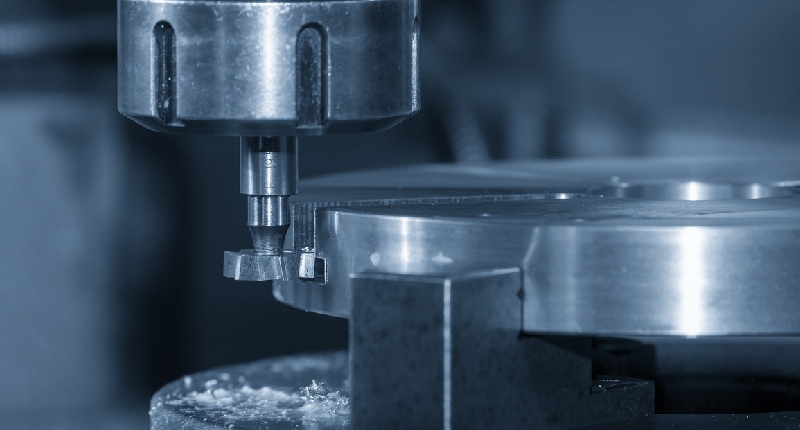
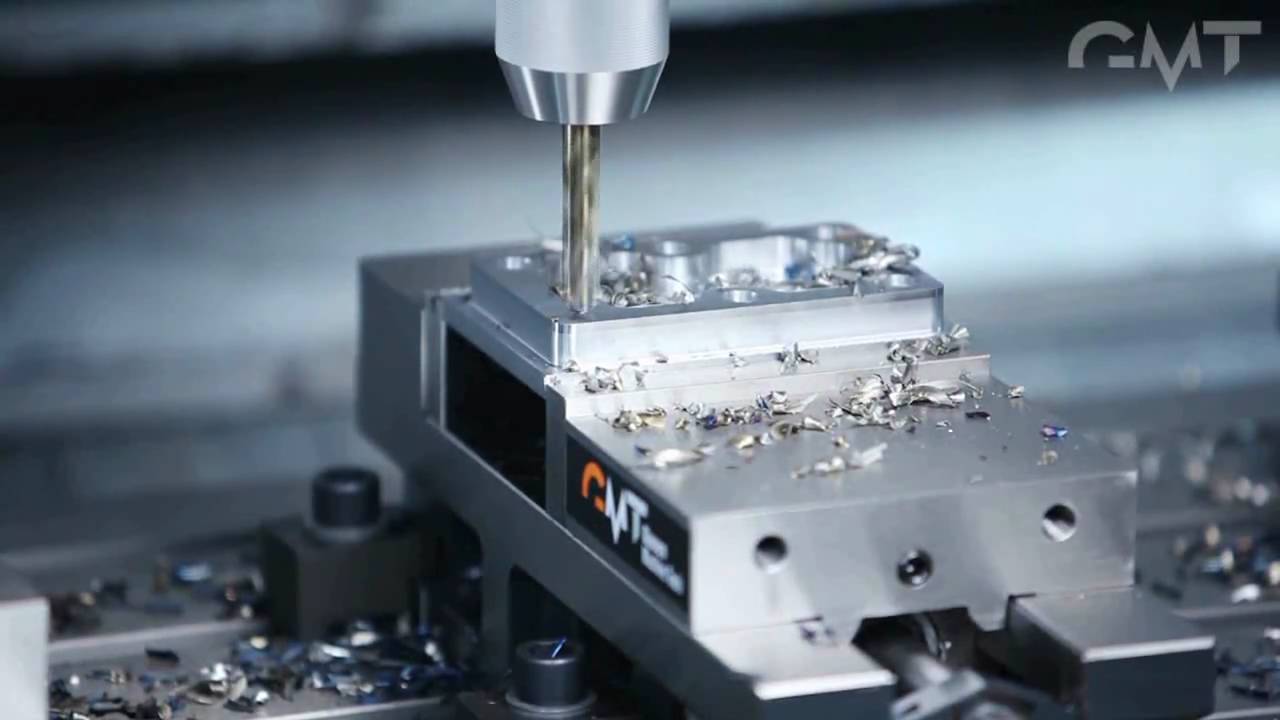
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for milling machine operation
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, the challenge of sourcing efficient milling machine operations can significantly impact production quality and operational costs. As businesses from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their manufacturing capabilities, understanding the intricacies of milling operations becomes paramount. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of various milling processes, including face milling, end milling, and CNC milling, along with their applications across different industries.
Buyers will gain insights into the nuances of each milling type, enabling them to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs. The guide also covers critical factors such as supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and best practices for integrating milling operations into existing workflows. By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable knowledge, this resource empowers them to optimize their sourcing strategies and enhance their operational efficiency. Whether you’re in the automotive sector in Nigeria or the aerospace industry in Vietnam, understanding milling machine operations is essential for driving innovation and maintaining a competitive edge in today’s global market.
Understanding milling machine operation Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Face Milling | Uses a flat cutting tool to create smooth surfaces. | Aerospace, automotive, and general machining | Pros: High surface finish, versatile; Cons: Slower for deep cuts. |
| End Milling | Can cut on both ends and sides; versatile in shape creation. | Custom part manufacturing, molds, and dies | Pros: Highly adaptable; Cons: Requires precise setup for optimal results. |
| Thread Milling | Specialized for creating threads on fasteners. | Manufacturing of screws, bolts, and fittings | Pros: High accuracy and durability; Cons: Limited to thread profiles. |
| Profile Milling | Capable of producing complex shapes and contours. | Molds, dies, and intricate components | Pros: Exceptional detail; Cons: Often requires CNC for best results. |
| Slot Milling | Creates slots or grooves using a slot cutter. | Keyways, channels, and mechanical assemblies | Pros: Efficient for making narrow cuts; Cons: Limited to specific shapes. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Face Milling?
Face milling is characterized by its use of a flat cutting tool that removes material from the surface of a workpiece, resulting in a smooth finish. This method is particularly suitable for applications in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision and surface quality are critical. B2B buyers should consider the material and thickness of the workpiece, as face milling is most effective for larger, flat surfaces and may require slower feed rates for deeper cuts.
How Does End Milling Stand Out in Versatility?
End milling is distinguished by its ability to cut on both the end and sides of the tool, making it highly versatile for creating various shapes, pockets, and contours. This operation is essential for custom part manufacturing and mold-making, where intricate designs are necessary. When purchasing end milling tools, buyers should evaluate the desired part complexity, material compatibility, and the required precision, as these factors will influence tool selection and overall machining efficiency.
Why Choose Thread Milling for Precision Fasteners?
Thread milling is a specialized operation designed to create threads on fasteners such as screws and bolts. Its key feature is the cutting tool’s multiple edges, which enable it to produce threads with high accuracy and durability. This method is ideal for manufacturers focusing on fastener production, as it allows for a variety of thread sizes and profiles. B2B buyers should assess their threading requirements, including material types and thread specifications, to ensure they select the right milling tools for their production needs.
What Advantages Does Profile Milling Offer for Complex Components?
Profile milling excels in producing complex shapes and contours, making it a preferred choice for applications requiring intricate designs, such as molds and dies. This operation often utilizes CNC technology to achieve high precision, which is crucial for industries such as automotive and aerospace. Buyers should consider the complexity of the designs they intend to produce, as well as the capabilities of their milling machines, to ensure they can effectively implement profile milling in their manufacturing processes.
How Efficient is Slot Milling for Creating Narrow Cuts?
Slot milling is specifically designed to create narrow cuts, such as grooves or keyways, using a slot cutter. This method is particularly efficient for applications in mechanical assemblies where precise channels are required. B2B buyers should focus on the dimensions of the slots needed and the material type, as these factors will determine the choice of cutter and milling machine setup. While slot milling is efficient, it may be limited to specific shapes, so understanding the application requirements is essential.
Key Industrial Applications of milling machine operation
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of milling machine operation | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of complex engine components | High precision and lightweight parts enhance fuel efficiency | Certification of materials and compliance with aerospace standards |
| Automotive | Production of gears and transmission parts | Enhanced performance and reliability of vehicles | Supplier reliability and capacity for large-scale production |
| Medical Devices | Creation of surgical instruments and implants | High precision and biocompatibility ensure patient safety | Quality assurance and regulatory compliance in manufacturing |
| Construction Equipment | Fabrication of heavy machinery components | Durability and performance in harsh environments | Material selection and cost-effectiveness in sourcing |
| Electronics | Production of intricate circuit boards | Improved functionality and miniaturization of devices | Expertise in handling diverse materials and rapid prototyping capabilities |
How is Milling Machine Operation Applied in the Aerospace Industry?
In the aerospace sector, milling machines are crucial for producing complex engine components, such as turbine blades and casings. These parts require high precision and lightweight materials to enhance fuel efficiency and performance. B2B buyers in this industry must consider the certification of materials and compliance with strict aerospace standards to ensure safety and reliability. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers with proven capabilities in advanced machining techniques is essential to meet the demanding specifications of aerospace applications.
What Role Does Milling Machine Operation Play in Automotive Manufacturing?
Milling operations are integral to the automotive industry, particularly in the production of gears and transmission parts. These components must exhibit high durability and precision to ensure the performance and reliability of vehicles. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from suppliers who can deliver large-scale production while maintaining quality is critical. Buyers should also evaluate the technological capabilities of their suppliers to ensure they can produce complex geometries necessary for modern automotive designs.
How is Milling Machine Operation Utilized in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical device sector, milling machines are employed to create surgical instruments and implants that require exceptional precision and biocompatibility. The ability to produce complex shapes and fine details is vital for ensuring that these devices function correctly and safely. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adhere to stringent quality assurance processes and regulatory compliance, as these factors are critical for maintaining patient safety. Additionally, understanding the sourcing of biocompatible materials is essential for successful procurement in this field.
In What Ways Does Milling Machine Operation Benefit Construction Equipment Fabrication?
Milling operations are fundamental in fabricating components for heavy machinery used in the construction industry. These components need to withstand harsh environments while maintaining high performance and durability. For buyers in Africa and the Middle East, sourcing materials that meet these durability requirements is crucial. Furthermore, cost-effectiveness in sourcing and the ability to provide timely delivery are important considerations, as construction projects often operate under tight deadlines.
How is Milling Machine Operation Essential in Electronics Manufacturing?
Milling machines are vital in the electronics industry for producing intricate circuit boards and components. The demand for miniaturization and improved functionality drives the need for precise milling operations that can handle diverse materials. International B2B buyers should seek suppliers with expertise in rapid prototyping and advanced machining capabilities to meet the fast-paced demands of the electronics market. Additionally, evaluating the supplier’s ability to manage material sourcing effectively can lead to significant cost savings and efficiency improvements in production.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘milling machine operation’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Precision in Complex Designs
The Problem: B2B buyers, especially those in industries like aerospace and automotive, often struggle to achieve the required precision for complex components using traditional milling methods. This challenge can lead to significant delays in production schedules and increased costs due to material waste and rework. Buyers may find that their current milling machines lack the capability to handle intricate designs, resulting in parts that do not meet stringent specifications.
The Solution: To overcome this issue, buyers should consider investing in advanced CNC milling machines equipped with multi-axis capabilities. These machines allow for more intricate movements and can produce complex geometries with high precision. When sourcing machinery, buyers should prioritize vendors that offer customizable CNC solutions tailored to their specific requirements. Additionally, working closely with skilled programmers who can translate complex designs into G-code will enhance the machining process. Providing comprehensive training for operators on the latest CNC technologies can further ensure that the machines are utilized to their fullest potential, reducing the likelihood of costly errors and improving overall productivity.
Scenario 2: Frequent Machine Downtime and Maintenance Issues
The Problem: Many manufacturers face unexpected machine downtime due to inadequate maintenance protocols or the use of outdated machinery. This not only disrupts production but can also lead to missed delivery deadlines, damaging relationships with clients. For B2B buyers, the financial implications of downtime can be severe, affecting both operational efficiency and profitability.
The Solution: Implementing a proactive maintenance strategy is essential for minimizing machine downtime. Buyers should work with suppliers who provide comprehensive maintenance packages, including regular inspections and timely replacement of worn components. Additionally, investing in predictive maintenance technologies that utilize IoT sensors can help monitor machine health in real time, allowing for timely interventions before issues escalate. Establishing a strong partnership with a reputable service provider for ongoing support will also ensure that any technical problems are addressed swiftly, keeping operations running smoothly and efficiently.
Scenario 3: Inconsistent Material Quality and Tool Wear
The Problem: Inconsistent material quality and premature tool wear are common pain points for B2B buyers in the milling machine operation. These issues can lead to variations in product quality, which can compromise the integrity of finished parts. Buyers often find themselves caught between the need for high-quality materials and the rising costs associated with frequent tool replacements, ultimately impacting their bottom line.
The Solution: To address these challenges, buyers should implement a rigorous material selection process that includes sourcing from reputable suppliers known for their consistency and quality. Conducting thorough testing on incoming materials can help ensure that only the best quality is used in production. Additionally, investing in high-performance cutting tools designed for specific materials can significantly reduce wear and extend tool life. Buyers should also establish a routine for monitoring tool performance, utilizing metrics such as tool wear rates and surface finish quality to inform when to replace or recondition tools. By optimizing the entire milling process—from material selection to tooling—buyers can enhance product quality while controlling costs effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for milling machine operation
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Milling Machine Operations?
When selecting materials for milling machine operations, it’s essential to consider their key properties, which directly influence the performance of the final product. Here, we analyze four common materials: aluminum, stainless steel, brass, and plastic composites.
Aluminum: A Lightweight and Versatile Option
Aluminum is widely used in milling operations due to its lightweight nature and excellent machinability. It has a low density, making it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor. Key properties include good corrosion resistance and a melting point of around 660°C, which allows for effective machining at high speeds.
Pros: Aluminum is cost-effective, easy to machine, and can be anodized for enhanced surface protection. It also has a good strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for aerospace and automotive applications.
Cons: While durable, aluminum can be less resistant to wear compared to harder materials. Additionally, it may require specific tooling to prevent deformation during machining.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, making it suitable for both structural and aesthetic applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards like ASTM B211 for aluminum alloys. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable suppliers who adhere to these standards is crucial.
Stainless Steel: Strength and Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel is known for its exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for applications in harsh environments. Key properties include high tensile strength and a melting point of approximately 1400-1450°C, allowing for machining under high temperatures.
Pros: Its durability and resistance to oxidation make stainless steel suitable for food processing, medical devices, and marine applications.
Cons: The material can be more challenging to machine compared to aluminum, often resulting in higher tooling costs. It also tends to be heavier, which may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with various chemicals and environments makes it ideal for applications requiring hygiene and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 is essential. Buyers from regions like the Middle East should also consider local corrosion factors when selecting grades of stainless steel.
Brass: A Traditional Choice for Precision Parts
Brass, an alloy of copper and zinc, is frequently used in milling operations for precision components such as fittings and valves. Its key properties include good machinability and excellent corrosion resistance, especially in marine environments.
Pros: Brass is easy to machine, offers a pleasing aesthetic finish, and has good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for electrical applications.
Cons: It is generally more expensive than aluminum and can be less durable than stainless steel under heavy loads.
Impact on Application: Brass is particularly compatible with low-pressure applications and is often used in plumbing and electrical components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ASTM B16 for brass fittings. In Europe, adherence to EN standards may also be necessary.
Plastic Composites: Lightweight and Cost-Effective
Plastic composites, including materials like polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly popular in milling operations due to their lightweight and cost-effective nature. Key properties include good impact resistance and a lower melting point compared to metals, typically around 250-300°C.
Pros: They are easy to machine and can be produced in various colors and finishes, making them ideal for consumer products.
Cons: Plastic composites may not be suitable for high-temperature applications and can be less durable than metals in demanding environments.
Impact on Application: These materials are often used in consumer goods, automotive parts, and electronic housings where weight and cost are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for plastic materials is important. Buyers should also consider the availability of specific grades in their region, particularly in emerging markets.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Milling Operations
| Material | Typical Use Case for milling machine operation | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less wear-resistant than harder metals | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, food processing equipment | High strength and corrosion resistance | Higher tooling costs | High |
| Brass | Plumbing fittings, electrical components | Excellent machinability | More expensive than aluminum | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Consumer goods, automotive parts | Lightweight and cost-effective | Not suitable for high-temperature use | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for milling machine operations, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for milling machine operation
What Are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process for Milling Machine Operation?
Milling machine operation is a critical component in various manufacturing sectors, involving multiple stages that ensure the production of high-quality parts. The primary stages in the manufacturing process are material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Does Material Preparation Impact Milling Efficiency?
Material preparation is crucial for optimizing milling operations. The process begins with selecting appropriate raw materials, often metals or plastics, that meet the specifications required for the final product. This stage involves cutting the raw material to size and ensuring that it is clean and free from impurities. For instance, using high-quality aluminum or steel can enhance the durability and performance of the finished product.
Additionally, suppliers often conduct initial inspections to verify the quality of the raw materials against industry standards, which is a vital step for ensuring that the subsequent milling operations yield precise and accurate components.
What Techniques Are Commonly Used in the Forming Stage?
The forming stage involves the actual milling process, where various techniques can be employed depending on the desired outcome. Common milling operations include face milling, end milling, and slot milling, each serving distinct purposes.
-
Face Milling: This technique is used to create flat surfaces and is particularly effective for large components. The cutting tools have teeth on their face and shave off material horizontally.
-
End Milling: This versatile method can create pockets, slots, and contours. The end mill cuts both vertically and horizontally, making it suitable for complex designs.
-
Slot Milling: Used to create grooves and keyways, slot milling utilizes a slot cutter that operates similarly to a circular saw blade.
The choice of milling technique should align with the material properties and the specifications of the final product. Furthermore, modern CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines enhance the precision and efficiency of these operations, allowing for intricate designs that would be challenging to achieve manually.
What Are the Key Aspects of the Assembly Stage in Milling Operations?
Once the components are formed, the assembly stage focuses on integrating these parts into a complete product. This process may include welding, fastening, or adhesive bonding, depending on the product’s requirements.
Quality assurance during assembly is essential to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. This may involve the use of jigs and fixtures to maintain accuracy during the assembly process. B2B buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques used by suppliers to ensure compatibility with their operational standards.
How Is Finishing Achieved in Milling Operations?
The finishing stage is critical for enhancing the aesthetic and functional properties of the machined parts. Common finishing techniques include grinding, polishing, and coating.
-
Grinding: This process removes small amounts of material to achieve a precise dimension and smooth surface finish.
-
Polishing: Often used for aesthetic purposes, polishing enhances the appearance of parts, making them visually appealing.
-
Coating: Applying protective coatings can improve corrosion resistance and wear properties, extending the lifespan of the components.
Investing in finishing processes can significantly enhance the product’s marketability, particularly in industries where aesthetics and durability are paramount.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Milling Machine Operations?
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to milling machine operations, ensuring that the final products meet the required standards and specifications. Implementing robust QA measures helps mitigate risks and enhances customer satisfaction.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Consider?
International standards, such as ISO 9001, serve as a benchmark for quality management systems across various industries. Adhering to these standards ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications, like CE marking for European markets or API standards for the oil and gas sector, are crucial for compliance and market access.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate adherence to these international standards, as this reflects their commitment to quality and reliability.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are essential for maintaining product quality throughout the manufacturing process. Common QC checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, ongoing inspections help identify any deviations from quality standards, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, a final inspection verifies that the finished products meet all specifications and quality requirements.
These checkpoints ensure that any potential quality issues are addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of defective products reaching the market.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports that outline inspection results, corrective actions taken, and overall quality performance.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing third-party inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes and product compliance.
These measures not only enhance buyer confidence but also foster stronger partnerships between manufacturers and suppliers.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is essential. Differences in regulations, standards, and practices across regions can impact the quality assurance processes.
-
Cultural Considerations: Buyers should be aware of cultural differences that may affect communication and quality expectations.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulations regarding product safety and quality. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with local laws to avoid legal complications.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing transparency in the supply chain can help buyers track product quality from the source to the final destination, reducing the risk of non-compliance.
By understanding these nuances, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and ensure that they partner with suppliers who prioritize quality in their milling machine operations.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in milling machine operations is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can enhance their procurement strategies and ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘milling machine operation’
Introduction
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure milling machine operation services. Whether you’re in the manufacturing sector or a related industry, understanding the milling process and how to effectively source these operations is crucial for ensuring quality and efficiency in your production line.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, clearly outline the technical specifications required for your milling operations. This includes dimensions, tolerances, materials, and desired finishes. Having a detailed specification helps suppliers understand your needs and enables them to provide accurate quotes and timelines.
- Consider Material Types: Identify the materials you need to mill (e.g., metals, plastics) and their properties, as different materials may require specific milling techniques.
- Detail Complexity: Specify the complexity of the parts you require, as intricate designs may demand advanced machinery and skilled operators.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in milling machine operations. Utilize online directories, industry forums, and trade shows to gather a list of candidates.
- Check Industry Experience: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry, as they will better understand your unique requirements.
- Evaluate Capabilities: Ensure the suppliers have the necessary machinery and technology to handle your specified milling operations.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before moving forward, verify the certifications and quality standards of your potential suppliers. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate that a supplier adheres to international quality management principles.
- Request Documentation: Ask for copies of certifications and quality assurance processes to ensure they maintain high standards in their operations.
- Understand Compliance: Ensure that the suppliers comply with local and international regulations relevant to your industry.
Step 4: Request and Compare Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request detailed quotes that include pricing, lead times, and terms of service. Comparing these quotes will help you assess the best value for your investment.
- Analyze Cost Breakdown: Look for a detailed breakdown of costs, including material, labor, and any additional fees, to understand where your money is going.
- Consider Lead Times: Ensure that the lead times align with your production schedule to avoid delays in your operations.
Step 5: Conduct Site Visits or Virtual Tours
If feasible, arrange site visits or virtual tours of the suppliers’ facilities. This allows you to assess their operational capabilities and quality control measures firsthand.
- Inspect Equipment: Check the condition and technology of their milling machines to ensure they are up to date and suitable for your requirements.
- Meet the Team: Engage with the team that will be handling your orders to gauge their expertise and commitment to quality.
Step 6: Establish Communication Protocols
Clear communication is vital for the successful execution of milling operations. Establish protocols for regular updates and feedback throughout the production process.
- Define Points of Contact: Identify key contacts on both sides to streamline communication and resolve issues promptly.
- Set Reporting Cadence: Agree on a schedule for progress reports and updates to keep all stakeholders informed.
Step 7: Finalize Contractual Agreements
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize the contractual agreements. This should include all terms discussed, including pricing, lead times, quality standards, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Review Terms Thoroughly: Ensure that all aspects of the agreement align with your expectations and that you understand the implications of each clause.
- Include Flexibility Provisions: Consider including terms that allow for adjustments in case of unexpected changes in demand or other circumstances.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for milling machine operations, ensuring a successful partnership with their selected suppliers.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for milling machine operation Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Milling Machine Operations?
Understanding the cost structure of milling machine operations is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in international markets. The main components of cost include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Metals such as aluminum, steel, and titanium vary greatly in price and availability. Buyers should consider local sourcing options to minimize costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is often a major expense in milling operations. Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographic location, skill level, and local labor laws. For instance, countries in Europe may have higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production processes can reduce overhead costs, impacting the overall pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for specialized milling operations. Custom tooling may be required for unique projects, which can further increase costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring precision and quality in machining operations is critical. QC processes, including inspections and testing, add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining product standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping and transportation costs can vary significantly depending on the origin and destination. International buyers should be aware of potential delays and additional fees associated with cross-border logistics.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the perceived value of the service provided.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Milling Machine Operation Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of milling machine operations, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize cost-effectiveness.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs due to the need for specialized tools and processes. Buyers should balance customization needs with budget constraints.
-
Material Selection: Different materials have varying cost implications. High-performance materials may offer long-term benefits but can significantly increase upfront costs.
-
Quality Certifications: Suppliers with recognized quality certifications may charge a premium. However, this can assure buyers of the quality and reliability of the products.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international transactions. They dictate who bears the risk and cost at various stages of the supply chain, influencing the overall pricing.
What Tips Can Help Buyers Optimize Costs in Milling Machine Operations?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Building a long-term relationship can also lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime, which can significantly impact overall expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that may affect pricing. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough market research to understand prevailing prices and supplier offerings. This knowledge can help in making informed decisions and negotiating better terms.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the cost components, pricing influencers, and strategic tips can empower B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding milling machine operations. Always consult multiple suppliers and consider the broader implications of each sourcing decision to achieve the best possible outcome.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing milling machine operation With Other Solutions
Introduction: Exploring Alternatives to Milling Machine Operations
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, businesses must evaluate various production methods to determine the most efficient and cost-effective solutions. While milling machine operations are renowned for their precision and versatility, alternative technologies may offer unique advantages depending on specific project requirements. This analysis compares milling machine operations against two viable alternatives: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing).
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Milling Machine Operation | CNC Machining | Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision, versatile | High precision, complex designs | Moderate precision, complex geometries |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Moderate to high initial investment | Low to moderate initial investment |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators | Requires skilled programmers and operators | User-friendly for design, complex for production |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed | Regular maintenance needed | Minimal maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | High-volume production with complex geometries | Custom parts with intricate designs | Prototyping and low-volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Machining: What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks?
CNC machining is a method that automates the movement of cutting tools based on pre-programmed software. This technology excels in producing parts with intricate geometries and high precision. The main advantage of CNC machining lies in its ability to handle complex designs with tight tolerances efficiently. However, it often requires a substantial initial investment in equipment and programming. Additionally, skilled personnel are needed to set up and operate the machinery, which can add to labor costs. While CNC machining is suitable for a wide range of industries, it may not be the best option for projects with very low production volumes due to the high setup costs.
Additive Manufacturing: When Is It the Right Choice?
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, builds components layer by layer, allowing for the creation of complex shapes that may be difficult to achieve with traditional machining. One of the most significant advantages of additive manufacturing is its low initial cost for prototypes and its ability to produce parts without the need for extensive tooling. This method is particularly beneficial for low-volume production runs or custom parts. However, the precision of 3D printing can vary, and it may not be suitable for applications requiring high strength or durability. Moreover, the production speed can be slower than traditional machining methods, making it less ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Conclusion: How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the most suitable manufacturing method, B2B buyers should assess their specific project requirements, including production volume, part complexity, and budget constraints. Milling machine operations offer unparalleled precision and versatility for high-volume production, while CNC machining provides the ability to create complex designs efficiently. On the other hand, additive manufacturing presents an economical solution for prototyping and low-volume runs. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for milling machine operation
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Milling Machine Operations?
Understanding the technical specifications of milling machines is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing equipment for manufacturing. Here are several essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material grade of the milling machine’s components, such as the frame, spindle, and cutting tools, directly affects durability and performance. Common materials include cast iron for frames and high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide for cutting tools. Selecting the right material ensures longevity and reduces downtime, which is vital for maintaining production schedules.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in a machined part. Precision milling typically requires tighter tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm), especially in industries like aerospace or medical devices where part accuracy is critical. Understanding tolerance levels helps businesses ensure that the finished products meet industry standards and customer specifications.
3. Cutting Speed
Cutting speed, measured in surface feet per minute (SFM), is the speed at which the cutting tool engages the material. Optimizing cutting speed is essential for maximizing efficiency and tool life. B2B buyers should consider the recommended cutting speeds for different materials to balance production rates and tooling costs effectively.
4. Feed Rate
Feed rate indicates how quickly the workpiece moves past the cutting tool, usually measured in inches per minute (IPM). This specification impacts the quality of the finish and the overall machining time. A well-calibrated feed rate can enhance productivity while ensuring that the integrity of the machined surface is maintained.
5. Spindle Power
The spindle power rating, typically expressed in horsepower (HP), determines the machine’s capability to handle various materials and cutting operations. A higher spindle power allows for more aggressive cutting and machining of tougher materials. For B2B buyers, understanding spindle power is essential to ensure the chosen milling machine aligns with their production requirements.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Milling Machine Operations?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication in the milling machine market. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the milling industry, sourcing from OEMs can ensure high-quality components that are compatible with existing machinery. This is particularly relevant for buyers looking for reliable replacements or upgrades.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating on tight budgets or managing inventory. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases to avoid overstocking or production delays.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a standard business process where a buyer requests pricing information from suppliers for specific products or services. In milling operations, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and terms from different vendors, facilitating informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in the shipping process. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B transactions, as they clarify who bears the risks and costs associated with the delivery of milling machines and components.
5. CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
CNC refers to the automated control of machining tools via computer programming. CNC milling machines offer enhanced precision and efficiency, making them a preferred choice for modern manufacturing. Familiarity with CNC technology is essential for buyers looking to invest in advanced milling operations.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ultimately leading to better procurement strategies and successful manufacturing outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the milling machine operation Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Milling Machine Operations?
The milling machine operation sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by several global factors. Key market dynamics include the increasing demand for precision manufacturing across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking advanced milling technologies that enhance production efficiency and reduce lead times. The adoption of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling machines is becoming a standard, as these systems offer versatility and the ability to execute complex designs with high accuracy.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT) are also reshaping sourcing trends. These innovations enable predictive maintenance, real-time monitoring, and enhanced automation, which can significantly reduce operational costs. Additionally, the growing trend of Industry 4.0 emphasizes the integration of smart manufacturing practices, compelling businesses to invest in sophisticated milling solutions that support data-driven decision-making.
Moreover, geographical diversification in sourcing is gaining traction. Buyers from emerging markets are increasingly looking beyond traditional suppliers in Europe and North America to engage with manufacturers in Asia and local suppliers who can provide competitive pricing and shorter delivery times. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for international buyers to navigate the complexities of the milling machine operation landscape effectively.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Milling Machine Operation Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a critical consideration in the milling machine operation sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, prompting businesses to adopt more sustainable practices. For B2B buyers, sourcing from suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes is becoming increasingly important. This shift not only addresses regulatory pressures but also aligns with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
Ethical sourcing is another vital aspect of this trend. Companies are expected to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and that they engage with suppliers who uphold ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety are gaining relevance. These certifications provide assurance to buyers that suppliers are committed to minimizing their environmental footprint and promoting worker safety.
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials in milling operations, such as recycled metals and biodegradable lubricants, is gaining traction. Adopting these materials not only reduces environmental impact but also enhances the brand image of companies committed to sustainability. As international B2B buyers evaluate potential suppliers, they should consider the sustainability practices and certifications of those suppliers to ensure alignment with their corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals.
What Is the Historical Context of Milling Machine Operations Relevant to Today’s Market?
The evolution of milling machine operations dates back to the late 18th century, where the first milling machines were developed during the Industrial Revolution. Initially, these machines were manually operated and limited in capability. However, the introduction of CNC technology in the 1960s marked a significant turning point, allowing for greater precision and automation in milling processes. This technological advancement enabled manufacturers to produce complex parts with ease, catering to the growing demands of various industries.
As milling technology continued to advance, the focus shifted towards enhancing efficiency and reducing waste. The adoption of computerized systems not only streamlined operations but also facilitated the implementation of quality control measures. Today, the milling machine operation sector stands at the forefront of modern manufacturing, characterized by smart technologies and sustainable practices. Understanding this historical context helps B2B buyers appreciate the advancements that have shaped the current landscape and the ongoing trends that will drive future developments in milling operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of milling machine operation
-
How do I choose the right milling operation for my project?
Selecting the appropriate milling operation depends on several factors, including the material type, the complexity of the part, and the desired surface finish. For example, face milling is ideal for achieving smooth surfaces on large workpieces, while thread milling is best for creating precise threads on fasteners. Evaluate the specific requirements of your project, including dimensions and tolerances, and consult with suppliers who can offer insights based on their expertise and capabilities. -
What are the most common types of milling operations and their applications?
The most common milling operations include face milling, end milling, slot milling, and thread milling. Face milling is often used for creating flat surfaces, while end milling is versatile for various shapes, including slots and contours. Slot milling is specifically for creating grooves, and thread milling is tailored for producing threads on screws and bolts. Understanding these operations helps you select a supplier with the right expertise for your specific needs. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for milling machine operations?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience in your industry, quality certifications (like ISO), and production capabilities. Ask for references and examples of past projects to assess their expertise. Additionally, inquire about their equipment, technology (CNC vs. manual), and their ability to handle your specific material requirements. A supplier with a robust quality assurance process is essential for ensuring consistency and reliability in your products. -
How can I customize milling operations to meet my specific needs?
Customization options vary by supplier but often include adjustments to tooling, cutting speeds, and machine settings to accommodate unique project specifications. Discuss your requirements in detail with potential suppliers, including material types, dimensions, and desired tolerances. Many suppliers also offer prototype services, allowing you to test custom solutions before committing to larger orders. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) for milling machine operations?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on factors such as the complexity of the operation and the type of materials used. Some suppliers may accept small batch orders, while others might require larger quantities to justify setup costs. Clarify MOQ policies upfront to avoid surprises and to ensure that the supplier can accommodate your production needs without compromising on quality or delivery timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing milling operations internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely based on supplier policies, country regulations, and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include advance payments, net 30/60/90 days, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that are favorable for both parties and to ensure that they align with your cash flow needs. Always consider using secure payment methods and contracts to protect your interests. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in milling operations?
To ensure quality assurance, choose suppliers that implement rigorous quality control measures, including in-process inspections and final product evaluations. Request certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Additionally, consider arranging for third-party inspections or audits to verify that the supplier adheres to the agreed-upon specifications and standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing milling operations internationally?
When sourcing milling operations internationally, consider shipping costs, customs regulations, and lead times. Ensure that your supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. Evaluate potential logistics partners and their capabilities in handling your materials and products. Planning for potential delays and understanding the full costs involved in shipping will help you manage your supply chain effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 5 Milling Machine Operation Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Winndeavor – Precision Milling Solutions
Domain: winndeavor.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Milling is a common machining process in metalworking and manufacturing with various operations including: 1. Slot Milling – creates slots in workpieces using thin cutters. 2. Vertical Milling – features a vertical spindle and uses end mills or flat-bottomed cutters. 3. Horizontal Milling – forms flat surfaces and gears, operating through up milling. 4. Side Milling – produces flat vertical surfac…
2. ToolNotes – Milling Operations Guide
Domain: toolnotes.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Milling Operations include various types such as Face Milling, Peripheral Milling, Slab Milling, Profile Milling, Slotting, Straddle Milling, Slitting, End Milling, Shoulder Milling, Pocketing, Profiling, and Contouring. Face Milling creates a broad, flat surface; Peripheral Milling uses the circumference of a round tool; Slab Milling removes material to flatten a workpiece; Profile Milling shapes…
3. RTB – Milling Machine Operations
Domain: elearning.rtb.gov.rw
Introduction: Course Code: PRTMM501
Course Title: Milling Machine Operations
Description: The course covers the milling process performed with machines where cutters rotate to remove material from workpieces. It includes operations for both small and large objects, emphasizing high precision manufacturing in machinery shops and industries. The course discusses various types of milling machines, including manual…
4. IQS Directory – CNC Milling Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: CNC milling is a highly precise, computer-controlled manufacturing method that transforms digital designs into physical parts and components. It involves securing a workpiece, installing appropriate milling tools, and loading a CNC program generated from CAD or CAM software. CNC milling can be performed in horizontal or vertical orientations and utilizes multi-axis machines (3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-a…
5. Milling Techniques – Key Processes
Domain: mhcc.pressbooks.pub
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: 1. Conventional Milling: Feeding the work against the cutter’s direction of rotation, commonly used for most jobs. 2. Climb Milling: Feeding the work in the same direction as the cutter’s rotation, requiring less power and producing a better finished surface. 3. Depth of Cut: Involves roughing cuts (deep and heavy feed) and finishing cuts (finer feed and shallow cut). 4. Plain Milling: Cutting sur…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for milling machine operation
In conclusion, the landscape of milling machine operations presents a wealth of opportunities for international B2B buyers. Understanding the various types of milling processes—such as face milling, end milling, and CNC milling—enables businesses to select the most suitable methods for their production needs, enhancing efficiency and precision. Strategic sourcing is paramount; it allows companies to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and ensure access to high-quality machinery and materials that can support diverse manufacturing requirements.
As industries evolve, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for advanced milling solutions will grow. Buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide innovative technologies and tailored services. Investing in state-of-the-art milling operations not only boosts productivity but also positions businesses to meet the challenges of a competitive global market.
Looking ahead, the focus should be on cultivating relationships with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and technological advancements. By doing so, businesses can not only secure their operational success but also contribute to a more resilient manufacturing ecosystem. Engage with industry experts today to explore how you can enhance your milling operations for a prosperous future.