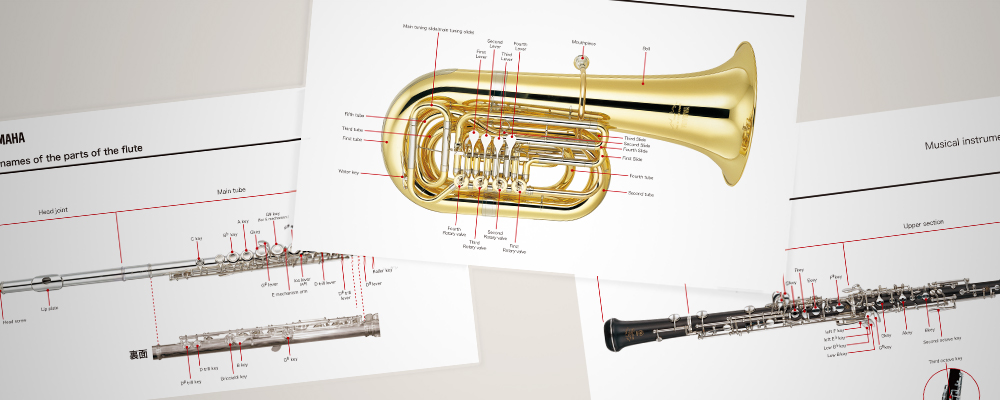
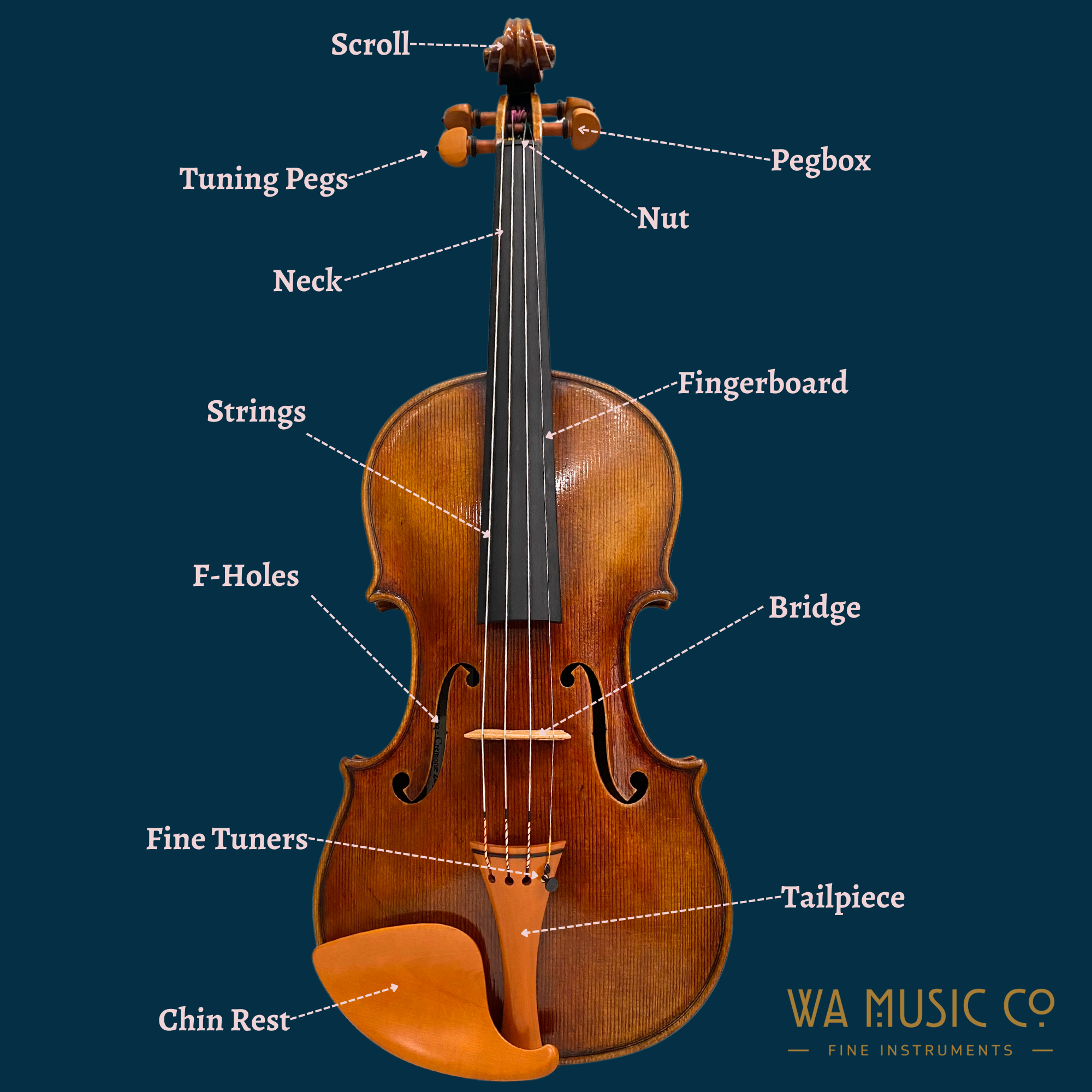
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for music instrument parts
In the dynamic landscape of the global music instrument parts market, sourcing high-quality components can pose significant challenges for B2B buyers. With a vast array of parts ranging from tuning machines to bridges and knobs, it’s essential for businesses to navigate this complexity effectively. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, such as Saudi Arabia and Germany. By addressing key factors like types of parts, applications, supplier vetting, and cost considerations, we aim to equip you with the knowledge necessary for informed purchasing decisions.
Understanding the diverse components that make up musical instruments is crucial for ensuring quality and performance. This guide delves into the various categories of parts, exploring their specific applications across different instrument types. Additionally, we provide actionable insights on how to evaluate suppliers, ensuring that you partner with reliable manufacturers and distributors. With a focus on cost-effectiveness and quality assurance, this guide empowers B2B buyers to streamline their sourcing processes and enhance their supply chain efficiency. Whether you are a retailer, manufacturer, or repair shop, navigating the intricacies of the music instrument parts market is key to sustaining your business and meeting customer demands.
Understanding music instrument parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bridges & Tailpieces | Essential for sound transmission; varies by instrument type. | Guitar manufacturing and repair, orchestras. | Pros: Improves sound quality; customizable options. Cons: Requires expertise for installation. |
| Tuning Machines | Mechanisms for adjusting pitch; available in various ratios and styles. | Instrument manufacturing, repair shops. | Pros: Enhances tuning stability; variety for different instruments. Cons: Can be costly; may require specific fittings. |
| Pickguards | Protects the instrument’s body; available in multiple materials and designs. | Guitar production, repair shops. | Pros: Aesthetic enhancement; prevents damage. Cons: May affect tone; limited to certain models. |
| Screws & Fasteners | Used to assemble and secure instrument parts; various sizes and materials. | General assembly, repair services. | Pros: Essential for structural integrity; widely available. Cons: Quality can vary; may require specific tools for installation. |
| Pads & Resonators | Critical for woodwind instruments; affects sound quality and playability. | Woodwind repair shops, orchestras. | Pros: Improves sound clarity; essential for maintenance. Cons: Requires skilled installation; limited lifespan. |
What are the Key Characteristics of Bridges and Tailpieces?
Bridges and tailpieces play a pivotal role in the sound production of string instruments, such as guitars and violins. They are responsible for transferring string vibrations to the instrument’s body, significantly influencing tone and resonance. B2B buyers should consider the material and design variations, as these can affect sound quality and durability. Additionally, the compatibility with specific instrument models is crucial, requiring buyers to have a solid understanding of their inventory to avoid mismatches.
Why are Tuning Machines Important for Instrument Performance?
Tuning machines are critical components that allow musicians to adjust the pitch of their instruments accurately. They come in various designs, including open and closed gear types, with different gear ratios that provide varying levels of precision. For B2B buyers, understanding the specific needs of their customers—such as the type of instrument and the desired tuning stability—can guide purchasing decisions. It’s essential to consider the quality and reliability of these components, as they directly impact performance.
How Do Pickguards Enhance Instrument Value?
Pickguards serve both protective and aesthetic functions, shielding the instrument’s finish from scratches while also allowing for customization. They come in various materials, such as plastic and wood, and can be tailored to fit different instrument shapes. B2B buyers in guitar manufacturing or repair should evaluate the design options available to meet customer preferences. While pickguards can enhance the visual appeal of an instrument, buyers must weigh this against potential tonal impacts, as some materials may dampen sound.
What Role Do Screws and Fasteners Play in Instrument Assembly?
Screws and fasteners are fundamental components in the assembly of musical instruments, ensuring that parts are securely held together. They come in various sizes and materials, catering to different instrument types and assembly requirements. For B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality fasteners is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of instruments. However, buyers should be aware that the quality can vary significantly, and they may require specific tools for installation, which can add to the overall cost.
Why are Pads and Resonators Critical for Woodwind Instruments?
Pads and resonators are essential for woodwind instruments, affecting both sound quality and playability. These components help seal tone holes, ensuring optimal sound production. B2B buyers in the woodwind repair sector should consider the materials and designs that best suit their clients’ needs, as the choice can influence instrument performance. Additionally, buyers should factor in the installation expertise required, as improper fitting can lead to significant sound issues, making it crucial to partner with skilled technicians.
Key Industrial Applications of music instrument parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Music Instrument Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Musical Instrument Manufacturing | Production of guitars, pianos, and brass instruments | Streamlined production and enhanced product quality | Compatibility with existing designs and materials |
| Repair and Maintenance Services | Replacement parts for instrument repairs | Increased customer satisfaction and loyalty | Availability of high-quality, durable parts |
| Music Education Institutions | Parts for educational instruments | Improved learning experiences for students | Cost-effective sourcing and bulk purchase options |
| Live Music Venues | Upgrading and maintaining sound equipment | Enhanced performance quality and reliability | Supplier reputation and support services |
| Custom Instrument Builders | Specialized parts for bespoke instruments | Unique product offerings that attract niche markets | Customization options and lead times |
How Are Music Instrument Parts Used in Manufacturing?
In the musical instrument manufacturing sector, companies utilize various parts, such as tuning machines, bridges, and pickguards, to assemble high-quality instruments like guitars and pianos. These components are crucial for ensuring sound quality and playability, which directly impacts customer satisfaction. B2B buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East must consider factors such as material compatibility and compliance with international quality standards when sourcing these parts to maintain their production efficiency and brand reputation.
What Role Do Music Instrument Parts Play in Repair Services?
Repair and maintenance services rely heavily on music instrument parts to restore instruments to their optimal condition. From saxophone pads to guitar strings, these components are essential for effective repairs. Businesses in this sector benefit from quick access to a diverse inventory of parts, which helps reduce downtime for their clients. For international buyers, especially in Africa and South America, sourcing durable and reliable parts is critical to ensuring long-term customer loyalty and service excellence.
How Do Music Instrument Parts Enhance Educational Institutions?
Music education institutions utilize instrument parts to maintain and upgrade their educational instruments, such as flutes and violins. This ensures that students have access to well-functioning instruments, which is vital for effective learning. For B2B buyers in this sector, cost-effective sourcing options are essential, particularly when purchasing in bulk. Ensuring that parts meet educational standards can significantly enhance the learning experience and foster a positive environment for budding musicians.
Why Are Music Instrument Parts Important for Live Music Venues?
Live music venues depend on high-quality parts for sound equipment and instruments to deliver exceptional performances. Components such as jack plates and tuning machines are crucial for maintaining sound clarity and reliability during shows. B2B buyers in this industry should prioritize suppliers with a strong reputation for quality and support services, ensuring they can quickly resolve any issues that arise during performances. This focus on quality can lead to improved audience experiences and repeat business.
What Benefits Do Custom Instrument Builders Gain from Specialized Parts?
Custom instrument builders often require specialized music instrument parts to create unique instruments that cater to niche markets. These builders rely on bespoke components to differentiate their offerings and meet specific customer demands. For buyers in this sector, sourcing options that allow for customization and timely delivery are vital. Understanding the specific needs of their clientele can lead to innovative designs and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘music instrument parts’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Quality Concerns in Sourcing Instrument Parts
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the challenge of ensuring that the music instrument parts they source meet specific quality standards. This concern is amplified when dealing with international suppliers, where differences in manufacturing practices can lead to discrepancies in quality. For instance, a buyer from Europe sourcing guitar tuners from a supplier in South America might find that the tuners do not fit properly or fail to perform as expected, potentially damaging their brand reputation.
The Solution: To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should implement a thorough vetting process when selecting suppliers. This includes requesting samples before placing larger orders, allowing for an evaluation of the parts’ quality and compatibility with existing instruments. Additionally, maintaining clear communication with suppliers regarding specifications can help ensure that the parts meet the required standards. Buyers can also leverage third-party quality assurance services that specialize in the music instrument industry, providing an extra layer of confidence in the products sourced.
Scenario 2: Managing Inventory and Supply Chain Disruptions
The Problem: Inventory management poses a significant challenge for B2B buyers in the music instrument parts sector, particularly when facing supply chain disruptions. For example, a retailer in the Middle East may rely on specific parts to maintain their production schedule. However, unexpected delays in shipments can lead to stockouts, resulting in lost sales and unhappy customers. This situation is further complicated by fluctuating demand, making it difficult to maintain optimal inventory levels.
The Solution: Implementing a robust inventory management system that integrates real-time data analytics can help buyers anticipate demand fluctuations and manage stock levels more effectively. Buyers should consider establishing relationships with multiple suppliers to diversify their sourcing options, reducing dependency on any single source. Additionally, utilizing just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices can help maintain lean stock levels while ensuring that parts are available as needed. Regularly reviewing inventory turnover rates and aligning purchasing strategies with sales forecasts can further enhance inventory management efficiency.
Scenario 3: Understanding Technical Specifications and Compatibility
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently encounter difficulties in understanding the technical specifications and compatibility of various music instrument parts. This is particularly evident when sourcing parts for diverse instruments, such as electric guitars and brass instruments. A buyer from Africa, for instance, might struggle to determine the correct gauge of strings or the appropriate size of replacement pads for woodwind instruments, leading to costly mistakes and delays in production.
The Solution: To address this knowledge gap, buyers should invest in comprehensive product training and resources. This may include workshops, webinars, or even partnerships with manufacturers who can provide detailed insights into their product lines. Creating a centralized database of specifications and compatibility information for different instruments can serve as a valuable reference tool for buyers. Additionally, engaging with industry forums and communities can provide practical advice and experiences from other professionals in the field, enhancing overall understanding and decision-making capabilities. Providing your purchasing team with access to technical support from suppliers can also streamline the selection process and ensure that the right parts are sourced for specific applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for music instrument parts
What Are the Key Properties of Wood in Music Instrument Parts?
Wood is one of the most traditional materials used in the construction of musical instruments. Its natural acoustic properties make it ideal for various applications, particularly in string and wind instruments. Key properties of wood include its ability to resonate sound, which varies based on species, density, and grain structure. Additionally, wood has excellent thermal insulation properties, which can help maintain sound quality under varying environmental conditions.
Pros and Cons of Wood for Musical Instrument Parts
The primary advantage of wood is its superior acoustic qualities, which enhance the tonal richness of instruments. However, wood can be susceptible to warping, cracking, and insect damage, which can compromise durability. The cost of high-quality wood can be significant, and manufacturing complexity increases with the need for careful selection and treatment processes. For international buyers, sourcing sustainably harvested wood is essential, as compliance with environmental regulations is becoming increasingly important.
How Does Metal Perform in Music Instrument Parts?
Metals, such as brass, stainless steel, and aluminum, are widely used in various instrument components, including keys, valves, and hardware. Metals are known for their strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Specific alloys can also be engineered to enhance sound characteristics, particularly in brass instruments.
Pros and Cons of Metal for Musical Instrument Parts
The main advantage of metal is its durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it suitable for high-wear applications. However, metals can be heavier than other materials, which may affect the overall weight and balance of an instrument. The cost can vary significantly based on the type of metal and the complexity of manufacturing processes involved. International buyers should be aware of compliance with specific metal standards (e.g., ASTM for the U.S., DIN for Germany) and consider the implications of tariffs and trade regulations.
What Role Does Plastic Play in Music Instrument Parts?
Plastic is increasingly popular in the production of musical instrument parts due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Common applications include pickguards, knobs, and various small components. Plastics can be engineered to mimic the properties of wood or metal, providing an attractive alternative.
Pros and Cons of Plastic for Musical Instrument Parts
The key advantage of plastic is its lightweight nature and resistance to moisture, making it ideal for outdoor instruments or those exposed to humidity. However, plastics may not provide the same acoustic quality as wood or metal, potentially affecting sound performance. The manufacturing process for plastic parts can be less complex, leading to lower costs. Buyers should consider the environmental impact of plastic production and disposal, especially in regions with strict environmental regulations.
How Do Composites Enhance Music Instrument Parts?
Composite materials, which combine different substances to create a product with enhanced properties, are gaining traction in the musical instrument industry. These materials can include combinations of wood, plastic, and metal, designed to optimize performance characteristics such as strength, weight, and acoustic properties.
Pros and Cons of Composites for Musical Instrument Parts
The primary advantage of composites is their ability to offer tailored solutions that leverage the strengths of various materials while mitigating their weaknesses. They can be engineered for specific applications, providing excellent durability and stability. However, the complexity of manufacturing composites can lead to higher costs and longer lead times. For international buyers, understanding the specific certifications and standards for composite materials is crucial, as these can vary widely by region.
| Material | Typical Use Case for music instrument parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | Acoustic guitars, violins, pianos | Superior acoustic properties | Susceptible to warping and damage | High |
| Metal | Brass instruments, hardware components | Durability and corrosion resistance | Heavier and potentially more expensive | Medium to High |
| Plastic | Knobs, pickguards, lightweight components | Lightweight and moisture resistant | May compromise acoustic quality | Low |
| Composites | Advanced instrument parts, hybrid instruments | Tailored performance characteristics | Higher manufacturing complexity and cost | Medium to High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for music instrument parts
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Music Instrument Parts?
The manufacturing of music instrument parts involves several critical stages, each ensuring that the final products meet the high standards required by musicians and manufacturers alike. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Music Instrument Parts?
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. It involves selecting high-quality raw materials such as wood, metal, plastic, or composite materials. Each material type is chosen based on its specific acoustic properties and durability. For example, hardwoods are often used for acoustic guitars due to their resonance qualities, while metals may be selected for parts like tuning machines due to their strength and longevity.
Once the materials are sourced, they undergo various treatments, such as drying or chemical treatments, to enhance their performance characteristics. This stage is crucial, as any imperfections or inconsistencies in the raw materials can significantly affect the quality of the final product.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Music Instrument Parts?
Forming is the next stage where the prepared materials are shaped into the desired components. This can involve several techniques, including:
- Machining: Precision tools carve out parts from larger blocks of material. This technique is essential for components that require tight tolerances, such as tuning machines and bridges.
- Injection Molding: For plastic parts, this technique allows for mass production while maintaining consistent quality. It is commonly used for knobs, pickguards, and other non-structural components.
- Die-Casting: This is often used for metal parts where molten metal is poured into a mold to create intricate shapes. This method is popular for parts like tuning pegs and hardware fittings.
Each technique has its specific applications and benefits, and manufacturers often utilize a combination to optimize production efficiency and product quality.
How Are Music Instrument Parts Assembled?
Assembly involves putting together the various components produced in the forming stage. This process can be manual or automated, depending on the complexity of the parts and the production scale. Skilled workers often conduct manual assembly to ensure that delicate components are handled with care, especially in instruments where sound quality is paramount.
During assembly, quality checks are performed at different stages to ensure that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. This is crucial for components like bridges and necks in string instruments, where precise alignment affects playability and sound.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Music Instrument Parts?
Finishing is the final stage of manufacturing, where parts receive treatments that enhance their appearance and durability. This may include:
- Sanding and Polishing: To achieve a smooth surface finish, parts are sanded down and polished, improving their aesthetic appeal.
- Coating: Various coatings, such as lacquer or varnish, are applied to protect the materials from wear and environmental factors while enhancing their visual appeal.
- Plating: Metal components may undergo plating processes to resist corrosion and improve their appearance, particularly for hardware parts.
The finishing process is vital for both functional and aesthetic reasons, as it can influence the overall quality of the instrument.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for Music Instrument Parts Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for music instrument parts, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for consistent quality management systems across industries, including musical instrument manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes for quality control and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industry certifications such as CE marking in Europe indicate that products meet safety and environmental requirements. For parts intended for specific applications, certifications like API (American Petroleum Institute) may also be relevant, especially for instruments used in specific environments.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing Music Instrument Parts?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each component meets the required specifications. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet quality standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, inspections are conducted at various stages to catch defects early. This is particularly important in processes like machining and assembly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the parts are fully assembled and finished, a final inspection ensures that they meet all specifications and quality requirements before shipment.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential for ensuring product reliability. Here are several strategies to consider:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards. This can be done by the buyers themselves or through third-party auditing firms.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documentation on their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. These reports can give insights into their operational quality standards.
- Utilize Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices and the final product quality.
What Are the Nuances of Quality Control for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers operating in diverse markets must consider regional standards and practices that may influence quality control. For instance, suppliers targeting the European market must comply with stricter environmental and safety regulations compared to those in other regions.
Additionally, cultural differences may affect communication and expectations regarding quality. Buyers should establish clear quality benchmarks and maintain open lines of communication with suppliers to ensure mutual understanding and compliance with quality standards.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in the production of music instrument parts is crucial for B2B buyers. By recognizing the importance of each stage in manufacturing and the relevant quality standards, buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately ensuring the reliability and excellence of the music instruments they provide.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘music instrument parts’
To ensure a successful procurement process for music instrument parts, B2B buyers need a structured approach. This guide provides a clear checklist to help you navigate the complexities of sourcing, ensuring you acquire high-quality components while minimizing risks.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding the exact specifications of the music instrument parts you need is critical. This includes dimensions, materials, and functionality. Clear specifications help prevent costly mistakes and ensure compatibility with existing instruments or systems.
- Detail the requirements: Include technical drawings or examples of desired parts.
- Consider performance needs: Different materials and designs can affect sound quality and durability.
Step 2: Research and Identify Reliable Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to compile a list of potential suppliers. Look for companies with a proven track record in the industry, particularly those that serve your target markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Utilize industry directories: Websites like Full Compass Systems and StewMac can provide insights into reputable suppliers.
- Check reviews and testimonials: Feedback from other businesses can reveal a supplier’s reliability and product quality.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before finalizing any agreements, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website.
- Assess certifications: Verify if suppliers have industry-standard certifications, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Review product quality: Ask for samples to evaluate the quality of the parts firsthand.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Pricing
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed quotes for your required parts. This process helps you understand market pricing and allows for better negotiation.
- Include all costs: Ensure quotes cover shipping, taxes, and any additional fees.
- Evaluate value over price: Sometimes a higher-priced supplier may offer better quality or support, which can save money in the long run.
Step 5: Check Supply Chain Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s ability to deliver on time is vital. Investigate their supply chain logistics, including lead times and shipping methods.
- Ask about production capacity: Can they handle your volume needs?
- Inquire about inventory management: Reliable suppliers should have strategies to manage stock levels effectively.
Step 6: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is crucial throughout the sourcing process. Establish who your point of contact will be and ensure they are responsive and knowledgeable.
- Set expectations: Clearly outline your needs and timelines to avoid misunderstandings.
- Utilize technology: Tools like video calls can enhance communication, especially when dealing with international suppliers.
Step 7: Finalize Terms and Place Your Order
Once you are satisfied with your supplier’s capabilities and pricing, finalize the terms of the agreement. Ensure all parties understand the payment terms, delivery schedules, and return policies.
- Draft a contract: Include all agreed-upon terms to protect both parties.
- Confirm order details: Double-check all specifications before placing the order to avoid discrepancies.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can navigate the sourcing process for music instrument parts with confidence, ensuring they secure quality products that meet their technical needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for music instrument parts Sourcing
When sourcing music instrument parts, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here, we break down the critical components of costs, the influencers on pricing, and provide actionable tips for international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Music Instrument Parts Sourcing?
The cost structure for music instrument parts comprises several components:
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials significantly impact costs. For example, high-quality woods for string instruments or specialized metals for brass instruments can increase the base cost. Buyers should be aware of the material specifications they require to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the region of production. Skilled artisans may command higher wages, particularly for custom or high-quality parts. Understanding local labor markets can help buyers assess fair pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and maintenance of manufacturing facilities. Overhead can vary significantly between suppliers, affecting the final price of parts.
-
Tooling: The initial setup costs for manufacturing can be substantial, especially for custom parts. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs when placing larger orders, as these may be amortized over larger volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specified standards can add to costs. Suppliers with rigorous QC processes may charge more, but this can be justified by the reduction in defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs should not be overlooked, particularly for international transactions. Factors like distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better deals.
How Do Pricing Influencers Affect the Cost of Music Instrument Parts?
Several factors influence the pricing of music instrument parts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider their needs and potential for bulk purchasing to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom parts tailored to specific instruments typically come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the need for customization against the potential cost benefits of off-the-shelf parts.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Parts made from premium materials or those that meet specific industry certifications may have higher prices. Understanding the trade-offs between cost and quality is crucial.
-
Supplier Factors: Relationships with suppliers can influence pricing. Established partnerships may yield better pricing terms due to trust and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon shipping terms can affect total costs. Buyers should clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected charges.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for International B2B Buyers?
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the long-term costs associated with parts, including maintenance, potential replacements, and logistical costs. A lower upfront cost may not always equate to better value.
-
Research and Benchmark Pricing: Familiarize yourself with market prices for similar parts. This knowledge empowers you during negotiations and helps you identify fair pricing.
-
Leverage Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms. Regular communication fosters trust, which can be advantageous during negotiations.
-
Be Transparent About Needs: Clearly communicating your requirements can help suppliers offer tailored solutions that may reduce costs.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing from local manufacturers can minimize logistics costs and lead to faster turnaround times.
Conclusion
Navigating the cost structure and pricing of music instrument parts requires a strategic approach. By understanding the various cost components, recognizing pricing influencers, and employing effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions. While prices may vary, a thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership and supplier relationships will ultimately lead to more informed and beneficial purchasing outcomes. Always remember that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, and it is prudent to approach negotiations with flexibility and preparedness.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing music instrument parts With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternative Solutions for Music Instrument Parts
In the dynamic landscape of the music industry, B2B buyers are often faced with the decision of selecting the best solutions for their instrument parts needs. While traditional music instrument parts play a crucial role in instrument performance and maintenance, various alternative solutions exist that can provide similar benefits. This analysis will compare music instrument parts against two viable alternatives: 3D printing technology and modular instrument systems.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Music Instrument Parts | 3D Printing Technology | Modular Instrument Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality, tested parts that enhance sound and playability | Variable quality; depends on the material used | Consistent performance due to standardized components |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on the part and brand | Potentially low, but initial setup can be expensive | Higher upfront cost due to design and manufacturing |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to replace or install with basic tools | Requires skilled operators and software | User-friendly; designed for easy assembly and disassembly |
| Maintenance | Regular checks needed, but parts are durable | Minimal maintenance; however, printed parts may wear faster | Low maintenance, as components can be easily swapped |
| Best Use Case | Traditional instruments requiring specific parts | Custom or unique designs for niche markets | Versatile for musicians needing adaptability in their setups |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
3D Printing Technology
3D printing is revolutionizing the way musical instrument parts are created. It allows for rapid prototyping and custom designs tailored to individual musician needs. The primary advantage of this technology is cost-effectiveness for small batches or unique parts that may not be commercially available. However, the quality of 3D printed parts can vary significantly based on the materials used and the printing process. Additionally, while initial costs can be lower, the investment in quality equipment and skilled personnel can be substantial.
Modular Instrument Systems
Modular instrument systems are designed to provide flexibility and adaptability for musicians. These systems allow players to easily swap out components, making it easier to customize their instruments based on performance needs. The primary benefit is the consistent performance derived from standardized parts, which can be a significant advantage for professional musicians. On the downside, the initial investment for modular systems can be higher, and not all musicians may require the level of customization they offer.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between music instrument parts and alternative solutions like 3D printing technology or modular instrument systems, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific needs. Consider factors such as performance requirements, budget constraints, and the technical expertise available within your organization. For traditional applications, music instrument parts may be the best choice, while 3D printing may serve niche markets effectively. Modular systems can provide the flexibility needed for dynamic performance environments. Ultimately, the right solution will depend on aligning your operational capabilities with the demands of your target market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for music instrument parts
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Music Instrument Parts?
Understanding the technical specifications of music instrument parts is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing components for manufacturing or repair. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade refers to the quality and type of material used in the production of instrument parts, such as metals (e.g., brass, stainless steel) or woods (e.g., mahogany, maple). This specification is vital as it affects the durability, sound quality, and overall performance of the instrument. High-grade materials can enhance the instrument’s lifespan and resonance, making them more appealing to professional musicians. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance denotes the permissible variation in dimensions of a part. For example, a tuning machine may have a tolerance of ±0.5 mm. In the music instrument industry, precise tolerances are essential for ensuring parts fit together correctly, which is critical for performance and sound quality. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to issues such as poor playability or mechanical failure. -
Finish
– The finish of a part refers to the surface treatment applied, such as polishing, plating, or lacquering. The finish not only affects the aesthetic appeal of the instrument but also its protection against environmental factors like moisture and corrosion. A high-quality finish can improve the longevity of parts, making them more attractive for buyers looking for durability. -
Weight
– The weight of parts, particularly in stringed instruments, can influence playability and sound projection. For instance, heavier bridges may enhance sustain and tonal depth, while lighter parts can improve ease of handling. Buyers must consider how the weight of parts aligns with the intended use of the instrument. -
Compatibility
– Compatibility indicates whether a part can be used with other components or instruments. This is especially important for replacement parts or upgrades, as buyers need assurance that new components will fit seamlessly with existing instruments. Providing detailed compatibility information can enhance buyer confidence and streamline the procurement process.
Which Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know for Music Instrument Parts?
Familiarizing oneself with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the music instrument parts market. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are used in the manufacturing of instruments by other brands. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers seeking high-quality, branded components that maintain the original specifications of instruments. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For B2B buyers, knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory planning, as it can impact the overall cost of procurement. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific quantities of parts. This is an essential step in the purchasing process, allowing buyers to compare costs and terms from different suppliers to make informed decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and duties. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B buyers to understand shipping costs and liability, ensuring smoother cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. In the music instrument parts industry, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and ensuring timely delivery of products to meet market demand. -
Aftermarket
– The aftermarket encompasses parts and accessories sold after the initial sale of an instrument. This term is significant for B2B buyers focusing on replacement parts or upgrades, as it indicates a market for ongoing sales and customer support.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they acquire the right components for their needs while optimizing their supply chain processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the music instrument parts Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Music Instrument Parts Sector?
The global market for music instrument parts is experiencing significant growth, driven by several key factors. Increased consumer interest in music, the rise of home recording, and a growing appreciation for musical craftsmanship are propelling demand. Emerging markets in Africa and South America are seeing a surge in both amateur and professional musicians, which is boosting the need for quality instrument parts. Furthermore, technological advancements are reshaping the sourcing landscape, with digital platforms enabling B2B buyers to connect with manufacturers worldwide more efficiently. Key trends include the integration of e-commerce solutions for streamlined procurement processes and the adoption of data analytics to forecast demand more accurately.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like the Middle East and Europe, are also witnessing an increasing shift towards customized and high-quality parts. As brands differentiate themselves, they are investing in innovative materials and designs, enhancing the overall performance and aesthetics of musical instruments. The rise of online marketplaces facilitates easier access to specialized parts, allowing businesses to source unique components that cater to niche markets. Additionally, sustainability and ethical considerations are becoming paramount, with buyers increasingly seeking suppliers who adhere to environmentally friendly practices.
How Is Sustainability Influencing Sourcing Trends in the Music Instrument Parts Sector?
Sustainability is a crucial factor influencing sourcing strategies in the music instrument parts sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning wood and other raw materials, has prompted many companies to reassess their supply chains. Ethical sourcing is not just a trend but a necessity as consumers and businesses alike prioritize eco-friendly practices. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of certified woods and recycled materials.
Green certifications such as FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) and PEFC (Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification) are becoming essential criteria for sourcing decisions. Buyers are also interested in parts made from alternative materials, such as synthetic compounds that reduce reliance on traditional resources. Additionally, manufacturers are exploring innovative processes that minimize waste and energy consumption. By prioritizing sustainability, businesses not only meet regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to a growing demographic of environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of the Music Instrument Parts Sector?
The music instrument parts sector has evolved significantly over the centuries, transitioning from handcrafted components to mass-produced parts that leverage advanced technology. Historically, instrument makers relied on local materials and artisanship, which defined the quality and uniqueness of each instrument. However, the Industrial Revolution marked a shift towards mass production, allowing for a wider distribution of musical instruments and their parts.
In recent decades, globalization has facilitated international sourcing, enabling manufacturers to access a broader array of materials and components. This evolution has led to increased competition and innovation within the industry, pushing suppliers to adopt cutting-edge technologies and sustainable practices. The current landscape reflects a blend of tradition and modernity, where craftsmanship meets industrial efficiency, catering to a diverse and discerning global market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of music instrument parts
-
How do I solve quality issues when sourcing music instrument parts?
To address quality issues, it is essential to establish a robust quality assurance (QA) process. Begin by vetting suppliers through references, certifications, and quality audits. Request samples to evaluate the materials and craftsmanship before placing larger orders. Implement clear quality specifications in your contracts and consider third-party inspections to ensure compliance with your standards. Regular communication with suppliers can also help address issues promptly and maintain quality consistency. -
What is the best material for guitar strings?
The best material for guitar strings depends on the desired sound and playability. Common options include nickel-plated steel for bright tones, pure nickel for a warmer sound, and phosphor bronze for a balanced tone. Stainless steel is also popular for its durability and resistance to corrosion. Consider the genre of music and the player’s preference when selecting strings, as each material produces unique tonal characteristics. -
How can I find reliable suppliers for music instrument parts internationally?
Finding reliable international suppliers involves thorough research and due diligence. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to identify potential suppliers. Check their reputation through reviews and ratings, and request references from other clients. Conduct video calls to assess their operations and quality control processes. It may also be beneficial to start with small orders to evaluate their service and product quality before committing to larger purchases. -
What are the typical payment terms for B2B transactions in the music instrument parts industry?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include advance payments, net 30, or net 60 terms. It’s essential to discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payments or larger orders. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and that you have a clear invoice detailing the terms to protect your business interests. -
What should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact your purchasing decisions. Evaluate your inventory needs and production capacity to determine the feasibility of meeting a supplier’s MOQ. Consider negotiating lower MOQs, especially if you are a new buyer or if the parts are specialized. Some suppliers may be willing to accommodate smaller orders, particularly if you establish a long-term relationship or commit to future purchases. -
How can I ensure timely delivery of music instrument parts?
To ensure timely delivery, establish clear timelines and expectations with your suppliers at the outset. Discuss logistics options, including shipping methods and lead times. Utilize tracking systems to monitor shipments in real-time and maintain open communication with suppliers regarding any potential delays. It may also be beneficial to work with logistics partners experienced in international shipping to navigate customs and regulatory requirements effectively. -
What customization options are typically available for music instrument parts?
Many suppliers offer customization options for music instrument parts, including materials, sizes, finishes, and designs. When seeking custom parts, clearly outline your specifications and expectations to the supplier. Inquire about their capabilities, lead times, and any additional costs associated with customization. Collaborating closely with the supplier can help ensure the final product meets your exact requirements and enhances your brand’s offerings. -
How can I verify the compliance of music instrument parts with international standards?
To verify compliance with international standards, request certifications and test reports from your suppliers. Familiarize yourself with the relevant regulations for your target market, such as CE marking in Europe or ISO standards globally. Conduct audits or assessments of the supplier’s production processes to ensure adherence to quality and safety standards. Engaging third-party testing laboratories can also provide an unbiased evaluation of the parts’ compliance before shipment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Music Instrument Parts Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Votaw Tool – Clarinet Parts
Domain: votawtool.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: INSTRUMENT PARTS
– Oversize clarinet thumb rest screw (SKU: 9503) – $3.00
– Head diameter: 3mm
– Thread diameter: 2mm
– Overall length: 5.3mm
– Jupiter 631NT barrel (SKU: J61D004) – $23.34
– Material: Plastic
– Fits models: Jupiter 631NT
– Jupiter Bass Clarinet 673N peg lock screw nut (SKU: J67C207) – $14.97
– Fits models: Jupiter 673N
– Bass clarinet throat Bb key adjusting screw …
2. J.L. Smith – Musical Instrument Repair Tools and Accessories
Domain: jlsmithco.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Musical Instrument Repair Services, Tools, Parts and Supplies – J.L. Smith includes a variety of products such as:
1. **Accessories**: Flute plugs, instrument care, repair kits, stands, straps, teaching aids, and ergonomics.
2. **Pads and Shims**: Bassoon, clarinet, cork pads, flute, piccolo, oboe, saxophone shims (washers).
3. **Parts**: Bumpers, case repair, corks, flute bushings and washers, f…
3. StewMac – Luthier Tools & Supplies
Domain: stewmac.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Musical Instrument Parts and Hardware – StewMac Luthier Tools + Supplies. Categories include: Tools by Job (Bending Sides, Binding, Bridges, Crack + Brace Repair, Electronics, Finishing, Fretting, Gluing, Inlay + Pearl Cutting, Inspection, Knob + Bushing Pullers, Leveling, Maintenance, Measuring, Necks + Fingerboard, Nuts + Saddles, Pickguards, Sanding, Truss Rods, Tuner Installation, Violins), Ty…
4. Elderly – Moon Compensated Banjo Bridge
Domain: elderly.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Elderly – Moon Compensated Banjo Bridge, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Yamaha – Musical Instruments
Domain: yamaha.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Instruments are collections of small parts. The guide includes components for various instruments such as Woodwinds (Oboes, Saxophones, Bassoons, Flutes, Recorders), Brass (Trumpets, Trombones, Horns), Strings (Acoustic Guitars, Electric Guitars, Classical Guitars, Violins), Keyboards (Celesta, Pipe Organ, Piano), and Percussion (Timpani, Drums, Marimba).
6. Music Medic – Musical Instrument Repair Supplies
Domain: musicmedic.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Repair Supplies include a variety of items for musical instrument repair, such as:
1. **Saxophone Pads**: Individual pads, SoftFeel pads, RooPads, Jim Schmidt pads, and pad sets.
2. **Clarinet Pads**: Single and medium pressed felt pads, RooPads, and pad sets.
3. **Flute and Piccolo Pads**: Individual pads, Jim Schmidt pads, and pad sets.
4. **Bassoon Pads**: Custom pads and pad assortments.
5. *…
7. Mouthpiece Express – Brass Instrument Parts
Domain: mouthpieceexpress.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Brass Instrument Parts available include: Aftermarket 4 7/8″ 124MM Bb Trumpet Bells, Bach Parts, Benge Parts, Blessing Parts, Bundy Parts, C.G.Conn Parts, Eastman Parts, Finger Buttons, Getzen Parts, Hans Hoyer Parts, Holton Parts, Jupiter Parts, King Parts, Olds Parts, Schilke Parts, Yamaha Parts. Genuine Original Manufacturer Parts (OEM parts) from top brands like Bach, Yamaha, Schilke, and more…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for music instrument parts
The global market for music instrument parts presents a wealth of opportunities for B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By embracing strategic sourcing, businesses can streamline procurement processes, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. Key considerations include evaluating suppliers based on reliability, product range, and responsiveness to market demands.
In addition, staying informed about the latest trends—such as the growing demand for sustainable materials and the rise of custom parts—will empower buyers to make informed decisions that align with their business goals. As the landscape of musical instrument parts continues to evolve, fostering strong partnerships with suppliers will be critical to navigating challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.
Moving forward, it is essential for international buyers to actively engage with suppliers, leverage technology for efficient sourcing, and remain adaptable to market changes. By taking these proactive steps, businesses can not only enhance their competitive edge but also contribute to the vibrant global music community. Start your strategic sourcing journey today to unlock the full potential of your business in the music instrument parts market.