Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for most corrosion resistant stainless steel
In an increasingly competitive global market, sourcing the most corrosion-resistant stainless steel is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance product longevity and reduce maintenance costs. With industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe facing unique environmental challenges, the need for high-performance materials has never been more pressing. This comprehensive guide is designed to empower international B2B buyers by providing valuable insights into various types of corrosion-resistant stainless steel, their specific applications, and critical factors to consider when selecting suppliers.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the key differences between popular grades such as 304 and 316 stainless steel, exploring their performance in diverse environments—from coastal areas exposed to saltwater to chemical processing facilities. Additionally, we will address essential aspects of supplier vetting, including quality certifications and service offerings, to ensure that your procurement decisions are both informed and strategic. Cost considerations will also be examined, highlighting how investing in superior materials can lead to significant long-term savings.
By equipping buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the complexities of the stainless steel market, this guide aims to facilitate better purchasing decisions, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and product reliability in a variety of industrial applications.
Understanding most corrosion resistant stainless steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | 18% chromium, 8% nickel; good general corrosion resistance | Food processing, kitchen equipment, indoor structures | Pros: Cost-effective, versatile. Cons: Limited resistance to chlorides. |
| 316 Stainless Steel | 16% chromium, 10% nickel, 2-3% molybdenum; superior to 304 in corrosive environments | Marine applications, chemical processing, medical devices | Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, longevity. Cons: Higher cost than 304. |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Combination of austenitic and ferritic structures; high strength and corrosion resistance | Oil and gas, chemical processing, pulp and paper | Pros: High strength, reduced weight. Cons: More expensive, complex fabrication. |
| Super Duplex Stainless Steel | Higher chromium and molybdenum content than duplex; outstanding resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion | Offshore oil and gas, desalination plants, chemical processing | Pros: Exceptional corrosion resistance, durability. Cons: Premium pricing, specialized applications. |
| Alloy 20 Stainless Steel | Niobium-stabilized; excellent resistance to sulfuric acid | Pharmaceutical, chemical processing, food industry | Pros: Specialized for aggressive environments. Cons: Limited availability, higher cost. |
What Are the Characteristics of 304 Stainless Steel?
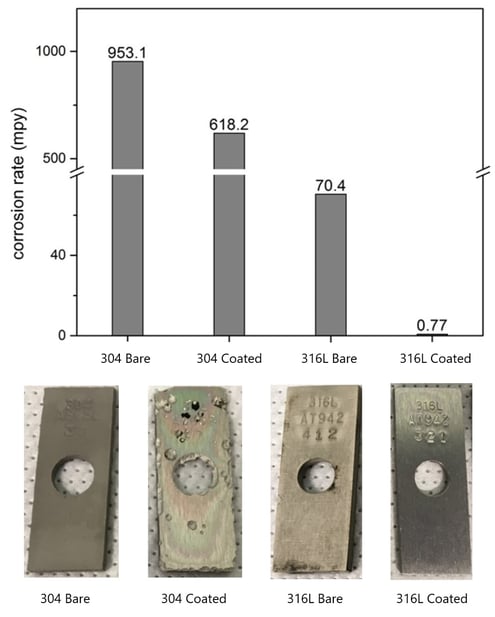
304 Stainless Steel is the most widely used stainless steel grade, characterized by its composition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel. It offers decent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications, particularly in food processing and kitchen equipment. However, its performance diminishes in environments with high chloride concentrations, which can lead to pitting. Buyers should consider the balance between cost and the specific environmental conditions when selecting this grade.
Why Choose 316 Stainless Steel for Corrosive Environments?
316 Stainless Steel stands out for its enhanced corrosion resistance due to the addition of 2-3% molybdenum. This makes it ideal for applications in marine environments, chemical processing, and medical devices where exposure to chlorides and acids is common. Although it comes at a higher price point than 304, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement costs can justify the initial investment. Buyers should assess the corrosive risks in their specific applications to determine the value of upgrading to 316.
How Does Duplex Stainless Steel Compare?
Duplex Stainless Steel combines the best features of austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, providing high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. This makes it particularly valuable in demanding applications such as oil and gas and chemical processing. While it tends to be more expensive and can be challenging to fabricate, its strength-to-weight ratio can result in overall savings on material costs. B2B buyers should evaluate their structural requirements and potential cost benefits when considering duplex options.
What Are the Advantages of Super Duplex Stainless Steel?
Super Duplex Stainless Steel offers even higher levels of chromium and molybdenum compared to standard duplex grades, resulting in outstanding resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. This makes it suitable for extreme environments like offshore oil and gas operations and desalination plants. However, its specialized nature means it comes with a premium price tag. Buyers must weigh the benefits of its durability and performance against the higher costs and ensure it aligns with their project specifications.
When to Use Alloy 20 Stainless Steel?
Alloy 20 Stainless Steel is specifically designed to withstand corrosive environments, particularly those involving sulfuric acid. Its niobium stabilization enhances its resistance to corrosion, making it a preferred choice in the pharmaceutical and chemical processing industries. While it may not be as widely available as other grades and comes at a higher price, its specialized properties can be invaluable in aggressive environments. Buyers should consider the specific chemical exposures in their applications when evaluating Alloy 20 for their needs.
Key Industrial Applications of most corrosion resistant stainless steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of most corrosion resistant stainless steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Chemical piping and storage tanks | Enhanced durability and reduced maintenance costs | Compliance with safety regulations and material certifications |
| Food and Beverage | Food processing equipment and surfaces | Improved hygiene standards and resistance to harsh cleaning agents | Compliance with food safety standards and certifications |
| Marine and Coastal Engineering | Structural components for marine environments | Increased lifespan in corrosive saltwater conditions | Material performance in saline environments |
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Medical equipment and pharmaceutical processing | Assurance of product integrity and safety | Regulatory compliance and traceability of materials |
| Oil and Gas | Offshore drilling equipment and pipelines | Reliability in extreme conditions and reduced downtime | Material certifications for high-pressure and corrosive environments |
How is ‘Most Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel’ Used in Chemical Processing?
In the chemical processing industry, most corrosion-resistant stainless steel is crucial for applications such as chemical piping and storage tanks. These environments often expose materials to aggressive chemicals that can cause rapid degradation. By utilizing grades like 316 stainless steel, businesses can significantly enhance the durability of their equipment, leading to lower maintenance costs and extended operational life. Buyers need to ensure that materials comply with safety regulations and possess necessary certifications to withstand harsh chemical environments.
What Role Does Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Play in Food and Beverage Industries?
In food processing, the use of most corrosion-resistant stainless steel is vital for equipment such as mixers, conveyors, and storage containers. This material not only meets stringent hygiene standards but also withstands the frequent cleaning with harsh detergents. By opting for higher-grade stainless steel, food and beverage manufacturers can ensure product safety and minimize contamination risks. Buyers must consider compliance with food safety standards and certifications when sourcing materials for this sector.
Why is Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Important in Marine Applications?
Marine and coastal engineering applications heavily rely on most corrosion-resistant stainless steel for structural components exposed to saltwater. This material is essential for building durable vessels, offshore platforms, and other marine structures. The resistance to corrosion ensures a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent repairs or replacements. For international buyers, particularly in coastal regions, understanding the material’s performance in saline environments is critical when sourcing for such applications.
How Does Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Benefit Pharmaceutical Manufacturing?
In the pharmaceutical industry, most corrosion-resistant stainless steel is used in manufacturing medical devices and processing equipment. The high level of corrosion resistance ensures the integrity and safety of products that must meet strict regulatory standards. Utilizing such materials can prevent contamination and ensure the reliability of equipment. Buyers should focus on regulatory compliance and traceability of materials to ensure they meet industry standards.
What are the Advantages of Using Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel in Oil and Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas sector, most corrosion-resistant stainless steel is integral to offshore drilling equipment and pipelines. The harsh conditions, including high pressures and corrosive environments, necessitate the use of robust materials that can maintain structural integrity. Implementing higher-grade stainless steel can lead to increased reliability and reduced downtime, which is vital for profitability. Buyers must ensure that the materials sourced have the necessary certifications for high-pressure and corrosive applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘most corrosion resistant stainless steel’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the Right Grade for Specific Applications
The Problem: Many B2B buyers often struggle with selecting the appropriate grade of stainless steel for their specific environmental conditions. For instance, a buyer in the food processing industry may initially consider using 304 stainless steel due to its lower cost and good corrosion resistance. However, in a coastal area or in environments exposed to high levels of chlorides, the long-term performance of 304 could be severely compromised. This oversight can lead to increased maintenance costs and shortened product lifespans, ultimately impacting the bottom line.
The Solution: To effectively address this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of their operating environment and application requirements before making a purchase. Understanding the specific corrosive elements present—such as salt, acids, or other harsh chemicals—is critical. For environments with elevated chloride levels, opting for 316 stainless steel is recommended due to its superior corrosion resistance, attributed to the addition of molybdenum. B2B buyers should also engage with suppliers who can provide expert guidance on material selection based on specific use cases, ensuring that the chosen grade maximizes both performance and cost-effectiveness over time.
Scenario 2: The Challenge of Coating Compatibility
The Problem: Another common pain point arises when buyers attempt to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel through coatings. Often, they may assume that any coating will significantly improve the performance of a lower-grade stainless steel, such as 304. However, if the base metal is unsuitable, the coating may not adhere properly or may degrade quickly in harsh environments, leading to premature failure and unexpected costs. This scenario often leaves businesses frustrated, having invested in coatings that do not deliver the anticipated protection.
The Solution: To mitigate this risk, it is crucial for buyers to ensure that the substrate material and the chosen coating are compatible. For instance, when selecting a coating for 316 stainless steel, buyers should look for high-quality options specifically designed for that alloy, such as SilcoTek’s Dursan coating. This combination not only enhances corrosion resistance but also improves the overall lifespan of the component. Buyers should also consider working with suppliers who can provide detailed specifications and case studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of specific coatings in various corrosive environments. This strategic approach will help in making informed decisions that align with operational needs.
Scenario 3: Navigating Cost vs. Performance Dilemmas
The Problem: B2B buyers frequently face the dilemma of balancing cost with performance when selecting stainless steel for their projects. While 304 stainless steel is often perceived as a more economical choice, its limited corrosion resistance can lead to higher long-term maintenance and replacement costs in challenging environments. Buyers may find themselves in a situation where initial savings are outweighed by the expenses associated with repairs or replacements, causing frustration and potential project delays.
The Solution: To navigate this cost-performance conundrum, it is essential for buyers to adopt a lifecycle cost analysis approach. This involves evaluating not only the upfront costs of stainless steel but also the projected maintenance, replacement, and operational costs over time. By investing in higher-grade materials like 316 stainless steel, buyers can achieve significant savings in the long run, particularly in corrosive environments where lower grades would fail prematurely. Engaging in discussions with suppliers about the total cost of ownership and obtaining performance data on various grades can aid buyers in making more informed decisions that align with both their budget and operational requirements.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for most corrosion resistant stainless steel
What Are the Key Properties of Common Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Materials?
When selecting stainless steel for applications requiring high corrosion resistance, it is essential to understand the properties and performance of various grades. Here, we analyze three common materials: 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel, and duplex stainless steel.
What Are the Key Properties of 304 Stainless Steel?
304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used stainless steel grades, primarily due to its excellent corrosion resistance and formability. It contains approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel, making it suitable for a variety of applications. Its temperature rating can reach up to 870°C (1600°F) in intermittent service, and it performs well in mildly corrosive environments.
Pros:
– Cost-effective and readily available.
– Good mechanical properties and weldability.
– Suitable for a wide range of applications, including food processing and storage.
Cons:
– Limited resistance to chlorides and acids compared to higher-grade alloys.
– Not ideal for marine environments or applications involving high salinity.
Impact on Application:
304 stainless steel is often used in water piping, kitchen equipment, and decorative trim. However, its limitations in highly corrosive environments can lead to premature failure.
How Does 316 Stainless Steel Compare in Corrosion Resistance?
316 stainless steel is recognized for its superior corrosion resistance, especially against chlorides and acids, due to the addition of 2-3% molybdenum. This material is suitable for environments exposed to saltwater and acidic conditions, with a temperature rating similar to that of 304.
Pros:
– Excellent resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
– Ideal for pharmaceutical and food processing applications.
– Can withstand harsher cleaning agents without damage.
Cons:
– Higher initial cost compared to 304 stainless steel.
– Slightly less formable than 304, which may complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in chemical processing, medical equipment, and marine applications, 316 stainless steel significantly enhances the lifespan of products exposed to corrosive environments.
What Are the Advantages of Duplex Stainless Steel?
Duplex stainless steel combines the properties of both austenitic and ferritic stainless steels, offering high strength and excellent corrosion resistance. With a composition of approximately 22% chromium and 5% nickel, duplex stainless steel is particularly effective in environments with high chloride concentrations.
Pros:
– High strength-to-weight ratio, allowing for thinner sections and reduced weight.
– Exceptional resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
– Suitable for high-pressure applications.
Cons:
– More expensive than both 304 and 316 grades.
– Requires specific welding techniques, which may complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application:
Duplex stainless steel is often used in oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine applications, where both strength and corrosion resistance are critical.
What Should International B2B Buyers Consider When Selecting Stainless Steel?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local and international standards (such as ASTM, DIN, and JIS) is crucial. Buyers should also consider the availability of materials and local manufacturing capabilities. For instance, 316 stainless steel may be preferred in coastal regions due to its enhanced resistance to saltwater, while 304 may suffice in less demanding environments. Understanding the specific requirements of the application and the local market conditions can lead to significant cost savings and improved product performance.
Summary Table of Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Materials
| Material | Typical Use Case for most corrosion resistant stainless steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | Water piping, kitchen equipment | Cost-effective and widely available | Limited resistance to chlorides and acids | Low |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, medical equipment | Excellent resistance to pitting and crevice | Higher initial cost compared to 304 | Med |
| Duplex Stainless Steel | Oil and gas, marine applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive and requires specific welding | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the most corrosion-resistant stainless steel options available, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for most corrosion resistant stainless steel
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel?
The manufacturing process for corrosion-resistant stainless steel involves several critical stages, each designed to enhance the material’s integrity and performance in demanding environments. Understanding these stages helps international B2B buyers ensure they are sourcing high-quality products.
Material Preparation: How Is Raw Stainless Steel Processed?
The first stage in manufacturing corrosion-resistant stainless steel involves the careful selection and preparation of raw materials. The most common grades, such as 304 and 316, are chosen based on their specific corrosion resistance properties. The material is typically sourced in the form of billets or slabs and is subjected to rigorous quality checks to ensure it meets industry standards.
Once the raw material is selected, it undergoes processes such as melting, refining, and alloying. In the case of 316 stainless steel, for example, the addition of molybdenum is critical for enhancing corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich environments. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for the performance characteristics of the final product.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape Stainless Steel?
After material preparation, the next stage is forming, which involves shaping the stainless steel into the desired dimensions. This can be achieved through various techniques, including:
-
Hot Rolling: This process involves heating the steel above its recrystallization temperature and then rolling it into sheets, plates, or other shapes. Hot rolling helps improve the steel’s ductility and reduces the risk of defects.
-
Cold Rolling: This technique is performed at room temperature and provides a smoother finish and tighter tolerances. Cold-rolled stainless steel is often used in applications requiring precise dimensions and surface quality.
-
Forging: Forging involves shaping the metal through compressive forces, typically at high temperatures. This method enhances the mechanical properties of the steel, making it stronger and more durable.
-
Welding and Fabrication: Once the steel is shaped, it may be welded or fabricated into complex components. Techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are commonly used for stainless steel due to their ability to produce clean, strong welds.
Finishing: How Is Stainless Steel Treated for Enhanced Corrosion Resistance?
The finishing stage is critical for enhancing the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. This involves several processes, including:
-
Pickling and Passivation: This chemical treatment removes surface contaminants and oxides, improving corrosion resistance. Passivation creates a thin, protective layer of chromium oxide on the surface, which significantly enhances the steel’s resistance to corrosion.
-
Coating: In some applications, additional coatings such as electropolishing or specialized surface treatments may be applied to further enhance performance. These coatings act as barriers against corrosive environments, extending the lifespan of the components.
-
Surface Finishing: Techniques like grinding, polishing, or bead blasting may be employed to achieve the desired aesthetic and functional qualities. A smooth surface finish not only improves appearance but also reduces the likelihood of corrosion by minimizing the potential for contaminants to adhere.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel?
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in ensuring the performance and reliability of corrosion-resistant stainless steel. Various international and industry-specific standards guide the QA processes.
What International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. For stainless steel, adherence to standards such as ASTM A240 for general specifications and ASTM A312 for seamless pipe and tubing is also crucial.
In addition to ISO standards, specific certifications may be relevant depending on the application. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European market, while API (American Petroleum Institute) standards are critical for products used in the oil and gas industry. Buyers should request documentation proving compliance with these standards from their suppliers.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process, ensuring that potential issues are identified and addressed promptly. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor processes and detect deviations from quality standards. This may include dimensional checks, surface inspections, and testing of mechanical properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, a final inspection ensures that the finished product meets all specifications. This includes visual inspections, dimensional checks, and performance testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers. Here are some strategies:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to international standards. This can include both scheduled audits and surprise inspections to gauge compliance.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide detailed reports on their quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC checks.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. This can be particularly beneficial for large orders or critical applications.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control and certification processes. Differences in regulatory requirements, cultural practices, and logistical challenges can impact the procurement process.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards. This may require additional documentation or certifications specific to the buyer’s region.
-
Cultural Considerations: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate smoother negotiations and establish trust between buyers and suppliers.
-
Logistics and Supply Chain: International shipping can introduce variables affecting product quality. Buyers should work with suppliers who have robust logistics strategies to mitigate risks associated with transportation and handling.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for corrosion-resistant stainless steel is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on these key areas, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘most corrosion resistant stainless steel’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of stainless steel with superior corrosion resistance can be complex, especially for international B2B buyers. This practical sourcing guide provides a step-by-step checklist to help you make informed decisions, ensuring that you select the right materials that meet your specific application needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your application requirements is essential. Determine the operating environment, including exposure to chemicals, humidity, and temperature variations. This clarity will help you identify the appropriate stainless steel grade, such as 304 or 316, with 316 often being preferred for environments with high chloride exposure.
Step 2: Research Stainless Steel Grades
Familiarize yourself with the most corrosion-resistant stainless steel grades. Look into the composition, such as the percentage of chromium and molybdenum, and their implications on corrosion resistance. For instance, 316 stainless steel, which includes 2-3% molybdenum, offers enhanced protection against corrosive substances compared to 304 stainless steel.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, perform due diligence. Review company profiles, request case studies, and seek references from other businesses in your industry. Pay special attention to their experience with corrosion-resistant coatings, as this can impact the overall longevity and effectiveness of the stainless steel.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that your potential suppliers possess relevant certifications. Look for ISO certifications or other industry-specific quality standards that indicate a commitment to quality and safety. This verification helps mitigate risks associated with subpar materials and ensures compliance with international standards.
Step 5: Request Material Samples
Don’t hesitate to request samples of the stainless steel you are considering. This allows you to assess the quality and suitability for your specific applications. Conduct tests on the samples, such as corrosion resistance evaluations, to confirm they meet your requirements before making a bulk purchase.
Step 6: Discuss Coating Options
Inquire about available protective coatings that can enhance corrosion resistance. Some coatings, like those offered by SilcoTek, provide additional barriers against corrosive environments. Understanding the synergy between the stainless steel substrate and its coating can significantly extend the material’s lifespan.
Step 7: Evaluate Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
While initial pricing is important, consider the total cost of ownership over the product’s life cycle. Assess how the corrosion resistance of higher-grade stainless steel like 316 can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs. This long-term perspective is crucial for making a financially sound decision.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing corrosion-resistant stainless steel, ensuring they select the best materials for their needs while optimizing both performance and cost-effectiveness.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for most corrosion resistant stainless steel Sourcing
When sourcing corrosion-resistant stainless steel, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. Here, we break down the key components that contribute to the pricing of stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, which are renowned for their corrosion resistance.
What Are the Key Cost Components in Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel?
-
Material Costs: The primary factor in the cost of stainless steel is the raw materials used. Grades like 304 and 316 differ in composition, with 316 containing molybdenum, which enhances corrosion resistance but also raises costs. The prices of nickel and chromium, which fluctuate based on global market conditions, significantly impact the overall material cost.
-
Labor and Manufacturing Overhead: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region of production. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, these expenses can be substantial. Manufacturing overhead, including energy, equipment maintenance, and facility costs, also contributes to the final price. Efficient production processes can mitigate these costs, making it important to choose suppliers with proven operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling and Quality Control (QC): The initial investment in tooling for stainless steel fabrication can be significant, particularly for customized products. Additionally, rigorous quality control measures are necessary to ensure compliance with industry standards, especially for high-stakes applications in pharmaceuticals or food processing. These QC measures can add to the cost but are essential for maintaining product integrity.
-
Logistics and Distribution: Shipping costs, including freight charges and insurance, can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer. For international shipments, Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a vital role in determining who bears the cost of transportation and risk. Understanding these terms can help buyers negotiate better shipping arrangements.
-
Supplier Margin: Finally, the supplier’s margin is a critical cost component that can vary significantly. Factors like supplier reputation, market demand, and the exclusivity of the product can influence margins. Buyers should evaluate multiple suppliers to understand the market rate and ensure they are getting a fair price.
What Influences Pricing for Corrosion-Resistant Stainless Steel?
Several factors can influence the pricing of stainless steel:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to reduced unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs to negotiate better terms based on volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses during production.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications, such as ISO or ASTM standards, may incur higher costs due to additional processing and documentation.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, lead times, and historical performance can all impact pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can provide leverage for better pricing.
How Can International B2B Buyers Optimize Their Sourcing Costs?
-
Negotiation Strategies: Engage in open negotiations with suppliers. Understanding market prices and being willing to explore multiple suppliers can lead to better deals.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the initial purchase price but also long-term costs associated with maintenance, durability, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality materials may lead to lower TCO.
-
Understanding Pricing Nuances: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional pricing variations due to economic conditions, import tariffs, and logistics. Tailoring sourcing strategies to these nuances can yield significant savings.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Regularly monitor global stainless steel market trends, as fluctuations in raw material prices can affect sourcing decisions. Being proactive can help in locking in prices before increases occur.
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices
Prices for corrosion-resistant stainless steel can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers should conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing most corrosion resistant stainless steel With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Most Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel
In the quest for materials that withstand corrosive environments, businesses often evaluate various options beyond the commonly used corrosion-resistant stainless steels, such as 316L and higher-grade alloys. While these stainless steels are renowned for their durability and performance, alternative solutions may provide additional benefits depending on specific applications, budget constraints, and operational requirements. This analysis compares the most corrosion-resistant stainless steel with other viable solutions, highlighting their respective advantages and limitations.
| Comparison Aspect | Most Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel | Coated Carbon Steel | Titanium Alloy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Excellent corrosion resistance; ideal for harsh environments | Moderate corrosion resistance; performance varies with coating quality | Superior corrosion resistance; lightweight and strong |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; cost-effective over time due to longevity | Lower initial cost; potential higher maintenance costs | High initial cost; longer lifespan can justify investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Readily available; easy to fabricate and install | Requires proper application of coatings; may need specialized installation | More complex fabrication; requires specialized knowledge |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance due to inherent properties | Regular inspections needed to ensure coating integrity | Minimal maintenance; highly durable and resistant to wear |
| Best Use Case | Chemical processing, marine environments, food industry | Construction, automotive components, less corrosive environments | Aerospace, medical implants, high-performance applications |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Coated Carbon Steel?
Coated carbon steel is a cost-effective alternative to stainless steel, particularly in applications where the corrosive environment is moderate. Coatings, such as galvanization or polymer layers, enhance the corrosion resistance of carbon steel, making it suitable for a range of applications. However, the effectiveness of these coatings can vary significantly, and they may require regular maintenance and inspections to ensure their integrity. In extreme environments, the protective layer can deteriorate, exposing the underlying steel to corrosion, which could lead to higher long-term costs.
How Does Titanium Alloy Compare for Corrosion Resistance?
Titanium alloys offer remarkable corrosion resistance and are significantly lighter than stainless steels, making them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and medical devices. Their resistance to a wide range of corrosive environments, including saltwater, is exceptional. However, titanium alloys come with a higher price tag and require specialized fabrication techniques. While the upfront investment is substantial, their longevity and minimal maintenance needs often provide a compelling return on investment, especially in demanding applications.
Conclusion: Which Solution is Right for Your Needs?
When selecting the right material for corrosion resistance, B2B buyers must consider the specific requirements of their applications, including environmental factors, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities. While the most corrosion-resistant stainless steels like 316L offer excellent performance and durability, alternatives like coated carbon steel and titanium alloys may present viable options depending on the context. Evaluating the trade-offs between initial costs and long-term benefits is crucial in making an informed decision that aligns with operational goals and financial considerations. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative, buyers can choose the best solution to meet their unique needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for most corrosion resistant stainless steel
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel?
When selecting corrosion resistant stainless steel for industrial applications, understanding the technical properties is crucial. Here are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade: The most common grades for corrosion resistance are 304 and 316 stainless steel. While 304 contains 18% chromium and 8% nickel, 316 includes 16% chromium, 10% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum. The addition of molybdenum in 316 significantly enhances its resistance to chlorides and acids, making it suitable for harsher environments, such as marine and chemical processing applications.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Corrosion resistance is often quantified by the material’s ability to withstand environmental factors such as humidity, temperature, and exposure to corrosive substances. For instance, 316 stainless steel offers superior performance in chloride-rich environments, which is vital for industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. Buyers should assess the specific corrosive elements present in their operational environments to select the appropriate grade.
-
Tensile Strength: This property measures the maximum amount of tensile (stretching) stress that a material can withstand before failure. High tensile strength is essential for applications where the stainless steel will be subjected to mechanical stress, such as structural components in construction or heavy equipment. Typically, 316 stainless steel has a higher tensile strength than 304, making it a better option for demanding applications.
-
Ductility: Ductility refers to the material’s ability to deform under tensile stress without breaking. This property is crucial for forming and shaping stainless steel into specific designs. A more ductile stainless steel allows for greater flexibility in manufacturing processes, which can lead to cost savings and reduced waste during production.
-
Surface Finish: The surface finish of stainless steel can impact its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Options range from mill finish to polished surfaces. A smoother finish can reduce the likelihood of corrosion by minimizing the spaces where contaminants can accumulate. Buyers should consider the required finish based on the application and environmental exposure.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel?
Understanding industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiations in B2B transactions. Here are several key terms that buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of stainless steel, buyers often collaborate with OEMs for customized solutions tailored to specific operational needs.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is vital for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure that they meet their operational demands without overcommitting financially.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It typically includes detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. This process is essential for comparing pricing and ensuring competitive offers.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers navigate shipping, insurance, and delivery responsibilities, minimizing risks and misunderstandings in global trade.
-
Passivation: This is a chemical treatment process that enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by removing free iron from the surface and forming a protective oxide layer. Buyers in industries with stringent hygiene and corrosion resistance requirements should consider passivation as part of their material specifications.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that optimize their investments in corrosion resistant stainless steel, ensuring longevity and performance in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the most corrosion resistant stainless steel Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Sector?
The global market for corrosion-resistant stainless steel is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing industrial applications and the rising demand for durable materials across various sectors. The oil and gas, chemical processing, and marine industries are particularly influential, as they frequently encounter harsh environmental conditions that necessitate the use of superior corrosion-resistant materials. With an expanding focus on infrastructure development in emerging markets such as Africa and South America, international B2B buyers are increasingly seeking high-performance stainless steel solutions that can withstand extreme conditions.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced surface coatings and alloy formulations, are transforming sourcing strategies. Buyers are now leveraging innovative coatings, like those offered by SilcoTek, which enhance the performance of traditional stainless steel grades such as 304 and 316. These coatings provide a protective barrier, significantly extending the lifespan of the materials, thus reducing maintenance costs over time. Additionally, digital transformation in procurement processes, including the use of AI-driven analytics and e-sourcing platforms, is enabling buyers to optimize their supply chains and make informed decisions based on real-time market data.
How Does Sustainability Impact the Sourcing of Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the sourcing of corrosion-resistant stainless steel. As global awareness of environmental issues rises, B2B buyers are prioritizing suppliers who adopt sustainable practices throughout their supply chains. The production of stainless steel, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, is increasingly scrutinized for its environmental impact, leading to a push for ethical sourcing and green certifications.
Buyers are encouraged to seek out stainless steel products that are made from recycled materials or that come with sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001 or LEED. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to minimizing environmental harm, which is becoming a significant factor in procurement decisions. Furthermore, companies that emphasize ethical sourcing not only reduce their ecological footprint but also enhance their brand reputation, making them more appealing to environmentally conscious customers.
What Is the Historical Context of Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel?
The development of corrosion-resistant stainless steel can be traced back to the early 20th century when the first alloy was created to combat rust in various applications. The introduction of grades like 304 and 316 marked a pivotal moment in material science, offering enhanced resistance to corrosion due to their unique compositions. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing processes have led to the emergence of specialty alloys and coatings that further improve corrosion resistance.
Today, the focus is not only on the inherent properties of the materials but also on how they can be optimized through advanced surface treatments and innovative coatings. This evolution reflects a broader trend in the industry towards creating materials that are not only functional but also sustainable, aligning with the global shift towards greener practices in manufacturing and procurement. As such, B2B buyers must remain informed about the historical developments in this sector to make educated sourcing decisions that align with current market demands and sustainability goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of most corrosion resistant stainless steel
-
How do I select the most corrosion resistant stainless steel for my application?
To select the most corrosion resistant stainless steel, consider the specific environment and conditions the material will face. Grades like 316 stainless steel are ideal for exposure to chlorides and acids due to their molybdenum content, which significantly enhances resistance. Conducting a thorough analysis of the corrosive agents present and matching them with the appropriate grade will ensure optimal performance. Consulting with suppliers who specialize in corrosion resistance can also provide tailored recommendations based on industry-specific needs. -
What is the best stainless steel grade for marine applications?
For marine applications, 316 stainless steel is generally regarded as the best choice due to its excellent resistance to saltwater corrosion. The addition of molybdenum in 316 provides superior protection against chlorides, making it suitable for boats, marine structures, and offshore installations. When sourcing, consider grades that have been treated or coated for additional protection, especially in highly corrosive environments. -
How can I verify the quality of stainless steel before purchasing?
To verify the quality of stainless steel, request certification documents from suppliers, such as ASTM, EN, or ISO certifications, which indicate compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider asking for material test reports (MTRs) that detail the chemical composition and mechanical properties. Engaging in third-party inspections can also be beneficial for large orders, ensuring that the materials meet the specified requirements before shipment. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for stainless steel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for stainless steel can vary widely among suppliers and depend on factors such as the grade, form (sheets, bars, pipes), and processing requirements. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred kilograms to several tons. Discussing your specific needs with suppliers can help negotiate MOQs that align with your project requirements while potentially reducing costs. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing stainless steel internationally?
Payment terms for international stainless steel sourcing can vary, but common options include letters of credit, wire transfers, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to clarify these terms with suppliers before finalizing any agreements. Additionally, consider discussing payment schedules based on milestones, especially for large orders, to facilitate better cash flow management. -
How do I ensure timely logistics and delivery for my stainless steel order?
To ensure timely logistics and delivery, work closely with your supplier to establish clear shipping timelines and methods. Discuss Incoterms to determine responsibilities for shipping and customs clearance. Consider partnering with logistics companies experienced in handling international freight to avoid delays. Regular communication with your supplier and logistics provider can help track the shipment and address any potential issues proactively. -
What customization options are available for stainless steel products?
Many suppliers offer customization options for stainless steel products, including specific dimensions, finishes, and coatings tailored to your application. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to explore available options. Customization can enhance the performance of the material in specific environments, so it’s essential to provide detailed specifications to ensure that the final product meets your needs. -
How do I vet potential suppliers of corrosion resistant stainless steel?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry reputation, years of experience, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients to gauge their reliability and quality of service. Evaluate their certifications and compliance with international standards, as well as their ability to provide technical support and after-sales service. Engaging in direct communication can also help assess their responsiveness and willingness to meet your specific requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Most Corrosion Resistant Stainless Steel Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Dahlstrom Roll Form – Corrosion-Resistant Metals Overview
Domain: blog.dahlstromrollform.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: The text discusses various corrosion-resistant metals and their properties, including:
1. **Carbon Steel**: Least resistant to corrosion; requires protective coating in moist environments.
2. **Galvanized Steel**: Somewhat resistant due to a zinc coating; resistance increases with thicker zinc layers (e.g., G90 is more resistant than G30).
3. **Aluminum**: Mildly resistant; forms a self-passivati…
2. Spyderco – Corrosion Resistance Ranking of Stainless Steels
Domain: forum.spyderco.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Corrosion Resistance Ranking of Stainless Steels: 1. S110V 2. 204P/M390/20CV 3. S90V/20CP 4. S30V/S35VN 5. VG10 (suggested to be above S30V) 6. H1, LC200N (not rusting) 7. S110V (rust spots only under specific conditions) 8. S90V/CTS-20CP, CTS-XHP, CTS-204P/CPM 20CV/M390 9. VG-10, S30V/S35VN, 440C, Elmax, CTS-B70P, GIN-1, 440A, 12C27, 154CM 10. AUS-8, Cruwear, ZDP-189 11. D2, PSF27, Sleipner 12. M…
3. Tough Stainless Steels – Key Types
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Tough stainless steels mentioned include: 1. 3V steel – known for toughness but prone to corrosion. 2. LC200N – offers similar toughness to 3V with excellent corrosion resistance. 3. AEB-L – reportedly tougher and more corrosion resistant than 3V. Knife Steel Nerds is recommended as a resource for learning about different knife steels.
4. Suncor Stainless – Stainless Steel Solutions
Domain: suncorstainless.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Suncor Stainless primarily uses grade 304 and 316 stainless steel from the Austenitic family, which are nonmagnetic and hardenable only by cold working. They also utilize Martensitic grades like grade 440 for applications requiring resistance to oxidation and corrosion, with products such as Quick Attach Wedges featuring plating for added protection. Key elements in stainless steel include Nickel …
5. Britannica – Austenitic Stainless Steels
Domain: britannica.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Austenitic stainless steels usually have the highest corrosion resistance. They contain 16 to 26 percent chromium and up to 35 percent nickel. They are not hardenable by heat treatment and are nonmagnetic. The most common type is the 18/8, or 304, grade, which contains 18 percent chromium and 8 percent nickel.
6. Polycase – 304 Stainless Steel Solutions
Domain: polycase.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: 304 Stainless Steel: Strong resistance to corrosion, high durability and hardness, excellent heat and cold resistance, more weldable and workable than other types of stainless steel, most easily available and least expensive austenitic steel. Melting Point: 1400-1450°C, Tensile Strength: 515-620 MPa, Yield Strength: 205-310 MPa, Max Service Temperature in Air: 870°C (intermittent), 925°C (continuo…
7. Protolabs – Aluminum Solutions
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Aluminum: Strong, lightweight, non-magnetic, electrically conductive. Four grades available: 6061-T651 (general-purpose), 7075-T651 (aerospace), 5052-H32 (superior formability), AlSi10Mg (3D printing). Anodizing available for tougher coating.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for most corrosion resistant stainless steel
As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate the complexities of corrosion resistance, strategic sourcing of stainless steel is pivotal. Understanding the differences between grades, especially 304 and 316 stainless steel, enables businesses to make informed decisions that align with their operational environments. While 304 offers standard corrosion resistance, 316 provides superior protection against harsh chemicals and saline conditions, ensuring longer product lifespans and reduced maintenance costs.
B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing high-quality materials that meet specific environmental challenges. Selecting the appropriate stainless steel not only enhances product durability but also optimizes overall cost efficiency over time. By leveraging advanced coating technologies, such as CVD coatings, businesses can further enhance corrosion resistance, creating a comprehensive solution tailored to their needs.
Looking ahead, the demand for corrosion-resistant materials will only grow. International buyers should seize this opportunity to partner with trusted suppliers who can deliver not only quality products but also valuable insights into the latest advancements in stainless steel technology. By investing in superior materials today, companies can secure a competitive edge for tomorrow.