Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for micro injection moulding machines
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing micro injection moulding machines presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers aiming to produce high-precision components efficiently. As global markets expand, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the need for reliable, cost-effective, and technologically advanced solutions becomes paramount. This guide is designed to equip international buyers with essential insights into the diverse types of micro injection moulding machines available, their applications across various industries, and critical factors for supplier vetting.
From understanding the nuances of different machine specifications to evaluating production capabilities and cost considerations, this comprehensive resource empowers decision-makers to navigate the complexities of sourcing micro injection moulding technology. Whether you are a manufacturer seeking to enhance your production line or a startup looking to innovate with custom plastic parts, the insights provided here will enable informed purchasing decisions.
Moreover, with an emphasis on the latest advancements in micro injection moulding technology, this guide addresses common pain points, such as precision, efficiency, and scalability, ensuring that your investment aligns with your operational goals. Dive into the world of micro injection moulding and discover how to leverage these machines to meet your production needs effectively and sustainably.
Understanding micro injection moulding machines Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop Micro Injection Molders | Compact design, user-friendly interface, low production volume | Prototyping, small-scale production | Pros: Affordable, easy to use. Cons: Limited production capacity. |
| All-Electric Micro Injection Machines | High precision, energy-efficient, low maintenance | Medical devices, electronics | Pros: High precision, consistent quality. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| Hybrid Injection Molding Machines | Combines electric and hydraulic systems for flexibility | Automotive components, consumer goods | Pros: Versatile, adaptable to various materials. Cons: Complexity in operation. |
| Micro Injection Units | Specialized for tiny parts, FIFO melt preparation | Micro-components, specialized applications | Pros: Optimized for small shots, high precision. Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Turnkey Micro Production Systems | Fully automated, integrates multiple processes | High-volume production, complex assemblies | Pros: Streamlined operations, reduced labor costs. Cons: Significant upfront costs. |
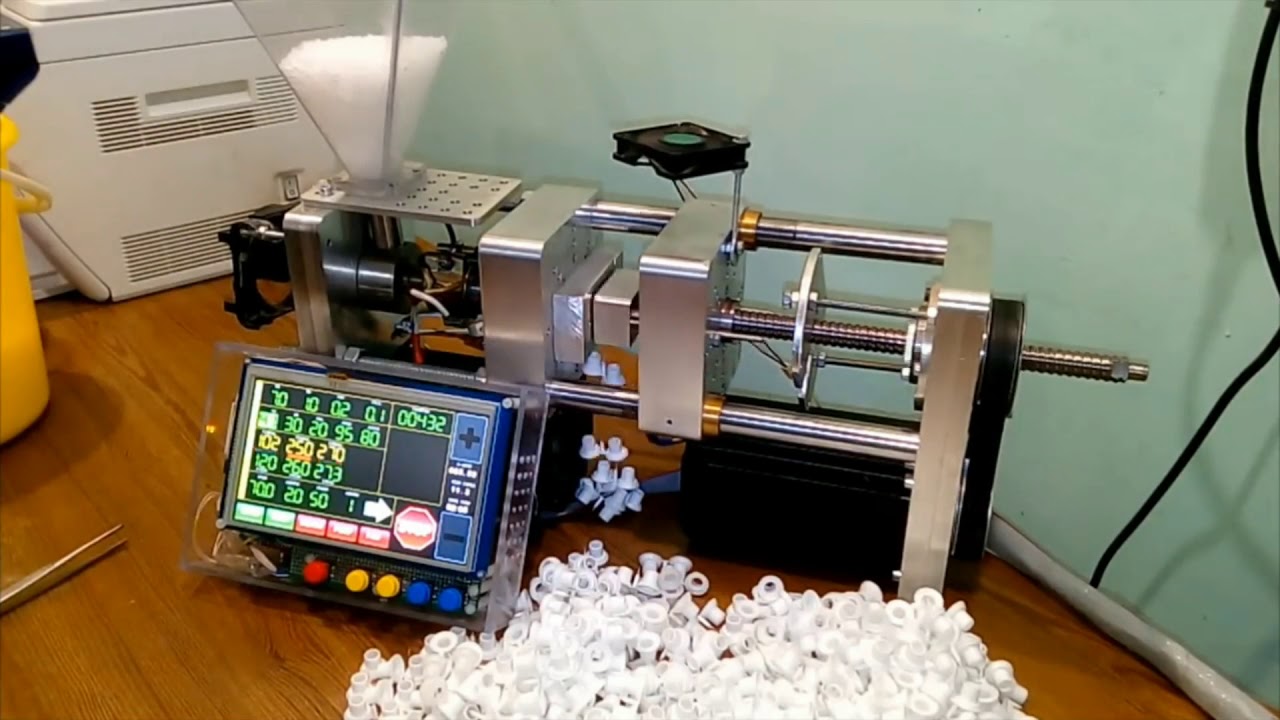
What Are Desktop Micro Injection Molders and Their Benefits?
Desktop micro injection molders are compact, automated machines designed for small-scale production. They typically feature user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible for hobbyists and small businesses. Ideal for prototyping and low-volume manufacturing, these machines allow for rapid iteration and customization of plastic parts. However, their limited production capacity may not meet the demands of larger operations, making them best suited for niche applications.
How Do All-Electric Micro Injection Machines Stand Out?
All-electric micro injection machines are renowned for their precision and energy efficiency. Utilizing direct-drive technology, they offer tight dimensional tolerances and minimal maintenance needs. These machines are particularly favored in industries like medical devices and electronics, where high-quality standards are crucial. While they provide exceptional repeatability, the higher initial investment can be a barrier for some buyers, necessitating a careful evaluation of long-term ROI.
What Are the Advantages of Hybrid Injection Molding Machines?
Hybrid injection molding machines combine electric and hydraulic systems, providing flexibility in production. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, including automotive components and consumer goods. Their adaptability allows manufacturers to work with various materials and mold designs. However, the complexity of operation may require specialized training, which can be a consideration for companies looking to integrate these machines into their workflow.
Why Choose Micro Injection Units for Specialized Applications?
Micro injection units are tailored for producing tiny components, utilizing a first-in, first-out (FIFO) melt preparation process. This technology ensures consistent quality and precision for micro-components used in specialized applications. Industries such as electronics and micro-mechanics benefit from these machines, although they often require skilled operators to maximize their capabilities. Buyers must consider the training and expertise needed for optimal operation.
What Are Turnkey Micro Production Systems and Their Impact on Efficiency?
Turnkey micro production systems offer a fully automated solution that integrates multiple processes, enhancing production efficiency. These systems are ideal for high-volume manufacturing and complex assemblies, significantly reducing labor costs and cycle times. While they streamline operations, the initial investment can be substantial. Companies must weigh the benefits of automation against upfront costs to determine if this option aligns with their production goals.
Key Industrial Applications of micro injection moulding machines
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of micro injection moulding machines | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Devices | Production of micro components for diagnostic equipment | High precision and compliance with regulations | Need for clean-room capabilities and materials certifications |
| Electronics | Manufacturing tiny connectors and housings | Enhanced durability and reduced assembly time | Compatibility with various thermoplastics and quick turnaround |
| Automotive | Creation of micro parts for sensors and switches | Improved efficiency and performance of vehicles | Robust machinery for high-volume production and precision |
| Consumer Products | Production of intricate designs for cosmetic packaging | Customization options and aesthetic appeal | Flexibility in tooling and the ability to handle colorants |
| Telecommunications | Molding of small components for mobile devices | Lightweight and compact parts for better design | Adaptability to different polymers and automated production |
How Are Micro Injection Moulding Machines Used in Medical Devices?
In the medical sector, micro injection moulding machines are crucial for producing small, intricate components used in diagnostic equipment, surgical instruments, and drug delivery systems. These machines enable the creation of parts with extremely tight tolerances, ensuring functionality and safety. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing machines with clean-room capabilities and materials that meet strict regulatory standards is essential to ensure compliance and product reliability.
What Role Do Micro Injection Moulding Machines Play in Electronics?
Micro injection moulding is widely utilized in the electronics industry for manufacturing tiny connectors, housings, and other essential components. This technology allows for the production of durable, lightweight parts that can significantly reduce assembly times and improve overall product performance. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should focus on sourcing machines that can handle a variety of thermoplastics and offer fast production cycles, thereby enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
How Are Micro Injection Moulding Machines Beneficial for Automotive Applications?
In the automotive sector, micro injection moulding machines are instrumental in creating micro components for sensors, switches, and other critical systems. The precision offered by these machines leads to improved efficiency and performance of vehicles, as well as reduced weight. B2B buyers in regions like Brazil and Nigeria should consider sourcing equipment that supports high-volume production while ensuring the durability and reliability of the parts produced.
Why Are Micro Injection Moulding Machines Important for Consumer Products?
Micro injection moulding machines are essential for producing detailed designs in cosmetic packaging and other consumer products. These machines provide customization options, enabling businesses to create unique and aesthetically appealing packaging solutions. For international buyers, flexibility in tooling and the ability to incorporate colorants into the production process are key factors to consider when sourcing machinery for this application.
How Do Micro Injection Moulding Machines Enhance Telecommunications Manufacturing?
In telecommunications, micro injection moulding is employed to mold small components for mobile devices, such as housings and connectors. The lightweight and compact nature of these parts contributes to better overall device design and functionality. Buyers should seek machines that offer adaptability to different polymers and automation capabilities to streamline production, particularly in competitive markets across Africa and South America.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘micro injection moulding machines’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Precision and Tolerances in Micro Parts Production
The Problem: B2B buyers often face difficulties in achieving the required precision and dimensional tolerances when manufacturing micro parts. Industries such as medical technology and electronics demand extremely tight tolerances, sometimes within microns. Buyers may struggle with inconsistent quality, leading to increased scrap rates and production costs. This challenge becomes particularly pronounced when dealing with complex geometries or when switching between different materials, which can affect the melting and flow characteristics during the injection process.
The Solution: To overcome these precision challenges, it is essential to invest in advanced micro injection moulding machines that feature state-of-the-art control systems and precision components. Buyers should look for machines equipped with technologies such as closed-loop control systems and high-precision injection units. For example, machines like Sumitomo (SHI) Demag’s SE7M series utilize advanced servo motor technology to achieve high levels of repeatability and precision. Additionally, implementing regular maintenance schedules and calibration checks can help ensure that the machines operate within their specified tolerances consistently. Buyers should also consider collaborating with manufacturers who provide comprehensive training and support, enabling their teams to optimize machine settings for different materials and geometries effectively.
Scenario 2: Inefficient Production Cycles Affecting Time-to-Market
The Problem: Many businesses experience prolonged production cycles, hindering their ability to respond quickly to market demands. This inefficiency can stem from outdated machinery, slow cycle times, and manual setups that require excessive downtime. For companies aiming to introduce new products rapidly, this delay can result in lost opportunities and reduced competitive advantage, particularly in fast-paced industries such as consumer electronics and automotive components.
The Solution: To enhance production efficiency, businesses should evaluate their current micro injection moulding setups and consider upgrading to all-electric machines designed for speed and reliability. Modern machines often feature optimized cycle times due to faster clamping and injection processes. For instance, the ARBURG ALLROUNDER series allows for the integration of automation systems that can streamline the entire production workflow, from mold setup to part removal. Investing in automation not only reduces manual intervention but also increases throughput. Additionally, implementing lean manufacturing principles, such as continuous flow and just-in-time production, can significantly reduce lead times and improve responsiveness to market changes.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Material Compatibility and Processing
The Problem: A common pain point for B2B buyers is the limited compatibility of micro injection moulding machines with various materials. Different applications may require specialized materials, such as liquid silicone rubber (LSR) or high-performance engineering plastics. Buyers often find themselves constrained by their machines’ capabilities, leading to challenges in product development and increased costs due to the need for multiple machines or extensive retooling.
The Solution: To address material compatibility issues, buyers should prioritize machines that offer a modular design and the flexibility to process a wide range of materials. For example, the MicroMolder series allows users to customize their setups easily, accommodating various thermoplastics and additives, including colorants for custom blends. Furthermore, buyers should engage with suppliers who have expertise in material science and can provide guidance on optimizing processing parameters for different materials. Conducting pilot runs and utilizing simulation software can also help in understanding material behavior during the injection process, ensuring that the chosen materials meet performance requirements without compromising production efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for micro injection moulding machines
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
Micro injection moulding machines require materials that can withstand specific performance demands. Here, we analyze four commonly used materials in this context: Polypropylene (PP), Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), Polycarbonate (PC), and Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR). Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that B2B buyers should consider, especially in diverse international markets.
What Are the Key Properties of Polypropylene (PP) in Micro Injection Moulding?
Polypropylene is a versatile thermoplastic known for its excellent chemical resistance and low density. It has a temperature rating of up to 100°C and can withstand moderate pressure. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for applications involving various chemicals.
Pros & Cons: PP is durable and cost-effective, making it a popular choice for mass production. However, it has lower impact resistance compared to other materials, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, its manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for specific mould designs.
Impact on Application: PP is compatible with a range of media, including acids and bases, making it suitable for containers and automotive parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM and DIN, particularly for food-grade applications.
How Does Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) Perform in Micro Injection Moulding?
ABS is a widely used engineering plastic known for its strength, toughness, and impact resistance. It can handle temperatures up to 80°C and has good dimensional stability under pressure.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of ABS is its excellent surface finish and ease of machining, making it ideal for aesthetic applications. However, it is less resistant to UV light and can degrade over time when exposed to sunlight, which may limit its outdoor applications.
Impact on Application: ABS is commonly used in consumer electronics and automotive components due to its aesthetic appeal and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for ABS quality across regions, particularly in Europe where stricter regulations may apply.
What Are the Key Features of Polycarbonate (PC) in Micro Injection Moulding?
Polycarbonate is known for its high impact resistance and optical clarity, making it suitable for applications requiring transparency. It can withstand temperatures up to 130°C and has excellent dimensional stability.
Pros & Cons: The major advantage of PC is its toughness and ability to withstand high temperatures, which makes it ideal for safety applications like eyewear and protective equipment. However, it is more expensive than PP and ABS, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application: PC’s optical properties allow for use in lenses and light covers, making it a preferred choice for the electronics and automotive sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with safety standards, such as those set by the European Union for optical materials, is crucial for B2B buyers in Europe.
How Does Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) Fit into Micro Injection Moulding?
LSR is a unique material known for its flexibility, high-temperature resistance, and biocompatibility. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -60°C to 200°C, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Pros & Cons: LSR offers exceptional durability and is ideal for medical applications due to its biocompatibility. However, the cost of LSR is relatively high, and the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: LSR is widely used in medical devices, automotive seals, and kitchenware due to its flexibility and safety.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that their LSR products meet local medical and safety standards, which can vary significantly between regions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Micro Injection Moulding Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for micro injection moulding machines | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Containers, automotive parts | Excellent chemical resistance | Lower impact resistance | Low |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer electronics, automotive components | Good surface finish | Degrades under UV exposure | Medium |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Safety eyewear, light covers | High impact resistance | More expensive than PP and ABS | High |
| Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) | Medical devices, automotive seals | Biocompatible and flexible | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their micro injection moulding processes. Understanding the properties, advantages, and market considerations of each material will help in making informed purchasing decisions tailored to specific applications and regional requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for micro injection moulding machines
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
Micro injection moulding machines are intricate devices that require precise manufacturing processes to ensure high-quality output. The typical manufacturing process can be broken down into several main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting the right thermoplastics or liquid silicone rubber (LSR). Materials must be compatible with micro injection moulding techniques and capable of achieving the desired mechanical properties. Advanced material preparation techniques, such as optimized plastification, ensure a homogeneous melt, which is crucial for producing parts with tight tolerances. This may involve using specialized screws and heaters to maintain consistent temperature profiles. -
Forming
The forming stage is where the actual injection takes place. The process utilizes precision-engineered components, such as multi-zone heated injectors, to inject the molten material into custom-designed molds. Technologies like the first-in, first-out (FIFO) principle are essential in this stage to minimize residence times and ensure uniform melt preparation. This results in high-quality micro-components that meet stringent specifications. -
Assembly
Once the components are formed, they undergo assembly. This stage may include integrating additional features, such as ejector pins or inserts, depending on the complexity of the parts produced. Automation plays a crucial role in this stage, with robotic systems often employed to enhance efficiency and reduce human error. For example, systems like the MULTILIFT H robotic technology can streamline the assembly process by automating part removal and placement. -
Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that may include trimming, surface treatment, and quality inspection. Finishing techniques are vital to ensure that the components meet the aesthetic and functional requirements. Advanced finishing methods can also improve adhesion for subsequent coatings or treatments.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into Micro Injection Moulding Machine Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is an essential aspect of manufacturing micro injection moulding machines, ensuring that each unit meets international and industry-specific standards. Key elements of QA include adherence to standards like ISO 9001, regular inspections, and various testing methods throughout the production cycle.
-
International Standards for Quality Assurance
Compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 is crucial for B2B buyers. This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system, focusing on enhancing customer satisfaction and ensuring consistent quality in products and services. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be necessary, particularly for machines intended for use in regulated industries. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process, typically categorized into three main types:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify and rectify issues in real-time, reducing the risk of defects.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection stage ensures that the completed machines meet all design specifications and quality standards before delivery. -
Common Testing Methods for Quality Assurance
Various testing methods are employed to verify the performance and reliability of micro injection moulding machines. These may include:
– Dimensional Testing: Ensuring that parts meet specified tolerances using precise measuring tools.
– Functional Testing: Evaluating the machine’s operational capabilities and efficiency under real-world conditions.
– Durability Testing: Assessing how well the machine performs over extended periods or under stress.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital for ensuring reliable partnerships.
-
Conducting Audits
One effective way to verify a supplier’s quality control processes is through on-site audits. These audits can provide insight into the supplier’s operations, including their adherence to international standards and their internal quality management practices. During an audit, buyers can assess documentation, observe processes, and evaluate the overall environment. -
Reviewing Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed quality reports that document their QA processes, including any certifications obtained, inspection results, and corrective actions taken in case of defects. Buyers should look for transparency in these reports, as they reflect the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of verification. These independent organizations can conduct thorough assessments of the supplier’s quality control measures and provide unbiased reports on compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances to ensure they receive high-quality micro injection moulding machines. Key considerations include:
-
Understanding Regional Standards
Different regions may have specific standards and regulations that need to be met. For example, CE marking is crucial for products sold in the European Union, while local certifications may be required in Africa or South America. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these standards to ensure compliance. -
Cultural and Communication Factors
Effective communication with suppliers is essential to establish clear expectations regarding quality standards. Buyers should consider cultural differences that may impact how quality is perceived and addressed. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better understanding and adherence to quality expectations. -
Ongoing Monitoring and Feedback
Establishing a system for ongoing monitoring and feedback can help maintain quality over time. Regular evaluations and open lines of communication can ensure that suppliers remain aligned with buyers’ quality expectations, addressing any issues before they escalate.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for micro injection moulding machines is crucial for B2B buyers. By paying attention to each stage of production and the relevant quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions and establish successful partnerships in this specialized industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘micro injection moulding machines’
When sourcing micro injection moulding machines, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of technical requirements, supplier capabilities, and market dynamics. This guide provides a practical checklist to help you make informed purchasing decisions and ensure you acquire the right machinery for your production needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before exploring suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. Consider factors such as the size and weight of parts you intend to produce, the types of materials you will use, and the desired production speed. Having specific criteria will help you identify machines that match your operational needs and avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Technologies
Stay informed about the latest advancements in micro injection moulding technology. Understanding current trends, such as automation capabilities, precision control systems, and energy efficiency, can provide you with insights into which features will add value to your production. This knowledge also helps in negotiating with suppliers by allowing you to ask informed questions regarding their offerings.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers to ensure they can meet your requirements. Look for established companies with a proven track record in micro injection moulding. Request case studies, client testimonials, and references, particularly from companies in similar industries or regions. This evaluation process is critical for assessing the reliability and quality of the machines offered.
- Check certifications: Ensure the supplier complies with international standards such as ISO 9001.
- Review after-sales support: Inquire about warranty terms, training, and maintenance services.
Step 4: Request Detailed Proposals
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request detailed proposals that include technical specifications, pricing, delivery timelines, and payment terms. A comprehensive proposal allows for easy comparison between different suppliers and helps you assess the total cost of ownership, including installation and potential operational costs.
Step 5: Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Analyze the cost implications of each proposal against the expected benefits. Consider not only the initial purchase price but also factors such as energy consumption, potential downtime, and maintenance costs. A machine that appears cheaper upfront may incur higher long-term costs if it lacks efficiency or requires frequent repairs.
Step 6: Assess Training and Support Options
Evaluate the training and support services offered by the supplier. Proper training for your staff is essential to maximize the machine’s capabilities and ensure safe operation. Suppliers that provide comprehensive training programs and ongoing technical support can significantly enhance your production efficiency.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase and Negotiate Terms
Once you have selected a supplier, finalize your purchase agreement while negotiating favorable terms. This may include payment plans, delivery schedules, and warranty extensions. A well-structured agreement can safeguard your investment and establish a strong partnership with the supplier for future needs.
By following this checklist, you can streamline your sourcing process for micro injection moulding machines, ensuring that you make a well-informed decision that supports your business objectives.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for micro injection moulding machines Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
When considering the sourcing of micro injection moulding machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of thermoplastics, which can range from general-purpose plastics like Polypropylene to specialized engineering plastics, significantly impacts costs. Higher-grade materials usually entail increased prices due to their enhanced properties.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the region and the level of expertise required for machine operation and maintenance. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but skilled labor for precise operations might still be a consideration.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production environment, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Machines designed for high precision and automation typically have higher overhead due to advanced technology and maintenance needs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is often necessary for specific applications. The initial investment in molds and tooling can be significant, but it’s essential for achieving desired part specifications and quality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures adds to the cost but is vital for ensuring product reliability and compliance with international standards, particularly for buyers in regulated industries.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can escalate depending on the machine size and weight, as well as the distance from the supplier. International shipping may involve additional fees, including tariffs and insurance.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin, which can vary based on market demand and competition. Understanding the balance between quality and cost is essential for negotiation.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Micro Injection Moulding Machine Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of micro injection moulding machines, which B2B buyers must consider:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can impact pricing. Larger orders often qualify for volume discounts, making it essential for buyers to assess their production needs against their purchasing capabilities.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications, such as advanced control systems or specialized materials, can lead to higher costs. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials chosen for production have a direct effect on pricing. Buyers should evaluate the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality materials versus lower-cost alternatives.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that comply with specific international standards or certifications may come at a premium. Buyers in regulated markets should prioritize these features despite the higher upfront costs.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, location, and operational efficiency can impact pricing. Established suppliers may offer better reliability and service but could command higher prices.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms agreed upon in the contract will clarify who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and duties, which can significantly affect the total price.
What Are the Best Negotiation Tips for Buyers of Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
To achieve cost efficiency and maximize value, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime, which can significantly affect long-term expenses.
-
Leverage Multiple Quotes: Request quotes from multiple suppliers to compare not only prices but also the quality and features of the machines. This competitive approach can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms, including payment schedules, delivery timelines, and warranty conditions. Flexibility in these areas can lead to better overall terms.
-
Consider Long-Term Partnerships: Building a long-term relationship with a supplier may yield benefits such as better pricing, priority service, and access to the latest technology.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that may influence the overall cost structure.
Disclaimer
Prices for micro injection moulding machines can vary significantly based on the factors outlined above. The information provided here is indicative and should be verified with suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to specific requirements and conditions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing micro injection moulding machines With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives in Micro Injection Moulding
In the landscape of manufacturing, particularly for small and intricate plastic components, micro injection moulding machines stand out for their precision and efficiency. However, there are several alternative solutions that buyers should consider, each offering unique advantages and potential drawbacks. This analysis will compare micro injection moulding machines with two viable alternatives: 3D printing and traditional injection moulding.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Micro Injection Moulding Machines | 3D Printing | Traditional Injection Moulding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and repeatability | Moderate precision, variable quality | High volume, consistent quality |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Lower initial cost but higher per-part cost | High initial investment, cost-effective for large runs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled setup and operation | User-friendly, less training needed | Complex setup, requires specialized training |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for precision | Low maintenance, mainly software updates | High maintenance, especially for molds |
| Best Use Case | High precision small parts | Prototyping and small runs | Large volume production |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
3D Printing: What Are Its Advantages and Disadvantages?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, offers a flexible and cost-effective solution for producing small parts, especially during prototyping phases. Its ease of implementation means that even businesses with limited technical expertise can start using it quickly. However, the trade-off comes in the form of variable quality and moderate precision, making it less suitable for high-volume production runs where consistency is critical. Additionally, while initial costs may be lower, the per-part cost can become significant as production scales up.
Traditional Injection Moulding: When Is It the Best Choice?
Traditional injection moulding is a well-established method for producing large quantities of plastic parts. It excels in high-volume production scenarios where consistent quality and low per-unit costs are paramount. However, the initial investment in molds and machinery can be substantial, and the setup process is complex, requiring skilled personnel. Maintenance can also be demanding, particularly for the molds used, which may need frequent repairs or replacements. This method is best suited for businesses that require high output and can afford the upfront costs.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When evaluating whether to invest in micro injection moulding machines or consider alternatives like 3D printing or traditional injection moulding, B2B buyers should carefully assess their specific production needs. Key factors include the required precision, volume of parts needed, budget constraints, and available technical expertise. For businesses focusing on high precision and small part production, micro injection moulding machines often represent the best choice. Conversely, for those needing flexibility in design and lower initial investment, 3D printing may be more appropriate. Lastly, companies that anticipate high volume production should consider traditional injection moulding despite its higher initial costs, as it can lead to significant savings in the long run.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for micro injection moulding machines
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
Micro injection moulding machines are designed for producing small, intricate components with high precision. Understanding their technical specifications is crucial for B2B buyers who aim to optimize production and ensure product quality. Here are some essential properties:
1. Material Compatibility
Micro injection moulding machines are compatible with a variety of thermoplastics, including engineering plastics like ABS, Polycarbonate, and Polypropylene. This versatility allows manufacturers to select materials that best meet their product requirements, such as durability, flexibility, or temperature resistance. For B2B buyers, understanding material compatibility can help in choosing the right machine for their specific applications, ultimately leading to cost savings and increased product performance.
2. Shot Weight
The shot weight refers to the volume of plastic that can be injected into a mold in a single cycle. Micro injection moulding machines typically handle shot weights of less than one gram. This is particularly important for industries such as medical devices and microelectronics, where precision and miniaturization are critical. Buyers should assess their production needs to select machines that can efficiently handle the required shot weight, ensuring optimal production rates without sacrificing quality.
3. Dimensional Tolerance
Dimensional tolerance indicates how closely a finished part can match its specified dimensions. Micro injection moulding machines offer extremely tight tolerances (often within ±0.01 mm), which is vital for applications where precision is paramount. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications can directly influence part performance and reliability, affecting customer satisfaction and compliance with industry standards.
4. Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time taken to complete one production cycle, from injection to cooling and ejection. Micro injection moulding machines are engineered to achieve short cycle times, often as low as 10-30 seconds. This efficiency is crucial for maximizing productivity and minimizing operational costs. B2B buyers should evaluate the cycle time of machines to ensure they can meet their production demands while maintaining quality.
5. Control Systems
Advanced control systems, such as those utilizing servo motors and digital sensors, allow for precise monitoring and adjustment of the injection process. This enhances repeatability and consistency in production. For buyers, understanding the capabilities of these control systems can lead to improved operational efficiency and reduced waste, ultimately translating to better profit margins.
What Are Common Trade Terms Associated with Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce equipment or components that are used in another company’s end product. In micro injection moulding, OEMs often provide specialized parts for various industries, including automotive and electronics. B2B buyers should consider OEM partnerships to ensure high-quality components that meet specific standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is critical for buyers as it impacts inventory management and production planning. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses negotiate better terms and ensure they have enough stock to meet demand without overcommitting resources.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific quantities of goods or services. For buyers, issuing an RFQ is essential for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding supplier capabilities, enabling informed decision-making.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms used in international sales contracts that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers involved in cross-border transactions, as they clarify who bears the risk at different stages of the shipping process.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time it takes from placing an order until the goods are delivered. Understanding lead times is vital for B2B buyers to effectively manage supply chains and meet production schedules, thus avoiding delays that could impact customer satisfaction.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in micro injection moulding machines, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the micro injection moulding machines Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Micro Injection Moulding Machines?
The global market for micro injection moulding machines is witnessing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for precision components across various industries, including medical technology, electronics, and automotive. The rise of miniaturization in product design has led to a surge in the need for micro components that require high precision and reliability. Emerging technologies such as automation and smart manufacturing are reshaping the landscape, with manufacturers increasingly adopting advanced features like modular designs and integrated robotics to enhance productivity and reduce cycle times.
International B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are seeking to capitalize on these trends by sourcing machines that offer flexibility and adaptability. For instance, machines that can accommodate different materials and allow for customization are becoming increasingly popular. Buyers are also looking for cost-effective solutions, as the entry of desktop micro moulding machines democratizes access to high-precision manufacturing, making it feasible for small businesses and startups to enter the market.
Furthermore, the industry is experiencing a shift towards sustainability, with an emphasis on eco-friendly practices and materials. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions and are prioritizing suppliers that align with their sustainability goals. This trend is not only a response to regulatory pressures but also a market expectation, as end consumers increasingly prefer products from companies with strong environmental credentials.
How Is Sustainability Shaping Sourcing in the Micro Injection Moulding Sector?
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of micro injection moulding machines. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted buyers to seek solutions that minimize their carbon footprint. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient machines and sourcing materials responsibly.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining traction, with buyers emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in their sourcing decisions. This includes ensuring that materials are sourced from suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the use of recycled or bio-based materials in production processes are becoming important criteria for selecting suppliers.
In addition, companies are exploring innovative materials that reduce environmental impact, such as biodegradable plastics and eco-friendly additives. As the demand for sustainable products continues to rise, buyers in the micro injection moulding sector are increasingly looking for partners who can provide not only high-quality machines but also contribute to their sustainability objectives.
What Is the Historical Context of Micro Injection Moulding Machines for B2B Buyers?
The evolution of micro injection moulding machines can be traced back to the late 20th century when the need for smaller, more precise components began to emerge. Initially, traditional injection moulding machines were adapted to produce smaller parts, but this approach often resulted in inefficiencies and quality issues.
As industries such as electronics and medical devices evolved, the demand for specialized equipment that could produce micro components with high precision and repeatability led to the development of dedicated micro injection moulding machines. Over the years, advancements in technology have allowed for increased automation, improved control systems, and the integration of clean-room capabilities, making these machines indispensable for modern manufacturing processes.
Today, micro injection moulding machines are at the forefront of innovation, enabling businesses to meet the challenges of miniaturization while maintaining the highest standards of quality and sustainability. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial in making informed sourcing decisions that align with both current needs and future trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of micro injection moulding machines
-
How do I choose the right micro injection moulding machine for my production needs?
When selecting a micro injection moulding machine, consider factors such as the size and complexity of the parts you intend to produce, the materials you will use, and your production volume. Evaluate the machine’s precision, cycle times, and whether it can accommodate multi-cavity molds. Additionally, check the machine’s compatibility with various thermoplastics and colorants to ensure it meets your specific manufacturing requirements. -
What is the typical lead time for ordering micro injection moulding machines internationally?
Lead times for micro injection moulding machines can vary significantly based on the supplier, machine specifications, and shipping logistics. Generally, expect a lead time of 8 to 16 weeks from order placement to delivery. Ensure you discuss production timelines with your supplier and factor in customs clearance, especially for international shipments to regions like Africa or South America. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for micro injection moulding machines?
Minimum order quantities can differ based on the manufacturer and model of the machine. Some suppliers may offer single-unit purchases, while others might require bulk orders to optimize production efficiency and cost. Always confirm MOQs with your supplier and explore potential negotiation options if you’re a smaller business or a start-up. -
How can I ensure the quality and reliability of a micro injection moulding machine?
To ensure quality, source machines from reputable manufacturers with a proven track record in the industry. Request certifications and performance reports, and consider visiting the supplier’s facility to see the machines in action. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support, as these factors are critical for long-term reliability. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of micro injection moulding machines?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include upfront payments, partial payments with the balance due on delivery, or financing arrangements. It’s essential to clarify payment conditions upfront and consider using secure payment methods to protect your investment, especially in international transactions. -
How should I vet suppliers of micro injection moulding machines?
When vetting suppliers, conduct thorough research to assess their reputation, experience, and customer reviews. Request references from other clients, check their certifications, and evaluate their production capabilities. Communication is also key; a responsive supplier is often a good indicator of reliable service. -
What customization options are available for micro injection moulding machines?
Customization options can include specific mold designs, additional features for automation, and specialized control systems tailored to your production needs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to understand the extent of customization they offer, and consider the implications on cost and lead time. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing micro injection moulding machines?
When importing machines, consider factors like shipping costs, import duties, and customs regulations in your country. Engage with logistics experts to navigate these processes effectively and ensure timely delivery. Additionally, evaluate whether the supplier offers assistance with logistics, which can simplify the importation process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Micro Injection Moulding Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
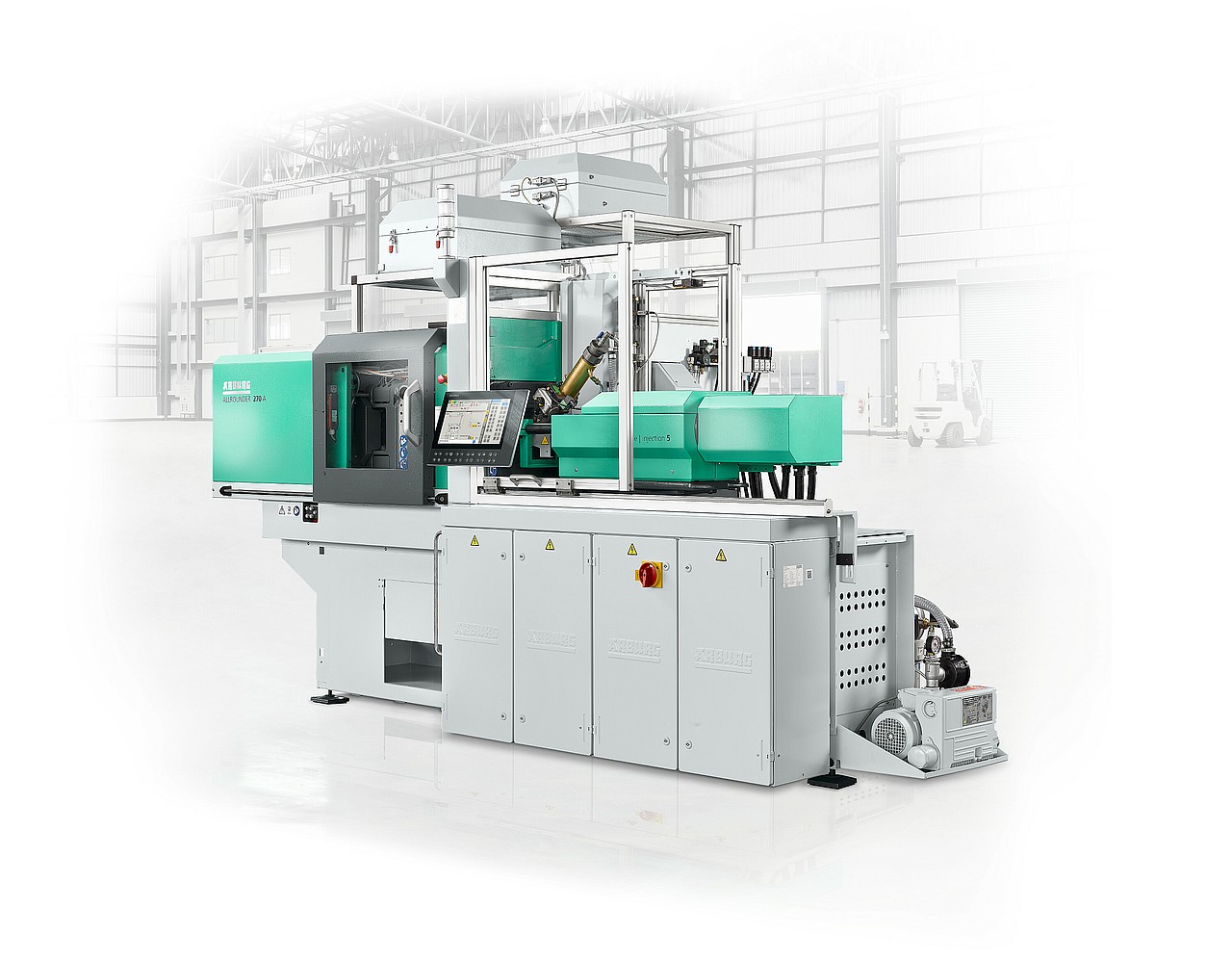
1. Arburg – Micro Injection Molding Technology
Domain: arburg.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Micro injection molding technology for producing precise parts smaller than a single granule. Key features include:
– Injection screws starting from 8 mm and a micro injection unit 5.
– FIFO (First In, First Out) principle for homogeneous melt preparation and short residence times.
– Capable of producing high-quality micro components in series using standard ALLROUNDER machines, avoiding the need …
2. Sumitomo (SHI) Demag – SE7M Micro Injection Molding Machines
Domain: sumitomo-shi-demag.us
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: SE7M Micro Injection Molding Machines – Sumitomo (SHI) Demag North America
– Model: SE7M
– Type: Direct-drive all-electric injection molding machines
– Applications: Micro-molding requiring high precision and productivity
– Features:
– Four direct-drive Sumitomo AC servo motors with closed-loop control and digital sensors
– Ball screw used for all motions except plasticizing
– Beltless desi…
3. Dr. Boy – Micro Injection Molding Machines
Domain: boymachines.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Dr. Boy Spritzgiessautomaten offers micro injection molding machines designed for producing molded parts with very small shot weights, specifically less than one milligram. The machines utilize well-proven standard technologies and components, including a reciprocating screw, to enhance metering accuracy and dynamic injection processes. BOY injection molding machines are capable of processing vari…
4. Matrix Tool – Micro Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: matrixtoolinc.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Micro Injection Molding refers to part sizes or features that are significantly smaller than traditional parts. Matrix Tool specializes in high precision, complex injection molds and has developed Micro Tool Building and Molding capabilities to meet customer demands for smaller products with tighter tolerances. Key features include:
– Molding parts that weigh as little as 0.002 grams and have gat…
5. Micronano Tools – Mini Automatic Injection Molding Machine MAIM-100
Domain: micronanotools.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Mini Automatic Injection Molding Machine MAIM-100”, “price”: “$7,580.00 USD”, “description”: “Designed for mass production of small and precise plastic components such as seals, gaskets, caps, fixing, and gears.”, “verified_materials”: [“Polypropylene”, “Polyethylene”, “HDPE”, “LDPE”, “ABS”, “Styrene”, “POM”, “GPPS”, “PA612”, “PA (100% Nylon)”], “features”: [“All moving parts mad…
6. MHS – M3 Series Micro Molding Machines
Domain: mhs-hot-runners.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: M3 series micro molding machines offer unparalleled performance in a compact, user-friendly package. Features include patented ISOKOR™ injection technology for molding very small, direct gated plastic parts, with models available in 8, 16, and 32 drop configurations. The machines use modular inserts containing eight small cavities, eliminating the need for larger, costly plate structures. The ISOK…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for micro injection moulding machines
In navigating the landscape of micro injection moulding machines, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to unlock the full potential of their investments. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting machines that offer precision, versatility, and automation capabilities, as these factors significantly enhance production efficiency and product quality. Understanding the unique requirements of various industries—ranging from medical technology to consumer goods—will further refine sourcing strategies.
Investing in advanced micro injection moulding technologies not only drives innovation but also positions businesses competitively in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As global demand for high-quality, small-scale production surges, leveraging strategic partnerships with reputable manufacturers can lead to enhanced operational agility and cost savings.
Looking ahead, the future of micro injection moulding is bright, with ongoing advancements in technology promising greater efficiency and customization options. International buyers are encouraged to stay informed about evolving trends and to engage with suppliers who can provide tailored solutions that meet their specific needs. By embracing these opportunities, businesses can secure a robust foothold in the rapidly changing market landscape.