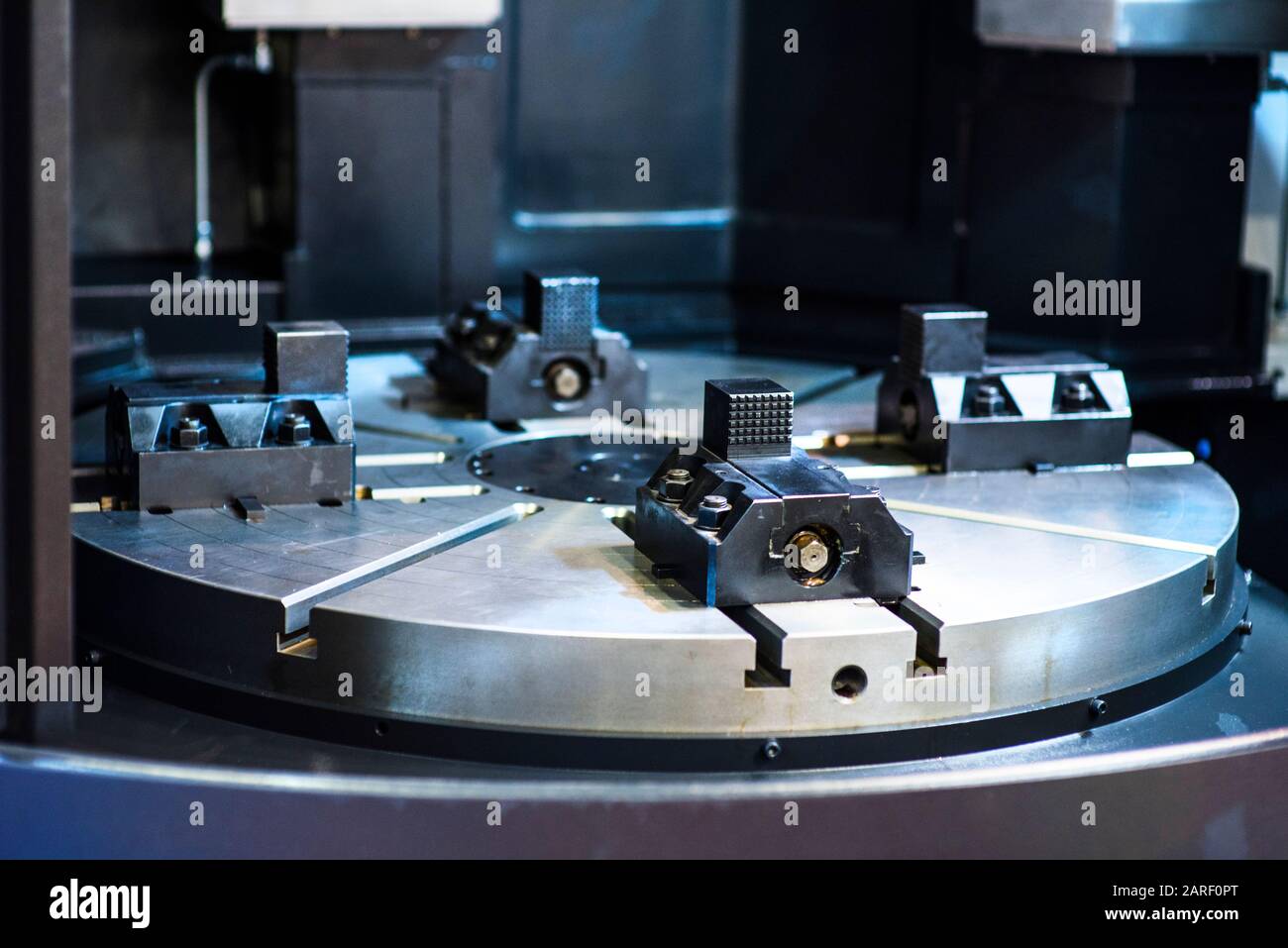
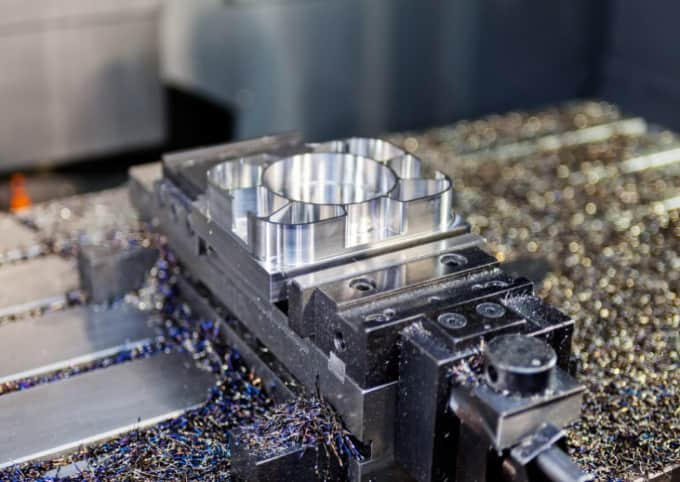
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal molding machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing the right metal molding machine can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. Whether you are in Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, or elsewhere in Africa, South America, or Europe, understanding the nuances of metal injection molding (MIM) technology is crucial to meeting your production needs. This guide offers an in-depth exploration of various types of metal molding machines, including their applications across industries, the intricacies of supplier vetting, and a thorough breakdown of cost considerations.
Navigating the global market requires not only knowledge of the machinery but also insights into material properties, production processes, and market trends that influence pricing and availability. By arming yourself with the information contained in this comprehensive guide, you will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions that align with your operational goals and budget constraints.
From assessing the capabilities of desktop models like the INJEKTO M to understanding the scalability of larger industrial systems, this guide is designed to facilitate a seamless acquisition process. It aims to enhance your strategic sourcing efforts, ensuring that you select a metal molding machine that not only meets your technical specifications but also provides long-term value for your business.
Understanding metal molding machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metal Injection Molding (MIM) | Combines plastic injection molding with powdered metallurgy; allows for complex geometries. | Automotive, aerospace, medical devices | Pros: Cost-effective for high volumes; produces intricate parts. Cons: Initial setup cost can be high. |
| Desktop Metal Injection Molding | Compact, user-friendly machines designed for small-scale production; often come fully assembled. | Prototyping, small batch production | Pros: Low entry cost; easy to use; quick turnaround. Cons: Limited production capacity compared to industrial machines. |
| Cold Chamber Die Casting | Uses a separate furnace for metal melting; ideal for high melting point metals. | Automotive parts, electronics | Pros: High production rates; excellent surface finish. Cons: More complex machinery; requires skilled operators. |
| Hot Chamber Die Casting | Metal is melted in the machine itself; suitable for low melting point alloys. | Consumer goods, toys, plumbing fittings | Pros: Faster cycle times; lower operational costs. Cons: Limited to non-ferrous metals; not suitable for high melting point materials. |
| Investment Casting | Uses a wax pattern coated in ceramic; allows for high precision and detail. | Aerospace, jewelry, industrial components | Pros: Excellent dimensional accuracy; suitable for complex shapes. Cons: Higher per-part cost; longer lead times. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Metal Injection Molding (MIM)?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is recognized for its ability to produce high-strength parts with intricate designs at lower costs compared to traditional machining methods. The process involves mixing fine metal powders with thermoplastic binders, which are then injected into molds. This method is particularly suitable for high-volume production of small, complex components, making it ideal for industries such as automotive and aerospace. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment and the technical expertise required for setup and operation.
How Do Desktop Metal Injection Molding Machines Differ?
Desktop Metal Injection Molding machines, like the INJEKTO M, cater to smaller-scale operations and prototyping needs. These machines are compact, user-friendly, and often come fully assembled, enabling quick setup and operation. They are particularly advantageous for businesses looking to create prototypes or small batches of metal parts without the significant investment typically associated with larger industrial machines. Buyers should evaluate the machine’s capacity and material compatibility to ensure it meets their specific production needs.
What Are the Benefits of Cold Chamber Die Casting?
Cold Chamber Die Casting is a method that excels in producing parts from high melting point metals, such as aluminum and magnesium. This technique is characterized by its separate melting furnace, allowing for greater control over the metal’s temperature and quality. It is commonly used in automotive and electronic applications due to its ability to achieve high production rates and excellent surface finishes. However, B2B buyers must consider the complexity of the machinery and the necessity for skilled operators.
What Advantages Does Hot Chamber Die Casting Offer?
Hot Chamber Die Casting is designed for the production of low melting point alloys and is known for its rapid cycle times, making it suitable for high-volume production. This method is often employed in consumer goods and plumbing fittings. While it offers lower operational costs and faster production speeds, buyers should note its limitations in working with high melting point materials, which could restrict its application in certain industries.
How Does Investment Casting Compare to Other Methods?
Investment Casting is a versatile process that allows for the creation of highly detailed parts through the use of a wax pattern coated in ceramic material. This technique is favored in industries such as aerospace and jewelry for its precision and ability to produce complex shapes. Despite its advantages, the higher per-part cost and longer lead times associated with this method may deter some buyers. It’s crucial for B2B buyers to assess their production volume and budget when considering investment casting.
Key Industrial Applications of metal molding machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal molding machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of complex engine components | Reduces manufacturing costs and improves precision | Look for machines that can handle high-volume production and offer quick changeover capabilities. |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing lightweight structural parts | Enhances fuel efficiency and performance | Ensure compliance with industry standards and certifications for safety and quality assurance. |
| Medical Devices | Creation of intricate surgical instruments | Provides high precision and reliability | Source machines that can work with biocompatible materials and offer traceability features. |
| Electronics | Production of connectors and housings | Increases production speed and reduces waste | Consider machines with advanced automation features to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs. |
| Jewelry and Art | Crafting detailed metal designs | Allows for customization and intricate detailing | Look for machines that support small batch production and offer a variety of material options. |
How is a Metal Molding Machine Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, metal molding machines are crucial for producing complex engine components such as pistons and valve bodies. These machines enable manufacturers to create high-strength parts with intricate geometries that are often impossible to achieve through traditional machining methods. By utilizing metal injection molding (MIM), companies can significantly reduce production costs while enhancing precision and consistency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing machines that can handle high-volume production and provide quick changeover capabilities is essential to meet local demand efficiently.
What Role Does Metal Molding Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Metal molding machines are integral in the aerospace industry for manufacturing lightweight structural parts, such as brackets and housings, that contribute to overall fuel efficiency and performance. The MIM process allows for the creation of complex shapes with minimal waste, which is critical in an industry where weight reduction is paramount. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing machines that comply with stringent industry standards and certifications, ensuring safety and quality assurance in their production processes.
How Are Metal Molding Machines Transforming Medical Device Production?
In the medical device sector, metal molding machines are employed to create intricate surgical instruments and implants that require high precision and reliability. The MIM process allows manufacturers to produce complex geometries while maintaining strict tolerances, which is vital for ensuring the functionality and safety of medical devices. For B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, it is important to source machines capable of working with biocompatible materials and offering traceability features to comply with regulatory standards.
What Advantages Do Metal Molding Machines Offer Electronics Manufacturers?
Electronics manufacturers utilize metal molding machines to produce connectors, housings, and other small components that require high precision and rapid production capabilities. The MIM process enhances production speed while reducing material waste, making it an attractive option for companies looking to streamline their operations. International buyers, particularly from Europe and South America, should consider machines with advanced automation features to improve efficiency and minimize labor costs in their production lines.
How Can Jewelry and Art Benefit from Metal Molding Machines?
In the jewelry and art sectors, metal molding machines enable artisans to craft detailed metal designs and custom pieces. The flexibility of the MIM process allows for intricate detailing and personalization that traditional methods may not achieve. Buyers in these industries should look for machines that support small batch production and offer a variety of material options to cater to diverse customer preferences, enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal molding machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: High Initial Investment Costs in Metal Molding Machines
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, particularly in emerging markets like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia, face significant financial barriers when considering the purchase of metal molding machines. The upfront costs for machines, materials, and ancillary equipment (such as furnaces) can be daunting, often leading to hesitation in making a purchase. This financial strain can hinder companies from scaling their operations or adopting modern manufacturing techniques, ultimately limiting their competitive edge.
The Solution: To mitigate the high initial investment, B2B buyers should explore financing options such as leasing or installment plans offered by equipment suppliers. Additionally, buyers can negotiate bulk purchase discounts or inquire about financing programs specifically designed for emerging markets. It is also advisable to conduct a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis that emphasizes the long-term savings and efficiency gains from adopting metal molding technology. By understanding the potential return on investment, companies can justify the initial expenditure and position themselves for future growth.
Scenario 2: Complexity in Material Selection for Specific Applications
The Problem: Selecting the right material for metal molding applications can be overwhelming, especially for companies new to the technology. With a variety of metals and alloys available, B2B buyers often struggle to determine which material will best meet their specific production requirements, leading to potential production delays and quality issues. This complexity can be particularly pronounced in regions where technical support and expertise are limited.
The Solution: To simplify material selection, buyers should engage with suppliers who provide comprehensive technical support and educational resources. Suppliers often have extensive experience with different materials and can recommend the best options based on the desired properties and end-use applications. Additionally, conducting pilot projects with small batches of various materials can provide valuable insights into performance, cost-effectiveness, and manufacturability. Buyers should also look for suppliers that offer a range of material samples and technical data sheets to facilitate informed decision-making.
Scenario 3: Lack of Skilled Labor for Operating Metal Molding Machines
The Problem: A common challenge faced by B2B buyers in regions such as South America and the Middle East is the scarcity of skilled labor to operate advanced metal molding machines. This shortage can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased downtime, and difficulties in maintaining quality control. Companies may find it challenging to train existing staff or attract new talent, further exacerbating the problem.
The Solution: To address the skills gap, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs for their existing workforce. Partnering with equipment manufacturers for on-site training sessions can provide employees with hands-on experience and technical knowledge. Additionally, companies can collaborate with local technical schools or vocational training centers to develop tailored training programs aimed at equipping future workers with the necessary skills. Establishing mentorship programs within the organization can also help foster a culture of continuous learning, ensuring that employees are well-versed in operating and maintaining metal molding machines effectively.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal molding machine
What Are the Key Materials Used in Metal Molding Machines?
When selecting materials for metal molding machines, several factors must be considered, including the properties of the materials, their suitability for specific applications, and compliance with international standards. Below are analyses of four common materials used in metal injection molding, tailored for B2B buyers from diverse regions.
What Are the Properties and Applications of Stainless Steel in Metal Molding?
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and can handle pressures exceeding 200 MPa.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for producing complex parts that require longevity. However, it is more expensive than other materials and may involve complex manufacturing processes, increasing production time and costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly suitable for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries, where components must endure harsh environments. Its compatibility with various media, including chemicals and high-pressure fluids, makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A276 and DIN 1.4301 is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure that suppliers can meet these standards to guarantee product quality.
How Does Aluminum Compare as a Material for Metal Molding?
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity, and offers good corrosion resistance. It can withstand temperatures up to 600°C and is suitable for applications requiring low weight.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and ease of machining, which can significantly reduce production times. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in consumer goods, automotive parts, and electronic housings, where weight reduction is critical. Its compatibility with various coatings enhances its usability in diverse environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum meets standards such as ASTM B221 and JIS H4000. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost sensitivity is high, aluminum’s affordability can be a significant advantage.
What Advantages Does Copper Offer for Metal Molding Applications?
Key Properties: Copper has excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. It can withstand moderate temperatures up to 400°C and has good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons: Copper is particularly advantageous for electrical components and thermal applications due to its conductivity. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be more challenging to mold due to its softness.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in electrical connectors, heat exchangers, and plumbing fittings. Its compatibility with various media, including water and gases, makes it a favorable choice for plumbing and HVAC applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B170 is essential for quality assurance. Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia should also consider the availability of copper alloys that meet local specifications.
What Role Does Bronze Play in Metal Molding?
Key Properties: Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, offers good corrosion resistance and high wear resistance. It can handle temperatures up to 600°C and provides excellent mechanical properties.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of bronze is its strength and durability, making it suitable for high-load applications. However, it can be more expensive than both aluminum and copper, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application: Bronze is often used in marine applications, bearings, and bushings due to its resistance to seawater corrosion. Its compatibility with various lubricants enhances its performance in moving parts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B584. In Europe, the preference for bronze in marine applications is often dictated by environmental regulations.
Summary of Material Selection for Metal Molding Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal molding machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Aerospace, automotive components | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Consumer goods, automotive parts | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable than stainless steel | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical connectors, heat exchangers | Superior electrical conductivity | More expensive and challenging to mold | High |
| Bronze | Marine applications, bearings | High strength and wear resistance | Higher cost compared to aluminum and copper | Medium |
This guide provides essential insights into material selection for metal molding machines, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal molding machine
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Metal Molding Machines?
The manufacturing process of metal molding machines is a complex procedure that involves several stages, each critical for ensuring the machine’s performance and reliability. Here are the main stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first stage involves selecting and preparing the appropriate materials. Metal powders, often combined with thermoplastic or wax binders, are sourced based on the desired properties of the final product. This step includes grinding metals to create fine powders, which are then mixed to form a feedstock. The quality of the metal powder is paramount, as it directly influences the performance and durability of the finished machine.
2. Forming
In the forming stage, the prepared feedstock is injected into a mold under high pressure, akin to traditional plastic injection molding. This process creates a “green” part that retains its shape but is not yet fully solid. The injection molding phase is critical, as it determines the geometric precision and surface finish of the component.
3. Assembly
Once the green parts are formed, they undergo assembly, where various components of the machine are brought together. This can include the integration of electronic controls, mechanical parts, and safety features. Precision in assembly is essential, as any misalignment can affect the machine’s operation and the quality of the molded parts.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves sintering, where the assembled parts are heated to a temperature that allows the binders to evaporate and the metal particles to fuse, resulting in a solid, dense component. After sintering, additional finishing processes such as polishing, coating, or machining may be required to enhance surface quality and performance.
What Quality Assurance Practices Are Essential for Metal Molding Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that metal molding machines meet international standards and customer expectations. Here are key aspects of QA:
Relevant International Standards for Metal Molding Machines
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for effective quality management systems (QMS). Compliance with these standards ensures that manufacturers maintain a consistent level of quality throughout the production process. Additionally, region-specific certifications, such as CE marking in Europe or API standards in the oil and gas industry, may be required depending on the intended application of the metal molding machine.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the manufacturing process. These typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any deviations in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and evaluation of the completed machine before it leaves the facility. This step often includes performance testing to verify that the machine operates as intended.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used in Quality Assurance?
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the quality and reliability of metal molding machines. These include:
- Dimensional Inspection: Measuring critical dimensions of components to ensure they conform to specifications.
- Functional Testing: Assessing the performance of the machine under operational conditions to verify its effectiveness.
- Material Testing: Evaluating the physical properties of the materials used, such as tensile strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to ensure product reliability and compliance. Here are some actionable steps:
Conducting Audits
Buyers should consider conducting on-site audits of potential suppliers. This allows for a firsthand assessment of the manufacturing process, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
Reviewing Quality Reports
Requesting detailed quality reports and documentation from suppliers can provide insight into their QA processes. This includes data on past performance, defect rates, and corrective actions taken in response to quality issues.
Utilizing Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an additional layer of assurance. These independent organizations can conduct inspections and audits, providing unbiased assessments of the supplier’s capabilities and compliance with international standards.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific quality control and certification nuances:
- Regional Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulatory requirements. For instance, machinery sold in the EU must comply with CE regulations, which can involve extensive testing and certification processes.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of suppliers can also influence quality perceptions. Establishing strong communication and relationships can facilitate better quality outcomes.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who are transparent about their supply chains. Knowing the origin of materials and the manufacturing processes used can help in assessing overall product quality.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for metal molding machines are multi-faceted and critical for ensuring product excellence. By understanding the stages of manufacturing and the importance of robust quality control measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Emphasizing quality assurance not only safeguards investments but also builds trust and long-term partnerships in the global marketplace.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal molding machine’
Introduction
Sourcing a metal molding machine is a significant investment for any business looking to enhance production capabilities. This guide provides a practical checklist to help B2B buyers navigate the procurement process effectively. By following these steps, you can ensure that you select the right machine that meets your operational needs and budget constraints.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the purchasing process, it is essential to clearly define your technical requirements. This includes understanding the types of materials you will be working with, the required production volume, and the complexity of the parts you intend to manufacture.
– Key specifications: Maximum injection volume, mold dimensions, and material compatibility.
– Why it matters: Having well-defined specifications helps you identify machines that meet your specific operational needs and avoid overspending on unnecessary features.
Step 2: Research Available Technologies
Take the time to explore various metal molding technologies available in the market, such as Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and traditional methods.
– Look for: Innovations that improve efficiency, reduce waste, and lower production costs.
– Importance: Understanding the technology landscape enables you to make informed decisions based on the latest advancements that could benefit your business.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vet potential suppliers before making any commitments. Request detailed company profiles, case studies, and references from businesses in similar industries or regions.
– Check for: Supplier experience, customer reviews, and after-sales support.
– Why it’s crucial: A reliable supplier can significantly impact your operational efficiency and provide support when issues arise.
Step 4: Request Product Demonstrations
Whenever possible, request demonstrations of the machines you are considering. This allows you to see the equipment in action and assess its performance.
– Focus on: Ease of use, setup times, and the quality of output.
– Significance: Observing a machine’s operation firsthand can help you gauge its suitability for your production line and provide insights into the learning curve for your team.
Step 5: Verify Compliance and Certifications
Ensure that the machines meet industry standards and comply with relevant regulations in your region.
– Look for certifications: ISO, CE, and other pertinent quality assurance certifications.
– Importance: Compliance not only assures quality but also minimizes legal risks and potential operational disruptions.
Step 6: Analyze Total Cost of Ownership
Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each machine, which includes purchase price, maintenance costs, and operational expenses over its lifespan.
– Consider: Energy consumption, spare parts availability, and warranty terms.
– Why it matters: Understanding the TCO helps you make a more informed financial decision and ensures you stay within budget.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Once you have selected a potential supplier, engage in negotiations to finalize terms and conditions, including pricing, payment schedules, and delivery timelines.
– Key points: Warranty coverage, service agreements, and return policies.
– Significance: Clear agreements protect your interests and ensure that both parties are aligned on expectations and responsibilities.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can streamline the procurement process for metal molding machines, ensuring that their investment aligns with their operational goals and contributes to long-term success.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal molding machine Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Metal Molding Machines?
When sourcing metal molding machines, understanding the cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in the machine significantly impact the overall cost. For instance, high-grade steel or specialized alloys will incur higher costs compared to standard materials. Additionally, consumables like metal powders and binders used in the molding process also contribute to ongoing material costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect expenses. Direct costs refer to the wages of the workers involved in the manufacturing process, while indirect costs may include administrative and support staff. Labor rates can vary significantly across regions, which is an important consideration for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with the production facility, utilities, maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient factories may have lower overhead costs, which can translate into more competitive pricing for buyers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific machine components can add to the initial investment. The complexity and size of the molds required for production will influence tooling costs, as more intricate designs typically require more advanced tooling.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing quality control measures to ensure the machines meet specified standards can add to the total cost. This includes testing and inspection processes that may require additional labor and equipment.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international buyers. These costs can vary based on the machine’s size, weight, and destination, as well as the chosen shipping method. International buyers should also consider customs duties and taxes that may apply.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically incorporate a profit margin into their pricing. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s business model, market conditions, and competitive landscape.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Molding Machine Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of metal molding machines:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to reduced per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing structures based on order size, incentivizing bulk purchases.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized machines tailored to specific production needs will generally cost more than standard models. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the increased costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Machines built with high-quality materials and those that meet industry certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may carry a premium price. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in higher-quality machines.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and service offerings of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their track record, while new entrants may offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery (Incoterms) can significantly affect total costs. Buyers should clarify whether prices include shipping, insurance, and duties to avoid unexpected expenses.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Metal Molding Machine Sourcing?
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing metal molding machines, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations with suppliers to secure better pricing or additional value-added services. Leverage volume commitments or long-term partnerships as bargaining chips.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess the TCO rather than just the purchase price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A slightly higher initial investment in a reliable machine can lead to lower long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand regional market dynamics, including currency fluctuations and local economic conditions, which can affect pricing. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local regulations that may impact costs.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, comparing their offerings, prices, and customer reviews. This helps in identifying the best value without compromising quality.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: If feasible, sourcing from local manufacturers can reduce logistics costs and lead times, potentially resulting in a more favorable total cost structure.
By carefully analyzing these cost components, price influencers, and employing strategic purchasing tips, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing metal molding machines effectively.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal molding machine With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Metal Molding Machines
When considering the procurement of a metal molding machine, it’s essential to explore viable alternatives that may meet specific manufacturing needs. Different methods can provide varying advantages in terms of performance, cost-effectiveness, and operational simplicity. This analysis compares the metal molding machine against two popular alternatives: traditional machining and metal additive manufacturing.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Molding Machine | Traditional Machining | Metal Additive Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with complex geometries | Excellent for large, simple parts | Produces intricate designs with high customization |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment, low material waste | High tooling and setup costs | Generally high per-part cost, lower for mass production |
| Ease of Implementation | Quick setup with desktop models | Requires skilled labor and extensive setup | Requires specialized knowledge and equipment |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, easy to operate | High maintenance due to wear and tear | Moderate maintenance, dependent on technology used |
| Best Use Case | Prototyping and low to mid-volume production | High-volume, low-complexity parts | Custom, low-volume, complex parts |
In-Depth Analysis of Alternatives
Traditional Machining
Traditional machining encompasses a range of processes, such as turning, milling, and drilling, to create parts from solid blocks of metal. While this method excels in producing high-volume, low-complexity parts with exceptional surface finishes, it requires significant investment in tooling and setup. The operational costs can be substantial, especially for small production runs. Moreover, traditional machining often results in higher material waste, making it less sustainable. However, its strength lies in its ability to produce durable components with tight tolerances, making it suitable for industries that prioritize performance over flexibility.
Metal Additive Manufacturing
Metal additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, offers significant advantages in customization and design complexity. This method allows for the creation of intricate geometries that are often unattainable through traditional methods. While the initial setup may be costly, particularly for high-end systems, the per-part cost can decrease with larger production runs. This technology is ideal for industries requiring custom, low-volume parts, such as aerospace and medical sectors. However, the learning curve and operational expertise required can be a barrier for some businesses, and the speed of production may not match that of traditional methods.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the appropriate solution for metal part manufacturing, B2B buyers must consider their specific requirements, including production volume, complexity of parts, and budget constraints. Metal molding machines are an excellent choice for those focused on prototyping and low to mid-volume production with minimal waste. In contrast, traditional machining may be more suitable for high-volume, simple parts, while metal additive manufacturing is ideal for custom, intricate designs. By carefully evaluating these factors, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal molding machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Metal Molding Machines?
When considering the procurement of a metal molding machine, understanding its technical properties is crucial for ensuring it meets your operational needs. Here are several critical specifications to evaluate:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the type of metal alloy used in the molding process, such as stainless steel, bronze, or copper. The choice of material significantly impacts the strength, durability, and corrosion resistance of the final product. For B2B buyers, selecting the right material grade is essential to ensure that the produced components fulfill specific performance requirements. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the allowable variation in dimensions of the molded parts. High tolerance levels are essential in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision is critical. Understanding tolerance is vital for buyers to ensure that the machine can produce components that fit seamlessly into larger assemblies, reducing the risk of defects and rework. -
Injection Capacity
This specification indicates the maximum amount of metal paste that can be injected per cycle, often measured in grams. A higher injection capacity allows for the production of larger or more complex parts in fewer cycles, enhancing efficiency. B2B buyers should consider their production volume and part complexity when evaluating injection capacity. -
Shrinkage Rate
Shrinkage refers to the percentage reduction in size of the molded part after the sintering process. For example, a shrinkage rate of 12% means that the final product will be 12% smaller than its original mold size. Understanding shrinkage rates is crucial for ensuring that final dimensions meet design specifications. -
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time required to complete one production cycle, from injection to cooling. Shorter cycle times can lead to increased throughput and productivity, making it a key consideration for companies looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. -
Operating Voltage
The operating voltage of the machine indicates the electrical requirements for operation, which can vary based on regional standards (e.g., 110V or 220V). B2B buyers must ensure that the machine’s voltage is compatible with their facility’s electrical infrastructure to avoid additional costs for converters or modifications.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Understand in Metal Molding?
Navigating the procurement process for metal molding machines involves familiarizing oneself with specific industry jargon. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reputable suppliers and ensure product quality. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for smaller companies or startups that may not require large volumes. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and other details for specific products or services. This process helps businesses compare offerings from different suppliers, enabling informed decision-making. -
Incoterms
Incoterms are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers manage logistics and understand their liabilities, ensuring smooth transactions across borders. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for inventory planning and production scheduling, allowing businesses to maintain efficient operations. -
Sintering
Sintering is the process of heating the molded part to a temperature below its melting point to bond the metal particles. A solid grasp of sintering is crucial for buyers to understand how it affects the final properties of the molded parts.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in metal molding machines, ultimately enhancing their production capabilities and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal molding machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Metal Molding Machine Sector?
The global metal molding machine market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in manufacturing technologies and rising demand for lightweight, complex parts across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. Key trends include the increasing adoption of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, which enhance productivity and precision in metal molding processes. Additionally, the emergence of desktop metal injection molding machines, like the INJEKTO M, is democratizing access to metal part manufacturing, allowing smaller businesses and individual entrepreneurs to engage in metal production.
International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking suppliers that can offer flexible, cost-effective solutions tailored to their specific needs. The growing emphasis on rapid prototyping and short production runs is also pushing companies to explore innovative sourcing strategies. As competition intensifies, buyers are prioritizing suppliers that can demonstrate agility and responsiveness to market changes, ensuring they can meet evolving customer demands efficiently.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Enhance Your Metal Molding Machine Procurement Strategy?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of metal molding machines. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning resource consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. As such, B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that adhere to sustainable practices and can provide eco-friendly certifications for their products.
Ethical sourcing also plays a vital role in building a responsible supply chain. Suppliers that ensure fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials can enhance their appeal to conscientious buyers. For instance, using recyclable or biodegradable materials in the production of molding machines and their components can significantly reduce the overall environmental footprint. Additionally, investments in energy-efficient technologies not only minimize operational costs but also align with global sustainability goals.
What Is the Brief Evolution of Metal Molding Technology Relevant to Today’s B2B Buyers?
The evolution of metal molding technology has been marked by significant milestones that have enhanced production capabilities. Initially, traditional machining methods dominated the sector, but the introduction of metal injection molding (MIM) revolutionized the landscape by combining the benefits of plastic injection molding and powdered metallurgy. This technology allowed for the production of complex geometries at a lower cost and with minimal waste.
In recent years, advancements in desktop metal injection molding machines have further transformed the industry, making metal part production more accessible to smaller manufacturers and entrepreneurs. This shift not only democratizes the manufacturing process but also fosters innovation as businesses can experiment with designs and materials without significant upfront investment. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about technological advancements and their implications will be crucial for B2B buyers looking to maintain a competitive edge.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal molding machine
-
How do I choose the right metal molding machine for my business needs?
Choosing the right metal molding machine involves assessing your production volume, part complexity, and material requirements. Consider factors such as the maximum injection weight, mold dimensions, and the types of metals you plan to use. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s compatibility with your existing equipment and the overall production workflow. Consult with suppliers to understand the features that best align with your operational goals, and consider future scalability to accommodate growth. -
What is the best type of metal molding machine for small-scale production?
For small-scale production, desktop metal injection molding machines like the INJEKTO M are ideal. They are compact, user-friendly, and designed for low-volume production while maintaining high precision. These machines allow for flexibility in design iterations without significant material waste, thanks to the reusability of materials like MASTE. Additionally, they often come fully assembled, making them accessible for businesses with limited technical expertise. -
What are the key considerations when sourcing metal molding machines internationally?
When sourcing metal molding machines internationally, prioritize supplier reliability, quality certifications, and after-sales support. Evaluate the supplier’s experience in your specific industry and their track record with international customers. Additionally, consider logistics, including shipping costs, import duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that the machine complies with local regulations and standards in your country to avoid compliance issues. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for metal molding machines?
Minimum order quantities for metal molding machines can vary significantly by supplier and machine type. For standard machines, MOQs may range from one to several units, while custom or specialized machines may have higher MOQs. Discuss your requirements with potential suppliers to negotiate terms that accommodate your budget and production needs. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time buyers or smaller businesses. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a metal molding machine?
Payment terms for metal molding machines often depend on the supplier and the transaction size. Common arrangements include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%) with the balance due before shipment or on delivery. Some suppliers may offer financing options or payment plans for larger orders. Always clarify the terms in the contract and ensure that they align with your cash flow capabilities to avoid any financial strain. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing from an international supplier?
To ensure quality assurance when purchasing from an international supplier, request detailed specifications and certifications for the metal molding machine. Conduct a factory audit if possible, or ask for third-party inspection services. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, warranty terms, and return policies. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication regarding quality concerns. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing metal molding machines?
When importing metal molding machines, consider shipping methods, transit times, and potential delays at customs. Evaluate the total landed cost, including shipping fees, import duties, and taxes. It’s crucial to work with a logistics partner experienced in heavy machinery to navigate complexities. Ensure that proper documentation is prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance and avoid unexpected costs. -
Can I customize a metal molding machine to fit my specific production requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for metal molding machines to meet specific production needs. Customizations can include modifications to mold sizes, injection capacities, and additional features such as automated systems or enhanced cooling capabilities. Discuss your requirements with the supplier during the initial inquiry to understand the feasibility, costs, and lead times associated with the customization process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 6 Metal Molding Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Alpha Precision PM – Metal Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: alphaprecisionpm.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is a technology that combines plastic injection molding and powdered metallurgy to produce complex parts. Key details include: 1. Cost-Effectiveness: MIM can create parts for half the cost of traditional methods. 2. High-Strength End-Products: MIM produces parts with complex geometries and superior corrosion resistance. 3. Material Versatility: MIM works with a wide r…
2. Schunk – Metal Injection Molding Solutions
Domain: schunk-group.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Metal Injection Molding (MIM) combines plastic injection molding versatility with metal’s mechanical properties, enabling the production of complex, precise components in large quantities with minimal waste. Schunk specializes in MIM for various industries, offering solutions for power electronics, medical technology, consumer products, aerospace, automotive, and defense. Key features include:
– C…
3. Bole Machinery – EVOlution Hy
Domain: bolemachinery.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Manufacturer: Bole Machinery
Business Type: Manufacturer, Trade Company
Main Markets: Africa, Americas, Asia, Caribbean, East Europe, Europe, Middle East, North Europe, Oceania, Other Markets, West Europe, Worldwide
Exporter: 51%-60%
Certifications: CE, ISO9001, TUV, UL
Key Products:
1. EVOlution Hybrid Power Injection Moulding Machine
2. Magnesium Alloy Semi-solid Injection Moulding Equipment
3. …
4. Japan Steel Works – Injection Molding Machines
Domain: jswamerica.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Molding Machine from Japan Steel Works America, Inc. offers large tonnage machines available for shipment within 4 weeks and small/medium machines for immediate delivery. They provide a full line of all-electric injection molding machines ranging from 30-3000 metric tonnes. Features include ease of operation, safety, energy-saving, and space-saving improvements. Manufacturing and assembly for the …
5. OptiMIM – Precision Metal Injection Molding
Domain: optimim.com
Registered: 2002 (23 years)
Introduction: OptiMIM specializes in Precision Metal Injection Molding (MIM) technology, producing high-precision metal components with complex shapes and fine details. Their offerings include custom alloys tailored to project specifications, ensuring superior performance. Key materials include Low Alloy Steels known for exceptional hardness and strength, Special & Custom Materials with specific mechanical and …
6. Palmer Mfg – Universal Molding Machines
Domain: palmermfg.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Palmer Mfg – Universal Molding Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal molding machine
Why is Strategic Sourcing Crucial for Metal Molding Machines?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of metal molding technology, strategic sourcing is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to enhance their production capabilities. The advent of innovative solutions like the INJEKTO M desktop metal injection molding machine demonstrates the potential for cost-effective, high-quality manufacturing. By leveraging such technology, businesses can produce intricate metal components while minimizing waste and reducing overhead costs.
Moreover, understanding the intricacies of the metal injection molding process—from compounding to sintering—enables buyers to make informed decisions about materials and production methods that align with their operational goals. This knowledge is particularly valuable in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse market needs and manufacturing standards require tailored approaches.
What Should International Buyers Consider Next?
As you explore opportunities in metal molding, consider the long-term benefits of investing in advanced machinery and materials. Engage with suppliers who offer comprehensive support, including bulk purchasing options and international shipping, to maximize your investment. The future of metal molding is promising; now is the time to act. By embracing strategic sourcing, you position your business to thrive in a competitive global market.