Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for nylon water absorption
In an era where global sourcing strategies are paramount, understanding nylon water absorption is critical for B2B buyers worldwide. The challenge of selecting nylon materials—especially in humid climates prevalent in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—requires not only a solid grasp of the specifications but also insight into performance implications. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource detailing various types of nylon, their water absorption rates, and the resultant effects on dimensional stability and mechanical properties.
With an overview of the supplier landscape, this guide equips buyers with the tools to vet suppliers effectively, ensuring they partner with those who offer the right nylon formulations for their applications. Additionally, it addresses cost considerations and practical advice for mitigating the impact of moisture on nylon products. By demystifying the intricate nature of nylon water absorption, this guide empowers international B2B buyers—whether from burgeoning markets like Nigeria or established sectors in Europe—to make informed purchasing decisions that enhance the durability and functionality of their products.
Ultimately, understanding nylon’s water absorption behavior is not just about selecting materials; it’s about optimizing supply chains and enhancing product performance in diverse environmental conditions.
Understanding nylon water absorption Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | Highest water absorption (up to 9.4%), good flexibility | Consumer goods, textiles, automotive | Pros: High impact resistance; Cons: Risk of dimensional change under humid conditions. |
| Nylon 66 | Moderate absorption (2.5-3.5%), excellent strength and heat resistance | Industrial components, electrical fixtures | Pros: Superior mechanical properties; Cons: Performance can degrade in high-moisture environments. |
| Nylon 610 | Lower water absorption (~1.5%), resistant to chemicals | Packaging, textiles, automotive | Pros: Stable dimensions; Cons: Less flexibility compared to higher absorbent nylons. |
| Low-moisture Nylon | Engineered for reduced absorption, suitable for stable use in humid environments | Medical devices, food packaging | Pros: Maintains dimensions in moisture; Cons: Potentially higher costs due to specialized materials. |
| Super-Tough Nylon | Enhanced toughness and low moisture uptake | High-performance applications | Pros: Excellent impact resistance; Cons: May be over-engineered for simple applications. |
What Are the Characteristics of Nylon 6 in Terms of Water Absorption?
Nylon 6 is noted for having the highest water absorption rates, reaching up to 9.4% under certain conditions. Its hydrophilic amide groups attract water, making it ideal for applications requiring flexibility, such as textiles and consumer goods. However, its tendency to undergo significant dimensional changes when exposed to moisture can be a drawback for precision components. Buyers should assess their product’s installation environments to determine if the advantages in impact resistance outweigh the challenges presented by moisture.
How Does Nylon 66 Compare in Water Absorption and Applications?
Nylon 66 showcases moderate water absorption, typically ranging from 2.5% to 3.5%. This balance allows it to retain strong mechanical properties while still being used in demanding applications like industrial components and electrical fixtures. The durability and temperature resistance of Nylon 66 make it a reliable choice, but buyers must ensure it is suitable for their moisture-laden environments, as its performance can diminish significantly when exposed to high humidity.
Why Choose Nylon 610 for Low Water Absorption?
Nylon 610 exhibits a lower water absorption rate of approximately 1.5%, making it a prime candidate for applications where dimensional stability is paramount, such as in packaging and automotive industries. Its chemical resistance further adds to its appeal. While it may lack the flexibility of more absorbent nylons, the lower moisture uptake provides a more consistent performance profile, catering to buyers focused on durability and reliability in fluctuating environmental conditions.
What Is the Value of Low-Moisture Nylon for B2B Applications?
Low-moisture nylon is an engineered polymer explicitly designed to minimize absorption. Commonly used in medical devices and food packaging, this type of nylon offers crucial stability in humid environments. While potentially more expensive due to specialized manufacturing processes, the benefits of maintaining consistent dimensions often justify the investment for buyers who prioritize long-term performance and reliability.
How Does Super-Tough Nylon Perform in Terms of Moisture and Toughness?
Super-tough nylon is characterized by its enhanced toughness combined with lower moisture absorption properties. It is well-suited for high-performance applications, thanks to its ability to withstand impact stress without significant dimensional changes. However, this durability may lead to higher costs and might be unnecessary for applications with less demanding requirements. Buyers should evaluate the specific needs of their projects to determine if the premium on super-tough nylon aligns with their operational goals.
Key Industrial Applications of nylon water absorption
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of nylon water absorption | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Flexible components such as gaskets and seals | Resistant to moisture changes, enhancing durability and fit | Require low moisture absorption grades; ensure consistent quality, especially in humid climates. |
| Electronics | Insulation parts for cables and connectors | Increased impact resistance through moisture absorption | Focus on nylon grades with controlled absorption to maintain electrical insulation properties. |
| Construction | Water-resistant coatings for construction materials | Improved performance in high humidity environments | Look for nylon grades with high dimensional stability and moisture resistance. |
| Consumer Goods | Durable sporting goods and outdoor equipment | Enhanced flexibility and toughness, critical for user safety | Ensure compliance with safety standards, potential customization of nylon for specific applications. |
| Textile Industry | Fibers for clothing and upholstery | Increased comfort due to water absorption and flexibility | Consider moisture management in large batches; sourcing from certified suppliers for consistency. |
How Does Nylon Water Absorption Enhance Automotive Applications?
In the automotive industry, nylon’s water absorption plays a crucial role in the production of flexible components such as gaskets and seals. The ability of nylon to absorb moisture enables these parts to maintain their shape and integrity despite swelling, improving durability and ensuring a tighter fit. For buyers in Africa and the Middle East, it’s essential to seek nylon grades that exhibit low moisture absorption while complying with fluctuating environmental conditions, as these factors directly impact performance.
What Are the Benefits of Nylon Water Absorption in Electronics?
Nylon’s water absorption characteristics are especially valuable in electronics, where nylon insulation parts are commonly employed for cables and connectors. The moisture absorbed enhances the plasticity and impact resistance of these components, making them resilient against physical shocks. Buyers in Europe and South America should prioritize grades with consistent absorption rates to maintain the integrity of electrical properties, ensuring safety and compliance with international standards.
How Does Nylon Water Absorption Improve Construction Materials?
In the construction sector, nylon is utilized in water-resistant coatings that protect materials from harsh environmental conditions. The moisture absorption helps to enhance the performance of these coatings, providing resilience in humid climates where traditional materials would fail. International buyers, particularly from Nigeria and Vietnam, should focus on sourcing nylon with high dimensional stability to ensure the longevity and reliability of their construction projects in varying weather.
What Advantages Does Nylon Water Absorption Offer Consumer Goods?
For consumer goods, such as sporting equipment and outdoor gear, nylon’s ability to absorb water translates into increased flexibility and impact resistance, critical for user safety. This characteristic ensures that products can withstand the rigors of active use while still performing effectively. Buyers from South America should consider durable nylon grades that not only provide safety features but also cater to sustainability, as environmentally friendly products gain preference in the market.
Why Is Nylon Water Absorption Important for the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, nylon fibers benefit from moisture absorption, enhancing comfort and flexibility in clothing and upholstery. This property allows garments to conform to body movements while remaining breathable. Buyers should ensure consistent moisture management during sourcing, as sourced materials must maintain quality across large supplies. Additionally, compliance with hygiene and safety regulations is essential, especially for large-scale manufacturing in regions like Africa and Southeast Asia.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘nylon water absorption’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Managing Dimensional Changes in Nylon Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter significant dimensional changes in nylon products due to moisture absorption, which can compromise product specifications and lead to manufacturing inconsistencies. For instance, a manufacturer of precision components may find that their nylon parts swell after being exposed to humid environments, leading to issues such as misalignment in assembly and reduced performance in applications where tight tolerances are crucial. This not only affects product quality but also increases scrap rates and production costs.
The Solution: To mitigate the impact of water absorption on dimensional stability, it is crucial to select the right nylon grade based on its water absorption characteristics. Buyers should consider sourcing low-moisture-absorbing variants, such as Nylon 6.10 or specialty grades that are engineered specifically for high-humidity environments. These materials exhibit significantly lower hygroscopicity compared to standard nylon grades, thus maintaining dimensional integrity. Additionally, incorporating drying processes before and after molding can help ensure that nylon parts are not subjected to stress due to varying moisture content. Implementing a rigorous moisture control program during storage and handling will also aid in minimizing dimensional changes, thereby enhancing overall product reliability.
Scenario 2: Performance Degradation Due to Plasticization
The Problem: Another prevalent challenge faced by B2B buyers is the performance degradation of nylon parts due to plasticization from moisture absorption. When nylon absorbs moisture, it becomes more flexible and softer at the molecular level, which can dramatically decrease the material’s strength and stiffness. For industries that rely on the mechanical properties of nylon for load-bearing applications, such as automotive or industrial equipment, this change can lead to premature failure of components and costly operational downtimes.
The Solution: One effective strategy to prevent performance degradation is to establish a quality control mechanism that includes moisture testing for nylon before it enters production processes. Buyers should require suppliers to provide moisture content data for their nylon materials. Additionally, consider utilizing moisture-resistant additives during the molding process to help maintain the desired mechanical properties. For environments prone to high humidity, reinforcing nylon with fillers can also help improve strength and reduce the effects of plasticization. Educating engineering teams on the importance of moisture management during the design phase can lead to more durable products while ensuring consistent performance even in varying moisture conditions.
Scenario 3: High Costs from Inefficient Drying Operations
The Problem: B2B manufacturers often face high costs associated with inefficient drying operations for nylon materials that have absorbed moisture. Prolonged drying times or ineffective drying techniques can lead to production delays and unplanned downtime, ultimately affecting profitability. An example is a company that uses standard hot air dryers, which may not adequately remove moisture from thicker nylon molds, resulting in extended cycles and increased energy costs.
The Solution: To optimize drying practices, buyers should invest in advanced drying technology that is specifically designed for nylon materials. Equipment such as desiccant dryers can provide more efficient moisture removal by utilizing a continuous process that maintains optimal drying conditions. Furthermore, conditioning the nylon prior to processing can significantly reduce the total drying time required. Implementing a comprehensive drying schedule that aligns with production planning can also streamline operations, ensuring that materials are in optimal condition when needed without excessive drying-related delays. Additionally, buyers should engage with suppliers who can provide guidance on the most effective drying practices based on the specific nylon grade being utilized, which will help eliminate inefficiencies and cut down associated costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for nylon water absorption
What Are the Key Types of Nylon Used in Water-Absorbing Applications?
Nylon’s inherent hygroscopic properties can significantly influence product performance, particularly in environments with varying humidity levels. Understanding the different types of nylon, their attributes, and application compatibilities is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize material performance in their applications. Here we will examine three common nylon grades: Nylon 6, Nylon 66, and Nylon 610, alongside their unique characteristics and considerations.
What Are the Key Properties of Nylon 6 in Terms of Water Absorption?
Nylon 6 is a widely employed nylon variant, known for its moderate water absorption rate of about 3.5% under standard conditions. The polymer features high strength, excellent toughness, and a good temperature tolerance, with a melting point of around 225°C. However, as it absorbs moisture, it undergoes dimensional changes, impacting precision applications.
Pros and Cons: Nylon 6’s advantages include enhanced impact resistance, flexibility, and toughness brought about by moisture absorption. Its primary drawback includes a significant loss of tensile strength when saturated. Additionally, molding complexities can arise due to its hygroscopic nature; moisture can cause issues during the injection molding process, leading to reduced product quality.
Impact on Applications: Nylon 6 is suitable for components in mechanical systems that require flexibility and strength. However, B2B buyers need to account for moisture’s potential to compromise dimensional stability, especially in high-precision applications.
How Does Nylon 66 Compare for Applications Requiring Water Resistance?
Nylon 66 offers improved mechanical properties compared to Nylon 6, with lower moisture absorption rates of about 2.5%. This made it an attractive choice for applications requiring higher strength and thermal stability, with a melting point near 255°C.
Pros and Cons: The primary benefits of Nylon 66 include enhanced fatigue resistance and lower elongation, making it ideal for parts that require consistent shape and performance under mechanical stress. However, its cost is typically higher than Nylon 6, and it can be less forgiving in the molding process, often requiring more stringent drying before production.
Impact on Applications: For industrial and automotive applications with sensitive tolerances, Nylon 66’s properties can significantly enhance product longevity. Buyers from diverse regions need to be aware of its stringent compliance requirements relating to environmental regulations and performance standards.
What Benefits Does Nylon 610 Bring to Water-Absorbing Applications?
Nylon 610 features a uniquely low water absorption rate of about 1.5%. This variant is particularly known for its chemical resistance and reduced moisture sensitivity compared to other nylons. Its melting point is slightly lower at around 220°C.
Pros and Cons: Nylon 610 offers excellent dimensional stability and durability, which are beneficial in diverse climates. However, its lower tensile strength than Nylon 66 might limit its use in highly demanding mechanical applications. The relative rarity of Nylon 610 can also lead to higher procurement costs.
Impact on Applications: This nylon type is often utilized in environments with extreme humidity, or for applications where chemical exposure occurs, such as in automotive fuel lines or industrial processing. Buyers should consider compliance with relevant industry standards for durability to avoid early failure.
Summary Table of Key Nylon Types and Their Water Absorption Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for nylon water absorption | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | Components requiring flexibility and toughness, such as housing and connectors | Increased impact resistance and flexibility | Significant strength loss when saturated | Medium |
| Nylon 66 | High-precision industrial and automotive parts | Enhanced fatigue resistance and lower moisture absorption | Higher cost and stricter molding requirements | High |
| Nylon 610 | Chemical-resistant applications like fuel lines | Low moisture absorption and excellent dimensional stability | Lower tensile strength and potential higher prices | High |
This guide serves as a resource for B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions about nylon types based on specific water absorption properties, application needs, and regional compliance requirements. Understanding these factors can optimize material selection for improved performance and reliability across diverse applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for nylon water absorption
What are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Nylon?
The manufacturing process of nylon involves several key stages that enable the production of high-quality nylon products with controlled water absorption characteristics. This process typically includes material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How is Material Prepared in Nylon Manufacturing?
Material preparation begins with sourcing high-purity nylon resin that meets specific mechanical and thermal properties needed for the intended application. Various grades of nylon, such as Nylon 6, Nylon 66, and Nylon 610, are evaluated based on their moisture absorption rates. Manufacturers often implement pre-drying processes to minimize moisture content in the resin. This is crucial, as excess moisture can affect subsequent processes and the final product’s properties.
The drying process can last from a few hours to a full day, depending on the grade of nylon and the degree of moisture retained. Understanding the resin’s characteristics is essential to ensure proper handling and performance in the manufacturing process.
What Forming Techniques are Commonly Used in Nylon Production?
After preparing the materials, the next step is forming, which generally employs techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding. Injection molding is particularly popular due to its versatility and ability to produce complex shapes and high precision in dimensions.
During injection molding, the dried nylon is heated until it flows and is then injected into a mold. The cooling time can significantly impact the water absorption rates and dimensional stability of the final product. Each technique requires precise control over temperature and pressure, as these factors influence moisture retention and mechanical properties after molding.
How is Assembly Handled in Nylon Manufacturing?
Assembly may include integrating various nylon components into larger systems or products. This can involve bonding, screwing, or other mechanical fastening methods. It is important to ensure compatibility between assembled parts, which may require consideration of water absorption properties, especially for applications where dimensional accuracy under varied humidity conditions is critical.
While assembling, manufacturers often conduct initial quality checks to identify any dimensional inconsistencies or potential issues due to water absorption, ensuring that the final product meets specifications before moving to the finishing stage.
What Finishing Processes are Involved in Nylon Production?
Finishing processes can encompass various techniques aimed at enhancing the product’s performance, aesthetic appeal, and environmental resistance. Techniques such as surface treatment, coloring, and coating can be applied. For nylon, applying anti-moisture coatings may also be beneficial to reduce the likelihood of water absorption during its lifecycle.
Dedicated finishing processes also afford an opportunity to perform final quality checks. Products may undergo stress testing to evaluate the mechanical strength and resilience characteristics, especially critical for high-performance nylon products in demanding applications.
What Quality Control Standards Are Relevant for Nylon Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) in nylon production is critical for ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant QC standards can serve as baseline requirements for sourcing suppliers.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
Adhering to ISO 9001 is paramount, as it outlines the criteria for a quality management system, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. This standard can cover all stages of nylon production, emphasizing continuous improvement and process efficiency.
Apart from ISO, industry-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API certifications in the oil and gas sector, may be relevant depending on end applications of the nylon products. These certifications often require compliance with specific safety and performance standards.
What QC Checkpoints Should Be Implemented in Nylon Manufacturing?
Implementing comprehensive QC checkpoints is vital in maintaining the quality of nylon products. The following checkpoints are commonly used:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspection of raw materials before usage, confirming that the nylon resin and any additives meet the specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring throughout the manufacturing process. Parameters such as temperature and humidity levels must be checked to mitigate water absorption issues during production.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducted on finished products to test their moisture absorption rates, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties. Testing can involve assessing the degree of water absorption and its impact on physical characteristics, ensuring alignment with desired specifications.
What Testing Methods Offer Insights into Nylon’s Water Absorption?
Acceptance testing activities are essential in confirming the water absorption characteristics and overall durability of nylon products. Common testing methods include:
-
Immersion Testing: Nylon samples are submerged in water for specified periods, and moisture absorption is measured to determine the equilibrium absorption rate.
-
Desiccator Methods: Products are placed in desiccators to control humidity levels, providing insights into how moisture absorption varies under specific environmental conditions.
-
Thermal Testing: Assessing the dimensional changes in nylon at various temperatures helps predict performance in high-temperature applications.
How Can Companies Verify Supplier QC Practices and Certifications?
Verifying supplier QC practices is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Potential strategies include:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate compliance with quality management systems and production processes can provide clarity about the supplier’s capabilities.
-
Reviewing QC Reports: Request suppliers to provide quality control documentation, showcasing results of testing conformance to specified standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can offer unbiased evaluations and certifications to validate supplier adherence to industry quality standards.
For international buyers, particularly in diverse markets like Vietnam and Nigeria, ensuring that suppliers maintain robust quality assurance practices is essential to mitigate risks associated with sourcing high-quality products.
What Nuances Should International Buyers Be Aware of Regarding QC Certifications?
Understanding the nuances of QC certifications is vital for effective procurement. B2B buyers must acknowledge that the interpretation of certifications can vary significantly by region and industry. In markets where local regulations are stringent, certifications might carry more weight than in others where oversight is loose.
Furthermore, navigating language barriers and differing interpretation of standards may pose challenges. Engaging with local experts or consultants familiar with regional compliance requirements can provide B2B buyers with an advantage in verifying supplier capabilities effectively.
In conclusion, navigating the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices surrounding nylon water absorption can be complex but critical for ensuring product quality and performance. By understanding the key processes, QC standards, testing methodologies, and supplier verification protocols, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their business needs and market demands.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘nylon water absorption’
In order to successfully source nylon with specific water absorption characteristics, it’s essential to follow a structured approach. This checklist will guide businesses through the critical steps to ensure that they procure the right nylon grade for their applications, especially tailored to the needs of international markets, which may have varied environmental conditions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly articulate what you require from the nylon you are sourcing. This includes understanding the specific water absorption levels desirable for your applications, which can vary significantly between grades (e.g., Nylon 6 has a higher absorption rate than Nylon 66). Defining the technical specifications ensures you communicate effectively with suppliers and prevents the selection of an inappropriate material.
Step 2: Research Different Nylon Grades
Different nylon grades exhibit varying levels of water absorption. For instance, Nylon 6 can absorb up to 9.4%, while Nylon 12 absorbs only about 1.4%. Researching the properties of different types allows you to match the nylon’s performance characteristics with the demands of your application—especially in high-humidity environments.
Step 3: Evaluate Suppliers’ Product Offerings
Investigate potential suppliers for their range of nylon products. Each supplier may have diverse grades with unique characteristics regarding water absorption. Request detailed technical datasheets and samples to assess conformity to your specifications and performance expectations.
Step 4: Assess Supplier Manufacturing Processes
Understanding how suppliers manufacture their nylon products is crucial. Certain processes, such as drying and molding conditions, impact the water absorption characteristics of nylon. Inquire about the conditions they utilize, which can determine the nylon’s end performance under varying moisture scenarios.
Step 5: Request Certifications and Test Reports
Verify that suppliers comply with relevant industry standards and quality certifications. This can include ISO certifications or compliance with local regulations specific to your region. Furthermore, request test reports that benchmark the nylon’s water absorption performance against required standards.
Step 6: Communicate Your Application Needs
Be transparent about the application in which the nylon will be used. Discuss climatic conditions, potential exposure to water, and other use-case specifics that may affect moisture absorption and performance. This dialogue can lead to tailored recommendations from suppliers that suit your operational context.
Step 7: Plan for Material Drying and Maintenance
Understanding the drying process is essential to maintenance and performance longevity of nylon products. Determine the supplier’s recommendations for drying times and methods before use, as neglecting to do so can lead to undesired outcomes like decreased strength or dimensional instability. Budget for proper drying equipment if necessary to maintain optimal performance.
By meticulously following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively source nylon materials tailored to their specific needs concerning water absorption, ensuring optimal performance in their respective applications.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for nylon water absorption Sourcing
Cost structure and pricing dynamics surrounding nylon water absorption sourcing can significantly impact international B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies. Understanding these components ensures strategic decision-making and improved supply chain efficiency.
What Are the Key Components of the Cost Structure for Nylon Water Absorption?
-
Material Costs
The type of nylon chosen is the primary determinant of material costs. For instance, Nylon 6 tends to have a higher water absorption rate than Nylon 66, affecting both performance and pricing. The cost of raw nylon material can vary based on regional shortages, local manufacturing capabilities, and global oil prices since nylon is derived from petrochemical sources. -
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead
Labor costs fluctuate based on geographic location. In regions like Southeast Asia, labor is more economical, possibly lowering overall manufacturing overheads. Additionally, factories must account for expenses related to energy, maintenance, and equipment depreciation which can alter pricing significantly. -
Tooling and Quality Control (QC)
Investment in tooling for mold creation is considerable, especially for custom shapes tailored to specific applications. Quality control processes ensure that the nylon meets necessary performance standards, particularly critical for applications in humid environments. QC costs include testing for moisture absorption characteristics and dimensional changes. -
Logistics and Distribution Costs
Shipping costs can vary widely based on the Incoterms used. For buyers in Africa, South America, or the Middle East, understanding CIF (Cost Insurance and Freight) versus FOB (Free on Board) can impact budget allocations. Efficient logistics and reliable shipping routes can reduce overall costs. -
Profit Margin
Manufacturers typically apply a margin that reflects operational risk, market demand, and competitive positioning. Buyers should consider this when negotiating prices, recognizing that lower margins may sometimes indicate limitations in quality or service.
What Influences Pricing Dynamics in Nylon Procurement?
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
Larger orders typically attract lower per-unit pricing due to economies of scale. International buyers should negotiate with suppliers to maximize their volume discounts, ensuring that MOQ requirements align with their production needs. -
Specifications and Customization Needs
Customization in nylon characteristics—such as low moisture absorption variants—can drive costs higher. Buyers must assess whether these specifications are necessary to meet their end-use demands, balancing performance needs against budget constraints. -
Material Quality and Certifications
Products that come with certifications (e.g., ISO or specific industry certifications) may carry a premium price. Depending on application requirements, it is essential to weigh the necessity for such certifications against potential market benefits. -
Supplier Experience and Reliability
Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance processes. For regions like Africa and South America, where supply chain disruptions can occur, selecting dependable partners can mitigate risks.
How Can Buyers Optimize Their Purchasing Strategy?
-
What are the Key Negotiation Strategies?
Start negotiations by gathering sufficient market data regarding pricing benchmarks and potential suppliers’ reputation. Highlighting long-term partnerships can leverage better deals and favorable terms. -
How to Calculate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)?
Analyze not just initial costs but long-term implications, including maintenance, replacement, and operational efficiency stemming from moisture absorption properties. This holistic view ensures smarter investment decisions. -
What Pricing Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
Understanding local market fluctuations and tariffs applicable to nylon imports can influence overall cost assessments. Buyers should also account for potential currency fluctuations and local regulations that might affect pricing.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for nylon materials can vary significantly based on geographical factors, market demand, and specific customer requirements. This analysis serves as a guideline to empower buyers in making informed sourcing decisions but may not reflect real-time pricing. It is advisable to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers for the most accurate assessment.
By leveraging the insights presented, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring that they not only meet their material needs but also optimize their supply chain operations.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing nylon water absorption With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Nylon Water Absorption
Understanding the water absorption characteristics of nylon helps businesses determine the best materials for their applications. However, there are alternative materials and methods that offer varying benefits for different industries. Here, we analyze nylon water absorption in comparison with thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) and polyether ether ketone (PEEK) to provide insights relevant to international B2B buyers.
| Comparison Aspect | Nylon Water Absorption | Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs) | Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Absorbs up to 9.4% water, leading to enhanced flexibility and toughness but reduced strength | Excellent flexibility; lower water absorption, but impact resistance varies | High strength, chemical resistance; minimal water absorption (<0.1%) |
| Cost | Generally lower, but varies by grade | Moderate; competitive with nylon in specific applications | Higher cost due to superior properties and manufacturing complexity |
| Ease of Implementation | Straightforward to mold and process; drying may be necessary | Easy processing; no special drying required, providing flexibility in designs | Requires specialized processing, often limiting application scope |
| Maintenance | Regular drying required for performance conservation | Low maintenance; good dimensional stability | High-performance material with minimal upkeep but more complex repairs |
| Best Use Case | Applications requiring toughness and flexibility, especially in humid conditions | Automotive seals, sports equipment, and applications needing high elasticity | High-temperature or chemically demanding applications, such as aerospace and medical devices |
What Are the Advantages and Drawbacks of Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPEs)?
Thermoplastic elastomers offer a compelling alternative to nylon in many applications where moisture absorption is a concern. One of their key benefits lies in their flexibility and resilience, which can match or even surpass nylon’s performance in specific contexts. TPEs have a lower tendency to absorb water, leading to improved dimensional stability. However, they may fall short in impact resistance for certain applications unless specifically engineered for that purpose. Their moderate pricing makes them an appealing choice for producers looking to save costs without sacrificing essential quality attributes.
How Does Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) Compare to Nylon Water Absorption?
PEEK is known for its superior physical properties, including a minimal water absorption rate of less than 0.1%. This makes it an excellent choice for high-performance applications in challenging environments, where exposure to moisture can impact product integrity. Its high melting point and excellent mechanical strength enable its use in settings that require both thermal and chemical resistance. However, PEEK is more expensive than both nylon and TPEs, which may limit its applicability for budget-constrained projects. Additionally, the processing of PEEK requires specialized equipment, making implementation more complex.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Application?
Selecting between nylon water absorption and its alternatives—TPEs and PEEK—requires a careful consideration of your specific application requirements. It is essential to evaluate factors such as performance needs, cost constraints, ease of integration, and maintenance implications. For businesses operating in humid environments where flexibility and toughness are critical, nylon could be the ideal fit. However, if your project’s demands lean toward high-performance engineering applications, PEEK may be worth the investment. Conversely, for organizations seeking a balance between performance and cost, TPEs offer solid benefits with lower moisture absorption.
Ultimately, aligning the right material with the performance characteristics required for your applications will enable a more efficient and cost-effective manufacturing process.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for nylon water absorption
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Nylon Related to Water Absorption?
Understanding nylon’s crucial technical properties is essential for B2B buyers, especially when moisture absorption could affect the performance and durability of products. Here are the key specifications you should consider:
1. Water Absorption Rate
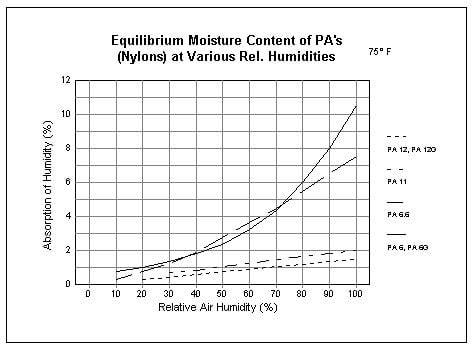
Nylon is inherently hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from its environment. The water absorption rates vary by grade – for example, nylon 6 absorbs approximately 3.5% at 23°C under 60% relative humidity, while nylon 66 absorbs about 2.5%. This rate is crucial for applications in humid or wet environments where the materials’ integrity may be compromised.
2. Dimensional Change
Water absorption leads to dimensional changes in nylon products, which can have significant ramifications in precision applications. Typically, for every 1% increase in water absorption, dimensional changes can be expected to increase by 0.2% to 0.3%. Buyers must factor in these changes to ensure proper fit and functionality of components in end-use applications.
3. Mechanical Properties Alteration
As nylon absorbs moisture, its mechanical properties shift, often resulting in decreased strength and stiffness but improved flexibility and impact resistance. Understanding these changes is vital for engineers who need materials to maintain performance under varying conditions.
4. Temperature Effects
Moisture absorption is exacerbated by temperature, meaning that nylon parts in heated environments may absorb more water. This fact necessitates careful consideration of operating conditions, especially in extreme climates. Buyers should ensure that the selected nylon types are suitable for the thermal environment of their applications.
5. Material Grade Selection
Different nylon grades exhibit differing moisture absorption characteristics. Nylon 6 may saturate at 9.4% compared to nylon 12 at 1.4%. Selecting the right grade reduces the likelihood of performance issues, making it essential for buyers to assess the operational environment to choose the most appropriate material.
6. Drying and Processing Conditions
The effectiveness of drying processes can vary based on the type of nylon and the degree of moisture uptake. Specific drying times range from 2-3 hours to over a full day. Understanding these requirements helps in planning manufacturing processes and ensuring product quality before dispatch.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in the Context of Nylon Water Absorption?
Navigating the procurement landscape involves understanding industry jargon that influences purchasing decisions. Here are critical terms related to nylon water absorption that buyers should be familiar with:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEMs are the companies that manufacture products or components that are sold under another company’s brand. For buyers in different markets, selecting an OEM knowledgeable about nylon’s moisture sensitivity is crucial in ensuring reliable supply chains.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs helps buyers manage their inventory and budget effectively while also ensuring they meet supplier requirements to maintain a consistent supply of nylon products.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer inviting suppliers to submit price offers for specific quantities of nylon products. Buyers can leverage RFQs to compare costs and delivery terms, ensuring they get the best deal while considering moisture absorption properties.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are predefined shipping terms that clarify responsibilities between buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, risk, and liability. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is essential when shipping nylon products across international borders.
5. Technical Data Sheet (TDS)
A TDS provides essential technical specifications and performance metrics for nylon grades, including moisture absorption rates and mechanical properties. B2B buyers should always request a TDS to make informed decisions based on the material’s ability to perform under specific conditions.
6. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
An MSDS details safety considerations and handling protocols for nylon. Understanding the safety protocols can prevent mishaps and ensure compliance with local regulations, making it a necessary resource for companies dealing with bulk nylon materials.
Equipped with this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed choices regarding nylon’s use in their applications, ensuring that the products meet performance expectations even under varying moisture conditions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the nylon water absorption Sector
What Are the Global Drivers and Current Trends Influencing the Nylon Water Absorption Market?
The nylon water absorption market is experiencing significant growth driven by multiple global factors. Increasing demand from industries such as automotive, consumer goods, and electronics is fostering innovation in nylon applications. Particularly, the trend towards lightweight and durable materials is pushing manufacturers to seek high-performance nylon grades that exhibit varying moisture absorption levels. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing an upsurge in demand for nylon composites that can deliver enhanced properties without compromising structural integrity. Furthermore, technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as 3D printing and advanced injection molding, are influencing sourcing decisions, enabling buyers to achieve customized solutions tailored to specific applications.
Emerging technologies are paving the way for innovative nylon formulations that mitigate the challenges associated with water absorption. Trends such as low-hygroscopic nylon, like NYCOA’s NXTamid and other engineered polyamides, are gaining traction as global buyers look for cost-effective and high-performance alternatives. Moreover, there is a growing interest in bio-based and recycled nylon options, particularly in Europe and North America, as companies strive for a more circular economy. This shift is particularly relevant for B2B buyers looking to enhance their sustainability profiles while not sacrificing performance.
How Can B2B Buyers Incorporate Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing into Nylon Water Absorption Procurement?
As environmental concerns gain prominence in supply chain management, B2B buyers in the nylon sector must navigate the complexities of sustainability and ethical sourcing. Nylon production is often associated with high energy consumption and emissions. Therefore, sourcing from manufacturers who adhere to sustainable practices can mitigate environmental impacts. Buyers should consider suppliers with certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates an effective environmental management system, and look for nylon products that incorporate recycled materials or are produced through renewable energy sources.
In addition, many companies are becoming transparent about their supply chains, enabling buyers to assess whether their suppliers prioritize ethical labor practices and environmentally responsible production methods. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate commitment to green initiatives not only meets stakeholders’ expectations but can also enhance brand reputation in markets sensitive to sustainability concerns. This is particularly crucial for B2B buyers servicing industries plagued by scrutiny over environmental impact, such as aerospace and automotive sectors.
How Has the Nylon Water Absorption Sector Evolved Over Time?
The history of nylon dates back to the 1930s when it was first developed as a synthetic alternative to silk. Over the decades, its application has evolved significantly, transitioning from consumer textiles to high-performance industrial materials. The moisture absorption characteristics of nylon have also been thoroughly analyzed and leveraged in various sectors. Originally, the focus was largely on nylon’s mechanical properties; however, recent emphasis on hygroscopic properties has opened new avenues for applications that require specific moisture management solutions. This shift in perspective reflects the material’s versatility and the ongoing evolution of industry needs, particularly for manufacturers looking to optimize products for changing environmental conditions.
With increasing industrial demands and innovations in material science, the nylon water absorption sector continues to adapt and grow, promising exciting opportunities for international B2B buyers in diverse markets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of nylon water absorption
1. How can I prevent nylon from absorbing too much water during storage and transportation?
To prevent excessive water absorption, consider utilizing desiccants during transportation and storage to maintain low humidity levels. Additionally, ensure that nylon products are stored in climate-controlled environments, ideally at stable, low relative humidity. Manufacturers can also treat nylon with moisture-resistant additives or employ low-moisture absorption grades, which can significantly reduce the tendency to absorb water. Proper drying before storage and utilizing breathable packaging can further mitigate moisture absorption risks.
2. What are the most suitable nylon grades for high humidity environments?
For high humidity applications, nylon 6.10 and nylon 6.12 are excellent options due to their lower water absorption rates compared to standard nylon 6 or nylon 66. These materials provide improved dimensional stability and maintain better mechanical properties when exposed to moisture. When selecting nylon grades, always assess how critical strength and flexibility are for your application, as materials with lower moisture absorption may perform better in challenging conditions.
3. How can the water absorption of nylon impact its performance in my application?
Water absorption in nylon can lead to dimensional changes, increased flexibility, and decreased stiffness. While these changes might be beneficial in applications requiring greater impact resistance, they can compromise the strength of components, especially in precision applications. Understanding the balance between mechanical performance and environmental exposure is crucial. Conducting thorough testing under real-world conditions can inform whether a nylon material’s water absorption characteristics will positively or negatively affect its performance.
4. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for nylon materials, especially when customizing?
Minimum order quantities for nylon materials can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specifics of your order. Typically, MOQs range from 100 kg to several tons for standard grades, while customized grades may have higher MOQs depending on the complexity of the formulation and production setup. It’s advisable to discuss your needs with various suppliers to find one that offers flexibility in MOQs, particularly for first-time orders or smaller projects.
5. What payment terms should I expect when purchasing nylon globally?
Payment terms for international nylon purchases can differ widely among suppliers. Common practices include upfront payments (20-30%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 days for larger orders or established buyers. Always negotiate payment terms that are favorable while ensuring they protect both your interests and those of the supplier. Ensure clarity on currency exchange rates and additional fees that may apply, especially in cross-border transactions.
6. How do I vet suppliers of nylon materials?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials. Request samples to assess product quality and conformity with specifications. Analyze their production capabilities, certifications, and compliance with international standards. Networking within industry forums can also yield insights on supplier reliability. Lastly, consider visiting the facility or conducting audits if you intend to place significant orders, ensuring they can consistently deliver quality materials.
7. What should be included in a quality assurance (QA) plan for nylon products?
A comprehensive QA plan for nylon products should include testing for moisture content, tensile strength, and dimensional stability under varying humidity conditions. Outline specific testing protocols and frequency, adhering to relevant industry standards such as ISO or ASTM. Documentation of all quality checks and procedures should be maintained, including supplier certifications. Regular audits and feedback loops with suppliers can also enhance quality control and ensure ongoing compliance with required specifications.
8. What logistics considerations are important when exporting nylon materials?
Logistics considerations for exporting nylon include selecting reliable freight forwarders familiar with handling plastics and ensuring the materials are packaged to prevent damage and moisture absorption during transit. Understand the customs regulations of the importing country to avoid delays. Temperature and humidity controls during transport are important, especially for moisture-sensitive materials. Working closely with experienced logistics partners can streamline the shipping process and minimize potential risks.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Nylon Water Absorption Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Toray – AMILAN™ Nylon Resin Properties
Domain: plastics.toray
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Physical Properties of AMILAN™ Nylon Resin:
1. Water Absorption Rate:
– Nylon 6: 3.5%
– Nylon 66: 2.5%
– Nylon 610: 1.5%
– Water absorption affects dimensional changes.
– Speed of water absorption varies based on shape of the product.
– Example conditions: 23°C/60%RH, 100°C water.
– Constants (m, n) for water absorption determined by type of nylon and product shape.
2. Diffus…
2. NYCOA – NXTamid Polyamide
Domain: nycoa.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: NYCOA manufactures various grades of nylon including NXTamid, a unique long-chain polyamide with low moisture absorption, and effective as an alternative to nylon 11 and nylon 12. NYCOA also offers low-moisture absorption engineered Nylon materials such as Nylon 6.10 and 6.12, and grades of Super-Tough nylon. They products are used in multiple industries and applications including fasteners, hook …
3. Intech Power – PowerCore PA12GC
Domain: intechpower.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: PowerCore Product Line: Intech Power-Core™ PA12GC (Gravity Cast); Moisture Absorption: Maximum of 1.4%; Comparison: Nylon 6 absorbs over 10%; Dimensional Change: PowerCore – 0.2%, Nylon 6 – 2%, Nylon 6.6 – 3.5%; Tensile Strength Drop: Nylon 6 – over 80% drop from dry to saturated, Nylon 6.6 – over 60% drop; Physical Properties: Superior tensile strength characteristics; Additional Effects: Reduced…
4. UL Prospector – Nylon Materials
Domain: ulprospector.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Polyamide nylon materials are hygroscopic, capable of absorbing up to 8% moisture by weight at saturation. The data for dry nylon is obtained with moisture content typically <0.2%, while conditioned data is taken after absorbing moisture at 50% relative humidity. Moisture acts as a plasticizer, reducing strength and stiffness but increasing elongation and toughness. Dimensional stability of nylon …
5. Reddit – Nylon Performance
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Nylon is a hygroscopic material, meaning it will absorb water from the environment, which can lead to changes in flexibility and stiffness. When printed, nylon parts best perform in dry conditions, necessitating a sealed filament path to maintain optimal properties. Over time, absorbed moisture makes nylon less stiff, reducing strength by approximately half when saturated. Alternatives to nylon in…
6. Dotmar – Ertalon 6PLA (Cast Nylon 6)
Domain: dotmar.com.au
Introduction: Product: Ertalon 6PLA (Cast Nylon 6)\n- Water Absorption: Absorbs moisture slowly over time; full saturation of 20mm thickness takes approximately 15.6 years. \n- Saturation after 10 months of submersion (2.3mm) indicates material expansion based on wall thickness. \n- Thickness Guidance: \n – Up to 5mm wall thickness: Consider moisture absorption expansion. \n – 5mm to 10mm wall thickness: Some…
7. Madison Group – Nylon Performance Insights
Domain: madisongroup.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Nylon, also known as polyamide (PA), is a widely used thermoplastic material with varying water absorption properties that impact its performance. Key characteristics include mechanical properties, thermal characteristics, degradation resistance, and how these are influenced by the molecular structure, particularly the ratio of paraffinic content to amide functionality. Higher paraffinic content r…
8. UNITIKA – Nylon 6
Domain: unitika.co.jp
Introduction: Nylon Type: UNITIKA Nylon 6; Key Properties: Excellent chemical resistance; Water Absorption: Due to hydrophilicity from amide bonds; Effects of Humidity: Equilibrium water content varies with relative humidity and environmental conditions; Dimensional Change: Water absorption leads to dimensional changes that affect design accuracy; Water-Absorbing Speed: Varies by thickness, temperature, and hum…
9. Eng-Tips – Nylon 6 Molded Parts Solutions
Domain: eng-tips.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Nylon 6 molded parts; issues with brittle fracture; must condition parts for elongation; potential moisture loss in dry environments (e.g., New Mexico, Phoenix); requires toughness and flexibility; thick plastic piece (3/8″ thick) must withstand bending loads up to 400 lbf; exploring alternatives such as acetals, copolymers (e.g., PPO), and impact-modified nylon; nylon retains moisture but may dry…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for nylon water absorption
As international markets expand, strategic sourcing remains essential for businesses exploring nylon applications. Understanding the moisture absorption properties of nylon, including variations across different grades such as Nylon 6, Nylon 66, and nylon 610, equips buyers with the knowledge to select materials based on specific environmental conditions. The hygroscopic nature of nylon is a double-edged sword; while it can enhance flexibility and impact resistance during certain conditions, it may also lead to dimensional changes and decreased material strength.
For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing relationships with suppliers who offer specialized low-moisture absorption nylon grades can be a game changer. By investing in high-performance materials, companies can improve product reliability and satisfy stringent industry standards, thereby enhancing their competitive edge.
Looking ahead, we encourage you to prioritize suppliers who understand the intricacies of moisture management in nylon. As you navigate sourcing decisions, remember that tailored solutions and innovative materials will be pivotal in adapting to global market demands. Embrace these insights to future-proof your sourcing strategies and drive sustainable growth in your operations.