Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal surface finishing techniques
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, sourcing effective metal surface finishing techniques is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance product quality and longevity. With diverse challenges such as corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and performance optimization, international B2B buyers must navigate a multitude of finishing processes to meet specific requirements. This comprehensive guide delves into a range of metal finishing techniques, including electroplating, anodizing, and polishing, providing insights into their applications and benefits.
Understanding the nuances of each technique not only aids in improving the durability and functionality of metal products but also assists in making strategic purchasing decisions that align with budget constraints and operational efficiency. The guide further explores key considerations for vetting suppliers, evaluating costs, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—where market dynamics and resource availability can vary significantly—this guide serves as an essential resource. By empowering decision-makers with actionable insights, it facilitates informed choices that enhance product offerings and bolster competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
Understanding metal surface finishing techniques Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electroplating | Uses electric current to deposit metal ions onto a substrate. | Automotive, electronics, and decorative items. | Pros: Enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness. Cons: Time-consuming and requires careful handling of chemicals. |
| Anodizing | Creates a protective oxide layer through an electrochemical process. | Aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods. | Pros: Increases corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Cons: Limited to non-ferrous metals like aluminum. |
| Powder Coating | Applies a dry powder that is cured under heat for a durable finish. | Appliances, automotive parts, and outdoor furniture. | Pros: Excellent durability and variety of colors. Cons: Requires specialized equipment and may not be suitable for intricate designs. |
| Electropolishing | Removes surface impurities using an electrochemical process. | Medical devices, food processing equipment. | Pros: Produces a smooth, shiny finish that is easy to clean. Cons: Limited to specific metals and can be costly. |
| Magnetic Polishing | Utilizes magnetic fields to polish small and intricate parts. | Jewelry, precision engineering, and small components. | Pros: Effective on complex shapes and provides uniform finish. Cons: Not suitable for larger components and can be slow. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of electroplating for B2B buyers?
Electroplating involves immersing a metal part in a bath of metal ions, where an electric current facilitates the deposition of a thin metal layer onto the substrate. This technique is particularly suitable for industries requiring enhanced durability and corrosion resistance, such as automotive and electronics. B2B buyers should consider the specific metal being plated, the desired thickness, and the environmental impact of the chemicals used in the process. While electroplating can significantly improve the lifespan of components, it requires careful management of hazardous materials and can be time-intensive.
Why is anodizing a preferred choice for aluminum and non-ferrous metals?
Anodizing is an electrochemical process that enhances the surface of aluminum and other non-ferrous metals by creating a durable oxide layer. This technique is favored in sectors like aerospace and consumer goods for its ability to improve corrosion resistance and provide a decorative finish. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific application requirements, including color preferences and environmental exposure, as anodizing is limited to specific metals. While it offers aesthetic benefits, the anodized finish can be susceptible to abrasion, making it less ideal for high-wear applications.
How does powder coating compare to traditional painting methods?
Powder coating is a modern finishing technique that applies a dry powder to metal surfaces, which is then cured under heat to create a hard, protective layer. This method is widely used in industries such as appliances and outdoor furniture due to its superior durability and variety of colors. Buyers should consider the initial investment in specialized equipment and the complexity of the parts being coated. While powder coating is generally more resilient than traditional paint, it may not be suitable for highly intricate designs due to coverage limitations.
What are the advantages of electropolishing for medical and food industries?
Electropolishing is a process that improves the surface finish of metal components by removing surface imperfections through an electrochemical reaction. This technique is particularly advantageous for industries like medical devices and food processing, where hygiene and cleanliness are critical. B2B buyers should assess the material compatibility and the level of finish required, as electropolishing is often more expensive than other methods. While it produces a highly polished and easy-to-clean surface, it is limited to specific metals and may not be cost-effective for all applications.
How does magnetic polishing enhance surface quality for intricate parts?
Magnetic polishing employs magnetic fields to facilitate the polishing of small and complex metal components. This technique is especially beneficial in sectors like jewelry and precision engineering, where uniformity and surface smoothness are essential. Buyers should consider the size limitations of magnetic polishing equipment, as it is not suitable for larger parts. While it offers a safe and effective means of achieving high-quality finishes, the process can be slower compared to traditional methods.
Key Industrial Applications of metal surface finishing techniques
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Metal Surface Finishing Techniques | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Anodizing of aluminum components | Enhances corrosion resistance and reduces weight | Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications |
| Automotive | Electroplating for engine parts | Improves durability and wear resistance | Supplier reliability and material certifications |
| Oil & Gas | Coating for pipeline components | Provides corrosion protection in harsh environments | Compatibility with specific environmental conditions |
| Medical Devices | Polishing for surgical instruments | Ensures hygiene and reduces bacterial adhesion | ISO certification and biocompatibility standards |
| Electronics | Electropolishing of connectors and components | Increases conductivity and reduces surface roughness | Precision in tolerances and electrical properties |
How is Metal Surface Finishing Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, anodizing is extensively utilized for aluminum components to enhance their resistance to corrosion while maintaining a lightweight structure. This process creates a protective oxide layer that not only improves durability but also contributes to the aesthetic quality of parts. International buyers, especially from regions with rigorous aviation standards, must ensure that suppliers comply with specific aerospace certifications and quality control measures to mitigate risks associated with material failures.
What Role Does Electroplating Play in the Automotive Sector?
Electroplating is a key technique in the automotive sector, particularly for engine parts and decorative components. This process enhances the durability and wear resistance of metal surfaces, thus extending the lifespan of critical components. Buyers from emerging markets should consider supplier reliability and the availability of material certifications to ensure that the electroplated products meet industry standards and can withstand harsh operating conditions.
How is Metal Finishing Applied in the Oil & Gas Industry?
In the oil and gas sector, protective coatings are essential for pipeline components to guard against corrosion in challenging environments. These coatings can significantly extend the life of pipelines, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. When sourcing these coatings, businesses should focus on compatibility with specific environmental conditions and the supplier’s ability to provide products that meet the industry’s stringent safety and performance standards.
Why is Polishing Crucial for Medical Devices?
Polishing techniques are critical in the manufacturing of surgical instruments within the medical device industry. This process not only enhances the aesthetic appearance but also ensures that instruments are hygienic and minimize bacterial adhesion. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who comply with ISO certifications and biocompatibility standards, as the safety and efficacy of medical devices are paramount in this highly regulated market.
How Does Electropolishing Benefit the Electronics Industry?
Electropolishing is increasingly important in the electronics sector for connectors and components. This process smooths surfaces, enhancing conductivity and reducing roughness, which is vital for high-performance electrical connections. Buyers from regions with growing electronics markets should emphasize precision in tolerances and the electrical properties of components to ensure reliable performance in their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal surface finishing techniques’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Selecting the Right Metal Finishing Technique
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face significant challenges when it comes to selecting the appropriate metal finishing technique for their specific application. With various options like anodizing, electroplating, and powder coating, the decision can be overwhelming. Each technique has its own unique benefits, costs, and suitability for different metals and end-uses. Misalignment in the choice can lead to product failure, increased production costs, and compromised quality, ultimately impacting customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
The Solution: To effectively navigate this selection process, buyers should first conduct a thorough analysis of their product requirements. This includes understanding the intended use of the metal components, environmental exposure, desired aesthetics, and performance characteristics. Once the requirements are established, consult with surface finishing specialists or suppliers who can provide insights on the best techniques suited for specific applications. Additionally, creating a decision matrix that compares the advantages, limitations, and costs associated with each technique can streamline the selection process. Prioritize suppliers who offer sample runs or prototypes, allowing you to evaluate the finishing results before full-scale production.
Scenario 2: Managing Production Timelines and Costs in Metal Finishing
The Problem: Tight production schedules are a common concern for B2B buyers, particularly when dealing with metal surface finishing. Techniques like electroplating can be time-consuming, leading to delays in delivery and increased operational costs. If not managed properly, these delays can disrupt supply chains, frustrate customers, and ultimately result in lost business opportunities.
The Solution: To mitigate these challenges, it is crucial to develop a clear production timeline that incorporates the finishing processes involved. Begin by mapping out the entire manufacturing process, identifying the specific metal finishing techniques required and their estimated durations. Engage with suppliers early in the process to negotiate lead times and explore methods to expedite finishing without compromising quality, such as investing in advanced equipment or outsourcing certain processes. Implementing just-in-time inventory management can also help reduce delays. Regular communication with all stakeholders throughout the production cycle will ensure everyone is aligned and can proactively address any potential issues.
Scenario 3: Addressing Quality Control Issues in Metal Finishing
The Problem: Quality control is a significant pain point for B2B buyers involved in metal surface finishing. Variability in the finishing process can lead to inconsistent results, such as uneven coatings, poor adhesion, or surface imperfections. These quality issues not only affect the aesthetic appeal of the products but can also compromise their functionality and longevity, leading to costly rework or product recalls.
The Solution: Establishing a robust quality control framework is essential to address these issues effectively. Begin by defining clear quality standards and specifications that align with industry benchmarks for the desired finishing techniques. Implement regular inspections at various stages of the finishing process to identify any deviations from the specified standards. Utilizing advanced technologies such as laser scanning or optical inspection systems can enhance the accuracy of quality assessments. Additionally, fostering strong relationships with finishing suppliers can facilitate open communication regarding quality expectations and continuous improvement initiatives. Consider conducting training sessions for staff involved in the finishing processes to ensure they are equipped with the latest techniques and standards in quality control.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal surface finishing techniques
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Metal Surface Finishing Techniques?
When selecting materials for metal surface finishing techniques, understanding their key properties is essential for ensuring optimal performance in various applications. Below, we analyze four common materials: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, and Copper, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Corrosion-Resistant
Aluminum is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and lightweight properties, making it suitable for various applications, particularly in the automotive and aerospace industries. It can withstand moderate temperatures and pressures but may not be ideal for high-stress environments.
Pros: Aluminum offers a good strength-to-weight ratio and is relatively easy to machine and finish. Its natural oxide layer enhances corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for outdoor applications.
Cons: While generally durable, aluminum can be more expensive than some alternatives, and its lower tensile strength compared to steel may limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various finishing techniques, including anodizing and powder coating, which enhance its aesthetic appeal and durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and EN is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of the availability of aluminum in local markets, as sourcing can vary significantly across regions like Africa and South America.
Stainless Steel: Strength and Versatility
Stainless steel is renowned for its high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and staining. It performs well in high-temperature and high-pressure environments, making it suitable for applications in the food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical industries.
Pros: Its durability and aesthetic appeal make stainless steel a popular choice for both functional and decorative applications. It can withstand harsh environments without significant degradation.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel is generally higher than that of carbon steel, and its machining can be more complex due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in applications requiring hygiene and corrosion resistance, such as in food processing equipment. Its compatibility with electropolishing enhances its surface finish.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local regulations regarding food safety and corrosion resistance standards. Compliance with ASTM and ISO standards is also essential for international trade.
Carbon Steel: Cost-Effective and Strong
Carbon steel is widely used due to its high strength and cost-effectiveness. It is ideal for applications where high tensile strength is required, such as in construction and manufacturing.
Pros: Carbon steel is generally less expensive than stainless steel and aluminum, making it an attractive option for large-scale applications. It can also be easily welded and machined.
Cons: Its susceptibility to corrosion without proper finishing can limit its use in outdoor or humid environments. Additional surface treatments are often necessary to enhance its durability.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is compatible with various surface finishing techniques, including galvanizing and painting, which improve its resistance to corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards for structural integrity and corrosion resistance. Compliance with ASTM and other relevant standards is critical for ensuring product quality.
Copper: Excellent Conductivity and Aesthetic Appeal
Copper is valued for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties. It is often used in electrical applications and decorative finishes.
Pros: Copper’s natural antimicrobial properties make it suitable for applications in healthcare settings. Its aesthetic appeal is also a significant advantage in decorative applications.
Cons: Copper is more expensive than carbon steel and can tarnish over time, requiring regular maintenance to preserve its appearance.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in electrical components and plumbing, where its conductivity is crucial. Surface finishing techniques such as plating can enhance its durability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of copper and its compliance with international standards for electrical applications. Knowledge of local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental impact is also essential.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Metal Surface Finishing Techniques
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal surface finishing techniques | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive and aerospace components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost compared to alternatives | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and pharmaceutical equipment | High strength and durability | More expensive and complex to machine | High |
| Carbon Steel | Construction and manufacturing | Cost-effective and strong | Susceptible to corrosion without finishing | Low |
| Copper | Electrical components and decorative finishes | Excellent conductivity and antimicrobial | More expensive and requires maintenance | Medium |
This analysis serves as a strategic guide for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal surface finishing techniques
In the world of metal surface finishing, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. This section delves into the typical manufacturing processes and quality control (QC) practices for metal finishing techniques, providing actionable insights tailored for international buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What are the Main Stages of the Manufacturing Process in Metal Surface Finishing?
The manufacturing process for metal surface finishing typically comprises several key stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring that the final product meets performance and aesthetic standards.
How is Material Prepared for Surface Finishing?
Material preparation is the initial step where raw metal components are cleaned, degreased, and sometimes pre-treated to remove contaminants. Techniques such as sandblasting or chemical cleaning are commonly used. Proper material preparation is vital as it directly influences the adhesion of subsequent finishing processes. For instance, if a metal surface is not adequately cleaned, coatings like paint or powder may peel or chip, leading to premature failure.
What Forming Techniques are Used Before Finishing?
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo forming processes, which can include cutting, bending, or machining. The choice of forming technique depends on the desired shape and specifications of the final product. For example, laser cutting and CNC machining are popular for their precision and ability to produce complex geometries. This stage is critical, as any imperfections in the forming process can affect the efficiency of finishing techniques later on.
How is Assembly Handled in Metal Finishing?
In some cases, components are assembled before finishing. This approach is common in industries where parts need to be integrated for functional testing before applying final finishes. For example, in automotive or aerospace applications, assemblies may be subjected to pre-finishing inspections to ensure they meet design specifications. This step ensures that any surface finishing applied will enhance the overall product’s performance.
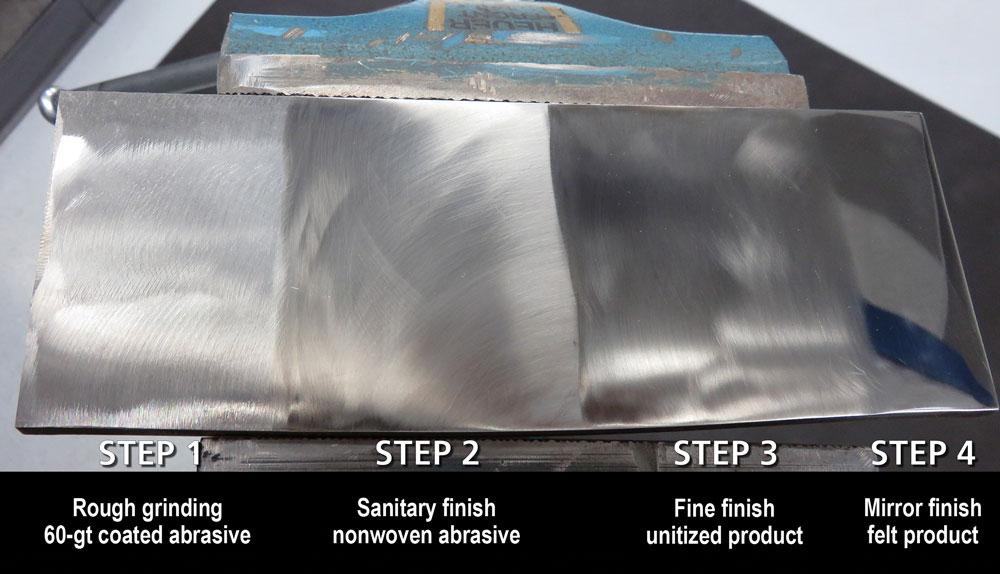
What Finishing Techniques are Typically Used?
The finishing stage encompasses a variety of techniques designed to enhance both the performance and aesthetics of metal components. Common finishing methods include:
- Electroplating: Used to apply a thin layer of metal for improved corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
- Anodizing: Primarily for aluminum, this technique enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
- Powder Coating: Provides a durable finish that can be tailored to various colors and textures.
- Polishing: Enhances surface smoothness and appearance, often used for decorative applications.
Each technique has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the final product, such as durability, appearance, and environmental resistance.
What Quality Assurance Practices are Essential in Metal Surface Finishing?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the metal finishing industry. Adherence to international and industry-specific standards ensures that products meet customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Look For?
ISO 9001 is the most recognized international standard for quality management systems. It provides a framework for consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Suppliers adhering to this standard demonstrate their commitment to quality processes. In addition, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for Europe or API standards for the oil and gas sector can provide additional assurance of product quality.
What are the Key QC Checkpoints in the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Ensures that raw materials meet specified criteria before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Involves monitoring production processes to detect and address issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducted on finished products to verify they meet all specifications before delivery.
Implementing these checkpoints helps prevent costly errors and ensures product integrity.
What Common Testing Methods are Used for Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of finished products. These can include:
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects or inconsistencies.
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensuring that components meet specified measurements using tools like calipers and micrometers.
- Coating Thickness Measurement: Verifying that finishes meet required thickness specifications using non-destructive testing techniques.
- Adhesion Testing: Assessing the bond strength of coatings to ensure durability.
These methods can help B2B buyers ascertain the quality and reliability of their products.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some strategies to ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards:
- Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices and adherence to standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should be willing to provide documentation of their QC processes, including test results and compliance with standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality practices and product reliability.
By implementing these strategies, buyers can mitigate risks associated with poor quality and ensure that their suppliers meet international standards.
What are the Unique QC Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, and the Middle East, understanding the nuances of quality control in different markets is essential. Variations in regulatory requirements, cultural perceptions of quality, and logistical challenges can affect the supply chain.
Engaging with suppliers who have experience in international markets can help mitigate these challenges. Additionally, understanding local regulations and standards can guide buyers in selecting suppliers that can consistently meet their quality requirements.
By focusing on comprehensive manufacturing processes and stringent quality assurance practices, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their product offerings and ensure long-term reliability and performance in their metal finishing projects.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal surface finishing techniques’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide serves as a checklist for B2B buyers seeking to procure metal surface finishing techniques. Understanding the nuances of various finishing methods is essential for ensuring that the final products meet specific performance and aesthetic requirements. This guide provides actionable steps to navigate the procurement process effectively.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider factors such as the type of metal, desired finish quality, and specific application requirements. This clarity will help you communicate your needs effectively to potential suppliers, ensuring that you receive appropriate solutions.
- Identify Finish Type: Determine whether you need plating, anodizing, polishing, or another method based on your product’s requirements.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Assess conditions like exposure to moisture or chemicals, which may dictate the type of finish required.
Step 2: Research Available Finishing Techniques
With numerous finishing methods available, understanding each option’s benefits and limitations is crucial. Take the time to research techniques such as electroplating, powder coating, or magnetic polishing.
- Evaluate Performance Characteristics: Different methods offer varying levels of durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal.
- Consider Industry Standards: Be aware of any industry-specific standards that may influence your choice of finishing technique.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, vet suppliers thoroughly to ensure they can meet your technical specifications. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
- Assess Experience and Expertise: Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific industry and the finishing techniques you require.
- Check for Certifications: Ensure that suppliers possess relevant certifications that demonstrate their adherence to quality standards.
Step 4: Request Sample Finishes
Obtaining samples of the proposed finishes can provide valuable insight into the quality and suitability of the work. This step allows you to assess the aesthetic and functional aspects of the finishing techniques firsthand.
- Evaluate Quality: Examine the samples for uniformity, surface smoothness, and overall appearance.
- Test Compatibility: Ensure the sample finish meets your performance requirements under expected operational conditions.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified potential suppliers and evaluated their offerings, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and contract terms. Aim for a balance between cost and quality to maximize value.
- Discuss Volume Discounts: Inquire about pricing structures for bulk orders, as many suppliers offer discounts based on quantity.
- Clarify Delivery Schedules: Confirm lead times and any penalties for delays, as timely delivery is crucial in maintaining your production schedules.
Step 6: Review and Finalize Contracts
Before finalizing any agreements, review contracts carefully to ensure all terms are clearly defined. Pay attention to aspects such as quality assurance, warranties, and liability clauses.
- Ensure Clarity on Specifications: Contracts should explicitly state the agreed-upon specifications and performance criteria for the finishing processes.
- Include Quality Control Measures: Outline the procedures for quality inspections and the recourse available should the finished product not meet the specified standards.
Step 7: Monitor and Evaluate Supplier Performance
After initiating production, continue to monitor the supplier’s performance. Regular evaluations will help ensure that they meet your expectations and maintain quality over time.
- Establish Feedback Mechanisms: Implement processes for providing feedback on quality and delivery, fostering a collaborative relationship.
- Conduct Periodic Audits: Schedule audits to assess compliance with quality standards and adherence to contractual obligations.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the sourcing process for metal surface finishing techniques, ensuring they procure high-quality finishes that enhance the durability and appearance of their products.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal surface finishing techniques Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Surface Finishing Techniques?
Understanding the cost structure of metal surface finishing techniques is essential for B2B buyers. The primary components contributing to the overall cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and the supplier’s profit margin.
-
Materials: The type of finishing chosen significantly impacts material costs. For instance, anodizing and electroplating require specific chemicals and metals, which can vary in price based on market conditions and purity levels. Custom finishes may also require unique materials, further increasing costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is often necessary for complex finishing processes. The cost of labor can vary by region, with skilled labor being more expensive in Europe compared to South America or Africa. Additionally, labor costs can fluctuate based on the level of automation in the manufacturing process.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, equipment depreciation, and indirect labor costs. Highly specialized processes like electropolishing may have higher overhead due to the need for advanced machinery.
-
Tooling: Depending on the finishing technique, tooling costs can vary. Techniques requiring custom molds or specialized equipment, such as magnetic polishing or lapping, may involve higher upfront investments.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that finished products meet industry standards necessitates rigorous QC procedures, which can add to the cost. Certifications for quality, especially for industries such as aerospace or medical, can also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international transactions. Incoterms will dictate who bears the cost of logistics, and buyers should factor these into their total cost analysis.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will vary based on competition, demand, and the complexity of the finishing process. Niche or high-quality providers may charge a premium, while larger suppliers might offer volume discounts.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Finishing Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of metal finishing services, significantly impacting total costs for buyers.
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often have minimum order quantities (MOQ), and larger orders can lead to reduced per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and consider bulk purchases for cost savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the additional labor and materials required. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of base metal and finishing material plays a crucial role in pricing. For example, the cost of nickel for electroplating can be volatile, affecting overall pricing.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products requiring specific certifications or higher quality standards will generally incur higher costs. Buyers should evaluate whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reliability, experience, and reputation of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and consistent quality.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms will dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks during transport. It is crucial for buyers to understand these terms to accurately calculate total costs.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Cost-Efficiency for Metal Finishing?
B2B buyers should adopt specific strategies to enhance cost-efficiency when sourcing metal surface finishing techniques.
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may offer discounts for long-term contracts or high-volume purchases.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider the long-term costs associated with each finishing technique, including maintenance and durability. A higher initial investment in quality finishing may result in lower overall costs due to reduced wear and maintenance.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers must be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect pricing. Understanding local regulations and potential tariffs can help in budgeting accurately.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Conduct thorough research to find suppliers that offer a balance of quality and cost. Request samples to assess the finish and durability before committing to larger orders.
Buyers should approach the sourcing of metal surface finishing techniques with a comprehensive understanding of these cost components and pricing influencers. This knowledge will enable them to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal surface finishing techniques With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Metal Surface Finishing Techniques
In the realm of metal processing, surface finishing is crucial for enhancing both the performance and aesthetics of metal components. However, various alternative solutions exist that can achieve similar objectives, offering unique benefits and drawbacks. Understanding these alternatives can help B2B buyers make informed decisions based on specific project requirements and constraints.
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Surface Finishing Techniques | Laser Surface Treatment | Chemical Surface Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High durability, corrosion resistance, and improved aesthetics. | Excellent precision and minimal thermal impact. | Effective for specific coatings and cleaning. |
| Cost | Moderate to high, depending on the technique used. | Typically higher initial investment; operational cost varies. | Often lower initial costs, but can incur high waste disposal fees. |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and equipment setup. | Complex setup; requires specialized knowledge and equipment. | Generally easier to apply but needs proper safety measures. |
| Maintenance | Regular maintenance needed for equipment. | Low maintenance once set up; minimal wear on tools. | Maintenance can be high due to chemical handling requirements. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for consumer products, automotive parts, and machinery. | Best for high-precision applications in aerospace and medical industries. | Suitable for industrial cleaning and preparing surfaces for coatings. |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Laser Surface Treatment?
Laser surface treatment is a cutting-edge technology that uses focused laser beams to alter the surface properties of metals. One of its main advantages is precision; lasers can target very specific areas without affecting the surrounding material, making it ideal for applications requiring fine detail, such as aerospace components. Additionally, the process produces minimal thermal distortion, which is beneficial for maintaining the integrity of sensitive parts. However, the initial setup costs can be significant, and the technology requires specialized training to operate effectively.
How Does Chemical Surface Treatment Compare?
Chemical surface treatment involves the use of chemical solutions to clean, etch, or coat metal surfaces. This method is often more cost-effective than traditional metal finishing techniques, making it appealing for large-scale industrial applications. It can effectively prepare surfaces for subsequent treatments, such as painting or plating. However, the process can generate hazardous waste, leading to potential environmental compliance costs. Additionally, safety measures must be strictly adhered to when handling chemicals, which can complicate implementation.
Conclusion: How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right Solution for Their Needs?
When selecting a surface treatment solution, B2B buyers should consider factors such as project requirements, budget constraints, and the intended application of the metal components. Metal surface finishing techniques excel in providing durability and aesthetics for a wide range of products, while laser surface treatment offers precision for specialized applications. On the other hand, chemical treatments can be more economical for large-scale operations but come with environmental responsibilities. Evaluating these aspects will empower buyers to choose the best solution tailored to their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal surface finishing techniques
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Metal Surface Finishing Techniques?
Understanding the technical properties of metal surface finishing is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when selecting processes that align with specific project requirements. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the metal based on its composition and mechanical properties. Different grades exhibit varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade ensures that the finished product meets performance expectations and regulatory standards, ultimately affecting durability and cost-effectiveness.
2. Surface Roughness (Ra)
Surface roughness, expressed in micrometers (µm), quantifies the texture of a metal surface. A lower Ra value indicates a smoother finish, which can enhance aesthetic appeal and functional performance, such as reducing friction in moving parts. B2B buyers must specify the desired surface roughness to ensure compatibility with the intended application, as certain industries require strict tolerances for optimal functionality.
3. Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a manufactured part’s dimensions. It is critical for ensuring that components fit together correctly in assemblies. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels is vital to ensure product interoperability and to minimize waste during production, which can lead to significant cost savings.
4. Coating Thickness
Coating thickness pertains to the depth of the finish applied to the metal surface, such as paint or electroplating. This property is important as it directly impacts both the aesthetic qualities and protective capabilities of the finish. B2B buyers should specify coating thickness to ensure that the product meets environmental resistance requirements, particularly in industries like automotive and aerospace.
5. Adhesion Strength
Adhesion strength measures how well a finish bonds to the substrate material. High adhesion strength is essential for durability, especially in environments subject to mechanical stress or corrosion. For B2B buyers, understanding adhesion properties helps in choosing finishes that will withstand the operational conditions of the final product.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Metal Surface Finishing?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Below are common trade terms relevant to metal surface finishing:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of metal finishing, understanding OEM specifications is crucial for ensuring that the finishing processes align with the original product design and performance standards.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This is particularly important in metal finishing, where economies of scale can significantly affect pricing. B2B buyers should assess their needs against MOQ requirements to optimize costs and inventory levels.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For metal finishing, an RFQ should detail the finishing specifications, including material grade, surface roughness, and coating type, to obtain accurate and competitive quotes from suppliers.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in a transaction. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers engaged in cross-border transactions, as they clarify aspects such as risk, shipping costs, and delivery obligations related to metal finishing supplies.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the period from when an order is placed until it is fulfilled. In metal finishing, lead times can vary significantly based on the complexity of the finishing process and the supplier’s capacity. B2B buyers should consider lead times in their project planning to ensure timely delivery and avoid production delays.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance the quality and efficiency of their metal surface finishing processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal surface finishing techniques Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in Metal Surface Finishing Techniques?
The metal surface finishing sector is witnessing significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer demands. Global market dynamics indicate a robust growth trajectory, with an increasing emphasis on enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal in metal products. Key trends include the rise of automation and digitalization in manufacturing processes, which are streamlining operations and reducing lead times. For B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, adopting these technologies can enhance competitiveness and operational efficiency.
Emerging sourcing trends highlight a shift towards specialized techniques such as powder coating and anodizing, which are favored for their durability and corrosion resistance. Additionally, buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers who can provide customized solutions tailored to specific industrial requirements. The demand for eco-friendly finishes is also rising, with companies seeking coatings that align with their sustainability goals. This trend is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to enhance their market positioning through environmentally responsible practices.
Furthermore, global supply chains are adapting to disruptions by diversifying sourcing strategies. For instance, manufacturers in Brazil and Nigeria are exploring local suppliers to mitigate risks associated with global logistics. These market dynamics present opportunities for buyers to forge strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers that offer innovative finishing techniques while ensuring consistent quality and timely delivery.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting Metal Surface Finishing Techniques?
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the metal surface finishing sector. The environmental impact of traditional finishing processes, such as high energy consumption and the use of hazardous materials, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who implement eco-friendly techniques and materials, such as water-based coatings and recyclable substrates.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers’ practices to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and ethical labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the ResponsibleSteel certification are gaining traction, signaling a commitment to sustainability. By partnering with certified suppliers, businesses can enhance their reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Moreover, the adoption of “green” materials in metal finishing processes not only reduces environmental footprints but also meets regulatory requirements. For instance, transitioning to non-toxic coatings can significantly diminish hazardous waste, providing a dual benefit of compliance and enhanced product safety. This focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing is reshaping buyer-supplier relationships, driving demand for transparency and accountability in the metal surface finishing industry.
What Is the Historical Context of Metal Surface Finishing Techniques?
The evolution of metal surface finishing techniques can be traced back to ancient civilizations, where basic polishing methods were employed to enhance the appearance and durability of metal artifacts. Over the centuries, advancements in technology have transformed these processes significantly. The industrial revolution introduced mechanized methods, allowing for more efficient and consistent finishes.
In the late 20th century, the introduction of electroplating and anodizing marked a significant leap in surface treatment capabilities, providing enhanced corrosion resistance and aesthetic qualities. Today, the sector is characterized by sophisticated techniques that leverage automation, digital technologies, and sustainable practices, catering to the growing demands of various industries. This historical context not only highlights the technological advancements in the field but also underscores the ongoing need for innovation and adaptation in response to market trends.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal surface finishing techniques
-
How do I select the right metal surface finishing technique for my project?
Choosing the appropriate metal surface finishing technique hinges on several factors, including the type of metal, the desired finish quality, and the specific application requirements. For instance, if corrosion resistance is paramount, consider electroplating or anodizing. Conversely, if aesthetics and smoothness are your goals, polishing or powder coating may be more suitable. It’s also essential to evaluate cost-effectiveness and turnaround times, as some methods may be more labor-intensive than others. Consulting with experienced suppliers can provide valuable insights tailored to your project needs. -
What is the best metal finishing method for improving corrosion resistance?
Electroplating and anodizing are two of the most effective metal finishing techniques for enhancing corrosion resistance. Electroplating involves depositing a layer of protective metal, such as nickel or chromium, on the substrate, creating a barrier against environmental factors. Anodizing, particularly for aluminum, enhances the natural oxide layer, making it thicker and more resistant to corrosion. The choice between these methods depends on the base metal and the intended application, so assessing your specific needs is crucial for optimal results. -
What factors should I consider when vetting a metal finishing supplier?
When vetting suppliers for metal finishing, consider their industry experience, certifications, and production capabilities. Request samples of their work to assess quality, and inquire about their adherence to international standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, evaluate their communication practices and customer service responsiveness, as these factors can significantly impact your project’s success. It’s also wise to check reviews or testimonials from other B2B clients to gauge their reliability and consistency. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal finishing services?
Minimum order quantities for metal finishing services can vary widely based on the supplier and the specific technique employed. Some suppliers may have MOQs as low as 50 units for standard processes, while more specialized techniques could require larger quantities to offset setup costs. Discussing your needs with potential suppliers can help determine their flexibility regarding MOQs, especially if you are a small or medium-sized business seeking tailored solutions. -
How can I customize my metal finishing process?
Customization in metal finishing is achievable through various methods, including selecting specific coatings, finishes, or treatments that align with your product requirements. Engaging directly with your supplier to discuss your unique specifications is crucial; they can often accommodate adjustments to processing techniques or materials. Additionally, consider requesting prototypes or samples to ensure that the final product meets your expectations before full-scale production. -
What are the typical payment terms for international metal finishing orders?
Payment terms for international orders can vary by supplier but often include options such as upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. Many suppliers may also accept letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risk. It’s essential to clarify payment terms during negotiations and ensure they align with your cash flow and budgeting strategies. Establishing clear agreements upfront can help avoid misunderstandings later in the process. -
How do I ensure quality assurance during the metal finishing process?
To ensure quality assurance in metal finishing, request a detailed quality control plan from your supplier. This should outline their inspection processes, testing methods, and compliance with relevant standards. Regular communication during production can help address any issues promptly. Additionally, consider implementing third-party inspections to verify quality before shipment, particularly for large orders or critical applications. Establishing these protocols will help you maintain high standards throughout the finishing process. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing metal finishing services internationally?
When sourcing metal finishing services internationally, consider shipping costs, delivery times, and customs regulations. It’s crucial to work with suppliers who have experience in exporting to your region and can navigate these logistics efficiently. Additionally, ensure that you have a clear understanding of lead times and any potential delays that may arise from customs clearance. Collaborating with a logistics partner can also streamline the process, helping to manage shipping and tracking effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Metal Surface Finishing Techniques Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Metal Supermarkets – Metal Finishing Processes
Domain: metalsupermarkets.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Different types of metal finishing processes include: 1. Plating (or conversion coatings) – Covers the substrate with thin layers of another metal (e.g., zinc, nickel, chromium, cadmium) to improve durability, surface friction, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics. Types: – Electroplating: Involves immersing the component in a metal ion bath and applying direct current to deposit ions. – Electro…
2. IQS Directory – Metal Finishing Solutions
Domain: iqsdirectory.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Types of Metal Finishing: Metal plating, chemical coating, grinding, buffing, electroplating, sandblasting. Principles: Protective coating application, surface quality enhancement, corrosion resistance, rust prevention, increased strength. Applications: Automotive, aerospace, electronics, construction, manufacturing. Key Processes: Electroplating, electroless plating, surface preparation (cleaning…
3. Universal Grinding – Metal Finishing Solutions
Domain: universalgrinding.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Types of Metal Finishing: 1. Plasma Spray Coating: High-temperature coating process providing protection against corrosion, erosion, and wear. 2. Sand Blasting: Removes dirt and debris, increasing productivity and efficiency; uses various abrasive materials for different finishes. 3. Brushed Metal: Creates a textured grain finish by applying friction, resulting in a smooth exterior. 4. Chemical Fi…
4. Endura Steel – Electroless Plating Solutions
Domain: endura-steel.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: 1. Electroless Plating: A chemical deposition process that does not require an external power source, offering reduced water and chemical consumption, improved uniformity of coating thickness, and the ability to deposit on non-conductive surfaces. Applications include automotive (corrosion protection), electronics (circuit board manufacturing), and aerospace (coating components for durability).
…
5. Benchmark Abrasives – Abrasive Tools & Accessories
Domain: benchmarkabrasives.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Backing Pad, Blade, Buffing Compound, Buffing Wheels, Carbide Burr, Cartridge Roll, Change Disc, Chop Saw Wheel, Convolute Wheel, Cut-off Wheel, Fiber Disc, Flap Disc, Flap Wheel, Grinding Cup Wheel, Grinding Wheel, Hand Pads, Hole Saw, Hook & Loop Disc, Mandrel, Non-Woven Abrasives, Nylon Wire Product, PSA Disc, Recip Blade, Shop Roll, Spiral Band, Steel Brush, Stud Cutter, Surface Conditioning, …
6. Kramer Industries – Metal Finishing Methods
Domain: kramerindustriesonline.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: The text discusses various metal finishing methods and their importance. Key methods include: 1. Sanding – uses abrasive materials like sandpaper for surface finishing. 2. Ultrasonic Polishing – employs a fine-tipped tool on an ultrasonic spindle for precise polishing. 3. Tumbling – involves rotating abrasive media with products to clean and finish surfaces. 4. Magnetic Polishing – uses magnetized…
7. Valence Surface Technologies – Metal Finishing Services
Domain: valencesurfacetech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Valence Surface Technologies offers a wide range of metal finishing services including: 1. Chemical Processing: Aluminum Etch, Anodizing (Boric, Tartaric, Chromic, Sulfuric, Hard, Phosphoric), Nital Etch, Passivation of Stainless Steel, Phosphate, Fluoride, Titanium Etch and Clean, Zinc Phosphate, Chemical Film. 2. Nondestructive Testing: Boroscope Inspection, Conductivity Inspection, Copper Sulfa…
8. Metal Cutting – Surface Finish Chart
Domain: metalcutting.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: A metal surface finish chart is a reference tool used for quality assurance in metal surface finishes. It provides guidelines on standard surface finishes, including parameters like Roughness Average (Ra), Root Mean Square Roughness (RMS), Maximum Roughness Depth (Rmax), and Mean Roughness (Rz). The chart helps in understanding the texture of a surface, characterized by its lay, roughness, and wav…
9. Wayken – Metal Surface Finishing Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Metal surface finishing is essential in metal component manufacturing, enhancing aesthetics and durability. Key types of metal surface finishes include: 1. Plating or Conversion Coatings: Involves coating substrates with metals like zinc or nickel to improve durability and corrosion resistance. Types include Electroplating (using electric current) and Electroless Plating (autocatalytic). 2. Anodiz…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal surface finishing techniques
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of metal surface finishing techniques is essential for enhancing product longevity, performance, and aesthetic appeal. By understanding the various methods—such as anodizing, electroplating, and powder coating—businesses can select the most appropriate finishing processes that align with their specific requirements and budget constraints. This not only improves the quality of the final product but also helps in reducing waste and operational costs.
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in emerging markets like Brazil, Nigeria, and across the Middle East and Europe, the ability to source high-quality surface finishing services can significantly impact competitiveness. Investing in the right finishing techniques will not only meet local standards but also open doors to global markets, where product quality is paramount.
As you consider your sourcing strategies, prioritize partnerships with reputable finishing service providers who demonstrate innovation and reliability. The future of metal finishing is dynamic, and those who adapt to advancements in technology and sustainability will lead the way. Embrace these opportunities to enhance your supply chain and elevate your product offerings in the global marketplace.