Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal laser cutter for sale
In the fast-evolving landscape of manufacturing, international buyers face a significant challenge when sourcing high-quality metal laser cutters for sale. The need for precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness has never been greater, especially for businesses aiming to enhance their metal fabrication capabilities. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for B2B buyers, detailing various types of metal laser cutters, including fiber and CO2 lasers, and their specific applications in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace.
Throughout this guide, we will explore critical factors such as supplier vetting processes, pricing structures, and the long-term benefits of investing in advanced laser cutting technology. By understanding the intricacies of the global market, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets such as Saudi Arabia and Nigeria—buyers will be empowered to make informed purchasing decisions.
With detailed insights into the latest technologies, operational efficiencies, and market trends, this guide aims to equip businesses with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing metal laser cutters. By leveraging the information provided, international buyers can confidently select the right equipment that not only meets their production needs but also positions them for future growth in a competitive landscape.
Understanding metal laser cutter for sale Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Laser Cutter | High efficiency, low operational costs, solid-state technology | Sheet metal fabrication, automotive parts, electronics | Pros: Fast cutting speeds, low maintenance; Cons: Higher initial investment. |
| CO2 Laser Cutter | Versatile for various materials, suitable for thicker cuts | Signage, art, packaging, and textiles | Pros: Good for non-metal materials; Cons: Slower than fiber lasers for metals. |
| Crystal Laser Cutter | High precision, ideal for intricate designs | Aerospace components, medical devices | Pros: Exceptional cut quality; Cons: Higher energy consumption. |
| Gas Laser Cutter | Utilizes gases like CO2 or nitrogen for cutting | Heavy industrial applications, large sheets | Pros: Cost-effective for large operations; Cons: Less precision compared to fiber lasers. |
| Tube Laser Cutter | Specialized for cutting metal tubes and profiles | Structural components, furniture, automotive | Pros: Efficient for complex shapes; Cons: Limited to tube applications. |
What are the Characteristics and Suitability of Fiber Laser Cutters?
Fiber laser cutters are renowned for their efficiency and low operational costs. Utilizing solid-state technology, they deliver rapid cutting speeds with minimal maintenance requirements. These machines excel in applications such as sheet metal fabrication, automotive parts manufacturing, and electronics. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment against the long-term operational savings, as fiber lasers can significantly reduce production costs over time.
How Do CO2 Laser Cutters Compare in Versatility?
CO2 laser cutters are highly versatile and can handle a variety of materials, making them suitable for industries like signage, art, packaging, and textiles. They are particularly effective for cutting thicker materials. However, while they offer good performance for non-metal applications, they generally have slower cutting speeds for metals compared to fiber lasers. Buyers should assess their specific material needs and production speed requirements when considering CO2 lasers.
What Makes Crystal Laser Cutters Ideal for Precision Work?
Crystal laser cutters are designed for high precision and are particularly suited for intricate designs. Industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing benefit from the exceptional cut quality these machines provide. However, they tend to consume more energy than other types of lasers, which may affect operational costs. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of precision against energy consumption when selecting this type of cutter.
In What Scenarios are Gas Laser Cutters Most Effective?
Gas laser cutters, which use gases like CO2 or nitrogen, are often chosen for heavy industrial applications due to their cost-effectiveness in processing large sheets. They are particularly advantageous for operations with high-volume cutting needs. Despite being less precise than fiber lasers, they can be a viable option for businesses looking to minimize operational costs. Buyers should consider their production volume and precision requirements when evaluating gas laser options.
What are the Unique Features of Tube Laser Cutters?
Tube laser cutters are specialized machines designed for cutting metal tubes and profiles. They are ideal for applications in structural components, furniture, and automotive manufacturing, where complex shapes are often required. While tube lasers offer significant efficiency in these specific applications, their use is limited to tube cutting. B2B buyers should assess whether their production needs align with the capabilities of tube laser cutters.
Key Industrial Applications of metal laser cutter for sale
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal laser cutter for sale | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Cutting components for vehicles | High precision and speed reduce production time and costs | Consider power options and cutting thickness capabilities |
| Aerospace | Fabrication of lightweight structural components | Enhanced material efficiency and reduced weight | Ensure compliance with industry standards and certifications |
| Construction | Fabrication of metal frames and structural supports | Cost-effective, scalable production for large projects | Evaluate machine size and compatibility with local materials |
| Electronics | Production of enclosures and heat sinks | Improved design flexibility and rapid prototyping | Assess software compatibility for design integration |
| Jewelry and Art | Custom designs and intricate patterns | Unique offerings that attract niche markets | Look for precision and speed in cutting delicate materials |
How is a Metal Laser Cutter Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, metal laser cutters are used to create precise components such as chassis parts, brackets, and panels. These machines enable manufacturers to achieve high-speed cuts with minimal waste, significantly enhancing production efficiency. For international buyers, especially in regions like Nigeria or Saudi Arabia, sourcing a laser cutter that can handle various metal thicknesses and types is crucial to meet diverse automotive requirements while ensuring compliance with local manufacturing standards.
What Role Does a Metal Laser Cutter Play in Aerospace Fabrication?
Aerospace manufacturers utilize metal laser cutters to fabricate lightweight structural components, such as wing frames and fuselage parts. The precision offered by laser cutting reduces material wastage and ensures components meet stringent weight requirements. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should prioritize machines that comply with aerospace regulations and can handle advanced materials like titanium, which are often required in this industry.
How is Metal Laser Cutting Beneficial in Construction?
In the construction industry, metal laser cutters are essential for fabricating metal frames, beams, and supports. The ability to produce complex shapes quickly and accurately allows contractors to scale their operations efficiently. For businesses in South America and Africa, it is vital to consider the machine’s size and capabilities to ensure compatibility with locally sourced materials and to meet the demands of large-scale projects.
How Does Metal Laser Cutting Enhance Electronics Production?
Metal laser cutters are integral in the electronics sector for producing enclosures, heat sinks, and other components that require high precision. The technology allows for rapid prototyping, enabling manufacturers to innovate quickly in a competitive market. Buyers in regions like Europe should evaluate the software compatibility of laser cutting machines with their design systems to streamline the production process.
Why is Metal Laser Cutting Important for Jewelry and Art?
In the jewelry and art industries, metal laser cutters are used to create intricate designs and custom pieces. The precision of laser cutting allows artisans to produce detailed patterns that would be challenging with traditional methods. International buyers should focus on the cutter’s ability to handle delicate materials and ensure fast processing speeds to meet market demands for unique, high-quality designs.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal laser cutter for sale’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating High Operational Costs in Laser Cutting
The Problem: B2B buyers often grapple with the high operational costs associated with running metal laser cutters. This includes expenses related to energy consumption, maintenance, and material wastage. For businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where budget constraints are common, the financial burden can be overwhelming. Many buyers are concerned that the initial investment in a metal laser cutter will be offset by ongoing operational costs, especially if they are not effectively managed.
The Solution: To mitigate operational costs, buyers should focus on selecting energy-efficient models and optimizing their cutting processes. When sourcing a metal laser cutter, look for machines that utilize advanced fiber laser technology, which typically consumes less power compared to traditional CO2 lasers. Additionally, consider models that allow for programmable cutting settings, which can minimize material waste by ensuring precise cuts and reducing excess scrap. Regular maintenance schedules should also be established to prevent costly breakdowns, ensuring that the machine operates at peak efficiency. Implementing these strategies not only helps in controlling costs but also enhances overall productivity.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Equipment for Specific Needs
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face challenges in identifying a metal laser cutter that meets their specific operational requirements. This includes considerations for cutting thickness, material type, and production speed. For instance, a company in the Middle East specializing in automotive components may require a machine capable of cutting both aluminum and high-strength steel with precision. Misalignment between equipment capabilities and production needs can lead to inefficiencies and increased downtime.
The Solution: To address this issue, buyers should conduct a thorough needs assessment before making a purchase. This involves analyzing the types of materials they will work with, the thicknesses involved, and the expected production volumes. Once these factors are established, buyers can consult with manufacturers or suppliers to identify models that align with their specifications. It’s also beneficial to request demonstrations or trials to see the machines in action. Look for suppliers that offer customization options, allowing the laser cutter to be tailored to specific operational needs, ensuring optimal performance and productivity.
Scenario 3: Overcoming Skill Gaps and Technical Training Challenges
The Problem: Another common pain point is the lack of skilled operators to effectively utilize and maintain metal laser cutting machines. In many regions, including parts of Europe and Africa, there may be a shortage of trained personnel familiar with the latest laser cutting technologies. This can lead to operational inefficiencies, increased error rates, and underutilization of the equipment, ultimately affecting the return on investment.
The Solution: To overcome this challenge, companies should prioritize training and skill development for their employees. When purchasing a metal laser cutter, inquire about training programs offered by the manufacturer or supplier. Many companies provide on-site training sessions and comprehensive manuals that cover machine operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Additionally, consider establishing a mentorship program where experienced operators can train newer employees. Leveraging online resources, such as webinars and tutorials, can also supplement formal training. By investing in employee training, businesses can ensure that their staff is well-equipped to operate the machinery efficiently, leading to improved production outcomes and reduced errors.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal laser cutter for sale
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials for Metal Laser Cutting?
When selecting materials for metal laser cutting, understanding the properties and suitability of each type is essential for optimizing performance and achieving desired outcomes. Below, we analyze four common materials used in metal fabrication, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high strength and durability, making it a popular choice in various applications. It has excellent weldability and machinability, with a melting point around 1425-1540°C. Carbon steel’s corrosion resistance is moderate, often requiring protective coatings in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively low-cost compared to other metals, making it an attractive option for large-scale projects. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can lead to increased maintenance costs in humid or corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is ideal for structural components, automotive parts, and general manufacturing. Its compatibility with laser cutting allows for intricate designs and precise cuts.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A36 or EN 10025. In regions like Africa and South America, local sourcing of carbon steel may also influence costs and availability.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance and durability, with a melting point of approximately 1400-1450°C. Its chromium content provides a protective layer against oxidation, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is more expensive than carbon steel, its longevity and low maintenance requirements can justify the initial investment. However, its hardness can make cutting more challenging, requiring more powerful laser systems.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is widely used in food processing, medical equipment, and architectural applications due to its hygienic properties and aesthetic appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East may prefer specific grades like 316 for marine applications, while European buyers may focus on sustainability certifications.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight with excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Its melting point ranges from 660-680°C, making it easier to cut compared to heavier metals.
Pros & Cons: The low weight of aluminum allows for easier handling and transportation, making it suitable for applications where weight is a concern. However, it can be more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized cutting techniques to avoid warping.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods, where lightweight and strength are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of standards such as ASTM B221 for extruded aluminum shapes. In regions like Europe, recycled aluminum is often preferred due to sustainability goals.
4. Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, with a melting point of about 1085°C. Its corrosion resistance is good, but it can tarnish over time.
Pros & Cons: Copper’s conductivity makes it ideal for electrical applications, but its higher cost and weight can be limiting factors. Additionally, cutting copper may require specialized laser settings to achieve optimal results.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in electrical components, plumbing, and roofing, copper’s properties make it suitable for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B152 is important. Buyers should also consider local market demand for copper products, especially in regions with growing infrastructure needs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Metal Laser Cutting
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal laser cutter for sale | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Structural components, automotive parts | Low cost and high strength | Moderate corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cutting difficulty and cost | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive, consumer goods | Lightweight and good corrosion resistance | Higher cost and potential warping | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical components, plumbing | Excellent conductivity | Higher cost and specialized cutting needs | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their metal laser cutting applications, ensuring informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal laser cutter for sale
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Metal Laser Cutters?
The manufacturing process of metal laser cutters is complex, involving several critical stages that ensure the production of high-quality machines. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers looking for reliable equipment.
Material Preparation: How Is the Right Material Selected and Processed?
The first step in manufacturing metal laser cutters involves the careful selection of materials. Typically, manufacturers use high-grade metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel. The chosen materials undergo various treatments to enhance their properties, such as heat treatment or surface hardening.
Once the materials are selected, they are cut into manageable sizes, often using preliminary cutting methods like shearing or plasma cutting. This stage ensures that the raw materials meet the specifications required for the laser cutter components, such as frames, gantries, and cutting heads.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage of Metal Laser Cutters?
The forming stage is crucial for shaping the components of the laser cutter. Techniques such as CNC machining, bending, and welding are commonly employed. CNC machining allows for precise shaping of parts, ensuring tight tolerances that are critical for the performance of the laser cutter.
Welding is particularly important for assembling the structural components of the cutter. Manufacturers often use robotic welding for its consistency and speed. This stage culminates in the creation of a robust frame that can withstand the rigors of continuous operation.
How Are Metal Laser Cutters Assembled and Finished?
Assembly involves integrating the various components, including the laser source, optics, control systems, and mechanical parts. This stage requires skilled technicians who follow detailed assembly instructions to ensure that all parts fit together perfectly.
Finishing touches include surface treatments such as powder coating or painting, which protect the machine from corrosion and wear. Additionally, manufacturers may install user-friendly interfaces and safety features, ensuring that the machines are not only efficient but also compliant with safety regulations.
What Quality Assurance Standards Should B2B Buyers Be Aware Of?
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for metal laser cutters. International standards such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems, are commonly implemented. This certification indicates that the manufacturer adheres to stringent quality control measures throughout the production process.
In addition to ISO certifications, industry-specific standards like CE marking (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may apply, depending on the intended application of the laser cutter. These certifications ensure that the equipment meets safety and performance requirements in various markets.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints During Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is integral to the manufacturing of metal laser cutters, with several checkpoints established to ensure product reliability:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery. Suppliers are required to provide documentation proving compliance with specified standards.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random samples are tested to verify that they meet quality standards. This includes checking dimensional tolerances and material properties.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, each laser cutter undergoes a comprehensive final inspection. This includes functionality tests, safety checks, and performance evaluations to ensure that the equipment operates according to specifications.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is crucial to verify the quality control processes of suppliers. Here are several actionable steps:
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the supplier’s manufacturing practices and quality assurance systems. This is particularly important for international buyers who may not be familiar with local suppliers.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality control reports can help buyers assess the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. These reports should include information on testing methods, inspection results, and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. This can be especially helpful in ensuring compliance with international standards.
What QC and Certification Nuances Should International Buyers Consider?
International buyers face unique challenges when it comes to quality control and certification. Different regions have varying regulations and standards, which can impact the acceptance of products across borders.
For instance, products sold within the European Union must have CE certification, while those in the Middle East may require compliance with local standards. Buyers should familiarize themselves with these regulations to avoid complications during importation.
Moreover, language barriers and cultural differences can influence communication with suppliers. Establishing clear channels of communication and documentation can help mitigate misunderstandings and ensure that quality expectations are met.
Conclusion: Ensuring Quality in Your Metal Laser Cutter Purchase
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for metal laser cutters is essential for B2B buyers. By familiarizing themselves with the key stages of production, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This diligence not only safeguards investments but also enhances the reliability and efficiency of their manufacturing capabilities.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal laser cutter for sale’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a comprehensive checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure metal laser cutters. Given the significant investment and the technical nature of these machines, it is crucial to approach the purchasing process methodically. This guide will help you navigate the essential steps to ensure you make an informed and strategic decision.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Establishing clear technical specifications is the foundation of your procurement process. Consider the types of materials you will be cutting, their thickness, and the required cutting speed. For instance, if you plan to cut stainless steel, ensure your chosen laser cutter has the appropriate power (measured in watts) and cutting capacity.
- Common Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Cutting Thickness: Specify the maximum and minimum thicknesses for your applications.
Step 2: Set Your Budget
Determining your budget upfront is essential to streamline your options. Metal laser cutters can vary significantly in price based on their capabilities and features. Include not only the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs in your budget.
- Price Range: Research typical costs for the type and model you need.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in costs for consumables, energy usage, and potential downtime.
Step 3: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reliable suppliers that specialize in metal laser cutters. Look for suppliers with a strong track record and positive customer reviews. This step is vital to ensure you partner with reputable companies that can meet your needs.
- Supplier Background: Check their years of experience and industry reputation.
- Product Portfolio: Ensure they offer the specific models and features you require.
Step 4: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify that potential suppliers have the necessary certifications and quality standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate a commitment to quality management systems, which can assure you of the reliability of their products.
- Quality Assurance: Look for certifications related to safety and performance.
- Warranty and Support: Understand the warranty terms and the level of post-sale support provided.
Step 5: Request Demonstrations or Samples
Before making a purchase, request demonstrations or samples of the laser cutters in action. This step allows you to evaluate the machine’s performance and see if it meets your specific requirements.
- In-House Demonstrations: Arrange for suppliers to bring their equipment to your facility.
- Trial Periods: Consider negotiating a trial period for long-term use.
Step 6: Assess After-Sales Support and Maintenance
After-sales support is crucial for the longevity and performance of your metal laser cutter. Investigate the supplier’s policies on maintenance, parts availability, and technical support.
- Service Agreements: Inquire about the details of service contracts.
- Response Times: Evaluate how quickly they can address issues or provide parts.
Step 7: Finalize Your Purchase Agreement
Once you have selected a supplier, review and finalize the purchase agreement carefully. Ensure that all terms, including delivery timelines, installation, and training, are clearly outlined to prevent misunderstandings later.
- Contract Clarity: Ensure the agreement covers all aspects of the sale.
- Payment Terms: Discuss payment options and schedules that align with your financial planning.
By following this checklist, you can make a more informed and confident decision when purchasing a metal laser cutter, ensuring that it aligns with your operational needs and business goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal laser cutter for sale Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Sourcing Metal Laser Cutters?
When evaluating the costs associated with sourcing metal laser cutters, several components come into play. The primary cost elements include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The type of materials used in the construction of the laser cutter significantly influences the overall cost. High-quality components, such as fiber optics and advanced electronics, can increase the price but enhance performance and longevity.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential in both the manufacturing and assembly of laser cutters. Labor costs vary by region, with markets in Europe generally facing higher labor costs compared to those in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs, making it vital to assess the production capabilities of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can add significant upfront costs but is often necessary for specialized applications. Buyers should weigh the benefits of custom solutions against their budget constraints.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures the reliability and performance of the cutters. However, it adds to the overall cost structure. Certifications (ISO, CE) also factor into pricing, as they require adherence to strict standards.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary greatly depending on the origin and destination of the equipment. International buyers should consider freight costs, insurance, and potential tariffs when budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. Understanding the market standards for margins in different regions can help buyers identify fair pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect the Cost of Metal Laser Cutters?
Several factors influence the pricing of metal laser cutters beyond the basic cost components.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Purchasing in bulk can lead to significant discounts. Understanding a supplier’s MOQ policy is crucial for optimizing costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: The more specialized the equipment, the higher the price. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary customization costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications can increase initial costs but may lead to lower maintenance and operational costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and service offerings (such as warranty and support) can also impact pricing. Conducting due diligence on suppliers is essential.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) can significantly affect total costs. Terms that place more responsibility on the buyer can lower initial prices but may lead to higher overall expenses.
What Buyer Tips Can Help in Negotiating Metal Laser Cutter Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic negotiation and understanding of pricing nuances can lead to better deals.
-
Negotiate Terms: Always negotiate payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranty conditions. Flexibility in these areas can provide significant cost savings.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the initial purchase price, consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Prices can vary significantly based on regional demand and supply dynamics. Buyers should research local market trends to inform their negotiations.
-
Consider Used Equipment: For companies with tight budgets, exploring the used market can yield significant savings. Ensure proper inspection and certification of used machines.
-
Stay Informed About Market Trends: Keep abreast of technological advancements and shifts in supplier dynamics. Being informed allows buyers to make better purchasing decisions and negotiate from a position of strength.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
While indicative pricing can provide a general idea, actual costs may vary based on the specific configurations, customizations, and market conditions at the time of purchase. Always request detailed quotes and conduct a thorough comparison before making procurement decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal laser cutter for sale With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Metal Cutting Solutions
When exploring options for metal cutting, businesses often encounter various technologies that can achieve similar results to metal laser cutters. Understanding these alternatives is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to optimize production efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. This analysis compares metal laser cutters with plasma cutting machines and waterjet cutting systems, evaluating their performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Laser Cutter For Sale | Plasma Cutting Machine | Waterjet Cutting System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision; kerf < 25µm | Moderate precision; kerf ~1mm | Excellent precision; kerf ~1mm |
| Cost | High initial investment; low operating costs | Lower initial cost; moderate operating costs | High initial investment; high operating costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled personnel | Easier to operate; less training needed | Complex setup; requires skilled personnel |
| Maintenance | Low; solid-state components | Moderate; consumables needed | High; frequent maintenance required |
| Best Use Case | Thin to medium metal sheets | Thick metals and rapid cuts | Complex shapes; delicate materials |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Plasma Cutting Machine
Plasma cutting machines utilize a high-temperature plasma arc to melt and cut through metal. They are particularly effective for thicker materials, making them ideal for applications such as heavy fabrication and shipbuilding. The lower initial cost and faster cutting speeds are significant advantages; however, they lack the precision of laser cutting. Plasma cutters are easier to operate and require less training, making them suitable for businesses with less experienced staff. Nevertheless, the kerf width is larger compared to laser cutting, which can lead to more material waste.
Waterjet Cutting System
Waterjet cutting employs high-pressure water mixed with abrasive materials to cut through metal. This method is renowned for its ability to cut intricate shapes without heat-affected zones, making it perfect for delicate materials and complex designs. However, waterjet systems come with a high initial investment and ongoing operating costs due to water and abrasive materials consumption. The setup can be complex and requires skilled personnel for optimal operation. While they offer excellent precision, the slower cutting speeds compared to laser and plasma cutting may hinder productivity in high-volume environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metal Cutting Solution
Selecting the appropriate metal cutting solution hinges on specific business needs, production volume, and budget constraints. For high-precision tasks involving thin to medium sheets, a metal laser cutter is often the best choice despite the higher initial costs. In contrast, for businesses focusing on thicker materials or requiring faster cuts, plasma cutting machines may provide a more cost-effective solution. Waterjet cutting is ideal for intricate designs but may not be suitable for all production environments due to its higher operational costs. Evaluating these factors will empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal laser cutter for sale
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of Metal Laser Cutters for Sale?
When considering the purchase of a metal laser cutter, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for making an informed decision. Here are some of the key properties that buyers should consider:
1. Laser Power
Laser power, typically measured in watts (W), determines the thickness of material that can be effectively cut. For instance, a 1000W fiber laser can handle up to 6mm of carbon steel, while higher power lasers (20,000W or more) can cut through thicker materials. Choosing the right power is essential for meeting production needs and ensuring efficiency.
2. Cutting Speed
Measured in meters per minute (m/min), cutting speed indicates how quickly a laser cutter can process materials. For example, advanced models may achieve speeds of up to 25 m/min. High-speed cutting reduces production time, which is vital for companies aiming to enhance throughput and meet tight deadlines.
3. Material Compatibility
Different laser cutters are designed to work with various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and more. Understanding the compatibility of a laser cutter with the materials used in production is vital for maximizing versatility and minimizing operational costs. This factor is especially important for businesses with diverse product offerings.
4. Tolerance and Precision
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified measurement, while precision indicates how closely the cutting process can replicate that measurement. A high tolerance (e.g., ±0.02 mm) is essential for applications requiring intricate designs, such as automotive or aerospace components. Precision ensures that parts fit together correctly, reducing waste and the need for rework.
5. Kerf Width
Kerf width is the width of the cut made by the laser, typically measured in micrometers (µm). A narrower kerf allows for more intricate designs and better material utilization. Understanding kerf width is important for industries focused on minimizing waste and maximizing yield from raw materials.
Which Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know When Purchasing Metal Laser Cutters?
In addition to technical specifications, familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common trade terms that buyers should understand:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is vital for ensuring product quality and compatibility with existing systems.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the minimum number of units a buyer must purchase from a supplier. Knowing the MOQ helps businesses plan their budgets and inventory levels effectively, especially when dealing with large machinery like laser cutters.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit pricing and terms from suppliers. This process is crucial for comparing costs and securing the best deal. A well-prepared RFQ can lead to more favorable terms and pricing.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms is essential for avoiding misunderstandings and ensuring compliance with international regulations.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is critical for supply chain planning, especially for businesses that rely on timely deliveries to meet production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in metal laser cutters, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal laser cutter for sale Sector
What Are the Key Trends Shaping the Metal Laser Cutter Market?
The global metal laser cutter market is experiencing a transformative phase driven by several key factors. First, the increasing demand for precision and efficiency in metal fabrication is propelling the adoption of fiber laser technology. Unlike traditional CO2 lasers, fiber lasers offer faster cutting speeds, reduced operational costs, and the ability to handle a wider variety of materials, including metals like aluminum, titanium, and copper. This trend is particularly significant for B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where industries are rapidly modernizing.
Another emerging trend is the shift towards automation and integration of Industry 4.0 technologies. Manufacturers are increasingly seeking laser cutting systems that can seamlessly connect with other machinery and software, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics. This integration not only enhances productivity but also provides valuable insights for optimizing operations. For instance, businesses in the Middle East and Europe are leveraging these advancements to improve supply chain efficiency and reduce lead times.
Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on cost-effectiveness. As competition intensifies, buyers are looking for machines that promise a quick return on investment (ROI). Models like the Atlas Alloy Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser highlight how lower running costs—such as using inexpensive nitrogen gas—can significantly enhance profitability. This focus on ROI is crucial for businesses in developing markets, where budget constraints are a common concern.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the Metal Laser Cutter Market?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the procurement of metal laser cutters. B2B buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impacts of their sourcing decisions. This awareness drives demand for machines that utilize eco-friendly technologies and materials. For instance, fiber laser cutters are often more energy-efficient than their CO2 counterparts, resulting in lower carbon footprints during operation.
Moreover, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to ethical sourcing practices, such as using responsibly sourced materials and maintaining fair labor practices. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management systems can serve as indicators of a manufacturer’s dedication to sustainability.
Additionally, companies are exploring the use of recyclable and biodegradable materials in their production processes. By investing in laser cutting technologies that support sustainable practices, businesses not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles but also appeal to a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers.
What Is the Historical Context of Metal Laser Cutting Technology?
The evolution of metal laser cutting technology dates back to the 1960s when the first lasers were developed. Initially, these devices were primarily used for industrial applications, including cutting and welding. Over the decades, advancements in laser technology led to the development of more efficient systems, including the introduction of fiber lasers in the early 2000s.
Fiber lasers revolutionized the industry by offering higher cutting speeds and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional CO2 lasers. This evolution has made laser cutting a preferred choice for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Today, metal laser cutters are integral to many production processes, providing unparalleled precision and versatility for B2B buyers worldwide.
As the market continues to evolve, keeping abreast of technological advancements and market dynamics will be essential for buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions in the metal laser cutter sector.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal laser cutter for sale
-
How do I choose the right metal laser cutter for my business needs?
Selecting the right metal laser cutter involves assessing your specific application requirements, including material type, thickness, and desired cutting speed. Consider the power of the laser (measured in watts) as it directly influences cutting capabilities. For instance, a higher wattage is ideal for cutting thicker materials quickly. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s bed size and whether you need a flatbed or a tube cutter. Finally, consult with suppliers about their machine specifications and customer support, ensuring they can meet your operational demands. -
What are the advantages of using fiber laser cutters over CO2 laser cutters?
Fiber laser cutters offer several advantages, particularly in efficiency and cost-effectiveness. They typically have a higher absorption rate for metals, resulting in faster cutting speeds and lower energy consumption. Fiber lasers also require less maintenance due to fewer moving parts and no mirrors to align. This technology is particularly effective for cutting materials like stainless steel and aluminum, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers looking to enhance productivity while minimizing operational costs. -
What customization options are available for metal laser cutters?
Many suppliers provide customization options to suit your specific production needs. These can include adjustments to laser power, cutting bed size, and additional features like automated loading systems or enhanced cooling mechanisms. You can also request specific software integrations for your production line. When sourcing equipment, discuss your requirements with the manufacturer to ensure they can accommodate your customizations, and ask for examples of previous custom solutions they have provided. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for purchasing a metal laser cutter?
The minimum order quantity (MOQ) for metal laser cutters can vary significantly based on the supplier and the type of machinery. Some manufacturers may offer single units, especially for specialized or custom machines, while others may have higher MOQs for standard models. Always inquire about the MOQ during your sourcing discussions, as negotiating may be possible, especially if you are considering future purchases or bulk orders. -
What payment terms are typically offered by suppliers for laser cutting machines?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include upfront payments, installment plans, or financing options. Many suppliers require a deposit (often 30-50%) upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. It’s essential to clarify these terms early in negotiations to ensure they align with your financial planning. Additionally, consider discussing payment methods that offer buyer protection, such as letters of credit or escrow services. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when purchasing a metal laser cutter?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the machine’s specifications, certifications, and performance metrics from the supplier. Look for suppliers who provide comprehensive warranties and after-sales support. It’s advisable to visit the manufacturer’s facility or request a demonstration of the machine in operation to evaluate its performance firsthand. Additionally, reviews and testimonials from other clients can provide insights into the reliability and quality of the equipment. -
What are the logistics considerations for importing a metal laser cutter?
When importing a metal laser cutter, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and local regulations regarding machinery imports. Work with a freight forwarder who specializes in industrial equipment to navigate these complexities. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, including commercial invoices and packing lists, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Finally, factor in delivery timelines, as international shipping can be subject to delays due to various factors. -
What kind of training and support should I expect after purchasing a laser cutter?
Most reputable suppliers offer training and support as part of the purchase package. This typically includes on-site training for your operators, covering machine operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. Additionally, inquire about ongoing technical support options, such as remote assistance or service agreements, to ensure quick resolution of any issues that may arise post-installation. A well-defined support structure is crucial for maximizing your investment and ensuring uninterrupted production.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
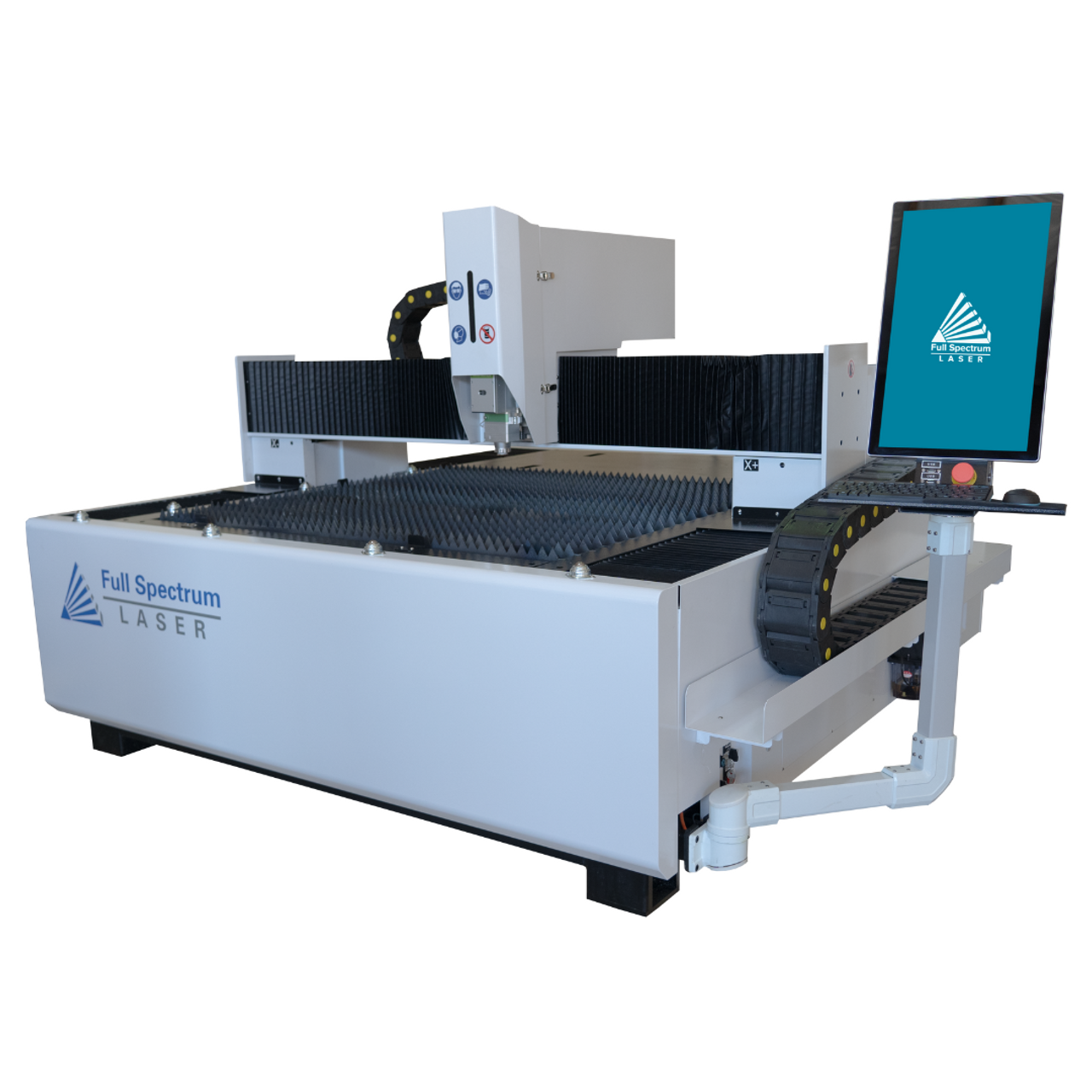
Top 7 Metal Laser Cutter For Sale Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. OMTech – Fiber Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: omtechlaser.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Best Fiber Laser Cutting Machine for Metal Fabrication
– OMTech Fiber Laser Metal Cutting Machines:
– FC22 1500W Enclosed Fiber Laser Cutting Machine: As low as *$828/MO (Price Match Guarantee)
– FC22-C 1500W Open Metal Laser Cutting Machine: As low as *$767/MO (Price Match Guarantee)
– FC-105 Fiber Laser Cutting Machine: As low as *$1,081/MO (Price Match Guarantee)
– FC-44 Fiber Laser Cu…
2. Hytek Tools – ROBOTUBE™ MODEL RT2 Fiber Laser Cutter
Domain: hytektools.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Hytek Tools – ROBOTUBE™ MODEL RT2 Fiber Laser Cutter, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. Atlas Alloy – Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser
Domain: fslaser.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Atlas Alloy Flatbed Metal Cutting Fiber Laser up to 20kW
– Model Options: 4’x8′ 1000W, 4’x8′ 1500W, 4’x8′ 2000W, 5’x10′ 3000W, 5’x10′ 6000W
– MSRP: $55,000.00
– Cutting Area: 47″ x 95″ (1100 mm x 2400 mm) or 59″ x 118″ (1500 mm x 3000 mm)
– Machine Dimensions: 4’x8′: 173″ x 90″ x 55″ (4.4m x 2.3m x 1.4m); 5’x10′: 197″ x 89″ x 75″ (5010 mm x 2260 mm x 1900 mm)
– Weight: 4’x8′: 6024 lbs (2732 kg); 5…
4. CNC Laser Cutters – Key Product Details
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Key Product Details: 1. Types of CNC Laser Cutters: – Gas Laser Cutting – Crystal Laser Cutting – Fiber Laser Cutting 2. Brands Available: – AMADA (8) – MITSUBISHI (5) – MAZAK (4) – TRUMPF (4) – BYSTRONIC (3) – AP LAZER (2) – BOSS LASER (2) – LASERPRO (2) – LVD STRIPPIT (2) – TROTEC (2) – BODOR (1) – CINCINNATI (1) – COHERENT (1) – HK LASER & SYSTEMS (1) – HYPERUSA (1) – IPG PHOTONICS (1) – NUKON …
5. Cloudray – 110V 100W CO2 Laser Power Supply
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Metalworking Laser Cutting Machines for sale on eBay. Key products include: 1. Cloudray 110V 100W CO2 Laser Power Supply – $169.99, New. 2. Ortur 20w Laser Module for Laser Engraving/Cutting – $529.00, Free shipping. 3. Cubiio2 Laser Engraving and Cutting – $599.99, Pre-Owned, Free shipping. 4. S&A CW-5000 Industrial Chiller for Laser Cutting – $500.00, Pre-Owned, $109.30 shipping. 5. Creality Las…
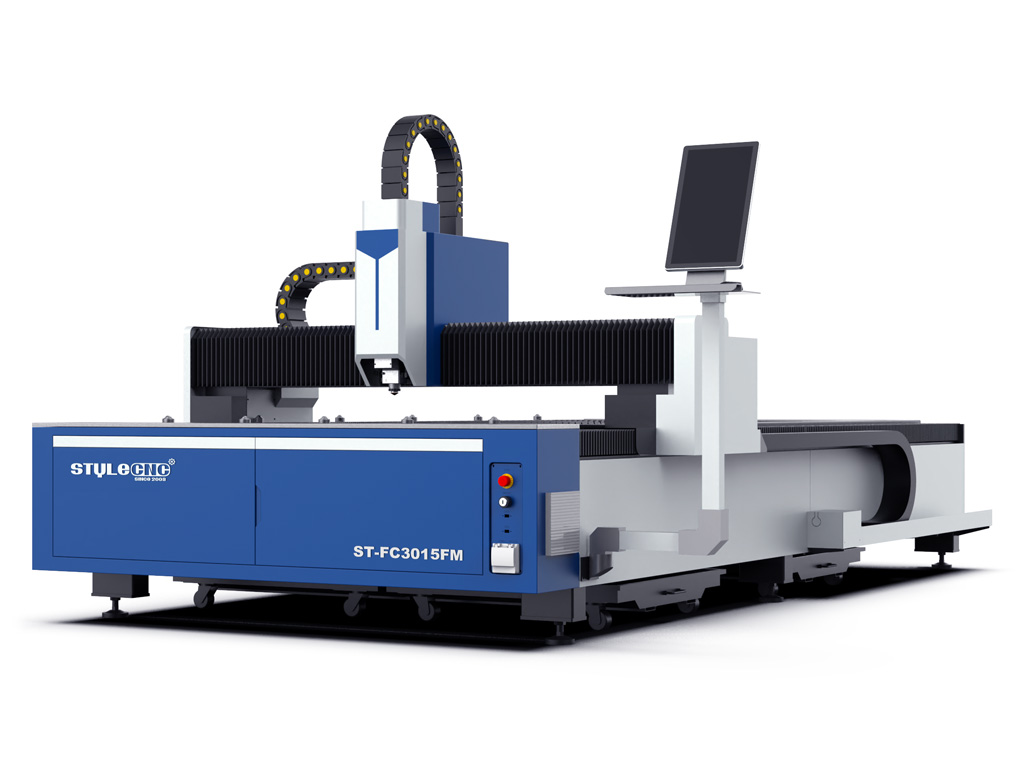
6. Style CNC – Metal Laser Cutting Machine
Domain: stylecnc.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: A metal laser cutting machine is an industrial equipment that uses high-energy CO2/fiber laser beams to accurately cut metal materials. It is a high-speed CNC system that works with CAM software to shape 2D/3D metal cuts made of various metals including stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, and more. Key features include:
– High precision, high efficiency, and flexibility
– Automation with CNC …
7. Wattsan – Metal Laser Cutting Machines
Domain: wattsan.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: This company, Wattsan – Metal Laser Cutting Machines, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal laser cutter for sale
In the evolving landscape of metal fabrication, strategic sourcing of metal laser cutters is pivotal for businesses looking to enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. By investing in advanced fiber laser technology, companies can achieve remarkable precision in cutting a variety of metals, which not only streamlines production processes but also boosts overall productivity. As highlighted, the potential for a quick return on investment—often within weeks—makes these tools an invaluable asset for manufacturers across sectors.
Furthermore, international buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should consider the growing trend towards automation and energy-efficient solutions. The ability to cut large metal sheets with minimal operating costs positions fiber laser cutters as a game-changer in competitive markets.
As you explore options for sourcing metal laser cutters, prioritize suppliers that offer comprehensive support and training, ensuring you maximize the benefits of your investment. The future of metal fabrication is bright, and with the right tools, your business can lead the way. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure the technology that will drive your success in the coming years.