Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for metal bending services
In today’s competitive landscape, sourcing high-quality metal bending services can pose significant challenges for international B2B buyers. The complexities involved in understanding material specifications, tolerances, and the intricacies of the bending process can lead to costly delays and suboptimal product outcomes. This guide aims to demystify the global market for metal bending services, offering insights into various types of bending techniques, their applications across industries, and essential considerations for supplier vetting.
From precision bending for custom parts to large-scale production runs, this comprehensive resource will equip buyers with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions. We delve into critical aspects such as cost structures, lead times, and the importance of clear communication between buyers and suppliers. Moreover, our focus extends to key markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including emerging players like Vietnam and Brazil, ensuring that regional nuances and market trends are thoroughly addressed.
By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, B2B buyers will not only enhance their understanding of metal bending services but also streamline their procurement processes, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and product quality. As you navigate the complexities of sourcing these services, our aim is to empower you with actionable strategies and expert knowledge to drive your business forward.
Understanding metal bending services Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Bending | Utilizes CNC machinery for high precision; supports complex designs. | Aerospace, automotive, electronics manufacturing. | Pros: High accuracy, repeatability. Cons: Higher initial setup costs. |
| Hydraulic Bending | Employs hydraulic pressure for bending; effective for thick materials. | Heavy machinery, construction, HVAC systems. | Pros: Handles large parts, powerful. Cons: Slower than CNC for small runs. |
| Manual Bending | Relies on manual tools; suitable for low-volume production. | Prototyping, custom one-off parts. | Pros: Cost-effective for small batches. Cons: Less precision and repeatability. |
| Press Brake Bending | Uses a press brake to create bends; versatile for various materials. | Metal fabrication, furniture manufacturing. | Pros: Suitable for high-volume runs. Cons: Requires skilled operators. |
| Laser Bending | Combines laser cutting with bending; allows intricate designs. | Artistic metalwork, signage, custom fabrication. | Pros: High detail, minimal material waste. Cons: Limited to thinner materials. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of CNC Bending Services?
CNC bending services leverage computer numerical control technology to achieve high precision in metal bending processes. This method is particularly advantageous for complex geometries and tight tolerances, making it a preferred choice in industries such as aerospace and automotive. When selecting CNC bending, buyers should consider the initial setup costs, which can be higher than other methods, but are often offset by the long-term benefits of accuracy and repeatability.
How Does Hydraulic Bending Differ from Other Methods?
Hydraulic bending utilizes powerful hydraulic pressure to bend thick materials, making it ideal for heavy machinery and construction applications. This method is particularly effective for producing large parts that require significant force to achieve desired shapes. Buyers should evaluate the production speed versus the volume of parts needed, as hydraulic bending may be slower than CNC methods for smaller runs but excels in handling robust materials.
When Should You Consider Manual Bending?
Manual bending is a traditional approach that relies on hand tools and skilled labor, making it suitable for low-volume production and prototyping. This method is cost-effective for creating custom one-off parts but may lack the precision and consistency found in automated processes. B2B buyers looking for flexibility and lower costs for small batches may find manual bending to be a viable option, although they should be aware of potential quality variations.
Why Is Press Brake Bending Popular in Metal Fabrication?
Press brake bending is a versatile technique that employs a press brake machine to create precise bends in various materials. This method is widely used in metal fabrication and furniture manufacturing due to its ability to handle high-volume production runs efficiently. Buyers should consider the skill level of operators required for press brake bending, as the process necessitates trained personnel to ensure quality and accuracy.
What Advantages Does Laser Bending Offer?
Laser bending combines cutting-edge laser technology with bending processes to achieve intricate designs with minimal material waste. This innovative approach is particularly beneficial for artistic metalwork and custom fabrication projects. While laser bending allows for high detail, it is typically limited to thinner materials. Buyers should assess the material thickness and design complexity to determine if laser bending aligns with their project requirements.
Key Industrial Applications of metal bending services
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of metal bending services | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Production of chassis components and brackets | Enhanced structural integrity and lightweight design | Precision tolerances, material compatibility, and lead times |
| Construction | Fabrication of structural steel supports | Cost-effective and durable solutions for infrastructure | Local sourcing for reduced shipping costs and faster delivery |
| Aerospace | Creation of complex aircraft components | High precision and weight reduction for performance | Compliance with industry standards and certifications |
| Electronics | Enclosures and housings for electronic devices | Improved aesthetics and protection of components | Custom design capabilities and rapid prototyping services |
| Furniture Design | Custom metal furniture pieces | Unique designs that enhance brand identity | Material selection and finishing options for aesthetic appeal |
How is Metal Bending Services Used in Automotive Manufacturing?
In the automotive sector, metal bending services are crucial for producing chassis components and brackets that ensure vehicle safety and performance. These components must meet stringent standards for precision and strength, necessitating advanced bending techniques that achieve tight tolerances. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers with ISO certifications and robust quality control measures to guarantee product reliability and compliance with local regulations.
What Role Does Metal Bending Play in Construction?
Metal bending is extensively used in the construction industry for fabricating structural steel supports, beams, and frames. These products are essential for creating durable and cost-effective infrastructure solutions. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider sourcing from local manufacturers to minimize transportation costs and lead times, while also evaluating the supplier’s ability to handle large-scale orders without compromising quality.
Why is Metal Bending Important in Aerospace Applications?
In aerospace, metal bending services are employed to create complex components such as fuselage sections and wing structures. The precision required in this industry is unparalleled, as even minor deviations can impact safety and performance. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to strict aerospace standards and can demonstrate a track record of delivering high-quality, lightweight components that meet regulatory requirements.
How Does Metal Bending Benefit the Electronics Sector?
In the electronics industry, metal bending is vital for producing enclosures and housings that protect sensitive components. These products often require intricate designs that not only provide protection but also enhance the aesthetic appeal of the final product. Buyers should seek suppliers who offer rapid prototyping and customization options, allowing for quick iterations and adjustments based on design feedback, particularly beneficial for businesses in competitive markets like Europe and South America.
What Advantages Does Metal Bending Offer in Furniture Design?
Metal bending services are increasingly utilized in furniture design to create custom metal pieces that stand out in the market. This application allows designers to craft unique shapes and forms that enhance the overall aesthetic of their products. When sourcing these services, businesses should focus on suppliers that offer a variety of material options and finishing techniques, ensuring that the final product aligns with their brand image and customer preferences.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘metal bending services’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Design Specifications for Metal Bending
The Problem: Many B2B buyers encounter challenges when their designs do not align with the specifications set by metal bending service providers. For instance, a company may submit a design with flanges that are too close to one another, leading to potential collisions during the bending process. This oversight not only delays production but also results in increased costs due to rework and extended lead times. Buyers often feel frustrated, especially when they are not well-versed in the technical aspects of metal bending.
The Solution: To mitigate this issue, buyers should invest time in understanding the specific bending requirements of their chosen provider. This includes familiarizing themselves with the bending guidelines, such as minimum flange lengths, bend radius specifications, and material thickness parameters. Many service providers offer downloadable resources or guidelines that detail these specifications. By utilizing these resources, buyers can ensure their designs are optimized for the bending process, thereby reducing the likelihood of collisions or other manufacturability issues. Furthermore, engaging in preliminary conversations with the service provider can yield valuable insights and lead to a smoother design submission process.
Scenario 2: Delays in Production Due to Inaccurate Quotes
The Problem: A frequent pain point for B2B buyers is receiving inaccurate quotes that do not reflect the final cost of their metal bending projects. This can occur when buyers upload their designs without a clear understanding of the associated costs, leading to unexpected price hikes after the initial quotation. Such discrepancies can disrupt project timelines and budgets, particularly for companies operating under tight financial constraints.
The Solution: To avoid these pitfalls, B2B buyers should seek out metal bending services that provide instant pricing calculators. These tools allow buyers to upload their designs and receive real-time cost estimates based on accurate parameters such as material type, thickness, and complexity of the bends. By using these calculators, buyers can adjust their designs to fit their budget before committing to production. Additionally, establishing a clear line of communication with the service provider can help clarify any uncertainties regarding pricing and ensure that all costs are accounted for upfront. This proactive approach helps maintain budgetary control and minimizes surprises later in the process.
Scenario 3: Complications with Material Selection
The Problem: Selecting the appropriate material for metal bending can be daunting for B2B buyers, especially when they must consider factors such as tensile strength, bendability, and finish. A common scenario arises when a buyer opts for a material that seems suitable but ultimately leads to complications during the bending process. For instance, a material may require a specific bend radius that the service provider cannot accommodate, resulting in redesigns and delays.
The Solution: To navigate material selection effectively, buyers should prioritize open communication with their metal bending service provider. Engaging in discussions about material properties and their implications for bending can significantly enhance decision-making. Many providers offer material catalogs that include detailed specifications, including bendability, recommended thicknesses, and finish options. By thoroughly reviewing these catalogs and consulting with technical experts from the service provider, buyers can make informed choices that align with their project requirements. Furthermore, considering prototyping services can allow buyers to test materials and designs before full-scale production, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring a smoother overall process.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for metal bending services
What Are the Key Properties of Common Materials Used in Metal Bending Services?
When selecting materials for metal bending services, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations. This analysis will focus on four commonly used materials: steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. Each material has unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and suitability of the final product.
Steel: A Versatile Choice for Structural Applications
Steel is renowned for its strength and durability, making it an excellent choice for structural applications. It typically has a high tensile strength and can withstand significant pressure and stress. However, steel is susceptible to corrosion if not properly treated, which may limit its use in certain environments.
Pros: Steel is generally cost-effective and widely available, making it suitable for large-scale production. Its strength allows for thinner sections in designs, reducing overall weight.
Cons: The need for surface treatments, such as galvanization or painting, to prevent rust can increase manufacturing complexity and cost. Additionally, steel’s weight can be a drawback in applications requiring lightweight materials.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for construction and automotive applications where strength is paramount. However, it may not be suitable for environments with high humidity or corrosive substances without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM A36 or EN 10025. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing may be influenced by local availability and pricing.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion-Resistant and Durable
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications exposed to moisture or chemicals. It maintains its strength at high temperatures and is easy to clean, which is a significant advantage in the food and medical industries.
Pros: Its aesthetic appeal and resistance to tarnishing make stainless steel a preferred choice for consumer products and architectural applications.
Cons: The higher cost compared to regular steel can be a limiting factor, especially for large projects. Additionally, stainless steel can be more challenging to bend due to its work-hardening properties.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for applications in harsh environments, such as marine or chemical processing. Its compatibility with a variety of media makes it versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM A240 or EN 10088 is crucial. Buyers in Europe may prefer specific grades like 304 or 316, which are commonly used in their markets.
Aluminum: Lightweight and Versatile
Aluminum is well-known for its lightweight properties, making it an excellent choice for applications where weight savings are critical. It has good corrosion resistance and can be easily formed into complex shapes.
Pros: Aluminum is relatively inexpensive and offers a high strength-to-weight ratio. It is also recyclable, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Cons: While aluminum is easier to bend than steel, it has lower tensile strength, which may limit its use in high-stress applications. Additionally, it can be more expensive than steel, depending on the alloy.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods where weight reduction is essential. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for many applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific alloy needed for their application, such as 6061 or 5052, and ensure compliance with relevant standards like ASTM B221.
Copper: Excellent Electrical Conductivity
Copper is primarily known for its exceptional electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for electrical applications. It also has good corrosion resistance and is relatively malleable.
Pros: Copper’s conductivity and thermal properties make it ideal for electrical wiring and components. It is also resistant to corrosion, particularly in non-oxidizing environments.
Cons: The high cost of copper can be a significant drawback, and it is heavier than aluminum, which may not be suitable for all applications. Additionally, its softness can limit its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Copper is often used in electrical and plumbing applications, where conductivity and resistance to corrosion are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM B170 or EN 1977 is essential. Buyers should also be aware of local market conditions, as copper prices can fluctuate significantly.
Summary Table of Material Properties
| Material | Typical Use Case for metal bending services | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, challenging to bend | High |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive parts | Lightweight, good corrosion resistance | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical wiring, plumbing | Exceptional electrical conductivity | High cost, limited stress resistance | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in metal bending services, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for metal bending services
What Are the Main Stages of the Metal Bending Manufacturing Process?
The manufacturing process for metal bending services typically comprises several critical stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring the final product meets the specifications required by B2B clients.
How Is Material Prepared for Metal Bending?
Material preparation is the first step in the metal bending process. This involves selecting the appropriate metal type—such as steel, aluminum, or copper—based on the project requirements. After selecting the material, it is cut to size using techniques like laser cutting or shearing. This initial cutting process must be precise, as any inaccuracies can affect the subsequent bending operations.
Once the material is cut, it undergoes inspection to ensure it meets quality specifications. This may include checking for surface defects, thickness, and overall integrity. Some companies may also use automated systems that scan the material for defects before it moves to the next stage.
What Techniques Are Used in the Forming Stage?
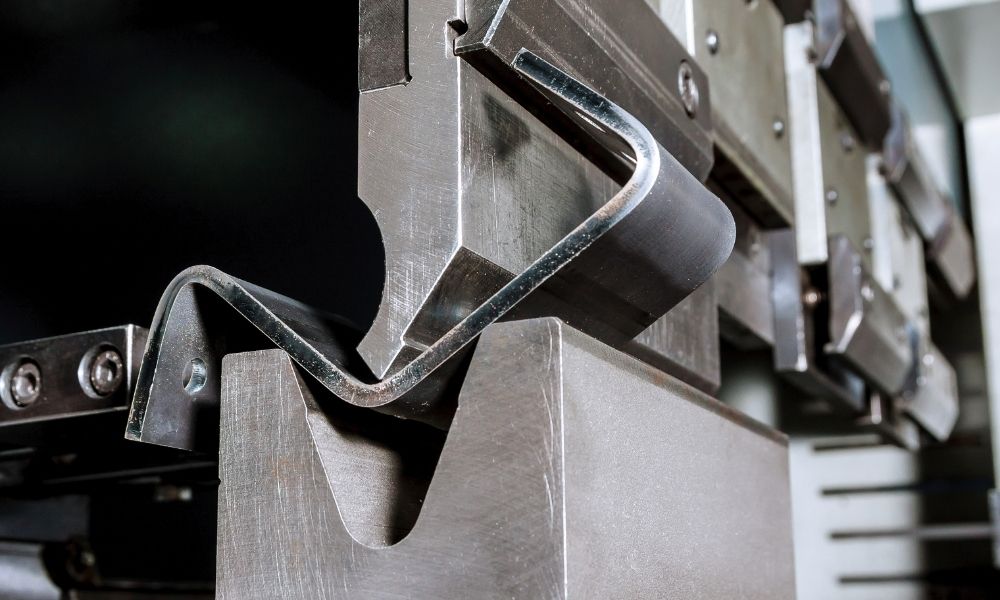
The forming stage is where the actual bending occurs. This is typically achieved using CNC (Computer Numerical Control) bending machines, which allow for high precision and repeatability. Advanced machines can achieve tolerances as tight as +/- 0.0001 inches, ensuring that each bend is accurate.
Key techniques in this stage include air bending, bottom bending, and coining. Air bending is the most common method, where the material is bent using a punch and die with a specific angle. Bottom bending, on the other hand, provides a more accurate bend but requires more force. Coining is used for high-precision applications, where the material is forced into the die to create exact angles.
How Are Components Assembled After Bending?
After the bending process, components may need to be assembled, especially for complex parts that consist of multiple bent sections. This may involve welding, fastening, or other methods of joining parts together. Proper assembly is crucial for maintaining the structural integrity and functionality of the final product.
During assembly, it’s essential to adhere to design specifications closely. Misalignment or incorrect joining can lead to failures in functionality or aesthetic issues in the finished product. Quality control checks are often implemented at this stage to ensure that all components fit together as intended.
What Finishing Processes Are Commonly Applied?
The final stage of the metal bending manufacturing process is finishing, which enhances the aesthetic and functional properties of the product. Common finishing processes include powder coating, anodizing, and surface treatment. Powder coating provides a durable and visually appealing finish that protects the metal from corrosion and wear.
Depending on the application, additional processes such as tapping, countersinking, or polishing may also be applied. These finishing touches not only improve the product’s appearance but also its usability, especially in components that will be interfacing with other parts or systems.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Essential for Metal Bending Services?
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of metal bending services that ensures the final product meets both international standards and customer expectations. Companies often adhere to various quality management systems, with ISO 9001:2015 being one of the most recognized standards globally.
How Do International Standards Impact Quality Control?
ISO 9001:2015 focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction, providing a framework for organizations to manage their quality processes effectively. In addition to ISO standards, industry-specific certifications like CE (Conformité Européenne) for the European market and API (American Petroleum Institute) for oil and gas applications may also be relevant. These certifications guarantee that the products meet rigorous safety and quality requirements.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Metal Bending?
Quality control in metal bending typically includes several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials for compliance with specifications. Any defects identified at this stage can prevent downstream issues.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the bending and assembly processes, operators conduct regular checks to ensure that each stage meets specified tolerances. This may involve measuring angles, lengths, and other critical dimensions.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the product is completed, a final inspection is conducted. This may include visual inspections, dimensional checks, and functional tests to ensure the product performs as intended.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used to Ensure Quality?
Various testing methods can be employed to verify the integrity of the bent metal parts. Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques, such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspections, can detect internal defects without damaging the product. Additionally, mechanical testing methods, like tensile testing, can assess the material’s strength and elasticity.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers. This can include:
-
Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality management systems firsthand.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation of quality inspections and testing results can provide insight into a supplier’s adherence to quality standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies to review the manufacturing process can offer an unbiased assessment of product quality.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of quality control is crucial. Different regions may have varying standards and regulations, which can affect product acceptance. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with local regulations, which may differ from international standards.
Additionally, buyers should consider language barriers and cultural differences that may impact communication regarding quality expectations. Clear, documented specifications and regular communication can help bridge these gaps.
Conclusion
The metal bending manufacturing process is multifaceted, involving precise techniques and rigorous quality assurance measures. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes is essential to ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific requirements. By focusing on quality control standards and actively verifying supplier capabilities, businesses can mitigate risks and enhance their procurement strategies.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘metal bending services’
In the competitive landscape of B2B procurement, sourcing metal bending services requires a strategic approach to ensure quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. This checklist will guide you through the essential steps to make informed decisions that align with your project needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Clearly outline the specifications for your metal bending project, including material type, thickness, bend radius, and tolerances. This step is crucial as it sets the foundation for communicating your needs to potential suppliers. Be specific about your design requirements, as different materials and bending techniques may influence the final product’s performance.
Step 2: Research and Shortlist Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in metal bending services. Look for companies with a strong reputation in your industry and positive customer reviews. Create a shortlist based on factors such as location, service capabilities, and expertise in handling materials that align with your requirements.
Step 3: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you are considering hold relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001:2015. Certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality management and consistency in production standards. Additionally, check if they comply with international standards, which is especially important for cross-border transactions.
Step 4: Evaluate Technical Capabilities
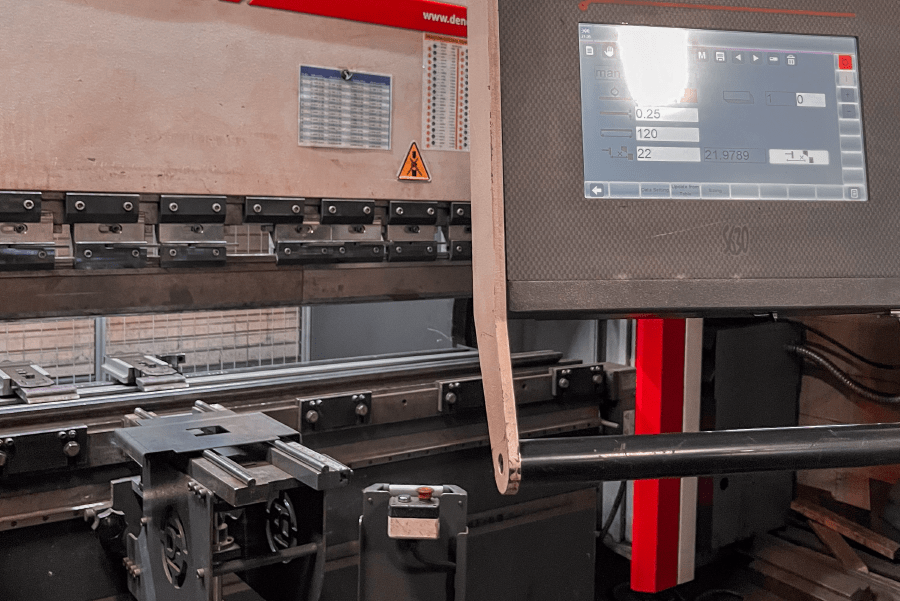
Assess the technical capabilities of shortlisted suppliers, including their machinery, technology, and expertise in precision bending. Verify that they can meet your specifications and tolerances, such as angle precision and material thickness. Inquire about their ability to handle complex designs and the availability of modern CNC equipment, which can enhance accuracy and reduce lead times.
Step 5: Request Samples and Prototypes
Before making a large commitment, ask for samples or prototypes of your designs. This step allows you to evaluate the quality of their work and confirm that their processes align with your expectations. Reviewing a sample can also help identify any potential issues early in the production process, saving time and costs down the line.
Step 6: Discuss Pricing and Lead Times
Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing structures and lead times for your projects. Understanding their pricing models—whether based on volume, complexity, or material—will help you budget effectively. Additionally, clarify lead times to ensure they align with your project timeline, as delays can impact your overall operations.
Step 7: Establish Clear Communication Channels
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process. Ensure that your chosen supplier is responsive and open to collaboration. Establish clear points of contact and protocols for feedback, revisions, and updates. This approach fosters a productive relationship and minimizes misunderstandings that can arise during the project.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing metal bending services with confidence, ensuring they select a supplier that meets their technical, quality, and logistical requirements.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for metal bending services Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Metal Bending Services?
Understanding the cost structure of metal bending services is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts costs. Common options such as steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and copper vary in price based on market conditions, thickness, and required specifications. For example, higher tensile strength materials may incur additional costs.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for precision bending. Labor costs can fluctuate based on the complexity of the job and local wage standards. Automated processes can reduce labor costs but may require higher initial investments in technology.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facility operation, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Companies with advanced CNC technology may have higher overhead but can offer superior precision and efficiency.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific bends can be a significant upfront cost. Standard tooling can reduce expenses, but it may limit customization options.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that parts meet specified tolerances requires investment in QC processes. Buyers should expect to pay for thorough inspections and testing, particularly for high-precision applications.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely, particularly for international orders. Factors include the distance, shipping method, and any customs duties applicable based on Incoterms.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on competition and market demand. Understanding the supplier’s positioning can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Metal Bending Costs?
Several factors influence the pricing of metal bending services:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to reduced per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate their needs.
-
Specs/Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should balance their need for specific features against potential cost increases. Clear communication of requirements can help minimize unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: As mentioned, material selection directly impacts pricing. Specialized or rare materials may incur higher costs, so buyers should consider alternatives that meet their needs without excessive expense.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with certifications (e.g., ISO 9001:2015) may charge more due to their commitment to quality. While this can ensure reliability, buyers should weigh the benefits against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and capacity can all influence pricing. Established suppliers with a good track record may command higher prices, but they often provide better service and reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total cost significantly, as they define responsibilities for shipping and insurance.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency in Metal Bending?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, here are some actionable tips:
-
Negotiate: Always seek to negotiate terms, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may have room for flexibility on pricing, payment terms, or additional services.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not only the initial price but also long-term costs, including maintenance, shipping, and potential delays. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher TCO if quality or service is compromised.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances for International Transactions: Be aware of currency fluctuations, customs fees, and local regulations that could affect pricing. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these challenges.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of costs for materials, labor, and any additional services. This transparency helps in making informed comparisons between suppliers.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online platforms for instant pricing and quoting. These tools can provide a clearer understanding of costs and streamline the ordering process.
In summary, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influences of metal bending services enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their budget and project requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing metal bending services With Other Solutions
Introduction: Understanding Alternatives to Metal Bending Services
When considering solutions for shaping metal, businesses often explore various methods to achieve their desired results. While metal bending services are a popular option due to their precision and versatility, alternative solutions may offer unique benefits depending on specific project requirements. This analysis compares metal bending services with other viable methods, helping B2B buyers make informed decisions tailored to their needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Metal Bending Services | Laser Cutting Services | Forming Presses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision with tolerances of +/- 1° | Excellent for intricate designs | Suitable for high-volume production |
| Cost | Moderate, varies by complexity | Generally lower for complex shapes | Higher initial investment, but cost-effective for large batches |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly with online quoting | Requires design expertise | Complex setup, often needs skilled operators |
| Maintenance | Low, mostly software updates | Moderate, involves equipment upkeep | High, requires regular maintenance checks |
| Best Use Case | Custom prototypes and small to medium runs | Complex shapes, intricate designs | Large volume production with consistent parts |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Laser Cutting Services
Laser cutting is a highly efficient method for producing complex shapes and designs in metal sheets. This technology utilizes focused laser beams to cut materials with exceptional precision. The major advantage of laser cutting is its ability to create intricate patterns that would be challenging or impossible with traditional bending techniques. Additionally, the cost per unit can be lower for complex shapes, making it economically favorable for specific applications. However, it may require design expertise to optimize files for cutting, which can introduce additional lead time.
Forming Presses
Forming presses are a traditional method used in manufacturing to shape metal sheets through mechanical force. This technique is particularly advantageous for high-volume production where consistent part geometry is critical. While the initial investment in forming presses can be substantial, the long-term cost savings for mass production can make it a viable option. However, the setup process is often complex and requires skilled operators to ensure quality. Forming presses are best suited for projects where large quantities of identical parts are needed, rather than one-off prototypes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate method for metal shaping depends largely on your project’s specific requirements. Metal bending services excel in precision and flexibility, making them ideal for custom prototypes or smaller production runs. In contrast, laser cutting services provide a cost-effective solution for intricate designs, while forming presses are best suited for large-scale production needs. B2B buyers should assess their project scope, budget, and desired outcomes to determine which solution aligns best with their operational goals. By weighing the pros and cons of each alternative, businesses can make strategic decisions that enhance their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for metal bending services
When engaging with metal bending services, understanding key technical properties and trade terminology is essential for making informed decisions. This section outlines critical specifications and common jargon that will enhance your knowledge and facilitate smoother transactions in the B2B marketplace.
What are the Critical Specifications for Metal Bending Services?
-
Material Grade
Material grade refers to the classification of the metal being used, such as steel, aluminum, or stainless steel. Each grade has unique properties, including tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and formability. Choosing the right material grade ensures that the final product meets performance requirements and complies with industry standards, which is particularly important for buyers in sectors like construction, automotive, and manufacturing. -
Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In metal bending, tolerances can affect the fit and function of parts. Common tolerances for bending services include angular tolerance (often ±1 degree) and length tolerance (typically ±0.015 inches). Understanding these tolerances helps buyers ensure that parts will fit correctly in assemblies, reducing the need for costly adjustments or rework. -
Bend Radius
The bend radius is the internal radius of a bent part. It plays a critical role in determining how well the material will perform during bending and its subsequent application. A smaller bend radius may lead to stress concentrations, which can compromise the part’s integrity. Buyers should be aware of the minimum bend radius specified for different materials to avoid design failures. -
K-Factor
The K-factor is a ratio that represents the relationship between the material’s thickness and its bend allowance. This specification is crucial for accurately calculating flat patterns from 3D designs. Knowing the K-factor helps buyers design parts that will maintain their intended dimensions after bending, which is vital for the manufacturability of complex geometries. -
Minimum Flange Length
Minimum flange length is the shortest length of a flange that can be bent without causing deformation or failure. This specification is essential for designs that incorporate flanges, as inadequate lengths can lead to operational issues. Understanding these limits allows buyers to optimize their designs for both aesthetics and functionality.
What Are Common Trade Terms in Metal Bending Services?
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are used in another company’s end products. In the context of metal bending, OEMs often require precision components that meet specific standards. Understanding this term is critical for buyers looking to source parts for larger manufacturing processes. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers, as it can impact inventory management and cash flow. Buyers should always confirm MOQs with suppliers to ensure they can meet their production needs without incurring excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a formal document sent to suppliers to solicit pricing and terms for specific products or services. For metal bending services, issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare options and negotiate better deals. Clear specifications in RFQs lead to more accurate quotations, which can streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms is crucial for international B2B transactions, as they define who is responsible for costs and risks at various stages of transportation. -
DFM (Design for Manufacturability)
DFM refers to the engineering practice of designing parts in a way that facilitates their manufacturing. When engaging with metal bending services, applying DFM principles can lead to more efficient production processes, reduced costs, and improved product quality. Buyers who prioritize DFM can significantly enhance their supply chain effectiveness.
By grasping these critical specifications and trade terms, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of metal bending services with greater confidence, ensuring their projects are completed on time and within budget.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the metal bending services Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends in Metal Bending Services
The global metal bending services market is experiencing significant growth, driven by an increasing demand for customized and precision-engineered components across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, seek to enhance their supply chain efficiencies, several key trends are emerging.
One prominent trend is the integration of advanced technology in metal bending processes. Companies are increasingly adopting automation and CNC technology, which allows for higher precision, reduced lead times, and lower labor costs. Instant pricing platforms and online design tools are also becoming commonplace, enabling buyers to receive real-time feedback on manufacturability and costs. This trend is particularly appealing to businesses in developing regions like Vietnam and Brazil, where rapid prototyping and reduced time-to-market can significantly impact competitiveness.
Moreover, the shift toward just-in-time manufacturing is compelling suppliers to streamline their operations and improve communication with clients. Enhanced transparency regarding bending specifications, tolerances, and capabilities helps buyers make informed decisions. As global supply chains become more interconnected, understanding local regulations and material sourcing options is essential for international buyers to mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
How is Sustainability Shaping Metal Bending Services in B2B?
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority for B2B buyers in the metal bending services sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including metal bending, has prompted businesses to seek out suppliers committed to ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing waste, recycling materials, and using energy-efficient technologies.
Ethical supply chains are not just a trend; they are becoming a requirement for many organizations looking to enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profiles. Buyers are increasingly interested in suppliers with relevant sustainability certifications, such as ISO 14001, which signifies effective environmental management systems. Additionally, the use of recycled metals and eco-friendly materials is gaining traction, as these choices not only reduce environmental impact but also can lead to cost savings.
Furthermore, as consumers become more environmentally conscious, B2B companies are finding that sustainable practices can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty. Suppliers that actively promote their green initiatives are likely to attract a growing segment of buyers who prioritize sustainability in their purchasing decisions.
What Has Been the Evolution of Metal Bending Services?
The evolution of metal bending services can be traced back to traditional hand-operated tools, which were primarily utilized for basic applications. Over the decades, the industry has witnessed a seismic shift with the advent of advanced machinery and computer numerical control (CNC) technology. This transformation has enabled manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of precision and efficiency, which are crucial in today’s competitive market.
In recent years, the focus has expanded from merely bending metals to providing comprehensive solutions that include design assistance, instant pricing, and rapid prototyping. This evolution reflects the changing needs of B2B buyers who require not only high-quality products but also flexible, responsive service that can adapt to the fast-paced nature of modern manufacturing. As the industry continues to advance, the integration of digital tools and sustainable practices will likely shape its future trajectory, ensuring that metal bending services remain a vital component of global supply chains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of metal bending services
-
How do I solve issues with part design for metal bending?
To avoid complications during the metal bending process, ensure your part design includes adequate clearances for flanges and bends. Utilize design guidelines provided by your bending service to confirm that your dimensions align with their specifications. Before submission, conduct a manufacturability check to identify potential issues such as tooling collisions or insufficient bend radii. Collaborating early with your supplier can streamline the process and minimize costly adjustments later in production. -
What is the best material for my metal bending project?
The ideal material for metal bending depends on your project requirements, including strength, weight, and corrosion resistance. Common choices include steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, each with unique properties. For high-stress applications, stainless steel may be preferable, while aluminum is ideal for lightweight structures. Always consult your supplier’s material catalog for detailed specifications, including bending tolerances and minimum flange lengths, to ensure optimal results. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for metal bending services?
Many metal bending service providers cater to both small prototypes and large production runs, often with no minimum order quantities. This flexibility allows businesses to test designs without the risk of overcommitting to large orders. However, it’s essential to confirm specific MOQs with your supplier, as they may vary based on material type, complexity of the design, or specific manufacturing capabilities. -
How do I ensure quality assurance in metal bending services?
Quality assurance in metal bending involves several steps, including selecting an ISO-certified supplier, utilizing advanced CNC technology, and implementing rigorous inspection protocols. Verify that your supplier employs real-time material thickness measurement and maintains strict tolerances for angle and length. Request samples or prototypes to evaluate the quality before committing to larger orders, and ensure that they provide documentation of their quality control processes. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing metal bending services?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, so it’s essential to clarify these before placing an order. Common terms may include upfront deposits, net 30 or net 60 days, or payment upon delivery. For international transactions, consider the implications of currency exchange and transaction fees. Establishing clear payment expectations early can help avoid misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process. -
How can I vet suppliers for international metal bending services?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, certifications (like ISO 9001), and customer reviews. Request references or case studies to gauge their reliability and quality of service. Additionally, evaluate their communication responsiveness and willingness to provide support during the design phase. If possible, visit their facility or utilize third-party audit services to assess their capabilities firsthand. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when ordering metal bending services?
Logistics is critical in ensuring timely delivery of your metal parts. Confirm the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including international shipping options and estimated lead times. Understand their packaging standards to prevent damage during transit. Furthermore, inquire about tracking options and their policies on handling delays or issues that may arise during shipping to ensure a smooth supply chain process. -
Can I customize my metal bending order?
Yes, most metal bending service providers offer customization options to meet specific project needs. This can include variations in material type, thickness, bend angles, and additional services such as powder coating or hardware installation. When placing an order, provide detailed specifications and any necessary CAD files to ensure your requirements are accurately captured. Collaboration with the supplier during the design phase can further enhance the customization process, allowing for adjustments based on manufacturability.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Metal Bending Services Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. OSH Cut – On-Demand Custom Metal Bending Services
Domain: oshcut.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: On-Demand Custom Metal Bending Services offered by OSH Cut include bending in steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper with thicknesses up to 5/16″. The service provides instant pricing and manufacturability feedback by allowing users to upload flat patterns with bend lines or 3D sheet metal models. Precision bending is achieved with back-gauge positioning within +/- 0.0001″, real-time materia…
2. SendCutSend – CNC Sheet Metal Bending Services
Domain: sendcutsend.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: SendCutSend offers CNC sheet metal bending services to transform flat designs into functional parts. Key features include:
– Accuracy: Bends within one degree of accuracy or better, meeting tight tolerances.
– No minimum quantity required.
– Pricing starts at $0.70 per bend in bulk.
– Available materials: 9 metals and 1 plastic, including 5052 H32 Aluminum, Brass, 4130 Chromoly, Copper, G90 Ga…
3. Fabworks – Precision Sheet Metal Bending Service
Domain: fabworks.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Sheet Metal Bending Service at Fabworks offers precision bending with CNC technology, allowing for custom bends between 1-135 degrees with a tolerance of +/- 1 degree angle and +/- .015″ length. No minimum order quantity is required, making it suitable for both prototypes and large production runs. Materials available include aluminum, steel, and stainless steel. Customers can upload 3D STEP files…
4. Bowstone – Metal Bending & Shaping Services
Domain: bowstone.net
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: Bowstone offers metal bending and shaping services using various methods including stamping, die-cutting, hydroforming, and press brake forming. Key services include: Press Brake Forming, Roll Bending, CNC Tube Bending, CNC Sheet Metal Folding, Hydroforming, and Tube End Forming. The company can bend metal up to 12 feet in length and focuses on minimizing waste and achieving precise angles. They p…
5. Eagle Stainless – Custom Metal Bending Services
Domain: eagletube.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Eagle Stainless offers custom metal bending and coiling services for precision bent components used in surgical devices, heat exchangers, instrumentation, and more. They specialize in bending stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and other materials, with sizes ranging from .032″ to 1″ diameters. The bending process adheres to industry standards to prevent kinking and maintain corrosion resistance. C…
6. LSC Metal Fab – Metal Bending and Rolling Solutions
Domain: lscmetalfab.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Metal Bending and Rolling Capabilities: 1. Bending Types: Angle Bending, Beam Bending, Bar Bending, Tube Bending, Pipe Bending, Channel Bending, T-Beam Bending, Spiral Bending. 2. Rolling Types: Plate Rolling, Sheet Rolling, Cone Rolling. 3. Materials: Steel, Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Corten Steel. 4. Industries Served: Agriculture, Architectural, Construction, Metal Artists and Sculptors, Mining…
7. eMachineShop – CNC Bending Services
Domain: emachineshop.com
Registered: 1999 (26 years)
Introduction: CNC Bending services for custom sheet metal parts; utilizes CNC bending equipment; 50+ materials available; free shipping in the USA; 100% quality guaranteed; common applications include brackets, enclosures, cams, and decorative items; materials for bending include aluminum (5052, 6061, 7075), stainless steel (301, 303, 304, 316), brass (260, 360), titanium, and more; thicknesses up to 0.25″ or m…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for metal bending services
In the competitive landscape of metal bending services, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial component for international B2B buyers. By leveraging suppliers that offer advanced technology, such as CNC bending and automated quoting systems, businesses can achieve enhanced precision and efficiency. Understanding critical specifications, such as bend radius and material tolerances, empowers buyers to make informed decisions that minimize errors and reduce lead times.
Furthermore, the trend toward on-demand services allows companies to adapt quickly to market demands, fostering agility in production capabilities. The availability of instant pricing and manufacturability feedback streamlines the design process, mitigating the risks associated with traditional sourcing methods that often involve lengthy back-and-forth communications.
As the metal bending industry evolves, embracing these innovations will be essential for businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to remain competitive. By prioritizing strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers, companies can not only enhance their operational efficiency but also drive sustainable growth. We encourage international buyers to explore these advanced solutions and take proactive steps toward optimizing their sourcing strategies for a successful future in metal bending services.