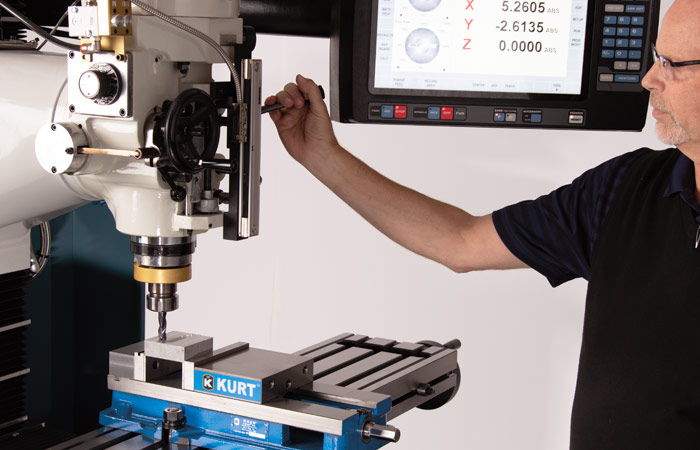
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for manual cnc machine
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, sourcing a manual CNC machine poses a significant challenge for international B2B buyers. With diverse needs spanning from precision engineering in aerospace to intricate designs in medical devices, understanding the nuances of manual CNC machines is critical for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide delves deep into the multifaceted world of manual CNC machines, covering essential aspects such as various types, applications across industries, supplier vetting processes, and cost considerations.
Navigating the global market for manual CNC machines requires a strategic approach, especially for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries where manufacturing demands are rapidly evolving. Each region presents unique challenges and opportunities, making it imperative for buyers to be equipped with the right knowledge and insights. This comprehensive guide empowers decision-makers by providing actionable information that addresses their specific needs and concerns. By highlighting best practices in supplier evaluation and cost management, this resource aims to facilitate successful procurement strategies, ensuring that businesses can enhance their operational efficiency and maintain a competitive edge.
As you explore this guide, you will gain valuable insights that will not only simplify your sourcing process but also align your investments with the latest technological advancements in manual CNC machining.
Understanding manual cnc machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manual Vertical Mill | Operates vertically; adjustable spindle; versatile tooling options | Prototyping, small batch production | Pros: Cost-effective, flexible; Cons: Requires skilled operators, limited automation. |
| Manual Lathe | Rotates workpiece against cutting tool; suitable for cylindrical shapes | Shaft production, custom parts manufacturing | Pros: High precision for round parts; Cons: Slower than CNC, manual skill-dependent. |
| Manual CNC Router | Uses a rotating bit; ideal for flat materials; programmable for complex shapes | Sign making, woodworking, plastics machining | Pros: Versatile for various materials; Cons: Limited to 2D machining, less precision than CNC. |
| Manual Surface Grinder | Uses abrasive wheels to achieve flat surfaces; essential for finishing | Tool making, precision part finishing | Pros: Excellent surface finish; Cons: Slower process, requires skilled operation. |
| Manual Bandsaw | Uses a continuous band of toothed metal; ideal for cutting various materials | Metal cutting, lumber processing | Pros: Efficient for large cuts; Cons: Limited precision, not ideal for intricate designs. |
What are the characteristics and suitability of Manual Vertical Mills for B2B buyers?
Manual vertical mills are characterized by their vertical spindle orientation, allowing for precise cutting and shaping of materials. They are particularly suitable for prototyping and small batch production, where flexibility and cost-effectiveness are crucial. B2B buyers should consider the machine’s adaptability to various tooling options and its ability to handle diverse materials. While manual mills are generally more affordable than their CNC counterparts, the requirement for skilled operators can be a drawback, especially in regions with limited technical training.
How do Manual Lathes serve different B2B applications?
Manual lathes are distinguished by their ability to rotate the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool, making them ideal for producing cylindrical shapes. They are commonly used in shaft production and custom parts manufacturing. For B2B buyers, the precision achieved with manual lathes is a significant advantage, particularly for specialized components. However, the slower production speed compared to CNC machines and the necessity for skilled machinists can pose challenges, especially in high-demand environments.
What advantages do Manual CNC Routers offer for various industries?
Manual CNC routers utilize a rotating bit to cut materials in a programmable manner, making them versatile for flat materials like wood, plastics, and composites. They are widely used in sign making and woodworking applications. B2B buyers appreciate the flexibility in design that manual CNC routers provide, allowing for intricate shapes and patterns. However, their limitations in 2D machining and reduced precision compared to full CNC systems should be considered, particularly for industries requiring high accuracy.
In what ways are Manual Surface Grinders essential for precision part finishing?
Manual surface grinders are designed to achieve flat surfaces through the use of abrasive wheels, making them essential for tool making and precision part finishing. Their ability to deliver excellent surface finishes is a key selling point for B2B buyers in sectors that prioritize quality. However, the slower grinding process and the necessity for skilled operators can be limiting factors, particularly in high-volume production environments. Buyers should weigh these pros and cons when considering investments in surface grinding technology.
How do Manual Bandsaws fit into the manufacturing landscape?
Manual bandsaws operate using a continuous band of toothed metal, making them efficient for cutting a variety of materials, including metals and lumber. They are especially useful in applications requiring large cuts, such as metal cutting and lumber processing. For B2B buyers, the efficiency and capability of manual bandsaws can lead to significant time savings. However, their limitations in precision and suitability for intricate designs may deter buyers in industries that demand high accuracy and detail.
Key Industrial Applications of manual cnc machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Manual CNC Machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing | High accuracy for critical parts, ensuring safety | Certifications for aerospace standards, materials quality |
| Automotive | Custom tooling and prototyping | Flexibility in design changes, rapid prototyping | Supplier reliability, machine versatility, lead times |
| Medical Devices | Fabrication of surgical instruments | Strict adherence to precision and safety standards | Compliance with medical regulations, material sourcing |
| Education & Training | Hands-on training for machining students | Skill development and practical experience | Availability of training programs, equipment support |
| Oil & Gas | Maintenance and repair of equipment | Cost-effective solutions for specialized components | Local sourcing options, availability of spare parts |
How is Manual CNC Machining Used in Aerospace?
In the aerospace industry, manual CNC machines are essential for the manufacturing of precision components, such as brackets and fittings, that require tight tolerances. These machines allow for meticulous control and adjustments, ensuring that each part meets strict safety and performance standards. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing machines with certifications for aerospace applications is crucial. Additionally, understanding local material quality and compliance with international aerospace standards will enhance operational efficiency.
What Role Does Manual CNC Machining Play in Automotive Customization?
Manual CNC machines are widely used in the automotive sector for creating custom tooling and prototypes. This flexibility enables manufacturers to rapidly adapt designs based on market demands or specific client needs. For buyers in South America and Europe, selecting suppliers with a proven track record in automotive applications is vital. They should also consider the versatility of the machines and the supplier’s ability to meet quick turnaround times for tooling changes, which can significantly impact production schedules.
Why is Precision Critical in Medical Device Manufacturing?
In the medical devices sector, manual CNC machining is pivotal for fabricating surgical instruments and implantable devices. The high precision required in these applications ensures patient safety and device efficacy. International B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that comply with rigorous medical regulations and standards. Additionally, understanding the sourcing of biocompatible materials is essential to meet safety requirements, particularly for buyers in regions with stringent health regulations.
How Can Educational Institutions Benefit from Manual CNC Machines?
Educational institutions utilize manual CNC machines for training students in machining techniques. These machines provide hands-on experience that is crucial for skill development in the field of manufacturing. For international buyers, especially in emerging markets, investing in reliable machines with adequate support and training programs can enhance educational outcomes. Institutions should also consider the machine’s ease of use and the availability of instructional materials to facilitate effective learning.
What are the Advantages of Manual CNC Machining in Oil & Gas Maintenance?
In the oil and gas industry, manual CNC machines are utilized for the maintenance and repair of specialized equipment. These machines allow for the precise fabrication of replacement parts, which can be more cost-effective than purchasing new equipment. For buyers in regions like Nigeria and Saudi Arabia, sourcing from local suppliers can reduce lead times and transportation costs. It’s also essential to ensure that the machines can handle the specific materials and tolerances required for oil and gas applications, thus ensuring reliability and safety in operations.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘manual cnc machine’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Struggling with Precision and Consistency in Production
The Problem: A manufacturing company in Nigeria is experiencing challenges with precision and consistency when using manual CNC machines. Their operators, while skilled, often produce parts with slight variations in dimensions, leading to quality control issues and increased scrap rates. This inconsistency not only affects production efficiency but also results in dissatisfied customers who require tight tolerances for their components.
The Solution: To enhance precision, the company should invest in operator training programs focused on best practices in manual machining. This includes emphasizing the importance of setup, tool calibration, and measurement techniques. Implementing a robust quality control system that incorporates regular inspections and feedback loops can also help identify and rectify issues early in the production process. Additionally, sourcing high-quality cutting tools and maintaining them properly will lead to improved outcomes. By encouraging a culture of continuous improvement and precision, the company can achieve better consistency in their production runs, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing waste.
Scenario 2: High Operational Costs Due to Inefficient Machine Use
The Problem: A small machining shop in Saudi Arabia finds that their operational costs are rising due to inefficient use of manual CNC machines. Operators are spending excessive time on setups and adjustments, which leads to longer lead times and reduced profitability. This inefficiency is particularly concerning for projects with tight deadlines and competitive pricing.
The Solution: To address this issue, the shop should conduct a thorough analysis of their workflow and setup processes. Implementing standardized operating procedures (SOPs) for common tasks can significantly reduce setup times. Moreover, investing in fixtures and jigs designed for specific parts can streamline the machining process, allowing operators to achieve faster turnaround times. Additionally, adopting a lean manufacturing approach can help identify waste and improve overall efficiency. Regular team meetings to discuss workflow challenges and share best practices can further enhance productivity. By optimizing their operational processes, the shop can lower costs and improve their competitive edge in the market.
Scenario 3: Difficulty in Adapting to Complex Part Designs
The Problem: A machine shop in Brazil is facing difficulties when clients request complex part designs that require intricate machining operations. The limitations of their manual CNC machines become apparent as operators struggle to execute these designs accurately, leading to increased rework and customer dissatisfaction.
The Solution: To effectively handle complex part designs, the shop should consider integrating CAD/CAM software with their manual CNC machines. This technology enables operators to visualize the machining process and generate more accurate toolpaths, reducing the likelihood of errors. Investing in training for operators on how to use these software tools can significantly enhance their ability to tackle intricate projects. Furthermore, collaborating with clients during the design phase can provide valuable insights into the manufacturability of the parts, allowing for adjustments that facilitate easier machining. By leveraging technology and enhancing communication with clients, the shop can improve its ability to meet complex design requests and strengthen customer relationships.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for manual cnc machine
What Are the Key Materials for Manual CNC Machines?
When selecting materials for manual CNC machines, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, and limitations to ensure optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in manual CNC machining, focusing on their key properties, pros and cons, and implications for international B2B buyers.
How Does Aluminum Perform in Manual CNC Machining?
Aluminum is a widely used material in manual CNC machining due to its lightweight nature and excellent machinability. It typically exhibits good corrosion resistance and can withstand moderate temperatures, making it suitable for various applications, including aerospace and automotive components.
Pros: Aluminum is durable yet lightweight, which helps reduce overall machine weight and improve efficiency. Its ease of machining allows for complex shapes and designs, making it ideal for prototyping and custom parts.
Cons: While aluminum has good mechanical properties, it is not as strong as steel and may deform under high stress. Additionally, the cost can vary significantly based on the alloy used, with some specialized aluminum alloys being more expensive.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s compatibility with various media, including air and water, makes it suitable for fluid handling applications. However, it is not recommended for high-temperature applications due to its lower melting point compared to other metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions such as Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with local standards, such as ASTM or DIN, when sourcing aluminum. Additionally, understanding the specific alloy properties is vital for meeting performance requirements.
What Role Does Steel Play in Manual CNC Machining?
Steel is another prevalent material in manual CNC machining, known for its strength and durability. Various grades of steel, including carbon steel and stainless steel, offer different properties suited for specific applications.
Pros: Steel provides excellent strength and toughness, making it suitable for high-stress applications. Its availability in various grades allows for flexibility in selecting the right type for specific needs.
Cons: Steel is heavier than aluminum, which can impact machine dynamics. It is also more challenging to machine, often requiring specialized tools and techniques, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Steel’s high-temperature resistance makes it ideal for applications in the automotive and aerospace industries, where components are subjected to extreme conditions. However, its susceptibility to corrosion necessitates protective coatings in humid environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific steel grades and their compliance with international standards. For instance, stainless steel grades may be preferred in regions with high humidity, such as parts of South America.
How Does Brass Compare in Manual CNC Machining?
Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It is often used in applications requiring good electrical conductivity, such as electrical connectors and fittings.
Pros: Brass is easy to machine and can achieve high-quality finishes, making it ideal for intricate components. Its resistance to corrosion enhances its longevity in various environments.
Cons: Brass is more expensive than aluminum and steel, which may impact cost-sensitive projects. Additionally, it has lower strength compared to steel, limiting its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is particularly suitable for applications involving water and gas, as it maintains integrity in these environments. However, it should not be used in high-pressure applications without proper engineering considerations.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the brass used complies with local standards for electrical and plumbing applications, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where regulations can be stringent.
What Are the Advantages of Using Plastics in Manual CNC Machining?
Plastics, such as polycarbonate and nylon, are increasingly used in manual CNC machining for various applications. They offer unique properties that can be advantageous depending on the use case.
Pros: Plastics are lightweight, resistant to corrosion, and can be easily molded into complex shapes. They are also generally less expensive than metals, making them a cost-effective option for many applications.
Cons: Plastics may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals, limiting their use in demanding environments. Additionally, the machining process can produce more waste compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Plastics are suitable for applications requiring chemical resistance, such as in the food and pharmaceutical industries. However, they may not be appropriate for structural components where strength is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with food safety and chemical resistance standards, especially in regions with strict regulations, such as Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Manual CNC Machines
| Material | Typical Use Case for Manual CNC Machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | Lightweight and good machinability | Lower strength than steel | Medium |
| Steel | High-stress components in automotive and aerospace | Excellent strength and toughness | Heavier and harder to machine | Medium to High |
| Brass | Electrical connectors, plumbing fittings | Excellent machinability and corrosion resistance | More expensive and lower strength | High |
| Plastics | Chemical containers, consumer products | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited temperature and stress resistance | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the most common materials used in manual CNC machining, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific requirements and regional compliance needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for manual cnc machine
What Are the Key Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Manual CNC Machines?
The manufacturing process for manual CNC machines consists of several critical stages that ensure the final product meets performance and quality standards. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
-
Material Preparation: This stage involves selecting high-quality materials such as steel, aluminum, or composites, which are essential for durability and performance. The materials are cut to size, and any necessary treatments (like heat treatment) are applied to enhance their mechanical properties. Careful consideration of material properties is crucial, as it directly impacts the machine’s functionality and longevity.
-
Forming: In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into parts using various machining techniques. Common methods include milling, turning, and drilling. Each technique is chosen based on the specific requirements of the part being manufactured. For example, turning is ideal for cylindrical components, while milling is more suited for flat or complex geometries. Precision is paramount, as the accuracy of these processes affects the overall machine performance.
-
Assembly: Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final machine. This stage requires meticulous attention to detail to ensure proper alignment and functionality. Various techniques such as welding, bolting, and riveting may be used, depending on the design specifications. Skilled technicians often perform this step, as it requires a good understanding of mechanical systems.
-
Finishing: The final stage involves applying surface treatments, such as painting, anodizing, or coating, to improve aesthetics and protect against corrosion. Additionally, any necessary calibrations or adjustments are made to ensure that the machine operates within specified tolerances. This stage is crucial for enhancing the machine’s durability and performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Integrated into the Manufacturing of Manual CNC Machines?
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process for manual CNC machines, ensuring that each product meets the required standards and specifications. International standards, such as ISO 9001, and industry-specific certifications like CE and API, play a significant role in guiding QA practices.
-
Relevant International Standards: ISO 9001 outlines the criteria for a quality management system, focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with this standard is often a prerequisite for B2B transactions, particularly in regions like Europe and the Middle East. For specific industries, such as oil and gas, adherence to standards like API (American Petroleum Institute) is critical.
-
Quality Control Checkpoints: Several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process help maintain quality. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) verifies the quality of raw materials before they enter production. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) involves monitoring processes and materials during production to catch defects early. Finally, Final Quality Control (FQC) assesses the completed machine to ensure it meets all specifications before delivery.
-
Common Testing Methods: Various testing methods are employed to ensure quality, including dimensional inspections, functional tests, and material analysis. Dimensional inspections utilize tools like calipers and micrometers to verify that components meet specified tolerances. Functional tests simulate real-world conditions to ensure the machine operates correctly under expected loads.
What Strategies Can B2B Buyers Use to Verify Supplier Quality Assurance?
For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality assurance is crucial to mitigating risks associated with purchasing manual CNC machines.
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting supplier audits is one of the most effective ways to assess a manufacturer’s quality assurance processes. Audits can be either announced or unannounced and should cover all aspects of the manufacturing process, including material sourcing, production practices, and QA protocols. An audit provides insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality and adherence to international standards.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should request quality assurance documentation, including inspection reports, testing results, and compliance certificates. This documentation can provide a clear picture of the supplier’s quality management system and their ability to consistently produce high-quality products.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s processes and products. These services can conduct independent quality assessments, ensuring that the machinery meets all required standards and specifications before shipping.
What Are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Understanding the nuances of quality control is vital for B2B buyers operating in diverse international markets. Factors such as regional standards, language barriers, and cultural differences can significantly influence the quality assurance process.
-
Regional Standards Compliance: Different regions may have varying quality standards and regulations. For instance, European buyers may require CE certification, while buyers in the Middle East may prioritize compliance with local standards. Understanding these requirements is essential for ensuring that purchased equipment meets legal and operational standards.
-
Language and Communication Barriers: Effective communication is critical in quality assurance processes. Language differences can lead to misunderstandings regarding specifications, leading to quality issues. B2B buyers should ensure clear communication channels with suppliers and may consider employing bilingual professionals to facilitate discussions.
-
Cultural Differences in Business Practices: Different regions may have unique approaches to business and quality assurance. Understanding these cultural nuances can help B2B buyers establish stronger relationships with suppliers, fostering collaboration and ensuring a smoother quality assurance process.
In conclusion, the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for manual CNC machines are multifaceted and require careful consideration by B2B buyers. By understanding these processes and implementing effective verification strategies, buyers can ensure they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘manual cnc machine’
To assist B2B buyers in procuring a manual CNC machine, this guide provides a structured checklist that highlights essential steps and considerations. This process ensures that you make informed decisions, maximizing your investment while aligning with your operational needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating your search, clearly outline the technical specifications you require from a manual CNC machine. Consider factors such as size, material compatibility, precision levels, and the complexity of the parts you intend to manufacture. This step is critical as it helps narrow down options and ensures that you select a machine that meets your production needs without over-investing in unnecessary features.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Prices
Understanding the current market trends and pricing for manual CNC machines is vital. Investigate the average costs within your region and industry, as well as the demand for specific features or brands. This knowledge not only aids in budget planning but also empowers you to negotiate better terms with suppliers by having a clear understanding of fair market value.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Thoroughly vetting suppliers is crucial to ensuring quality and reliability. Request company profiles, product certifications, and references from other businesses, particularly those within your region or industry. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering manual CNC machines and check for customer reviews or case studies to gain insights into their service quality and machine performance.
Step 4: Assess After-Sales Support and Warranty
Inquire about the after-sales support offered by suppliers, including training, maintenance, and repair services. A robust support system is essential, especially for manual CNC machines, which may require operator training to maximize efficiency. Additionally, review warranty terms and conditions to ensure protection against defects and issues that may arise post-purchase.
Step 5: Verify Compliance with International Standards
Ensure that the manual CNC machines you consider comply with relevant international manufacturing and safety standards. Compliance is not only important for operational efficiency but also for avoiding potential legal issues. Look for certifications such as ISO or CE, which signify adherence to high-quality manufacturing processes and safety regulations.
Step 6: Conduct a Risk Assessment
Before finalizing your purchase, conduct a risk assessment related to the investment in a manual CNC machine. Analyze potential risks including supply chain disruptions, machine compatibility with existing tools, and the learning curve for your operators. This proactive approach helps you prepare for challenges and ensures a smoother integration of the new equipment into your operations.
Step 7: Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
Once you have identified a suitable supplier and machine, enter negotiations to finalize terms. Discuss payment options, delivery timelines, and installation procedures. Clear communication during this phase is essential to establish a solid partnership with the supplier and to ensure that both parties have aligned expectations.
By following this structured checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the procurement process for manual CNC machines with confidence, ensuring that their investment aligns with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for manual cnc machine Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components of Sourcing Manual CNC Machines?
When sourcing manual CNC machines, understanding the complete cost structure is essential for B2B buyers. The cost components typically include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margins.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost. High-quality metals and composites used in machine construction can drive up prices. Buyers should assess material specifications to ensure they meet their operational needs without overspending.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the region and skill level required for assembly and maintenance. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower, but the availability of skilled technicians can affect overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Buyers should consider suppliers’ production efficiencies to gauge how overhead costs might influence pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary based on the complexity of the machine and the type of tools needed. Custom tooling can lead to higher upfront costs but may enhance operational efficiency in the long run.
-
Quality Control: Investing in robust QC processes ensures the machines meet industry standards, which can prevent costly errors and rework. Buyers should inquire about the quality certifications held by suppliers to assess their commitment to quality.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can add significantly to the final price, especially for international shipments. Understanding the supplier’s logistics capabilities and potential hidden costs is crucial.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically mark up their costs to ensure profitability. Buyers should be aware of the typical margins in the industry to better understand pricing structures.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Manual CNC Machine Costs?
Several factors can influence the pricing of manual CNC machines, making it essential for buyers to consider these elements during negotiations.
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs. Buyers should evaluate their production needs to determine if they can benefit from bulk purchasing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to the need for specialized materials or tooling. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The use of high-grade materials and adherence to international quality standards can increase costs. Buyers should ensure that the materials align with their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices but often provide better quality assurance and customer service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of delivery (Incoterms) can help buyers manage logistics costs and responsibilities effectively. Different Incoterms can alter the overall cost of procurement.
What Are Effective Buyer Tips for Negotiating Manual CNC Machine Prices?
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, effective negotiation strategies are vital for achieving cost efficiency.
-
Leverage Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Instead of focusing solely on the purchase price, buyers should consider the TCO, which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about payment terms, delivery schedules, and warranties. Favorable terms can enhance cash flow and reduce risk.
-
Research Market Prices: Understanding market pricing trends can empower buyers during negotiations. Buyers should gather quotes from multiple suppliers to benchmark costs effectively.
-
Assess Supplier Capabilities: Evaluate suppliers not just on price, but also on their ability to deliver quality and support. A slightly higher initial investment might be justified by better service and reliability.
-
Be Mindful of Cultural Differences: When negotiating with suppliers from diverse regions, be aware of cultural nuances that may impact negotiation styles and expectations.
Conclusion
Sourcing manual CNC machines involves a multifaceted approach to understanding costs and pricing. By considering the various cost components, price influencers, and employing effective negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can optimize their purchasing decisions and ensure they achieve the best value for their investment.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing manual cnc machine With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternative Solutions in Machining
When considering machining solutions, it’s essential to evaluate various alternatives to manual CNC machines. Each option presents unique advantages and challenges that can significantly impact production efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and overall suitability for specific applications. This analysis will compare manual CNC machines with two viable alternatives: traditional manual machining and CNC machining, offering insights that can guide B2B buyers in making informed decisions.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Manual CNC Machine | Traditional Manual Machining | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for complex parts | Moderate precision; operator-dependent | Very high precision; consistent results |
| Cost | Moderate initial investment; lower operating costs | Low initial cost; higher labor costs | High initial investment; cost-effective in high volumes |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires training; user-friendly interfaces | Minimal training; skill-dependent | Requires programming knowledge; complex setup |
| Maintenance | Moderate; regular calibration needed | High; frequent manual adjustments | Low; automated maintenance systems available |
| Best Use Case | Small to medium production runs | Prototyping, repairs, low volume | High-volume production, intricate designs |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Manual Machining?
Traditional manual machining involves the use of manually operated tools like lathes and milling machines. This method is often preferred for simple tasks or small-scale operations due to its lower initial cost and minimal investment in technology. However, the precision and consistency of traditional manual machining heavily rely on the operator’s skill and experience. While it can be effective for prototyping and repairs, the risk of human error and slower production speeds can be significant drawbacks for businesses aiming for high efficiency.
How Does CNC Machining Compare to Manual CNC Machines?
CNC machining represents a more advanced alternative, leveraging computer programming to control machine tools with high precision. This method is particularly advantageous for producing complex parts consistently and efficiently, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing. Although the initial investment is considerable, the long-term cost savings can be substantial due to reduced labor costs and improved accuracy. However, CNC machining requires skilled programming knowledge and can be less flexible for rapid changes in design, which may not suit all production environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When selecting the most appropriate machining solution, B2B buyers must carefully assess their specific requirements, including production volume, budget constraints, and the complexity of parts to be manufactured. Manual CNC machines offer a balanced approach for those needing flexibility and moderate precision, while traditional manual machining can serve niche applications effectively. Conversely, CNC machining is recommended for businesses focused on high-volume production and intricate designs. By thoroughly evaluating these alternatives, companies can align their operational capabilities with market demands, ensuring both competitiveness and efficiency in their manufacturing processes.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for manual cnc machine
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Manual CNC Machines?
When evaluating manual CNC machines, several technical properties are critical for ensuring optimal performance and suitability for specific applications. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
– The material grade of the machine components, such as the frame, spindle, and table, is crucial. Common materials include cast iron for stability and steel for durability. Higher-grade materials enhance the machine’s longevity and resistance to wear and deformation, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In manual CNC machining, achieving tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) is vital for producing high-quality parts. Understanding tolerance requirements helps businesses meet industry standards and customer specifications, which is essential for sectors like aerospace and automotive. -
Spindle Speed
– The spindle speed, measured in revolutions per minute (RPM), determines how quickly the machine can cut through materials. High spindle speeds allow for faster machining, which can increase productivity. However, the appropriate spindle speed also depends on the material being machined, making it essential for buyers to consider application-specific needs. -
Axis Configuration
– Manual CNC machines typically come in various axis configurations, such as 3-axis, 4-axis, or 5-axis. Each additional axis allows for more complex machining capabilities, enabling the production of intricate parts. Understanding the axis configuration helps businesses assess the machine’s versatility and suitability for their machining tasks. -
Feed Rate
– The feed rate indicates how quickly the cutting tool moves through the material during machining, usually expressed in inches per minute (IPM). A suitable feed rate contributes to the quality of the finish and the lifespan of the cutting tool. Buyers must evaluate feed rate options based on the specific materials and designs they plan to work with. -
Weight Capacity
– The weight capacity of the machine indicates the maximum weight it can handle while maintaining performance. This specification is essential for ensuring that the machine can accommodate the size and weight of the materials and components typically processed.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Manual CNC Machines?
Understanding industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of CNC machines, OEM components are often critical for ensuring compatibility and reliability in machine performance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ denotes the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is significant for B2B buyers, as it impacts inventory costs and purchasing strategies. Understanding MOQ can help businesses optimize their supply chain and manage cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers. In the manual CNC machine market, submitting an RFQ is a common practice to gather information from multiple vendors, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. They clarify who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risks during transit, which is essential for international transactions involving CNC machines. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. In the context of manual CNC machines, understanding lead times helps businesses plan their production schedules and manage expectations regarding delivery dates. -
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership)
– TCO encompasses the total cost of acquiring and operating a machine over its lifespan. This includes initial purchase price, maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. For B2B buyers, calculating TCO is critical for making financially sound investments in manual CNC machinery.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when investing in manual CNC machines, ensuring they meet their operational needs and business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the manual cnc machine Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics for Manual CNC Machines?
The manual CNC machine market is witnessing a significant transformation driven by several global factors. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to modernize, there is an increasing demand for precision manufacturing capabilities. Key drivers include the growth of small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require cost-effective machining solutions, especially in regions with developing manufacturing sectors, such as Nigeria and Saudi Arabia. Moreover, the rise of prototyping and low-volume production runs has created a niche for manual CNC machines that offer flexibility and lower initial investment compared to fully automated CNC systems.
Emerging B2B tech trends are reshaping sourcing strategies in this sector. The integration of advanced software solutions, including CAD/CAM systems, enhances the capabilities of manual CNC machines, allowing operators to produce complex designs with greater efficiency. Additionally, the increasing availability of online marketplaces is facilitating easier access to both new and used manual CNC machines, thus broadening options for international buyers. As companies seek to optimize their supply chains, the emphasis is shifting towards sourcing machines that can quickly adapt to changing production needs.
Market dynamics are also influenced by the ongoing shift towards localized production. International buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can provide not only quality machines but also support and service in their regions. This trend underscores the importance of building strong supplier relationships that can offer technical support, training, and maintenance services.
How Are Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Influencing Manual CNC Machine Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the manual CNC machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes has led companies to prioritize ethical sourcing and sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing the supply chains of their machine manufacturers, seeking transparency regarding material sourcing, waste management, and energy consumption.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies that prioritize sustainability are not only meeting regulatory requirements but also appealing to a growing base of environmentally conscious customers. This is particularly relevant in regions such as Europe, where stringent environmental regulations demand compliance from manufacturers.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ certifications and materials is gaining traction. Buyers are encouraged to seek out manufacturers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, such as recycled metals and non-toxic lubricants. These practices not only reduce the environmental footprint but can also lead to cost savings in the long run through efficient resource use.
What Is the Historical Context of Manual CNC Machines in B2B Manufacturing?
The evolution of manual CNC machines can be traced back to the early days of machining technology. Initially developed in the 1800s, these machines were pivotal in advancing manufacturing capabilities, allowing for greater precision and versatility compared to traditional manual methods. Over the decades, the technology has undergone significant refinement, incorporating advancements such as digital readouts and programmable controls that enhance operator efficiency.
Despite the rise of fully automated CNC systems, manual CNC machines continue to play a vital role in the manufacturing landscape. They are particularly valuable in small-scale operations and repair shops where flexibility and low investment costs are essential. The ongoing relevance of manual CNC machines underscores their adaptability in meeting the diverse needs of B2B buyers across various industries, from aerospace to automotive, ensuring they remain a critical component of the global manufacturing ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of manual cnc machine
-
How do I choose the right manual CNC machine for my business needs?
Selecting the right manual CNC machine involves assessing your specific manufacturing requirements, such as material types, part complexity, and production volume. Consider factors like machine precision, available tooling, and the skill level of your operators. Additionally, evaluate the machine’s ability to accommodate future growth or changes in your production line. Consulting with suppliers for demos or technical specifications can also provide clarity on the best fit for your operations. -
What is the best manual CNC machine for small-scale manufacturing?
For small-scale manufacturing, a manual CNC milling machine or lathe with versatile capabilities is often recommended. Look for machines that offer a good balance between precision and ease of use, such as those with digital readouts and programmable features. Brands known for reliability and support, like Bridgeport or Haas, can be excellent choices. Always consider the machine’s footprint and energy consumption to ensure it fits within your operational constraints. -
What are the common payment terms for purchasing manual CNC machines internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases typically include options like letter of credit, advance payment, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect both parties, such as partial payments during production milestones. Be aware of the implications of currency fluctuations and potential fees associated with international transactions. Consulting with your financial institution can provide insights into the safest and most cost-effective payment methods. -
How can I vet suppliers of manual CNC machines before making a purchase?
To vet suppliers effectively, start by researching their reputation within the industry. Look for customer testimonials, case studies, and reviews on independent platforms. Verify their certifications, such as ISO compliance, and ask for references from other businesses similar to yours. Additionally, consider visiting the supplier’s facility or requesting a virtual tour to assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes. -
What customization options are available for manual CNC machines?
Many suppliers offer customization options to tailor manual CNC machines to your specific needs. Common customizations include modifications to tooling, software enhancements for specific applications, and adjustments to machine size or configuration. When discussing customization, clearly communicate your production requirements and any unique challenges you face. This ensures that the supplier can provide solutions that enhance your operational efficiency. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for manual CNC machines?
The minimum order quantity for manual CNC machines can vary significantly based on the supplier and the specific model. Generally, established manufacturers may have a higher MOQ, while smaller suppliers might accommodate lower quantities. It’s advisable to inquire directly with suppliers about their MOQ policies, as some may offer flexibility based on your specific needs or the potential for future orders. -
What quality assurance processes should I expect when purchasing a manual CNC machine?
Quality assurance processes for manual CNC machines typically include thorough inspections during production, testing of machine functionality, and adherence to industry standards. Reputable suppliers will provide documentation of quality control measures, such as certification of materials and performance testing results. Ensure that you receive a warranty and after-sales support, which are critical for addressing any quality concerns post-purchase. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing manual CNC machines?
When importing manual CNC machines, consider logistics factors such as shipping methods, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling machinery to navigate the complexities of international shipping. Ensure all necessary documentation, such as invoices and certificates of origin, is prepared to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Planning for potential delays and understanding local regulations will also help streamline the import process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 8 Manual Cnc Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Mazak – 3EVS
Domain: cncmachines.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Manual Mills & Lathes – Used Machining – CNCMachines.com
Key Brands:
– Mazak Mills
– Haas Mini Mills
– Bridgeport
– CNC Masters
– Birmingham
– Clausing
– European Lion
– Hammond
– Lodge & Shipley
– Milltronics
– Tarus
– Webb
– Webster & Bennett
– Xydroid
Key Models:
– 3EVS
– 600
– C10T
– LGCONT
– Liberty
– Series
– Supra X6323A
– TPTCGD5X8
– Versa Flow VSF1200P
– VKM4
– VTL 72
– YCL26120
Year R…
2. CNC Cookbook – Manual vs CNC Machining
Domain: cnccookbook.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: CNC machines are generally preferred over manual machines, but there are specific scenarios where manual machining may be better. Key points include: 1. CNC machines may be busy with production runs, making manual machines a viable option for simple jobs. 2. Manual machines can be cheaper, especially older models that are already paid off. 3. CNC machines may lack specific options that manual mach…
3. Wayken RM – CNC Machining Solutions
Domain: waykenrm.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: CNC Machining: Highly scalable, automated process using pre-programmed computer software, minimal human intervention, produces complex geometric shapes from various materials (metal, plastic), faster production speed, higher output, consistent results, lower labor cost, capable of complex designs. Initial investment is higher, costly maintenance, requires skilled programming. Manual Machining: Ope…
4. CNC Manuals – Comprehensive User Guides
Domain: cncmanual.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: CNC Programming Manuals User Guides PDF Files – CNC Manual. The site offers a comprehensive collection of manuals for various CNC machines and robotics, including brands like Fanuc, Haas, Mazak, and KUKA. It features manuals for CNC programming, operating, and maintenance, covering a wide range of models and applications. Users can browse manuals alphabetically by brand and can upload their own do…
5. Southwestern Industries – Trak TRL1630RX Lathe & DPM RX3 Mill
Domain: practicalmachinist.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: Hybrid manual/CNC machines discussed include the Trak TRL1630RX lathe and DPM RX3 Mill from Southwestern Industries. Users express interest in machines that maintain manual operation capabilities while also offering CNC functionality. The Romi M17 lathe is highlighted as a capable option with both hand and CNC controls, featuring hardened bed ways and a full chip enclosure. The conversation indica…
6. A & A Machine & Fabrication – CNC Machining Services
Domain: aagroup.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: A & A Machine & Fabrication LLC provides high-quality CNC machining services. CNC machining utilizes computer-controlled machines for precise, consistent results, excelling at producing intricate and complex parts. Manual machining, while faster to set up, relies on the machinist’s skill and has limitations in producing complex parts. The company operates in La Marque, Texas, and offers machining …
7. Homeshop Machinist – CNC Mill Operation
Domain: bbs.homeshopmachinist.net
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
Introduction: CNC mill operation similar to manual mills with DROs and power feeds; commands include G0 for rapid positioning and G1 for feedrate movement; spindle control commands; tool changer commands; coolant control commands; Milltronics CNC features include Bridgeport type head, electronic handwheel, 3-axis function, easy operation without programming, and conversational programming.
8. Emco – CNC Mills and Manual Pulse Generators
Domain: model-engineer.co.uk
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: CNC mills can be operated manually or via G-code. Some machines feature a ‘manual pulse generator’ (MPG) for manual control, allowing for setup and manual milling. Popular software for CNC control includes Mach3, which allows manual operation through keyboard commands or MPGs. Machines like the Emco F1 and Emco VMC can switch between manual and CNC modes. Users can also connect rotary encoders to …
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for manual cnc machine
The landscape of manual CNC machines remains pivotal for various industries, particularly in regions where investment in fully automated systems may not be feasible. By understanding the nuances of manual versus CNC machining, international buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. Manual CNC machines offer flexibility and skill-based precision, making them invaluable for small-scale manufacturing, prototyping, and maintenance tasks.
Strategic sourcing is essential for optimizing procurement processes and ensuring access to high-quality equipment that meets specific manufacturing requirements. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that not only provide competitive pricing but also demonstrate a commitment to after-sales support and training, which are critical for maximizing the operational efficiency of manual CNC machines.
Looking ahead, the demand for manual CNC machines is expected to grow, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, and the Middle East. As industries evolve and diversify, the need for versatile and adaptable machining solutions will be paramount. Engage with trusted suppliers to explore innovative manual CNC options that can enhance your production capabilities and drive business growth. Your proactive approach today will position you for success in the dynamic manufacturing landscape of tomorrow.