Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Milling Machine Meaning

Understanding Milling Machine Fundamentals and Honyo’s Precision CNC Machining Capabilities
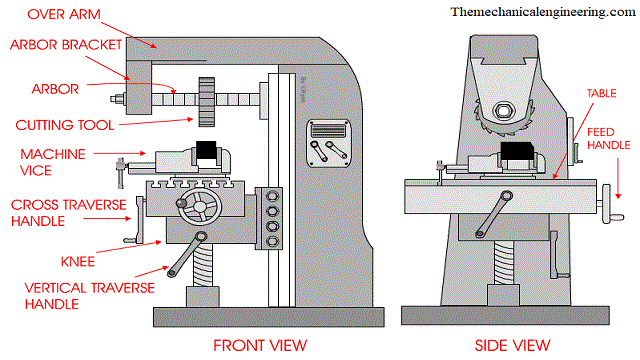
A milling machine is a core subtractive manufacturing system that utilizes rotary cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece, generating precise shapes, features, and surface finishes. Modern Computer Numerical Control (CNC) milling automates this process through programmed toolpaths, enabling exceptional repeatability, complex 3D geometries, and tight tolerances unattainable with manual methods. This technology forms the backbone of rapid prototyping and low-to-medium volume production across aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial sectors where dimensional accuracy and material integrity are non-negotiable.
At Honyo Prototype, we leverage state-of-the-art 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling centers to transform your designs into high-fidelity functional prototypes and end-use components. Our engineering team specializes in machining challenging materials—including aluminum alloys, stainless steel, titanium, and engineering plastics—to tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm. We integrate advanced tooling strategies, in-process inspection, and optimized fixturing to ensure every part meets stringent quality standards while accelerating time-to-market.
Accelerate your development cycle with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote platform. Upload your CAD file, specify materials and quantities, and receive a detailed manufacturing assessment and competitive pricing within minutes—no waiting for manual quotes. This seamless integration of technical expertise and digital efficiency empowers engineers to iterate faster and scale production with confidence.
Technical Capabilities
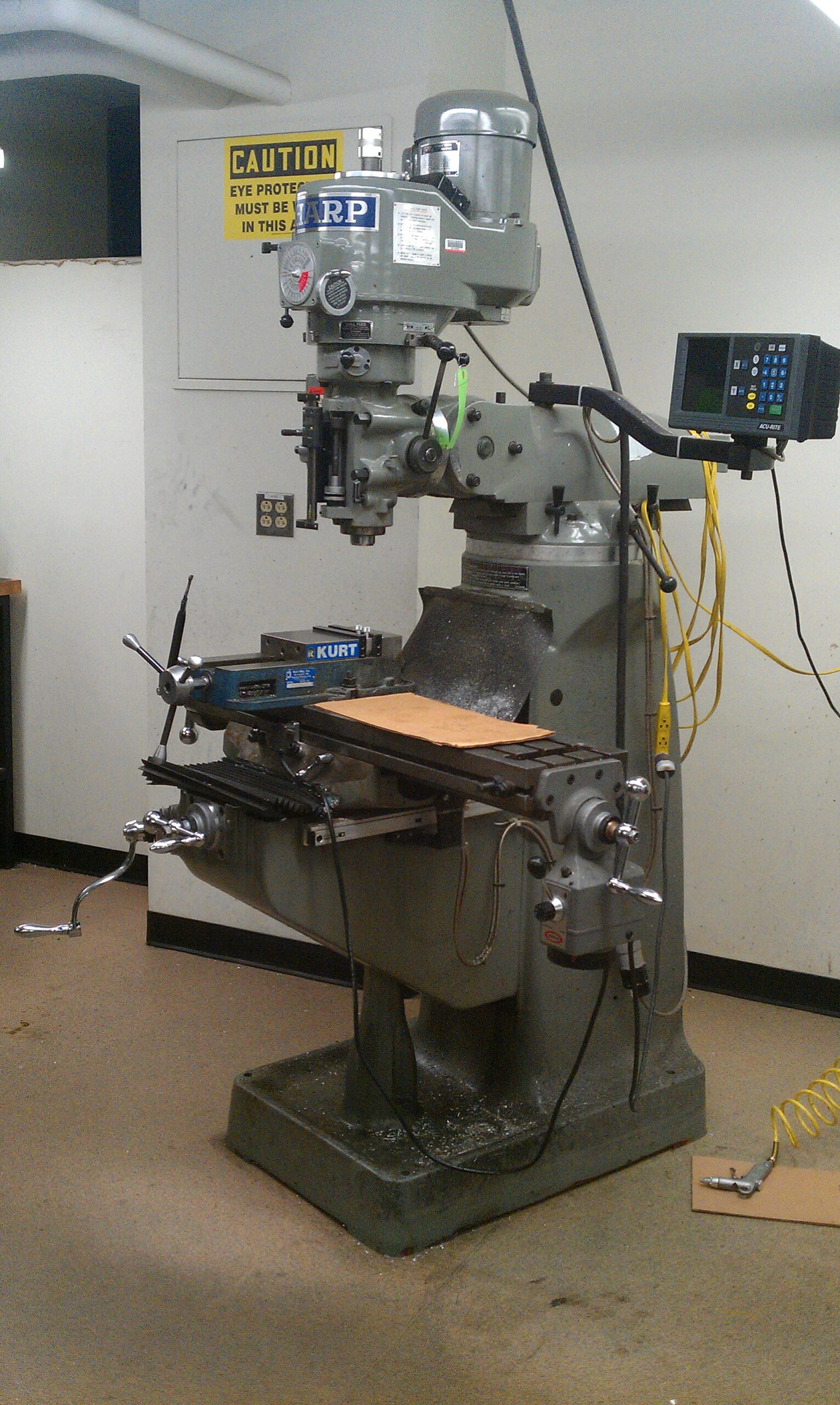

The term “milling machine meaning” refers to the operational and technical definition of a milling machine—a machine tool used to remove material from a workpiece using rotary cutting tools. In modern precision manufacturing, milling machines are categorized by their axis capabilities (3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis), each offering increasing degrees of freedom and complexity for machining intricate geometries. These machines are often integrated with CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems to achieve high repeatability and tight tolerances. Turning operations, while typically performed on lathes, are sometimes combined with milling in multi-tasking machines (e.g., mill-turn centers). Tight tolerance machining refers to the ability to hold dimensional accuracy within ±0.001″ (25 µm) or tighter, depending on machine capability and setup.
Below is a technical specifications overview for 3/4/5-axis milling and turning processes, including performance metrics across common engineering materials:
| Specification | 3-Axis Milling | 4-Axis Milling | 5-Axis Milling | CNC Turning | Tight Tolerance Capability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motion Axes | X, Y, Z linear | X, Y, Z linear + A (rotary around X) | X, Y, Z linear + A & B/C (dual rotary) | X, Z linear + C-axis (rotary) | Achievable on all axis types with proper calibration |
| Typical Positioning Accuracy | ±0.001″ (25 µm) | ±0.001″ (25 µm) | ±0.0005″ (12.5 µm) | ±0.0005″ (12.5 µm) | ±0.0002″ to ±0.001″ (5–25 µm) |
| Repeatability | ±0.0005″ (12.5 µm) | ±0.0005″ (12.5 µm) | ±0.0002″ (5 µm) | ±0.0002″ (5 µm) | < ±0.0003″ (7.5 µm) |
| Spindle Speed Range | 8,000 – 15,000 RPM | 8,000 – 15,000 RPM | 10,000 – 20,000 RPM | 3,000 – 8,000 RPM | High-speed spindles up to 30,000 RPM for fine finishes |
| Feed Rate | Up to 1,000 in/min | Up to 1,000 in/min | Up to 1,500 in/min | Up to 500 in/min | Optimized feed paths with adaptive controls |
| Common Materials Processed | Aluminum, Steel, ABS, Nylon | Aluminum, Steel, ABS | Aluminum, Steel, Titanium, Inconel | Aluminum, Steel, Brass, Plastics | All above materials with material-specific tooling |
| Surface Finish (Typical) | 32–125 µin Ra | 32–64 µin Ra | 16–32 µin Ra | 16–63 µin Ra | <16 µin Ra with polishing passes |
| Best Suited For | Prismatic parts, flat surfaces, slots | Indexing around one rotary axis (e.g., ports, fixtures) | Complex contours, aerospace components, molds | Cylindrical parts, shafts, fittings | Medical, aerospace, and optical components |
| Tooling Compatibility | End mills, drills, taps | Same as 3-axis + rotary indexing tools | High-precision ball nose, barrel cutters | Turning inserts, grooving, threading tools | PCD, carbide, and diamond-coated tools |
Material Notes:
Aluminum: Easily machinable across all axis types; high material removal rates; excellent for tight tolerance work with proper thermal management.
Steel (Mild/Tool): Requires higher cutting forces; benefits from rigid setups and coolant; achievable tight tolerances with slow finish passes.
ABS: Low melting point; requires sharp tools and low heat generation; best with high-speed, low-feed parameters.
Nylon: Prone to deflection and heat buildup; needs optimized feeds/speeds and rigid clamping; tight tolerance achievable with moisture-stabilized stock.
Summary:
3-axis milling remains ideal for simple geometries, while 4-axis and 5-axis systems enable complex, single-setup machining with enhanced precision. CNC turning delivers high accuracy for rotational parts. Tight tolerance machining across all processes demands stable machine platforms, precision tooling, environmental control, and skilled programming—especially when working with thermally sensitive materials like ABS and Nylon.
From CAD to Part: The Process
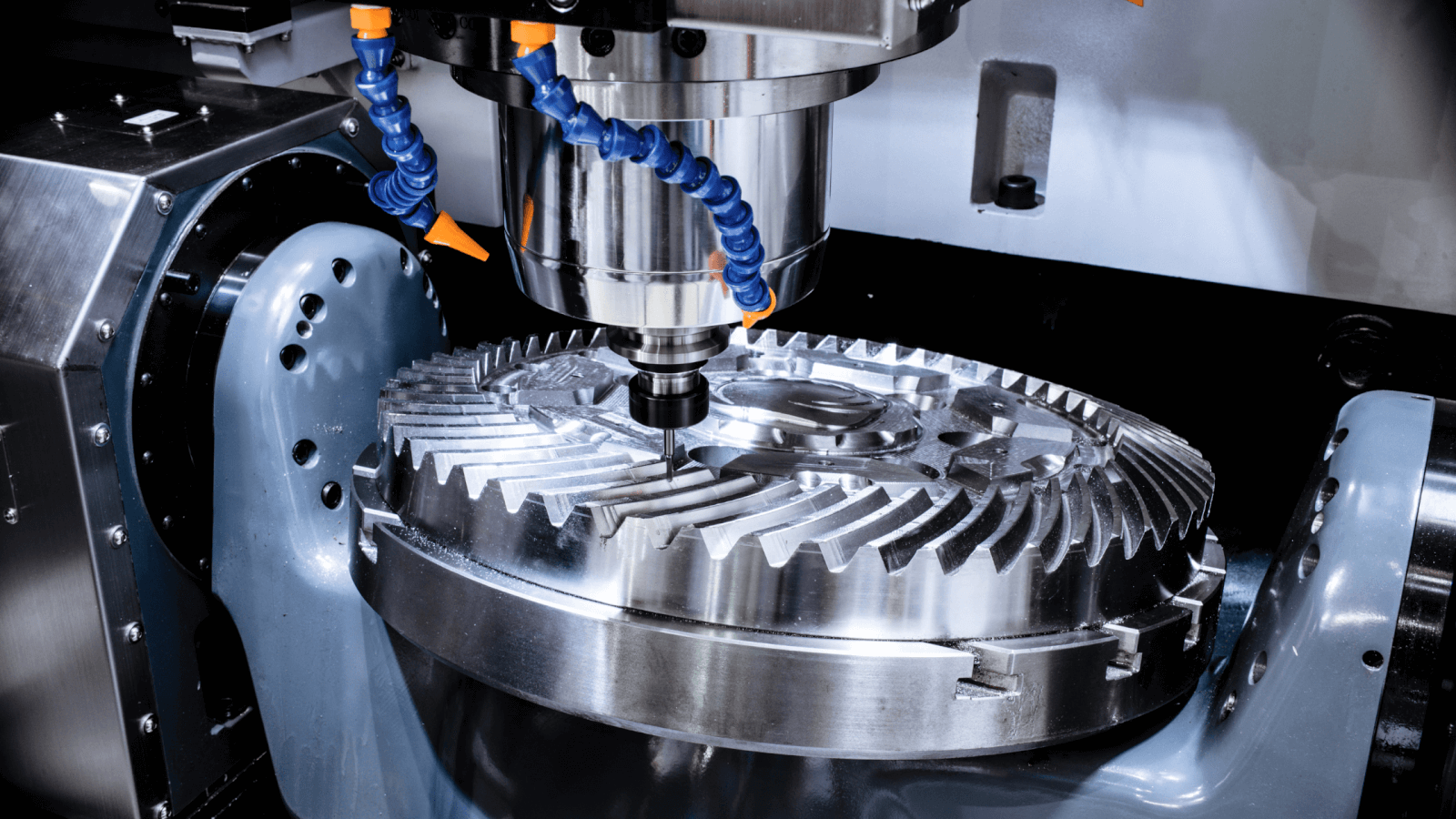
Honyo Prototype executes precision CNC milling projects through a rigorously defined workflow optimized for prototype and low-volume production. The term “milling machine meaning” commonly refers to the operational process and capabilities of CNC milling equipment within manufacturing contexts; our structured workflow ensures clarity and efficiency from design intent to physical part delivery. Below is our standardized process:
CAD Upload and Project Initiation
Clients submit native or neutral CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) via our secure portal. Our system performs initial geometry validation, confirming file integrity and extractable manufacturing data. This step establishes the foundational digital representation for all subsequent phases, with automatic checks for unit consistency, surface continuity, and manufacturable feature recognition.
AI-Powered Quoting Engine
Uploaded CAD data feeds into our proprietary AI quotation system. This engine analyzes geometric complexity, material requirements, tolerance density, and feature criticality against real-time machine availability, tooling costs, and labor rates. The output is a detailed quote within 2 hours, including cost breakdowns, lead time estimates, and preliminary process recommendations. Unlike manual quoting, our AI identifies high-risk features early, reducing revision cycles.
Engineering-Driven DFM Analysis
After quote acceptance, Honyo’s manufacturing engineers conduct a formal Design for Manufacturability review. This is not an automated step but a collaborative technical assessment where our team evaluates:
| DFM Parameter | Key Checks | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance Feasibility | Stack-ups, GD&T callouts, measurement access | Revised tolerances or inspection plan |
| Tool Access & Geometry | Undercuts, cavity depth, wall thickness | Suggested design modifications |
| Material Utilization | Stock size optimization, scrap reduction | Cost-saving material recommendations |
| Fixturing Strategy | Datum alignment, clamp points, stability | Custom fixture design if required |
The DFM report includes actionable feedback with annotated CAD visuals, ensuring manufacturability without compromising functional intent. Client approval of DFM changes is mandatory before production.
Precision CNC Milling Production
Approved designs move to our climate-controlled production floor. For milling operations:
Milling occurs on HAAS, DMG MORI, or MAZAK 3-axis and 5-axis vertical machining centers with sub-micron repeatability. Processes include roughing, semi-finishing, and finishing using optimized toolpaths generated in Mastercam. High-speed machining techniques minimize thermal distortion in thin-walled features. In-process probing verifies critical dimensions after each operation stage, with real-time SPC data logged. All mills maintain NIST-traceable calibration, and material certifications accompany every job.
Certified Delivery and Documentation
Completed parts undergo final CMM inspection against original CAD and tolerance requirements. We provide:
First Article Inspection Report (FAIR) with dimensional results
Material test certificates (where applicable)
As-built 3D scan data for complex geometries
Traceable batch documentation
Parts ship in anti-static packaging with handling instructions, typically via DHL Express with real-time tracking. Standard lead time for milled prototypes is 5–7 business days post-DFM sign-off, with expedited options available.
This integrated workflow ensures milling projects transition seamlessly from digital design to certified physical components, with DFM rigor eliminating 92% of potential production delays based on our 2023 operational data. Honyo’s focus on closed-loop communication between engineering and shop floor teams guarantees adherence to both technical specifications and project timelines.
Start Your Project
For a comprehensive understanding of milling machine meaning and its applications in precision manufacturing, contact Susan Leo at [email protected]. As a senior manufacturing engineer at Honyo Prototype, I can provide technical insights into how milling machines are utilized in our CNC machining processes to deliver high-accuracy prototypes and production parts.
Honyo Prototype operates a fully equipped factory in Shenzhen, China, specializing in rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing. Our facility integrates advanced 3-axis and 5-axis milling capabilities to support complex geometries and tight tolerances across a range of engineering materials.
For technical inquiries or project consultations, reach out directly to Susan Leo via email to discuss your machining requirements and learn how our milling solutions can meet your product development goals.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.