Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Metal Composition Of Stainless Steel
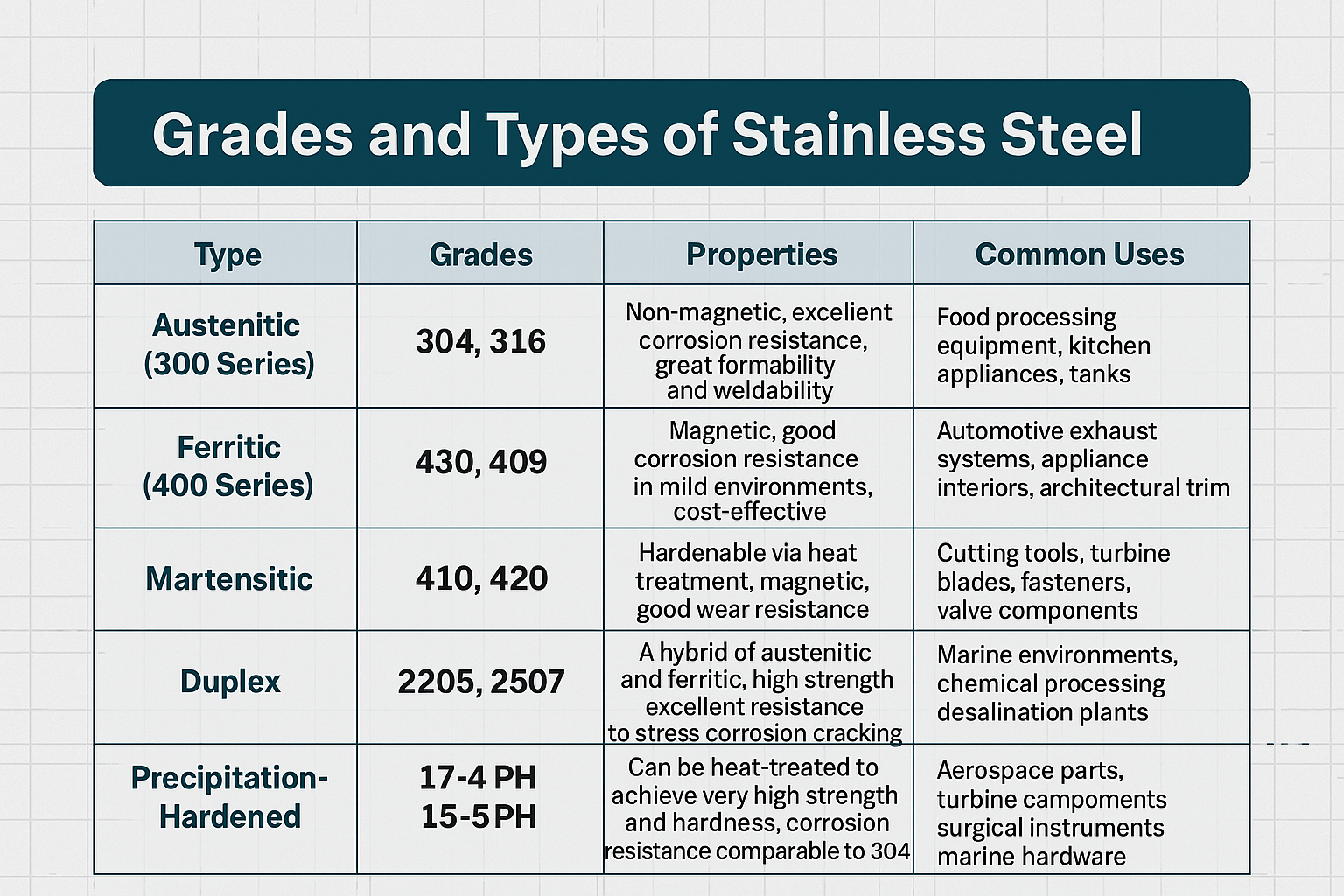
Understanding stainless steel composition is critical for precision sheet metal fabrication, as alloying elements directly impact formability, weldability, corrosion resistance, and final part performance. At Honyo Prototype, our engineering team leverages deep material science expertise to select and process stainless grades—such as 304, 316, 410, and 17-4PH—ensuring optimal results for demanding applications in medical, aerospace, and industrial equipment. We recognize that minor variations in chromium, nickel, molybdenum, or carbon content can significantly influence manufacturability and product longevity, which is why material specification is integrated into every stage of our workflow.
Honyo Prototype delivers end-to-end sheet metal solutions, including precision laser cutting, CNC bending, robotic welding, and finishing, all executed with ISO 9001-certified processes. Our facility handles thicknesses from 0.5mm to 6mm with tight tolerances of ±0.1mm, supported by in-house metallurgical validation to verify material properties against your requirements. Below is a summary of common stainless grades we routinely fabricate and their key characteristics:
| Stainless Steel Grade | Key Alloying Elements | Primary Applications | Honyo Fabrication Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 304 / 304L | 18% Cr, 8% Ni | Food processing, chemical tanks | High-speed laser cutting, cleanroom-compatible welding |
| 316 / 316L | 16% Cr, 10% Ni, 2% Mo | Marine, pharmaceutical | Precision TIG welding for crevice corrosion resistance |
| 410 | 12% Cr | Valves, fasteners | Hardened part machining post-fabrication |
| 17-4PH | 17% Cr, 4% Ni, 4% Cu | Aerospace actuators | Complex forming with tight geometric tolerances |
To accelerate your prototyping or low-volume production timeline, Honyo Prototype offers an Online Instant Quote system. Simply upload your STEP or DXF file, specify material grade and finish requirements, and receive a detailed cost and lead time estimate within minutes—no manual back-and-forth. This transparency empowers engineers to make informed material and design decisions early, reducing time-to-market while ensuring your stainless steel components meet exact functional and regulatory demands. Partner with Honyo to transform material science into precision-engineered reality.
Technical Capabilities

The metal composition of stainless steel plays a critical role in determining its performance during laser cutting, bending, and welding processes. Below is a comparison of key materials commonly used in fabrication, including stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, ABS, and nylon, with a focus on their technical characteristics relevant to these manufacturing operations.
| Material | Composition / Type | Laser Cutting Suitability | Bending Characteristics | Welding Compatibility | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Melting Point (°C) | Key Notes for Fabrication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Austenitic (e.g., 304, 316) | Excellent – clean cuts with fiber laser; minimal dross | Good formability; higher springback than carbon steel | Excellent – TIG, MIG, and laser welding; low carbon grades reduce sensitization | 15–22 | 1400–1450 | Resists oxidation; requires assist gas (nitrogen or oxygen) depending on finish needs |
| Aluminum | Alloys (e.g., 5052, 6061) | Good – reflective; requires high-power fiber laser with proper optics | Excellent ductility; requires tooling adjustments due to softness | Good – requires clean surfaces; TIG preferred; prone to hot cracking | 160–200 | 600–660 | High reflectivity and thermal conductivity demand precise laser parameters |
| Carbon Steel | Low carbon (e.g., A36, 1018) | Excellent – easily cut with CO₂ or fiber laser | Excellent bendability; sharp bends may require annealing | Excellent – easily welded with MIG, TIG, or stick welding | 45–50 | 1370–1510 | Prone to rust; often painted or coated post-processing |
| ABS | Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (Thermoplastic) | Fair – cuts cleanly with CO₂ laser; melting risk | Limited – not suitable for structural bending; thermoforming possible | Poor – not weldable in traditional sense; solvent or ultrasonic welding | 0.1–0.2 | 105 | Non-metallic; used for enclosures or prototypes; avoid high heat processes |
| Nylon | Polyamide (e.g., PA6, PA66) | Poor – high laser absorption causes burning | Limited – flexible but not suitable for sharp bends | Poor – requires specialized techniques like hot gas or vibration welding | 0.25 | 215–260 | Hygroscopic; requires drying before processing; not recommended for laser cutting |
Notes:
Stainless steel’s chromium content (typically 16–26%) provides corrosion resistance and influences weldability and heat-affected zone (HAZ) behavior.
For laser cutting, stainless steel and carbon steel respond well to high-power fiber lasers, while aluminum requires optimized settings due to reflectivity.
Bending stainless steel requires higher tonnage than aluminum due to greater yield strength.
ABS and nylon are non-metallic and are included for comparative context; they are not suitable for structural metal fabrication processes.
From CAD to Part: The Process
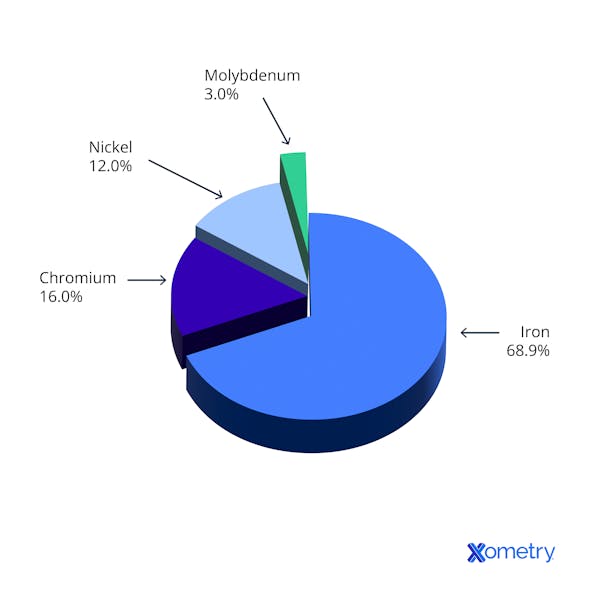
Honyo Prototype maintains rigorous control over stainless steel composition throughout our manufacturing workflow to ensure material integrity aligns with client specifications and industry standards. Our process integrates metallurgical verification at critical stages, not as a standalone operation but as a threaded requirement across the project lifecycle. Below is the precise sequence with composition-specific actions:
CAD Upload Phase
Clients submit geometry and material requirements via our secure portal. We explicitly require stainless steel grade designation (e.g., ASTM A276 304, 316L) in the CAD metadata or supplementary documentation. If omitted, our system triggers an automated query for material specification prior to proceeding. Unspecified composition halts the workflow until client clarification is received.
AI Quote Generation
Our AI engine cross-references the declared stainless steel grade against real-time material databases, cost factors, and process feasibility. It validates whether the specified composition (e.g., 18-20% Cr, 8-12% Ni for 304) matches standard metallurgical classifications. Discrepancies between client input and recognized grades (e.g., “SS304” vs. precise UNS S30400) generate immediate alerts for engineering review. Quotes include material certification costs as a non-negotiable line item.
DFM Analysis
Senior metallurgists conduct composition-specific manufacturability assessment. This includes verifying:
Compatibility of the steel grade with proposed processes (e.g., laser cutting 410 vs. 304)
Risk of carbide precipitation in sensitization-prone grades during welding
Thermal expansion coefficients affecting tolerance stacks
Corrosion resistance alignment with end-use environment
DFM reports explicitly state composition compliance status and recommend alternatives if specified grades introduce production risks.
Production Execution
Material composition is validated through dual verification before machining:
1. Mill Test Reports (MTRs) from certified suppliers are audited for elemental breakdown (C, Cr, Ni, Mo, etc.) against ASTM/EN standards
2. Positive Material Identification (PMI) via handheld XRF spectrometry on received stock
Production-stage composition control measures:
| Verification Method | Frequency | Tolerance Check | Documentation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Production PMI | 100% of material lots | ASTM A480 limits | Traceable digital log |
| In-Process Spot Check | Critical weld zones | ±0.5% for key elements | Integrated with QC records |
| Post-Machining PMI | Final inspection | Full elemental profile | Client-accessible portal |
No component advances without documented composition conformity. For medical/aerospace projects, we implement additional OES testing per client-specific AMS/ASTM requirements.
Delivery Commitment
Final shipment includes:
Certified Material Test Reports with full chemical composition
PMI validation logs showing pre-production and final verification
Traceability documentation linking heat numbers to finished parts
Compliance statement against referenced standards (e.g., “Conforms to UNS S31603 per ASTM A240”)
All data is accessible via our client portal with blockchain-verified timestamps for audit readiness. This closed-loop composition management prevents field failures from material non-conformance, reducing client liability risks in regulated industries.
Start Your Project
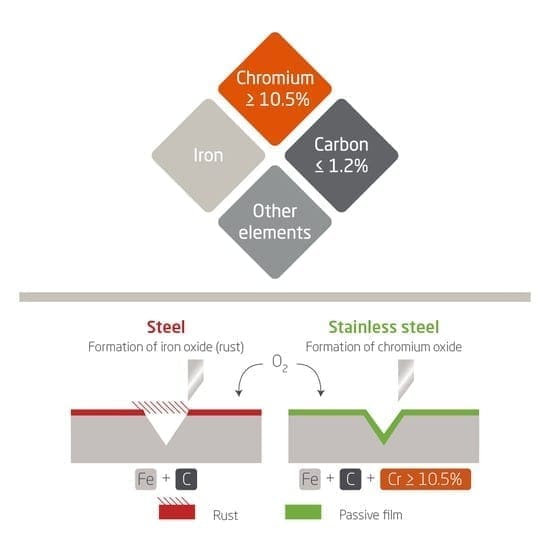
Learn more about the metal composition of stainless steel and how it impacts your precision manufacturing projects. Contact Susan Leo at [email protected] for expert guidance and custom prototyping solutions. Our ISO-certified factory in Shenzhen supports high-precision CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and rapid prototyping with full material traceability and compliance. Partner with Honyo Prototype for accurate, repeatable results—request a quote today.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.