Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for parts fabrication
In today’s rapidly evolving global market, sourcing parts fabrication services can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. Factors such as fluctuating material costs, varying manufacturing standards, and the complexity of international logistics can complicate the purchasing process. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify parts fabrication by exploring various types, applications, and methodologies, from custom sheet metal to CNC machining. We will also delve into the intricacies of supplier vetting, cost analysis, and quality assurance, providing actionable insights tailored for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers will gain a clearer understanding of the parts fabrication landscape, empowering them to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are a manufacturer seeking reliable suppliers or an engineer looking for specific components, this resource will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of global sourcing. From identifying the right materials to understanding turnaround times, you will find valuable information that enhances your procurement strategy and drives operational efficiency. Ultimately, our goal is to facilitate smoother transactions and foster partnerships that contribute to your business’s growth and success in the competitive international market.
Understanding parts fabrication Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication | Quick turnaround, precision cutting, and bending services | Automotive parts, electronic housings, fixtures | Pros: Fast production, low minimum orders. Cons: Material limitations may apply. |
| CNC Machining | High precision, complex geometries, and multiple materials | Aerospace components, medical devices, prototypes | Pros: Exceptional accuracy, versatile. Cons: Higher costs for low volumes. |
| Injection Molding | Mass production, consistent quality, and diverse materials | Consumer products, automotive parts, packaging | Pros: Cost-effective for large runs. Cons: High initial setup costs. |
| 3D Printing | Rapid prototyping, complex designs, and material flexibility | Custom tooling, prototypes, small batch production | Pros: Quick iterations, minimal waste. Cons: Slower for large production runs. |
| Waterjet Cutting | No heat-affected zones, versatility with various materials | Architectural elements, custom signage, industrial parts | Pros: Precise cuts, eco-friendly. Cons: Slower than laser cutting for thin materials. |
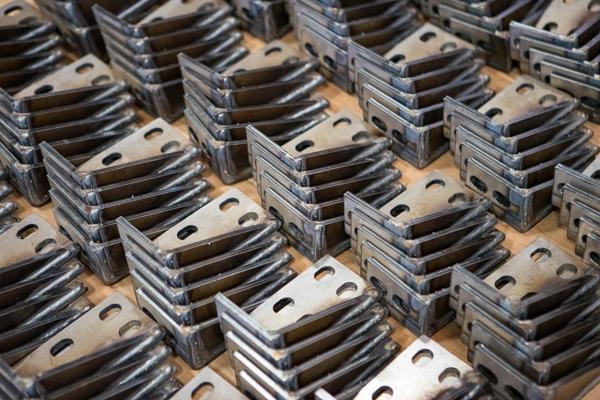
What are the Key Characteristics of Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Custom sheet metal fabrication is characterized by its ability to quickly produce parts through processes like laser cutting and bending. It is particularly suitable for industries requiring components such as electronic housings and automotive parts. B2B buyers should consider the turnaround time and the flexibility in order quantities, as many providers accept low minimum orders. However, buyers must also be aware of potential material limitations, which could affect their design choices.
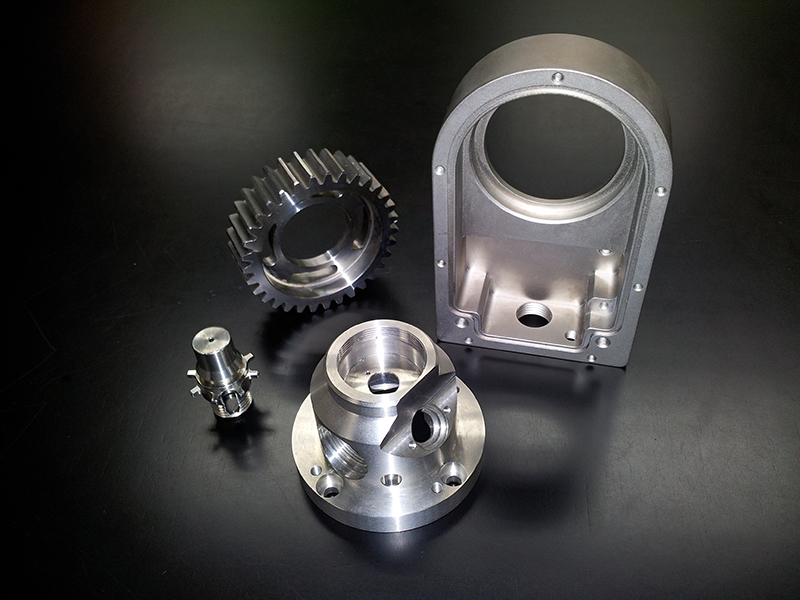
How Does CNC Machining Stand Out in Parts Fabrication?
CNC machining is known for its precision and ability to work with a variety of materials, making it ideal for producing complex geometries. This method is prevalent in industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where accuracy is critical. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the provider’s capabilities in handling specific material types and their ability to produce intricate designs. While CNC machining offers exceptional accuracy, it can be more costly for low-volume orders.
Why is Injection Molding a Preferred Choice for Mass Production?
Injection molding is favored for its efficiency in mass-producing parts with consistent quality. It is commonly used in consumer products and automotive components. For B2B buyers, the primary consideration is the high initial setup cost, which can be a barrier for smaller production runs. However, once the mold is created, the cost per unit decreases significantly, making it an attractive option for large-scale production.
What Advantages Does 3D Printing Offer for Prototyping?
3D printing excels in rapid prototyping and allows for the creation of complex designs that traditional methods may struggle to achieve. This method is suitable for custom tooling and small batch production, appealing to industries that require quick iterations. Buyers should consider the material options available and the speed of production, as 3D printing is not always the best choice for large quantities. Its strengths lie in reducing waste and enabling fast design changes.
How Does Waterjet Cutting Compare to Other Methods?
Waterjet cutting is distinguished by its ability to cut through various materials without creating heat-affected zones, which can alter material properties. This technique is suitable for architectural elements and industrial parts. B2B buyers should evaluate the precision and eco-friendliness of waterjet cutting, as it produces minimal waste. However, it is generally slower than laser cutting for thinner materials, which may affect production timelines.
Key Industrial Applications of parts fabrication
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Parts Fabrication | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Custom chassis and body parts fabrication | Enhances vehicle performance and safety | Ensure compliance with regional regulations and material standards |
| Aerospace | Precision components for aircraft manufacturing | Increases reliability and reduces maintenance costs | Focus on certifications and traceability for materials used |
| Oil & Gas | Specialized piping and fittings fabrication | Improves efficiency and reduces downtime | Assess supplier capabilities for high-pressure and temperature applications |
| Electronics | Enclosures and heat sinks for electronic devices | Protects components and enhances thermal management | Evaluate material compatibility and lead times for rapid prototyping |
| Construction | Structural components and custom fixtures | Supports project timelines and cost efficiency | Consider logistics and local sourcing options to minimize delays |
How is Parts Fabrication Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, parts fabrication plays a crucial role in producing custom chassis and body parts. This process allows manufacturers to create components that enhance vehicle performance and safety, addressing specific design requirements or modifications. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers that understand local regulations and can provide materials that comply with safety standards. Additionally, the ability to produce low to high volumes without compromising quality is essential for meeting market demands.
What Are the Precision Requirements for Aerospace Parts Fabrication?
Aerospace manufacturers require precision components that are critical for aircraft performance and safety. Parts fabrication in this industry involves creating specialized components such as brackets, housings, and structural elements that must meet stringent regulatory standards. For international buyers, especially from the Middle East and Europe, sourcing from suppliers with the necessary certifications (like AS9100) is vital. Traceability of materials and adherence to strict quality controls are paramount to ensure reliability and reduce maintenance costs.
How Does Parts Fabrication Support the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, parts fabrication is essential for producing specialized piping and fittings that withstand extreme conditions. These components must be designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, making it crucial for suppliers to demonstrate their capabilities in meeting such demands. Buyers from regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia should evaluate potential suppliers based on their experience with industry-specific challenges and their ability to deliver products that enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Why is Parts Fabrication Important for Electronics?
The electronics industry relies on parts fabrication for the development of enclosures and heat sinks that protect sensitive components. This fabrication process ensures that products are not only functional but also meet thermal management requirements, which is critical for performance. International B2B buyers should consider suppliers that can provide materials compatible with various electronic applications, along with fast lead times for rapid prototyping. This agility can significantly impact product development cycles and market readiness.
How Can Construction Benefit from Custom Parts Fabrication?
In construction, parts fabrication is utilized to create structural components and custom fixtures that support building projects. This application allows for tailored solutions that can enhance project timelines and cost efficiency. Buyers, particularly from South America and Europe, should focus on sourcing local suppliers who can effectively manage logistics and provide timely deliveries. This consideration is crucial for minimizing delays and ensuring that construction schedules are met without compromising quality.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘parts fabrication’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Long Lead Times in Parts Fabrication
The Problem:
B2B buyers in industries such as automotive or manufacturing often face significant delays in the delivery of custom fabricated parts. These delays can arise from a variety of factors, including supply chain disruptions, inefficiencies in production processes, or high demand for specific materials. For companies operating on tight schedules, these prolonged lead times can lead to project delays, increased costs, and even lost contracts. The pressure to maintain production schedules while waiting for critical components can be overwhelming, especially when alternative suppliers may also face similar challenges.
The Solution:
To combat long lead times, B2B buyers should prioritize working with fabrication partners that offer transparent production timelines and expedited services. When sourcing parts, buyers should ask potential suppliers for detailed information about their production capabilities and lead times. Utilizing online platforms that provide instant pricing and allow for rapid design uploads can also significantly shorten the ordering process. Additionally, establishing a close relationship with a reliable fabricator can facilitate better communication and allow for quicker adjustments in orders, ensuring that buyers receive their parts as swiftly as possible. Investing in local suppliers when feasible can further reduce shipping times and costs, enabling businesses to react quickly to changing demands.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Material Sourcing Challenges
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers struggle with sourcing the right materials for parts fabrication, particularly in regions where access to certain metals or composites is limited. This challenge is compounded by fluctuating material costs and availability, which can disrupt project budgets and timelines. Buyers may find themselves frustrated by the lack of transparency in material sourcing, leading to unexpected delays and increased costs when they need to pivot to alternative materials last minute.
The Solution:
To mitigate material sourcing issues, buyers should conduct thorough market research to identify multiple suppliers and manufacturers who specialize in the required materials. Establishing relationships with a diverse network of suppliers can provide more options when certain materials are unavailable or too costly. Additionally, leveraging technology to monitor material prices and availability can help buyers make informed decisions about when to purchase. Buyers should also consider engaging with fabrication partners that offer a range of materials, as this can streamline the procurement process and provide flexibility in production. Collaborating with suppliers to forecast demand can further enhance material planning and ensure that projects remain on schedule.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality and Precision in Fabricated Parts
The Problem:
Quality assurance is a critical concern for B2B buyers, especially when the fabricated parts are integral to larger systems or products. Variations in quality can lead to product failures, increased warranty claims, and damage to a company’s reputation. Buyers may experience anxiety over whether their suppliers can consistently meet their quality standards, particularly when working with new vendors or less familiar materials.
The Solution:
To ensure high-quality fabricated parts, buyers should implement a rigorous vendor selection process that includes evaluating suppliers’ certifications, production capabilities, and quality control measures. Requesting samples or prototypes can provide insight into a fabricator’s precision and adherence to specifications. Buyers should also establish clear quality criteria and communicate these expectations upfront to their suppliers. Regular audits and feedback loops can foster ongoing improvements and accountability. Furthermore, utilizing advanced technologies such as 3D printing or CNC machining, which offer high precision and repeatability, can enhance the overall quality of parts. By prioritizing quality throughout the sourcing process, buyers can minimize risks and ensure reliable product performance.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for parts fabrication
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Parts Fabrication?
When selecting materials for parts fabrication, understanding the properties of each material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in the intended application. Here, we analyze four common materials: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and Plastic, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
How Does Carbon Steel Perform in Parts Fabrication?
Carbon steel is known for its high strength and excellent machinability. It typically offers a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and is resistant to deformation under pressure, making it suitable for structural applications. Its key advantages include durability and cost-effectiveness, particularly for bulk orders. However, carbon steel is prone to corrosion unless properly coated, which can increase manufacturing complexity and costs.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or equivalent local standards is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, particularly in humid or coastal environments.
What Are the Benefits of Using Stainless Steel in Fabrication?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as food processing or chemical handling. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,500°F (815°C) and is available in various grades, such as 304 and 316, which offer different levels of corrosion resistance.
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and low maintenance requirements. However, it tends to be more expensive than carbon steel and can be challenging to machine due to its hardness. For international buyers, ensuring compliance with standards like ASTM A240 is critical, particularly in industries with strict hygiene requirements.
Why Choose Aluminum for Parts Fabrication?
Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with a temperature rating of approximately 1,200°F (649°C). It offers excellent corrosion resistance and is easily machinable, making it a popular choice for aerospace and automotive applications. The main advantages of aluminum include its low weight, which can reduce shipping costs, and its recyclability, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
On the downside, aluminum can be more expensive than steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications without proper alloying. International buyers should consider the availability of specific aluminum alloys and compliance with standards such as ASTM B221, especially in regions where lightweight materials are preferred for transportation.
What Role Do Plastics Play in Parts Fabrication?
Plastics, such as ABS or polycarbonate, are increasingly used in parts fabrication due to their versatility and lightweight properties. They can withstand temperatures between 180°F (82°C) and 250°F (121°C), depending on the type, and offer good chemical resistance. The main advantages of plastics include lower costs and ease of manufacturing, especially for complex shapes.
However, plastics may not be suitable for high-load applications or extreme temperatures, limiting their use in certain industries. International buyers should consider compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties and ensure that the selected plastic meets local regulations regarding safety and environmental impact.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Parts Fabrication
| Material | Typical Use Case for parts fabrication | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, frames | High strength and cost-effective | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing equipment, chemical tanks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining difficulty | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace parts, automotive components | Lightweight and recyclable | More expensive, limited high-stress use | Medium |
| Plastic | Enclosures, consumer products | Low cost and easy to manufacture | Not suitable for high-load applications | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with essential insights into the various materials used in parts fabrication, allowing for informed decision-making tailored to specific applications and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for parts fabrication
What Are the Key Stages in Parts Fabrication Manufacturing Processes?
The manufacturing process for parts fabrication typically involves several critical stages, each essential for ensuring the quality and functionality of the final product. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Parts Fabrication?
Material preparation is the foundational stage where raw materials are selected based on the specifications of the parts to be fabricated. Common materials include various metals, plastics, and composites. This stage often involves cutting raw materials into manageable sizes, cleaning them to remove contaminants, and sometimes pre-treating surfaces for better adhesion during later stages. Techniques like laser cutting and CNC machining are frequently employed to achieve precise dimensions, which are crucial for maintaining tolerances in the final product.
What Forming Techniques Are Common in Parts Fabrication?
The forming stage is where the raw materials are shaped into the desired forms. This can involve various techniques such as bending, stamping, and welding.
- Bending is often used for sheet metal parts, where the material is bent to create angles and shapes.
- Stamping involves pressing a die onto the material to create specific shapes or features, making it ideal for mass production.
- Welding is critical for assembling different parts together, ensuring structural integrity.
Each of these techniques requires specialized machinery and skilled operators to ensure that the parts meet the required specifications.
How Is Assembly Conducted in Parts Fabrication?
Once the individual components are formed, assembly is the next step. This stage can involve manual assembly or the use of automation, depending on the complexity of the parts and the production volume. Common assembly methods include fastening (using screws, bolts, and nuts), welding, and adhesive bonding.
Quality assurance during assembly is vital, as improper assembly can lead to product failures. For B2B buyers, it’s essential to understand the assembly capabilities of suppliers, especially if the end product requires intricate assembly or specialized skills.
What Finishing Processes Enhance the Quality of Fabricated Parts?
Finishing processes play a crucial role in enhancing both the aesthetics and functionality of parts. Common finishing techniques include:
- Anodizing: Often used for aluminum parts, this process increases corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Plating: This involves coating a part with a thin layer of metal to enhance appearance and protect against corrosion.
- Powder Coating: A popular method for applying a durable finish that can be customized in color and texture.
These finishing processes not only improve the visual appeal of the parts but also contribute significantly to their durability and performance.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential in Parts Fabrication?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the parts fabrication process. It ensures that the final products meet the necessary standards and specifications.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international standards such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for a quality management system. This certification demonstrates a supplier’s commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking for products sold in Europe or API standards for oil and gas components, should also be considered.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Parts Fabrication?
Quality control (QC) is typically segmented into various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to ensure that processes are operating within defined parameters.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once production is complete, finished parts are inspected for defects and compliance with specifications before shipment.
These checkpoints help identify and rectify issues at various stages of production, minimizing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Quality Assurance?
Common testing methods employed in parts fabrication include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using tools like calipers and micrometers to ensure parts meet specified dimensions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or radiographic testing to check for internal flaws without damaging the parts.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating parts under operational conditions to verify their performance and durability.
These testing methods are essential for ensuring that the parts not only meet aesthetic standards but also perform reliably in their intended applications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial to ensuring that they receive high-quality parts.
What Audit Processes Should Be Conducted?
Buyers should consider conducting supplier audits, which can include reviewing the supplier’s quality management systems, production processes, and compliance with international standards. This can be done through:
- On-site Audits: Visiting the supplier’s facility to observe operations and quality control measures in action.
- Document Reviews: Analyzing quality control records, inspection reports, and certifications to assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Third-Party Inspections Enhance Confidence?
Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. These services can conduct inspections at various stages of production, providing reports that detail compliance with specifications and standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and compliance can affect communication and expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements; ensuring that suppliers comply with local laws is essential.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: International shipping can introduce additional risks, making thorough inspections and quality checks even more critical.
By understanding these nuances, buyers can better navigate the complexities of international sourcing and ensure they receive products that meet their quality expectations.
In summary, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for parts fabrication are intricate and multifaceted. B2B buyers must engage thoroughly with suppliers, understand the manufacturing stages, and rigorously verify quality control practices to ensure the delivery of high-quality parts that meet their specifications and standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘parts fabrication’
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of parts fabrication can be challenging for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing internationally. This guide provides a practical checklist to streamline your procurement process, ensuring that you secure quality parts while minimizing risks and costs. Follow these steps to make informed decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline your technical requirements, including dimensions, tolerances, material types, and surface finishes. This step is critical as it ensures that suppliers understand your exact needs, reducing the risk of errors during production.
– Considerations: Include specific CAD files, drawings, or templates if available. Be precise about the performance requirements and any industry standards that must be adhered to.
Step 2: Identify and Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in parts fabrication. Look for companies with a proven track record in your industry and region.
– Key Actions: Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry associations to compile a list of candidates. Evaluate their capabilities, technology, and experience in handling similar projects.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with a supplier, check their certifications and compliance with relevant industry standards. This step ensures that the supplier adheres to quality management systems and safety regulations.
– Important Certifications: Look for ISO certifications, quality assurance programs, and any specific certifications required for your industry, such as AS9100 for aerospace or IATF 16949 for automotive.
Step 4: Request and Evaluate Quotes
Solicit detailed quotes from shortlisted suppliers, ensuring they include all costs associated with production, shipping, and any additional services. This step allows for accurate budgeting and comparison.
– What to Compare: Pay attention to lead times, payment terms, and any hidden costs. Assess whether the quotes are based on your technical specifications and if they provide a breakdown of materials and labor.
Step 5: Assess Supplier Capabilities and Capacity
Evaluate the supplier’s production capabilities and capacity to meet your order volume and delivery timelines. This assessment is vital for ensuring that the supplier can fulfill your needs without compromising quality.
– Key Questions: Inquire about their equipment, workforce expertise, and production processes. Ask for information on their ability to scale operations in case of increased demand.
Step 6: Request Samples or Prototypes
Before finalizing your order, request samples or prototypes of the parts you need. This step is crucial for validating the supplier’s quality and ensuring that the final product meets your specifications.
– What to Look For: Evaluate the samples for accuracy, finish, and material quality. This step can help identify potential issues before mass production begins.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication and Terms
Once you select a supplier, establish clear communication channels and define the terms of your agreement. This step is essential to ensure a smooth collaboration throughout the fabrication process.
– Key Components: Outline expectations regarding timelines, quality checks, and reporting. Regular updates and feedback loops can significantly enhance the relationship and mitigate risks.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the parts fabrication sourcing process, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers and receive high-quality components tailored to their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for parts fabrication Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Parts Fabrication?
Understanding the cost structure of parts fabrication is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts costs. Prices can vary widely based on type, quality, and market conditions. For instance, aluminum may be more expensive than steel, affecting the overall pricing.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass wages, benefits, and any additional training required for specialized tasks. Regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but quality assurance must be monitored.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient operations can reduce overhead costs, which in turn, lowers the price for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specific parts, which adds to the initial setup costs. However, these costs can be amortized over larger production runs, making bulk orders more cost-effective.
-
Quality Control: Ensuring that parts meet required specifications can incur additional costs, particularly if third-party certifications are needed. Companies must factor in these costs when evaluating suppliers.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, shipping method, and customs duties. This is especially pertinent for international buyers who need to account for potential delays and tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their risks and operational costs. Understanding market rates can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Parts Fabrication Costs?
Several factors influence pricing in parts fabrication, particularly for international buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can lead to economies of scale. Higher volume orders typically reduce per-unit costs, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their purchasing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts often require additional design and engineering work, which can increase costs. Standardized designs may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Materials with specific certifications or higher quality standards generally command higher prices. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their application.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, experience, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer premium pricing but also deliver superior quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. This can influence total costs, including insurance and duties.
What Are Essential Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Parts Fabrication?
International B2B buyers can adopt several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing parts fabrication.
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchases to negotiate better terms. Suppliers are often willing to adjust pricing for larger orders, providing significant savings.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but all associated costs, including shipping, duties, and potential rework. A lower initial price may not always translate to lower TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, local economic conditions, and geopolitical factors that can impact pricing. Establishing a clear communication channel with suppliers can help mitigate misunderstandings.
-
Research and Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Evaluate their capabilities, quality standards, and past performance to ensure they align with your requirements.
Disclaimer on Pricing
Prices for parts fabrication can vary significantly based on numerous factors, including market conditions and specific requirements. The prices mentioned in various sources are indicative and may not reflect actual costs at the time of purchase. Always obtain quotes directly from suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing parts fabrication With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Alternatives in Parts Fabrication
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing and product development, businesses often seek alternative solutions to parts fabrication. While traditional methods such as custom sheet metal fabrication offer numerous benefits, it is essential to evaluate other viable options that may align better with specific project requirements, budget constraints, or operational capabilities. This analysis will compare parts fabrication with two notable alternatives: additive manufacturing (3D printing) and traditional machining.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Parts Fabrication | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Traditional Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and durability for various materials | Excellent for complex geometries, but material limitations exist | High precision and surface finish, but slower for complex designs |
| Cost | Competitive for small to medium runs; bulk discounts available | Higher initial costs for equipment; cost-effective for low-volume production | Generally higher due to labor and machine costs; less flexible for small batches |
| Ease of Implementation | Relatively straightforward; requires design files | Requires specialized knowledge and software; setup can be complex | Requires skilled labor and setup time; tooling needs can be substantial |
| Maintenance | Moderate; depends on the equipment used | Low maintenance for printers, but requires regular calibration | High; machines need regular maintenance and skilled operators |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for custom components and high-volume production | Best for prototyping and complex, lightweight designs | Suitable for precision parts with tight tolerances in metal and plastics |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, has revolutionized the way parts are produced. This technology builds components layer by layer, allowing for intricate designs that may be impossible to achieve with traditional methods. The primary advantage of additive manufacturing lies in its ability to create complex geometries while minimizing waste. However, material limitations and slower production speeds for larger items can hinder its application for mass production, making it more suitable for prototyping or specialized components.
Traditional Machining
Traditional machining encompasses various processes such as turning, milling, and drilling, which utilize cutting tools to shape materials. This method excels in producing high-precision parts with excellent surface finishes, making it ideal for applications where tight tolerances are essential. The drawbacks include higher costs associated with labor and tooling, alongside longer lead times for setup and production. Traditional machining is best suited for high-volume runs of standardized parts rather than custom or low-volume orders.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate manufacturing solution, B2B buyers must consider their specific project requirements, including production volume, complexity of design, and budget constraints. Parts fabrication remains a strong contender for custom and high-volume production due to its competitive pricing and versatility. However, for projects requiring intricate designs or rapid prototyping, additive manufacturing may offer significant advantages. Conversely, traditional machining is the go-to method for high-precision components in industries where quality and accuracy are paramount. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for parts fabrication
What are the Key Technical Properties in Parts Fabrication?
Understanding the essential technical properties of parts fabrication is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure that their products meet performance and compliance standards. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
– Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability. Common grades include stainless steel (e.g., 304, 316) and aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075). Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring durability and functionality in the end product, which can affect overall production costs and service life. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance defines the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In parts fabrication, tighter tolerances often indicate higher quality and precision, which is essential in industries like aerospace and medical devices. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers ensure that parts will fit and function correctly in their applications, minimizing the risk of costly reworks. -
Surface Finish
– Surface finish pertains to the texture or smoothness of a part’s surface after fabrication. Different processes, such as anodizing, powder coating, or polishing, can enhance aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. Buyers must consider surface finish specifications to ensure their parts meet both functional requirements and regulatory standards. -
Thickness
– Thickness is a critical property that affects the strength, weight, and cost of the material used in fabrication. For example, sheet metal thickness can range from 0.030″ to 0.500″ depending on the application. Understanding the implications of thickness helps buyers balance the need for durability with cost-effectiveness. -
Mechanical Properties
– Mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility, describe how materials react under various conditions of stress and strain. These properties are essential for ensuring that parts can withstand operational demands. Buyers should specify mechanical properties to avoid failures in critical applications.
What are Common Trade Terms in Parts Fabrication?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in parts fabrication. Here are some common trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify trustworthy suppliers who can provide quality components essential for their products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ refers to the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is critical for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider MOQ when evaluating suppliers, as it can impact their purchasing strategy and cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. This term is important for establishing cost expectations and comparing different suppliers. An effective RFQ can lead to better pricing and terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is crucial for managing risks related to shipping, insurance, and customs clearance, especially for international buyers. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product. This term is essential for project management and supply chain planning. Buyers must consider lead times when scheduling production to avoid delays in their operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality and streamline procurement processes in parts fabrication.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the parts fabrication Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics in Parts Fabrication?
The parts fabrication sector is currently experiencing significant transformation driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving customer demands. As businesses seek to optimize their supply chains, factors like rapid prototyping, customization, and just-in-time manufacturing are gaining traction. International B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly leveraging digital platforms to streamline sourcing processes. Technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are enhancing supply chain visibility, enabling predictive analytics for inventory management, and facilitating real-time communication between suppliers and buyers.
Emerging trends also highlight the importance of agile manufacturing capabilities. Buyers are looking for suppliers who can offer rapid turnaround times without sacrificing quality. For instance, platforms that provide instant pricing and allow for quick design uploads are becoming increasingly popular among B2B buyers. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on collaborative design processes, allowing companies to engage suppliers early in the product development phase to reduce costs and improve product outcomes.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Affecting the Parts Fabrication Sector?
Sustainability is no longer just a buzzword; it is a fundamental aspect of modern B2B procurement strategies. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability. This includes implementing energy-efficient practices, reducing waste, and utilizing eco-friendly materials.
Ethical sourcing is also paramount, as businesses recognize the importance of maintaining responsible supply chains. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and those who adhere to ethical labor practices. By choosing suppliers that prioritize sustainability and ethical standards, companies can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute positively to the environment and society.
The demand for ‘green’ materials, such as recycled metals and biodegradable composites, is on the rise. B2B buyers should actively seek suppliers who offer sustainable alternatives, ensuring that their procurement strategies align with broader corporate social responsibility goals.
What Is the Evolution of the Parts Fabrication Industry?
The parts fabrication industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from traditional manual processes to highly automated and technologically advanced manufacturing. Initially, the sector relied on labor-intensive methods, but advancements in computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machining have revolutionized production capabilities.
In recent years, the advent of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has further transformed the landscape, allowing for rapid prototyping and complex designs that were previously unattainable. This evolution has not only improved efficiency but has also enabled greater customization, catering to the diverse needs of international B2B buyers.
As the industry continues to adapt to technological innovations and changing market dynamics, it is essential for buyers to stay informed about emerging trends and practices to remain competitive in the global marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of parts fabrication
-
How do I choose the right fabrication supplier for my business?
Selecting the right fabrication supplier involves assessing their capabilities, experience, and reputation. Start by reviewing their portfolio to ensure they have experience with the specific materials and processes you require. It’s also crucial to check client testimonials and case studies. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards, as this can affect product reliability. Finally, consider their communication skills and responsiveness, as these factors can greatly impact project timelines and collaboration. -
What are the benefits of custom parts fabrication?
Custom parts fabrication allows businesses to create components tailored to their specific needs, which can enhance functionality and efficiency. Custom solutions can lead to improved performance, reduced waste, and cost savings over time. Additionally, working with a fabricator who offers customization can help you differentiate your products in the market, providing a competitive edge. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for industries with unique requirements or those looking to innovate rapidly. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for parts fabrication?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the parts being fabricated. Some suppliers may have no minimums, especially for custom orders, while others might require a minimum of 100 units or more. When sourcing internationally, it’s essential to discuss MOQs upfront to avoid unexpected costs. Suppliers that offer lower MOQs can be advantageous for startups or businesses testing new products in the market. -
How can I ensure quality assurance in parts fabrication?
To ensure quality assurance in parts fabrication, it’s important to establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier at the outset. Request samples or prototypes before finalizing large orders to assess their quality firsthand. Inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including inspections and testing methods. Additionally, consider third-party audits or certifications to ensure compliance with industry standards, especially if you are sourcing from international suppliers. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing parts fabrication internationally?
Payment terms for international sourcing can vary significantly. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments before production, and final payments upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that work for both parties while ensuring financial security. Many buyers use letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to mitigate risks. Always clarify the payment methods accepted and any currency conversion fees that may apply when dealing with international suppliers. -
How do I manage logistics and shipping for fabricated parts?
Managing logistics for fabricated parts involves coordinating with your supplier to determine the best shipping methods and timelines. Discuss the options for freight forwarding, customs clearance, and delivery to your location. Ensure that the supplier provides tracking information and updates throughout the shipping process. Additionally, consider potential tariffs or import duties applicable to your order, as these can affect overall costs and delivery times. -
What types of materials can I choose for parts fabrication?
The choice of materials for parts fabrication is vast and depends on the intended application. Common materials include various metals (like aluminum and steel), plastics, and composites. Each material offers distinct advantages, such as weight, strength, and corrosion resistance. When selecting materials, consider factors like the environment the part will operate in, mechanical properties required, and cost-effectiveness. Consulting with your supplier can help in making an informed decision tailored to your specific needs. -
How can I request a quote for custom parts fabrication?
Requesting a quote for custom parts fabrication typically involves submitting detailed specifications of your project. This includes design files (e.g., CAD drawings), desired materials, dimensions, and any specific finishing requirements. Many suppliers provide online tools for instant pricing based on uploaded files. After submitting your request, expect a follow-up from the supplier for any clarifications. Ensure you inquire about lead times and any additional costs that may arise during production.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Parts Fabrication Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. SendCutSend – Custom Sheet Metal Fabrication
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: SendCutSend offers custom sheet metal fabrication services including laser cutting, CNC routing, waterjet cutting, anodizing, bending & forming, countersinking, dimple forming, hardware insertion, plating, powder coating, tapping, tumbling, and deburring. They provide instant pricing for custom parts with no minimum quantities and free US shipping on orders over $39. Key materials include cold rol…
2. Barnes 4WD – DOM Sleeve & Poly Bushing
Domain: barnes4wd.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: DIY Off Road Fabrication Parts including Battery Box, DOM Tubing, Grade Eight Nuts and Bolts, Gussets, Misc. DIY Fab Parts, Poly Bushings and Bushing Kits, Cage & Crossmember Components, Weld Washers, Bolt Head Protectors, Bumper Build Essentials. Key products include: 1) DOM Sleeve & Poly Bushing (2 5/8 Inch Mounting Width, 9/16 Inch Bolt Hole) – $14.06; 2) Crossmember Mounting Set – $48.24; 3) D…
3. Midnight 4×4 – Aluminum Set Up Bushings
Domain: midnight4x4.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Aluminum Set Up Bushings – $16.50, Delrin Bushings – $14.99, Zip Tie Tabs – From $3.75, Bolt Retainer – Bolt On – $2.99, Optima Series 34 Battery Box – BAT0003 – $64.99, 7/8″ Race Series Heim Joint Kit – $106.57, 3/4″ High Misalignment Spacers – $17.99, U-Bolt Plates – From $25.99.
4. Protolabs – Metal Fabrication Services
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers a range of metal fabrication services including soft metals (Aluminum, Magnesium, Brass, Copper) and hard metals (Steel, Stainless Steel, Inconel, Chrome, Titanium). Their manufacturing techniques include machining, casting, molding, and 3D printing for complex designs. They provide sheet metal options and various post-processing methods for metal parts.
5. eMachineShop – Custom Steel Machining Services
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Custom steel parts machined service with over 15 years of experience. Design and order parts using free CAD software or upload your own CAD file for a fast quote. Features include: FREE Shipping in the USA, No Minimum Order Quantity, and 100% Quality Guaranteed. Steel is a popular metal alloy consisting mostly of iron and carbon, known for its thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, ductility,…
6. All Metals Fabricating – Metal Parts Fabrication
Domain: ametals.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: All Metals Fabricating specializes in metal parts fabrication, offering a wide range of capabilities including: tube laser cutting, laser cutting, CNC punching, CNC machining, forming, welding (including robotic welding), hardware and electromechanical assembly, powder coating, and silk screening. The company serves various industries such as telecommunications, electrical enclosures, oil, gas, al…
7. PDF, Inc. – Specialty Design & Manufacturing
Domain: pdf-inc.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: This company, PDF, Inc. – Specialty Design & Manufacturing, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. CBC Pro – Bushing Sleeve Kits
Domain: cbcpro.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: {“products”:[{“name”:”Bushing Sleeve Kit 1-7/8\” OD”,”sale_price”:”$22.95″,”savings”:”$1″},{“name”:”Bushing Sleeve Kit HD – 2\” OD”,”sale_price”:”$24.95″,”savings”:”$3″},{“name”:”Bushing Sleeve – Outer”,”sale_price”:”$7.95″,”savings”:”$2″},{“name”:”Tube End Weld Bungs , 1-1/4\” x .120 tube, 3/4\”-16 thread”,”regular_price”:”$9.95″},{“name”:”Tube End Weld Bungs, 1-1/2\” x .188 tube, 3/4\”-16 thread…
9. Offroad Anonymous – Fabrication Parts
Domain: offroadanonymous.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Fabrication Parts – Offroad Anonymous offers a variety of components for off-road vehicle customization. Key categories include: Miscellaneous Fabrication Parts (16), Tube Flanges & Caps (6), Gussets (11), Brackets (20), Basic Tabs (27), Trick Tabs (10). Notable products include: Adjustable Frame Link Mount Bracket ($35.00), Angled Link Bracket ($25.00 – $27.50), Axle Link Tower Bracket ($32.00 – …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for parts fabrication
In the evolving landscape of parts fabrication, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for international B2B buyers. By leveraging advanced technologies such as instant pricing tools and expedited production timelines, companies can significantly reduce lead times and costs. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters stronger supplier relationships, which are essential for navigating the complexities of global supply chains.
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize suppliers that offer flexibility in order quantities and a diverse range of materials. This adaptability allows for customization that meets specific project requirements, catering to the diverse needs of various industries. Additionally, the emphasis on post-processing services can provide added value, ensuring that the final products meet the highest quality standards.
Looking ahead, the global market for parts fabrication is set to expand, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for customized solutions. International buyers are encouraged to embrace these innovations and foster partnerships that will enhance their competitive edge. By strategically sourcing materials and services, companies can position themselves for success in this dynamic environment.