppliers that provide certifications for sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 or materials sourced from recycled content, are becoming increasingly appealing. This shift is not just about compliance; it reflects a growing consumer preference for environmentally responsible products, which can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
In terms of materials, the use of biodegradable plastics and recycled thermoplastics is on the rise. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but can also lower overall production costs in the long run, as they often require less energy to process. B2B buyers should actively seek out suppliers who offer “green” certifications and demonstrate a commitment to sustainability, as this can lead to more competitive pricing and long-term cost savings.
What Is the Historical Context of Plastic Injection Mold Costs?
The evolution of plastic injection mold costs can be traced back to the mid-20th century when the industry began to adopt more sophisticated manufacturing techniques. Initially, molds were crafted from metal using labor-intensive methods, resulting in high costs and long lead times. However, as technology advanced, the introduction of CNC machining and, later, 3D printing revolutionized the mold-making process.
These advancements allowed for increased precision and reduced production times, which contributed to lowering costs. In recent years, the growing emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing has further transformed the landscape, compelling manufacturers to innovate not only in production efficiency but also in environmental responsibility. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers to understand how market dynamics have shifted and the importance of aligning with suppliers who are not only cost-effective but also forward-thinking in their approach to manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic injection mold cost
-
How do I determine the total cost of a plastic injection mold?
To accurately calculate the total cost of a plastic injection mold, consider several key factors: the complexity of the part design, the materials used for the mold, production volume, and the type of machinery required. Mold costs typically range from $1,000 for simple designs to over $100,000 for complex, multi-cavity molds. Additionally, factor in raw material costs, labor, and potential maintenance expenses. By evaluating these elements, you can create a comprehensive budget that reflects both initial and ongoing costs. -
What is the average cost of a plastic injection mold for mass production?
The average cost of a plastic injection mold for mass production is approximately $12,000 for simple designs. However, this price can vary significantly based on the part’s size and complexity. For instance, a mold designed for high-volume production, such as an automotive component, could range from $60,000 to $80,000 or more. Understanding your production needs and collaborating with suppliers can help you find a mold that balances cost and efficiency. -
What are the payment terms typically offered for plastic injection molding projects?
Payment terms for plastic injection molding projects can vary widely depending on the supplier and project size. Common arrangements include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%), followed by progress payments throughout the project, with the final payment due upon completion and delivery. It’s essential to negotiate clear terms that align with your cash flow and project timelines. Always ensure that these terms are documented in your contract to avoid misunderstandings. -
How do I vet a supplier for plastic injection molding services?
When vetting suppliers for plastic injection molding, consider factors such as their industry experience, quality certifications (like ISO), and customer reviews. Request case studies or references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and capability. Additionally, assess their technological capabilities, including the types of machines they use and their approach to quality assurance. A thorough evaluation can help ensure that you partner with a supplier who meets your production requirements. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for plastic injection molding?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for plastic injection molding can vary based on the supplier and the complexity of the mold. Generally, MOQs may range from a few hundred to several thousand units. For low-volume needs, consider suppliers that offer rapid prototyping or low-volume production options, which can help you avoid excessive upfront costs. Always discuss MOQs during the initial negotiations to ensure they align with your production goals. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in my injection molded products?
To ensure quality assurance in injection molded products, establish clear specifications and quality standards with your supplier before production begins. Implement regular inspections during the manufacturing process, such as in-process quality checks and final inspections. Consider utilizing third-party quality assurance services for unbiased evaluations. Additionally, maintaining open communication with your supplier throughout the project can help address any issues promptly. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing injection molds internationally?
When sourcing injection molds internationally, logistics considerations include shipping costs, customs duties, and import regulations specific to your country. Assess the supplier’s shipping capabilities and timelines to ensure they align with your production schedule. It’s also important to consider the impact of lead times on your overall project timeline. Collaborating with a logistics partner who understands international trade can help streamline the process and mitigate potential delays. -
What materials are commonly used for plastic injection molds?
Common materials for plastic injection molds include aluminum, stainless steel, and hardened tool steel. Aluminum molds are suitable for low-volume production due to their lower cost and quicker manufacturing time. In contrast, steel molds are ideal for high-volume runs as they offer durability and longevity. The choice of material will depend on your project’s specific requirements, such as the volume of parts needed and the type of plastic being used. Always consult with your supplier to determine the best material for your application.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Plastic Injection Mold Cost Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Rex Plastics – Injection Molding Costs
Domain: rexplastics.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Injection molding costs range from $100 to $100,000+, depending on project scope and complexity. A small single-cavity mold costs between $1,000 and $5,000, while complex molds can exceed $80,000. Average mold cost at Rex Plastics is around $12,000. Factors affecting cost include part size, complexity, material, and quantity. Equipment costs vary from small desktop machines (most cost-effective fo…
2. Protolabs – Injection Molding Services
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers a range of injection molding services, including plastic injection molding, liquid silicone rubber molding, overmolding, insert molding, family and multi-cavity molding, and prototyping. They provide cost-effective molds for production quantities as low as 25 pieces, with the capability to produce up to 25,000 parts or more from the same tool. The cost of injection molding is infl…
3. Plastopia Ltd – Key Products
Domain: plastopialtd.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Key Products: 1. Plastics Injection Molding 2. Micro Injection Molding 3. Silicone Molding 4. Blow Molding 5. Extrusion Molding 6. Vacuum Forming 7. Metal Zinc Die Casting 8. CNC Machining 9. Custom Metal Parts 10. 3D Printing Service 11. Product Design Services 12. Texture Cards & Books including: – Plastopia™ VDI 3400 Texture Card (VDI #12~45) – Plastopia™ SPI Surface Finish Card (SPI A1~D3) – P…
4. CustomPartNet – Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: custompartnet.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Injection Molding Cost Calculator, General Injection Molding Reports, Part Information including Name, Description, Images, Manufacturer, Designer, Contact, Website, Category. Basic Shapes: Cube, Cylinder, Disk, Hollow box, Hollow tube, Sheet, Sphere. Containers and covers: Caps, Enclosures, Liquid containers, Panels, Storage containers. Fasteners: Clamps, Connectors, Inserts, Spacers, Threaded fa…
5. Molding Costs – Rubber vs. Plastic
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The discussion compares the costs and processes involved in molding rubber parts versus plastic parts. Key points include: 1. Mold costs for rubber and plastic parts can be similar, but the molding equipment differs. 2. Rubber requires less tonnage and typically involves simpler molds, often without lifters or slides. 3. Rubber molds are generally made from mild steel and do not require extensive …
6. Wayken – Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Injection molding is a manufacturing technology used for producing multiple parts and components across various applications. Key factors affecting injection molding costs include: 1. Molding Tooling Cost: Involves machining molds using methods like CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and 3D printing. 2. Equipment Cost: Different types of injection molding machines (Electric, Hydr…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic injection mold cost
What Are the Key Insights for B2B Buyers on Plastic Injection Mold Costs?
In conclusion, understanding the complexities of plastic injection mold costs is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their manufacturing processes. The initial investment in molds can vary significantly, from as low as $100 for low-volume 3D printed molds to over $100,000 for intricate, high-volume production molds. However, as production scales, the cost per unit decreases, making injection molding an economically viable option for mass production.
Strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in this landscape. By partnering with reputable suppliers who offer transparent pricing and robust support, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance their supply chain efficiency. Engaging in thorough market research and cost analysis will empower companies from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed decisions that align with their production needs.
As we move forward, it is vital to embrace innovative technologies and practices that can further streamline costs and improve quality. We encourage you to explore partnerships with local and international manufacturers who can provide tailored solutions for your specific requirements. Taking this proactive approach will not only enhance your competitive edge but also ensure sustainable growth in an increasingly complex global market.