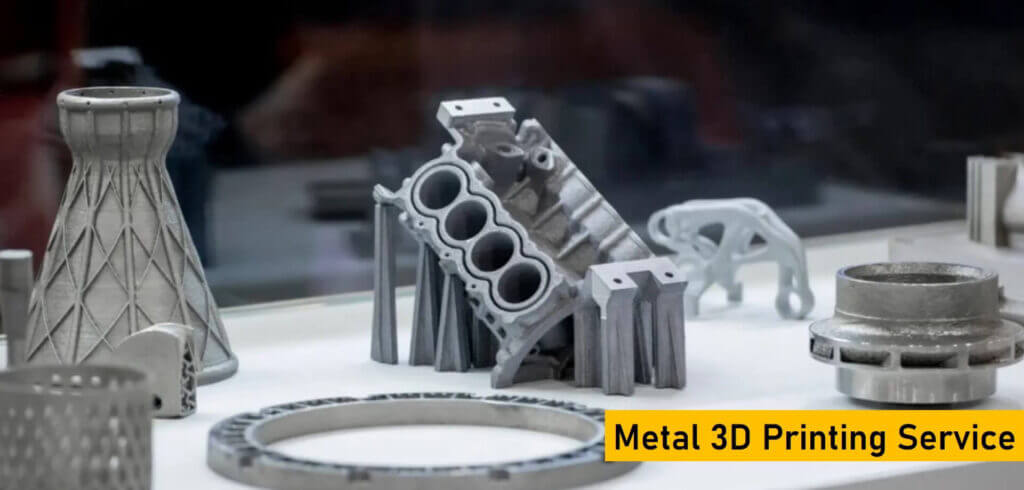
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal printing services
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial landscape, sourcing reliable metal printing services can pose a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With the increasing demand for customized metal parts that meet diverse specifications, understanding the nuances of metal 3D printing is crucial. This guide delves into the various types of metal printing technologies, including Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Binder Jetting, alongside their unique applications across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. By exploring material properties, post-processing techniques, and the intricacies of supplier vetting, we aim to equip businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—regions characterized by diverse manufacturing needs—with the knowledge necessary for informed purchasing decisions.
Navigating the global market for metal printing services requires a strategic approach. Buyers must not only assess cost implications but also evaluate the capabilities and certifications of potential suppliers. This guide provides actionable insights into determining the right fit for your specific requirements, ensuring that you can leverage the benefits of advanced manufacturing technologies. From understanding the mechanical properties of different metals to recognizing the importance of compliance with international standards, this comprehensive resource is designed to empower B2B decision-makers to optimize their sourcing processes and enhance their competitive edge in the marketplace.
Understanding metal printing services Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) | Utilizes a laser to fuse metal powders layer by layer; produces fully dense parts. | Aerospace, automotive, medical devices | Pros: High precision, excellent mechanical properties. Cons: Higher cost, longer lead times. |
| Metal Binder Jetting | Involves binding agents to hold metal powder, followed by sintering; less dense than DMLS. | Prototyping, low-volume production | Pros: Cost-effective, faster production. Cons: Lower strength, requires post-processing. |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | Similar to DMLS, but focuses on melting layers rather than sintering; ideal for complex geometries. | Aerospace components, tooling | Pros: High-quality surface finish, complex designs. Cons: More expensive, limited material options. |
| Metal 3D Printing with Aluminum | Focuses on aluminum alloys; lightweight and corrosion-resistant. | Automotive parts, consumer goods | Pros: Lightweight, good strength-to-weight ratio. Cons: Limited to specific applications. |
| Hybrid Manufacturing | Combines additive and subtractive processes for enhanced part quality and detail. | Aerospace, tooling, complex assemblies | Pros: Versatile, improved accuracy. Cons: More complex setup, potentially higher costs. |
What are the Characteristics of Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)?
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is a highly advanced metal 3D printing technology that employs a laser to selectively fuse metal powders layer by layer. It is particularly suitable for producing fully dense parts, making it a preferred choice for high-performance applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. When considering DMLS, B2B buyers should weigh its high precision and superior mechanical properties against its relatively high costs and longer lead times.
How Does Metal Binder Jetting Differ from Other Methods?
Metal Binder Jetting is a unique process that uses a binding agent to hold metal powders together before sintering. This method allows for faster production rates and is often more cost-effective than DMLS, making it ideal for prototyping and low-volume production. However, the resulting parts typically exhibit lower strength compared to those produced via DMLS. B2B buyers should consider the trade-off between cost and mechanical performance when selecting this service for their applications.
Why Choose Selective Laser Melting (SLM)?
Selective Laser Melting (SLM) is closely related to DMLS, focusing on melting rather than sintering the metal layers. This technique is particularly effective for creating complex geometries and achieving high-quality surface finishes. SLM is widely used in aerospace components and tooling. Buyers should consider its advantages in detail and complexity against the higher costs and limited material options compared to other methods.
What are the Benefits of Using Aluminum in Metal 3D Printing?
Metal 3D printing with aluminum alloys is gaining traction due to the material’s lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties. This process is particularly beneficial for automotive parts and consumer goods where weight reduction is crucial. While aluminum parts provide an excellent strength-to-weight ratio, buyers should be aware of the material’s limitations in terms of applications and potential post-processing requirements.
How Does Hybrid Manufacturing Enhance Metal Printing Services?
Hybrid Manufacturing combines additive and subtractive processes to improve part quality and detail. This method is particularly advantageous for complex assemblies in the aerospace and tooling sectors. While it offers versatility and enhanced accuracy, the complexity of setup and potentially higher costs may deter some buyers. Understanding these factors can help B2B clients make informed decisions about their manufacturing needs.
Key Industrial Applications of metal printing services
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal printing services | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight components for aircraft | Reduces weight and fuel consumption, enhancing performance | Look for suppliers with certifications like AS9100D and ITAR. |
| Automotive | Custom tooling and prototyping for parts | Accelerates development cycles and reduces costs | Ensure rapid turnaround capabilities and material certifications. |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of surgical instruments and implants | Enables complex geometries for better patient outcomes | Verify biocompatibility and regulatory compliance of materials. |
| Oil & Gas | Creation of durable components for drilling equipment | Increases operational reliability and reduces downtime | Assess material properties suitable for harsh environments. |
| Industrial Equipment | Custom parts for machinery and tooling | Improves efficiency by minimizing assembly complexity | Evaluate post-processing options to meet specific tolerances. |
How Are Metal Printing Services Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, metal printing services are pivotal for producing lightweight components such as brackets, housings, and engine parts. This technology allows for the creation of complex geometries that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve, leading to significant weight reductions. For international buyers, it is crucial to source from suppliers who have the necessary certifications, such as AS9100D and ITAR, to ensure compliance with stringent aerospace regulations.
What Role Does Metal Printing Play in the Automotive Sector?
Metal printing services in the automotive sector are primarily used for rapid prototyping and the production of custom tooling. This process enables manufacturers to quickly iterate designs, reducing time-to-market for new models. International buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate fast turnaround times and possess the appropriate material certifications, ensuring that parts meet industry standards and can withstand rigorous testing.
How Are Metal Printing Services Transforming Medical Device Manufacturing?
In medical device manufacturing, metal printing services are essential for creating surgical instruments and implants with intricate designs that enhance functionality and patient safety. The ability to customize designs for specific surgical procedures improves patient outcomes. Buyers in this sector must confirm that the materials used are biocompatible and comply with relevant health regulations to ensure safety and efficacy.
Why Are Metal Printing Services Important for the Oil & Gas Industry?
Metal printing services offer significant advantages in the oil and gas industry by enabling the production of robust components for drilling equipment. These parts are designed to withstand extreme conditions, thus improving operational reliability and reducing maintenance costs. Buyers should evaluate the material properties of printed components to ensure they can endure harsh environments, and consider suppliers with a proven track record in this sector.
How Do Metal Printing Services Benefit Industrial Equipment Manufacturing?
In industrial equipment manufacturing, metal printing services facilitate the creation of custom parts that streamline machinery operations. This technology allows manufacturers to reduce the number of components required in an assembly, thus minimizing potential points of failure. When sourcing, buyers should assess the available post-processing options to ensure that the final parts meet their specific tolerances and performance requirements.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal printing services’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Material Selection for Unique Applications
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face significant challenges when selecting the right materials for their metal printing projects. With a wide array of metal options available, such as stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium, making an informed decision can be overwhelming. Buyers may struggle to understand the mechanical properties and suitable applications for each material, leading to potential project delays, increased costs, and subpar product performance.
The Solution:
To effectively navigate material selection, buyers should start by clearly defining their project’s requirements, including strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties. Collaborating with the metal printing service provider is crucial; they typically offer material guides and comparison charts that outline the characteristics of each option. Additionally, buyers can request sample parts to evaluate material performance firsthand. Engaging in early discussions about the intended application will enable suppliers to recommend the most appropriate material, ensuring that the final parts meet the required specifications and performance standards.
Scenario 2: Managing Production Time and Lead Times
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often encounter issues with production timelines. For companies operating in fast-paced industries, delays in the metal printing process can disrupt supply chains and affect project timelines. Buyers may be unsure of how long the metal printing process will take, especially when factoring in design revisions, production schedules, and shipping times. This uncertainty can lead to frustration and a lack of trust in the supplier.
The Solution:
To mitigate concerns about production time, buyers should prioritize open communication with their metal printing service provider. Establishing a clear timeline at the project outset is essential. Buyers can ask for a detailed project plan that outlines each stage of the process, from initial design review to final delivery. Additionally, utilizing online quoting and project management tools can streamline communication and provide real-time updates on progress. It is also beneficial to build flexibility into project timelines by discussing the potential for expedited services if necessary. This proactive approach ensures that both parties are aligned on expectations and can adapt quickly if changes arise.
Scenario 3: Ensuring Quality Control and Compliance
The Problem:
Quality control and compliance with industry standards are major concerns for B2B buyers in sectors such as aerospace and automotive, where precision and safety are critical. Buyers may struggle to verify that the metal printing services they select meet necessary certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100D) and that the parts produced adhere to rigorous quality standards. Without proper oversight, there is a risk of receiving defective parts that could jeopardize safety and compliance.
The Solution:
To ensure quality control and compliance, buyers should conduct thorough due diligence before selecting a metal printing service. This includes reviewing the supplier’s certifications, quality assurance processes, and past project case studies. Requesting documentation of previous work and any relevant test results can provide insights into their quality standards. Additionally, establishing a quality assurance agreement that outlines specific inspection criteria and testing methods can help maintain accountability. Buyers should also consider implementing regular communication checkpoints throughout the production process to address any quality concerns as they arise. By taking these steps, buyers can secure confidence in their supplier’s ability to deliver high-quality, compliant parts.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal printing services
What Are the Key Properties of Stainless Steel in Metal Printing Services?
Stainless steel, particularly grades like 17-4 PH and 316L, is a popular choice in metal printing due to its excellent mechanical properties. Key properties include high tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and the ability to withstand high temperatures. For instance, 17-4 PH has an ultimate tensile strength of around 199 ksi and is known for its hardness and durability, making it suitable for demanding applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Stainless Steel?
The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and corrosion resistance, which makes it ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as in the oil and gas sector. However, the cost of stainless steel can be relatively high compared to other materials, which may be a consideration for budget-conscious projects. Additionally, the complexity of manufacturing intricate designs can increase production time and costs.
How Does Stainless Steel Impact Application Suitability?
Stainless steel is highly compatible with various media, including chemicals and high-pressure environments, making it suitable for components like valves and pumps. International buyers should also note that stainless steel parts often require adherence to specific standards, such as ASTM A564 for stainless steel, which can affect compliance and quality assurance processes.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum in Metal Printing Services?
Aluminum, particularly the AlSi10Mg alloy, is another widely used material in metal printing. Its lightweight nature combined with good corrosion resistance makes it ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor. Aluminum exhibits a tensile strength of approximately 39 ksi, which is sufficient for many structural applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Aluminum?
One of the main advantages of aluminum is its lower cost compared to stainless steel, making it an attractive option for high-volume production. However, aluminum’s lower strength compared to stainless steel may limit its application in high-stress environments. Additionally, while aluminum is easier to machine, it may require more post-processing to achieve desired surface finishes.
How Does Aluminum Impact Application Suitability?
Aluminum is particularly suited for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries, where weight reduction is essential. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and the cost implications of importing aluminum materials, as well as compliance with standards like ISO 9001 for quality management.
What Are the Key Properties of Inconel in Metal Printing Services?
Inconel, especially the Inconel 718 alloy, is known for its exceptional heat resistance and strength at elevated temperatures. With an ultimate tensile strength of around 143 ksi, Inconel is often used in extreme environments, such as aerospace and chemical processing applications.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Inconel?
The primary advantage of Inconel is its ability to perform under high-stress and high-temperature conditions, making it ideal for critical applications. However, the cost of Inconel is significantly higher than other materials, which may not be justifiable for all projects. Additionally, the complexity of processing Inconel can lead to longer lead times and increased manufacturing costs.
How Does Inconel Impact Application Suitability?
Inconel is suitable for applications in the aerospace and energy sectors, particularly for components exposed to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. International buyers should ensure compliance with industry-specific standards, such as AMS 5663 for Inconel, to maintain quality and performance.
What Are the Key Properties of Titanium in Metal Printing Services?
Titanium, particularly Ti6Al4V, is recognized for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance. With a tensile strength of around 153 ksi, titanium is often used in aerospace and medical applications where performance and reliability are paramount.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Titanium?
The key advantage of titanium is its lightweight nature combined with high strength, making it ideal for applications where weight savings are critical. However, titanium is one of the more expensive materials, which can limit its use in cost-sensitive projects. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
How Does Titanium Impact Application Suitability?
Titanium is particularly well-suited for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications due to its biocompatibility and strength. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider local regulations regarding titanium use in medical applications, as compliance with standards like ASTM F136 is crucial.
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal printing services | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Aerospace components, oil and gas fittings | High durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to other metals | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive parts, lightweight structures | Lower cost and lightweight | Lower strength in high-stress applications | Medium |
| Inconel | Aerospace, chemical processing components | Exceptional heat resistance | Very high cost and complex processing | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | High strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal printing services
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process for Metal Printing Services?
Metal printing, specifically through processes such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Binder Jetting, encompasses several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality metal parts. The primary stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Printing?
The process begins with the careful selection and preparation of metal powders. The choice of material—such as aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium—depends on the intended application and desired mechanical properties. The metal powders must be of high purity and specific particle size to ensure optimal flowability and packing density. Prior to printing, the powders may undergo treatments to improve their properties, such as sieving to remove contaminants or blending to achieve desired characteristics.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
Forming is the heart of the metal printing process. In DMLS, a laser beam selectively fuses the metal powder layer by layer, creating a fully dense part. This method allows for the production of complex geometries that are often impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques. In contrast, Binder Jetting uses a binding agent applied to the powder bed, which is subsequently cured and sintered. Both methods have distinct advantages, with DMLS typically yielding parts with superior mechanical properties.
How Are Parts Assembled and Finished?
While many components produced via metal printing can be used directly, some may require assembly or additional finishing processes. Assembly can involve post-processing steps such as heat treatment to relieve stresses or enhance mechanical properties. Finishing techniques, including surface polishing, sandblasting, or coating, may be employed to achieve desired surface qualities or meet specific regulatory requirements.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential in Metal Printing Services?
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the metal printing industry, especially for B2B buyers who require reliable, high-performance components. The QA process typically aligns with international standards and incorporates various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing stages.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Consider?
Compliance with international standards is crucial. ISO 9001:2015 is a widely recognized quality management standard that ensures consistent product quality and continual improvement in processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking (for products sold in the European Economic Area) or API certification (for oil and gas industry components) can further assure buyers of the quality and safety of products.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) in metal printing services typically involves several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves the inspection of raw materials and powders to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the printing process, real-time monitoring is essential. Parameters such as temperature, layer thickness, and laser power are continuously checked to ensure consistency.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After printing, parts undergo rigorous testing to verify dimensions, surface finish, and mechanical properties against design specifications. Common methods include dimensional inspection using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) and mechanical testing (e.g., tensile, hardness tests).
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Measures?
For international B2B buyers, ensuring supplier quality control can be challenging yet essential. Here are several strategies:
-
Conduct Supplier Audits: Regular audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into the supplier’s processes, quality management systems, and adherence to standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC processes, test results, and certifications. This transparency helps buyers assess reliability.
-
Utilize Third-Party Inspection Services: Engaging independent inspection agencies can verify the quality of parts before shipment. This is particularly valuable for buyers in regions with stringent regulatory requirements.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various certification and regulatory landscapes. Understanding these nuances can help mitigate risks associated with cross-border trade.
How Do Regional Standards Affect Metal Printing?
Different regions may have unique standards and certifications that impact the acceptability of metal parts. For instance, European buyers often require CE marking, while buyers in the Middle East may need compliance with local standards. Buyers should be well-informed about the specific requirements applicable to their markets to avoid delays or rejections upon import.
What Should Buyers Know About Material Traceability?
Material traceability is crucial in industries such as aerospace and medical devices. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide detailed records of the materials used in production, including batch numbers and supplier certifications. This documentation is vital for compliance with industry regulations and for maintaining product integrity.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Metal Printing Services
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in metal printing services are designed to meet the complex demands of modern industries. By understanding these processes, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they receive high-quality, reliable products tailored to their specific needs. Whether through rigorous supplier audits, adherence to international standards, or leveraging third-party inspections, buyers can mitigate risks and enhance their supply chain effectiveness in the evolving landscape of metal printing.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal printing services’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide aims to assist B2B buyers in navigating the complexities of procuring metal printing services. With the rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, understanding the nuances of metal 3D printing is essential for making informed decisions that align with your project requirements and operational goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before engaging with potential suppliers, clearly outline your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, material types, tolerances, and surface finishes. A well-defined specification helps suppliers provide accurate quotes and ensures that the final product meets your operational needs.
- Considerations: Identify the specific metal alloys required (e.g., stainless steel, aluminum) and any special requirements like heat treatment or post-processing finishes.
Step 2: Research Available Printing Technologies
Understanding the different metal printing technologies available, such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Metal Binder Jetting, is crucial. Each method has its own advantages, costs, and suitable applications.
- DMLS: Ideal for high-precision parts with complex geometries.
- Binder Jetting: Often more cost-effective for larger batches but may require additional post-processing.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers to ensure they meet your project requirements. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from similar industries or regions.
- Key Factors: Look for suppliers with relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, AS9100) and proven experience in your specific industry to ensure quality and reliability.
Step 4: Request Quotes and Compare Costs
Once you have a shortlist of suppliers, request quotes based on your defined specifications. Comparing costs is essential, but ensure that you are also evaluating the value offered in terms of quality, lead times, and customer support.
- Cost Breakdown: Analyze the quotes for hidden costs, such as shipping, handling, and potential post-processing fees.
Step 5: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering are compliant with industry standards and possess relevant certifications. This step is vital for ensuring quality control and adherence to safety regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Check for certifications like ITAR for defense-related parts or any specific regional standards relevant to your industry.
Step 6: Assess Lead Times and Production Capabilities
Inquire about the lead times for prototyping and production to align with your project timelines. Understand the supplier’s production capabilities to ensure they can meet your demand, especially during peak periods.
- Flexibility: Look for suppliers that can accommodate changes in order volume or specifications without significant delays.
Step 7: Establish Communication Protocols
Effective communication is key to a successful partnership. Discuss communication channels, frequency of updates, and points of contact to ensure a smooth workflow throughout the project.
- Transparency: Establishing clear communication protocols helps to manage expectations and promptly address any issues that may arise during the production process.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy for metal printing services, ensuring that they partner with suppliers who meet their technical and operational needs effectively.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal printing services Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Printing Services?
When evaluating the costs associated with metal printing services, several key components come into play. Understanding these can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions and optimize their sourcing strategies.
-
Materials: The choice of metal significantly influences costs. Common materials like stainless steel and aluminum tend to be less expensive than high-performance alloys such as Inconel and titanium. Additionally, the quality and grade of the metal can affect pricing, with higher-grade materials commanding a premium due to their superior mechanical properties.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for both the setup and operation of metal printing machines. Labor costs can vary by region; for instance, rates may be higher in Europe compared to parts of Africa or South America. The complexity of the design and the need for post-processing also influence labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to equipment maintenance, utilities, and facility costs. Overhead can be a significant part of the overall cost structure, particularly for suppliers that invest heavily in advanced machinery and technology.
-
Tooling: While metal 3D printing typically requires less tooling than traditional methods, any specialized tooling for custom jobs can add to costs. This is especially relevant for high-volume orders where initial setup costs can be amortized over larger quantities.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the final product meets specified tolerances and quality standards is crucial. The cost of QC processes—ranging from in-process inspections to final testing—can vary based on the complexity of the parts and the certifications required (e.g., ISO certifications).
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are particularly important for international buyers. Incoterms can affect logistics expenses, with options like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost Insurance Freight) impacting the total cost based on shipping responsibilities and risks.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a markup to cover their operational risks and profit. Understanding the margin expectations in different markets can provide insights into pricing flexibility.
What Influences Pricing in Metal Printing Services?
Several factors can influence pricing for metal printing services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on order quantities, making it beneficial for buyers to consolidate orders.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom designs may require additional engineering time and resources, which can increase costs. Standardized parts are generally cheaper, so buyers should consider whether customization is necessary.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of material and the need for specific certifications can significantly impact costs. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and capabilities can also affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their reliability and quality assurance processes.
How Can International Buyers Optimize Costs in Metal Printing?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, can adopt several strategies to optimize costs:
-
Negotiate Effectively: Buyers should engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially for larger orders. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond initial pricing. TCO includes all costs associated with the product over its lifecycle, including maintenance and operational costs. This broader view can lead to more sustainable sourcing decisions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of how currency fluctuations, import duties, and local market conditions can affect overall costs. Collaborating with local experts can help navigate these complexities.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online quoting tools and digital communication for quicker responses and better transparency in pricing. This can lead to more competitive offers and faster turnaround times.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Pricing for metal printing services can vary widely based on specific project requirements, market conditions, and supplier capabilities. The information provided here is indicative and should be validated through direct quotes from suppliers to ensure accuracy for your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal printing services With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Metal Printing Services
As businesses explore various manufacturing methods, it’s essential to consider alternatives to metal printing services. Metal 3D printing, known for its ability to create complex geometries and rapid prototyping, may not always be the best fit for every application. Understanding the strengths and limitations of different manufacturing solutions can help B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints.
Comparison Table of Metal Printing Services and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Printing Services | CNC Machining | Metal Casting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and complexity; isotropic properties | Excellent precision; limited by tool design | Good for high-volume production; less precision in detail |
| Cost | Higher initial costs; economical for low volumes | Lower costs for high volumes; tooling can be expensive | Economical for high volumes; setup costs can be significant |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick turnaround; requires CAD files | Longer setup time; needs skilled operators | Time-consuming; requires molds and setup |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance; technology dependent | Regular maintenance required for machines | Low maintenance once set up; mold wear is a concern |
| Best Use Case | Custom parts, rapid prototyping, complex geometries | High-volume production with tight tolerances | Large quantities, lower-cost items, traditional designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that utilizes computer-controlled tools to remove material from a solid block. This method excels in producing precise parts with excellent surface finishes, making it ideal for applications requiring high dimensional accuracy. However, it is limited by the complexity of designs that can be achieved and can incur significant tooling costs, especially for custom parts. While CNC machining is cost-effective for large production runs, it may not be the best choice for small batches due to higher setup times and costs.
Metal Casting
Metal casting involves pouring molten metal into a pre-formed mold to create parts. This method is particularly advantageous for producing large quantities of items at a lower cost per unit, making it suitable for mass production. However, the process can be time-consuming, and the initial setup for molds can be costly. Additionally, cast parts may lack the intricate details and precision that metal 3D printing can achieve. Although casting is effective for traditional designs, it may not accommodate the rapid changes in design requirements that modern industries often face.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When deciding between metal printing services and alternative manufacturing methods, B2B buyers should assess their specific requirements, including production volume, design complexity, and budget. Metal printing services are ideal for projects that demand high precision and the ability to create complex geometries quickly. In contrast, CNC machining and metal casting may be more suitable for high-volume production where cost efficiency is paramount. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can select the manufacturing method that best aligns with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal printing services
What Are the Key Technical Properties in Metal Printing Services?
Understanding the technical properties of metal printing services is crucial for B2B buyers when evaluating options for their manufacturing needs. Below are some critical specifications that are often considered:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the specific alloy or metal used in printing, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or titanium. Each grade has unique mechanical properties, including tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Choosing the right material grade is essential for ensuring the final product meets performance requirements, especially in demanding applications like aerospace or medical devices.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the manufacturing process. In metal printing, common tolerances can range from ±0.003 inches (0.075 mm) for the X/Y dimensions to ±0.006 inches for the Z dimension. Tight tolerances are crucial for parts that must fit precisely within an assembly, impacting the overall performance and reliability of the product.
3. Layer Thickness
Layer thickness defines the resolution of the print, measured in microns. Typical values range from 20 microns (high resolution) to 60 microns (normal resolution). A thinner layer thickness can yield finer details and smoother surfaces, making it vital for applications requiring high precision. However, finer layers may also lead to longer production times, which can influence project timelines.
4. Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the final texture and appearance of the printed part, which can significantly affect its functionality and aesthetic appeal. Options may include standard finishes, brushed, satin, or polished. The choice of surface finish can impact performance characteristics, such as friction and wear resistance, making it an important consideration for end-use applications.
5. Maximum Build Volume
This specification indicates the largest dimensions that can be achieved in a single print run. Understanding the maximum build volume is essential for B2B buyers to ensure their designs can be accommodated without the need for complex assembly or multiple prints, which can increase costs and lead times.
What Are the Common Trade Terms in Metal Printing Services?
Navigating the landscape of metal printing services also requires familiarity with specific industry jargon. Below are key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another company. In the context of metal printing, an OEM may utilize 3D printing services to create components for their products, necessitating a focus on quality and precision in manufacturing.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ denotes the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to produce for a given order. Understanding MOQ is critical for buyers as it can affect inventory levels and cash flow, especially for companies looking to minimize upfront costs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document issued by a buyer to request price estimates from suppliers. This process is essential for comparing costs and ensuring that the buyer receives the best value for their metal printing needs.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is vital for international transactions, helping to avoid misunderstandings and ensuring compliance with legal obligations.
5. DMLS (Direct Metal Laser Sintering)
DMLS is a specific type of metal 3D printing technology that uses a laser to fuse metal powders layer by layer. This method is known for producing high-density parts with excellent mechanical properties. Understanding DMLS can help buyers make informed decisions about the suitability of different printing technologies for their applications.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can better navigate the metal printing landscape, ensuring they select the right services and materials for their specific requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal printing services Sector
What Are the Key Trends Influencing the Metal Printing Services Market?
The metal printing services sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for lightweight, complex components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices is propelling the adoption of metal 3D printing technologies. Emerging technologies like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Metal Binder Jetting are becoming vital as they allow for the production of intricate designs that traditional manufacturing methods cannot achieve.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide rapid prototyping and production capabilities. The ability to produce parts in less than a week is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions. Additionally, as companies strive for digital transformation, integrating CAD software with 3D printing processes is becoming a preferred approach, allowing for seamless transitions from design to production.
Sourcing trends also show a growing preference for suppliers that offer comprehensive services, including post-processing and material selection. The rise of sustainable practices is influencing buyer decisions, with a focus on suppliers that demonstrate environmental responsibility and ethical sourcing. As global supply chains become more interconnected, the ability to source locally while still maintaining quality and cost-effectiveness is essential for international buyers.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in Metal Printing Services?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming paramount in the metal printing services industry. As environmental concerns grow, businesses are under pressure to minimize their ecological footprint. Metal 3D printing is inherently more sustainable than traditional manufacturing methods, as it generates less waste and allows for the use of recycled materials. This process not only reduces material waste but also lowers energy consumption during production.
International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who adhere to environmental standards and possess certifications such as ISO 14001, which demonstrates a commitment to environmental management. Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials, such as those derived from recycled metals, is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the sourcing of materials and the environmental impact of production processes.
Furthermore, ethical supply chains are crucial for maintaining brand integrity and meeting consumer expectations. Companies that invest in sustainable practices often find themselves with a competitive advantage, as they can attract environmentally conscious clients and partners. By aligning with suppliers who share a commitment to sustainability, businesses not only contribute positively to the environment but also enhance their own market positioning.
What Has Been the Evolution of Metal Printing Services?
The evolution of metal printing services has been marked by rapid technological advancements and growing acceptance in various industries. Initially, metal 3D printing was limited to prototyping applications due to high costs and technical challenges. However, as technologies such as DMLS and Binder Jetting matured, the focus shifted toward production applications.
In the early 2000s, the introduction of DMLS revolutionized the sector by enabling the production of fully dense metal parts, making it a viable alternative to traditional manufacturing. The subsequent development of materials specifically designed for 3D printing, including advanced alloys, further expanded the capabilities and applications of metal printing.
Today, metal printing services are recognized for their ability to produce complex geometries and reduce assembly components, driving efficiencies in manufacturing. As the technology continues to evolve, its integration with digital workflows and automation is expected to streamline production processes, making metal printing an indispensable part of the modern manufacturing landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal printing services
-
How do I choose the right metal printing service for my project?
Selecting the right metal printing service involves several key factors. First, evaluate the service provider’s expertise in the specific metal printing technology you require, such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Binder Jetting. Check their portfolio for previous projects that align with your needs. Additionally, consider their production capacity, turnaround time, and the range of materials they offer. Finally, assess their quality assurance certifications and customer support to ensure a smooth collaboration. -
What are the advantages of using metal 3D printing over traditional manufacturing methods?
Metal 3D printing offers significant advantages compared to traditional methods like CNC machining or casting. It allows for the creation of complex geometries and lightweight designs that are often impossible with conventional techniques. This technology can reduce material waste and lead times, as parts can typically be produced in less than a week. Moreover, it enables the integration of multiple components into a single part, enhancing structural integrity and reducing assembly costs. -
What materials are commonly used in metal printing services?
Common materials for metal printing include stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, cobalt chrome, and Inconel. Each material has unique properties suited for different applications; for instance, titanium is favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio, while stainless steel is known for its corrosion resistance. When selecting a material, consider factors like mechanical properties, finish requirements, and the intended application of the final part. Discuss your specific needs with your supplier to ensure optimal material selection. -
What is the typical turnaround time for metal printed parts?
Turnaround times for metal printed parts vary based on the complexity of the design, the technology used, and the supplier’s capacity. Generally, most services can produce prototypes or production parts within a week. However, more complex designs or larger orders may require additional time for processing and post-production finishing. It is advisable to discuss timelines upfront with your supplier to align expectations and accommodate any urgent requirements. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal printing services?
Minimum order quantities for metal printing services can vary widely among suppliers. Some providers may have no MOQs for prototype orders, while others might set a minimum for production runs to optimize costs. When sourcing services, clarify the MOQ policies with potential suppliers, especially if you’re looking for small batch productions or one-off prototypes. This will help you budget accurately and avoid unexpected costs. -
How can I ensure quality control in my metal printing projects?
Ensuring quality control starts with selecting a reputable supplier who adheres to international standards and has relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001. Discuss their quality assurance processes, including material traceability, testing methods, and post-processing inspections. Request samples or prototypes before committing to larger orders to assess the quality of their work. Additionally, consider engaging third-party quality inspectors if required, especially for critical applications. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing metal printing services?
Payment terms for metal printing services can vary significantly based on the supplier, order size, and your business relationship. Common practices include upfront payments for prototypes or smaller orders, while larger production runs may involve partial payments or net terms upon delivery. Always negotiate terms that are favorable and ensure they are clearly outlined in your contract to avoid misunderstandings later. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing metal printed parts internationally?
When sourcing metal printed parts internationally, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Partner with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) options to simplify the process. Ensure that the supplier has clear packaging and labeling practices to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, discuss potential risks and insurance options to protect your investment during transit.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Metal Printing Services Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Proto Labs – Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
Domain: protolabs.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) is an industrial metal 3D printing process that builds fully functional metal prototypes and production parts in 7 days or less. It is used for prototyping in production-grade materials, creating complex geometries, producing functional end-use parts, and reducing metal components in an assembly. Protolabs offers quality metal 3D-printed prototypes and productio…
2. In3Dtec – Metal 3D Printing Services
Domain: in3dtec.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Metal 3D Printing Service using Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) technology. Key features include:
– Wide Material Options: Aluminum-AlSi10Mg, Stainless Steel 316L, Stainless Steel 17-4PH, Maraging Steel (18Ni300), Titanium Ti64 Grade 5, Nickel Alloy, Cobalt-chrome (Co_Cr), Copper.
– Rapid Turnaround: Parts can be produced in 4 days or less.
– Printing Volume: EOS (SLM) – 300x300x400mm; Farsoon…
3. Craftcloud – 3D Printing & Manufacturing Services
Domain: craftcloud3d.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Craftcloud offers a range of manufacturing services including 3D Printing, CNC Machining, Sheet Metal Fabrication, and Casting & Molding. They provide over 170 unique materials for 3D printing, including SLS Nylon PA12, 316L Stainless Steel, HP® MJF Nylon PA12, PLA, and Standard Resin. The platform supports over 35 file formats for model uploads and offers more than 20 different technologies and o…
4. PCBWay – Metal 3D Printing Services
Domain: pcbway.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Metal 3D Printing Services offered by PCBWay include:
– **Materials Available:**
– Aluminum: Corrosion-resistant, non-magnetic, heat treatable.
– Stainless Steel: Good corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and polishing properties; maintains excellent physical and mechanical properties at high temperatures.
– Titanium (TC4): Highest strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for lightweight applicatio…
5. 3D Metal Printing – Steel and Aluminum Services
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: User is looking for 3D metal printing services, specifically for steels, stainless steel, or aluminum. They mention varying prices for a stainless steel part (connecting rod, 40mm length, 4mm thickness, 5mm holes) with quotes from different services: PCBWay at around $50 plus shipping, JLCPCB at about $12 including shipping, and Craftcloud starting at $15 plus $20+ shipping. Craftcloud is noted fo…
6. Shapeways – 3D Printing Services
Domain: shapeways.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: 3D Printing Service Online; Manufacturing Technologies: Additive Manufacturing, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), Binder Jetting, Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Material Jetting, Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Wax Casting; Materials: Nylon 12 (PA12), Nylon 11 (PA11), Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE), Stainless Steel 17-4 PH, Stainless Steel 316L, Full…
7. JLC 3DP – Custom 3D Printing Services
Domain: jlc3dp.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Online 3D Printing Service offering custom 3D printed parts using various technologies including Stereolithography (SLA), Multi Jet Fusion (MJF), Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and White Jet Process (WJP). Materials available include Resin, Nylon (MJF), Metal (SLM), Plastic, and Nylon (SLS). Tolerances down to 0.2mm for 3D printing …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal printing services
In today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape, strategic sourcing of metal printing services emerges as a vital component for international B2B buyers. By leveraging advanced technologies such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Binder Jetting, businesses can access high-performance, complex metal parts that optimize design flexibility and production efficiency. This transition from traditional manufacturing methods not only reduces lead times but also minimizes costs associated with tooling and machining.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the importance of sourcing quality metal printing services cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with reputable providers that offer certifications and a range of material options, ensuring compliance with industry standards and specific project requirements.
Looking ahead, the future of metal printing services is bright, with ongoing advancements promising even greater capabilities and applications. Businesses are encouraged to stay ahead of the curve by embracing these innovations and integrating them into their supply chains. By doing so, they will not only enhance their competitive edge but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient manufacturing ecosystem. Engage with trusted metal printing service providers today to elevate your production capabilities and drive your business forward.