Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for micrometer cylinder
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality micrometer cylinders is crucial for businesses aiming to maintain precision and efficiency in manufacturing and engineering applications. However, international B2B buyers often face challenges in identifying reliable suppliers, understanding various product specifications, and navigating the complexities of pricing and logistics. This comprehensive guide addresses these challenges by offering a deep dive into the diverse types of micrometer cylinders available, their specific applications across industries, and essential supplier vetting processes.
Throughout this guide, we will cover the critical factors that influence purchasing decisions, including material quality, measurement accuracy, and technological advancements in micrometer design. Additionally, we will provide insights into cost considerations and strategies for negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, ensuring that buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly in countries like Saudi Arabia and Brazil—can make informed choices.
By leveraging the information presented here, B2B buyers will be empowered to select the right micrometer cylinders that meet their operational needs while optimizing their procurement processes. Whether you’re looking to enhance measurement capabilities in construction, automotive, or manufacturing sectors, this guide serves as your essential resource for navigating the global market effectively.
Understanding micrometer cylinder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cylinder Bore Inside Micrometer | Carbide-faced tips, spherical contact, adjustable standards | Automotive, machinery, and manufacturing | Pros: Portable, precise readings; Cons: Limited range options. |
| Depth Micrometer | Long measuring range, depth-specific design | Construction, engineering, quality control | Pros: Accurate depth measurements; Cons: Bulkier than other types. |
| Concrete Cylinder Micrometer | Hardened steel spindles, chrome finish, specific diameter ranges | Concrete testing, construction projects | Pros: Designed for concrete; Cons: Not versatile for other materials. |
| Digital Micrometer | Digital display, electronic measurement | Laboratories, precision engineering | Pros: Easy-to-read measurements; Cons: Requires batteries, less durable. |
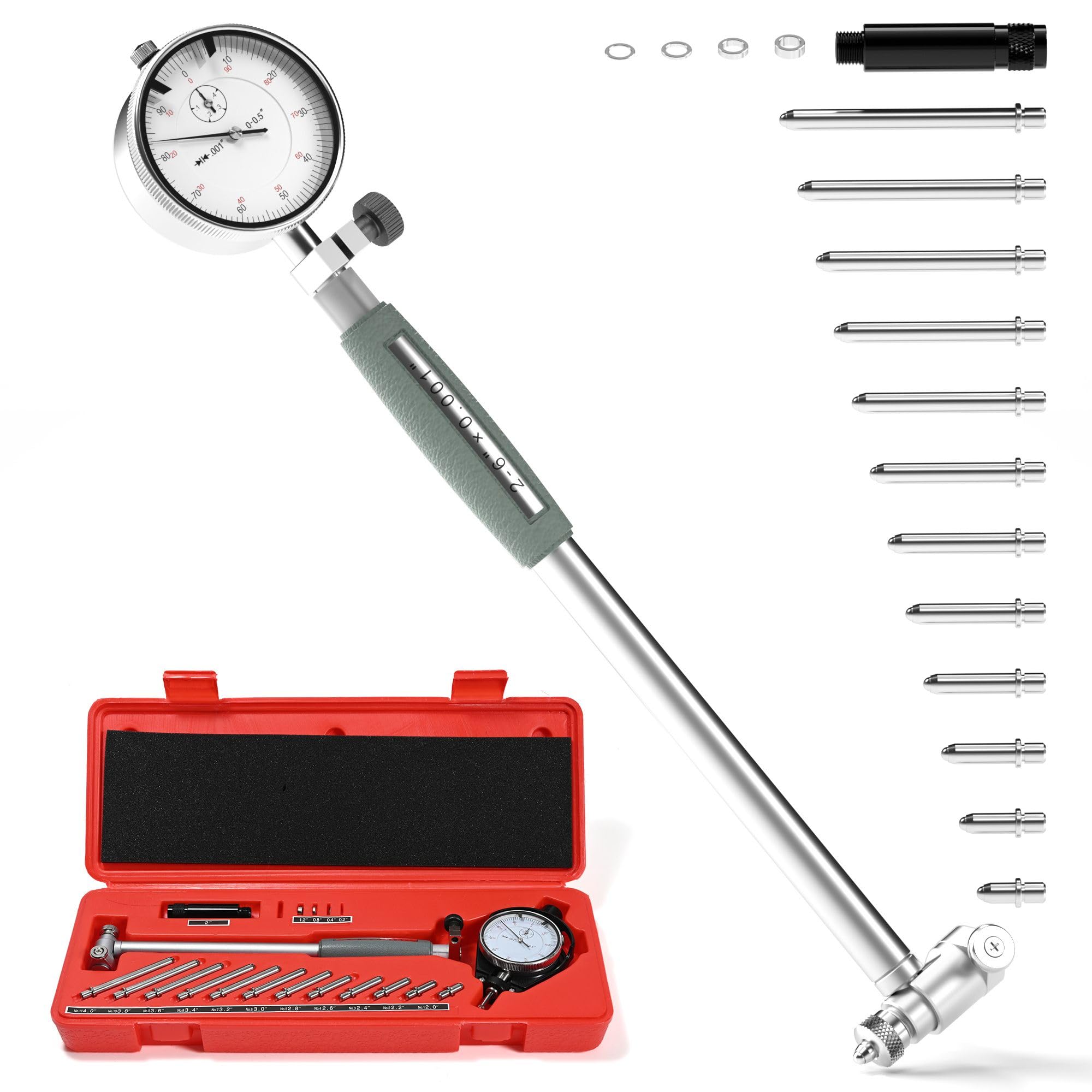
| Indicator Cylinder Bore Gauge | Dial gauge, metric measurements, precise adjustment | Mechanical engineering, automotive repair | Pros: High precision; Cons: Can be more expensive. |
What Are the Characteristics of Cylinder Bore Inside Micrometers?
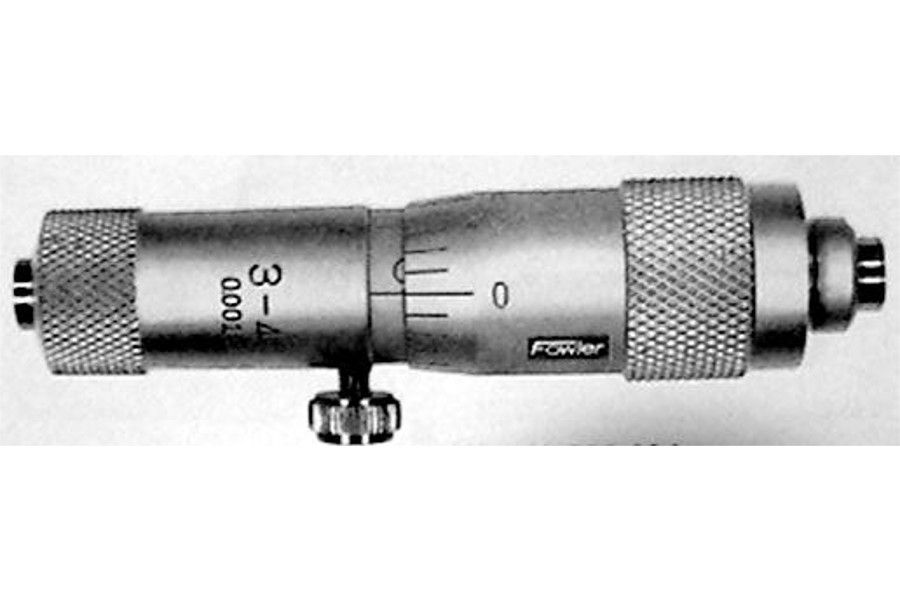
Cylinder bore inside micrometers are essential tools for measuring the internal diameter of cylindrical objects, particularly in automotive and manufacturing sectors. Their carbide-faced tips ensure a precise point of contact against cylinder walls, allowing for accurate measurements. With features like adjustable standards and a range of sizes, these micrometers are particularly suited for applications requiring portability and quick adjustments. B2B buyers should consider the specific range and precision required for their operations, as well as the ease of use in tight spaces.
How Do Depth Micrometers Differ from Other Types?
Depth micrometers are designed specifically for measuring the depth of holes, slots, and recesses. They typically feature a long measuring range, making them ideal for applications in construction and engineering where depth accuracy is critical. The bulkier design compared to other micrometers can be a drawback in terms of portability; however, their accuracy in depth measurement is unmatched. B2B buyers should evaluate their need for depth measurement against the potential limitations in mobility and storage.
What Are the Unique Features of Concrete Cylinder Micrometers?
Concrete cylinder micrometers are specialized tools tailored for measuring the diameters of concrete specimens. They are made with hardened steel spindles and feature chrome finishes for durability. Typically, these micrometers are available in specific ranges suitable for various concrete cylinder sizes, making them indispensable in construction and quality testing environments. Buyers should consider the specific diameter ranges required for their projects, as these tools are not versatile for measuring other materials.
Why Choose Digital Micrometers for Precision Measurement?
Digital micrometers offer a modern approach to measurement with electronic displays that provide easy-to-read results. They are particularly beneficial in laboratories and precision engineering applications where accuracy is paramount. While they may require batteries and can be less durable than mechanical options, the convenience of digital measurement often outweighs these concerns. Buyers in sectors requiring high precision should prioritize digital micrometers, considering their ease of use and readability in demanding environments.
What Advantages Do Indicator Cylinder Bore Gauges Offer?
Indicator cylinder bore gauges feature dial displays for metric measurements and allow for precise adjustments, making them ideal for mechanical engineering and automotive repair. Their high precision is a significant advantage, though they often come at a higher price point. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the balance between precision requirements and budget constraints, ensuring that they invest in a tool that meets their specific measurement needs while providing long-term reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of micrometer cylinder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of micrometer cylinder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Measuring cylinder bore dimensions | Ensures precise fitment of engine components, reducing wear and tear. | Accuracy of measurements, material durability, and ease of use. |
| Construction & Civil Engineering | Measuring concrete cylinder diameters | Facilitates quality control in concrete testing for structural integrity. | Range of measurement, calibration standards, and supplier reliability. |
| Aerospace | Inspecting aerospace components for dimensional accuracy | Enhances safety and performance by ensuring all parts meet specifications. | Compliance with industry standards, precision engineering, and traceability. |
| Oil & Gas | Evaluating bore sizes in drilling equipment | Optimizes equipment performance and reduces operational failures. | Resistance to harsh environments, measurement range, and support for calibration. |
| Metalworking | Setting machining tolerances for cylindrical parts | Improves production efficiency and product quality through precise measurements. | Calibration services, measurement resolution, and availability of specific ranges. |
How Is the Micrometer Cylinder Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, micrometer cylinders are essential for measuring the internal diameters of engine cylinders. This precise measurement is crucial for ensuring that engine components fit together perfectly, which minimizes wear and enhances performance. Buyers in this sector should prioritize accuracy, durability, and ease of use, especially in regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions may affect tool longevity. Additionally, suppliers must offer calibration services to maintain measurement precision over time.
What Role Does the Micrometer Cylinder Play in Construction and Civil Engineering?
In construction, micrometer cylinders are used for accurately measuring the diameters of concrete cylinders during testing. This application is vital for quality control, as it ensures that concrete meets required specifications for structural integrity. For international buyers in regions like the Middle East, it’s important to consider the measurement range and calibration standards to comply with local regulations. Suppliers should also provide reliable customer support to address any technical issues that may arise on-site.
How Does the Micrometer Cylinder Enhance Safety in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, micrometer cylinders are utilized to inspect components for dimensional accuracy, ensuring that they meet stringent safety and performance standards. The precision provided by these tools is critical, as even minor deviations can lead to significant failures. Buyers from Europe, particularly in the aerospace sector, should focus on sourcing tools that comply with industry standards and offer traceability. This guarantees that all measurements are documented and can be verified during audits.
What Benefits Does the Micrometer Cylinder Offer in Oil and Gas Operations?
In the oil and gas industry, micrometer cylinders are employed to evaluate bore sizes in drilling equipment. Accurate measurements are essential to optimize equipment performance and minimize the risk of operational failures. Buyers in this sector, especially in harsh environments, must consider the micrometer’s resistance to corrosion and wear. Additionally, they should ensure that the supplier can provide support for calibration and maintenance, which is crucial for long-term operational reliability.
How Is the Micrometer Cylinder Used in Metalworking for Machining Tolerances?
In metalworking, micrometer cylinders are critical for setting machining tolerances for cylindrical parts. This ensures that products are manufactured to exact specifications, thereby improving production efficiency and product quality. Buyers should look for micrometers that offer high-resolution measurements and calibration services. In markets like Brazil, where manufacturing is rapidly growing, sourcing reliable tools that can withstand the demands of high-volume production is essential for maintaining competitiveness.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘micrometer cylinder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inaccurate Measurements Leading to Production Delays
The Problem: B2B buyers often face the challenge of inaccurate measurements when using micrometer cylinders, particularly in high-stakes manufacturing environments. This can lead to production delays, increased costs, and compromised product quality. For instance, if a micrometer cylinder is not calibrated correctly or if the operator lacks proper training, even minor measurement errors can cascade through the production process, resulting in parts that do not fit or function as intended. This scenario is especially critical in industries like automotive or aerospace, where precision is paramount.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, organizations should implement a robust calibration and training program for their micrometer cylinders. Regularly scheduled calibration checks should be part of the quality assurance process, ensuring that each micrometer is functioning within its specified tolerances. Moreover, investing in comprehensive training for operators can significantly enhance their understanding of how to use the micrometer effectively. Providing access to detailed manuals and hands-on workshops can empower workers to take ownership of their tools, ultimately leading to more accurate measurements and fewer production delays.
Scenario 2: Limited Range of Measurement Options
The Problem: Another common pain point is the limited range of measurement options available with standard micrometer cylinders. B2B buyers may find that their specific applications require a wider range of measurements than what traditional micrometers can provide. For example, when measuring different bore sizes in machinery, having a micrometer that only covers a narrow range can necessitate the purchase of multiple devices, complicating inventory management and increasing costs.
The Solution: Buyers should consider sourcing adjustable or interchangeable micrometer systems that can accommodate various measurement ranges. Look for models that offer a modular design, allowing users to easily switch out measuring heads or anvil sizes to suit different applications. This not only streamlines the measurement process but also reduces the need for multiple tools. Additionally, working closely with suppliers to customize solutions based on specific measurement needs can lead to better long-term partnerships and more tailored support.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Reading Measurements Accurately
The Problem: Many B2B buyers struggle with accurately reading measurements on micrometer cylinders due to the small scale of graduations and potential for parallax errors. This problem is exacerbated in environments with poor lighting or when operators are not adequately trained to interpret the readings correctly. Such difficulties can result in miscalculations that affect product specifications and ultimately lead to costly reworks or scrap.
The Solution: To improve measurement accuracy, buyers should invest in micrometer cylinders that feature enhanced readability options, such as larger dials, digital displays, or backlit screens. These features can significantly reduce the risk of misreading measurements. Additionally, implementing a standardized procedure for measuring, including proper positioning and angle for reading the micrometer, can help mitigate parallax errors. Training sessions focused on these best practices will empower employees to confidently and accurately read measurements, ultimately ensuring that the products meet the required specifications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for micrometer cylinder
What Are the Key Materials for Micrometer Cylinders and Their Properties?
When selecting materials for micrometer cylinders, it is essential to consider properties that affect performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of micrometer cylinders: alloy steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and plastic composites.
How Does Alloy Steel Perform in Micrometer Cylinders?
Alloy steel is a popular choice for micrometer cylinders due to its excellent strength and durability. Key properties include high tensile strength, good wear resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. However, alloy steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
Pros:
– High durability and resistance to wear.
– Cost-effective compared to other metals.
– Suitable for high-pressure applications.
Cons:
– Requires protective coatings to prevent rust.
– Heavier than some alternative materials, which may affect portability.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel is ideal for applications involving heavy machinery or automotive components, where precision and durability are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that their suppliers adhere to these specifications for quality assurance.
What Advantages Does Stainless Steel Offer for Micrometer Cylinders?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. It maintains its mechanical properties across a wide temperature range and is non-reactive, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros:
– Excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for humid or corrosive environments.
– Long lifespan due to resistance to wear and tear.
– Easy to clean and maintain.
Cons:
– Higher cost compared to alloy steel.
– More challenging to machine, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel micrometer cylinders are particularly suited for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals, where hygiene and corrosion resistance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A240 and EN 10088 is essential for ensuring quality. Buyers in South America and Africa should also consider local suppliers who can meet these standards.
Why Choose Aluminum for Micrometer Cylinders?
Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance, making it a favorable option for portable micrometer cylinders. Its thermal conductivity is beneficial for applications requiring quick temperature adjustments.
Pros:
– Lightweight, enhancing portability.
– Good corrosion resistance without additional coatings.
– Cost-effective for mass production.
Cons:
– Lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
– Prone to scratching and denting.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive industries, where weight savings are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B221 is important. Buyers in regions like Europe should ensure that aluminum is sourced from reputable suppliers who meet these standards.
How Do Plastic Composites Compare for Micrometer Cylinders?
Plastic composites offer unique advantages, particularly in terms of weight and resistance to chemical corrosion. They are often used in specialized applications where metal may not be suitable.
Pros:
– Very lightweight and easy to handle.
– Excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals.
– Can be manufactured in various colors and finishes.
Cons:
– Generally lower strength and durability compared to metals.
– Limited temperature resistance, which can restrict application use.
Impact on Application: Plastic composites are suitable for applications in the chemical industry or environments where metal corrosion is a concern.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. Understanding local regulations regarding plastic use is vital, especially in regions like the Middle East.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Micrometer Cylinders
| Material | Typical Use Case for Micrometer Cylinder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Steel | Heavy machinery and automotive components | High durability and wear resistance | Requires protective coatings | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Chemical industry applications | Excellent chemical resistance | Limited strength and temperature tolerance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for micrometer cylinder
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Micrometer Cylinders?
The manufacturing process for micrometer cylinders involves several critical stages, each contributing to the precision and reliability of the final product. Understanding these stages helps B2B buyers assess the quality and performance of the instruments they intend to procure.
Material Preparation
The foundation of any quality micrometer cylinder is the choice of materials. Typically, manufacturers use high-grade alloy steels or carbide for their durability and resistance to wear. The first step in material preparation involves sourcing these materials from reputable suppliers, ensuring compliance with international standards. Once received, the materials undergo rigorous inspection to confirm their specifications, such as hardness and tensile strength.
Forming Techniques
After material preparation, the next phase is forming, where the raw materials are shaped into the micrometer cylinder’s components. This can involve various techniques such as:
- Turning and Milling: These processes create the cylindrical shape and precise dimensions required for the micrometer’s body and measuring tips.
- Grinding: Precision grinding is employed to achieve the necessary tolerances and surface finishes, critical for ensuring accurate measurements.
- Heat Treatment: To enhance the mechanical properties of the materials, heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering are applied. This step is vital for producing components that can withstand operational stresses.
Assembly Process
The assembly phase brings together all the individual components into a complete micrometer cylinder. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail, as any misalignment can lead to measurement errors. Key assembly techniques include:
- Precision Fitting: Components such as the spindle, anvil, and thimble are fitted together with a high degree of precision to ensure smooth operation.
- Calibration: Post-assembly, the micrometer undergoes calibration to confirm that it provides accurate measurements. This step often involves using standardized gage blocks.
Finishing Techniques
Finishing processes enhance both the functionality and aesthetics of micrometer cylinders. Common finishing techniques include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing or applying chrome plating can improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction.
- Marking and Branding: Finally, the micrometer is marked with graduation lines and branding information, ensuring that measurements can be easily read and the product is identifiable.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Implemented?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of micrometer cylinders. It ensures that each instrument meets stringent performance criteria and international standards.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should look for suppliers who adhere to recognized quality standards such as ISO 9001. This standard outlines the criteria for establishing a quality management system and emphasizes continuous improvement. Additionally, specific industry standards like CE marking for products sold in Europe and API standards for those used in the oil and gas sector may apply.
Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining the integrity of the manufacturing process. Common QC stages include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks raw materials against specifications before they enter the production line.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during the manufacturing process help identify defects early. This includes monitoring dimensions and surface finishes at various stages.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembled, micrometers undergo final inspections to ensure they meet all specifications. This may include testing for accuracy, functionality, and durability.
Common Testing Methods Used in QC
Testing methods vary based on the specific requirements of the micrometer cylinder but typically include:
- Calibrated Gage Blocks: Used to verify the accuracy of measurements.
- Functional Testing: Ensures that the micrometer operates smoothly and provides consistent readings.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting the micrometer to stress tests to assess its performance under various conditions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC practices is crucial for ensuring product quality and compliance with regional standards.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One of the most effective ways to assess a supplier’s quality control is through on-site audits. During these audits, buyers can evaluate the manufacturing processes, QC checkpoints, and overall quality management systems. Key areas to focus on include:
- Documentation Practices: Ensure that the supplier maintains comprehensive records of inspections and testing.
- Employee Training: Assess whether staff are adequately trained in quality control procedures and standards.
Requesting Quality Control Reports
Buyers should request detailed QC reports that outline the results of inspections and tests performed during the manufacturing process. These reports should include:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) Data: Information on process capability and consistency over time.
- Non-Conformance Reports (NCR): Documentation of any defects or issues encountered and how they were addressed.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can conduct independent testing and verification of compliance with international standards, providing an additional layer of assurance for B2B buyers.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
B2B buyers operating across different regions must navigate various certifications and quality nuances that may affect their procurement processes. Understanding these can lead to better decision-making and compliance.
Region-Specific Certifications
Each region may have unique certification requirements. For example, products sold in Europe often require CE marking, while those intended for the Middle East might need to meet GSO standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these requirements to ensure compliance and avoid potential delays in shipment.
Cultural and Regulatory Considerations
Cultural differences may also influence quality expectations and communication styles. Building strong relationships with suppliers through clear communication and understanding of local practices can enhance collaboration and lead to better quality outcomes.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for micrometer cylinders is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust QC practices, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality instruments that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘micrometer cylinder’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring micrometer cylinders effectively, this guide outlines key steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. By following this checklist, you can make informed decisions that align with your technical needs and business goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s essential to establish your technical requirements. Determine the range of measurements you need, the precision required, and the specific materials suitable for your applications. Consider factors like:
- Measurement Range: Ensure the micrometer can handle the dimensions of the cylinders you’ll be working with.
- Precision Level: Look for specifications that meet or exceed your industry standards.
Step 2: Research Supplier Options
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers. Utilize online resources, industry directories, and trade shows to compile a list of manufacturers and distributors specializing in micrometer cylinders. Focus on:
- Reputation: Look for reviews and testimonials from other businesses in your region or industry.
- Product Range: Ensure the suppliers have a variety of micrometer models that fit your specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Consider:
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO or industry-specific standards, which indicate quality assurance.
- Experience: Evaluate their track record in supplying micrometer cylinders and their understanding of your specific market needs.
Step 4: Request Samples and Demonstrations
Once you narrow down your list of suppliers, request samples or demonstrations of the micrometer cylinders. This step allows you to:
- Test Performance: Evaluate the accuracy and usability of the micrometers in real-world applications.
- Assess Quality: Ensure that the materials and craftsmanship meet your expectations before making a bulk purchase.
Step 5: Compare Pricing and Terms
Analyze pricing structures and terms from different suppliers. While cost is a significant factor, consider:
- Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in shipping, warranties, and potential maintenance costs over time.
- Payment Terms: Look for flexible payment options that can ease financial strain, especially for larger orders.
Step 6: Confirm After-Sales Support
Strong after-sales support is crucial for ongoing operations. Ensure that your chosen supplier offers:
- Technical Assistance: Access to support for troubleshooting and maintenance inquiries.
- Warranty Policies: Clear information regarding warranties and return policies to safeguard your investment.
Step 7: Finalize Your Order
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize your order by confirming all details, including specifications, quantities, and delivery schedules. Ensure that:
- Documentation: All agreements are documented clearly to avoid misunderstandings.
- Delivery Expectations: Confirm lead times and shipping methods to align with your operational needs.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can confidently navigate the sourcing process for micrometer cylinders, ensuring they select the right tools for their business requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for micrometer cylinder Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Micrometer Cylinder Manufacturing?
When sourcing micrometer cylinders, understanding the cost structure is crucial for B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts the cost. High-quality alloys and precision components, such as carbide-faced measuring tips, often command higher prices. For instance, special alloy steel is commonly used in micrometer cylinders to enhance durability and precision.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for manufacturing precision instruments. Labor costs can vary significantly based on the region and the level of expertise required for assembly and calibration.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom specifications. Tooling costs are amortized over production runs, making them a critical consideration for larger orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the micrometer cylinders meet industry standards. This can add to the overall cost but is essential for maintaining product reliability.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are influenced by the weight and dimensions of the products. Buyers should consider the total logistics costs when sourcing from international suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a markup to cover their operational costs and profit margins. Understanding average industry margins can assist buyers in evaluating pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Micrometer Cylinder Sourcing?
Several factors can influence pricing in the micrometer cylinder market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to price reductions. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on the order quantity, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate their orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom micrometer cylinders tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can justify higher prices. Buyers should assess the value of these certifications based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Established suppliers with robust QC processes might charge more but offer greater reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for cost forecasting. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the total landed cost.
What Negotiation Strategies Can Buyers Use for Cost Efficiency?
To optimize sourcing costs for micrometer cylinders, buyers can employ several strategies:
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: Buyers should communicate their purchasing plans clearly to negotiate better rates based on anticipated order volumes.
-
Explore Multiple Suppliers: Obtaining quotes from various suppliers can provide insights into competitive pricing and help identify the best value.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and potential downtime.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade regulations that could affect pricing.
-
Build Long-term Relationships: Establishing a rapport with suppliers can lead to better terms, exclusive discounts, and priority service.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Keep in Mind When Sourcing Micrometer Cylinders?
While indicative prices for micrometer cylinders can vary widely—from approximately $110 for basic models to significantly higher for specialized applications—buyers should focus on the total cost structure and pricing influencers. By understanding these elements and employing effective negotiation strategies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing micrometer cylinder With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Micrometer Cylinders
When considering measurement solutions in industrial and manufacturing contexts, micrometer cylinders are a popular choice for their precision and reliability. However, there are several alternative methods and technologies that can achieve similar goals, each with its own unique advantages and drawbacks. This analysis will compare micrometer cylinders with other viable measurement solutions, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific requirements.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Micrometer Cylinder | Cylinder Bore Inside Micrometer | Digital Caliper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for internal diameters | Accurate for cylinder walls, less versatile | Moderate precision for various measurements |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable (approx. $110) | Low to moderate (varies widely) |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training for effective use | User-friendly and portable | Very easy to use and widely available |
| Maintenance | Requires calibration and care | Low maintenance, durable materials | Low maintenance, but batteries may need replacement |
| Best Use Case | Precision measurement in manufacturing | Automotive and mechanical applications | General-purpose measuring tasks |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Cylinder Bore Inside Micrometer
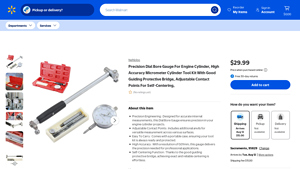
This alternative tool is specifically designed for measuring the internal dimensions of cylindrical objects, making it ideal for automotive and mechanical applications. The carbide-faced measuring tips ensure a positive point contact, enhancing accuracy. Its affordability, with prices around $110, makes it accessible for small businesses and individual users. However, its specialization means it may not be suitable for broader measurement needs, limiting its versatility compared to a micrometer cylinder.
Digital Caliper
Digital calipers are versatile measuring tools that provide quick and accurate readings for a variety of applications, including internal and external dimensions, depths, and steps. Their ease of use and immediate digital readouts make them a preferred choice for many technicians and engineers. The price range for digital calipers varies significantly, from budget-friendly options to more advanced models. However, while they offer convenience, they may not match the precision of micrometer cylinders in critical measurement scenarios, particularly in industrial settings where minute variations are crucial.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Measurement Solution
Selecting the right measurement solution depends on various factors, including the specific application, required precision, budget constraints, and ease of use. For industries where precision is paramount, a micrometer cylinder may be the best option despite its higher cost and maintenance requirements. Conversely, if affordability and versatility are critical, alternatives like the cylinder bore inside micrometer or digital caliper could be more suitable. B2B buyers should assess their unique operational needs and consider long-term implications, such as maintenance and calibration, to make an informed decision that aligns with their business objectives.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for micrometer cylinder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Micrometer Cylinder?
When selecting a micrometer cylinder, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring precision and reliability in measurements. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
The material composition of a micrometer cylinder significantly impacts its durability and measurement accuracy. Common materials include special alloy steel or hardened steel, which provide robustness against wear and tear. For B2B buyers, choosing a high-grade material ensures longevity and reduces the frequency of replacements, ultimately leading to cost savings.
2. Measurement Range
The measurement range indicates the span of sizes the micrometer can accurately gauge. For instance, a cylinder bore inside micrometer may have ranges like 3”-4” or 4”-5”. Understanding the range is essential for buyers to ensure that the tool meets their specific application needs, especially in industries such as automotive or construction where precision is paramount.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. For micrometer cylinders, a tolerance of ±0.001” is common. High tolerance levels are critical for applications requiring extreme precision, such as in aerospace or medical device manufacturing. B2B buyers must assess their operational requirements to choose a micrometer that aligns with their precision standards.
4. Graduation
Graduation indicates the smallest increment that can be read on the tool. A micrometer with micro-fine graduations, such as those marked in thousandths of an inch, allows for more precise measurements. This is particularly important in engineering and manufacturing sectors, where even minor discrepancies can lead to significant issues in product quality.
5. Anvil and Spindle Construction
The anvil and spindle are integral components that facilitate accurate measurements. They should be hardened and precision-ground for durability and stability. Buyers need to consider these features to ensure that the micrometer can withstand rigorous use without compromising measurement accuracy.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Micrometer Cylinders?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are several common terms associated with micrometer cylinders:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts that are sold to another company for assembly into their products. In the context of micrometer cylinders, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure they receive high-quality components.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For micrometer cylinders, knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their inventory effectively, ensuring they meet operational demands without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For B2B buyers looking for micrometer cylinders, issuing an RFQ can help in comparing offers and negotiating better deals based on quality and price.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks associated with purchasing micrometer cylinders from abroad.
5. Calibration
Calibration is the process of verifying and adjusting the accuracy of measuring instruments. For micrometer cylinders, regular calibration is vital to maintain precision. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer calibration services or equipment to ensure their tools remain accurate over time.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing micrometer cylinders, ensuring they choose the right tools for their specific needs while optimizing operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the micrometer cylinder Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers and Trends Influencing the Micrometer Cylinder Sector?
The global micrometer cylinder market is witnessing significant growth, driven by advancements in manufacturing technology and increasing demand for precision measurement tools across various industries. Key drivers include the automotive, aerospace, and construction sectors, where the need for accurate measurements is paramount for quality assurance and compliance with industry standards. Emerging technologies such as digital micrometers and automated measurement systems are reshaping sourcing trends, making it essential for international B2B buyers to adapt to these innovations.
In regions like Africa and South America, the market is expanding due to infrastructural development and industrialization, which require high-quality measurement tools. Buyers in the Middle East, particularly in countries like Saudi Arabia, are also investing heavily in precision instruments to support their growing manufacturing sectors. Furthermore, European markets are increasingly focusing on integrating smart technologies into micrometer cylinders, allowing for real-time data collection and analysis. This trend towards digitization is prompting buyers to seek suppliers who can provide advanced, tech-enabled solutions.
Additionally, the rise of e-commerce platforms is facilitating easier access to a wider range of micrometer cylinder products, enabling buyers from diverse regions to compare prices and specifications efficiently. As global supply chains become more interconnected, international buyers must stay informed about regional sourcing capabilities and supplier reliability to navigate market dynamics effectively.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Micrometer Cylinder Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the decision-making process for B2B buyers in the micrometer cylinder sector. As environmental concerns rise, companies are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices. This includes the use of eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes that minimize waste and energy consumption. For instance, manufacturers that utilize recycled metals or sustainable alloys for their micrometer cylinders not only reduce their carbon footprint but also appeal to environmentally conscious buyers.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are keen to work with suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices and labor conditions. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable and ethical practices. By prioritizing suppliers with these certifications, international buyers can mitigate risks associated with unethical sourcing and enhance their brand reputation.
The focus on sustainability is also driving innovation in product development. Suppliers are exploring the use of biodegradable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes, leading to the emergence of “green” micrometer cylinders. This shift not only meets the growing demand for sustainable products but also positions suppliers favorably in a competitive market, making it imperative for B2B buyers to consider these factors when sourcing.
What Is the Historical Context of the Micrometer Cylinder Market?
The history of the micrometer cylinder dates back to the late 18th century when the micrometer screw was invented by the renowned engineer and inventor, William Gascoigne. Initially designed for astronomical measurements, this precision tool quickly found applications in various industries, particularly in mechanical engineering and manufacturing. Over the years, the design and functionality of micrometer cylinders have evolved significantly, with advancements in materials and technology enhancing their accuracy and durability.
The introduction of digital micrometers in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for easier readings and increased precision. Today, the micrometer cylinder sector continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the continuous improvement in measurement technologies and the importance of adapting to emerging trends in precision measurement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of micrometer cylinder
-
How do I choose the right micrometer cylinder for my application?
Selecting the appropriate micrometer cylinder depends on several factors, including the measurement range, material, and specific application needs. For instance, if you are measuring cylinder bores in automotive applications, a cylinder bore inside micrometer with carbide-faced tips is ideal for precision. Additionally, consider the ease of reading the graduations; satin chrome finishes often provide better visibility. Assess the tool’s durability, as hardened and precision-ground components ensure longevity, especially in high-use environments. -
What are the key features to look for in a micrometer cylinder?
Essential features of a micrometer cylinder include measurement accuracy, range, and material quality. Look for models with carbide-tipped measuring points for enhanced durability and precision. A well-marked graduation system (e.g., 0.001”) aids in easy reading. Consider the construction material; special alloy steel is often preferred for its strength and resistance to wear. Additionally, features such as a fitted case for storage and portability can enhance the overall value of the tool. -
How can I verify the quality of a micrometer cylinder supplier?
To ensure quality, start by researching the supplier’s reputation and customer reviews. Verify if they adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Request product samples to evaluate craftsmanship and precision firsthand. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes, such as calibration and testing procedures. Engaging with suppliers who have a transparent operational history can also provide insights into their reliability and product quality. -
What are the typical payment terms for purchasing micrometer cylinders internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely depending on the supplier and the buyer’s location. Common options include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It is essential to negotiate terms that are favorable and secure, especially for large orders. Ensure that the terms include details about currency, payment methods (e.g., bank transfer, PayPal), and any potential deposit requirements. Always consult with your finance team to align with your budget and cash flow. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for micrometer cylinders?
The MOQ can differ significantly among suppliers and may depend on factors such as the type of micrometer cylinder and the material used. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for specialized tools to larger quantities for standard products. Discussing your requirements with the supplier can sometimes lead to flexibility in MOQs, especially if you are willing to establish a long-term partnership. Always evaluate the cost implications of purchasing at or above the MOQ. -
How do I ensure efficient logistics when sourcing micrometer cylinders internationally?
Efficient logistics begin with selecting a supplier who has a reliable shipping process. Discuss shipping options, including air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Understand the customs regulations in your country to avoid delays. Consider partnering with a logistics provider experienced in handling international shipments, as they can navigate the complexities of customs clearance and duty payments. Tracking shipments and establishing clear communication with the supplier can also help manage the logistics process effectively. -
Can I customize micrometer cylinders to meet specific needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for micrometer cylinders, allowing you to specify dimensions, materials, and features that align with your unique requirements. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications, including desired measurement ranges and any additional features you may need, such as digital displays or specific calibration. Be aware that customized products may have longer lead times and potentially higher costs, so plan accordingly in your procurement strategy. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from a micrometer cylinder supplier?
A reputable supplier should implement stringent quality assurance measures, including regular calibration of tools, adherence to manufacturing standards, and thorough testing of each product. Inquire whether they provide certificates of calibration or inspection reports with your order. Some suppliers also conduct periodic audits and reviews to ensure consistent quality. Understanding these measures not only helps in verifying the product’s accuracy but also builds confidence in the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Micrometer Cylinder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Mitutoyo – Digital Micrometer
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Cylinder micrometer products for sale on eBay include various types such as outside micrometers, inside micrometers, digital micrometers, bore micrometers, depth micrometers, indicating micrometers, groove micrometers, and tube micrometers. Key brands featured are Lufkin, Mitutoyo, Shars Tool, Starrett, Tesa, and Unbranded. Measurements range from 0 inches to 60 inches, with specific listings for …
2. INSIZE – 4179-10 10 Inch Special Alloy Steel Tool
Domain: higherprecision.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: {“Product Code”: “4179-10”, “MFGID”: “4179-10”, “Brand”: “INSIZE”, “Length”: “10 inch”, “Material”: “Special Alloy Steel”, “Features”: “Made of special alloy steel, hardness HRC64, high stability, wear resistance and easy combination”, “Compliance”: “Meets ASME B89.1.9—2002 Grade AS-1”, “Price”: “$1,364.27”, “Lowest Price Guaranteed”: true}
3. Mitutoyo – Dial Bore Gauge & Outside Micrometer
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: The user is looking for a dial bore gauge and outside micrometer with measurement accuracy to the ten thousandths of an inch, specifically for ranges from 2″ to 5″. They express concern about the quality of tools from Harbor Freight and seek decent quality tools that won’t break the bank. Recommendations include Mitutoyo digital outside micrometers and telescoping gauges for bore measurement, thou…
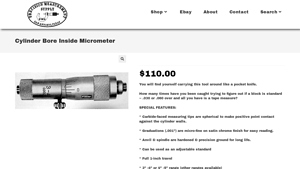
4. Precision Measure – Cylinder Bore Inside Micrometer
Domain: precisionmeasure.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: {“name”: “Cylinder Bore Inside Micrometer”, “price”: “$110.00”, “features”: [“Carbide-faced measuring tips are spherical for positive point contact against cylinder walls”, “Micro-fine graduations (.001″) on satin chrome finish for easy reading”, “Hardened & precision ground anvil & spindle for long life”, “Can be used as an adjustable standard”, “Full 1-inch travel”, “Available ranges: 3″-4” or 4…
5. Precision Internal Diameter Gauge – 35-50mm Range
Domain: aliexpress.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, Precision Internal Diameter Gauge – 35-50mm Range, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
6. Walmart – Dial Bore Gauge
Domain: walmart.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Walmart – Dial Bore Gauge, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
7. Instructables – DIY Micrometer Substitute
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: This DIY project involves creating a substitute micrometer using a wooden block and steel rods to measure cylinder wear without a traditional micrometer. Key steps include measuring the cylinder’s diameter, rounding the ends of the block for a better fit, drilling a hole through the block for the steel rod, making a notch for the rod, cutting the rod into two pieces, and using the device to measur…
8. River Dave’s Place – Micrometer Hone
Domain: riverdavesplace.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Micrometer Hone is used for garage-built engine rebuilds, capable of honing cylinders outwards of 0.020″ to 0.030″. Users report it is more effective for finishing a bore or taking off a few thousandths rather than significant enlargements. Commonly used grit stones include 80, 180, and 280. It is noted that the hone should run dry and requires constant cleaning of the stones. The tool is often co…
9. AHEX – Cylinder Bore Micrometer
Domain: ahexp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Cylinder Bore Micrometer, 2 1/2 inch ID micrometer, used for measuring cylinder bores to ensure they are within specifications.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for micrometer cylinder
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Micrometer Cylinder Procurement?
In the competitive landscape of precision measurement tools, strategic sourcing of micrometer cylinders plays a pivotal role in optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring product quality. Buyers should focus on partnering with reputable manufacturers that offer a range of micrometer solutions tailored to diverse applications—from automotive to construction—ensuring accuracy and durability.
By leveraging strategic sourcing, international buyers can gain access to innovative technologies and materials, such as carbide-faced tips and special alloy steel, which enhance measurement accuracy and longevity. Additionally, understanding regional supply chain dynamics can lead to significant cost savings and reduced lead times, particularly for markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As you consider your procurement strategies, prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to quality and customer service. By doing so, you not only secure the best products but also foster long-term relationships that can adapt to evolving market needs.
Embrace the future of precision measurement by initiating discussions with trusted suppliers today. The right micrometer cylinder can transform your operations, driving both productivity and profitability in your business.