Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for mold costs
In an increasingly competitive global market, understanding mold costs is a crucial challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The complexities surrounding the pricing of molds—ranging from low-volume 3D printed options to high-end, multi-cavity steel molds—can significantly impact production budgets and timelines. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, meticulously detailing the various types of molds, their applications across different industries, and essential factors affecting costs.
By delving into the intricacies of mold design, tooling costs, and supplier vetting, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. It highlights key strategies to optimize costs, from selecting appropriate materials to understanding the nuances of production volumes. Additionally, it addresses regional considerations, ensuring that buyers from diverse markets, such as Nigeria and Brazil, can navigate their unique challenges effectively.
Ultimately, this guide is designed to equip B2B buyers with actionable insights and a clear understanding of mold costs, enabling them to enhance their procurement processes, maximize ROI, and drive operational efficiency in their manufacturing endeavors.
Understanding mold costs Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D Printed Molds | Cost-effective for low volumes; rapid prototyping capability | Prototyping, low-volume production | Pros: Lower upfront costs; quick turnaround. Cons: Limited lifespan; not suitable for high-volume runs. |
| CNC Machined Molds | High precision; suitable for complex designs | Medium to high-volume production | Pros: High accuracy; versatile material options. Cons: Higher initial costs; longer lead times. |
| EDM Molds | Ideal for intricate designs; high precision | Aerospace, medical devices, automotive parts | Pros: Excellent for complex geometries; minimal post-processing. Cons: Expensive; longer production time. |
| Aluminum Molds | Lightweight; faster production than steel molds | Short to medium production runs | Pros: Lower cost than steel; quicker to manufacture. Cons: Less durable; may not withstand high volumes. |
| Steel Molds | High durability; best for high-volume production | Mass production of consumer goods | Pros: Long lifespan; withstands high production rates. Cons: High initial cost; longer manufacturing time. |
What Are 3D Printed Molds and Their B2B Use Cases?
3D printed molds are an innovative solution primarily used for low-volume production and prototyping. They allow manufacturers to quickly create molds without the lengthy and costly processes associated with traditional methods. This type of mold is particularly suitable for businesses testing new designs or products before committing to large-scale production. However, while they are cost-effective and fast to produce, their lifespan is limited, making them unsuitable for high-volume applications where durability is crucial.
How Do CNC Machined Molds Benefit B2B Manufacturers?
CNC machined molds are known for their high precision and ability to accommodate complex designs. They are ideal for medium to high-volume production and are often used in industries where accuracy is paramount, such as electronics and consumer goods. The versatility of materials used in CNC machining, including aluminum and stainless steel, allows for a wide range of applications. However, the initial costs can be higher, and the lead times may be longer, which is a critical consideration for businesses with tight production schedules.
What Role Do EDM Molds Play in Specialized Manufacturing?
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) molds are essential for creating intricate designs that require high precision. They are commonly employed in specialized industries such as aerospace and medical devices, where the complexity of the part geometry is a significant factor. While EDM molds offer excellent accuracy and require minimal post-processing, they come with a higher price tag and longer production times. B2B buyers should consider these factors when evaluating the feasibility of using EDM molds for their projects.
Why Choose Aluminum Molds for Short Runs?
Aluminum molds provide a lightweight and cost-effective alternative to steel, making them suitable for short to medium production runs. They can be produced more quickly than steel molds, allowing businesses to bring products to market faster. However, while aluminum molds are less expensive and faster to manufacture, they do not have the same durability as steel molds and may not be ideal for high-volume production. B2B buyers should weigh their production needs against the longevity and cost of aluminum molds.
What Advantages Do Steel Molds Offer for Mass Production?
Steel molds are the gold standard for high-volume production due to their durability and long lifespan. They can withstand the rigors of mass production, making them ideal for consumer goods and other applications where consistency and quality are critical. Although the initial investment is higher and the manufacturing process can be longer, the long-term savings from reduced maintenance and replacement costs make steel molds a wise choice for businesses committed to large-scale production. Buyers must assess their production volume and budget to determine if steel molds align with their operational strategy.
Key Industrial Applications of mold costs
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of mold costs | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior and exterior plastic components | High-volume production reduces per-unit costs significantly | Consider local suppliers for reduced shipping times |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing of enclosures and housings | Precision molding ensures product quality and aesthetics | Evaluate material compatibility and design complexity |
| Medical Devices | Creation of specialized components and devices | Compliance with health standards while maintaining cost-efficiency | Ensure suppliers adhere to regulatory certifications |
| Packaging | Custom mold designs for containers and closures | Enhances product shelf life and reduces material waste | Focus on suppliers with sustainable practices and materials |
| Construction | Molds for architectural features and fixtures | Customization leads to unique designs that differentiate products | Assess the supplier’s ability to handle large-scale production |
How Are Mold Costs Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, mold costs are critical for producing various plastic components, including dashboards, panels, and trims. High-volume production significantly reduces the per-unit cost, enabling manufacturers to maintain competitive pricing. International buyers must consider local suppliers to mitigate shipping delays and costs, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics can be challenging.
What Role Do Mold Costs Play in Consumer Electronics Manufacturing?
For consumer electronics, mold costs are essential for creating high-precision enclosures and housings that protect sensitive components. The ability to produce aesthetically pleasing and functional parts at scale is vital for market success. Buyers should evaluate material compatibility and design complexity to ensure that molds meet the technical specifications and performance criteria required in this fast-paced industry.
Why Are Mold Costs Important in Medical Device Production?
In the medical device industry, mold costs are associated with the creation of specialized components that must comply with stringent health regulations. The challenge lies in balancing cost-efficiency with the need for high-quality, precise parts that meet safety standards. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who possess the necessary regulatory certifications, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where compliance is heavily enforced.
How Do Mold Costs Affect Packaging Solutions?
Mold costs in packaging are crucial for developing custom designs for containers and closures that enhance product protection and shelf life. By optimizing the design, businesses can also reduce material waste, contributing to sustainability goals. International buyers should focus on suppliers that utilize sustainable practices and materials, as this is becoming increasingly important in global markets, particularly in environmentally conscious regions.
What Is the Impact of Mold Costs on Construction Projects?
In construction, mold costs are pivotal for creating unique architectural features and fixtures that can differentiate projects. Custom molds allow for innovative designs while maintaining cost-effectiveness. Buyers in this sector should assess suppliers’ capabilities to manage large-scale production runs, ensuring timely delivery to meet project deadlines, especially in developing markets like Nigeria and Brazil, where construction projects are rapidly expanding.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘mold costs’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Understanding the High Initial Investment in Molds
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially those in emerging markets such as Nigeria or Brazil, face significant challenges due to the high initial investment required for injection molds. The upfront costs can range from hundreds to hundreds of thousands of dollars, which poses a financial strain for companies with limited capital or those just entering the manufacturing space. This can lead to hesitation in committing to production, creating a bottleneck in bringing products to market and ultimately affecting competitiveness.
The Solution: To mitigate the financial burden of mold costs, B2B buyers should consider using low-volume production methods such as 3D printed molds for initial runs. This approach allows businesses to validate their designs without incurring the high costs associated with traditional metal molds. By partnering with specialized manufacturers who offer rapid prototyping services, companies can produce small batches of parts at a fraction of the cost. Once the product is market-tested and demand is validated, transitioning to more permanent metal molds can be done strategically. Additionally, leveraging financing options or negotiating flexible payment terms with suppliers can help ease the initial financial impact.
Scenario 2: Navigating Complexity in Mold Design
The Problem: Complex mold designs often lead to increased costs due to higher manufacturing expenses and longer lead times. B2B buyers may find themselves overwhelmed by the intricate requirements of their product specifications, which can result in costly mistakes or delays in production. This is particularly true for industries such as automotive or electronics, where precision and quality are paramount.
The Solution: To address the challenges associated with complex mold designs, buyers should invest time in comprehensive design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis. Collaborating closely with design engineers during the initial stages can help identify potential issues and simplify the mold design. Utilizing software tools that simulate the injection molding process can also provide insights into how design modifications can reduce complexity and costs. Furthermore, buyers should consider working with suppliers that specialize in multi-cavity molds, which allow for simultaneous production of multiple parts, thereby reducing cycle times and per-unit costs. Regular communication and feedback loops with manufacturing partners can ensure alignment on design changes and cost management.
Scenario 3: Managing Fluctuations in Material Costs
The Problem: Fluctuations in the prices of materials used for molds can significantly impact overall project budgets. This is a common pain point for B2B buyers, particularly those in regions where sourcing high-quality raw materials is challenging. The unpredictability of material costs can complicate financial planning and lead to project overruns.
The Solution: To manage material cost fluctuations effectively, B2B buyers should adopt a proactive sourcing strategy that includes negotiating long-term contracts with suppliers. By locking in prices for a set period, companies can protect themselves from sudden price increases. Additionally, diversifying the supply chain by sourcing materials from multiple suppliers can provide more options and leverage in negotiations. Implementing a just-in-time inventory system can also help minimize holding costs and reduce the risk of material price inflation. Finally, buyers should stay informed about market trends and material innovations, which can lead to alternative materials that may offer cost savings without compromising quality.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for mold costs
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Mold Costs?
In the realm of injection molding, material selection is crucial as it directly influences both the cost and performance of the final product. Here, we analyze four common materials used for molds: Aluminum, Steel, P20 Steel, and 3D Printed Plastics. Each material presents unique properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations that international B2B buyers must be aware of.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Mold Applications?
Aluminum is a popular choice for low to medium-volume production due to its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity. It typically has a temperature rating of around 400°F (204°C) and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros: Aluminum molds can be produced quickly, leading to shorter lead times. They are generally less expensive than steel molds and are easier to machine, which reduces manufacturing complexity.
Cons: However, aluminum molds are less durable than steel, making them less suitable for high-volume production runs. They may wear out faster, leading to increased replacement costs over time.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various thermoplastics and is particularly effective for parts that require rapid prototyping or short production runs.
International Considerations: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, as aluminum mold production may not meet certain industrial requirements.
What Are the Advantages of Using Steel for Molds?
Steel, particularly tool steel, is known for its strength and durability, making it ideal for high-volume production. It can withstand temperatures up to 1,200°F (649°C) and has excellent wear resistance.
Pros: Steel molds can produce a high number of parts before any signs of wear, making them cost-effective in large production runs. Their robustness allows for intricate designs and complex geometries.
Cons: The primary drawback is the high initial cost and longer lead times associated with manufacturing steel molds. They are also more challenging to machine, requiring specialized equipment and skilled labor.
Impact on Application: Steel molds are suitable for a wide range of materials, including high-performance thermoplastics and elastomers, ensuring versatility in application.
International Considerations: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is critical for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, where quality assurance is paramount.
Why Choose P20 Steel for Mold Manufacturing?
P20 steel is a specific type of tool steel that combines the benefits of both aluminum and traditional steel. It has a temperature rating similar to that of standard steel and offers good corrosion resistance.
Pros: P20 is easier to machine than other steels, allowing for faster production times. It also has excellent dimensional stability, which is crucial for maintaining part tolerances over time.
Cons: While more affordable than other high-performance steels, P20 still comes with a significant upfront cost. Its performance in extreme temperatures is also limited compared to other steel grades.
Impact on Application: P20 is commonly used for molds that require a balance between cost and performance, making it suitable for medium-volume production.
International Considerations: Buyers should verify that P20 steel meets local and international standards to avoid compliance issues.
How Do 3D Printed Plastics Fit into Mold Cost Strategies?
3D printed plastics are increasingly used for low-volume production and prototyping. They can be produced quickly and are often less expensive than traditional molds.
Pros: The ability to create complex geometries without the need for extensive tooling makes 3D printed molds highly versatile. They are ideal for rapid prototyping and testing.
Cons: However, they are not suitable for high-volume production due to lower durability and heat resistance compared to metal molds.
Impact on Application: 3D printed molds are best for short runs and testing new designs, particularly in industries where speed to market is critical.
International Considerations: Buyers should be aware of the varying quality standards for 3D printed materials across different regions, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Mold Costs
| Material | Typical Use Case for mold costs | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Low to medium-volume production | Quick production and lower cost | Less durable, not suitable for high volumes | Medium |
| Steel | High-volume production | High durability and wear resistance | High initial cost and longer lead times | High |
| P20 Steel | Medium-volume production | Good machinability and stability | Limited performance in extreme temperatures | Medium |
| 3D Printed Plastics | Rapid prototyping and testing | Fast production and design flexibility | Not suitable for high-volume production | Low |
This strategic material selection guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with both budgetary constraints and production requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for mold costs
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Mold Costs?
The manufacturing process for molds is intricate and involves several critical stages that ensure precision and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions regarding their mold procurement.
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used in Mold Manufacturing?
The first step in the mold manufacturing process is material preparation. Commonly used materials include aluminum, stainless steel, and various thermoplastics. Aluminum molds are typically favored for lower volume production due to their cost-effectiveness and shorter lead times, while steel molds are preferred for high-volume production due to their durability and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
In addition to selecting the right material, buyers should also consider the method of sourcing these materials. Reliable suppliers should provide certifications for material quality, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Forming: How Are Molds Shaped and Crafted?
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming, which involves shaping the mold to meet specific design requirements. This is typically accomplished through several key techniques:
-
CNC Machining: This method utilizes computer-controlled tools to achieve high precision in mold creation. CNC machining is particularly effective for complex designs but can be time-consuming and costly for intricate geometries.
-
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): EDM is used for creating highly complex mold designs that require intricate detail. The process involves using electrical discharges to shape the material, making it suitable for molds with fine features.
-
3D Printing: An increasingly popular method, especially for prototyping, 3D printing allows for rapid production of molds with varying geometries. While 3D printed molds may not be suitable for high-volume production, they offer flexibility and quick turnaround times for initial designs.
Assembly: What Is Involved in Mold Assembly?
After the individual components of the mold are formed, they are assembled. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail, as the fit and alignment of parts are crucial for the mold’s performance. Assembly may involve the integration of cooling channels, which help regulate temperature during the injection process, ensuring consistent part quality.
Finishing: How Is the Mold Finished for Optimal Performance?
The final stage in the manufacturing process is finishing, which includes polishing and coating the mold to enhance its surface quality. A well-finished mold not only improves the aesthetic appeal of the final product but also reduces friction and wear during production, leading to longer mold life and consistent part quality.
What Quality Assurance Measures Should B2B Buyers Expect?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the mold manufacturing process, ensuring that the final products meet the required specifications and standards. B2B buyers should be aware of various international and industry-specific quality standards that govern mold production.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Mold Manufacturing?
ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards globally, applicable to all industries, including mold manufacturing. Compliance with ISO 9001 demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and continuous improvement.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industries may have additional certifications. For example, the CE mark is crucial for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Industries such as oil and gas may require compliance with API standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Mold Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial step involves inspecting raw materials and components before they are used in production. Ensuring that materials meet specifications is crucial for the overall quality of the mold.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the process and identify any deviations from the required specifications. This proactive approach helps prevent defects from progressing further down the production line.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the molds are completed, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure they meet all design and quality specifications before shipping. This may include dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and functional testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
Verification of a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing from international suppliers. Here are some methods to ensure compliance:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers allows buyers to assess their quality control processes firsthand. This can be done through on-site visits or third-party audit services.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and documentation from suppliers can provide insight into their QC practices. This may include inspection records, test results, and certifications.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality management system and production capabilities. This is particularly important for buyers in regions where local standards may differ significantly from international norms.
What Are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various challenges when it comes to quality assurance. Different countries may have distinct regulatory requirements and quality standards. For instance, buyers from Africa and South America may encounter different certification processes compared to those in Europe or the Middle East.
Additionally, language barriers and time zone differences can complicate communication with suppliers. Establishing clear expectations and maintaining regular communication can mitigate these challenges, ensuring that quality standards are consistently met.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with mold costs, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality molds that meet their specific needs while also aligning with international standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘mold costs’
To effectively navigate the complexities of mold costs, it is essential for B2B buyers to follow a structured approach. This guide provides a practical checklist to ensure that you make informed decisions when procuring molds, ultimately leading to cost-effective manufacturing solutions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is critical in determining the type of mold you need. This includes the dimensions, material, and production volume of the parts you intend to manufacture. Precise specifications help avoid miscommunication with suppliers and ensure that the mold is designed to meet your quality and performance standards.
Step 2: Assess Production Volume Requirements
Understanding your production volume is key to selecting the right mold type. Molds for high-volume production, such as multi-cavity molds, can be more expensive upfront but reduce the cost per part significantly. Conversely, if your needs are for low-volume production, consider options like 3D printed molds that can be more economical.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing to a supplier, assess their capabilities and expertise in mold manufacturing. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in producing molds similar to your requirements. Request case studies and references to understand their production processes, quality control measures, and lead times.
Step 4: Request Detailed Quotations
Solicit detailed quotations from multiple suppliers to compare costs effectively. Ensure that each quote includes a breakdown of costs, including tooling, materials, and any additional services. This transparency allows for better financial planning and helps identify any hidden costs that may arise during the production process.
Step 5: Consider Material Selection
The choice of material for both the mold and the parts being produced can greatly influence cost and performance. Discuss with your supplier the best materials for your application, considering factors such as durability, ease of molding, and overall cost. Different plastics, for example, have varying costs and properties that can affect your end product.
Step 6: Inquire About Lead Times and Flexibility
Understanding the lead times for mold production is essential for planning your project timeline. Ask suppliers about their production schedules and their ability to accommodate changes in your order volume or specifications. Flexibility in production can be crucial, especially if your project requirements evolve.
Step 7: Verify Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance should be a top priority when selecting a mold supplier. Inquire about their quality control procedures, including testing and inspection methods. A robust QA process ensures that the molds produced will meet your specifications and reduces the risk of defects during production, ultimately saving costs associated with rework and delays.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can streamline their sourcing process for mold costs, ensuring that they make well-informed decisions that align with their production needs and budget constraints.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for mold costs Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Mold Sourcing?
When assessing mold costs, it’s essential to break down the various components that contribute to the overall expense. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts cost. Common options like thermoplastics are generally more affordable, whereas specialized materials may drive costs higher due to their unique properties and processing requirements.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for mold design, production, and quality control. Labor costs can vary by region, with countries in Africa and South America typically having lower labor costs than Europe. However, the availability of skilled workers can influence this.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to machinery, utilities, and maintenance. High-quality injection molding machines can be a significant investment, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are often the most substantial part of the mold cost structure. The complexity of the mold design, whether it is produced via CNC machining, electrical discharge machining (EDM), or 3D printing, will affect the price. More complex molds require more time and resources to produce.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that molds meet specific standards requires thorough quality checks, which can add to costs. Certifications and adherence to industry standards can further inflate expenses.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs can vary widely, especially for international buyers. Understanding Incoterms and shipping options can help mitigate these costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and ensure profitability. The margin can fluctuate based on competition and market demand.
How Do Volume and Specifications Influence Mold Pricing?
Volume and specifications are crucial price influencers in mold sourcing. Generally, higher order volumes lead to lower per-unit costs as the fixed costs of tooling are spread over a larger number of parts. For instance, while a low-volume order might incur higher costs per part, a contract for thousands of pieces can significantly decrease this cost.
Customization also plays a vital role. Unique specifications or complex designs will increase tooling costs and may require specialized materials or processes, raising the overall price. Buyers should strive to balance customization needs with cost efficiency by considering standard designs when possible.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Mold Costs?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can employ several strategies to optimize mold sourcing costs:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Build relationships with suppliers and negotiate terms that benefit both parties. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Consider ongoing costs such as maintenance, logistics, and potential rework. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: Sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. However, ensure they can meet quality and specification requirements.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Understand how currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations can affect pricing when sourcing internationally. It’s crucial to factor these into your overall cost analysis.
Conclusion
Understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influences in mold sourcing is vital for B2B buyers. With various components at play—from materials and labor to tooling and logistics—buyers can make informed decisions that enhance cost efficiency. By leveraging negotiation strategies and focusing on the total cost of ownership, international buyers can navigate the complexities of mold costs effectively.
Disclaimer: The prices discussed are indicative and can vary based on specific project requirements, regional factors, and market conditions. Always consult with suppliers for accurate quotations tailored to your needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing mold costs With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Mold Costs
In the realm of manufacturing, particularly for plastic components, understanding the financial implications of mold costs is crucial. However, companies must also consider alternative solutions that can offer comparable benefits at different price points or with varying operational flexibility. This section evaluates mold costs against other viable manufacturing methods, allowing B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their unique production needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Mold Costs | 3D Printing | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for mass production; ideal for large volumes | Good for prototypes and low-volume runs; varying precision based on technology | High precision; suitable for both low and high volumes |
| Cost | $100 to $100,000+ (high initial investment, lower per-part cost at scale) | Variable; typically lower for small runs but higher for large quantities | Moderate; cost-effective for medium volumes but higher than molds for mass production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and time for tooling design | User-friendly; designs can be modified easily | Requires technical expertise and setup time |
| Maintenance | High maintenance for molds, especially for complex designs | Minimal maintenance; dependent on printer type | Regular maintenance required for machinery |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production of consistent parts | Rapid prototyping and custom parts | Complex geometries or materials that require high precision |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
3D Printing
3D printing has emerged as a robust alternative for manufacturing, particularly suited for prototyping and low-volume production. It allows for rapid iteration and the ability to produce highly customized parts without the upfront costs associated with molds. However, while initial costs may be lower, the per-unit price can become less economical at larger scales due to longer production times and material costs. Additionally, the range of materials available can limit performance compared to traditional injection molding.
CNC Machining
CNC machining offers a high degree of precision and flexibility in producing parts with complex geometries. This method is effective for both low and high volumes, making it a versatile solution for various manufacturing needs. The costs can be moderate, especially when considering setup times and material waste. However, CNC machining can be less cost-effective than injection molding for mass production due to the inability to achieve the same economies of scale. Maintenance of CNC machines also requires skilled labor, which can add to overall operational costs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Manufacturing Solution
When selecting between mold costs and alternative manufacturing methods, B2B buyers should consider factors such as production volume, required precision, and material types. For high-volume production with consistent quality, traditional molds are often the most cost-effective solution. In contrast, for projects requiring rapid prototyping or customization, 3D printing may offer greater flexibility at a lower initial cost. CNC machining serves as a middle ground, providing precision and versatility for various production scales. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on your specific operational goals, budget constraints, and the nature of your product requirements.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for mold costs
What Are the Key Technical Properties Impacting Mold Costs?
Understanding the technical properties that influence mold costs is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when sourcing molds for injection molding. Here are several key specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of the mold is a primary determinant of both cost and durability. Common materials include aluminum, which is cost-effective for low-volume production, and steel, which is preferred for high-volume runs due to its superior strength and longevity. Choosing the right material impacts not only the initial cost but also the mold’s lifespan and maintenance needs, making it essential for cost-efficient production.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the mold design. Tight tolerances ensure that parts fit together correctly, reducing the need for post-processing and minimizing waste. In industries such as automotive and aerospace, where precision is critical, investing in molds with strict tolerances can significantly enhance product quality and reduce long-term costs associated with defects.
3. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the duration it takes to complete one injection molding cycle, including injection, cooling, and ejection phases. Shorter cycle times lead to higher production rates, which can lower the per-unit cost as fixed costs are distributed over more parts. For businesses looking to scale production efficiently, understanding cycle times is essential for optimizing operational costs.
4. Surface Finish
The surface finish of a mold affects the aesthetic and functional quality of the final product. A smoother finish may reduce friction and improve part ejection, but it can also increase mold manufacturing costs. For B2B buyers, balancing the desired surface quality with budget constraints is vital, especially when targeting markets with specific aesthetic or performance requirements.
5. Mold Complexity
The complexity of the mold design, including features such as undercuts or multi-cavity configurations, can significantly influence costs. More complex molds require advanced manufacturing techniques and longer production times, leading to higher upfront costs. Simplifying mold designs where possible can help reduce costs while maintaining functionality.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Mold Sourcing?
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and negotiation processes for B2B buyers. Here are several important terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking to source high-quality components that meet specific industry standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is important for B2B buyers to understand as it affects budgeting and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps in negotiating better terms and assessing the feasibility of production runs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is essential for comparing costs and ensuring that suppliers meet the buyer’s specifications, thus facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms can help buyers clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, which is particularly important when sourcing molds from overseas suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. For mold production, lead times can vary significantly based on complexity and supplier capabilities. B2B buyers should consider lead times when planning production schedules to avoid delays in their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding mold costs, ultimately leading to more efficient production and better alignment with market demands.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the mold costs Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Influencing Mold Costs?
The global mold costs sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer demands, and economic fluctuations. The rapid adoption of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies is reshaping manufacturing processes, allowing for greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
One prominent trend is the increasing use of additive manufacturing, particularly 3D printing for prototyping and low-volume production. This method not only reduces the initial investment for mold creation but also allows for faster iterations and modifications, aligning with the agile manufacturing models many companies are adopting. Moreover, as global supply chains evolve, buyers are increasingly looking for local sourcing options to mitigate risks associated with lengthy shipping times and tariffs, especially post-pandemic.
Additionally, the demand for customized and complex mold designs is on the rise, driven by the need for unique product offerings in competitive markets. B2B buyers should also be aware of fluctuating raw material costs, which can significantly impact overall mold expenses. The market is characterized by a growing emphasis on collaboration between manufacturers and suppliers to optimize production processes and reduce costs through shared knowledge and resources.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Mold Costs?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming increasingly important in the mold costs sector. As environmental concerns rise globally, B2B buyers are urged to consider the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. The injection molding process, while efficient, can contribute to significant waste and pollution if not managed responsibly. This reality pushes manufacturers to adopt greener practices, which can ultimately influence mold costs.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials or implementing energy-efficient production methods. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of bio-based plastics are becoming critical criteria for selecting suppliers. These certifications not only enhance brand reputation but can also lead to cost savings in the long term through reduced energy consumption and waste management expenses.
Investing in sustainable materials and processes may require higher upfront costs; however, these investments can lead to lower operational costs and compliance with increasingly stringent regulations. For international buyers, especially those in emerging markets, understanding the balance between cost and sustainability can provide a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
What Is the Historical Context of Mold Costs?
The evolution of mold costs is closely tied to advancements in manufacturing technologies. Initially, mold-making was a labor-intensive process requiring skilled artisans to shape and create molds from metal. Over the decades, the introduction of CNC machining and electrical discharge machining (EDM) revolutionized the industry, allowing for greater precision and efficiency in mold production.
As demand for plastic components surged in the latter half of the 20th century, the injection molding process gained prominence due to its ability to produce large quantities of parts quickly and at lower costs. The advent of 3D printing in the 21st century further transformed the landscape, enabling rapid prototyping and customization at a fraction of traditional costs. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers to appreciate the continuous innovation in the mold costs sector and to leverage these advancements for strategic sourcing decisions.
In summary, staying informed about market dynamics, embracing sustainability, and understanding the historical evolution of mold costs can significantly enhance the decision-making process for international B2B buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of mold costs
1. How do I determine the cost of custom molds for my production needs?
To determine the cost of custom molds, you need to consider several key factors: the complexity of the part design, the volume of parts you plan to produce, and the materials used for the mold. Generally, more complex designs with intricate features will incur higher tooling costs. Additionally, higher production volumes can reduce the cost per unit, as the initial investment in the mold is spread over a larger number of parts. Requesting quotes from multiple suppliers can also provide insights into competitive pricing.
2. What are the typical lead times for mold production?
Lead times for mold production can vary significantly based on the complexity of the mold and the manufacturer’s capabilities. Typically, simple molds may take anywhere from a few weeks to a month to produce, while more complex molds can take several months. It’s essential to communicate your timelines with potential suppliers and inquire about their production schedules. Building in buffer time for unexpected delays can also help ensure that your project stays on track.
3. How can I ensure quality control in my mold production?
To ensure quality control in mold production, establish clear specifications and standards with your supplier upfront. Request samples and prototypes before full-scale production to evaluate the quality and fit of the molds. Additionally, consider implementing periodic quality audits and using third-party quality assurance services to monitor the production process. Maintaining open communication with your supplier throughout the process is crucial for addressing any quality issues that may arise.
4. What factors should I consider when selecting a mold supplier?
When selecting a mold supplier, consider their experience in your specific industry, their production capabilities, and their track record for quality and reliability. Evaluate their certifications and adherence to international standards, especially if you are sourcing from different regions. Additionally, assess their customer service and responsiveness, as effective communication is vital for a successful partnership. Finally, request references from other clients to gauge their satisfaction with the supplier’s services.
5. What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mold production?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for mold production can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the mold. Some suppliers may accept orders as low as 25 pieces for certain products, while others may require higher MOQs, especially for more complex molds. Discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to find one that can accommodate your production volume while ensuring cost-effectiveness.
6. How do payment terms typically work for international mold suppliers?
Payment terms for international mold suppliers often vary by supplier and region. Common practices include partial upfront payments (30-50%) with the balance due upon completion or shipment. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as letters of credit or escrow services, especially for large transactions.
7. What are the logistics considerations for importing molds from abroad?
When importing molds from abroad, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and import regulations specific to your country. It’s essential to work with a logistics provider experienced in international shipping to navigate these complexities. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin, to facilitate a smooth customs clearance process. Planning for potential delays in transit is also advisable.
8. How can I customize molds for unique product requirements?
Customizing molds for unique product requirements involves collaboration with your supplier during the design phase. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, materials, and any special features needed. Utilizing advanced technologies such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design) can help visualize the mold design and ensure it meets your requirements. It’s also beneficial to conduct iterative testing and prototyping to refine the mold design before full production to avoid costly adjustments later.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Mold Costs Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Reddit – Smart Glasses Development
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
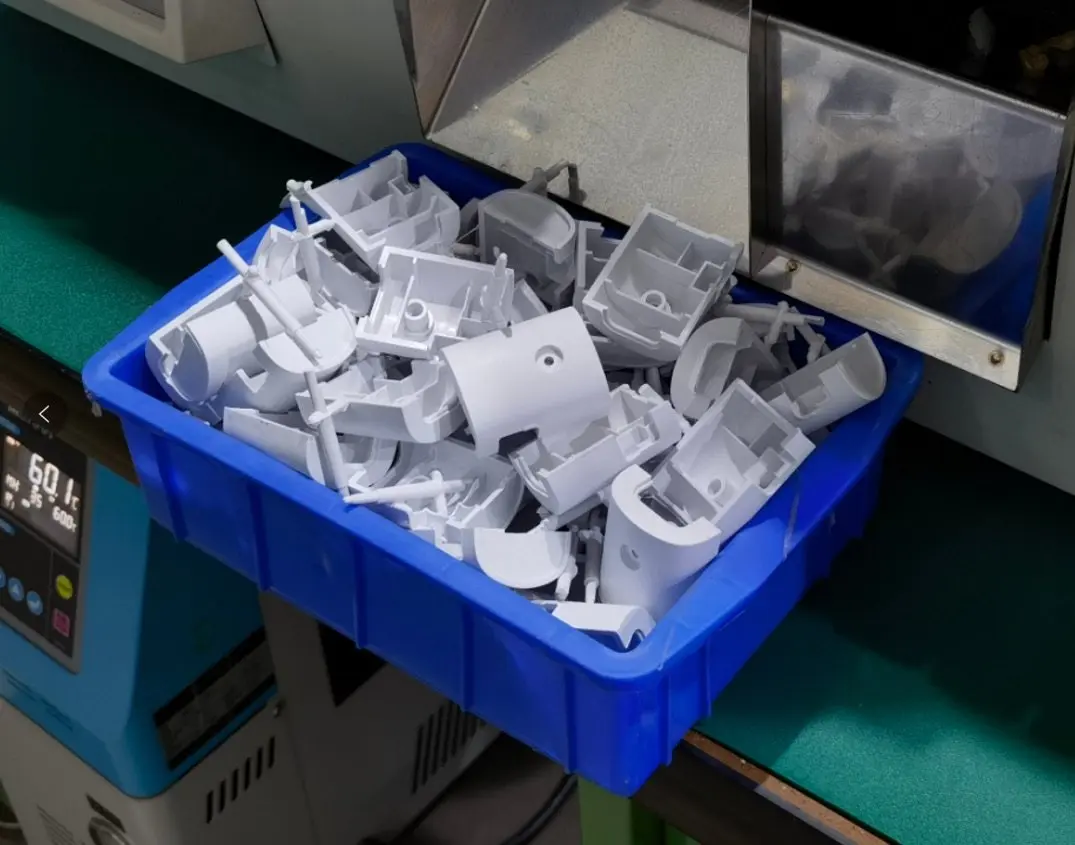
Introduction: Developing a pair of smart glasses with frames made using either injection molding or 3D printing. There will be 6 different pieces with a maximum size of 4mm x 160mm x 40mm, most well under this size. Tooling is noted as the most expensive part of injection molding. Consideration for using one mold for all parts, similar to plastic model kits. Discussion on costs includes prototype molds of Chine…
2. HouseLogic – Mold Remediation Costs
Domain: houselogic.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Mold remediation costs average $2,361, ranging from $373 to $7,000. Costs per square foot range from $2.50 to $25. Factors influencing costs include labor time, number and types of samples, amount of debris, access granted, visible mold amount, cross-contamination, regional variations, and required methods. Mold infestation levels range from limited contamination (Level 1) to HVAC system contamina…
3. Protolabs – Injection Molding Services
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Protolabs offers injection molding services for plastic parts, with the capability to produce up to 25,000 parts or more from a single mold. They provide cost-effective molds for production quantities as low as 25 pieces, often within a few days. Injection molding is a scalable solution for mass production, with costs determined by factors such as tooling complexity and material choice. Key design…
4. First Mold – Injection Mold Cost Breakdown
Domain: firstmold.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Injection Mold Cost: The cost is divided into explicit and implicit parts. Explicit costs include material costs (15% to 30%), processing fees (20% to 30%), design fees (10% to 15%), testing fees (3% for large/medium molds, <5% for small precision molds), packaging and transportation costs (3%), taxes (15%), and profit (5% to 15%). Implicit costs relate to indirect expenses incurred during mass pr…
5. Crescent Ind – Injection Molding Tooling Costs
Domain: crescentind.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Injection molding tooling costs can range from $15K for simple parts using a MUD Frame to over $500K for large tonnage and complex geometries. Key factors impacting costs include: 1. Manufacturing Location: USA vs Offshore, with USA typically offering higher quality but at a higher price (20%-40% more). 2. Mold Classifications: Different SPI classes (101-105) determine tool construction and life e…
6. Mold Cost Comparison – Rubber vs. Plastic
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: The discussion revolves around the cost comparison of molds for rubber parts versus plastic parts. Key points include: 1. Mold costs for rubber parts are generally similar to those for plastic parts, but the molding equipment differs. 2. Rubber requires less tonnage and typically involves simpler parts, often not needing lifters or slides. 3. Rubber molds are often made from mild steel and do not …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for mold costs
In the dynamic landscape of mold manufacturing, strategic sourcing remains a crucial element for B2B buyers aiming to optimize costs while ensuring quality. Key takeaways highlight that mold costs are largely influenced by complexity, volume, and material selection. By understanding these factors, businesses can effectively reduce per-unit costs through higher production quantities and thoughtful design choices, such as minimizing undercuts and unnecessary features.
Moreover, leveraging advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing and CNC machining can provide flexibility and cost savings in mold creation. For international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, establishing strong relationships with reliable suppliers can unlock further efficiencies and innovations.
As the global market continues to evolve, it is imperative for businesses to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies in mold manufacturing. Embrace strategic sourcing as a pathway to enhance your competitive edge and drive sustainable growth. Now is the time to assess your sourcing strategies and explore how optimized mold costs can benefit your production processes. Engage with experts and partners who can guide you in making informed decisions that align with your business goals.