Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal strength chart
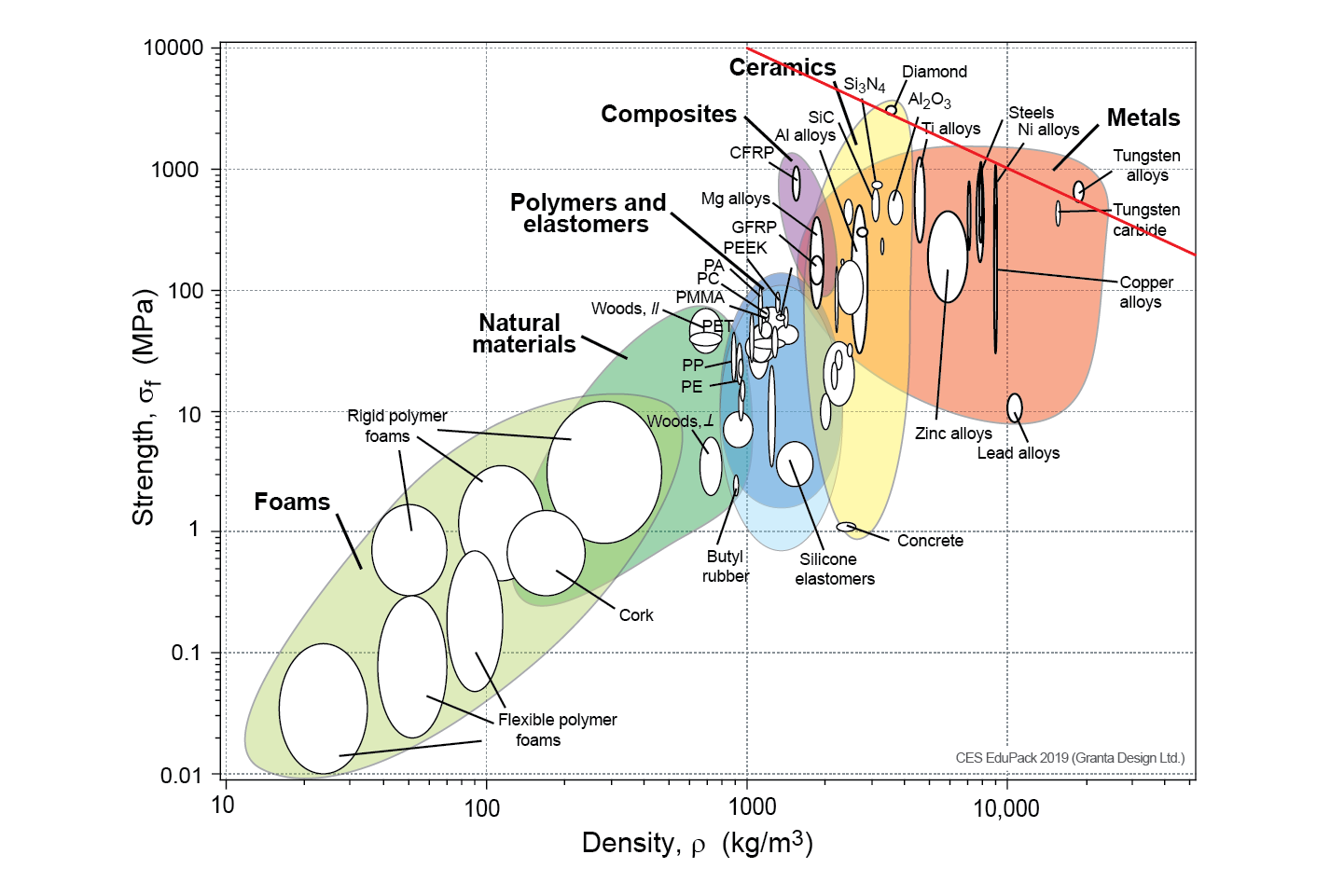
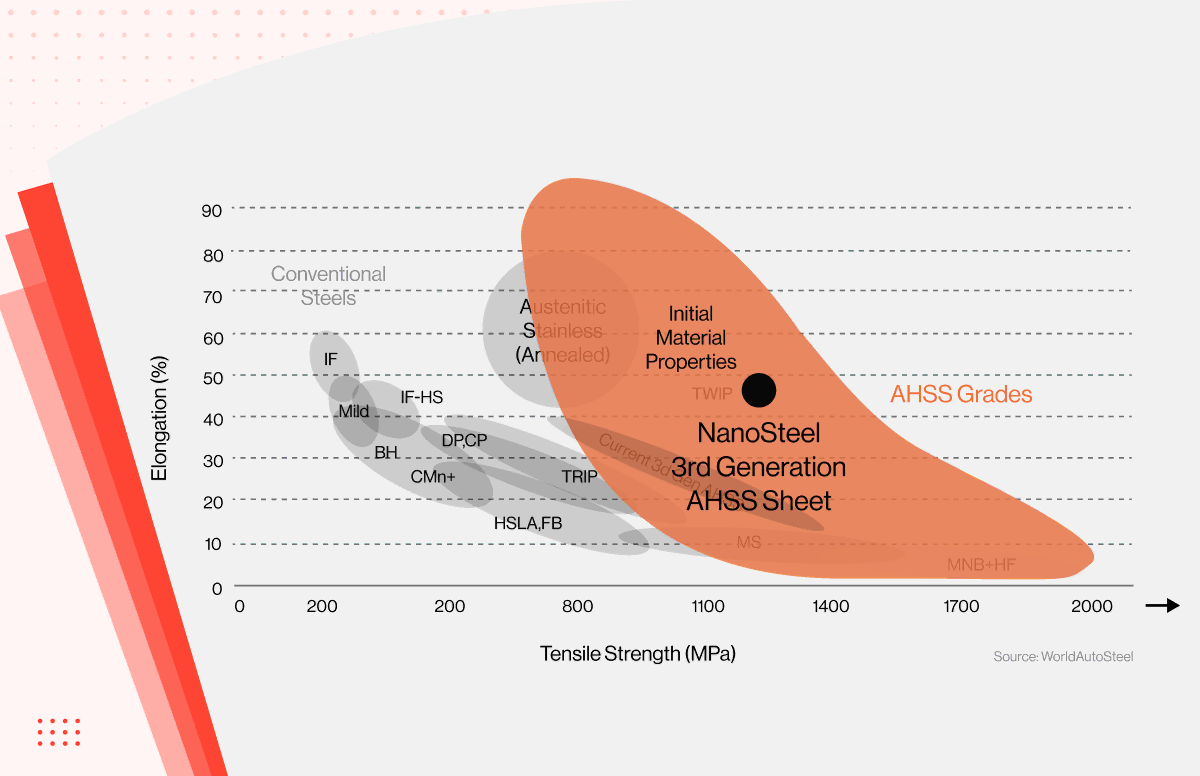
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, B2B buyers face the challenge of sourcing materials that meet stringent strength requirements while ensuring cost-effectiveness and reliability. Understanding the nuances of a metal strength chart is essential for making informed purchasing decisions, particularly when considering the diverse applications across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. This guide delves into the intricacies of metal strength, providing an in-depth analysis of various metals, their strengths, and how they compare under different conditions.
From tensile strength and yield strength to the effects of temperature and humidity, we explore the essential metrics that define metal performance. Additionally, we cover the critical aspects of supplier vetting, helping you identify reputable sources that align with your project specifications and budget constraints.
Tailored for international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Germany and Brazil—this comprehensive resource empowers you to navigate the complexities of metal sourcing with confidence. With actionable insights and practical tools, you’ll be equipped to select the optimal materials for your projects, ensuring safety, durability, and overall success in your manufacturing endeavors.
Understanding metal strength chart Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength Chart | Measures maximum tensile load before failure; includes yield strength. | Aerospace, Automotive, Construction | Pros: Essential for safety; provides clear strength metrics. Cons: May not account for all environmental factors. |
| Yield Strength Chart | Indicates the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically. | Manufacturing, Heavy Equipment | Pros: Useful for understanding material limits; aids in design. Cons: Limited in scope; does not reflect ultimate failure. |
| Hardness Chart | Assesses material resistance to deformation; includes Rockwell and Brinell scales. | Tooling, Machining, Metal Fabrication | Pros: Helps in selecting materials for wear resistance. Cons: Hardness does not correlate directly with tensile strength. |
| Impact Strength Chart | Evaluates a material’s ability to absorb energy during deformation. | Safety Equipment, Automotive, Aerospace | Pros: Critical for dynamic loading applications; ensures material reliability. Cons: Testing can be complex and expensive. |
| Compressive Strength Chart | Measures material’s ability to withstand axial loads without failure. | Construction, Civil Engineering | Pros: Vital for structural applications; ensures stability under load. Cons: Limited use in tensile applications; requires careful interpretation. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of a Tensile Strength Chart?
Tensile strength charts provide essential metrics for understanding a metal’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. This type of chart typically includes both ultimate tensile strength and yield strength, offering a comprehensive view of a material’s performance under stress. B2B buyers in industries such as aerospace and automotive must prioritize these metrics to ensure safety and structural integrity in their designs. When purchasing, it’s crucial to consider not just the numbers but also how these strengths relate to specific applications and environmental conditions.
How Does a Yield Strength Chart Differ from Other Strength Charts?
Yield strength charts focus on the point at which a material begins to deform permanently under stress. This is particularly important for industries like manufacturing and heavy equipment, where materials must maintain their shape and functionality under operational loads. Buyers should evaluate yield strength alongside other metrics, ensuring that the selected material can handle expected stress levels without compromising performance. Understanding the limitations of yield strength is vital, as it does not indicate the point of complete failure.
Why Is Hardness Measurement Important for B2B Buyers?
Hardness charts measure a material’s resistance to deformation and wear, often using scales such as Rockwell or Brinell. This information is crucial for industries like tooling and machining, where materials are subjected to abrasive conditions. While hardness is a valuable metric, it should not be the sole consideration when selecting materials, as it does not directly correlate with tensile strength. B2B buyers must balance hardness with other strength characteristics to ensure optimal performance for their applications.
What Role Does Impact Strength Play in Material Selection?
Impact strength charts assess how well a material can absorb energy during sudden impacts, making them essential for safety equipment and aerospace applications. Understanding a material’s impact resistance helps B2B buyers select appropriate materials for high-stress environments where failure could have catastrophic consequences. While these charts provide vital data, the complexity and cost of impact testing can be a downside, necessitating careful analysis of the results.
How Is Compressive Strength Relevant to Structural Applications?
Compressive strength charts measure a material’s ability to withstand axial loads, making them particularly relevant in construction and civil engineering. This type of strength is critical for ensuring stability and safety in structures such as buildings and bridges. When selecting materials based on compressive strength, B2B buyers must consider the specific loads expected in their applications, as well as any potential environmental factors that may affect performance. Understanding the relationship between compressive and tensile strength is also important for comprehensive material selection.
Key Industrial Applications of metal strength chart
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal strength chart | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Selection of materials for aircraft components | Ensures safety and compliance with stringent regulations | Need for certified materials and adherence to international standards |
| Construction | Choosing steel grades for structural frameworks | Guarantees durability and load-bearing capacity | Local availability of materials and compliance with building codes |
| Automotive | Evaluating metals for engine parts and chassis | Enhances performance and longevity of vehicles | Supplier reliability and material traceability |
| Oil and Gas | Determining suitable alloys for pipelines and drilling equipment | Minimizes risk of failure under extreme conditions | Need for corrosion-resistant materials and compliance with safety regulations |
| Electronics | Sourcing metals for heat sinks and enclosures | Improves thermal management and overall product reliability | Precision in material specifications and supplier capabilities |
How is the Metal Strength Chart Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, the metal strength chart is critical for selecting materials that can withstand high stress and extreme conditions. Engineers rely on these charts to choose alloys with specific tensile and yield strengths for components such as wings, fuselages, and landing gear. The consequences of using inappropriate materials can be catastrophic, leading to safety failures. International buyers must ensure that suppliers provide certified materials that comply with aviation standards, such as AS9100, to mitigate risks.
What Role Does the Metal Strength Chart Play in Construction?
In construction, the metal strength chart assists engineers and architects in selecting the right steel grades for structural frameworks, beams, and reinforcements. The chart provides essential data on load-bearing capacities, which is vital for ensuring structural integrity and safety. Buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, should consider the local availability of these materials and ensure compliance with local building codes and standards to avoid project delays or safety issues.
How is the Metal Strength Chart Important in Automotive Manufacturing?
Automotive manufacturers utilize metal strength charts to evaluate materials for engine parts, chassis, and safety components. High-strength steels and aluminum alloys are often selected based on their ability to endure mechanical stresses while maintaining lightweight properties. For international buyers, understanding the sourcing landscape is crucial, as they need reliable suppliers who can deliver materials that meet specific performance criteria and regulatory standards.
Why is the Metal Strength Chart Critical in Oil and Gas Industries?
In the oil and gas sector, the metal strength chart is essential for selecting alloys that can endure high pressures and corrosive environments in pipelines and drilling equipment. The right material choice minimizes the risk of equipment failure, which can lead to costly downtime and environmental hazards. Buyers must prioritize sourcing materials that are not only strong but also resistant to corrosion, ensuring compliance with industry safety regulations.
How Does the Metal Strength Chart Benefit Electronics Manufacturing?
For the electronics industry, the metal strength chart is used to identify suitable materials for heat sinks, enclosures, and other components that require effective thermal management. The right choice of metals can enhance product reliability and performance. International buyers should focus on precise material specifications and supplier capabilities to ensure that they receive metals that meet the required thermal and mechanical properties for their applications.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal strength chart’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Misunderstanding Metal Strength Metrics
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the various metrics used to evaluate metal strength, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue strength. This confusion can lead to miscalculations when selecting materials, resulting in project delays, safety hazards, or costly material failures. For example, an aerospace engineer may choose a metal based solely on its tensile strength without considering how it behaves under cyclic loading, ultimately jeopardizing the integrity of a critical component.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should familiarize themselves with the specific metrics relevant to their applications. A comprehensive understanding of different strength types can be achieved through training sessions, webinars, or by consulting with materials engineers. Additionally, utilizing a detailed metal strength chart that includes definitions and contextual examples for each metric can facilitate better decision-making. Buyers should also collaborate with suppliers who provide educational resources and technical support, ensuring that they select metals that not only meet tensile strength requirements but also perform well under the specific conditions they will face in use.
Scenario 2: Inadequate Specification of Material Properties
The Problem: Another common pain point occurs when buyers fail to specify detailed material properties in their orders. This oversight can lead to receiving materials that do not meet project requirements, such as incorrect alloy grades or thicknesses. For instance, a construction firm might specify “steel” without clarifying the needed grade, resulting in the delivery of a lower-strength alloy that cannot support the intended load, thereby risking structural failure.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, B2B buyers should create a standardized specification checklist that outlines all necessary material properties, including grade, thickness, and applicable strength metrics. This checklist should be based on the requirements identified in the metal strength chart relevant to their industry. Additionally, engaging in pre-order consultations with suppliers can help clarify these specifications. By thoroughly communicating their needs and confirming the details before placing an order, buyers can ensure they receive the correct materials that align with their project requirements.
Scenario 3: Ignoring Environmental and Operational Factors
The Problem: Many buyers overlook the impact of environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive elements, on metal strength. This oversight can lead to significant issues, especially in industries like oil and gas or construction, where materials are subjected to harsh conditions. For example, selecting a metal based solely on its strength without considering how it reacts to high temperatures can lead to catastrophic failures in critical infrastructure.
The Solution: To address this challenge, buyers should integrate environmental considerations into their material selection process. A thorough review of the metal strength chart should include not only mechanical properties but also a section on how different metals perform under varying conditions. Buyers can also leverage case studies and industry reports that provide insights into how specific metals have behaved in real-world applications. Collaborating with suppliers who understand these environmental factors and can recommend suitable materials will further enhance the durability and longevity of the products, ensuring they stand the test of time under operational stresses.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal strength chart
What Are the Key Properties of Common Metals in a Strength Chart?
When evaluating materials for manufacturing and engineering applications, understanding the properties of metals is crucial. Here, we analyze four common metals—steel, aluminum, copper, and titanium—focusing on their strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for various applications.
How Does Steel Perform in Terms of Strength and Durability?
Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability, making it a staple in construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries. Its temperature and pressure ratings are impressive, with many steel grades capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Additionally, steel exhibits good corrosion resistance when treated or alloyed, such as in stainless steel variants.
Pros: Steel’s primary advantages include its high strength-to-weight ratio, versatility in applications, and cost-effectiveness. It can be manufactured in various forms, including sheets, plates, and bars, which enhances its usability across different projects.
Cons: However, steel can be prone to rust if not properly protected, and its weight can be a disadvantage in applications where lighter materials are preferred. Manufacturing complexity can also increase with specific grades or treatments.
Impact on Application: Steel is suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as structural beams and machinery parts, where strength and reliability are paramount. It is compatible with various media, including water, oil, and gases, making it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, and Europe should consider compliance with international standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS when selecting steel. Local availability and cost fluctuations can also impact procurement strategies.
What Are the Benefits of Using Aluminum?
Aluminum is lightweight and boasts excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications in the aerospace, automotive, and packaging industries. Its thermal and electrical conductivity is also noteworthy, adding to its versatility.
Pros: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can lead to reduced transportation costs and improved energy efficiency in applications. It is also relatively easy to fabricate and can be anodized for additional protection.
Cons: However, aluminum generally has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. It can also be more expensive, particularly for high-grade alloys.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is particularly suited for applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aircraft components or lightweight vehicles. Its compatibility with various environments, including marine and chemical applications, further enhances its appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific aluminum grades and their corresponding standards, as well as potential import tariffs that may affect overall costs in different regions.
Why Choose Copper for Electrical Applications?
Copper is primarily recognized for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical wiring and components. It also has good corrosion resistance, particularly in non-oxidizing environments.
Pros: The key advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which is essential for electrical applications. It is also ductile, allowing for easy shaping and installation.
Cons: However, copper is heavier than aluminum and can be more expensive. It is also susceptible to corrosion in certain environments, particularly when exposed to moisture and air.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for electrical applications, such as wiring and circuit boards, where conductivity is paramount. Its compatibility with various media, including water and gases, further broadens its application scope.
Considerations for International Buyers: B2B buyers should consider the implications of copper pricing fluctuations and ensure compliance with relevant electrical standards in their regions.
What Makes Titanium a Unique Choice?
Titanium is known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments. It is often used in aerospace, medical, and high-performance applications.
Pros: The primary advantage of titanium is its strength combined with low weight, making it ideal for applications where performance is critical. Its biocompatibility also makes it suitable for medical implants.
Cons: However, titanium is significantly more expensive than other metals, and its manufacturing processes can be complex and time-consuming.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly effective in applications requiring high strength and corrosion resistance, such as in aerospace components and medical devices. Its compatibility with various media, including seawater, adds to its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the high costs associated with titanium and ensure they are selecting the right grade for their specific application, adhering to international standards.
Summary Table of Metal Strengths
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal strength chart | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural beams, machinery parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | Prone to rust | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, packaging | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower tensile strength | Medium to High |
| Copper | Electrical wiring, circuit boards | Superior electrical conductivity | Heavier and more expensive | Medium to High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | High cost and complexity | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of common metals in the strength chart, aiding B2B buyers in making informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal strength chart
Manufacturing processes and quality assurance are pivotal in the production of metals, particularly when considering their strength and application. Understanding these processes is essential for B2B buyers who require reliable materials that meet specific strength requirements. Below is an in-depth exploration of typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, and quality control measures relevant to the metal strength chart.
What Are the Main Stages of Metal Manufacturing Processes?
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Manufacturing?
The first step in metal manufacturing involves material preparation. This stage includes selecting the right type of metal or alloy, which is critical for ensuring the desired strength characteristics. Common materials include various grades of steel, aluminum, copper, and specialized alloys.
Material preparation also involves processes such as cutting, casting, or forging. This ensures that the metal is shaped into a form that can be further processed. For instance, steel plates may be cut to specific dimensions before being subjected to forming processes. The choice of material and the initial preparation can significantly impact the final product’s strength and durability.
What Forming Techniques Are Commonly Used in Metal Manufacturing?
Forming processes shape the prepared materials into the desired configurations. Techniques such as rolling, extrusion, and stamping are widely utilized.
-
Rolling: This involves passing metal between rollers to reduce thickness and improve strength through work hardening. Hot and cold rolling are common methods, with cold rolling often yielding higher tensile strength.
-
Extrusion: This technique involves forcing metal through a die to create specific cross-sectional profiles. It is particularly effective for creating complex shapes while maintaining material integrity.
-
Stamping: Used to create flat pieces from metal sheets, stamping can produce high volumes of parts quickly and efficiently, ensuring uniformity in thickness and strength.
Each of these techniques contributes to the overall mechanical properties of the metal, including tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue resistance.
How Does Assembly Fit Into Metal Manufacturing?
Assembly is a critical stage where formed parts are joined to create a final product. This can involve welding, riveting, or using adhesives, depending on the application. Each joining method can affect the overall strength of the assembly. For instance, welding can introduce heat-affected zones that may weaken the material if not managed correctly.
In sectors like automotive or aerospace, precise assembly is vital, as the failure of a single component can compromise safety. Therefore, attention to detail during assembly is paramount to ensure that the final product meets specified strength standards.
What Finishing Techniques Are Important for Metal Products?
Finishing processes enhance the surface characteristics of metals and can also affect their strength. Techniques such as coating, anodizing, and heat treatment are commonly employed.
-
Coating: This can provide corrosion resistance, which is crucial for metals used in harsh environments.
-
Anodizing: Specifically for aluminum, this process enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness, contributing to overall durability.
-
Heat Treatment: Methods like quenching and tempering are used to alter the microstructure of metals, significantly improving their strength and toughness.
These finishing techniques not only improve the appearance of the metal but also ensure that it performs reliably in its intended application.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Critical in Metal Manufacturing?
Which International Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance in metal manufacturing is governed by various international standards, with ISO 9001 being one of the most recognized. This standard emphasizes a process-oriented approach to managing quality and ensures that organizations consistently meet customer requirements.
In addition to ISO 9001, industry-specific standards such as CE marking for products sold in the European market or API standards for oil and gas applications are critical. These certifications assure buyers that the products meet specific safety and quality benchmarks.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control checkpoints are integral to ensuring that manufacturing processes yield products that meet the required specifications. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection assesses the quality of raw materials and components before they enter the production process.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during manufacturing, this ensures that processes are performed correctly and that the products are being produced within specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): This final inspection evaluates the finished product against predefined specifications before it is shipped to customers.
By implementing these checkpoints, manufacturers can identify and rectify issues early, reducing the likelihood of defects in the final product.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are several strategies to ensure the supplier meets quality standards:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturer’s processes, quality control measures, and adherence to relevant standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the manufacturing process, including results from various testing methods.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and product quality.
-
Certifications: Verify that the supplier holds relevant certifications, such as ISO or industry-specific standards, which can serve as a testament to their commitment to quality.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Quality Control?
To ensure that metals meet strength requirements, various testing methods are employed, including:
-
Tensile Testing: This determines the maximum amount of tensile stress a material can withstand before failure. It is essential for understanding the material’s behavior under load.
-
Hardness Testing: Methods like Rockwell or Brinell hardness tests assess a material’s resistance to deformation, which correlates with its strength.
-
Impact Testing: This evaluates the material’s toughness and ability to absorb energy during sudden impacts, crucial for applications in dynamic environments.
By understanding these testing methods, B2B buyers can better assess the quality and suitability of metal products for their specific applications.
Conclusion: The Importance of Manufacturing and Quality Assurance in Metal Strength
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for metals is essential. By carefully evaluating suppliers based on their manufacturing techniques, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards, buyers can ensure that they procure materials that not only meet but exceed their project requirements. Investing time in this evaluation process can lead to enhanced safety, reliability, and performance in their final products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal strength chart’
To ensure successful procurement of a metal strength chart tailored to your specific needs, it is essential to follow a structured approach. This guide will assist B2B buyers in making informed decisions, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the technical requirements relevant to your project. Consider factors such as the types of metals needed, their applications, and the specific strength properties you require, such as tensile strength or yield strength. This clarity will help you identify the appropriate materials and avoid costly mistakes.
Step 2: Research Available Metal Strength Charts
Conduct thorough research to find reputable sources of metal strength charts. Look for publications from recognized industry associations, academic institutions, or specialized materials suppliers. This ensures that the data you are referencing is accurate and reliable, as discrepancies can lead to significant project risks.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making a commitment, it’s crucial to vet potential suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions. Evaluate their expertise in providing metal strength charts and their ability to meet your specific requirements.
- Check certifications: Ensure the supplier has relevant industry certifications that confirm their adherence to quality standards.
- Look for experience: Prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in your industry to guarantee their understanding of unique material needs.
Step 4: Request Customization Options
Engage with suppliers about the possibility of customizing metal strength charts to suit your project requirements. Customization may include specific alloys, thicknesses, or additional data points that are critical to your application. This step is vital as it ensures the chart aligns precisely with your operational needs.
Step 5: Verify Data Accuracy and Relevance
Ensure that the metal strength charts you receive are up-to-date and relevant to your specific application. Cross-check the strength metrics against industry standards and other credible sources. This diligence helps to mitigate the risk of using outdated or incorrect information, which can jeopardize project integrity.
Step 6: Assess Additional Resources and Tools
Inquire if the supplier offers supplementary resources, such as calculators or conversion charts, that can aid in evaluating metal strengths. These tools can enhance your decision-making process by providing a clearer understanding of how different metals compare under various conditions.
Step 7: Understand Terms of Service and Support
Before finalizing your procurement, review the supplier’s terms of service, including support for any technical queries you may have post-purchase. A responsive supplier can significantly impact your experience, especially if you encounter issues or require further information regarding the metal strength chart.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process of metal strength charts, ensuring they select the most suitable materials for their projects while minimizing risks associated with material failure.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal strength chart Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Strength Chart Sourcing?
When sourcing metal strength charts, understanding the cost structure is vital for making informed decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of metal significantly influences costs. High-strength alloys or specialized materials will naturally incur higher prices compared to standard metals like aluminum or mild steel. Additionally, fluctuations in raw material prices can affect overall costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is often required to create accurate metal strength charts. This includes engineers and technicians who analyze materials and develop specifications. Labor costs can vary widely based on the location and expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, thus reducing the overall cost.
-
Tooling: The creation of custom tooling for specific metal types or thicknesses can add to the initial investment. This is particularly important for projects requiring unique specifications or high precision.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the accuracy of metal strength charts is crucial. Investing in rigorous QC processes adds to the cost but is essential for maintaining product integrity, especially in industries like aerospace or automotive where safety is paramount.
-
Logistics: The cost of transporting materials and finished products can vary based on distance, mode of transportation, and any customs duties applicable for international shipments. Efficient logistics planning can help optimize costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs. This margin can fluctuate based on market demand, competition, and the supplier’s pricing strategy.
How Do Price Influencers Impact Metal Strength Chart Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the sourcing of metal strength charts:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to determine the most cost-effective purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs. Standard charts may be more affordable, while tailored solutions for unique applications will incur additional charges.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Metals that meet specific industry standards or certifications (like ISO or ASTM) are typically more expensive due to the stringent requirements for quality assurance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but they often provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is crucial for international buyers. These terms define who bears the shipping costs and risks, impacting the overall price.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Metal Strength Chart Sourcing?
-
Negotiation: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices with suppliers. Building a relationship can lead to better pricing and terms, especially if you can commit to larger volumes or longer-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and potential savings from using higher-quality materials in the long run.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, import taxes, and tariffs that may affect pricing. Researching local suppliers or those with experience in your region can help mitigate these issues.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends that could impact material costs. Subscribing to industry reports or following relevant news can provide insights into when to buy or negotiate.
-
Request Samples: Before placing a large order, request samples to ensure the quality meets your standards. This helps avoid costly mistakes later in the production process.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always consult with suppliers for the most accurate and updated pricing information.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal strength chart With Other Solutions
Introduction: What Are the Alternatives to Metal Strength Charts?
In the realm of material selection for manufacturing and construction, metal strength charts serve as a vital resource for engineers and decision-makers. However, other methods and tools can complement or even replace the traditional strength chart. Understanding these alternatives is essential for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their material selection process. This comparison will evaluate metal strength charts against two viable alternatives: Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Material Property Databases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Strength Chart | Finite Element Analysis (FEA) | Material Property Databases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides general strength metrics for metals | Offers detailed simulations of stress and strain under specific conditions | Lists extensive material properties for various metals |
| Cost | Generally low-cost or free | Can be expensive; requires specialized software and training | Varies; often subscription-based or free for limited access |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to understand and use | Requires technical expertise and software | User-friendly, but requires understanding of material science |
| Maintenance | Minimal; periodic updates needed | Requires ongoing software maintenance and updates | Regular updates needed for accuracy |
| Best Use Case | Quick reference for material selection | Complex projects needing detailed analysis | Initial screening of materials based on properties |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
FEA is a numerical method that allows for the simulation of how materials respond to external forces. It provides in-depth insights into stress distribution, deformation, and potential failure points under various loading conditions. The advantage of FEA lies in its ability to model complex geometries and real-world scenarios, making it invaluable for high-stakes applications like aerospace or automotive engineering. However, the costs associated with FEA software and the requirement for specialized training can be prohibitive for smaller firms or less complex projects.
Material Property Databases
Material property databases compile extensive information on the physical and mechanical properties of various metals and alloys. These databases are often accessible online and can be a cost-effective way to gather data for material selection. They provide a broader range of properties than what is typically found in a metal strength chart, including thermal properties, corrosion resistance, and fatigue limits. While user-friendly, leveraging these databases effectively requires a foundational understanding of material science, which may be a barrier for some users.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate tool or method for assessing metal strength, B2B buyers should consider their specific project requirements, budget constraints, and technical expertise. Metal strength charts provide a quick and accessible reference but may lack the depth needed for complex applications. Conversely, FEA and material property databases offer detailed insights but may require more investment in terms of time and resources. Ultimately, the choice will depend on the nature of the project, the level of precision required, and the available budget, ensuring that manufacturers can make informed decisions tailored to their operational needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal strength chart
What Are the Key Technical Properties of a Metal Strength Chart?
When navigating the complexities of metal selection for industrial applications, understanding the critical specifications is essential. Here are some vital technical properties that inform decisions related to metal strength charts:
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of metals based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties. Different grades of metals possess distinct strength characteristics, which are crucial for specific applications. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the metal can withstand the required loads and environmental conditions, thereby minimizing the risk of structural failure.
Yield Strength
Yield strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation. This property is especially significant in applications where metals are subjected to high loads or forces. B2B decision-makers need to consider yield strength when assessing the durability of materials, as it directly impacts the longevity and safety of the final product.
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
Ultimate tensile strength is the maximum stress a material can endure while being stretched or pulled before breaking. For industries such as aerospace and automotive, where safety is paramount, understanding UTS helps manufacturers choose the right materials that can handle extreme conditions without compromising integrity.
Elongation
Elongation measures the extent to which a material can be stretched before it fractures, expressed as a percentage. This property is vital for applications requiring ductility and flexibility. B2B buyers should consider elongation when selecting materials for processes like forming or bending, as it affects the workability and performance of the final product.
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In metal fabrication, tight tolerances are essential for ensuring that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance specifications is crucial for maintaining quality and reducing the risk of costly rework or scrap.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Metal Strength Charts?
In the B2B realm, familiarity with industry jargon can significantly enhance communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms you should know:
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of metal strength charts, OEMs often require specific materials with defined strength properties to meet their production standards. Understanding OEM requirements helps buyers align their material choices with market needs.
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, as it impacts purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses evaluate the cost-effectiveness of their orders and manage cash flow efficiently.
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. In the context of metal procurement, issuing an RFQ with clear specifications, including strength properties, helps ensure that suppliers provide accurate pricing and material options, facilitating better decision-making.
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding these terms is vital for B2B transactions involving metal procurement, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs associated with shipping and delivery, thereby preventing disputes and ensuring smooth transactions.
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials)
ASTM standards are widely recognized benchmarks for material specifications and testing methods. When evaluating metal strength charts, familiarity with relevant ASTM standards helps B2B buyers ensure that the materials they are considering meet industry quality and performance criteria.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their project requirements and enhance their operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal strength chart Sector
What Are the Key Drivers and Trends in the Metal Strength Chart Market?
The global market for metal strength charts is influenced by several key drivers, including technological advancements, increasing demand for high-performance materials, and the ongoing expansion of industries such as construction, automotive, and aerospace. In recent years, the rise of Industry 4.0 has led to enhanced data analytics and automation, enabling manufacturers to optimize the selection of materials based on their specific strength requirements. This trend is particularly relevant for B2B buyers in regions such as Africa and South America, where emerging markets are rapidly industrializing and require reliable material data to ensure safety and performance.
Furthermore, international B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for sourcing. These platforms provide comprehensive databases of metal strength charts, making it easier for buyers in Europe and the Middle East to access real-time information on material properties. The demand for lightweight yet strong materials, driven by sustainability initiatives, is also reshaping sourcing strategies. As companies aim to reduce their carbon footprints, they are turning to materials that meet stringent strength requirements while being environmentally friendly.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Shaping the Metal Strength Chart Sector?
The environmental impact of metal production is a critical concern in today’s sourcing landscape. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes. As a result, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the ResponsibleSteel certification are becoming essential criteria in supplier selection.
Ethical sourcing goes hand in hand with sustainability. International buyers are now scrutinizing supply chains to ensure that materials are sourced from responsible vendors who respect labor rights and minimize environmental degradation. In the context of metal strength charts, this means opting for materials that not only meet technical specifications but also align with broader corporate social responsibility goals. By choosing “green” certified materials, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for responsible production practices.
What Is the Historical Context of Metal Strength Charts in B2B Sourcing?
The evolution of metal strength charts has been a significant aspect of materials science, tracing back to early engineering practices. Initially, strength assessments were rudimentary, relying on empirical data gathered from physical testing. However, as industries expanded and the complexity of projects grew, the need for standardized strength data became evident.
By the late 20th century, advancements in metallurgy and the development of sophisticated testing methods led to more comprehensive and reliable metal strength charts. These charts began to encompass a variety of metals and their alloys, providing essential data for engineers and manufacturers. Today, they serve as a critical tool for B2B buyers who require precise information to make informed sourcing decisions. The historical context underscores the importance of continual innovation in material science, reflecting the dynamic needs of global industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal strength chart
-
How do I choose the right metal strength chart for my project?
Selecting the appropriate metal strength chart involves understanding your project’s specific requirements, such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and material compatibility. Start by evaluating the types of metals you need, like steel, aluminum, or copper, and their respective properties. Look for charts that provide tensile strength, yield strength, and other relevant metrics. Additionally, consult with suppliers or engineers who can offer insights based on your application, ensuring you choose a chart that aligns with industry standards and your project’s unique needs. -
What is the best metal strength chart for construction applications?
For construction applications, the best metal strength chart typically focuses on steel grades, as they are commonly used due to their strength and durability. Look for charts that detail various steel types, such as structural steel, stainless steel, and alloy steels, along with their tensile and yield strengths. Ensure the chart also includes information on thickness and treatment processes, as these factors significantly impact performance. Collaborating with experienced suppliers can help you identify the right grades and specifications tailored to your construction needs. -
How can I ensure the quality of metal strength charts when sourcing internationally?
To ensure the quality of metal strength charts from international suppliers, start by verifying the supplier’s credentials and reputation in the industry. Request certifications, such as ISO 9001 or other relevant quality assurance standards, to confirm their commitment to quality. Additionally, consider asking for samples or test reports that validate the strength and properties of the metals listed in the charts. Engaging with local trade associations or industry groups can also provide valuable insights into reliable suppliers and their product offerings. -
What factors should I consider regarding minimum order quantities (MOQ) when sourcing metal strength charts?
When sourcing metal strength charts, consider the MOQ set by suppliers, which can vary widely based on the metal type and supplier’s capabilities. Assess your project requirements and budget to determine if you can meet the MOQ without overcommitting resources. Some suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or large-scale projects, so it’s beneficial to discuss your needs upfront. Additionally, inquire about the potential for bulk discounts or combined orders to optimize costs while ensuring you have the necessary materials. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers of metal strength charts?
Payment terms for suppliers of metal strength charts can vary depending on factors such as the supplier’s location and the size of your order. Common terms include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payments prior to shipment. It’s essential to clarify payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers, letters of credit, or online payment platforms. Establishing clear payment terms early in the negotiation process can help prevent misunderstandings and foster a trustworthy relationship with your supplier. -
How do logistics and shipping affect sourcing metal strength charts internationally?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in sourcing metal strength charts, especially when dealing with international suppliers. Consider factors such as shipping costs, delivery timelines, and customs regulations that may affect your order. Work with suppliers who have a robust logistics network and can provide estimated shipping times. Additionally, familiarize yourself with import duties and taxes that may apply, as these can impact overall project costs. Establishing a reliable shipping method and clear communication with your supplier can streamline the process. -
What are the advantages of customizing metal strength charts for my specific needs?
Customizing metal strength charts offers several advantages tailored to your project’s unique requirements. It allows you to focus on specific metals and their properties relevant to your applications, ensuring you select the best materials for performance and durability. Customized charts can also incorporate additional data, such as environmental factors and local standards, enhancing decision-making. Collaborating with suppliers to develop tailored charts can lead to improved efficiency and reduced risks in your manufacturing processes. -
How can I verify the accuracy of the metal strength information provided by suppliers?
Verifying the accuracy of metal strength information requires a multi-faceted approach. First, request third-party test reports or certifications that validate the strength properties of the metals in question. Cross-reference the information with reputable industry standards, such as ASTM or ISO specifications. Engaging with industry experts or engineers can also provide insights into the reliability of the data. Additionally, consider conducting independent testing if feasible, especially for critical applications where material integrity is paramount.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Metal Strength Chart Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Eziil – Metal Strength Insights
Domain: eziil.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: Metal Strength Chart: A Detailed Guide to Metal Strengths. Key metals discussed include steel, aluminum, copper, brass, iron, magnesium, zinc, and nickel. Focus on steel strength charts, which are essential for engineers and manufacturers to ensure safety and proper material selection. Steel thickness ranges from 3/16″ to 18″, with common thicknesses being 10, 11, 12, 14, and 16 gauge. Specific de…
2. WaykenRM – Metal Strength Insights
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: Metal Strength Types: Yield strength, Ultimate tensile strength, Compressive strength, Impact Strength. Strongest Metals: 1. Titanium – High tensile strength, low density, corrosion resistance, used in aerospace, automotive, medical. 2. Chromium – Hardest metal, used in stainless steel. 3. Tungsten – Ultimate tensile strength of 250,000 psi, used in military, aerospace, mining. 4. Steel – Stronges…
3. Materials – Strength and Toughness
Domain: www-materials.eng.cam.ac.uk
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Strength measures the resistance of a material to failure given by the applied stress (load per unit area). Yield strength in tension is shown for metals and alloys, while compressive strength is shown for ceramics. Toughness measures the energy required to crack a material, important for items that suffer impact. Increasing strength usually leads to decreased toughness. Tempered steel is tougher …
4. KDM Fab – Metal Strength Guide
Domain: kdmfab.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Metal Strength Chart: A guide illustrating different strengths of metals, crucial for selecting the right metal for specific applications. Key types of metal strength include: 1. Tensile Strength – measures how much a metal can stretch before failure, including yield strength, breakable strength, and ultimate strength. 2. Compressive Strength – the maximum pressure a metal can withstand. 3. Impact…
5. AT-Machining – Key CNC Machining Services
Domain: at-machining.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Metal Strength Chart: A Detailed Guide to Metal Strengths | AT-Machining
Key Product Details:
– Services Offered:
– CNC Machining Services
– CNC Milling Services
– CNC Turning Services
– Precision 5-Axis CNC Machining Services
– Swiss CNC Machining Services
– Small Batch CNC Machining Services
– Precision Micro Machining Services
– Sheet Metal Fabrication
– Surface Finishing Ser…
6. PartMFG – Metal Strength Chart 2025
Domain: partmfg.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Metal Strength Chart – A Pro Guide 2025 includes various metal types and their properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, compressive strength, density, strength-to-weight ratio, and hardness. Key metals discussed include: 1. Steel: Tensile Strength 400-2500 MPa, Yield Strength 250-1500 MPa, Density 7.8 g/cm³, Hardness 120-220 HB. 2. Aluminum: Tensile Strength 70-600 MPa, Yield Strength …
7. Runsom – Metal Strength Chart
Domain: runsom.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Metal Strength Chart includes various types of metals with their respective mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, hardness, and density. Key metals listed are: Stainless Steel 304 (Tensile Strength: 90,000 PSI, Yield Strength: 40,000 PSI, Hardness: 88 Rockwell, Density: 8000 kg/m3), Aluminum 6061-T6 (Tensile Strength: 45,000 PSI, Yield Strength: 40,000 PSI, Hardness: 60 R…
8. Tuofa – Precision CNC Machining Services
Domain: tuofa-cncmachining.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: Tuofa Precision CNC Machining offers a variety of CNC machining services including CNC Turning, CNC Milling, CNC Cutting, CNC Drilling, Wire EDM Machining, 5 Axis CNC Machining, Sheet Metal Fabrication, and Surface Finishing. They work with various materials such as metals (Aluminum, Brass, Tool Steel, Copper, Stainless Steel, Titanium, and more) and plastics (ABS, Acrylic, Delrin, HDPE, Nylon, PE…
9. Bolt Depot – Low Carbon Steel Bolts
Domain: boltdepot.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: US Bolts:
– 307A: Low carbon steel, 1/4″ thru 4″, Min. Tensile Strength: 60,000 psi, No Markings
– Grade 2: Low/medium carbon steel, 1/4″ thru 3/4″, Proof Load: 55,000 psi, Min. Yield Strength: 57,000 psi, Min. Tensile Strength: 74,000 psi, 3 Radial Lines; Over 3/4″ thru 1-1/2″, Proof Load: 33,000 psi, Min. Yield Strength: 36,000 psi, Min. Tensile Strength: 60,000 psi
– Grade 5: Medium carbon stee…
10. Tensile Strength – Metals Overview
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Tensile strength of various metals; sources for tensile strength data include ASM handbooks, MMPDS, MatWeb, Granta Selector, and Matmatch; tensile strength varies by vendor, country of origin, and batch quality; specific case discussed involving a trailer hitch with a UTS of 14 KSI, suggesting potential aluminum material.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal strength chart
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Metal Selection Process?
In the realm of manufacturing and construction, understanding metal strength is paramount for ensuring structural integrity and project success. The insights gained from a comprehensive metal strength chart allow B2B buyers to make informed decisions, minimizing risks associated with material failure. Key takeaways include the significance of tensile strength, the impact of alloying elements, and the necessity of considering environmental factors like temperature and humidity when selecting metals.
Strategic sourcing is a critical component of this process, enabling businesses to procure the right materials at optimal costs while maintaining quality. By leveraging detailed metal strength charts, international buyers can streamline their sourcing strategies, ensuring that they select metals that meet the specific demands of their projects.
As industries evolve and technological advancements shape material science, the future of metal procurement looks promising. Buyers are encouraged to stay ahead by continuously evaluating new materials and sourcing strategies. Engage with trusted suppliers who can provide up-to-date information and support your unique project needs. The right strategic partnerships will empower your business to thrive in competitive markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.