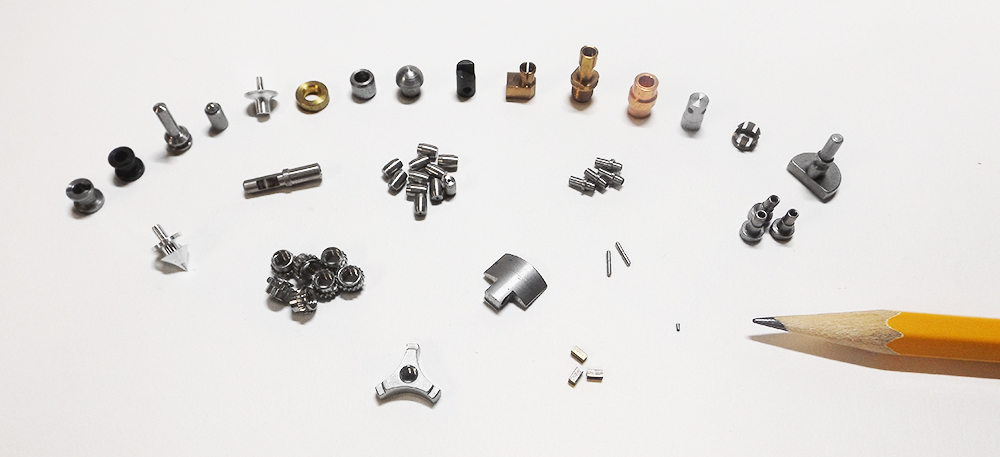
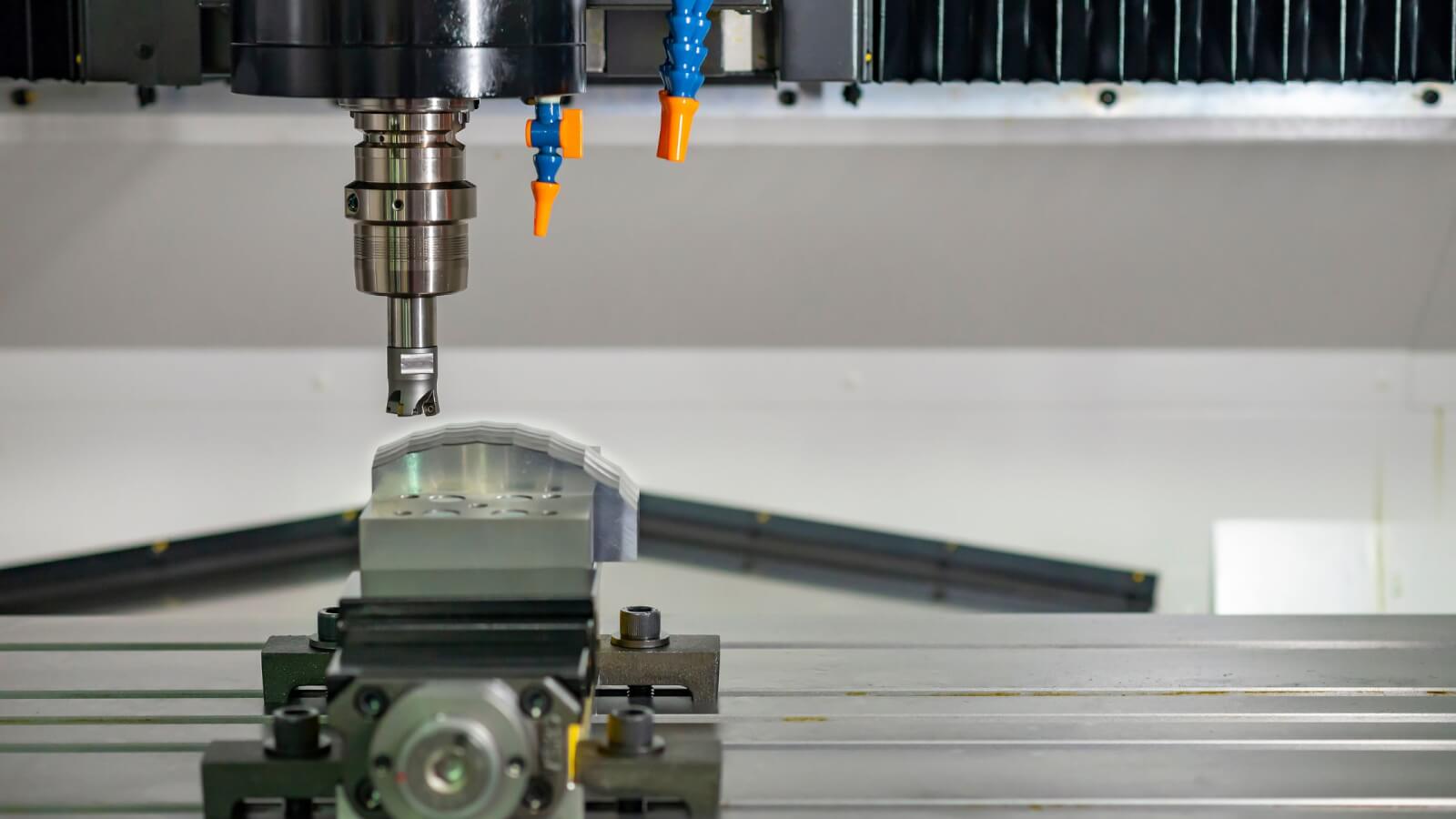
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for micro machining services
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, the challenge of sourcing reliable micro machining services can be daunting for B2B buyers across the globe. As industries demand increasingly intricate and precise components, the need for specialized machining solutions has surged, especially in sectors such as medical devices, aerospace, and telecommunications. This guide is designed to help international buyers navigate the complexities of the micro machining market, offering insights into the various types of services available, their applications, and the critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
From understanding the nuances of micro milling and electrical discharge machining (EDM) to evaluating the capabilities of potential vendors, this comprehensive resource equips you with the knowledge necessary for informed decision-making. We will explore essential criteria for supplier vetting, including quality certifications and production capabilities, while also providing an overview of cost considerations and market trends.
Whether you are based in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe—regions that are experiencing significant industrial growth—this guide empowers you to make strategic choices that align with your organization’s unique needs. By leveraging the insights shared here, you can confidently engage with suppliers who can deliver the precision and quality that your projects demand, ultimately driving innovation and success in your operations.
Understanding micro machining services Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micro Milling | Utilizes CNC technology with multiple axes for precision | Aerospace, Medical Devices, Electronics | Pros: High precision, complex geometries; Cons: Can be costlier for low-volume runs. |
| Micro Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) | Creates intricate shapes using electrical discharges | Automotive, Aerospace, Medical Devices | Pros: Excellent for hard materials; Cons: Slower processing time compared to traditional methods. |
| Laser Micromachining | Employs ultra-fast laser beams for extreme precision | Telecommunications, Medical Devices | Pros: High resolution, minimal thermal impact; Cons: Limited to certain materials. |
| Micro Turning | Specialized lathe operations for cylindrical parts | Automotive, Industrial Equipment | Pros: Ideal for round components; Cons: Less effective for complex geometries. |
| Micro Assembly | Combines micro components into subassemblies | Medical Devices, Electronics, Aerospace | Pros: Streamlines production; Cons: Requires precise coordination and handling. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Micro Milling Services?
Micro milling is a precision machining process that employs CNC technology with multiple axes of motion to create intricate and detailed components. This method is particularly suitable for applications requiring high precision and complex geometries, such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing. When considering micro milling, buyers should evaluate the supplier’s CNC capabilities, material compatibility, and the potential for high-volume production, as costs can escalate for smaller runs due to setup times.
How Does Micro EDM Work and What are Its Key Applications?
Micro Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a specialized process that uses electrical discharges to shape conductive materials into intricate designs. This method is particularly advantageous for hard materials and complex geometries, making it ideal for industries like automotive and aerospace. Buyers should consider the machine’s capabilities in terms of precision and speed, as well as the supplier’s experience with specific materials. While micro EDM offers exceptional detail, its processing times can be longer than traditional machining methods.
Why Choose Laser Micromachining for Your Projects?
Laser micromachining utilizes ultra-fast laser beams to achieve extremely high precision in manufacturing micro components. This technique is suitable for applications in telecommunications and medical devices, where minimal thermal impact and high resolution are critical. Buyers should assess the supplier’s laser technology, including the range of materials they can work with and their ability to produce complex shapes. While laser micromachining offers significant advantages, it may not be applicable for all materials.
What are the Benefits of Micro Turning Services?
Micro turning involves specialized lathe operations to produce cylindrical components with high precision. This method is particularly effective for industries such as automotive and industrial equipment manufacturing. Buyers should consider the supplier’s expertise in turning specific materials and their capacity for handling various diameters and lengths. While micro turning is highly effective for round components, it may not be the best choice for more complex geometries.
How Does Micro Assembly Enhance Production Efficiency?
Micro assembly services focus on integrating micro components into subassemblies, streamlining the production process for industries like medical devices and electronics. This service is essential for reducing fixed costs and speeding up development times. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s quality management systems and experience in handling delicate components, as precise coordination is crucial in micro assembly. While it enhances efficiency, the complexity of managing multiple small parts can pose challenges.
Key Industrial Applications of micro machining services
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of micro machining services | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of surgical instruments and implants | Enhanced precision improves patient outcomes | Compliance with medical standards, ISO certifications |
| Aerospace | Production of complex components like turbine blades | Lightweight, high-strength parts enhance efficiency | Material certifications, adherence to aerospace standards |
| Electronics | Fabrication of micro connectors and circuit components | Improved performance in compact devices | Compatibility with various materials, rapid prototyping capabilities |
| Telecommunications | Creation of fiber optic components and connectors | Increased data transmission efficiency | Quality control measures, precision tolerances |
| Automotive | Development of micro sensors and electronic controls | Enhanced safety and performance in vehicles | Supplier reliability, scalability of production |
How Are Micro Machining Services Applied in the Medical Device Industry?
In the medical device sector, micro machining services are crucial for producing intricate surgical instruments and implants. These components often require extreme precision to ensure they function correctly and safely within the human body. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers comply with rigorous medical standards, including ISO 13485 certification. Additionally, understanding the specific material requirements for biocompatibility and sterilization is essential to avoid costly recalls and ensure patient safety.
What Role Does Micro Machining Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Aerospace manufacturers utilize micro machining services to create complex components, such as turbine blades and intricate housing parts. These components must be lightweight yet durable to withstand extreme conditions. For businesses in this sector, sourcing from suppliers who can provide material certifications and adhere to stringent aerospace standards is vital. Moreover, the ability to produce small, precise parts can lead to significant improvements in fuel efficiency and overall performance.
How Is Micro Machining Transforming the Electronics Sector?
In electronics, micro machining services are employed to fabricate micro connectors and circuit components that fit into increasingly compact devices. The ability to create features at the micron level allows for enhanced performance and reliability in electronic applications. International buyers should focus on suppliers that offer rapid prototyping capabilities and can work with various materials. This flexibility is crucial for staying competitive in the fast-evolving electronics market.
Why Is Micro Machining Essential for Telecommunications?
Telecommunications companies leverage micro machining services to manufacture fiber optic components and connectors that facilitate high-speed data transmission. The precision of these components directly impacts the efficiency of data networks. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing from companies that implement strict quality control measures and can maintain the required precision tolerances. This ensures that the final products meet the high standards necessary for modern communication technologies.
How Are Automotive Manufacturers Benefiting from Micro Machining?
Automotive manufacturers increasingly rely on micro machining services to develop micro sensors and electronic controls that enhance vehicle safety and performance. These components must be produced to exact specifications to ensure reliability under various conditions. For international B2B buyers, assessing supplier reliability and their ability to scale production is crucial. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for materials and tolerances can help avoid production delays and ensure timely delivery of parts.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘micro machining services’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Complex Design Requirements and Tolerances
The Problem: B2B buyers often face challenges when their designs demand high precision and complex geometries that standard machining services cannot accommodate. For instance, industries such as medical devices or aerospace require components with intricate features and tight tolerances, often in the micrometer range. When these specifications aren’t met, it can lead to product failures, delays in production, and increased costs due to rework or redesign.
The Solution: To effectively address this challenge, buyers should thoroughly assess potential micromachining service providers based on their capabilities and technology. Look for companies that specialize in advanced techniques such as micro EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) and 5-axis CNC milling, which are essential for producing complex geometries. It’s crucial to communicate your design specifications in detail, including tolerances and material requirements, to ensure the provider can meet these demands. Request samples or case studies that demonstrate the provider’s expertise in handling similar projects. By partnering with a capable service provider and maintaining open communication, businesses can mitigate risks and achieve the desired precision in their components.
Scenario 2: Material Limitations and Compatibility Issues
The Problem: Another common pain point is the compatibility of materials with the micromachining processes. Many buyers find that their chosen materials may not be suitable for micromachining due to factors like brittleness, thermal conductivity, or machining difficulty. This can lead to unexpected costs and delays if the initial material selection does not align with the machining capabilities of the service provider.
The Solution: To overcome material compatibility issues, it is vital for buyers to conduct thorough research on both the materials they wish to use and the micromachining technologies available. Engage with your machining service provider early in the design process to discuss material options and their specific machining characteristics. For instance, materials like titanium and specialized alloys may require specific techniques such as laser micromachining or particular EDM processes. It is advisable to ask for a comprehensive material compatibility guide from the service provider, which outlines the best practices and limitations for various materials. By ensuring that the selected materials align with the machining capabilities, buyers can avoid costly setbacks and optimize production efficiency.
Scenario 3: Quality Assurance and Regulatory Compliance
The Problem: In sectors such as medical devices and aerospace, regulatory compliance and stringent quality assurance processes are critical. Buyers often struggle to find micromachining services that not only meet their precision needs but also adhere to industry-specific regulations like ISO 13485 for medical devices. Non-compliance can lead to costly recalls, legal issues, and damage to the brand’s reputation.
The Solution: To ensure quality and compliance, buyers should prioritize micromachining service providers that have robust quality management systems in place. Request documentation proving their compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ISO certifications and adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Additionally, inquire about their quality control processes, including how they test and validate the precision of machined parts. Establishing a partnership with a provider that offers transparency and documentation on their quality processes can significantly reduce the risk of non-compliance. Regular audits and reviews of the provider’s performance can also help maintain high standards and ensure that all components meet the required regulations. By taking these steps, buyers can safeguard their products’ quality and compliance, ultimately supporting their brand integrity in the market.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for micro machining services
What Are the Key Properties of Brass in Micro Machining Services?
Brass is a popular choice in micromachining due to its excellent machinability and good electrical conductivity. It typically exhibits moderate corrosion resistance and can withstand moderate temperatures, making it suitable for various applications, including gears and electrical connectors. However, brass is not as strong as some other metals, which can limit its use in high-stress environments.
Pros and Cons of Using Brass
The advantages of brass include its ease of machining, which often results in lower manufacturing costs and shorter lead times. Its good electrical conductivity makes it ideal for electronic applications. On the downside, brass’s lower strength and durability compared to materials like stainless steel can be a limitation in demanding applications, potentially leading to premature failure.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Brass is compatible with various media, including water and air, making it suitable for plumbing and HVAC applications. For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 (for fittings) and DIN 50930-6 (for corrosion resistance) is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should also consider the availability of brass alloys and their specific grades.
How Does Stainless Steel Perform in Micro Machining Services?
Stainless steel is renowned for its strength, corrosion resistance, and durability, making it a preferred material in micromachining for applications in medical devices, aerospace, and automotive industries. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures enhances its suitability for critical components.
Pros and Cons of Using Stainless Steel
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its exceptional resistance to corrosion and wear, which extends the lifespan of components. However, its hardness can complicate the machining process, often resulting in higher manufacturing costs and longer lead times. Additionally, certain grades of stainless steel can be challenging to work with due to their toughness.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for medical and food applications. International buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A276 and JIS G4303 for various grades of stainless steel. Buyers from the Middle East may prioritize materials that can withstand high temperatures and humidity.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Micro Machining Services?
Aluminum is favored in micromachining for its lightweight properties, excellent corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity. These characteristics make it suitable for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries, where weight reduction is critical.
Pros and Cons of Using Aluminum
Aluminum’s primary advantage is its low density, which allows for the production of lightweight components. It is also relatively easy to machine, resulting in lower production costs. However, aluminum is less durable than steel and may not perform well in high-stress applications, which can limit its use in some sectors.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, but may not be suitable for highly corrosive environments without proper coatings. International buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions and DIN 17615 for aluminum alloys. Buyers from Europe may have specific preferences for aluminum grades based on their applications.
How Does Titanium Compare as a Material for Micro Machining Services?
Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications in aerospace, medical, and chemical processing industries. It can withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments, enhancing its versatility.
Pros and Cons of Using Titanium
The key advantage of titanium is its strength and resistance to corrosion, which makes it suitable for demanding applications. However, titanium is more challenging to machine than other metals, leading to higher costs and longer lead times. Its brittleness can also pose challenges in certain applications.
Impact on Application and Considerations for International Buyers
Titanium is compatible with a variety of media, including aggressive chemicals, making it ideal for specialized applications. International buyers must consider compliance with standards such as ASTM F136 for medical-grade titanium and DIN 3.7035 for industrial applications. Buyers from regions like Saudi Arabia may prioritize titanium for applications in oil and gas due to its resistance to corrosion.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Micro Machining Services
| Material | Typical Use Case for micro machining services | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Electrical connectors, gears | Excellent machinability | Lower strength compared to steel | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Medical devices, aerospace components | High corrosion resistance | Higher machining complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight | Less durable than steel | Medium |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher machining costs | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their micromachining projects. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will facilitate informed decision-making in selecting the right material for specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for micro machining services
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Micro Machining Services?
The manufacturing process for micro machining services involves several critical stages, each contributing to the precision and quality of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers, as it allows them to evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: How Is Material Selected and Prepared for Micromachining?
Material selection is paramount in micromachining, as the properties of the material directly impact the machining process and the quality of the final component. Common materials used in micromachining include stainless steel, aluminum, brass, titanium, and specialized alloys like Hastelloy and Inconel.
Once selected, materials undergo preparation, which may involve cutting them into manageable sizes, surface cleaning, and sometimes pre-treating to enhance machinability. This stage is crucial to ensure that the material can withstand the rigors of the machining process without compromising integrity.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Micro Machining?
The forming stage encompasses various techniques tailored to produce intricate designs with high precision. Key methods include:
-
CNC Micro Milling and Turning: These processes utilize advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines equipped with multi-axis capabilities to create complex geometries and features at the micrometer scale.
-
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): This technique is particularly effective for hard materials and intricate shapes. Micro EDM processes, such as Wire EDM and Sink EDM, use electrical discharges to erode material, achieving high precision.
-
Laser Micromachining: This method employs ultra-fast lasers to create features with exceptional resolution. It is ideal for applications requiring fine details or complex internal geometries.
How Is the Assembly Process Managed in Micro Machining Services?
In cases where components require assembly, micromachining services may also provide micro-assembly capabilities. This stage involves the careful integration of micro parts, often using automated systems to ensure precision. Advanced techniques such as ultrasonic welding or adhesive bonding may be employed to join components without adding significant bulk or weight.
What Finishing Techniques Enhance the Quality of Micro Machined Components?
The finishing stage is crucial for achieving the desired surface quality and dimensional accuracy. Techniques may include:
-
Electropolishing: This process enhances the surface finish and reduces friction, making it ideal for components used in medical and aerospace applications.
-
Coating and Plating: Various coatings may be applied to improve corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
-
Quality Checks: Before final delivery, components undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet all specified tolerances and surface finishes.
What Quality Control Measures Are Implemented in Micro Machining Services?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of micro machining services, ensuring that components meet international and industry-specific standards. Buyers should be aware of the various quality control measures employed throughout the manufacturing process.
Which International Standards Are Relevant for Micro Machining Services?
Adherence to international standards is vital for ensuring product quality and consistency. ISO 9001 is the foundational quality management standard, applicable across industries. Additionally, industry-specific standards, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, CE marking for compliance in Europe, and API standards for oil and gas components, may be relevant depending on the application.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch potential defects early. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, components undergo regular inspections to monitor adherence to tolerances and identify any deviations in real-time.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once manufacturing is complete, a thorough inspection is conducted. This may involve dimensional checks, surface finish evaluations, and functional testing.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential for ensuring reliable partnerships. Here are several strategies to assess supplier quality effectively:
What Types of Audits Should Buyers Conduct?
Buyers should conduct comprehensive audits of potential suppliers, focusing on their quality management systems, processes, and capabilities. This can include:
-
On-Site Audits: Visiting the manufacturing facility allows buyers to observe quality control practices firsthand and assess the equipment and processes in use.
-
Documentation Reviews: Requesting documentation related to quality management systems, certifications, and previous audit reports can provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality.
How Can Buyers Utilize Third-Party Inspections?
Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures. These agencies can conduct inspections at various stages of the manufacturing process, ensuring that components meet specified standards before shipment.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality control that may arise due to regional differences in regulations and standards. For instance, suppliers in Europe may be more accustomed to stringent CE marking requirements, while those in the Middle East may follow different compliance guidelines.
Additionally, understanding cultural attitudes toward quality and safety can help buyers navigate potential challenges in establishing effective communication and collaboration with suppliers.
Conclusion: How Do Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance Impact the Success of Micro Machining Services?
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in micro machining services are integral to delivering high-quality components that meet the stringent demands of modern industries. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product reliability.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘micro machining services’
Introduction
Sourcing micro machining services requires a methodical approach to ensure you partner with a supplier that meets your precise needs. This checklist provides a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the procurement process effectively, ensuring you select a vendor capable of delivering high-quality, intricate components critical to your operations.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for the components you need, including dimensions, tolerances, and materials. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for your project and enables suppliers to assess their capability to meet your requirements. Be specific about any industry standards or certifications your components must adhere to.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in micro machining. Look for companies with proven expertise in your industry, particularly those that have experience with similar projects. Utilize online directories, industry publications, and trade shows to gather a list of candidates.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Assess the capabilities of each supplier by requesting detailed information about their machining technologies and processes. Inquire about their equipment, such as CNC mills, EDM machines, and laser systems, as well as their ability to handle complex geometries. Understanding their technical capabilities will help you determine if they can meet your specific needs.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 13485 for medical devices. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality management and consistent production standards. Ask for documentation of their quality control processes and any third-party audits they have undergone.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a long-term commitment, request samples or prototypes of their work. This allows you to evaluate the quality of their machining and the precision of their components firsthand. Pay close attention to the surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall craftsmanship to ensure they align with your standards.
Step 6: Discuss Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Engage in discussions regarding lead times and production capabilities. It’s essential to understand how quickly a supplier can deliver your components, especially if you are working on tight deadlines. Ask about their production capacity and whether they can accommodate fluctuations in demand.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Set up clear communication channels with your chosen supplier. Effective communication is vital for addressing any issues or changes that may arise during the production process. Determine the preferred modes of communication and establish regular check-ins to ensure transparency and alignment throughout the project.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for micro machining services, ensuring you partner with a supplier that meets your technical requirements and quality standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for micro machining services Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Micromachining Services?
When evaluating the costs associated with micromachining services, several critical components must be considered. These include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Common materials such as aluminum, brass, and stainless steel may have varying costs based on market fluctuations and availability. Specialized materials like Hastelloy or Inconel can further elevate expenses due to their unique properties and processing requirements.
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for micromachining, as precision is paramount. Labor costs can vary based on the region and the complexity of the machining process. For instance, regions with higher labor costs may see increased prices for micromachining services.
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs of production, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Manufacturers often allocate a portion of these overhead expenses to each project, affecting the overall cost.
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools and machinery is substantial in micromachining. Tooling costs are typically amortized over the production volume, meaning lower costs per unit for larger orders.
Quality Control (QC): Given the precision required in micromachining, robust quality control processes are critical. The costs associated with testing and certification can contribute significantly to the overall pricing structure.
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are particularly important for international buyers. The location of the supplier and the destination can affect logistics expenses, especially if special handling is required for delicate micromachined components.
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on competition, demand, and the supplier’s market positioning.
How Do Volume and Customization Influence Micromachining Prices?
Volume and minimum order quantities (MOQs) play a substantial role in determining the pricing of micromachining services. Larger orders typically benefit from economies of scale, resulting in lower per-unit costs. Conversely, small orders may incur higher prices due to the fixed costs associated with setup and tooling.
Customization is another influential factor. Complex designs with intricate specifications often require additional time and resources, leading to increased costs. Buyers should be prepared to provide detailed specifications to receive accurate quotes.
What Role Do Material Quality and Certifications Play in Pricing?
The quality of materials used in micromachining directly impacts the final price. High-quality materials that meet industry standards are generally more expensive but can provide superior performance and reliability, especially in critical applications like medical devices or aerospace components.
Certifications, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, can also affect pricing. Suppliers with advanced quality management systems may charge a premium for their services, reflecting their commitment to maintaining stringent quality standards.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Micromachining Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance negotiation outcomes:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the initial price but the long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and potential failures. Investing in higher-quality components can lead to significant savings over time.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If feasible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs and negotiate better rates based on larger volumes.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should understand the impact of Incoterms on pricing, as they dictate who bears the costs and risks during shipping. Selecting favorable terms can lead to significant cost savings.
-
Request Multiple Quotes: Engaging with several suppliers can provide a clearer picture of the market and assist in identifying competitive pricing.
What Disclaimer Should Buyers Consider Regarding Pricing?
While the insights provided can guide B2B buyers in understanding the cost and pricing landscape for micromachining services, it is essential to note that prices can vary widely based on specific project requirements, supplier capabilities, and market conditions. Always request detailed quotes tailored to your unique needs to ensure accurate budgeting.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing micro machining services With Other Solutions
When considering the manufacturing of precision components, businesses often evaluate various solutions to meet their specific needs. Micro machining services are a popular choice for producing intricate parts, but several alternatives also exist. This analysis will compare micro machining services against two viable alternatives: traditional machining and additive manufacturing (3D printing). Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option can assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Micro Machining Services | Traditional Machining | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with tolerances in micrometers | Good precision, limited to larger parts | Variable precision, best for complex shapes |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced technology | Generally lower cost for larger runs | Cost-effective for low-volume production |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specialized skills and equipment | Well-established processes, easier to implement | Requires expertise in design and software |
| Maintenance | High maintenance for precision equipment | Moderate maintenance, depending on equipment | Low maintenance, but requires software updates |
| Best Use Case | Medical devices, aerospace components | General manufacturing, larger components | Prototyping, custom designs, and low-volume production |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Machining?
Traditional machining involves processes like turning, milling, and drilling to create parts from solid materials. One of the main advantages is its lower cost for producing larger components, making it suitable for high-volume runs. However, traditional machining is limited in its ability to produce very small or complex geometries, which can be a drawback for industries requiring high precision and intricate designs. Moreover, the implementation process is more straightforward, as it relies on established techniques familiar to many engineers and machinists.
How Does Additive Manufacturing Compare?
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, allows for the creation of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. It is particularly advantageous for rapid prototyping and custom designs, as it can quickly adapt to changes in specifications. The primary downside is that the precision can vary significantly based on the technology used, and it is generally not as precise as micro machining services. Additionally, while the initial setup can be costly, it becomes cost-effective for low-volume production runs.
How Should B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution?
When selecting the right manufacturing method, B2B buyers must consider their specific project requirements, including the desired precision, production volume, and budget constraints. Micro machining services excel in applications where high precision and intricate designs are paramount, such as in the medical and aerospace industries. Traditional machining might be the best fit for larger components produced in bulk. On the other hand, additive manufacturing offers flexibility and rapid prototyping capabilities, making it ideal for custom projects or when speed is essential. By thoroughly assessing these factors, buyers can make an informed decision that aligns with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for micro machining services
What are the Key Technical Properties of Micro Machining Services?
Understanding the essential technical properties of micromachining is crucial for B2B buyers seeking precision components. Here are several critical specifications that define the quality and applicability of micromachining services:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific classification of materials used in micromachining, such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and specialized alloys like Hastelloy. The choice of material affects not only the performance of the final product but also its suitability for various applications, such as aerospace or medical devices. Selecting the right material ensures durability, functionality, and compliance with industry standards.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance denotes the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. In micromachining, tolerances can be extremely tight, often in the range of ±0.001 mm or smaller. This is critical in applications where precision is paramount, such as in medical devices or micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS). Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers ensure that suppliers can meet their specific design needs.
3. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a component’s surface after machining. For micro components, achieving a fine surface finish is essential to prevent wear and ensure optimal performance, especially in high-friction applications. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to ensure that the produced components meet their operational criteria.
4. Dimensional Accuracy
Dimensional accuracy indicates how closely a machined part’s dimensions align with the specified measurements. In micromachining, achieving high dimensional accuracy is critical due to the small scale of components. This property is particularly important in industries like aerospace and medical, where even minor deviations can lead to significant performance issues.
5. Microstructure
Microstructure refers to the internal structure of a material, which can influence its properties and performance. In micromachining, understanding the microstructure is vital when selecting materials, as it affects strength, ductility, and resistance to wear and corrosion. This insight can guide B2B buyers in choosing the right materials for their specific applications.
What are Common Trade Terms in Micromachining Services?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in micromachining services. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of micromachining, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify suppliers who have the capability to produce parts that meet specific design criteria.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ represents the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to produce or sell. This term is crucial for buyers to understand as it can impact inventory management and cost efficiency. Knowing the MOQ helps companies plan their purchases according to production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quote)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a detailed quotation for specific services or products. For micromachining services, an RFQ typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. This process is vital for obtaining competitive pricing and ensuring that suppliers can meet project requirements.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Understanding these terms is essential for B2B transactions, as they clarify obligations concerning shipping, insurance, and risk during transit. This knowledge helps mitigate misunderstandings and disputes in international trade.
5. CAD (Computer-Aided Design)
CAD refers to the use of computer software to create precise drawings and technical illustrations. In micromachining, CAD files are crucial for producing accurate components. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can work with the necessary CAD formats to facilitate seamless communication and production.
Familiarizing yourself with these technical properties and trade terms will enhance your ability to navigate the complexities of micromachining services, enabling informed decision-making and effective supplier interactions.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the micro machining services Sector
What Are the Key Market Drivers Influencing Micro Machining Services?
The global demand for micro machining services is largely driven by advancements in technology across various sectors, including medical devices, aerospace, and telecommunications. As industries increasingly require smaller, more complex components with tighter tolerances, micromachining becomes essential for meeting these specifications. The proliferation of miniaturized electronics and the rise of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as automation and smart manufacturing, further amplify this need. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can deliver precision at scale, thus creating a competitive landscape where quality and reliability are paramount.
Emerging trends in sourcing include the adoption of advanced manufacturing techniques such as micro-EDM, laser micromachining, and 5-axis CNC milling. These technologies not only enhance precision but also enable the production of intricate geometries that were previously unattainable. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on end-to-end digital solutions, allowing buyers to engage in real-time collaboration with suppliers. This responsiveness and agility in the supply chain are vital in a market characterized by rapid technological changes and evolving customer demands.
How Is Sustainability Shaping the Micro Machining Services Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a key consideration for B2B buyers in the micro machining services sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes is under scrutiny, and companies are increasingly expected to adopt practices that minimize waste and reduce energy consumption. Buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and waste recycling protocols.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, with firms seeking to ensure their supply chains are transparent and socially responsible. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 13485 for quality in medical device manufacturing are becoming essential for gaining buyer trust. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials—such as biodegradable polymers and recyclable metals—can enhance a supplier’s marketability. For international buyers, particularly in regions where regulatory standards are tightening, aligning with sustainable suppliers can be a competitive advantage and a means to meet local compliance requirements.
What Is the Evolution of Micro Machining Services and Its Importance in Today’s Market?
The evolution of micro machining services can be traced back to the early advancements in precision engineering in the late 20th century. Initially focused on the aerospace and defense industries, micromachining has since expanded into diverse sectors such as healthcare, consumer electronics, and automotive. The advent of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology revolutionized the field, enabling the production of components with unprecedented accuracy and repeatability.
Today, micromachining services are not only about producing smaller parts but also about delivering complex functionalities within those parts. This evolution has been driven by the need for innovation in product design and manufacturing efficiency. For B2B buyers, understanding the historical context of micromachining underscores the importance of choosing suppliers with a proven track record and advanced capabilities, ensuring that they can meet the demands of modern engineering challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of micro machining services
-
How do I choose the right micromachining service provider for my project?
Choosing the right micromachining service provider requires assessing their technical capabilities, industry experience, and certifications. Look for companies that specialize in your specific application, whether it’s medical devices, aerospace, or electronics. Review their portfolio to understand their past projects and the precision they can achieve. Additionally, consider their ability to handle various materials and processes, such as micro EDM or laser micromachining. Lastly, verify their quality management systems, such as ISO certifications, to ensure they meet international standards. -
What are the typical lead times for micromachining services?
Lead times for micromachining services can vary based on project complexity, material availability, and production capacity. Generally, expect initial quotes within a few days, with production timelines ranging from a week to several weeks for more intricate designs. If you require rapid prototyping or have urgent deadlines, communicate this upfront to the supplier, as many offer expedited services. Establishing clear timelines and milestones in your contract can help ensure timely delivery and minimize delays. -
What materials can be processed using micromachining techniques?
Micromachining can accommodate a wide range of materials, including metals like stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium, as well as specialized alloys such as Hastelloy and Inconel. Additionally, some providers can work with non-metal materials like plastics and ceramics. When selecting a supplier, inquire about their material capabilities to ensure they can meet your specific requirements. Understanding the properties of these materials will also help in determining the best machining process to use. -
What customization options are available for micromachined components?
Most micromachining service providers offer extensive customization options to meet specific design requirements. This includes adjustments in dimensions, tolerances, surface finishes, and intricate geometries. Collaborating with your supplier during the design phase can help refine your specifications and ensure that they can produce components that align with your needs. Additionally, some companies offer design assistance or engineering support to optimize your product for manufacturability. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for micromachining services?
Minimum order quantities for micromachining services can vary significantly among suppliers. Some may accept small batch sizes, while others prefer larger orders to optimize production efficiency. When sourcing services, discuss your needs directly with the provider to understand their MOQ policies. Keep in mind that smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs, so factor this into your budgeting and overall project planning. -
What payment terms should I expect when working with micromachining suppliers?
Payment terms for micromachining services can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common arrangements include upfront deposits, milestone payments during production, or payment upon completion. International transactions may also involve considerations such as currency exchange rates and banking fees. It’s advisable to clarify payment terms early in the negotiation process to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth financial transactions. -
How do micromachining service providers ensure quality and precision?
Quality assurance in micromachining is typically upheld through rigorous quality management systems, such as ISO 13485 or ISO 9001 certifications. Providers often employ advanced inspection techniques, including coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and optical comparators, to verify dimensions and tolerances. Regular maintenance of machinery and adherence to strict operational protocols further contribute to consistent quality. Requesting detailed reports and inspections can provide additional assurance of the component’s integrity. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing micromachining services internationally?
When sourcing micromachining services internationally, consider factors such as shipping times, customs regulations, and import duties. Collaborate with your supplier to establish a clear logistics plan that includes timelines for delivery and potential delays. Additionally, ensure that the supplier is familiar with the regulatory standards of your country, particularly if your components are for regulated industries like medical or aerospace. Having a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the shipping process and ensure timely receipt of your components.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Micro Machining Services Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Owens Industries – Precision Micromachining Services
Domain: owensind.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Owens Industries offers a nationwide precision micromachining service specializing in the CNC micromachining of complex small components. Their services include ultra-precision micromachining for medium-sized components, with a focus on strict tolerances. The micromachining process utilizes specialized tools such as micro-drills and micro-lathes to produce parts with dimensions in the micrometer r…
2. IMC Intertech – Micromachining Services
Domain: imcintertech.com
Registered: 2003 (22 years)
Introduction: Micromachining Services offered by IMC Intertech include: 1. Micro Milling & Turning – Utilizing CNC equipment for precise components. 2. Micro EDM Services – Creating intricate shapes on conductive materials with high accuracy. 3. Laser Micromachining Services – Manufacturing small features using ultra-fast laser beams for high resolution. 4. Micro Assembly Services – Expertise in micro manufactu…
3. Swissomation – Precision Micro-Machining Services
Domain: swissomation.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Micro-Machining services at Swissomation focus on precision machining with capabilities to produce parts as small as .004″ in diameter up to 1.625″ in diameter. The company utilizes state-of-the-art CNC Swiss machines that can perform multiple operations, reducing the need for secondary processing. They offer tolerances as tight as +/- .0001 and can handle materials including aluminum, beryllium c…
4. Microtec – Precision Micromachining Services
Domain: microtec-machining.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Microtec offers precision micromachining services, focusing on the production of tiny, accurate components and parts. The company has extensive experience in micromachining and continuously updates its facilities and equipment to maintain high quality standards. Their CNC machining workshop is equipped with advanced technology for precise micromachining, catering to both short and long run quantit…
5. EDM Intelligent Solutions – Precision Micro Milling Services
Domain: edmdept.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Precision Micro Milling Services offered by EDM Intelligent Solutions include: 3-Axis CNC mills capable of cutting tools smaller than a human hair, with precision tolerances as tight as 0.0002″ (2-3µm micron). The micro milling process utilizes advanced thermal controls, ultra-responsive servo motors, and high-speed motorized spindles to achieve micron level accuracy and superior surface finishes….
6. HyTech Spring – Precision Micro Machining
Domain: hytechspring.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: HyTech Spring and Machine Corp specializes in CNC micromachining services for the production of extremely small parts and miniature components. Key offerings include precision micro wire components with wire diameters ranging from .0015″ to .500″. The company utilizes advanced CNC technology including 4-axis vertical and horizontal milling, 7-axis Swiss turning, vacuum table machining systems, and…
7. KMM Group – CNC Precision Machining Services
Domain: kmmgrp.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: CNC Precision Machining Services including:
– Vertical Precision Machining (Milling):
– Ultra-precision CNC vertical milling with tolerances as low as 2.5 microns.
– 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling.
– Finishes to < 8 Ra.
– Envelope size: up to 41.3” x 31.5” x 11.86”.
– Ultra-precision wire EDM tolerances <.0001”.
– B-axis (Rotary) for 6-axis ‘Turn and Burn’.
– Robotic load…
8. Potomac Photonics – Laser Micromachining Services
Domain: potomac-laser.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Potomac Photonics offers laser micromachining services for a variety of materials including polymers, metals, ceramics, and glass. They utilize a range of laser sources from deep UV excimer to Nd:YAG lasers, with wavelengths including 193nm, 248nm, 266nm, 355nm, 532nm, 1064nm, and 10600nm. Their services include micro hole drilling, laser cutting, micro laser welding, and laser marking. They speci…
9. EPTAM Precision – Micro-Machining Solutions for Medical Devices
Domain: eptam.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: EPTAM Precision specializes in micro-machining for custom medical device components, focusing on implantable components for orthopedic, cardiovascular, vascular, endovascular, and pelvic health sectors. Their operations support Robot Assisted Surgery (RAS) and Minimally Invasive Surgery (MIS). The facility is FDA-registered and ISO 13485 certified, emphasizing a strong quality system. Key technolo…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for micro machining services
As the global demand for precision-engineered micro components surges, strategic sourcing in micromachining services becomes increasingly crucial for businesses across various sectors. With advancements in technology, including micro EDM, laser micromachining, and multi-axis CNC machining, companies can achieve unparalleled accuracy and efficiency in producing intricate parts. This not only enhances product quality but also reduces lead times and costs, allowing organizations to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, engaging with reliable micromachining service providers can unlock new opportunities for innovation and growth. Establishing partnerships with experienced manufacturers ensures access to advanced capabilities and materials, which are essential for meeting stringent industry standards, especially in sectors like medical and aerospace.
Looking ahead, the micromachining landscape is poised for further evolution, driven by continuous technological advancements and a growing emphasis on sustainability. Now is the time for businesses to leverage these trends by strategically sourcing micromachining services that align with their unique needs. Don’t hesitate to explore your options—connect with industry leaders today to enhance your operational efficiency and foster innovation in your product offerings.