Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal turning tools
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing high-quality metal turning tools poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With an array of options available, navigating the complexities of tool selection, application suitability, and supplier reliability can be daunting. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of metal turning tools, providing insights into various types, their applications, and the critical factors to consider when making purchasing decisions.
From understanding the differences between high-speed steel and carbide tools to evaluating the best suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge they need to make informed choices. It covers essential topics such as cost considerations, performance metrics, and supplier vetting processes, ensuring that businesses can optimize their operations without compromising on quality.
By leveraging this resource, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, streamline their sourcing processes, and ultimately improve their production efficiency. The insights provided will empower organizations to select the right metal turning tools that meet their specific machining needs, paving the way for increased productivity and competitiveness in the global market.
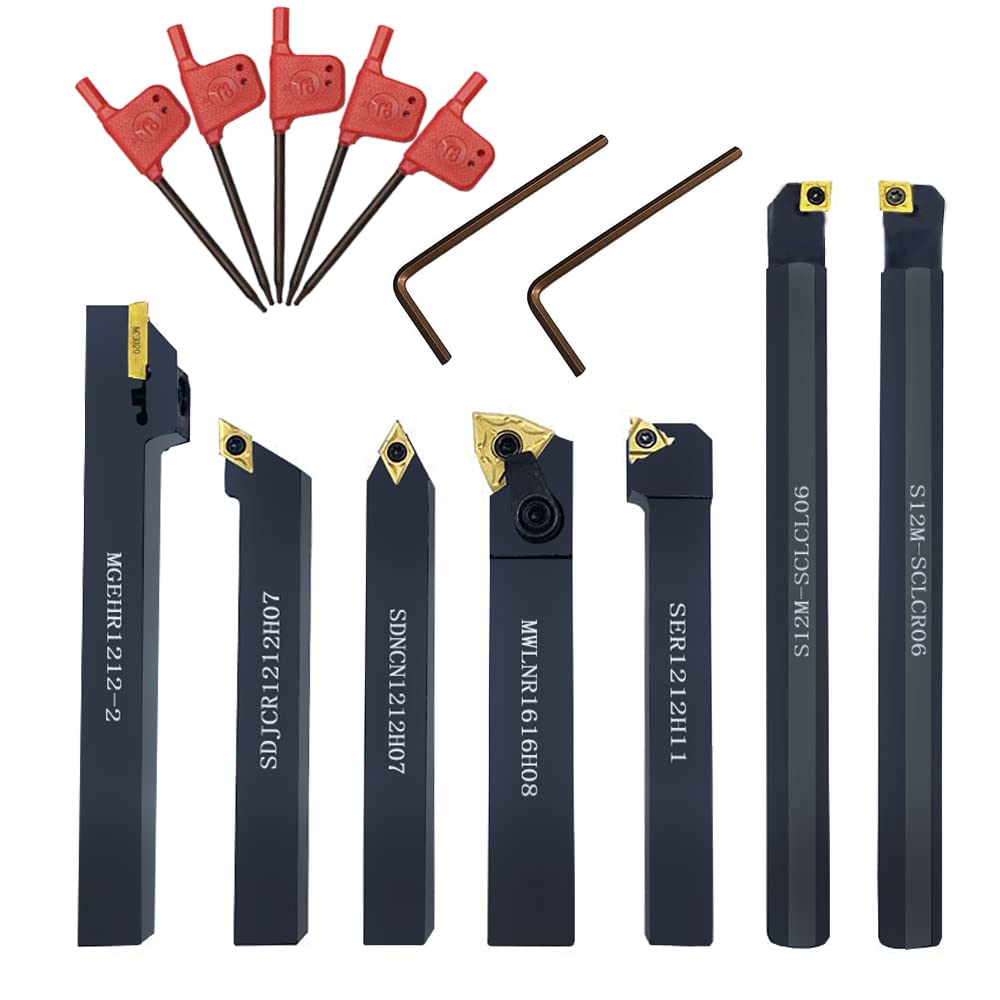
Understanding metal turning tools Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turning Tools | Used for shaping and reducing diameter; available in rough and finish variants | General machining, automotive, aerospace | Pros: Versatile, essential for many operations; Cons: May require frequent sharpening (HSS). |
| Boring Bars | Designed for enlarging holes; can be used internally or externally | Aerospace, manufacturing, construction | Pros: High precision; Cons: More expensive than standard tools. |
| Grooving Tools | Specialized for creating grooves or recesses on a workpiece | Pipe manufacturing, automotive parts | Pros: Enhances functionality of parts; Cons: Limited use for other operations. |
| Threading Tools | Designed specifically for creating threads; includes taps and dies | Fastener production, machinery assembly | Pros: Essential for threaded components; Cons: Requires precise setup for accuracy. |
| Cut-Off Tools | Used to sever materials; typically mounted on lathes | Metal fabrication, machining shops | Pros: Efficient for material removal; Cons: Limited to cutting operations only. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Turning Tools in Metalworking?
Turning tools are fundamental components in metal machining, primarily used to shape and reduce the diameter of workpieces. They come in two main types: rough turning tools, which remove large amounts of material quickly, and finish turning tools, which provide a smooth surface finish. These tools are essential across various industries, including automotive and aerospace, where precision and efficiency are critical. Buyers should consider the material (HSS or carbide) based on their specific operational needs and budget, as HSS tools are cost-effective but may require more frequent maintenance.
How Do Boring Bars Enhance Precision in Machining?
Boring bars are specialized tools designed for enlarging existing holes with high precision. They can be utilized for both internal and external boring operations, making them versatile for applications in aerospace, manufacturing, and construction. When selecting a boring bar, buyers should evaluate factors such as the diameter range, tool material, and the specific machining requirements. While they offer exceptional accuracy, the investment is typically higher than standard turning tools, making them a more specialized choice.
What Are the Applications of Grooving Tools in Manufacturing?
Grooving tools are specifically designed to create grooves or recesses in workpieces, which is essential in industries such as pipe manufacturing and automotive parts production. These tools enable the creation of intricate designs and functionalities within components. Buyers should assess the groove depth and width specifications required for their projects, as well as the tool’s material for durability. While grooving tools significantly enhance the functionality of parts, their specialization may limit their use in other machining operations.
Why Are Threading Tools Essential for Precision Engineering?
Threading tools, including taps and dies, are crucial for producing threaded components in fastener production and machinery assembly. They ensure the accuracy and quality of threads, which are vital for the assembly and functioning of various mechanical systems. When purchasing threading tools, it is essential to consider the thread size, pitch, and material compatibility. Despite their importance, threading tools require careful setup to achieve precise results, which can be a disadvantage for less experienced operators.
How Do Cut-Off Tools Improve Efficiency in Metal Fabrication?
Cut-off tools are specifically designed for severing materials and are commonly used in metal fabrication and machining shops. Their efficiency in material removal makes them indispensable for quick operations. Buyers should evaluate the tool’s compatibility with the lathe and the types of materials being processed. While cut-off tools excel in their designated function, their limited application outside cutting operations may necessitate investment in additional tool types for comprehensive machining capabilities.
Key Industrial Applications of metal turning tools
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal turning tools | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of engine components and shafts | Enhanced precision and efficiency in high-volume production | Need for durable, high-performance tools with consistent quality |
| Aerospace | Machining of turbine blades and landing gear | Critical for safety and performance; high precision required | Compliance with stringent industry standards and certifications |
| Oil and Gas | Fabrication of valves and fittings | Reliability in harsh environments; reduced maintenance costs | Tools must withstand extreme conditions and have long service life |
| Medical Devices | Production of surgical instruments and implants | High precision essential for patient safety and compliance | Sourcing from suppliers with proven quality control and certifications |
| General Engineering | Custom part production for machinery | Flexibility in design and reduced lead times | Availability of a variety of tool types and materials for diverse applications |
How Are Metal Turning Tools Applied in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, metal turning tools are crucial for producing components such as engine blocks, shafts, and transmission parts. These tools enable manufacturers to achieve high precision and repeatability, which are vital for performance and safety. International buyers should focus on sourcing tools that offer durability and can withstand the demands of high-volume production. Additionally, compatibility with existing machinery and adherence to quality standards are essential considerations.
What Role Do Metal Turning Tools Play in Aerospace?
Aerospace applications require metal turning tools for the machining of critical components like turbine blades and landing gear. The precision and reliability of these tools directly impact safety and performance, making them indispensable in this industry. Buyers, especially from regions with stringent aerospace standards, must ensure that tools are compliant with international certifications and can handle the unique challenges of aerospace materials, such as titanium and high-strength alloys.
How Are Metal Turning Tools Utilized in the Oil and Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, metal turning tools are used to fabricate valves, fittings, and other components that must perform reliably in extreme environments. The ability of these tools to withstand high pressures and corrosive substances is paramount. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that specialize in high-performance materials and have a track record of producing tools that meet industry-specific requirements, thus reducing maintenance and operational costs.
Why Are Metal Turning Tools Important for Medical Device Manufacturing?
Metal turning tools are essential in the production of surgical instruments and implants, where precision is critical for patient safety. The tools must ensure exact measurements and surfaces that comply with medical standards. International buyers must consider suppliers with robust quality control measures and certifications, as the stakes are high in terms of compliance and reliability in the medical field.
How Do General Engineering Firms Benefit from Metal Turning Tools?
In general engineering, metal turning tools facilitate the custom production of parts for various machinery, allowing for flexibility in design and rapid prototyping. This adaptability helps businesses respond quickly to market demands and reduces lead times. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer a diverse range of tool types and materials, enabling them to meet specific project requirements efficiently and effectively.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal turning tools’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggles with Tool Selection for Diverse Materials
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the challenge of selecting the right metal turning tools for varying materials in their production processes. This can be particularly daunting when dealing with a range of materials such as high-strength steel, aluminum, and composites. Buyers often find themselves overwhelmed by the different tool types, such as high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, and diamond tools, each with distinct properties and applications. The result can be increased downtime, suboptimal machining performance, and wasted resources due to inappropriate tool choices.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should conduct a thorough analysis of the materials they work with and the specific machining operations required. It is crucial to categorize the tools based on material compatibility. For example, carbide tools excel in machining hardened steels and stainless materials, while HSS tools are more suited for softer metals and general-purpose applications. Buyers should consult with suppliers to obtain detailed technical specifications and recommendations tailored to their specific applications. Moreover, investing in versatile tooling systems that allow for quick changes and adaptations can enhance flexibility and reduce the need for multiple specialized tools, thus streamlining operations.
Scenario 2: Overcoming Frequent Tool Wear and Breakage
The Problem: A common frustration for B2B buyers in the metalworking industry is the frequent wear and breakage of cutting tools, which can lead to unexpected production halts and increased operational costs. This issue is particularly prevalent when using tools not designed for the specific material or cutting conditions, such as feed rates and speeds. Buyers often find it challenging to balance tool longevity with performance, especially when managing high-volume production runs.
The Solution: To mitigate tool wear and breakage, buyers should implement a proactive maintenance and monitoring strategy. This includes regularly inspecting tools for signs of wear, utilizing proper cutting speeds and feeds based on the material being machined, and ensuring the correct tool geometry is used for each application. Buyers can also explore advanced coatings for their tools, such as titanium nitride (TiN) or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which can significantly enhance tool life by providing better wear resistance and reducing friction. Furthermore, establishing a reliable supply chain for quality tool inserts that can be easily replaced when worn out will ensure consistent performance without significant downtime.
Scenario 3: Challenges with Tool Compatibility and Setup
The Problem: In many machining environments, B2B buyers encounter compatibility issues when trying to integrate new metal turning tools with existing machinery. This often leads to delays in production as workers struggle with improper setups and adjustments. The complexity of aligning tool holders, quick-change systems, and various tool types can result in frustration and inefficiencies that ultimately affect overall productivity.
The Solution: To overcome compatibility challenges, buyers should invest in standardized tooling systems that are designed to be universally compatible with their existing machinery. This could involve selecting modular tool holders and ensuring that all new tools adhere to the same specifications as current inventory. It’s also advisable to engage with equipment manufacturers or tooling specialists to gain insights into recommended setups and configurations that facilitate smoother transitions. Providing comprehensive training for machine operators on tool setup and maintenance can further enhance productivity and minimize the risk of errors during production. This structured approach not only streamlines operations but also fosters a more adaptable and efficient manufacturing environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal turning tools
What Are the Key Properties of High-Speed Steel for Metal Turning Tools?
High-speed steel (HSS) is a traditional material widely used in the manufacturing of metal turning tools. One of its key properties is its ability to withstand high temperatures without losing hardness, making it suitable for high-speed applications. HSS tools typically exhibit good toughness and wear resistance, allowing them to maintain sharpness over extended periods. However, they may not perform as well as carbide tools when machining harder materials.
Pros: HSS tools are relatively inexpensive and can be easily sharpened, making them cost-effective for various applications. They are versatile and can handle a wide range of materials, including softer metals and plastics.
Cons: The primary limitation of HSS is its reduced durability compared to carbide and other advanced materials. They may require more frequent sharpening and are less effective for high-volume production runs.
Impact on Application: HSS tools are ideal for general machining tasks, including turning, facing, and grooving. They are particularly effective for softer materials but may struggle with harder alloys.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of HSS tooling and sharpening services. Compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN can also be a factor in procurement decisions.
How Does Carbide Compare as a Material for Metal Turning Tools?
Carbide is a popular choice for metal turning tools due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. It can maintain sharpness longer than HSS and is suitable for high-speed machining of tough materials like stainless steel and hardened alloys. Carbide tools are often used in the form of inserts, which can be replaced when worn out, offering a cost-effective solution.
Pros: The primary advantage of carbide tools is their durability, which leads to increased productivity and improved surface finishes. They require less frequent replacement and can operate at higher speeds than HSS tools.
Cons: However, carbide tools are more expensive upfront, and their brittleness can lead to chipping if not handled properly. This makes them less forgiving in less controlled machining environments.
Impact on Application: Carbide tools are ideal for high-volume production and precision machining, particularly in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the carbide tools they procure comply with international standards like ISO and JIS. They should also consider the availability of compatible tool holders and inserts in their region.
What Are the Advantages of Using Diamond Tools for Metal Turning?
Diamond tools offer unparalleled hardness and are best suited for specialized applications that require exceptional surface finishes. They are particularly effective for machining hard materials, including ceramics and composites.
Pros: The primary advantage of diamond tools is their longevity and ability to maintain a sharp edge, resulting in superior surface quality. They can also operate at high cutting speeds, making them suitable for high-precision applications.
Cons: The main drawback is their high cost, which can be prohibitive for many businesses. Additionally, diamond tools may not be suitable for all materials, particularly softer metals.
Impact on Application: Diamond tools are commonly used in industries requiring high precision, such as medical device manufacturing and aerospace components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Companies in regions with stringent quality requirements should verify that diamond tools meet relevant international standards. Given their cost, buyers should evaluate the return on investment based on the specific applications they intend to use them for.
Why Consider Cubic Boron Nitride for Metal Turning Tools?
Cubic boron nitride (CBN) is the second hardest material after diamond and is particularly effective for machining hard materials like cast iron and hardened steels. CBN tools provide excellent heat resistance and can maintain performance under high-speed conditions.
Pros: CBN tools offer outstanding durability and tool life, making them a valuable investment for industries that require consistent performance. They can also improve productivity due to their ability to withstand high cutting speeds.
Cons: The primary limitation of CBN tools is their cost, which can be significantly higher than HSS or carbide. Additionally, they are not as versatile and are typically used for specific applications.
Impact on Application: CBN tools are ideal for heavy-duty machining operations and are commonly used in the automotive and manufacturing sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that CBN tools comply with relevant international standards and consider the availability of compatible tool holders. Understanding local market conditions can also help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal turning tools | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | General machining tasks, turning, facing | Cost-effective and versatile | Requires frequent sharpening | Low |
| Carbide | High-speed machining of tough materials | Exceptional durability and performance | Higher initial cost, brittle | Medium |
| Diamond | Precision machining of hard materials | Superior surface finish and longevity | High cost, not suitable for all materials | High |
| Cubic Boron Nitride | Heavy-duty machining of hard materials | Outstanding tool life and heat resistance | High cost, limited versatility | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal turning tools
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Metal Turning Tools?
The manufacturing of metal turning tools involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure precision and quality. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Turning Tool Manufacturing?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. This phase involves selecting high-quality raw materials, such as high-speed steel (HSS), carbide, or even advanced materials like cubic boron nitride (CBN) and diamond. The chosen material is then cut into manageable sizes and shapes for further processing.
Quality control begins here, as the integrity of the raw materials significantly impacts the final product. Suppliers should provide certification of material properties, including hardness and tensile strength, to ensure compliance with industry standards.
What Techniques Are Used in Forming Metal Turning Tools?
Forming is the next stage, where the prepared materials undergo shaping and machining. Techniques such as forging, machining, and grinding are commonly employed to create the desired tool geometries.
-
Forging: This process involves deforming the material under compressive stress, which aligns the grain structure and enhances the tool’s strength and durability.
-
Machining: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often utilized for precision shaping, ensuring that the tools meet exact specifications. Machining includes processes like turning, milling, and drilling.
-
Grinding: This is used for achieving fine tolerances and smooth finishes. Precision grinding machines are essential for producing cutting edges that meet the strict demands of metalworking applications.
Each of these techniques requires skilled operators and sophisticated machinery to maintain high production standards.
How Is the Assembly of Metal Turning Tools Executed?
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into complete tools. This process can vary depending on the type of tool being manufactured. For instance, turning tools may require the integration of multiple components, including inserts and tool holders.
During assembly, it is crucial to ensure that all parts fit correctly and function as intended. This stage may also include the application of coatings that enhance the tool’s performance, such as titanium nitride (TiN) or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), which improve wear resistance and reduce friction.
What Finishing Processes Are Involved in Metal Turning Tool Manufacturing?
Finishing processes are essential for enhancing the tool’s performance and aesthetic appeal. This stage may involve:
- Polishing: To achieve a smooth surface that minimizes friction during operation.
- Coating: Applying specialized coatings to improve durability and resistance to heat and wear.
- Inspection: Conducting final inspections to verify that the tools meet the required specifications and quality standards.
These finishing techniques not only enhance the tool’s functionality but also its longevity, making them critical for B2B buyers looking for reliable products.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Typically Implemented?
Quality assurance (QA) in metal turning tool manufacturing is paramount, especially for international B2B buyers. Companies must adhere to various international standards, such as ISO 9001, which provides a framework for consistent quality management systems.
How Do International Standards Influence Quality Control?
International standards, including CE marking for compliance with European safety regulations and API standards for oil and gas applications, guide manufacturers in maintaining high-quality production. Compliance with these standards is often a requirement for suppliers targeting international markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control typically encompasses several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch any deviations from quality standards early.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products to ensure they meet all specifications before shipping.
Implementing these checkpoints helps mitigate risks and ensures that only high-quality products reach the market.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to assess the performance and durability of metal turning tools. Common tests include:
- Hardness Testing: Evaluating the material’s resistance to deformation.
- Tensile Testing: Measuring the strength and ductility of materials.
- Surface Roughness Measurement: Ensuring that the tool’s surface finish meets specified criteria.
These testing methods provide valuable insights into the tool’s performance and longevity, allowing buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers. This can include:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality assurance processes.
- Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing results and compliance with industry standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services to evaluate product quality and adherence to specifications.
These measures are particularly important for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where varying standards may exist.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial. Different regions may have specific regulations and standards that must be adhered to. For example, the European Union has strict regulations regarding the CE marking, while North American buyers may focus on ANSI and ASTM standards.
Additionally, buyers should consider the implications of local manufacturing practices and how they align with international quality expectations. Establishing clear communication with suppliers about quality requirements can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that products meet the necessary standards.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for metal turning tools are intricate and vital for ensuring product reliability and performance. By understanding these processes, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and product quality in their own manufacturing endeavors.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal turning tools’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure metal turning tools. It provides actionable steps to ensure that you select the right tools, engage reliable suppliers, and achieve optimal performance in your machining operations. By following this guide, you can make informed purchasing decisions that align with your business needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outlining your technical requirements is essential for sourcing the right metal turning tools. Consider factors such as the materials you will be machining, desired tolerances, and specific operations (e.g., turning, grooving, threading). A well-defined specification helps ensure that you select tools that meet your production needs and avoid costly mistakes.
- Material Requirements: Identify whether you need tools made from high-speed steel, carbide, or other materials based on the hardness of the materials you will be working with.
- Operation Types: Specify the types of operations (e.g., facing, boring) to ensure compatibility with your lathe machinery.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Begin your search by identifying suppliers that specialize in metal turning tools. Utilize online directories, trade shows, and industry networks to compile a list of potential vendors. A diverse supplier base increases your chances of finding the best quality and pricing.
- Check Industry Reputation: Look for suppliers with strong reputations in your industry, especially those who have experience serving businesses in your geographical region.
- Product Range: Ensure that the suppliers you consider offer a comprehensive range of tools that fit your specifications.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, it’s crucial to vet them thoroughly. Request company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies. Additionally, ask for references from other businesses in similar industries to gauge their reliability and service quality.
- Certifications and Standards: Verify that the suppliers adhere to industry standards and possess relevant certifications, which can indicate quality assurance.
- Customer Reviews: Look for testimonials and reviews from previous clients to understand their experiences with the supplier.
Step 4: Request Samples and Conduct Testing
Once you’ve narrowed down your options, request samples of the metal turning tools you are considering. Testing these samples in your machining environment will provide valuable insights into their performance, durability, and compatibility with your equipment.
- Performance Evaluation: Assess the samples based on cutting efficiency, tool life, and finish quality on your materials.
- Compatibility Check: Ensure the tools fit your existing lathe setup, including holders and posts.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Engage in discussions with potential suppliers regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing and terms that align with your budget and operational timelines.
- Bulk Purchase Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk orders or long-term contracts, which can significantly reduce costs.
- Return Policies: Understand the return and warranty policies to safeguard your investment in case of defects or performance issues.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order and Monitor Delivery
After selecting your supplier and agreeing on terms, finalize your order. Keep an open line of communication regarding the expected delivery timeline and any potential delays.
- Tracking Orders: Request tracking information to monitor the shipment and ensure timely delivery to avoid disruptions in your production schedule.
- Quality Control Upon Receipt: Upon arrival, inspect the tools for quality and compliance with your specifications before integrating them into your operations.
By following these steps, you can streamline your procurement process and ensure that you acquire the right metal turning tools to enhance your machining capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal turning tools Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing Metal Turning Tools?
When sourcing metal turning tools, understanding the cost structure is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. The main components of the cost structure include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s margin.
Materials represent a significant portion of the cost, particularly when it comes to the type of metal and tool material selected. High-speed steel (HSS), carbide, diamond, and cubic boron nitride (CBN) have different cost implications based on their properties and applications.
Labor costs are influenced by the skill level required for manufacturing and the region where production takes place. Countries with lower labor costs may offer more competitive pricing but may also affect quality and lead times.
Manufacturing overhead encompasses utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor, which can vary widely by region and supplier efficiency.
Tooling costs involve the initial investment in specialized equipment necessary for production.
Quality control is crucial, particularly for international buyers. The cost associated with QC processes helps ensure that the tools meet necessary specifications and certifications, which can be particularly important for buyers in regulated markets.
Logistics costs include shipping, customs duties, and insurance, which can significantly impact total costs, especially for international transactions.
Lastly, the supplier’s margin is the profit they add on top of their costs, which varies based on their business model and market positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Turning Tool Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of metal turning tools, including volume or minimum order quantity (MOQ), specifications and customization, materials, quality certifications, supplier factors, and Incoterms.
Volume and MOQ play a critical role; larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
Specifications and customization can also impact pricing. Tailored solutions typically incur higher costs, but they may be necessary for specific applications.
Material choices significantly affect costs. For example, carbide tools are generally more expensive than HSS but offer better performance and longevity, which can justify the higher upfront investment.
Quality certifications such as ISO and other industry standards can influence both pricing and buyer confidence. Tools that meet rigorous standards may command a premium but can reduce risks associated with performance and reliability.
Supplier factors, including reputation, reliability, and customer service, can also influence pricing. A supplier with a strong track record may charge higher prices but offer better value through superior service and product quality.
Incoterms, or international commercial terms, dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, which can affect total costs. Understanding these terms is crucial for international buyers to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Buyer Tips Can Enhance Cost-Efficiency in Metal Turning Tool Sourcing?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider several strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in their sourcing of metal turning tools.
Negotiation is vital. Buyers should be prepared to negotiate prices based on volume, long-term relationships, and the potential for repeat business. Leveraging multiple suppliers can also create competitive pricing opportunities.
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) is an essential concept. Buyers should evaluate not just the purchase price but also the costs associated with tool maintenance, potential downtime, and replacement frequency. Investing in higher-quality tools may result in lower overall costs.
Pricing nuances for international buyers include understanding currency fluctuations, import duties, and local taxes that can impact final costs. Additionally, buyers should be aware of the potential for longer lead times when sourcing from overseas, which can affect project timelines and costs.
Disclaimer: Prices for metal turning tools can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier practices, and changes in material costs. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure the best possible pricing for their specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal turning tools With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Metal Turning Tools
In the realm of machining, metal turning tools are a fundamental solution for shaping and finishing various materials. However, there are alternative technologies and methods that can achieve similar outcomes. Identifying these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers looking to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. This section compares metal turning tools with other viable solutions, helping buyers make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Turning Tools | CNC Machining Centers | Laser Cutting Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for cylindrical shapes | Versatile; handles complex geometries | Excellent for intricate designs |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; ongoing tool costs | High capital expenditure; lower operating costs | High initial setup; consumable costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled operators; setup can be time-consuming | Requires technical expertise; programming needed | User-friendly for basic operations; complex for advanced uses |
| Maintenance | Regular tool replacement and sharpening | Routine maintenance; higher complexity | Low maintenance; focus on optics |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for mass production of cylindrical parts | Best for complex parts and small batches | Optimal for cutting thin materials and intricate patterns |
What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of CNC Machining Centers?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining centers offer a versatile alternative to traditional metal turning tools. They excel in handling complex geometries and can perform multiple operations, such as drilling and milling, within a single setup. This flexibility allows manufacturers to produce intricate designs with high precision. However, the initial capital investment is significantly higher compared to turning tools, and the need for skilled operators to program and manage the machines can be a barrier for some businesses. Furthermore, while CNC machines have lower ongoing costs, they require regular maintenance and may involve higher downtime during repairs.
How Do Laser Cutting Systems Compare to Metal Turning Tools?
Laser cutting systems represent another innovative alternative, particularly for applications involving thin materials or intricate designs. They offer remarkable precision and can cut through various materials without the need for physical contact, reducing wear and tear on the tools. Additionally, laser systems are generally easier to operate for basic tasks, as they often come with user-friendly interfaces. Nevertheless, their high initial setup costs and ongoing consumable expenses can be prohibitive for some businesses. Moreover, laser cutting is less effective for thicker materials and may not provide the same surface finish quality as traditional turning methods.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate machining solution, B2B buyers must assess their specific operational requirements, budget constraints, and desired outcomes. Metal turning tools offer a reliable and cost-effective option for producing cylindrical parts, while CNC machining centers and laser cutting systems provide versatility and precision for more complex tasks. By carefully considering the performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance needs, and best use cases of each alternative, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their production goals and enhance their competitive edge in the market.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal turning tools
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Metal Turning Tools?
Understanding the technical properties of metal turning tools is vital for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating options for specific machining tasks. Here are some essential specifications that can influence tool selection:
1. Material Grade
The material of the cutting tool significantly affects its performance and longevity. Common materials include High-Speed Steel (HSS), carbide, and ceramic. HSS tools are versatile and cost-effective, suitable for a range of materials. Carbide tools, while more expensive, offer superior hardness and wear resistance, making them ideal for high-speed applications. Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the tools can withstand the demands of the specific machining process, enhancing productivity and reducing downtime.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In the context of metal turning tools, tighter tolerances lead to higher precision in machining operations. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance is critical, as it directly impacts the quality of the finished product. Tools that maintain stringent tolerances can significantly reduce scrap rates and improve overall efficiency, which is vital for businesses aiming to meet high-quality standards.
3. Coating
Coatings such as TiN (Titanium Nitride) or TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) enhance the cutting performance and lifespan of tools by providing increased hardness and reduced friction. Coated tools are particularly beneficial in high-temperature applications where tool wear can be accelerated. Understanding the advantages of different coatings can help buyers select tools that not only last longer but also deliver better surface finishes, thus adding value to their machining processes.
4. Geometry
The geometry of a turning tool, including rake angle, clearance angle, and cutting edge design, plays a crucial role in its cutting performance. Specific geometries are tailored for different operations, such as roughing or finishing. Familiarity with tool geometry helps buyers choose tools that optimize cutting efficiency and improve chip removal, which is essential for effective machining.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Metal Turning Tools Industry?
Navigating the terminology in the metal turning tools industry is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms that every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of metal turning tools, understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing quality products that meet their specific requirements.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or stockouts. It also helps in budgeting and financial planning, especially for international purchases.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. For B2B buyers, utilizing RFQs is an effective way to compare pricing and terms from multiple vendors, ensuring they secure the best deal for their metal turning tools.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B transactions, especially in international trade, as they outline who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thus minimizing misunderstandings and disputes.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms equips B2B buyers with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions when selecting metal turning tools, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal turning tools Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends Influencing Metal Turning Tools?
The global metal turning tools market is experiencing significant shifts driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for precision engineering, and a heightened focus on automation and efficiency. The rise of Industry 4.0 has introduced smart manufacturing solutions, allowing businesses to integrate IoT and AI into their operations. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe and North America, but is increasingly gaining traction in Africa and South America as well. As international B2B buyers seek to optimize production processes, there is a growing preference for suppliers who offer advanced tooling solutions that enhance productivity and reduce cycle times.
Additionally, sustainability is becoming a central theme in sourcing decisions. Buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers who utilize eco-friendly materials and practices. The demand for high-speed steel (HSS) and carbide tools is growing due to their durability and efficiency, but there is also a notable interest in innovations like cubic boron nitride (CBN) and diamond tools for specialized applications. Suppliers that can offer a diverse range of tooling options will be well-positioned to meet the varying needs of their clients across different sectors.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Reshaping the Metal Turning Tools Industry?
The importance of sustainability and ethical sourcing cannot be overstated in today’s B2B marketplace. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including the production of metal turning tools, has led to increased scrutiny from consumers and regulatory bodies alike. As a result, international buyers are prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and promoting responsible sourcing practices.
Many manufacturers are now pursuing green certifications and using sustainable materials in their production processes. This shift not only appeals to environmentally conscious buyers but also helps businesses comply with increasingly stringent regulations. In addition to selecting tools made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials, buyers are looking for suppliers who can provide transparent supply chain practices. This includes tracking the origin of materials and ensuring fair labor practices throughout the supply chain. By choosing suppliers with strong sustainability credentials, B2B buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles while also meeting the growing demand for environmentally friendly products.
What Is the Historical Context of Metal Turning Tools and Its Relevance to Current Trends?
The evolution of metal turning tools can be traced back to the industrial revolution when lathes were first mechanized. This innovation significantly increased the efficiency and precision of metalworking, laying the groundwork for modern machining processes. Over the decades, the introduction of high-speed steel (HSS) and carbide tools revolutionized the industry, allowing for faster cutting speeds and improved durability.
As manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, the tools themselves have become more specialized, catering to diverse applications and materials. The ongoing trend towards automation and smart manufacturing is reminiscent of earlier shifts in the industry, emphasizing the need for adaptability and innovation. Understanding this historical context is crucial for international B2B buyers as they navigate the complexities of today’s market, making informed decisions that align with both current capabilities and future trends in the metal turning tools sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal turning tools
-
How do I select the right metal turning tool for my application?
Selecting the right metal turning tool depends on several factors, including the material being machined, the required precision, and the type of operation (e.g., turning, facing, grooving). Consider the tool material, such as high-speed steel (HSS) for general use or carbide for tougher materials. Additionally, analyze the tool geometry, as different shapes are designed for specific operations. Consult with suppliers for detailed specifications and recommendations based on your operational needs to ensure optimal performance and productivity. -
What are the key features to look for in a supplier of metal turning tools?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the industry, product range, and reputation for quality. Assess their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management practices. Also, inquire about their customer service, lead times, and the ability to provide technical support. A supplier’s capability to offer customization and flexible payment terms can also be essential for establishing a long-term partnership. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for metal turning tools?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier, the type of tools, and the materials involved. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as 10 units for standard tools, while custom tools may require larger orders. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs with potential suppliers to negotiate favorable terms that align with your operational scale and budget. This flexibility can help manage inventory costs effectively. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for metal turning tools?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and certifications from suppliers, including material properties and manufacturing processes. Conduct regular inspections and tests on received tools to verify their performance against your requirements. Establishing a quality control agreement with your supplier can further ensure that you receive products meeting your standards consistently. Collaborating with suppliers who have robust QA processes can minimize risks associated with tool failures during production. -
What are the payment terms typically offered for international orders?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier’s policies, the order size, and the buyer’s location. Common options include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. For larger orders, suppliers may offer net 30 or net 60 days terms. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods and negotiate terms that suit both parties before finalizing orders, as this can impact cash flow and financial planning for your business. -
How do I handle logistics and shipping for metal turning tools?
When managing logistics, consider factors such as shipping method, costs, and transit times. Discuss with suppliers about their preferred shipping partners and practices. Ensure you account for customs regulations and import duties in your country, especially for international shipments. Collaborating with a logistics provider experienced in handling industrial goods can streamline the process, ensuring timely delivery while minimizing potential delays or additional costs. -
What customization options are available for metal turning tools?
Customization options can include tool dimensions, material selection, and specific geometries tailored to your machining processes. Many suppliers offer the ability to design tools to meet unique specifications, which can enhance efficiency and precision in your operations. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers and request samples or prototypes to evaluate performance before committing to larger orders. -
What should I do if I encounter issues with the metal turning tools?
If you encounter issues with the tools, first document the specific problems and gather evidence, such as photographs and performance reports. Contact the supplier immediately to discuss the issues and seek a resolution, which may include replacements or refunds. Establishing a clear communication channel and understanding the supplier’s return policy can facilitate a smoother resolution process. Regular feedback can also help improve future orders and supplier relations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Metal Turning Tools Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. LittleMachineShop – Cutting Tools for Lathes
2. Tormach – CNC Lathe Tooling
Domain: tormach.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: This company, Tormach – CNC Lathe Tooling, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Grizzly – Cutting Tools & Tooling
Domain: grizzly.com
Registered: 1991 (34 years)
Introduction: Cutting Tools & Tooling from Grizzly Industrial includes a wide range of products such as: CNC Cutting Tools & Tooling, Boring Bars, Clamping Kits, Collets, End Mills, Inserts, Lathe Centers, Lathe Chucks, Live Centers, Rotary Burrs, Rotary Tables, Slitting Saws, Spiral Cutterheads, Tap & Die Sets, and various types of drill bits including Auger Bits, Countersinks, Forstner Bits, Hammer Drills, Ho…
4. Anchor Lube – Lathe Cutting Tools
Domain: anchorlube.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Lathe cutting tools are categorized based on material, operations, structure, and feed direction. Common materials include: 1. High-Speed Steel (HSS): Known for hardness, toughness, and heat resistance; suitable for various operations; cost-effective; can be sharpened easily. 2. Carbide: Hard and wear-resistant; ideal for machining tough materials; used as replaceable inserts; offers high cutting …
5. Reddit – HSS Tooling and Stock
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: 1. HSS (High-Speed Steel) Tooling: Recommended for beginners due to its ease of sharpening and versatility. Suggested to start with pre-ground profiles that can be trimmed to length when resharpening. 2. HSS Stock: For those interested in grinding their own tools, HSS stock is economical and allows for customization. 3. Pedestal Grinder: Necessary for sharpening HSS tools. 4. Center Gage: Useful f…
6. eBay – Lathe Tools Collection
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Lathe Tools products for sale on eBay include various items such as: 21PCS 1/2″ 12mm Shank Indexable Carbide Lathe Turning Insert Tool Holder Bit Set ($35.98), 3/8in 1/2in Indexable Metal Lathe Turning Tool Holder with VCMT110304 inserts ($34.99), 10mm HSS Lathe Pre Formed Tools 8 Pieces Set ($59.50), 4pcs 12mm Lathe Turning Tool Holder Boring Bar CCMT060204 Carbide Inserts Set ($21.09), and many …
7. Warco – Metal Lathe Tools
Domain: warco.co.uk
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: The Warco range of metal lathe tools includes high-quality engineers’ tools at affordable prices. Key product categories include: 1. **Back Plates** 2. **Carbide Brazed Lathe Tools** 3. **HSS Lathe Tools** – High Speed Steel tool bits and complete sets for metal turning. 4. **Indexable Lathe Tools** – Available in sets of various sizes (6mm, 8mm, 10mm, 12mm, 16mm). 5. **Lathe Centres** 6. **Lathe …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal turning tools
In today’s competitive landscape, strategic sourcing of metal turning tools is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the diverse range of materials, tool types, and their specific applications, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and reduce downtime. Prioritizing high-quality tools, such as carbide and diamond options, ensures superior performance and longevity, ultimately leading to better returns on investment.
Moreover, leveraging supplier relationships and exploring innovative sourcing strategies can significantly impact your supply chain agility. As markets continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying ahead of industry trends and technological advancements becomes crucial.
As you consider your sourcing strategy, remember that the right tools are not just an expense; they are a critical investment in your business’s future success. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your operations by selecting the best metal turning tools tailored to your specific needs. Let’s forge ahead together into a future of precision engineering and operational excellence.