Contents
Manufacturing Insight: Medical Device Machining
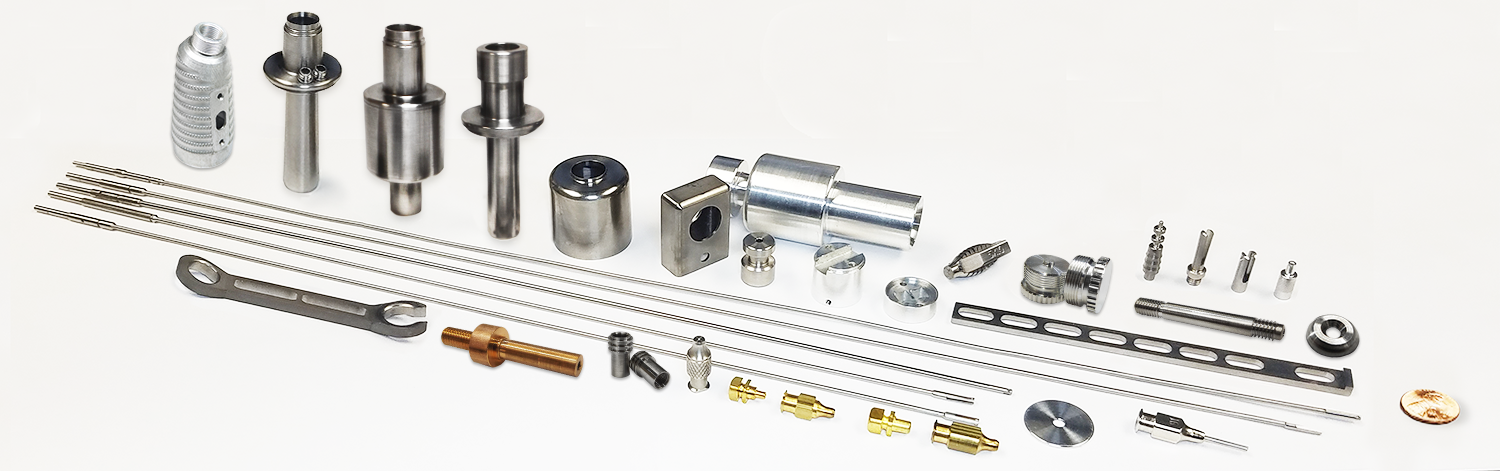

Precision Medical Device Machining: Engineered for Compliance and Performance
Medical device manufacturing demands uncompromising precision, strict regulatory adherence, and mastery of biocompatible materials. At Honyo Prototype, our CNC machining services are engineered specifically for the complexities of medical component production, from rapid prototyping to full-scale production runs. We leverage state-of-the-art multi-axis CNC mills and lathes to achieve micron-level tolerances on critical parts such as surgical instrument components, implant subassemblies, and diagnostic equipment housings. Our processes are rigorously validated under ISO 13485 standards, ensuring full traceability, material certification, and repeatable quality for every component.
Material expertise is central to our medical machining capability. We routinely machine titanium alloys, medical-grade stainless steels (e.g., 316LVM), PEEK, PTFE, and engineered polymers, with strict controls on surface finish and dimensional stability. Our engineering team collaborates closely with clients during DFM to optimize part geometry for manufacturability while meeting stringent biocompatibility and sterilization requirements. Accelerate your development timeline with Honyo’s Online Instant Quote system, providing detailed pricing and lead time estimates for CNC-machined medical components within minutes—no manual submission required. Submit your STEP or IGES file today to experience seamless quoting for precision-critical applications.
Technical Capabilities
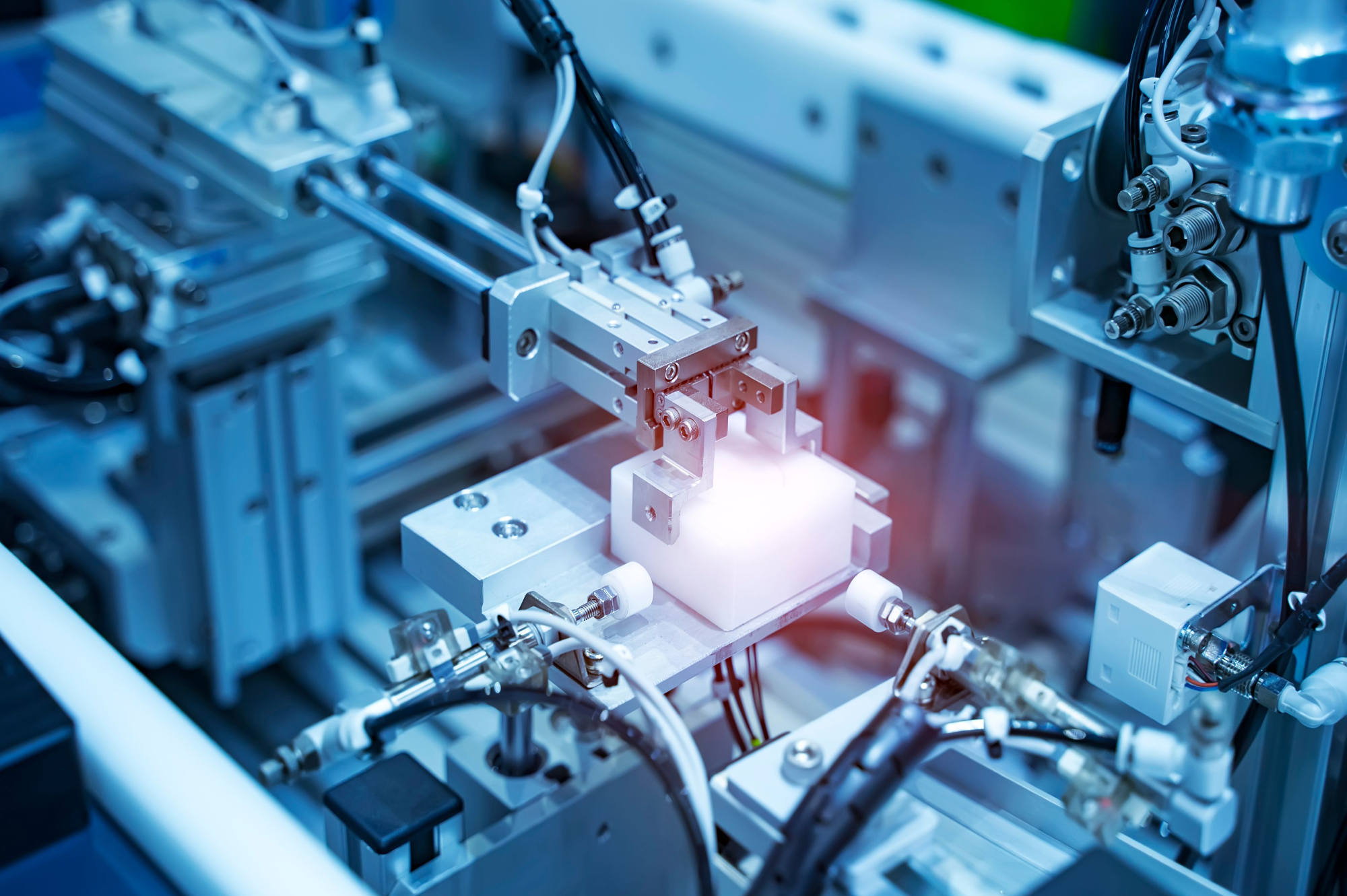
Medical device machining requires high precision, exceptional surface finish, and strict adherence to regulatory standards due to the critical nature of components used in surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis CNC milling, along with precision turning, are widely employed to produce complex geometries with tight tolerances. These processes support a range of biocompatible and sterilizable materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, ABS, and nylon.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Machining Processes | 3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis CNC Milling; CNC Turning |
| Typical Tolerances | ±0.0002″ (5 µm) to ±0.0005″ (12.7 µm) for critical features; tighter tolerances achievable with inspection validation |
| Surface Finish | 16–32 µin (0.4–0.8 µm) Ra standard; down to 8 µin (0.2 µm) Ra with polishing or grinding |
| Materials Supported | Aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075), Stainless Steel (e.g., 316L, 17-4 PH), Engineering Plastics (ABS, Nylon 6/66) |
| Aluminum Machining | High-speed milling with sharp carbide tools; excellent for lightweight housings and fixtures; anodizing compatible |
| Steel Machining | Stainless steels (especially 316L) for implants and surgical tools; requires rigid setups and coolant for chip control and work hardening mitigation |
| ABS Machining | Low melting point; requires sharp tools and light cuts; used for prototypes and non-implantable enclosures; post-processing for smooth finishes |
| Nylon Machining | Low friction and good chemical resistance; prone to creep; needs precise depth control and slow feed to avoid deformation |
| Fixturing & Probing | Precision chucks, vacuum fixtures, and automated touch probing for repeatability and first-article inspection |
| Regulatory Compliance | Machining performed in clean environments with documentation for ISO 13485, FDA 21 CFR Part 820 where applicable |
| Secondary Operations | Deburring (manual or automated), passivation (for steel), ultrasonic cleaning, laser marking, CMM inspection |
Advanced 5-axis milling enables single-setup machining of complex organic shapes common in cranial plates or joint implants, reducing error accumulation. Turning is used for cylindrical components such as threaded fittings or shafts, often in combination with milling for full contouring. Tight tolerance control is maintained through in-process gauging, thermal compensation, and post-process metrology using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or optical comparators.
From CAD to Part: The Process
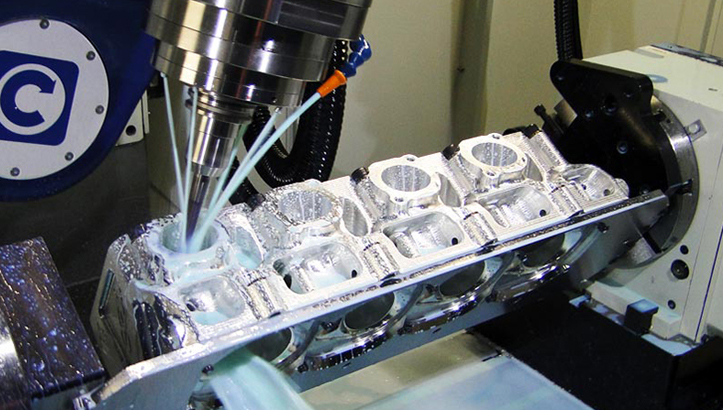
Honyo Prototype Medical Device Machining Process Overview
Honyo Prototype executes medical device machining through a rigorously controlled, end-to-end workflow designed for regulatory compliance, precision, and accelerated time-to-market. This process adheres strictly to FDA 21 CFR Part 820, ISO 13485, and IEC 60601 standards, ensuring all outputs meet stringent medical industry requirements. Below is a detailed explanation of each phase.
Upload CAD
Clients initiate the process by uploading native or neutral CAD files (STEP, IGES, Parasolid) via our secure customer portal. Honyo’s system validates file integrity, geometric completeness, and units consistency while flagging potential topology errors. Critical metadata—such as material specifications (e.g., ASTM F138 stainless steel, Ti-6Al-4V ELI), surface finish requirements (Ra ≤ 0.8 µm), and biocompatibility needs per ISO 10993—is captured during upload. This phase ensures dimensional accuracy and regulatory traceability from the earliest stage, reducing downstream rework risks.
AI Quote
Honyo’s proprietary AI engine analyzes the CAD geometry, material, tolerances, and finish requirements to generate a preliminary quote within 2 hours. Unlike generic quoting systems, our AI cross-references real-time data from 15,000+ medical projects, accounting for medical-specific factors: cleanroom overheads, sterilization-compatible material waste rates, and validation documentation costs. The output includes a technical feasibility score, estimated lead time, and non-conformance risk indicators. All AI outputs undergo mandatory review by a Senior Manufacturing Engineer to validate assumptions, ensuring quotes reflect actual producibility under medical device controls.
DFM (Design for Manufacturability)
Honyo’s dedicated medical DFM team conducts a comprehensive review within 24–48 hours of quote acceptance. This phase identifies critical manufacturability gaps, such as non-achievable tolerances per ISO 2768-mK, problematic undercuts for sterile packaging, or material selections incompatible with gamma/e-beam sterilization. We provide actionable redesign recommendations with quantitative impact analysis—e.g., “Relaxing ±0.025 mm to ±0.05 mm tolerance reduces cost by 22% and lead time by 5 days while maintaining ISO 13485 conformance.” All DFM reports include traceable rationales aligned with FDA design controls, and clients receive interactive 3D markup files for rapid iteration.
Production
Production occurs in Honyo’s ISO 13485-certified, Class 8 cleanroom facility using medical-grade CNC mills (e.g., DMG MORI CTX beta 1250) and Swiss-type lathes. Key protocols include:
Dedicated tooling and fixtures per project to prevent cross-contamination
In-process inspections via calibrated CMMs (e.g., Zeiss CONTURA) with SPC tracking
Material traceability via blockchain-secured batch records (mill certificates to finished part)
Real-time SPC dashboards accessible to clients showing Cpk/Ppk metrics
All processes follow documented work instructions validated per FDA process validation guidelines (IQ/OQ/PQ), with 100% first-article inspection per AS9102. Critical features undergo destructive testing per AQL 0.65 sampling plans.
Delivery
Final delivery integrates regulatory and logistical precision. Parts ship with a complete Device Master Record (DMR) subset, including: material certifications, inspection reports (GD&T, surface roughness), sterilization validation summaries, and biocompatibility documentation. Packaging complies with ISO 11607-1 for sterile barrier systems, with environmental monitoring logs for temperature/humidity during transit. Honyo coordinates direct shipping to FDA-registered contract sterilizers upon client request, providing chain-of-custody documentation. All deliveries include a certificate of conformance signed by our Quality Manager, with full traceability to the original CAD revision.
This closed-loop process ensures medical device components achieve zero-defect delivery while compressing development cycles by 30–50% versus traditional contract manufacturers. Honyo’s integration of AI-driven quoting with human engineering oversight and embedded regulatory controls delivers predictable outcomes for implantables, surgical instruments, and diagnostic equipment.
Start Your Project

For precision medical device machining, partner with Honyo Prototype for high-accuracy components manufactured to strict regulatory standards. Our Shenzhen-based factory is equipped with advanced CNC technology and quality control systems to support prototyping and low-to-mid volume production.
Contact Susan Leo for engineering consultations, quotes, or project evaluations:
Email: [email protected]
Let us help you bring medical innovations to market with reliable, repeatable manufacturing precision.
🚀 Rapid Prototyping Estimator
Estimate rough cost index based on volume.