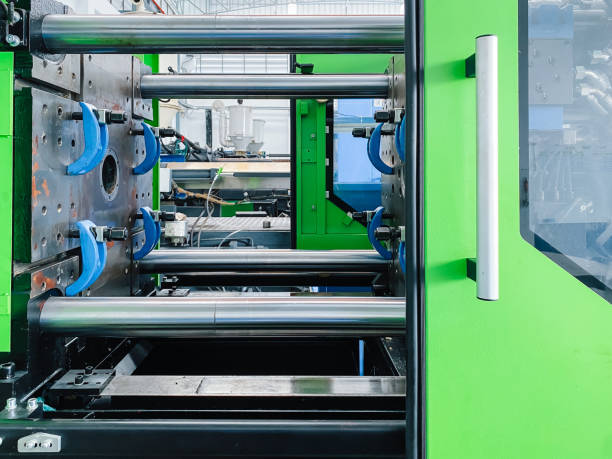
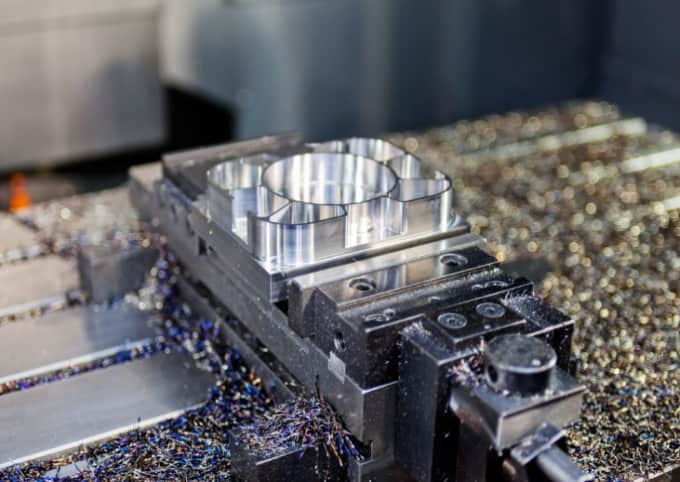
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal moulding machine
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the crucial challenge of sourcing metal moulding machines that not only meet their production needs but also align with budget constraints and quality standards. The ability to effectively navigate the global market for metal moulding machines can significantly impact operational efficiency and product quality across various industries, from automotive to aerospace and medical technology. This comprehensive guide delves into the nuances of metal moulding machines, exploring different types, applications, and advanced manufacturing processes such as Metal Injection Molding (MIM), which combines the versatility of plastic injection molding with the mechanical properties of metal.
Throughout this guide, we will equip buyers with actionable insights on how to evaluate suppliers, assess costs, and understand the latest technological advancements in the field. With a focus on regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, we aim to empower businesses with the knowledge necessary to make informed purchasing decisions. By addressing key factors such as supplier vetting, material selection, and production scalability, this guide serves as a valuable resource for B2B buyers seeking to enhance their manufacturing capabilities while ensuring quality and sustainability in their operations. Discover how to optimize your sourcing strategy and leverage the potential of metal moulding machines to drive innovation and growth in your business.
Understanding metal moulding machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Combines plastic molding versatility with metal properties; ideal for complex geometries. | Automotive, Aerospace, Medical Devices | Pros: High precision, reduced waste. Cons: Initial setup costs can be high. |
| Desktop Metal Molding | Compact size; plug-and-play setup; designed for small-scale production. | Jewelry making, Prototyping, Small batch manufacturing | Pros: User-friendly, low entry barrier. Cons: Limited production capacity. |
| Die Casting | Uses high pressure to inject molten metal into molds; excellent for high-volume production. | Automotive parts, Household appliances | Pros: High production rates, good surface finish. Cons: Higher tooling costs. |
| Sand Casting | Utilizes sand molds; suitable for large and complex parts; lower initial costs. | Industrial machinery, Art sculptures | Pros: Cost-effective for large parts. Cons: Lower precision compared to MIM. |
| Investment Casting | Involves creating a wax pattern; provides high accuracy and complex shapes. | Aerospace, Defense, Medical instruments | Pros: High dimensional accuracy, excellent surface finish. Cons: Time-consuming process. |
What is Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and Why is it Important for B2B Buyers?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a highly efficient manufacturing process that merges the benefits of plastic injection molding with the robust properties of metal. MIM is suitable for producing intricate components in high volumes, making it ideal for industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. Buyers should consider MIM for applications requiring high precision and minimal material waste, although they should also be aware of the initial setup costs, which can be significant.
How Does Desktop Metal Molding Cater to Small-Scale Production Needs?
Desktop metal molding machines are designed for ease of use and compactness, making them perfect for small-scale production or prototyping. They typically feature a plug-and-play setup, allowing users to create metal parts without extensive training. This type of machine is particularly beneficial for sectors like jewelry making and small batch manufacturing, where flexibility and quick turnaround times are crucial. However, buyers should note that these machines may have limitations in terms of production capacity compared to larger industrial machines.
What Are the Advantages of Die Casting in High-Volume Production?
Die casting is a metal molding process that employs high pressure to inject molten metal into molds, which is especially advantageous for producing large quantities of parts with high dimensional accuracy. This method is commonly used in the automotive and household appliance sectors. While die casting offers high production rates and excellent surface finishes, buyers must consider the higher tooling costs associated with this process, which can impact overall project budgets.
Why Choose Sand Casting for Larger Parts?
Sand casting is a traditional metal molding technique that uses sand molds to create metal parts. This method is particularly suited for larger and more complex components, making it a cost-effective option for industries such as industrial machinery and art sculptures. Although sand casting is generally less precise than MIM or die casting, its lower initial costs make it an attractive choice for companies looking to produce large parts without the investment in complex tooling.
What Makes Investment Casting a Go-To Choice for Precision Components?
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is a process that allows for the production of highly accurate and complex metal parts. This method is widely utilized in industries such as aerospace, defense, and medical instruments due to its ability to create parts with excellent surface finishes and intricate designs. While investment casting provides superior precision, it is often more time-consuming and may involve higher production costs, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their specific needs and timelines before opting for this method.
Key Industrial Applications of metal moulding machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal moulding machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Production of lightweight components for aircraft engines | Reduces weight and enhances fuel efficiency | Certification standards and material traceability |
| Medical Technology | Manufacturing of precision components for surgical instruments | Ensures high reliability and patient safety | Regulatory compliance and material biocompatibility |
| Automotive | Creation of durable parts for electric vehicles | Supports innovation in e-mobility and enhances performance | Supplier reliability and ability to meet large-scale demands |
| Consumer Electronics | Fabrication of components for smart devices and wearables | Meets consumer demand for high-quality, innovative products | Flexibility in design and quick turnaround times |
| Defense | Development of precision components for military applications | Ensures operational reliability under extreme conditions | Compliance with defense industry standards and certifications |
How is Metal Moulding Machine Used in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, metal moulding machines are essential for producing lightweight components such as brackets and housing for aircraft engines. The precision of these machines allows for complex geometries that enhance the overall efficiency of the aircraft. For international buyers, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, adherence to stringent certification standards and material traceability is crucial to ensure safety and compliance with aviation regulations.
What Role Does Metal Moulding Play in Medical Technology?
Metal moulding machines are utilized in medical technology to manufacture high-precision components for surgical instruments and diagnostic devices. These components require exceptional reliability and biocompatibility due to their direct contact with patients. Buyers from Africa and South America need to prioritize suppliers that can demonstrate regulatory compliance and provide materials that meet health standards, ensuring patient safety and quality assurance.
How is Metal Moulding Applied in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive industry, metal moulding machines facilitate the creation of durable parts for electric vehicles, such as connector housings and shielding components. This technology supports innovation in e-mobility by producing lightweight yet strong parts that improve vehicle performance. Buyers in regions like Brazil and the Middle East should focus on sourcing suppliers with a proven track record of reliability and the capacity to meet large-scale production demands.
What are the Benefits of Metal Moulding in Consumer Electronics?
The consumer electronics sector leverages metal moulding machines to fabricate intricate components for smart devices, wearables, and other high-tech products. The ability to produce high-quality and innovative parts quickly meets the growing consumer demand for advanced technology. International buyers must consider suppliers that offer flexibility in design and the capability for rapid prototyping to stay competitive in this fast-paced market.
How Does Metal Moulding Support Defense Applications?
In defense, metal moulding machines are crucial for developing precision components that must perform reliably under extreme conditions. These parts are often used in critical military applications, where failure is not an option. Buyers in this sector need to ensure their suppliers comply with strict industry standards and certifications, focusing on quality assurance to maintain operational reliability in defense systems.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal moulding machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Achieving Consistent Quality in Metal Parts
The Problem: One of the major challenges B2B buyers face when using metal moulding machines is the inconsistency in the quality of the produced parts. Factors such as variations in material properties, mold design, and machine calibration can lead to defects like warping or dimensional inaccuracies. This inconsistency can result in increased scrap rates, production delays, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers. In industries like aerospace or medical technology, where precision is paramount, such issues can have serious repercussions.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, buyers should prioritize investing in high-quality materials and robust design practices. When sourcing metal moulding machines, look for manufacturers that provide comprehensive training on machine operation and maintenance. Regularly calibrating the equipment and conducting routine quality checks can help maintain the consistency of the production process. Additionally, implementing a controlled environment for production can minimize external factors that might affect the final product. By focusing on these aspects, businesses can enhance their production quality and reduce the likelihood of defects.
Scenario 2: High Production Costs Due to Inefficient Processes
The Problem: Many businesses find themselves grappling with high production costs when utilizing metal moulding machines. This often stems from inefficient processes, such as excessive material waste during the molding process, energy inefficiency, or lengthy cycle times. For companies operating in competitive markets, high production costs can erode profit margins and hinder growth opportunities.
The Solution: To address these inefficiencies, companies should conduct a thorough analysis of their production workflow. Investing in advanced metal moulding machines that feature automated controls and energy-efficient operations can significantly reduce costs. Additionally, adopting a lean manufacturing approach can help streamline processes by eliminating waste and optimizing resource utilization. Training staff on best practices for machine operation and maintenance will also lead to more efficient production cycles. Lastly, consider partnering with suppliers who offer materials that are designed specifically for metal injection molding, as these can reduce waste and improve overall efficiency.
Scenario 3: Challenges in Adapting to Diverse Market Demands
The Problem: As global markets evolve, B2B buyers often face the challenge of adapting their metal moulding operations to meet diverse customer demands. This includes producing a wide range of complex parts with varying specifications and materials. The inability to quickly pivot and scale production can lead to lost business opportunities and a failure to compete effectively in the marketplace.
The Solution: To remain agile and responsive to market demands, businesses should invest in flexible metal moulding machines capable of handling a variety of materials and designs. Seek equipment that allows for quick changeovers and easy modifications in mold designs. Developing strong relationships with suppliers can also facilitate quicker access to different materials and components, enabling faster adaptation to customer needs. Regularly engaging with customers to gather feedback on their evolving requirements can help businesses anticipate changes in demand and adjust their production strategies accordingly. By creating a more adaptable production environment, companies can better position themselves to seize new opportunities and remain competitive.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal moulding machine
What Are the Key Materials for Metal Moulding Machines?
When selecting materials for metal moulding machines, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in metal moulding, focusing on their performance characteristics and implications for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Properties and Applications of Stainless Steel in Metal Moulding?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and can endure significant pressure, making it suitable for various moulding applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, ensuring long-lasting moulds that can withstand repeated use. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex machining processes, increasing manufacturing costs. Additionally, while it is suitable for many applications, it may not be the best choice for highly reactive media.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. Its durability ensures that it maintains dimensional stability over time, which is crucial for precision components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, when sourcing stainless steel moulds. Additionally, they should consider the availability of high-quality stainless steel in their regions to avoid supply chain issues.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Metal Moulding Applications?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has good thermal conductivity, and offers excellent corrosion resistance. It is typically rated for temperatures up to 400°C, making it suitable for lower-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce transportation costs and ease handling. It is also less expensive than stainless steel. However, its lower temperature tolerance may limit its use in high-temperature applications, and it may not be as durable as steel under heavy stress.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in automotive and aerospace components. Its thermal conductivity makes it suitable for heat exchangers and cooling systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: When purchasing aluminum moulds, buyers should be aware of the specific alloy grades and their compliance with international standards. In regions like the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, selecting the right alloy is crucial to avoid performance issues.
What Are the Advantages of Using Copper in Metal Moulding?
Key Properties: Copper has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat transfer. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and has good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, making it perfect for electrical components and heat exchangers. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to corrosion in certain environments, necessitating protective coatings.
Impact on Application: Copper is widely used in power electronics and thermal management applications. Its ability to dissipate heat efficiently makes it a preferred choice for components in electric vehicles and electronic devices.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of high-grade copper and ensure compliance with industry standards. In regions like Europe, where environmental regulations are strict, sourcing copper from compliant suppliers is essential.
What Role Does Bronze Play in Metal Moulding?
Key Properties: Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength. It can withstand high temperatures and has a good wear resistance profile.
Pros & Cons: Bronze is durable and suitable for applications requiring high strength and resistance to wear. However, it can be more expensive than aluminum and may require specialized machining techniques, increasing production complexity.
Impact on Application: Bronze is often used in marine applications and in components that require high wear resistance, such as gears and bearings. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for environments exposed to moisture.
Considerations for International Buyers: When sourcing bronze, buyers should be aware of the specific alloy compositions and their compliance with local standards. In regions like South America, where marine applications are prevalent, selecting the right bronze alloy is critical for performance.
Summary of Material Selection for Metal Moulding Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal moulding machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex machining | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace | Lightweight, lower cost | Limited high-temperature applications | Medium |
| Copper | Power electronics, thermal management | Superior electrical/thermal conductivity | Prone to corrosion, higher cost | High |
| Bronze | Marine applications, gears | High strength and wear resistance | Expensive, requires specialized machining | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the properties and applications of various materials used in metal moulding machines, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal moulding machine
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Metal Moulding Machines?
The manufacturing process of metal moulding machines involves several key stages that ensure precision, efficiency, and quality. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers assess the capabilities of potential suppliers.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the preparation of materials. Typically, this involves selecting high-quality metals and alloys, such as stainless steel or aluminum, that are suitable for the intended application. Suppliers often conduct a thorough analysis of the material properties, including tensile strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance, to ensure they meet specific industry requirements.
Additionally, suppliers may pre-treat the materials through processes like annealing or surface hardening to enhance performance. This stage is critical, as the quality of the raw materials directly impacts the durability and functionality of the final product.
2. Forming
The forming stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the desired components of the metal moulding machine. This is typically achieved through various techniques, including:
- Metal Injection Molding (MIM): This method combines metal powder with a binder, allowing for the creation of complex shapes with high precision. It is particularly beneficial for producing intricate components in bulk.
- Die Casting: In this technique, molten metal is injected into a mold under pressure, resulting in high-volume production with excellent dimensional accuracy.
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is used for precise shaping and finishing of components. It offers flexibility in design and can accommodate various materials.
Each technique has its advantages and is selected based on the specific requirements of the machine being produced, including complexity, volume, and material properties.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are formed, they proceed to the assembly stage. This involves the integration of various parts, such as the injection system, heating elements, and control systems, into a cohesive machine. Quality assurance during assembly is paramount to ensure that all components fit correctly and function as intended.
Automated assembly processes are often employed to enhance efficiency and consistency. However, manual assembly may still be necessary for complex components or systems requiring fine-tuning. It is crucial for suppliers to have skilled technicians who can ensure precision during this stage.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which may include surface treatments, coatings, and quality checks. Finishing techniques such as polishing, anodizing, or painting can improve aesthetics and protect against corrosion. This stage is vital for enhancing the longevity and performance of the machine.
In addition to aesthetic enhancements, suppliers conduct rigorous testing during the finishing stage to ensure that the machine meets all operational standards. This includes functionality tests and inspections for any defects.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Metal Moulding Machine Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process for metal moulding machines, ensuring that the final product meets international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards for Quality Assurance
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the supplier has established a systematic approach to quality management, enhancing customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for oil and gas applications can provide further assurance of quality and compliance. These certifications demonstrate that the manufacturing processes and products meet stringent regulatory requirements.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage assesses the quality of raw materials upon arrival. Suppliers should conduct material inspections and tests to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process is essential. This includes regular checks for dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and functionality to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once assembly and finishing are complete, a comprehensive final inspection is conducted. This may involve functional testing, performance evaluations, and visual inspections to ensure the machine operates correctly and meets all specifications.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used in Metal Moulding Machine Quality Control?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and reliability of metal moulding machines:
- Dimensional Inspection: This involves measuring the dimensions of components to ensure they adhere to specified tolerances. Tools such as calipers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are often used.
- Material Testing: Suppliers may conduct tensile tests, hardness tests, and fatigue tests to evaluate the mechanical properties of the materials used in the machines.
- Functional Testing: This includes operational tests to assess the machine’s performance, including injection accuracy, heating efficiency, and overall system functionality.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the components.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers should adopt a proactive approach to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting supplier audits can provide insight into their manufacturing practices and quality management systems. Buyers should evaluate the supplier’s adherence to international standards and their internal QC protocols.
- Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports can help buyers understand the supplier’s testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformance.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This can be particularly important for international buyers who may not have the ability to conduct on-site inspections.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations. Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance transparency and cooperation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements that may affect quality standards. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local regulations to avoid potential issues.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: International shipping can introduce risks related to product handling and damage. Buyers should discuss with suppliers their packaging and handling practices to mitigate these risks.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for metal moulding machines, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal moulding machine’
Introduction
Navigating the procurement of a metal moulding machine can be complex, especially for B2B buyers across diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This guide serves as a practical checklist to streamline your sourcing process, ensuring you make informed decisions that align with your production needs and business goals.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is crucial to ensure the machine meets your production requirements. Consider factors such as the types of metals you intend to mold, desired part dimensions, and production volume. Detailed specifications help in communicating effectively with potential suppliers and in evaluating their offerings accurately.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Stay updated on the latest trends and technologies in metal moulding machinery. This includes advancements in materials, machine efficiency, and production techniques like Metal Injection Molding (MIM). Understanding current market innovations can provide insights into potential suppliers and help you identify machines that offer competitive advantages.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before making any commitments, it’s essential to conduct thorough evaluations of potential suppliers. Request comprehensive company profiles, including their manufacturing capabilities, experience in your industry, and references from similar clients. This step helps ensure that you partner with a reliable supplier who can meet your quality and delivery expectations.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that your selected suppliers have relevant certifications and comply with international standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and any industry-specific certifications that validate their expertise. Compliance not only guarantees quality but also mitigates risks associated with regulatory challenges.
Step 5: Request Samples and Demonstrations
Before finalizing a purchase, request samples of the metal parts produced by the machine or ask for a live demonstration. This allows you to assess the machine’s performance, precision, and the quality of the finished product. Observing the machine in action can provide valuable insights into its usability and efficiency.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Inquire about the after-sales support services offered by the supplier, including training, maintenance, and availability of spare parts. A robust warranty and responsive customer service are vital to ensuring operational continuity and minimizing downtime in your production processes. Understanding these aspects upfront can save you time and costs in the long run.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Be clear about your expectations and any potential penalties for delays or quality issues. Effective negotiation can lead to favorable terms that align with your budget and operational timelines, ensuring a mutually beneficial partnership.
By following this checklist, you can enhance your sourcing strategy for a metal moulding machine, leading to informed decisions that contribute to your business’s success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal moulding machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Moulding Machine Sourcing?
When sourcing metal moulding machines, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. Key cost components include:
-
Materials: The primary material used in metal moulding machines can significantly impact pricing. High-quality alloys and specialty metals often command higher prices due to their enhanced properties, such as durability and resistance to corrosion. For example, components made from copper or bronze may be more expensive than those made from standard steel.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region of production and the complexity of the machine. Skilled labor is often required for the assembly and quality control of sophisticated machines, which can increase overall costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production facility, utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these costs, benefiting buyers.
-
Tooling: Tooling expenses are crucial in the production of metal moulding machines, especially for custom designs. High-quality tooling is necessary for precision manufacturing, and these costs should be factored into the total price.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the machines meet industry standards and specifications. The costs associated with testing and certification can influence the final price of the machine.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can be significant, particularly for international buyers. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and import duties must be considered in the overall budget.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This can vary based on market demand and the supplier’s positioning.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Moulding Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of metal moulding machines:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often lead to volume discounts, making it advantageous for buyers to negotiate bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom-built machines tailored to specific needs can lead to higher costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts both the performance and price of the machine. Buyers should balance material quality with budget constraints.
-
Quality and Certifications: Machines that comply with international quality standards or possess specific certifications may come at a premium but offer better reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can also affect price. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can influence the total cost of ownership. Understanding the terms of shipment, insurance, and liability is crucial for accurate cost estimation.
What Negotiation Tips Can Help B2B Buyers Optimize Costs?
For B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation can yield better pricing:
-
Understand Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also the long-term operational costs, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
-
Leverage Volume Discounts: If planning to make multiple purchases, negotiate for bulk pricing to lower the per-unit cost.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Insist on itemized quotes to understand the breakdown of costs, which can help identify areas for negotiation.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals and terms in the long run.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures due to local economic factors. Understanding these nuances can help in negotiations.
Conclusion: What Should Buyers Remember About Pricing?
As B2B buyers consider sourcing metal moulding machines, it is essential to approach the process with a clear understanding of the cost structure and pricing influencers. While indicative prices may vary, careful analysis and strategic negotiation can lead to favorable outcomes. Always conduct thorough research and consider the long-term implications of any investment in machinery.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal moulding machine With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Metal Moulding Machines
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional metal moulding machines to meet their production needs. These alternatives can provide varied advantages depending on factors such as cost, performance, and the specific requirements of the application. This section explores how metal moulding machines compare to other viable methods, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions.
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Moulding Machine | Desktop Metal Injection Molding | Metal Injection Molding (MIM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and detail for small to medium parts | Excellent for prototypes and small production runs | Exceptional for high volume and complex geometries |
| Cost | $2,499 (initial investment) | Lower initial cost, but material costs can accumulate | Higher setup costs; cost-effective for large volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Plug-and-play setup; minimal training required | User-friendly; quick to start production | Requires specialized knowledge and tooling for setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; easy to clean | Moderate maintenance; specific care for materials | Higher maintenance due to complexity and equipment requirements |
| Best Use Case | Small batch production, prototyping | Rapid prototyping and small-scale production | Large-scale production of complex components |
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Desktop Metal Injection Molding?
Desktop Metal Injection Molding, like the INJEKTO M, offers a cost-effective solution for businesses needing rapid prototyping or small-scale production. Its compact size and user-friendly design enable quick setup and operation, making it suitable for startups and small businesses. However, while the initial investment is lower, the material costs can add up, especially when scaling production. Additionally, it may not deliver the same performance as larger industrial machines for high-volume needs.
How Does Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Compare?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a robust alternative designed for high-volume production of complex parts. It combines the benefits of plastic injection molding with the strength of metal, allowing for intricate designs that traditional machining cannot achieve. MIM is particularly effective in industries like automotive and medical, where precision and reliability are paramount. However, it has higher setup costs and requires specialized knowledge and tooling, making it less accessible for smaller operations or those just starting in metal manufacturing.
How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
Selecting the most suitable manufacturing solution depends on several factors, including production volume, complexity of parts, budget, and operational capabilities. For businesses focused on small batch production or prototyping, a metal moulding machine or desktop metal injection molding could be ideal. In contrast, companies requiring high-volume production with intricate designs may benefit more from metal injection molding. Evaluating these aspects will help B2B buyers align their choice with their operational goals, ensuring efficiency and cost-effectiveness in their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal moulding machine
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Metal Moulding Machines?
When considering a metal moulding machine for your production needs, several technical properties are crucial for ensuring efficiency and product quality. Here are key specifications that B2B buyers should understand:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the quality and composition of the materials used in the machine’s construction, including the metal paste for moulding. Higher-grade materials typically offer better performance, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. For instance, using premium-grade copper or bronze can lead to superior end products, essential for industries like aerospace or medical technology where precision is paramount. -
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the finished product. In metal injection moulding, tight tolerances (often as low as ±0.1 mm) ensure that components fit together correctly, which is critical in applications such as automotive or electronics. Understanding the tolerance specifications helps buyers ascertain whether a machine can meet their production requirements. -
Maximum Injection Volume
This specification defines the maximum amount of material that can be injected into the mould in a single shot. For example, a machine with a maximum injection volume of 230g allows for the production of larger or more complex components. Knowing this capacity helps businesses plan their production runs and manage material costs effectively. -
Shrinkage Rate
The shrinkage rate, often expressed as a percentage, indicates how much a material will reduce in size after the sintering process. For metal moulding machines, a typical shrinkage rate is around 12%. Understanding this property is vital for achieving precise dimensions in the final product, allowing manufacturers to account for changes during production. -
Density Post-Sintering
This property refers to the density of the metal part after it has undergone the sintering process. A higher density, such as 8.00 g/cm³ for copper, translates to stronger and more durable components. For industries requiring robust materials, knowing the post-sintering density is essential for ensuring that the final products meet safety and performance standards.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know?
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the metal moulding sector. Here are some common terms that every B2B buyer should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the role of OEMs can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality of components used in their metal moulding machines. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory effectively and ensure they are not over-committing to large orders that may not sell. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price proposals from suppliers. It typically includes detailed specifications of the products needed, helping buyers compare offers and negotiate better pricing. -
Incoterms
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Understanding these terms helps buyers clarify shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations, ensuring smooth transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to receiving the goods. For metal moulding machines, understanding lead times is crucial for planning production schedules and meeting customer demands. -
Sintering
Sintering is the process of heating the metal paste to a temperature below its melting point to fuse particles together. Familiarity with sintering helps buyers appreciate the importance of temperature control in achieving the desired material properties.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right metal moulding machine that meets their production needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal moulding machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Metal Moulding Machine Sector?
The global market for metal moulding machines is witnessing significant growth driven by various factors, including the increasing demand for lightweight and complex metal parts across industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics. The rise of advanced manufacturing technologies, particularly Metal Injection Molding (MIM), is reshaping production capabilities. MIM allows manufacturers to create intricate geometries with high precision while reducing material waste, making it an attractive option for B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Emerging trends indicate a shift towards automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, which enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. This transition is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to streamline their sourcing processes. Additionally, the proliferation of desktop metal injection moulding machines, such as the INJEKTO M, caters to smaller businesses and startups, democratizing access to advanced manufacturing capabilities. This trend is gaining traction in developing markets, where local manufacturers are looking to compete on a global scale.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on sustainability is influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are now more inclined to partner with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to environmentally friendly practices and materials. As a result, understanding the latest technological advancements and sustainability initiatives is crucial for international B2B buyers to remain competitive.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Metal Moulding Machine Sector?
Sustainability has emerged as a key consideration for B2B buyers in the metal moulding machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Companies are increasingly expected to adopt practices that minimize their carbon footprint. This has led to a growing demand for machines that utilize recyclable materials and processes that reduce emissions.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers seek transparency in their supply chains. Suppliers that can demonstrate responsible sourcing of raw materials and adherence to social and environmental standards gain a competitive advantage. This is particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America, where ethical practices can influence purchasing decisions significantly.
Moreover, the certification of ‘green’ materials and processes is becoming essential. Buyers should look for suppliers who hold certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or those that use eco-friendly materials in their production processes. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers not only contribute to environmental preservation but also enhance their brand reputation and customer loyalty.
What Is the Brief Evolution and History of Metal Moulding Machines?
The evolution of metal moulding machines can be traced back to the early 20th century when traditional metalworking methods dominated the industry. The introduction of injection moulding technology in the 1940s marked a significant turning point, allowing for faster production and the ability to create complex shapes. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and manufacturing technology led to the development of Metal Injection Molding (MIM) in the 1970s, enabling the production of high-precision components with minimal waste.
Today, the sector continues to innovate with the advent of desktop metal moulding machines, making the technology more accessible to smaller businesses and startups. This democratization of technology is reshaping the landscape, allowing a broader range of companies to leverage advanced manufacturing capabilities. As the market matures, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing is expected to play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of metal moulding machines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal moulding machine
-
How do I choose the right metal moulding machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right metal moulding machine requires a clear understanding of your production requirements, including the types of materials you plan to use, the complexity of the parts needed, and your production volume. Consider factors such as the machine’s maximum injection capacity, available materials, and the ability to create intricate designs. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s ease of use and maintenance, as well as its compatibility with your existing manufacturing processes. Engaging with suppliers for demonstrations or consultations can also provide insights tailored to your specific needs. -
What is the best metal moulding machine for small to medium-sized businesses?
For small to medium-sized businesses, desktop metal injection moulding machines like the INJEKTO M offer a compact solution without compromising on quality. These machines are designed for ease of use, allowing quick setup and operation, ideal for businesses with limited floor space. They can produce high-quality metal parts with minimal waste, making them cost-effective. Moreover, their ability to work with reusable materials like MASTE enhances sustainability and reduces operational costs, making them a smart choice for growing enterprises. -
What are the typical lead times for ordering a metal moulding machine?
Lead times for ordering a metal moulding machine can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, machine specifications, and your location. Generally, standard machines may have lead times ranging from a few weeks to several months. Custom machines designed to meet specific requirements could take longer due to the additional engineering and testing involved. It’s advisable to discuss timelines directly with suppliers and factor in potential delays related to shipping and customs clearance, especially for international orders. -
What should I consider when evaluating suppliers for metal moulding machines?
When evaluating suppliers, consider their reputation, experience in the industry, and customer reviews. Assess their product range to ensure they offer machines that meet your specifications. It’s also essential to inquire about after-sales support, warranty policies, and the availability of spare parts. Verify if they have experience dealing with international clients, particularly in your region, as this can affect shipping and service efficiency. Finally, request references from other businesses that have purchased similar machines. -
Are there minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal moulding machines?
Most suppliers typically do not impose minimum order quantities (MOQs) for individual machines, as they understand the diverse needs of businesses. However, if you’re looking to purchase multiple machines or additional components, it’s advisable to inquire about bulk pricing or discounts. Establishing a relationship with the supplier can also lead to flexibility in order quantities, especially for repeat customers or long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms are common when purchasing metal moulding machines?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (often 30-50%) followed by the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders, particularly for established businesses. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfer, credit card) and ensure that the terms are documented in the sales agreement. For international transactions, consider any additional costs associated with currency exchange or transaction fees. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my metal moulding machine?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed specifications and compliance certifications from suppliers, including ISO standards relevant to manufacturing processes. Many reputable manufacturers conduct rigorous testing on their machines before shipment; inquire about these procedures. Additionally, consider asking for a demonstration of the machine’s capabilities or visiting the facility if possible. Establishing a clear QA process with the supplier, including inspection protocols upon delivery, can help mitigate any issues before production begins. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing a metal moulding machine?
When importing a metal moulding machine, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial machinery to navigate these complexities. Ensure that all shipping documents are accurate to avoid delays at customs. Additionally, assess the costs associated with shipping, insurance, and any local delivery services needed upon arrival. Planning for these logistics can save time and reduce unexpected expenses in the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Metal Moulding Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Schunk – Metal Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: schunk-group.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) combines plastic injection molding versatility with metal’s mechanical properties, allowing for the production of complex, precise components in large quantities with minimal waste. Schunk offers MIM solutions across various industries, including:
1. **Power Electronics**: MIM products made from pure copper, resistance alloys, and hardenable copper alloys for termina…
2. Bole Machinery – EVOlution H
Domain: bolemachinery.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Manufacturer: Bole Machinery
Business Type: Manufacturer, Trade Company
Main Markets: Africa, Americas, Asia, Caribbean, East Europe, Europe, Middle East, North Europe, Oceania, Other Markets, West Europe, Worldwide
Exporter: 51%-60%
Certifications: CE, ISO9001, TUV, UL
Key Products:
1. EVOlution Hybrid Power Injection Moulding Machine
2. Magnesium Alloy Semi-solid Injection Moulding Equipment
3….
3. Indiamart – Molding Machines
Domain: dir.indiamart.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Molding Machines available: 1000+ products. Key products include: 1. Plastic Injection Moulding Machine – Price: ₹ 8,20,000, Automation Grade: Semi-Automatic, Raw Material: PP, Mould Cavity: 2 cavity, Type: Stretch Blow Molding, Capacity: 200 ML-2000ML, Voltage: 440V. 2. Bakelite Moulding Press – Price: ₹ 8,50,000, Production Capacity: as per requirement, Material: Iron, Capacity: 1-5 Ton to >100 …
4. MAPLAN – Injection Moulding Machines
Domain: maplan.at
Introduction: MAPLAN offers a versatile portfolio of injection moulding machines with over 40 models, including horizontal, vertical, and C-frame presses. Key models include: RAPID+ (horizontal, high speed, automated), ERGO+ (vertical, precise, versatile), ERGOMAX+ (vertical, large size, high precision), CLEVER+ (vertical, basic model from 160 to 400 tons), EASY+ (vertical C-frame, compact for rubber articles),…
5. Powder Metallurgy – Metal Injection Molding Machine Overview
Domain: powdermetallurgy.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Metal Injection Molding Machine Overview: Used for producing tiny, high-precision components in various applications such as automotive, electronics, and medical devices. Main components include Injection Unit (types: plunger, screw, screw pre-plastic plunger), Clamping Unit, Hydraulic Unit, and Computer System. Types of MIM Machines: Hydraulic (fast mold changes, larger products, less energy effi…
6. Indo-MIM – Metal Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: indo-mim.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) combines the design flexibility of Plastic Injection Molding with the strength of wrought metals. The MIM process consists of four steps: Compounding, Molding, Debinding, and Sintering.
1. Compounding: Fine metal powder (less than 20µ particle size) is blended with thermoplastic and wax binders in a 60:40 ratio by volume, heated, mixed, cooled, and granulated into pe…
7. EPMA – Metal Injection Moulding Solutions
Domain: epma.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Metal Injection Moulding (MIM) is a competitive manufacturing process for small precision components, capable of producing complex shapes from various materials including metals, ceramics, intermetallic compounds, and composites. MIM is a development of traditional powder metallurgy (PM) and allows for the production of intricate parts without the limitations of conventional pressing and sintering…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal moulding machine
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of metal moulding machines presents significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. The advancements in technologies like Metal Injection Molding (MIM) not only enhance production capabilities but also reduce material waste and improve precision. The versatility of these machines caters to diverse sectors, from aerospace to medical technology, ensuring that businesses can meet their specific production needs effectively.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, leveraging strategic partnerships can yield substantial benefits. By sourcing high-quality machines and materials, companies can enhance their operational efficiency, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
As the demand for advanced manufacturing processes continues to rise, now is the time for B2B buyers to invest in metal moulding technologies. Engaging with reputable suppliers and exploring bulk purchasing options can lead to more sustainable and profitable business practices. Take action today to secure a future of enhanced productivity and growth in your manufacturing endeavors.