Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal laser welder
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing the right metal laser welder can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. With rapid advancements in technology and varying market standards across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, companies must navigate a complex array of options. This guide aims to demystify the global market for metal laser welders, providing insights into different types, applications, and the key factors to consider when selecting a supplier.
From portable handheld models that facilitate quick setups to more robust CNC systems designed for high-volume production, the market offers diverse solutions tailored to meet various industrial needs. Additionally, we will cover essential criteria for vetting suppliers, understanding cost structures, and recognizing the advantages of laser welding over traditional methods.
By equipping buyers with actionable insights and comprehensive knowledge, this guide empowers businesses to make informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are in Nigeria seeking efficient welding solutions for local manufacturing or in Germany looking for advanced technology to enhance production efficiency, this resource will serve as a vital tool in your quest for the ideal metal laser welder.
Understanding metal laser welder Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld Laser Welder | Portable, user-friendly, requires minimal training | Small-scale repairs, automotive, jewelry | Pros: Easy to learn, low heat distortion. Cons: Limited for high-volume production. |
| CNC Laser Welder | Computer-controlled, high precision, suitable for complex shapes | Industrial manufacturing, aerospace | Pros: Highly accurate, ideal for intricate designs. Cons: Higher initial investment, requires skilled operators. |
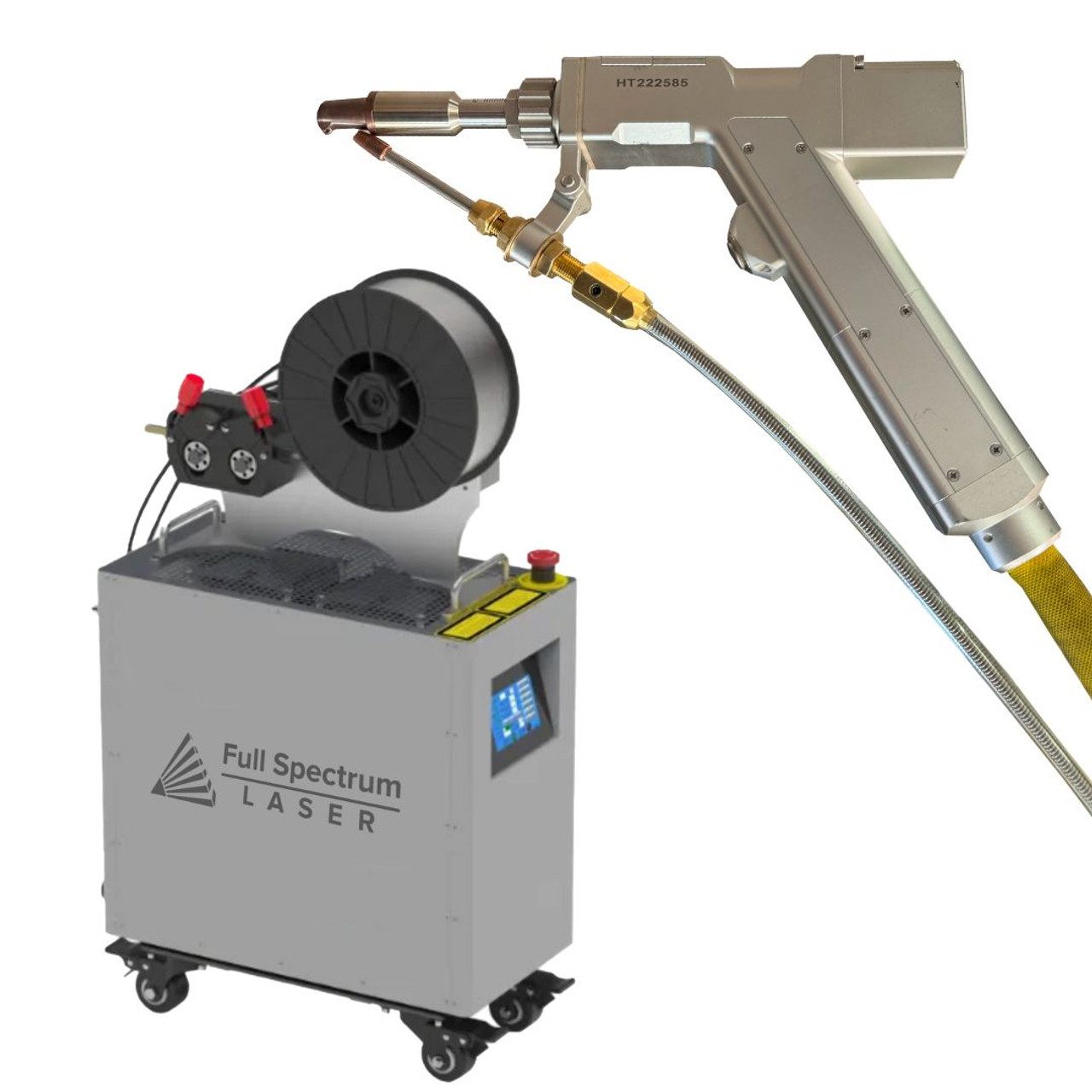
| Fiber Laser Welder | High power, efficient for thick materials, versatile | Heavy-duty applications, metal fabrication | Pros: Minimal material deformation, fast welding speed. Cons: Can be expensive to maintain. |
| MOPA Laser Welder | Adjustable pulse duration, suitable for various metals | Aerospace, automotive, high-end applications | Pros: Versatile for different materials, high-quality welds. Cons: Complexity may require specialized training. |
| Laser Cleaning Systems | Non-abrasive cleaning, eco-friendly, integrates with welding | Surface preparation, maintenance | Pros: Reduces need for chemicals, improves productivity. Cons: Limited to cleaning applications, may require additional equipment. |
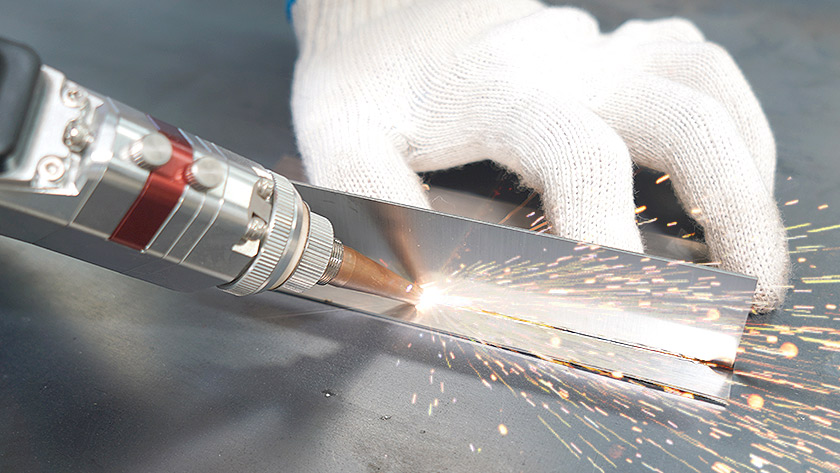
What are the Characteristics of Handheld Laser Welders?
Handheld laser welders are designed for portability and ease of use, making them ideal for small-scale applications, such as automotive repairs and jewelry making. They require minimal training, allowing operators to achieve professional results quickly. Their low heat generation minimizes material distortion, but they may not be suitable for high-volume production environments where consistency and speed are critical.
How Do CNC Laser Welders Enhance Precision in Manufacturing?
CNC laser welders utilize computer numerical control to achieve high precision and repeatability in welding processes. These machines are particularly suited for complex shapes and high-volume production in industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing. While they offer superior accuracy, the initial investment can be significant, and they require skilled operators to manage the advanced technology effectively.
Why Are Fiber Laser Welders Preferred for Heavy-Duty Applications?
Fiber laser welders are known for their high power and efficiency, especially when working with thicker materials. They are versatile and capable of welding a wide range of metals, making them a popular choice in metal fabrication and heavy-duty applications. The benefits include minimal material deformation and fast welding speeds, but buyers should consider the potential maintenance costs associated with these advanced machines.
What Makes MOPA Laser Welders Versatile?
MOPA (Master Oscillator Power Amplifier) laser welders are distinguished by their ability to adjust pulse durations, making them suitable for various metals and applications. They excel in high-end industries, such as aerospace and automotive, where quality and precision are paramount. However, the complexity of MOPA systems may necessitate specialized training for operators, which could be a consideration for B2B buyers.
How Do Laser Cleaning Systems Improve Surface Preparation?
Laser cleaning systems offer a non-abrasive, eco-friendly method for removing contaminants from metal surfaces, enhancing surface preparation before welding or coating. They integrate seamlessly with welding operations, improving overall productivity. While they provide significant advantages in reducing chemical usage, their applications are primarily limited to cleaning, which may require additional equipment for comprehensive metalworking solutions.
Key Industrial Applications of metal laser welder
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal laser welder | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Joining lightweight materials in vehicle frames | Enhances structural integrity while reducing weight | Ensure compatibility with various metals and thicknesses; consider portability for on-site repairs. |
| Aerospace | Precision welding of aircraft components | Increases safety and reduces maintenance costs | Look for machines with high accuracy and low heat input to prevent warping. |
| Electronics | Manufacturing of circuit boards and enclosures | Facilitates intricate designs with minimal thermal impact | Choose equipment that supports diverse materials and has easy programmability for complex tasks. |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | Ensures hygiene and precision, critical for patient safety | Verify compliance with international medical standards and certifications. |
| Construction & Fabrication | Repairing structural steel and frameworks | Reduces downtime and labor costs during repairs | Assess machine durability and ease of use in harsh environments; consider after-sales support. |
How is Metal Laser Welding Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, metal laser welders are employed for joining lightweight materials such as aluminum and high-strength steel in vehicle frames. This method not only enhances structural integrity but also contributes to overall weight reduction, leading to improved fuel efficiency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing laser welders that can handle varying metal thicknesses is crucial. Additionally, the ability to perform on-site repairs with portable units can significantly reduce operational downtime.
What Role Does Metal Laser Welding Play in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace manufacturing, precision is paramount, and metal laser welders excel in creating strong, lightweight joints in aircraft components. The low heat input minimizes the risk of warping, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of intricate parts. Buyers from Europe, such as Germany, should prioritize sourcing machines that comply with stringent aerospace standards, ensuring reliability and safety in high-stakes environments. The ability to produce high-quality welds consistently can lead to reduced maintenance costs and increased aircraft longevity.
Why is Metal Laser Welding Important for Electronics Manufacturing?
The electronics industry relies on metal laser welding for the fabrication of circuit boards and enclosures, where precision is essential. This technique allows for intricate designs with minimal thermal impact, preserving the integrity of sensitive components. B2B buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider machines that offer programmability for complex welding tasks, as well as compatibility with a variety of metals used in electronics. The efficiency and accuracy of laser welding can significantly enhance production speed and product reliability.
How is Metal Laser Welding Applied in Medical Device Manufacturing?
Metal laser welding plays a critical role in the fabrication of surgical instruments and other medical devices, where hygiene and precision are non-negotiable. The process ensures strong joints while minimizing the risk of contamination, which is vital for patient safety. Buyers in Africa and South America must ensure that the machines meet international medical device standards and certifications. Investing in high-quality laser welders can lead to improved product quality and compliance with regulatory requirements.
What Benefits Does Metal Laser Welding Offer in Construction and Fabrication?
In construction and fabrication, metal laser welders are used for repairing structural steel and frameworks, providing quick and efficient solutions that minimize downtime. This technology reduces labor costs and enhances the durability of repairs, making it an attractive option for businesses. For international buyers, especially in challenging environments, sourcing durable and user-friendly machines is essential. Additionally, considering after-sales support can ensure ongoing operational efficiency and reliability in the field.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal laser welder’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Challenges with Learning Curve for New Operators
The Problem: Many B2B buyers find that training new operators on traditional welding techniques can be time-consuming and costly. This is particularly true in regions with limited access to skilled labor. New employees may struggle with understanding the complexities of MIG or TIG welding, leading to inconsistent weld quality and increased production downtime. As a result, companies face the dual burden of wasted resources and potential project delays, which can impact their bottom line.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, B2B buyers should consider investing in a metal laser welder designed for ease of use. Portable laser welders, for instance, can be learned in as little as 5-30 minutes, making them accessible for operators with minimal training. When sourcing these machines, buyers should look for features such as user-friendly controls, intuitive interfaces, and robust training resources provided by manufacturers. Additionally, opting for machines with built-in safety features reduces the risk of accidents, allowing new operators to gain confidence quickly while maintaining a safe working environment. Implementing comprehensive training sessions alongside hands-on practice with the laser welder can ensure that operators are well-prepared, enhancing productivity and reducing the learning curve.
Scenario 2: Concerns About Material Deformation and Quality
The Problem: Another common pain point for B2B buyers is the risk of material deformation and compromised weld quality during the welding process. Traditional welding methods often generate excessive heat, which can warp thin metals or affect the structural integrity of components. Buyers in industries such as automotive or aerospace, where precision is critical, are especially concerned about these issues, as they can lead to costly rework and increased material waste.
The Solution: The solution lies in selecting a metal laser welder that minimizes heat-affected zones (HAZ) while delivering high-quality welds. Buyers should prioritize models that feature advanced technology, such as pulsed laser modes or adjustable power settings, which allow for precise control over the welding parameters. Additionally, investing in welders that provide real-time monitoring and adjustments can help maintain optimal conditions during the welding process. It is also advisable to engage with manufacturers that offer detailed technical support and training on best practices for specific materials. By focusing on these factors, companies can significantly reduce the risk of deformation and ensure that the final product meets stringent quality standards.
Scenario 3: Safety and Compliance Issues in the Workplace
The Problem: Safety and compliance are paramount concerns for B2B buyers, particularly in regions with strict regulatory standards. Many traditional welding processes involve hazardous fumes, intense light, and high temperatures, necessitating heavy protective gear and extensive safety measures. This not only complicates the workflow but also increases operational costs and can lead to employee dissatisfaction due to uncomfortable working conditions.
The Solution: To address these safety concerns, buyers should consider adopting metal laser welders that prioritize operator safety and compliance. Modern laser welders generate minimal fumes and have lower heat output, which significantly reduces the need for extensive protective gear. When sourcing these machines, buyers should look for features such as built-in safety alerts for low voltage, temperature extremes, and emergency shut-off mechanisms. Furthermore, conducting a thorough risk assessment before implementing new welding technologies can help ensure that all safety protocols are in place. Providing ongoing training and safety workshops for employees will also promote a culture of safety, enhancing overall workplace morale and compliance with local regulations. By adopting these practices, companies can streamline their operations while maintaining a safe and efficient working environment.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal laser welder
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Metal Laser Welding?
When selecting materials for metal laser welding, understanding their properties is crucial for optimizing performance and ensuring the durability of the final product. Here are three common materials used in metal laser welding, analyzed from a B2B perspective.
How Does Steel Perform in Laser Welding Applications?
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in metal laser welding due to its excellent mechanical properties. It exhibits high strength and toughness, making it suitable for a variety of applications, including automotive and construction. Steel’s temperature rating is significant, typically withstanding high temperatures without losing structural integrity. However, its susceptibility to corrosion can be a drawback unless treated or alloyed appropriately.
Pros: Steel is durable and cost-effective, making it a preferred choice for many industries. Its weldability is excellent, allowing for strong joints that can withstand significant loads.
Cons: The need for corrosion protection can add to the manufacturing complexity and cost. Additionally, the heat-affected zone (HAZ) can lead to distortion if not managed properly.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with various media makes it suitable for structural applications, but its weight can be a disadvantage in lightweight designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100, particularly in regions like Germany where strict regulations apply.
What Are the Advantages of Using Aluminum in Laser Welding?
Aluminum is favored in industries where lightweight materials are essential, such as aerospace and automotive sectors. It has a lower density compared to steel, which contributes to reduced overall weight in applications. Aluminum also offers excellent corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized or coated, and has good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Pros: The lightweight nature of aluminum allows for fuel efficiency in transportation applications. Its corrosion resistance reduces maintenance costs over time.
Cons: Aluminum can be more expensive than steel, and its higher thermal conductivity can lead to challenges in achieving proper weld penetration. The material also requires specific filler materials for effective welding.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various environments makes it ideal for marine applications, but its cost can be a limiting factor for some projects.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B209 or EN 573 is vital, especially in regions like Europe where quality assurance is critical.
How Does Stainless Steel Compare in Metal Laser Welding?
Stainless steel is renowned for its corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal, making it a popular choice in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and architectural applications. It maintains its strength at high temperatures and has a high melting point, which is advantageous in laser welding.
Pros: The durability and low maintenance requirements of stainless steel make it a long-term investment. Its ability to resist oxidation and corrosion is particularly beneficial in harsh environments.
Cons: The cost of stainless steel is generally higher than that of carbon steel, and it can be more challenging to weld due to its thermal properties. The presence of alloying elements can complicate the welding process.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for applications requiring hygiene and corrosion resistance, but its weight can be a drawback in lightweight constructions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Adherence to standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is crucial, especially in regions with stringent quality regulations like Germany.
What Is the Role of Copper in Laser Welding?
Copper is less common but highly effective in specific applications, especially in electrical and thermal conductivity. It has a high melting point and excellent ductility, which allows for intricate designs in electronic components and heat exchangers.
Pros: Copper’s excellent conductivity makes it ideal for electrical applications. Its ductility allows for complex shapes and designs, enhancing versatility.
Cons: Copper can be expensive and is more challenging to weld due to its high thermal conductivity, which can lead to rapid heat dissipation.
Impact on Application: Copper’s properties make it suitable for electrical and thermal applications, but its cost and welding complexity can limit its use in broader applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B152 is essential for ensuring quality, particularly in regions with robust electrical standards.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Metal Laser Welding
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal laser welder | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components in construction | High strength and cost-effective | Corrosion susceptibility | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight and corrosion resistant | Higher cost and welding challenges | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and pharmaceuticals | Corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and welding complexity | High |
| Copper | Electrical components and heat exchangers | Excellent conductivity and ductility | High cost and welding difficulty | High |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the materials available for metal laser welding, enabling informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal laser welder
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Metal Laser Welders?
The manufacturing process of metal laser welders involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets high standards of quality and performance. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Laser Welders?
Material preparation is the first step, where raw materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and other alloys are sourced from trusted suppliers. The quality of these materials is paramount, as they directly affect the performance of the laser welder. Suppliers often provide certification documents to verify the composition and quality of the materials, which B2B buyers should review.
During this phase, the materials undergo cutting and machining processes to achieve the desired dimensions. Precision is crucial here, as any discrepancies can lead to misalignments during assembly, affecting the overall welding accuracy.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
In the forming stage, various techniques such as laser cutting and CNC machining are employed to shape components. Laser cutting is particularly favored for its precision and ability to handle complex geometries, which are essential for the intricate parts of a laser welder.
After cutting, components may undergo bending or stamping processes to achieve specific shapes. Advanced forming techniques ensure that parts fit together seamlessly, which is vital for maintaining the integrity and functionality of the machine.
How Is the Assembly Process Conducted?
The assembly process involves the careful integration of all components, including the laser source, optics, cooling systems, and control electronics. Each assembly line is equipped with skilled technicians who follow standardized protocols to ensure that every machine is built consistently.
During assembly, real-time monitoring systems are often in place to track the process, ensuring that any deviations from specifications are immediately addressed. This level of oversight is crucial for maintaining high standards and minimizing defects.
What Finishing Techniques Are Applied?
Finishing techniques such as surface treatment, painting, and plating are employed to enhance the durability and aesthetics of the laser welders. Surface treatments may include anodizing for aluminum parts or powder coating for steel components, which not only improve corrosion resistance but also provide a polished look.
Additionally, the laser welder’s optical components are carefully cleaned and aligned during the finishing stage to ensure optimal performance. The final inspection is conducted to confirm that all parts meet the specified standards before the product is packaged for shipment.
What International Standards and Industry-Specific Certifications Apply to Metal Laser Welders?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of manufacturing metal laser welders, with various international standards guiding the process. ISO 9001 is one of the most recognized quality management standards, ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes and products.
In addition to ISO standards, specific industry certifications such as CE (Conformité Européenne) for the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) for industries like oil and gas are essential. These certifications not only demonstrate compliance with safety and performance standards but also enhance the credibility of the manufacturer in the global market.
How Are Quality Control Checkpoints Implemented?
Quality control (QC) is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, typically segmented into three main checkpoints: Incoming Quality Control (IQC), In-Process Quality Control (IPQC), and Final Quality Control (FQC).
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications. Any substandard materials are rejected and returned to the supplier.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, components are regularly inspected at various stages to identify defects early. This proactive approach minimizes rework and ensures that any issues are rectified before moving to the next stage.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, a comprehensive inspection is conducted on the finished product. This includes functional testing, safety checks, and performance evaluations to confirm that the welder operates as intended.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Metal Laser Welders?
Testing methods for metal laser welders vary but often include:
- Functional Testing: Ensures that all components work together seamlessly.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates the welding quality, such as bead appearance and penetration depth.
- Safety Testing: Checks for electrical safety and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the machine’s ability to withstand continuous use under specified conditions.
These tests are crucial for confirming that the laser welder meets both manufacturer and international standards.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Practices?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier QC practices is vital to ensure they receive high-quality products. Here are several strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should look for adherence to international standards and certifications.
-
Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting detailed QC reports can help buyers understand how suppliers monitor and control quality throughout the manufacturing process.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections can be conducted at various stages, including pre-shipment inspections.
-
Certification Verification: Buyers should verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications and that these are up to date. This includes checking for ISO certifications, CE markings, and other industry-specific credentials.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing metal laser welders. Regional differences in standards, regulations, and expectations can significantly impact procurement decisions.
For instance, buyers from Europe may have stricter compliance requirements compared to those in Africa or South America. Understanding these regional differences is crucial for successful sourcing. Additionally, buyers should be aware of the potential for language barriers and cultural differences that may affect communication regarding quality standards.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for metal laser welders is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality equipment that meets their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal laser welder’
When sourcing a metal laser welder, it’s essential to approach the process methodically to ensure you choose a machine that meets your operational needs and provides a good return on investment. This checklist serves as a practical guide for B2B buyers looking to procure a metal laser welder, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your sourcing process. Consider the types of metals you will be welding (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel, titanium) and the thickness range of those materials. Additionally, determine the required power output (e.g., 1500W) and the features you need, such as the ability to perform bead welds or spot welding.
Step 2: Assess Supplier Reputation and Experience
Research potential suppliers to gauge their industry reputation. Look for companies with a proven track record in laser welding technology, as well as positive customer testimonials. Check for their experience in your specific market region, as this can affect support and service levels.
- Tip: Seek out suppliers who are well-established and have a history of serving businesses similar to yours.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, thoroughly vet your shortlisted suppliers. Request detailed company profiles, including case studies and references from buyers in your industry. This helps ensure the supplier’s reliability and capability to meet your needs.
- Tip: Don’t just rely on online reviews; reach out directly to past customers if possible.
Step 4: Verify Certifications and Compliance
Ensure that the laser welders you are considering meet relevant international safety and quality standards. Look for certifications such as CE, SGS, or ISO, which indicate that the equipment adheres to stringent manufacturing practices and safety protocols.
- Why it matters: Compliance with these standards not only ensures safety but also enhances the durability and performance of the equipment.
Step 5: Analyze Pricing and Total Cost of Ownership
Request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers, but don’t just look at the initial purchase price. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes maintenance, consumables, and energy consumption.
- Tip: Ask about warranties and service agreements to understand ongoing costs better.
Step 6: Test the Equipment
If possible, arrange for a demonstration of the laser welder before making a purchase. Testing the machine allows you to evaluate its performance, ease of use, and suitability for your specific applications.
- Why it’s critical: A hands-on experience can reveal operational nuances that specifications alone might not convey.
Step 7: Review After-Sales Support and Training
Evaluate the supplier’s after-sales support and training offerings. Quality suppliers provide comprehensive training programs for operators, as well as ongoing technical support.
- Key aspect: A strong support system can greatly enhance the efficiency of your operations and mitigate downtime.
By following these steps, B2B buyers can effectively navigate the procurement process for metal laser welders, ensuring they select a solution that aligns with their operational needs and delivers value over time.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal laser welder Sourcing
What are the Key Cost Components in Metal Laser Welder Manufacturing?
When evaluating the cost structure for metal laser welders, several critical components must be considered. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. High-quality components such as fiber lasers and precision optics are essential for optimal performance and durability. Additionally, specific materials like aluminum and titanium may require specialized handling, adding to costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is crucial in both the manufacturing and assembly processes of laser welders. Technicians with expertise in laser technology are often necessary, and their wages can vary significantly based on geographical location and market demand.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overhead costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling and machinery can be substantial, particularly for manufacturers focusing on high precision and customization. Advanced CNC machines and laser cutting tools often require significant capital investment.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that each unit meets industry standards requires stringent quality control measures. This can involve testing, inspections, and certifications, contributing to the overall cost structure.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Factors such as distance, freight methods, and customs duties will influence the final price.
-
Margin: Suppliers generally apply a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure business sustainability. This margin can vary based on competition, brand positioning, and market demand.
What Factors Influence the Pricing of Metal Laser Welders?
Several factors can significantly influence the pricing of metal laser welders in the international market:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often yield lower per-unit prices. Buyers should negotiate for favorable terms based on their expected volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized solutions or advanced features will typically increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials Used: The choice of materials can affect both the performance and the price. High-performance materials may come at a premium but can offer long-term savings through durability.
-
Quality and Certifications: Certifications such as CE or ISO can add to the cost but often ensure higher quality and compliance with international standards, which is crucial for buyers in regulated markets.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record and better support services.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international buyers. These terms define responsibilities regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risks, which can significantly impact the total cost.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Sourcing Metal Laser Welders?
To maximize value when sourcing metal laser welders, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Wisely: Leverage volume discounts and explore flexible payment terms. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can often lead to better pricing and support.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Investing in a reliable, high-quality machine may lead to lower long-term costs.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Purchases: Currency fluctuations and international shipping costs can significantly affect pricing. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should account for these variables in their budgets.
-
Conduct Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can provide leverage during negotiations and help identify the best value options.
-
Request Demonstrations: Before making a purchase, ask for demonstrations or trial periods. This allows buyers to evaluate the machine’s performance and suitability for their specific needs.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for metal laser welders can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. The indicative prices mentioned in the references serve as a guideline and may not reflect current market rates. Buyers should conduct thorough research and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal laser welder With Other Solutions
Exploring Alternatives to Metal Laser Welding Solutions
In the landscape of metal joining technologies, various alternatives to metal laser welding exist, each catering to different operational needs and industry demands. While metal laser welders offer precision and efficiency, understanding other methods can help buyers make informed decisions based on their specific applications and requirements.
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Laser Welder | MIG Welding | TIG Welding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; minimal deformation | Good for thicker materials; versatile | Exceptional for thin materials; precise |
| Cost | Moderate to high initial investment | Lower initial cost; consumables needed | Higher upfront cost; slower process |
| Ease of Implementation | Easy to learn; quick setup | Requires skilled labor; moderate setup | Requires skilled labor; longer setup |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; periodic lens cleaning | Moderate; regular maintenance needed | High; needs frequent maintenance |
| Best Use Case | Automotive, electronics, fine fabrication | General fabrication, heavy machinery | Aerospace, artistic applications |
Understanding the Alternatives to Metal Laser Welding
MIG Welding: A Versatile Alternative
Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding is one of the most commonly used welding processes, particularly in industries that require high production speeds and the ability to weld thicker materials. Its initial setup costs are generally lower than those of laser welding systems, making it a cost-effective choice for many businesses. However, MIG welding requires skilled operators to achieve high-quality welds. While it is versatile, it does produce more heat, leading to potential warping of materials, which can be a significant downside for delicate or thin materials.
TIG Welding: Precision for Specialized Applications
Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is renowned for its precision and is often the method of choice for welding thin materials or applications where aesthetics are paramount, such as in artistic metalworking or aerospace manufacturing. While TIG welding delivers superior weld quality, it typically involves a higher initial investment in equipment and a longer learning curve for operators. This method also requires extensive maintenance and skilled labor, which can increase operational costs. However, its ability to produce clean and precise welds makes it ideal for specialized applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Metal Joining Needs
When selecting the appropriate welding solution, B2B buyers should consider several factors, including the materials to be welded, the desired strength and aesthetic quality of the weld, and the available budget for equipment and labor. Metal laser welders excel in high-precision applications with minimal thermal distortion, making them ideal for industries like electronics and automotive. In contrast, MIG welding is suitable for general fabrication and heavy machinery, while TIG welding is best for specialized, high-quality applications. By carefully evaluating these aspects, buyers can choose a welding solution that aligns with their operational goals and enhances productivity.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal laser welder
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Metal Laser Welders?
When evaluating metal laser welders, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
1. Laser Power Output
Laser power, measured in watts (W), directly influences the welding speed and penetration depth. For instance, a 1500W laser welder can handle both thick and thin metals efficiently, providing quick and precise welds. In a B2B context, selecting the appropriate power output is vital to meet production demands without compromising quality.
2. Welding Speed
Welding speed refers to how fast the laser can travel while welding, typically measured in millimeters per minute (mm/min). High-speed welding reduces production time, which is essential for manufacturers aiming to increase throughput. Fast welding speeds are particularly advantageous in high-volume environments, allowing for better allocation of resources and reduced labor costs.
3. Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
The HAZ is the area surrounding the weld that experiences changes in microstructure due to heat exposure. A smaller HAZ, which is achievable with laser welding, minimizes thermal distortion and preserves the integrity of the base material. For B2B buyers, this means improved product quality and reduced need for post-weld processing.
4. Material Compatibility
Metal laser welders can work with various materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and titanium. Understanding the machine’s compatibility with specific materials is essential for businesses engaged in diverse industries. This versatility allows for broader applications and helps companies adapt to changing market demands without investing in multiple machines.
5. Portability and Ease of Use
Many modern laser welders are designed to be portable and user-friendly, featuring intuitive controls and lightweight designs. This is particularly beneficial for companies that require onsite welding solutions. A welder that can be operated with minimal training can significantly reduce the time and costs associated with workforce development.
6. Safety Features
Safety is paramount in any welding operation. Advanced laser welders come equipped with features such as emergency stop buttons, low-voltage alerts, and built-in safety glasses. Ensuring that the equipment complies with safety standards is essential for B2B buyers to protect their workforce and minimize liability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Used in Metal Laser Welding?
Understanding industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiations in the B2B environment. Here are some common terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of laser welders, buyers may seek OEMs for specific components or machines that meet their unique specifications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their production needs.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services. It is an essential step in the procurement process, allowing businesses to compare costs and make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. Familiarity with these terms is essential for B2B transactions, as they dictate who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
5. Welding Filler Material
This refers to the material used to fill the gap between two pieces being welded. Understanding the type of filler material compatible with the laser welder is important for achieving strong, durable welds.
6. PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)
PPE includes safety gear required to protect workers from hazards associated with welding. Familiarity with the necessary PPE helps businesses ensure compliance with safety regulations and promote a safe working environment.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding metal laser welders, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal laser welder Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the Metal Laser Welder Sector?
The global market for metal laser welders is witnessing a transformative shift, driven by advancements in technology, increasing demand for precision in manufacturing, and the need for cost-effective solutions. Key trends include the growing adoption of handheld laser welding systems, which offer portability and ease of use compared to traditional welding methods. This trend is particularly appealing to B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where labor costs and skill levels may vary. Additionally, the versatility of laser welders to handle various materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium is enhancing their appeal across different industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Emerging technologies, such as automated welding processes and smart welding guns with real-time monitoring capabilities, are reshaping the market landscape. These innovations not only improve the quality of welds but also reduce the time and labor involved in the welding process. For international buyers, especially in Europe, the emphasis on efficiency and reduced waste aligns with broader industrial goals for sustainability and productivity. Furthermore, the competitive pricing of laser welders is making them more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), expanding the market reach.
How Does Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Metal Laser Welder Sector?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in the metal laser welder sector, as manufacturers and buyers alike recognize the environmental impact of their operations. Laser welding processes typically generate less heat and waste compared to traditional welding methods, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions. This efficiency is crucial for companies looking to enhance their green credentials and comply with stringent environmental regulations in markets like Germany and the broader European Union.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, with businesses prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices. This includes using eco-friendly materials and ensuring responsible supply chain management. Certifications such as ISO 14001 and adherence to local environmental laws are becoming essential criteria for B2B buyers when sourcing laser welders. By choosing suppliers with a strong sustainability profile, companies can not only improve their environmental impact but also enhance their brand reputation among eco-conscious consumers and stakeholders.
What Is the Evolution of Metal Laser Welding Technology?
The evolution of metal laser welding technology dates back to the 1960s when the first laser was developed. Initially, laser welding was limited to specialized applications due to high costs and technological constraints. However, as laser technology advanced and became more affordable, its adoption spread across various manufacturing sectors.
In recent years, the introduction of portable and handheld laser welders has democratized access to this technology, allowing even small businesses to leverage its benefits. The development of fiber lasers has further enhanced the precision and versatility of welding applications, enabling operations on thin materials with minimal deformation. This historical progression illustrates how laser welding has transitioned from a niche application to a mainstream solution, reflecting the growing demand for high-quality, efficient, and sustainable manufacturing processes in the global market.
In summary, the metal laser welder sector is poised for continued growth, driven by technological advancements and a heightened focus on sustainability. International B2B buyers can capitalize on these trends by sourcing innovative, eco-friendly welding solutions that meet their operational needs while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal laser welder
-
How do I choose the right metal laser welder for my business needs?
Selecting the right metal laser welder involves evaluating several factors, including the types of materials you work with, the thickness of those materials, and the desired welding speed. Consider the power output (measured in watts) that suits your application; for instance, 1500W is ideal for both thin and thick metals. Additionally, look for features like portability, ease of use, and maintenance requirements. It may also be beneficial to request demonstrations or trial periods from suppliers to assess the machine’s performance in real-world conditions. -
What are the advantages of using a metal laser welder over traditional welding methods?
Metal laser welders offer numerous advantages compared to traditional methods, including reduced heat-affected zones, which minimizes material distortion. They enable high-speed welding, allowing operators to complete tasks more quickly and efficiently. The learning curve is significantly shorter; users can often achieve professional results within 30 minutes of training. Moreover, laser welders produce cleaner welds with less flash, reducing the need for extensive post-weld cleanup. -
What customization options are available for metal laser welders?
Most manufacturers offer customization options such as adjustable power settings, various nozzle sizes, and specific attachments tailored for different welding tasks. You can also inquire about software capabilities that enable programmable settings for repetitive tasks. Customization may be crucial for businesses with unique requirements or specialized applications, so discussing your needs with the supplier during the procurement process is essential. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) for metal laser welders?
The minimum order quantity for metal laser welders can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the specific model. Generally, MOQs can range from a single unit for specialized machines to bulk orders for standard models. When negotiating, consider discussing your purchasing plans, as suppliers may offer flexibility on MOQs for first-time buyers or repeat customers. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing a metal laser welder?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a deposit upfront (typically 30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or installation. Some manufacturers may offer financing options or payment plans, especially for larger purchases. Always clarify payment terms before finalizing the agreement to ensure they align with your cash flow and budgeting needs. -
How can I ensure the quality and reliability of the metal laser welder I purchase?
To ensure quality and reliability, research potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for manufacturers with certifications such as CE, ISO, or SGS, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Request references or case studies from other businesses that have purchased similar equipment. Additionally, inquire about warranty terms and after-sales support, as these factors are critical in maintaining machine performance over time. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing a metal laser welder?
When importing a metal laser welder, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and lead times. Ensure that the supplier provides clear information about shipping arrangements, including Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. It’s also wise to partner with a reliable logistics provider who can handle customs clearance and ensure timely delivery, particularly for heavy machinery. -
What maintenance practices should I follow to extend the lifespan of my metal laser welder?
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of your metal laser welder. This includes routine cleaning of the laser head, optics, and internal components to prevent dust and debris build-up. Check and replace consumable parts like lenses and mirrors according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Additionally, keep the machine in a clean, dry environment and perform periodic inspections to identify any potential issues early, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Metal Laser Welder Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. FS Laser – Portable Laser Welder
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Portable Laser Welder
– MSRP: $13,000.00
– SKU: PRTWELD2
– Type: Portable water cooled welder
– Wire Feeder: None
– Truck Lift Gate Required For Delivery: Yes (+$160) / No
– Address Type: Residential/School (+$150) / Commercial
– Shipping Insurance: Yes (+$100) / No
– Current Stock: Available
Product Overview:
– Handheld laser welding is easy to learn and fast to set up.
– Provides consistent hig…
2. OmTech – Handheld Fiber Laser Welder
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Handheld Fiber Laser Welder with 3-in-1 Functionality, Price: $6,099.99 (Regular Price: $10,599.99, Save $4,500), 1500W Laser Power, capable of welding thick and thin metals, minimal material deformation, welds 2 mm aluminum plates, handles stainless, carbon steel, & zinc plates up to 4 mm thick, cleans weld joints up to 6 mm wide, includes 20 nozzles for 0.8-1.2 mm wire welding, cutting, or clean…
3. Hytek Tools – WeldTEK™ RAYCUS Fiber Laser Welder
Domain: hytektools.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: WeldTEK™ RAYCUS Fiber Laser Welder 1000-3000w
– Available Laser Sources: 1.5kw (1500w), 2kw (2000w), 3kw (3000w)
– Regular Price: $19,995.00
– Capable of welding: Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, and more
– Machine Electronics: 1000w-3000w IPG fiber laser, Schneider electrical components, Water chiller
– Required Power:
– 1kw or 1.5KW – 220V, 30a, single phase
– 2kw – 220V, 3 phase
…
4. DenaliWeld – JET EZ & JET MOPA
Domain: denaliweld.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: DenaliWeld offers a range of laser welding products including:
1. **JET EZ** – A portable laser welder weighing 48.5 lbs, featuring dual welding and seam cleaning capabilities with patented CUAL laser technology for precision on thin metals.
2. **JET MOPA** – A laser cleaning system that provides non-abrasive, eco-friendly solutions for removing rust, paint, and contaminants from metal surfaces, …
5. IPG Photonics – LightWELD Handheld Laser Welding & Cleaning Systems
Domain: ipgphotonics.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: LightWELD Handheld Laser Welding & Cleaning Systems are designed to enhance weld quality and productivity. Key features include: 4x faster than TIG welding, welding capability of up to 0.313″ for various materials, and 100 welding & cleaning presets. Made in the USA, these systems offer pre-weld and post-weld laser cleaning functionality. The product line includes three models: LightWELD 1000 (up …
6. USA Air-Cooled 1200W Laser Welder
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: USA Air-Cooled Handheld Laser Welding Machine 1200W Laser Welder for Metal – Brand New – Price: $4,844.05 (Was: $5,099.00, 5% off) – Free delivery – Located in United States – 44 watchers; 1500W Laser Welder Laser Welding Machine Laser Cutting Laser Cleaning 4-in-1 – Brand New – Price: $6,550.00 – Buy It Now – Free delivery – Located in United States – 65 watchers; Raycus 1500W 4 in 1 Fiber laser …
7. SFX – Handheld Mobile Laser Welder
Domain: sfxlyxc.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: SFX Handheld Mobile Laser Welder for Sale. Suitable for diverse metal welding applications including stainless steel, carbon steel, copper, aluminum, gold, silver, chromium, nickel, titanium. Features easy nozzle replacement and adjustable parameters post-welding for seam cleaning. Available models include: 1500W/2000W/3000W options, 2 in 1 function for welding and weld seam cleaning, prices rangi…
8. TRUMPF – Laser Welding Systems
Domain: trumpf.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Laser welding systems from TRUMPF offer versatile solutions for joining metals and other materials with precision. Key features include:
– Ability to join workpieces at the surface or produce deep weld seams.
– Compatibility with conventional welding processes and suitable for soldering.
– Capable of creating fine weld points (1 mm diameter) and deep penetration seams (meters long).
– Produces nar…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal laser welder
In navigating the evolving landscape of metal laser welding, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to harness the technology’s full potential. The advantages of laser welding—such as ease of use, reduced material deformation, and versatility across various metals—position it as a game-changer in manufacturing and fabrication processes. Investing in high-quality, reliable equipment from reputable suppliers ensures not only operational efficiency but also a significant return on investment.
Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider the long-term benefits of integrating advanced welding technologies into their operations. This includes evaluating the total cost of ownership, maintenance requirements, and the availability of technical support from manufacturers. As the demand for precision welding continues to grow, staying ahead of industry trends and technological advancements will be crucial.
As you assess your sourcing options, engage with manufacturers who demonstrate a commitment to innovation and customer service. By making informed decisions today, you can secure a competitive edge in your market and drive sustainable growth for your business in the future. Embrace the opportunities presented by metal laser welding and position your company for success.