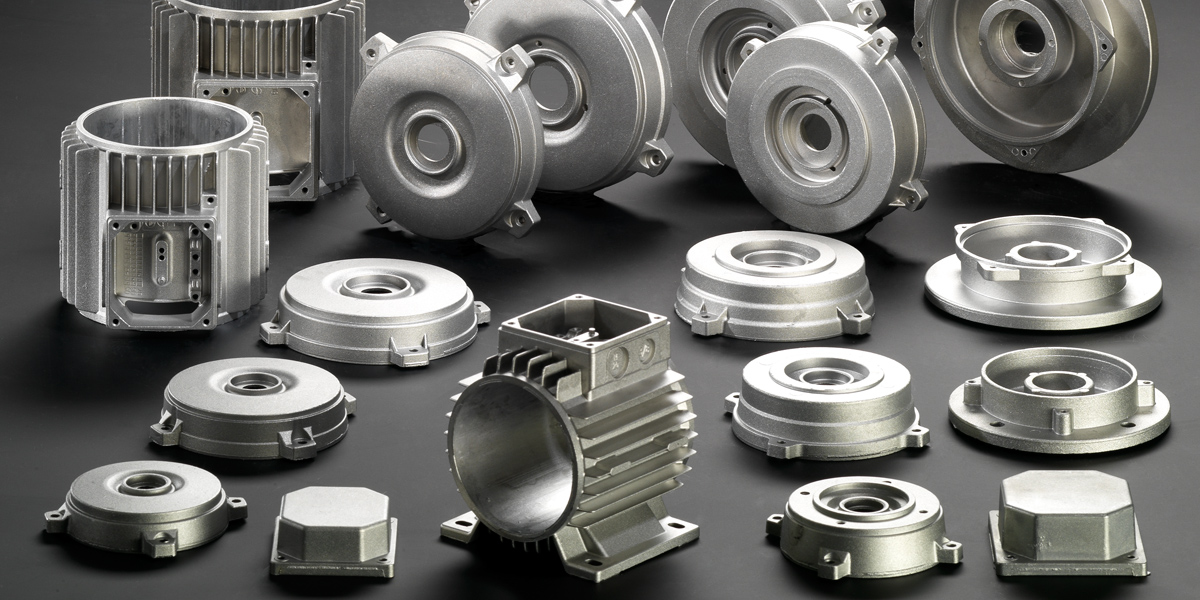
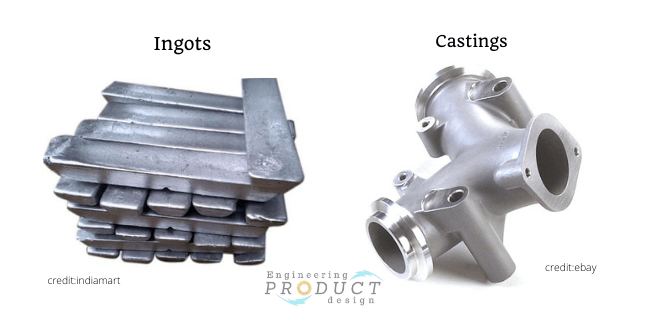
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal casting products
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing reliable metal casting products poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The intricacies of the global market require a keen understanding of various factors, including material types, manufacturing processes, and supplier credibility. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for navigating these complexities, empowering buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
From exploring different types of metal casting—such as sand casting, die casting, and investment casting—to examining their applications across industries like automotive, construction, and aerospace, this guide covers the essential aspects of sourcing metal casting products. It also delves into critical considerations for supplier vetting, including assessing quality standards, production capabilities, and compliance with international regulations. Additionally, buyers will find valuable insights on cost factors, enabling them to optimize their procurement strategies.
By equipping B2B buyers with actionable insights and practical knowledge, this guide aims to simplify the sourcing process for metal casting products. Whether you are in Nigeria, Brazil, or elsewhere, understanding the global market dynamics will enhance your ability to secure high-quality products that meet your operational needs, ultimately driving business success.
Understanding metal casting products Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand Casting | Utilizes sand molds; versatile for complex shapes | Automotive parts, machinery components, decorative items | Pros: Cost-effective, good surface finish; Cons: Slower production rates, less precision than other methods. |
| Die Casting | High precision with metal molds; ideal for mass production | Electronics housings, automotive components, consumer goods | Pros: Excellent dimensional accuracy; Cons: Higher initial costs for molds, limited to non-ferrous metals. |
| Investment Casting | Uses wax patterns; excellent for intricate designs | Aerospace, medical devices, precision machinery | Pros: Superior surface finish and detail; Cons: More expensive and longer lead times. |
| Permanent Mold Casting | Metal molds reused multiple times; efficient for large runs | High-volume production of automotive parts, appliances | Pros: Faster cycle times, good dimensional control; Cons: Higher initial mold costs, limited to simpler shapes. |
| Centrifugal Casting | Rotational method for cylindrical parts; strong structures | Pipes, tubes, and rings in construction and automotive | Pros: High strength and density; Cons: Limited to specific shapes, more complex setup. |
What Are the Characteristics of Sand Casting?
Sand casting is one of the most common methods for producing metal parts. It involves creating a mold from sand, which is then filled with molten metal. The process is highly versatile, allowing for the creation of complex shapes and large components. Sand casting is particularly well-suited for low to medium production runs, making it a cost-effective choice for various industries, including automotive and machinery. Buyers should consider the balance between production speed and the desired surface finish, as sand casting may not achieve the same precision as other methods.
How Does Die Casting Stand Out in Precision Manufacturing?
Die casting is characterized by its use of high-pressure techniques to inject molten metal into reusable steel molds. This method is ideal for high-volume production and is commonly used for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and zinc. The resulting parts exhibit excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish, making die casting a preferred choice for components in the electronics and automotive sectors. While the initial investment in molds can be high, the long-term cost savings and efficiency in mass production often justify the expenditure.
What Makes Investment Casting Ideal for Intricate Designs?
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, is renowned for its ability to produce highly intricate and detailed components. This method utilizes a wax pattern that is coated with a ceramic shell, which is then heated to remove the wax and form a mold. Investment casting is particularly favored in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where precision is critical. Buyers should weigh the benefits of superior finish and detail against the higher costs and longer lead times associated with this casting method.
Why Choose Permanent Mold Casting for High-Volume Needs?
Permanent mold casting employs reusable metal molds to produce parts, making it suitable for high-volume production. This method is particularly effective for simpler shapes and is commonly used in the automotive and appliance industries. The key advantages include faster cycle times and better dimensional accuracy compared to sand casting. However, buyers should be aware of the higher initial costs associated with mold creation and the limitations in the complexity of shapes that can be produced.
What Are the Advantages of Centrifugal Casting for Strength?
Centrifugal casting involves pouring molten metal into a rotating mold, which is ideal for creating cylindrical parts with high strength and density. This method is commonly used for pipes, tubes, and rings in construction and automotive applications. The centrifugal force helps to eliminate impurities and ensures a uniform density throughout the part. Buyers should consider the specific shape requirements and the complexity of setup, as this method is best suited for specific applications rather than general use.
Key Industrial Applications of metal casting products
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Metal Casting Products | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine blocks and components | Enhanced durability and performance | Quality certifications, local regulations, lead times |
| Construction | Structural components for machinery | Improved strength and reliability | Material specifications, customization options |
| Aerospace | Aircraft components like brackets and housings | Weight reduction and fuel efficiency | Aerospace standards compliance, precision requirements |
| Oil & Gas | Pump casings and valve bodies | Resistance to harsh environments and corrosion | Material grades, sourcing from reputable suppliers |
| Consumer Electronics | Enclosures for electronic devices | Aesthetic appeal and protection of internal components | Design flexibility, thermal properties, cost-effectiveness |
How Are Metal Casting Products Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, metal casting products are critical for manufacturing engine blocks and various components such as cylinder heads and transmission cases. These cast parts are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures while maintaining structural integrity. For international B2B buyers, sourcing quality castings that comply with automotive industry standards is essential, as is understanding local regulations regarding emissions and safety. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate consistent quality and reliability, as any failure in these components can lead to significant operational disruptions.
What Role Do Metal Casting Products Play in Construction?
Metal casting is pivotal in the construction industry for producing structural components like beams and machinery parts. These castings offer superior strength and durability, essential for supporting heavy loads and ensuring long-lasting performance. Buyers in this sector should consider the specific material requirements and customization options available to meet project specifications. Additionally, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce lead times and shipping costs, which is particularly advantageous for large-scale projects in developing regions like Africa and South America.
How Are Metal Casting Products Utilized in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, metal casting products are utilized for manufacturing high-performance components, including brackets and housings. These products must be lightweight yet strong to improve fuel efficiency and meet stringent safety regulations. International buyers must focus on suppliers that comply with aerospace standards, such as AS9100, and can provide traceability of materials. Precision requirements are critical, so buyers should verify the supplier’s capabilities in producing complex geometries and their adherence to rigorous quality control processes.
What Are the Applications of Metal Casting in the Oil & Gas Sector?
Metal casting products are extensively used in the oil and gas industry for components like pump casings and valve bodies. These products must exhibit high resistance to corrosion and extreme environmental conditions. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with experience in providing materials that meet industry-specific standards, such as API specifications. Understanding the importance of material grades and the supplier’s ability to deliver on time is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency in this high-stakes industry.
How Do Metal Casting Products Enhance Consumer Electronics?
In the consumer electronics sector, metal casting products are often used for enclosures that protect sensitive internal components. These castings not only provide structural protection but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of devices. International buyers should consider the design flexibility offered by suppliers and the thermal properties of the materials used to ensure optimal performance. Cost-effectiveness is also a significant factor, particularly for companies looking to scale production while maintaining quality standards.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal casting products’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Quality Assurance Challenges in Metal Casting Products
The Problem: One of the most significant challenges faced by B2B buyers in the metal casting industry is ensuring the quality and consistency of the products they procure. Variations in material properties, defects in casting, and discrepancies in dimensions can lead to costly production delays and client dissatisfaction. This is particularly critical in sectors like automotive or aerospace, where precision is paramount. Buyers often struggle with a lack of transparent quality control processes from suppliers, making it difficult to gauge whether the products will meet their stringent specifications.
The Solution: To mitigate these quality assurance challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers who have robust quality management systems (QMS) in place. This includes suppliers who are ISO-certified or have similar accreditation, as these certifications indicate adherence to international quality standards. Engage in detailed discussions with potential suppliers about their quality control processes, including material selection, testing methods, and inspection protocols. Request access to material certification reports and inspection records to verify that the products meet specified standards. Additionally, establishing a close working relationship with suppliers can facilitate better communication and quicker resolution of any issues that arise, enhancing trust and reliability.
Scenario 2: Long Lead Times Affecting Production Schedules
The Problem: Many B2B buyers face the frustration of long lead times when ordering metal casting products, which can significantly disrupt production schedules. Delays can stem from various factors, including supplier capacity constraints, unexpected demand surges, or logistical challenges. For companies that rely on just-in-time manufacturing practices, such delays can lead to production stoppages and increased operational costs.
The Solution: To address lead time issues, buyers should conduct thorough research when selecting suppliers, focusing on their production capabilities and historical performance regarding lead times. It is advisable to establish contracts that include clear timelines and penalties for delays, thus incentivizing suppliers to adhere to agreed-upon schedules. Additionally, consider diversifying your supplier base to include multiple sources for critical components. This strategy not only reduces reliance on a single supplier but also provides flexibility to switch sources in case of unforeseen delays. Implementing advanced planning and forecasting tools can also help anticipate needs and streamline order placements to align better with production schedules.
Scenario 3: Navigating Complex Specifications and Customizations
The Problem: B2B buyers often encounter complexities when dealing with custom metal casting products, particularly when specifications involve unique designs or materials. Misunderstandings in requirements can lead to products that do not meet client expectations, resulting in costly rework or scrap. This issue is exacerbated when working with international suppliers, where language barriers and cultural differences may further complicate communication.
The Solution: To effectively navigate the challenges of complex specifications, buyers should invest time in creating detailed and precise specifications for their casting needs. This includes clear drawings, material requirements, and performance criteria. Utilizing digital tools such as CAD software can enhance the clarity of designs and facilitate better communication with suppliers. It is also beneficial to conduct preliminary meetings or workshops with suppliers to discuss specific requirements and expectations, ensuring mutual understanding. Establishing a prototype phase before mass production can help catch any potential issues early, allowing for adjustments without significant cost implications. Finally, leveraging local suppliers who understand regional manufacturing practices can ease communication and streamline the customization process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal casting products
When selecting materials for metal casting products, it is essential to consider the properties, advantages, limitations, and specific applications of each material. This guide focuses on four common materials used in metal casting: iron, aluminum, magnesium, and zinc. Each material has unique characteristics that affect its performance and suitability for various applications, especially for international B2B buyers.
What Are the Key Properties of Iron for Metal Casting Products?
Iron, particularly cast iron, is renowned for its excellent castability and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. Cast iron exhibits good wear resistance and can be alloyed with other elements to enhance its properties further. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated or coated.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantages of iron include its strength and durability, making it ideal for components like engine blocks and heavy machinery parts. On the downside, iron can be heavier and more expensive to transport, which may be a consideration for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics can be challenging.
How Does Aluminum Compare in Metal Casting Applications?
Aluminum is a lightweight material that offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. It is commonly used in automotive and aerospace applications due to its favorable strength-to-weight ratio. Aluminum can be easily cast into complex shapes, making it a versatile option for various industries.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which contributes to fuel efficiency in vehicles. However, aluminum casting can be more expensive than iron, and its mechanical properties may not be suitable for high-stress applications. International buyers should be aware of the varying standards for aluminum quality, such as ASTM and DIN, which can affect sourcing decisions.
What Are the Benefits of Using Magnesium in Metal Casting?
Magnesium is another lightweight metal that is increasingly used in casting applications, particularly in the automotive industry. It has excellent strength and is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for components exposed to harsh environments. Magnesium alloys can be cast using various methods, including die casting and sand casting.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of magnesium is its low density, which significantly reduces the weight of cast components. However, magnesium can be more challenging to work with due to its flammability and higher cost compared to aluminum and iron. Buyers from regions with stringent safety regulations should consider these factors when selecting magnesium for their projects.
What Role Does Zinc Play in Metal Casting Products?
Zinc is often used in die casting applications due to its excellent fluidity and ability to fill intricate molds. It is highly resistant to corrosion and can be alloyed with other metals to improve its mechanical properties. Zinc castings are commonly used in the manufacturing of hardware, automotive parts, and decorative items.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of zinc is its ability to produce high-quality, detailed castings at a relatively low cost. However, zinc has a lower melting point than other metals, which may limit its use in high-temperature applications. For international buyers, understanding the local market’s demand for zinc products can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Metal Casting Products
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal casting products | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron | Engine blocks, heavy machinery parts | High strength and durability | Heavier, prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Automotive components, aerospace parts | Lightweight, excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, may not suit high-stress applications | High |
| Magnesium | Automotive parts, electronic housings | Low density, excellent corrosion resistance | Flammable, higher cost | High |
| Zinc | Hardware, automotive parts, decorative items | High-quality detailed castings | Lower melting point, limited high-temp use | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers looking to make informed decisions regarding metal casting products. Understanding the properties and applications of each material can help streamline procurement processes and ensure compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal casting products
What Are the Main Stages of the Metal Casting Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing process for metal casting products involves several critical stages that ensure the quality and precision of the final product. Understanding these stages is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in metal casting is material preparation, where raw materials, such as metals like aluminum, iron, and zinc, are sourced and processed. This may involve melting the metal to achieve the desired composition and removing impurities. The quality of the raw material is crucial, as it directly impacts the performance of the finished product. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers use high-grade materials and have effective sourcing strategies to guarantee consistency.
2. Forming the Mold
Once the materials are prepared, the next step is mold creation. This can be done using various techniques, including sand casting, investment casting, and die casting. Each method has its own advantages depending on the complexity and volume of the parts being produced. For instance, sand casting is often used for larger, less complex components, while investment casting is preferred for high-precision applications. B2B buyers should assess the mold-making capabilities of their suppliers to ensure they can meet specific product requirements.
3. Pouring the Metal
After the mold is ready, molten metal is poured into it. This stage requires precise temperature control to prevent defects such as porosity or shrinkage. Suppliers must have robust systems in place for monitoring and controlling the pouring process. Buyers should inquire about the technology used in the pouring phase, including any automation that ensures consistency and reduces human error.
4. Assembly and Finishing
Following the cooling and solidification of the metal, the cast parts are removed from the mold. This may involve processes such as trimming, grinding, or machining to achieve the desired dimensions and surface finish. Finishing processes can also include coating or plating, which enhance the product’s durability and aesthetic appeal. Buyers should consider the finishing capabilities of suppliers, as these can significantly influence the product’s quality and lifecycle.
What Quality Control Measures Are Important in Metal Casting?
Quality assurance in metal casting is critical to ensuring that the final products meet industry standards and customer specifications. A robust QC system not only minimizes defects but also builds trust with B2B buyers.
International Standards for Quality Control
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which outlines requirements for quality management systems. Compliance with these standards demonstrates a commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for products sold in Europe or API (American Petroleum Institute) standards for oil and gas components are essential for specific markets. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold relevant certifications to ensure compliance with international and local regulations.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in metal casting typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This phase ensures that raw materials meet specified standards before production begins. Buyers can request IQC reports to verify material quality.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During production, ongoing inspections are conducted to monitor the casting process. This includes checking mold integrity, temperature, and material flow. Buyers should inquire about the frequency and methods of IPQC checks.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, the final products undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet specifications. This may involve dimensional checks, visual inspections, and non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic or X-ray inspections.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is vital to minimize risks and ensure product reliability.
Conducting Supplier Audits
One of the most effective ways to verify a supplier’s quality control is through on-site audits. These audits allow buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, quality management systems, and compliance with industry standards firsthand. A comprehensive audit checklist should include evaluations of equipment, process controls, and employee training programs.
Requesting Quality Reports and Certifications
Buyers should request documentation related to quality control, including test reports, inspection records, and certifications. These documents provide insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and their adherence to international standards. Buyers should also seek references from previous clients to gauge the supplier’s reliability and performance.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
For added assurance, buyers can engage third-party inspection services to evaluate the supplier’s quality control measures independently. These services can conduct thorough inspections at various stages of production, providing an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
International B2B buyers must navigate various nuances when it comes to quality control and certifications. Understanding these differences can help mitigate risks and enhance supplier relationships.
Regional Compliance Requirements
Different regions have specific compliance requirements that suppliers must adhere to. For instance, the European Union has stringent CE marking requirements, while certain industries in the Middle East may require compliance with local standards. B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with these regional regulations to ensure that their suppliers are compliant.
Language and Documentation Barriers
Buyers should also consider potential language barriers and the availability of documentation in their preferred language. Clear communication regarding quality expectations is essential to prevent misunderstandings that could lead to costly errors.
Continuous Improvement Practices
Finally, buyers should look for suppliers that engage in continuous improvement practices. This includes regular training for employees, investment in advanced technologies, and a commitment to reducing waste and enhancing efficiency. Such practices not only improve product quality but also contribute to sustainability efforts, which are increasingly important to B2B buyers globally.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in metal casting is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on supplier capabilities, compliance with international standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable manufacturers that deliver high-quality products.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal casting products’
Introduction
This sourcing guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure metal casting products. By following these structured steps, you can ensure that your procurement process is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with your specific needs. Whether you are sourcing for the automotive, construction, or any other industry, this checklist will help you navigate the complexities of metal casting procurement.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your technical requirements is the foundation of a successful sourcing process. Clearly outline the type of metal, dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes needed for your projects. This clarity will help you communicate effectively with suppliers and ensure that you receive products that meet your exact specifications.
– Considerations: Are you looking for aluminum, steel, or another alloy? What are the critical dimensions and tolerances for your application?
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify suppliers with a solid reputation in the metal casting industry. Utilize online resources, trade directories, and industry associations to compile a list of potential suppliers. Look for companies that specialize in the specific type of casting you require, whether it’s sand casting, die casting, or investment casting.
– Tip: Pay attention to customer reviews and ratings on platforms like Trustpilot or industry-specific forums.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before entering into a business relationship, verify that potential suppliers hold relevant certifications. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards indicate a commitment to quality and continuous improvement. This step is crucial for ensuring that the products you receive meet international standards and regulations.
– Action: Request copies of certification documents and check their validity with the issuing bodies.
Step 4: Request Samples and Quotes
Once you have narrowed down your list of suppliers, request samples of their products and obtain detailed quotes. Samples allow you to evaluate the quality of the metal casting, while quotes provide insight into pricing structures and lead times. Ensure that the quotes include all potential costs, such as shipping and handling.
– Key Points: Assess the quality of the samples against your specifications. Are the quotes competitive, and do they align with your budget?
Step 5: Assess Production Capabilities
Understanding a supplier’s production capacity is vital to ensure they can meet your order quantities and deadlines. Inquire about their machinery, workforce, and production processes. A reliable supplier should be able to handle both large and small orders efficiently.
– Questions to Ask: What is their typical lead time for orders? Can they accommodate rush orders if necessary?
Step 6: Review Terms and Conditions
Before finalizing your order, carefully review the terms and conditions of the purchase agreement. Pay special attention to payment terms, warranty information, and return policies. Clear terms will help prevent disputes and ensure a smooth transaction.
– Advice: Consult with your legal team or a procurement expert to clarify any ambiguities in the contract.
Step 7: Establish a Communication Plan
Effective communication is crucial for a successful partnership with your supplier. Establish a clear communication plan that outlines how you will interact throughout the project. Specify key contacts, preferred communication channels, and regular update schedules to keep all parties informed.
– Consideration: How often do you need updates on production status? What methods of communication work best for both parties?
By following these steps, you can streamline your sourcing process for metal casting products and make informed decisions that will contribute to the success of your projects.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal casting products Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Casting Products Sourcing?
When sourcing metal casting products, understanding the cost structure is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, or copper alloys) significantly impacts pricing. Premium materials, like high-grade alloys, can elevate costs, while bulk purchasing can reduce unit prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary based on geographical location and the complexity of the casting process. Regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may lead to increased product prices.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are incurred in creating molds and dies. Custom tooling for unique designs can substantially raise initial costs, but they are amortized over larger production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with industry standards. This can lead to higher upfront costs but may reduce long-term expenses related to defects.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can fluctuate based on distance, weight, and method of transport. International buyers must account for customs duties and import taxes, which can further inflate costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. Understanding the market standards for margin can help buyers gauge the fairness of pricing.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Casting Product Costs?
Several factors can influence pricing in the metal casting industry:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for minimum order quantities (MOQs), making it essential for buyers to evaluate their purchasing strategies.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs due to the need for specialized tooling and production processes. Clear communication of requirements can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Selection: The type of metal chosen can drastically change the price. For example, specialty alloys may cost more than standard metals, and fluctuations in raw material prices can impact overall costs.
-
Quality Certifications: Products that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) may carry a premium price. However, these certifications can offer long-term value through reliability and reduced warranty claims.
-
Supplier Factors: A supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may command higher prices but offer greater assurance of quality.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is vital for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the final cost and risk distribution.
What Are the Best Practices for B2B Buyers in Metal Casting Procurement?
B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, should consider the following strategies for effective procurement:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in negotiations to secure better pricing, especially for larger orders. Build relationships to foster trust and long-term partnerships.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors like maintenance, energy consumption, and longevity when evaluating offers.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing dynamics. Currency fluctuations and local market conditions can significantly influence costs, so consider hedging strategies if applicable.
-
Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers. Check references, certifications, and past performance to ensure reliability and quality.
-
Clear Specifications: Providing clear and detailed product specifications can minimize misunderstandings and reduce costs associated with modifications and rework.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for metal casting products can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. The figures provided here are for illustrative purposes only and may not reflect current market rates. Always seek updated quotes and conduct market research to obtain accurate pricing tailored to specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal casting products With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternative Solutions to Metal Casting Products
In the realm of manufacturing, choosing the right method for producing metal components is crucial for operational efficiency and product quality. Metal casting products are widely recognized for their versatility and strength; however, there are alternative solutions that may better suit specific project requirements, especially for international B2B buyers. This analysis compares metal casting with additive manufacturing (3D printing) and forging, two viable alternatives that offer distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Casting Products | Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) | Forging |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High strength and durability | Good for complex shapes; variable strength | Excellent toughness and fatigue resistance |
| Cost | Moderate initial costs; can be high for small runs | High setup costs; lower for small runs | Higher initial investment; cost-effective for large volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires skilled labor and equipment | Relatively easy; minimal tooling needed | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor |
| Maintenance | Moderate; depends on equipment | Low; fewer moving parts | High; equipment wear and tear can be significant |
| Best Use Case | Large, complex parts | Prototyping and small batch production | High-volume production with uniform properties |
Pros and Cons of Each Alternative
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, allows for the creation of complex geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional casting methods. One of its primary advantages is the reduced material waste and the ability to produce parts on-demand, which can significantly lower inventory costs. However, the initial setup costs can be high, and the strength of printed parts can vary depending on the material and process used. This method is best suited for prototyping and small-scale production runs where customization is key.
Forging
Forging is a process that involves shaping metal using localized compressive forces, often resulting in parts that have superior mechanical properties compared to cast products. This method is known for producing strong, durable components that can withstand high stress. While the initial investment in forging equipment is typically higher, it can be more cost-effective for high-volume production due to lower per-unit costs. However, forging requires skilled labor and extensive setup time, making it less practical for small batches or highly complex designs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
When deciding between metal casting products and alternative methods like additive manufacturing and forging, B2B buyers should consider several factors specific to their needs. Evaluate the volume of parts required, the complexity of the designs, and the mechanical properties needed for the final products. Additionally, consider the total cost of ownership, including setup, maintenance, and potential waste. Each method has its unique strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice will depend on aligning these factors with your operational goals and market demands. By carefully analyzing these alternatives, businesses can optimize their manufacturing processes and achieve a competitive edge in their respective industries.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal casting products
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Metal Casting Products?
When sourcing metal casting products, understanding critical technical properties is essential for ensuring quality and performance. Here are several key specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal used in the casting process, such as aluminum alloy, cast iron, or brass. Each grade has distinct properties that affect strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial to meet application requirements and industry standards. -
Tolerance
Tolerance is the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension, such as thickness or diameter. Tight tolerances are essential for components that require precise fitting and functionality, especially in sectors like automotive and aerospace. Understanding tolerance specifications helps buyers ensure that cast parts will fit as intended in their assembly processes. -
Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture of the surface of a casting, which can significantly impact aesthetics and functionality. Common finishes include sanded, polished, or coated surfaces. Buyers should specify surface finish requirements to enhance product performance, reduce wear, and improve corrosion resistance. -
Weight and Volume
Knowing the weight and volume of metal castings is critical for shipping and handling considerations. These metrics influence logistics costs, packaging, and storage solutions. For international buyers, understanding these properties can aid in calculating shipping expenses and compliance with local regulations. -
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment processes, such as quenching and tempering, can alter the mechanical properties of metal castings, enhancing their strength and durability. Buyers should inquire about any heat treatment applied, as it can affect performance in demanding applications. -
Casting Method
The casting method (e.g., sand casting, die casting, investment casting) determines the complexity and surface finish of the final product. Each method has its advantages and limitations, influencing cost, lead time, and production volume. Understanding these methods allows buyers to select the most suitable option for their needs.
What Common Trade Terms Should B2B Buyers Know in Metal Casting?
Familiarity with industry jargon is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the metal casting market. Here are several key terms to understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In metal casting, working with an OEM can ensure that parts meet specific design and quality standards. Buyers should clarify OEM specifications to ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is important for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their production needs while minimizing excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal process where buyers solicit price proposals from suppliers for specific products or services. Issuing an RFQ helps buyers compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best deal. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms used in international trade to clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand their obligations and rights in international transactions, reducing the risk of misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the goods. It encompasses production and shipping time. Understanding lead times is critical for supply chain planning and ensuring timely delivery of essential components. -
Casting Tolerance
This term refers to the allowable deviation from specified dimensions in a casting. It is crucial for ensuring that parts will fit and function correctly in their intended applications. Buyers should specify casting tolerances to align with engineering requirements and avoid costly rework.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing metal casting products, ultimately leading to successful procurement outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal casting products Sector
What Are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Metal Casting Products Sector?
The metal casting products sector is experiencing significant transformations driven by globalization, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences. Key global drivers include the increasing demand for lightweight and high-performance materials across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction. Emerging technologies like 3D printing and advanced computer simulations are reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling manufacturers to produce complex geometries more efficiently and cost-effectively.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can offer not only competitive pricing but also innovative solutions that enhance product quality and reduce lead times. The trend toward digital procurement platforms is also gaining traction, allowing for streamlined communication and transaction processes, which is particularly beneficial for buyers in developing markets such as Nigeria and Brazil.
Moreover, the shift toward localized sourcing is becoming a prominent strategy as companies aim to minimize risks associated with long supply chains. This is especially relevant in the context of disruptions caused by global events, prompting buyers to consider suppliers closer to their operational bases. As a result, the landscape is shifting towards a more collaborative approach, where partnerships are formed based on shared values and mutual growth opportunities.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing in the Metal Casting Products Sector?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing have become paramount considerations for B2B buyers in the metal casting products sector. The environmental impact of traditional metal casting processes is significant, often involving high energy consumption and emissions. Therefore, there is a growing emphasis on adopting ‘green’ practices, such as utilizing recycled materials and implementing energy-efficient technologies. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications and eco-friendly materials.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining importance. Buyers are more inclined to partner with manufacturers that prioritize fair labor practices and transparent sourcing methods. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions where regulatory frameworks are evolving to enforce higher standards of corporate responsibility. As a result, suppliers that can provide evidence of compliance with international sustainability standards are better positioned to win contracts and build lasting relationships with discerning buyers.
Furthermore, the adoption of circular economy principles is influencing sourcing decisions. Buyers are now looking for suppliers that not only produce high-quality casting products but also offer solutions for reusing and recycling materials, thereby minimizing waste and extending the lifecycle of products.
How Has the Metal Casting Products Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the metal casting products sector is marked by significant technological and methodological advancements. Historically, metal casting dates back thousands of years, evolving from simple techniques to complex industrial processes. The introduction of electric furnaces and automated molding systems has revolutionized production capabilities, allowing for increased precision and efficiency.
In recent decades, the sector has witnessed a shift towards specialization, with manufacturers focusing on niche markets and custom solutions. The rise of digital technologies, such as CAD and simulation software, has further enhanced design capabilities, enabling producers to meet the specific needs of diverse industries more effectively. This evolution reflects a broader trend towards innovation and customization in manufacturing, positioning the metal casting products sector as a vital component of modern industrial processes.
Overall, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability imperatives, and historical evolution equips B2B buyers with the insights needed to navigate the complexities of sourcing metal casting products effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal casting products
-
1. How do I choose the right metal casting supplier for my needs?
Choosing the right metal casting supplier involves assessing their experience, capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your industry and positive client testimonials. Request samples of their work to evaluate the quality of their castings. Additionally, consider their manufacturing capabilities, such as the range of materials they can work with and their ability to handle custom projects. Lastly, ensure they comply with relevant international quality standards, which is crucial for maintaining consistency and reliability in your supply chain. -
2. What is the best metal casting method for my project?
The best metal casting method depends on your specific project requirements, including part complexity, material specifications, and production volume. Common methods include sand casting for large parts, die casting for high-volume production of smaller parts, and investment casting for intricate designs. Each method has its advantages; for instance, sand casting is versatile and cost-effective, while die casting offers high precision and surface finish. Engaging with a knowledgeable supplier can help you determine the most suitable method for your application, ensuring cost-effectiveness and optimal performance. -
3. What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal casting products?
Minimum order quantities for metal casting products can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific casting method. Generally, MOQs can range from a few dozen units for smaller, simpler castings to several hundred or even thousands for more complex or mass-produced items. It’s essential to discuss your project needs with potential suppliers to negotiate MOQs that align with your production requirements. Some suppliers may offer flexibility for first-time orders or prototypes, allowing you to test their services before committing to larger quantities. -
4. How do I ensure quality assurance in my metal casting orders?
To ensure quality assurance in your metal casting orders, request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control processes. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to international quality management standards. Additionally, inquire about their inspection methods, including dimensional checks, material testing, and any certifications for the metals used. Establishing clear communication regarding quality expectations from the outset and considering third-party inspections can further enhance your confidence in the final product’s quality. -
5. What payment terms should I expect when sourcing metal casting products?
Payment terms for metal casting products can vary by supplier and region. Common practices include partial upfront payments, with the balance due upon delivery or after an inspection of the goods. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established relationships, while others may require full payment in advance for new clients. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, such as using escrow services for large orders. Always clarify payment methods accepted, including wire transfers, letters of credit, or credit cards, to avoid delays. -
6. How can I navigate international shipping and logistics for my metal casting orders?
Navigating international shipping and logistics for metal casting orders involves understanding import/export regulations, shipping methods, and costs. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping options, considering factors like delivery timelines and budget. Familiarize yourself with customs procedures in your country to avoid unexpected delays. Engaging a freight forwarder can simplify the logistics process, ensuring compliance with all regulatory requirements and managing the transportation of heavy and bulky castings efficiently. -
7. Can I customize metal casting products to meet my specific requirements?
Yes, many metal casting suppliers offer customization options to cater to specific project requirements. This can include alterations in design, size, material composition, and surface finish. When discussing your project, provide detailed specifications and any technical drawings to help the supplier understand your needs. Be prepared for discussions about lead times and costs associated with custom work, as these can vary based on the complexity of the modifications. Collaborating closely with the supplier during the design phase can lead to better outcomes. -
8. What industries commonly use metal casting products?
Metal casting products are utilized across a diverse range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and consumer goods. Specific applications include components for machinery, automotive parts, plumbing fixtures, and decorative items. Understanding the industry standards and requirements for your specific sector is vital for ensuring compatibility and performance. When sourcing, consider suppliers that specialize in your industry to benefit from their expertise and knowledge of relevant regulations and quality standards, enhancing your supply chain reliability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Metal Casting Products Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. PMC Supplies – Sand Casting Set
Domain: pmcsupplies.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: This company, PMC Supplies – Sand Casting Set, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Castings for Industry – Industrial and Aluminum Castings
Domain: castingsforindustry.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Pump Housing, Ring Segment Castings, Industrial Furnace Doors, Fire Hydrant Housing, Fire Hydrant Neck, Heat Treatment Furnace, Large Aluminum Mounting Plate, Aluminum Gear Box, Aluminum Position Indicator, Blade Housing, Brass Chain Links, Wire Griper, Bronze Eye Bolt, Hand Wheel Casting, Brass Swing Support Casting, Powder Coated Alignment Casting, High Polished Stirrup, Aluminum Foot Petal, Cap…
3. Jets Inc – Casting and Melting Products
Domain: jetsinc.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Casting and Melting products include: Fluxes, Casting Flasks and Sprue Bases (Perforated Flasks, Rubber Bases, Stainless Steel Solid Casting Flasks), Crucible Handles and Tongs, Crucibles and Rods (Carbon Stirring Rod, Casting Crucible, Ceramics, Ceramic Melting Crucible Cups, Ceramic Melting Crucible Dish, Graphite Crucible, Induction Melting Crucible, Salamander, Clay Graphite Crucible, Delf Cla…
4. Dy-Kast Supply – Die Casting Equipment
Domain: dykast.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Dy-Kast Supply offers a wide range of products for die casters and foundries, including: Ladles, Skimmers, Electric Infrared Die Heaters, Die Clamps, T-Slot Bolts, Nuts, Washers, Nozzle Gaskets, Thermocouples, Tongs, Cleaning Tools, Pyrometers, Sow Molds, Ingot Molds, Graphite Molds, Portable Pumps, Mixers, Non-Ferrous Melting Equipment, Aluminum Furnaces, Gold and Silver Furnaces, Lead Metal Melt…
5. Pyrotek – Foundry and Die Casting Solutions
Domain: pyrotek.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Foundry and Die Casting Products include: Anode Bake Furnace, Casthouse, Potroom, Rod Shop, Acoustic and Thermal solutions, Glass (Container and Flat), Mineral Processing, Power Generation. Services offered: pump rebuild, refractory repair, metal quality evaluations, dross management, flux practices. Key product categories: Adhesives, Assembly, Cements, Cast Iron Casting Moulds, Sow Moulds, Crucib…
6. Cast Technologies – Automotive and Marine Metal Solutions
Domain: casttechnologies.net
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Top Casting Industries: 1. Automobile Industry: Uses cast iron and aluminum alloy for engine blocks, die castings made of zinc and magnesium for fuel-efficient vehicles. 2. Marine Industry: Produces high-quality metal products using stainless steel, aluminum, and copper alloys for valves, propellers, and pumps. 3. Construction: Relies on cast iron for foundational components, utility holes, manhol…
7. Midwest Metal Products – Metalcasting Solutions
Domain: midwestmetalproducts.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Metalcasting process involves pouring molten metal into molds made of sand, metal, or ceramic to create complex parts. Common metals used include iron, aluminum, magnesium, zinc, steel, and copper-based alloys. Casting weight capacity: up to 1500 lbs (iron) or 1100 lbs (steel). Available alloys: Stainless Steel, Low Alloy Steel, Plain Carbon Steel, Ductile and Cast Irons, Ni-Hard and Ni-Resist Cas…
8. Midwest Technology – Key Product: Foundry Supplies
Domain: midwesttechnology.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: Key product details for Foundry Supplies at Midwest Technology include:
1. **Crucibles**: Various types including graphite and silicon, available in different capacities and pour styles. Sizes include:
– Bay State Graphite Crucible, Top Pour, 7-1/8″H x 5-7/8″ dia. – $216.00
– Bay State Graphite Crucible, Top Pour, 11-1/2″H x 9-5/16″ dia. – $409.00
– Bay State Graphite Crucible, Bottom Po…
9. Chicago White Metal Casting – High Pressure Die Casting Solutions
Domain: cwmdiecast.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Chicago White Metal Casting, Inc. specializes in high pressure die casting with a focus on Aluminum, Magnesium, and Zinc alloys. They offer a complete range of services including engineering design, tooling, machining, finishing, and contract assembly. Their capabilities cater to various industries such as medical, automotive, transportation, recreational, and alternative energy. Key product offer…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal casting products
In navigating the complex landscape of metal casting products, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical factor for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse applications of metal castings—from automotive components to construction materials—enables businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to tailor their sourcing strategies effectively. Key takeaways include prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate reliability, quality, and adherence to international standards, which can significantly impact operational efficiency and product integrity.
Investing time in evaluating suppliers based on their capabilities, certifications, and industry reputation can lead to long-term partnerships that foster innovation and cost savings. Additionally, leveraging advanced technologies and sustainable practices in the sourcing process can enhance competitiveness in today’s market.
Looking ahead, as global demand for metal casting products continues to rise, the importance of proactive sourcing strategies will only increase. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed on industry trends and engage with suppliers who are committed to excellence and sustainability. By doing so, they position themselves not just as participants in the market but as leaders driving growth and innovation in their respective regions.