Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for make cnc router
In an increasingly competitive landscape, sourcing the right CNC router can be a daunting challenge for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of different types of CNC routers, their applications, and the various suppliers available is essential to making informed purchasing decisions. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of CNC routers, offering insights into the diverse range of machines—from compact models ideal for small workshops to advanced systems designed for high-volume production.
Buyers will find valuable information on key considerations such as supplier vetting, cost analysis, and potential applications across industries like woodworking, metalworking, and prototyping. We will also explore the importance of understanding local market dynamics, particularly for businesses operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including Brazil and Saudi Arabia.
By equipping decision-makers with the necessary tools and knowledge, this guide empowers organizations to navigate the complexities of sourcing CNC routers effectively. With actionable insights and expert recommendations, buyers can confidently select the right machines that align with their operational needs and strategic objectives, ensuring they remain competitive in the global market.
Understanding make cnc router Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moving Gantry CNC Router | Features a stationary table with a gantry that moves along the axes | Large-scale manufacturing, signage | Pros: Larger cutting area, better rigidity. Cons: Requires more space, potentially higher cost. |
| Moving Table CNC Router | Table moves while the gantry remains stationary | Small workshops, prototyping | Pros: Compact design, easier to construct. Cons: Limited cutting area compared to gantry types. |
| Mini CNC Router | Smaller, often desktop-sized machines | Hobbyists, small part fabrication | Pros: Cost-effective, space-saving. Cons: Limited functionality and cutting depth. |
| Hybrid CNC Router | Combines features of routers and mills for versatile applications | Metalworking, woodworking, prototyping | Pros: Multi-functional, adaptable. Cons: Complexity may lead to higher maintenance costs. |
| DIY CNC Router | Custom-built machines often using open-source designs | Educational purposes, custom projects | Pros: Tailored to specific needs, lower cost. Cons: Requires technical knowledge and time to build. |
What Are the Characteristics of a Moving Gantry CNC Router?
The moving gantry CNC router is characterized by its design where the table remains fixed while the gantry moves along the X and Y axes. This type is ideal for large-scale manufacturing and signage production due to its expansive cutting area. B2B buyers should consider the space requirements and potential costs associated with installation and operation, as this design tends to be more expensive but offers enhanced rigidity and precision.
How Does a Moving Table CNC Router Differ from Other Types?
In a moving table CNC router, the table itself moves while the gantry is stationary. This design is often favored in small workshops for prototyping due to its compact nature and ease of construction. Buyers looking for a cost-effective solution for smaller projects may find this type appealing, but they should be aware of its limited cutting area compared to moving gantry routers.
Who Benefits from Using Mini CNC Routers?
Mini CNC routers are designed for smaller applications, often suitable for hobbyists and small part fabrication. Their compact size makes them ideal for limited workspace environments. While they are cost-effective and easy to use, B2B buyers should keep in mind the limitations in functionality and cutting depth, which may restrict their use for larger-scale projects.
What Advantages Do Hybrid CNC Routers Offer?
Hybrid CNC routers combine the capabilities of both routers and mills, making them versatile for various applications, including metalworking and woodworking. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for businesses that require a single machine for multiple tasks. However, buyers should consider the complexity of these machines, which can lead to higher maintenance costs and require a more skilled workforce.
Why Consider a DIY CNC Router for Your Business?
DIY CNC routers are custom-built machines that often utilize open-source designs, making them suitable for educational purposes and unique projects. These routers allow businesses to tailor their machines to specific needs and can be more cost-effective than commercially available options. However, potential buyers must have the technical knowledge and time to build and maintain these machines, which may not be feasible for all businesses.
Key Industrial Applications of make cnc router
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of make cnc router | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Woodworking | Precision furniture manufacturing | Enhanced design flexibility and reduced material waste | Quality of cutting tools, spindle options, and software compatibility |
| Aerospace | Custom part fabrication for aircraft components | High accuracy and repeatability, essential for safety | Certifications for materials, precision tolerances, and supplier reliability |
| Automotive | Prototyping and production of intricate components | Faster turnaround times and cost-effective manufacturing | Material types (e.g., composites, metals), machine size, and tooling options |
| Signage and Displays | Production of custom signage and promotional displays | Increased market competitiveness through customization | Durability of materials, design software integration, and finishing capabilities |
| Electronics | PCB prototyping and casing fabrication | Streamlined product development cycle | Precision requirements, compatibility with CAD software, and supplier support |
How is ‘make CNC router’ Used in Woodworking?
In the woodworking industry, a make CNC router is employed for precision furniture manufacturing. These machines enable artisans to create intricate designs and patterns that traditional methods cannot achieve efficiently. By automating the cutting process, businesses can significantly reduce material waste and enhance design flexibility. International buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, should consider the quality of cutting tools and spindle options, as well as software compatibility, to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
What Role Does a CNC Router Play in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace sector, make CNC routers are vital for custom part fabrication, particularly for components that require high precision and repeatability. These machines help manufacturers produce lightweight yet durable parts essential for aircraft safety and performance. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East must prioritize sourcing suppliers that offer materials with appropriate certifications and can meet stringent precision tolerances, ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
How is a CNC Router Beneficial in Automotive Prototyping?
The automotive industry utilizes make CNC routers for both prototyping and production of intricate components, such as dashboards and body panels. These machines facilitate faster turnaround times, allowing manufacturers to iterate designs quickly and cost-effectively. B2B buyers, especially those from Brazil and Saudi Arabia, should focus on sourcing machines capable of handling various material types, including composites and metals, while ensuring that tooling options are adaptable to their specific needs.
In What Ways Does a CNC Router Enhance Signage and Display Production?
For businesses in the signage and displays sector, make CNC routers are essential for producing custom signage and promotional displays. The ability to create unique designs enhances market competitiveness and allows for rapid response to customer demands. Buyers should consider the durability of materials used, as well as the machine’s compatibility with design software, to ensure seamless integration into their production processes.
How is a CNC Router Used in Electronics Manufacturing?
In electronics manufacturing, make CNC routers are crucial for PCB prototyping and casing fabrication. These machines streamline the product development cycle by enabling rapid prototyping, which is essential in a fast-paced market. International buyers need to ensure that the CNC router meets precision requirements and is compatible with their existing CAD software, as well as evaluate the level of supplier support for troubleshooting and maintenance.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘make cnc router’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Costly Component Failures
The Problem:
B2B buyers often face challenges related to the reliability and quality of components when building a CNC router. A common pain point is experiencing failures in critical parts like stepper motors or spindles, which can lead to costly downtime and project delays. For businesses in regions like Africa and South America, where access to high-quality components may be limited, this issue is exacerbated. The financial implications of sourcing replacements or conducting repairs can hinder operations and affect overall productivity.
The Solution:
To mitigate the risk of component failures, buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality parts from reputable suppliers. It’s crucial to conduct thorough research to identify vendors who offer warranties and support. For example, instead of opting for generic or low-cost stepper motors, investing in well-known brands like Leadshine can ensure better performance and longevity. Additionally, establishing a relationship with local distributors can facilitate quicker replacements and support. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule for the CNC router can also help identify potential issues before they lead to failures, thus maintaining operational efficiency.
Scenario 2: Complex Software Integration Challenges
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers encounter difficulties with the integration of CNC software, such as CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) and control software, which can be overwhelming, especially for those new to CNC machining. The complexity of software like Mach3 or Fusion 360 can pose a significant barrier, leading to incorrect machine operations and wasted materials. This scenario is particularly frustrating for companies in the Middle East or Europe, where precision and quality are paramount for competitive advantage.
The Solution:
To overcome software integration challenges, companies should invest in comprehensive training programs for their teams. Many software providers offer tutorials and webinars that guide users through the setup and operational processes. Additionally, creating a network with other CNC users through forums or local workshops can provide valuable insights and troubleshooting support. For businesses looking to streamline operations, considering all-in-one CNC solutions that come with pre-installed software can eliminate compatibility issues and reduce the learning curve.
Scenario 3: Space and Design Limitations in Workshop Setup
The Problem:
Space constraints in workshops can significantly affect the functionality of CNC routers, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises. Buyers often struggle with configuring their workspace efficiently to accommodate the CNC router while ensuring it remains accessible for operation and maintenance. This challenge is prevalent in regions like South America, where workshop space may be at a premium, leading to frustration and inefficient workflows.
The Solution:
To optimize workshop space, buyers should consider modular CNC router designs that can be customized to fit their specific needs. Engaging with manufacturers who offer compact models or wall-mounted options can maximize available space without sacrificing performance. Additionally, using CAD software to plan the layout before installation can help visualize the best use of the workshop area. Incorporating mobile workstations or storage solutions can further enhance accessibility and organization, enabling smoother operations and reducing clutter. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the workshop layout as business needs evolve can also ensure continued efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for make cnc router
When selecting materials for building a CNC router, it is essential to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost. Below, we analyze four common materials used in CNC router construction: aluminum, steel, MDF (Medium Density Fiberboard), and plywood. Each material presents unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly affect the machine’s overall functionality and suitability for specific applications.
What Are the Key Properties of Aluminum for CNC Routers?
Aluminum is a lightweight yet strong material, making it a popular choice for CNC router frames and components. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, which is beneficial for dissipating heat generated during operation. The material’s low density allows for easier handling and assembly, while its ability to be machined with precision enhances the overall accuracy of the CNC router.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum is durable and resistant to rust, but it can be more expensive than other materials like MDF or plywood. Its manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specific tools for cutting and shaping. In terms of application, aluminum is suitable for a wide range of media, including wood, plastics, and soft metals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions such as Africa and South America should consider local availability and import costs. Compliance with international standards like ASTM and DIN can also impact sourcing decisions.
How Does Steel Compare as a Material for CNC Routers?
Steel is known for its exceptional strength and rigidity, making it ideal for heavy-duty CNC routers that require stability during operation. It has high-temperature resistance and can withstand significant mechanical stress, which is crucial for precision machining tasks.
Pros & Cons: While steel provides excellent durability and is often more cost-effective than aluminum, it is heavier, which can complicate transport and assembly. Additionally, steel is prone to corrosion unless adequately treated, which may increase maintenance requirements. Steel is suitable for cutting hard materials like metals and composites.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions such as the Middle East, where humidity can lead to corrosion, it is vital to choose treated or coated steel. Compliance with local regulations regarding material sourcing and environmental standards is also crucial.
What Role Does MDF Play in CNC Router Construction?
MDF is a cost-effective material often used for constructing CNC router tables and enclosures. It is easy to machine and provides a smooth surface finish, which is beneficial for precision work.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of MDF is its affordability and ease of use. However, it is less durable than metal options and can be susceptible to moisture damage, which limits its longevity. MDF is best suited for woodworking applications and light-duty tasks.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in humid regions must ensure proper sealing of MDF to prevent warping. Additionally, adherence to environmental regulations regarding formaldehyde emissions from MDF is essential, especially in Europe.
How Does Plywood Compare for CNC Router Applications?
Plywood is another economical choice for CNC router construction, particularly for parts that require moderate strength and weight. It is more resistant to moisture than MDF and can be used in various applications.
Pros & Cons: Plywood offers a good balance of strength and weight, making it suitable for both structural and aesthetic components. However, its quality can vary significantly based on the grade, and lower-quality plywood may not provide the necessary stability for precision work.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for plywood quality across different regions. Compliance with local regulations regarding wood sourcing and treatment is also critical, particularly in Europe.
Summary Table of Material Selection for CNC Routers
| Material | Typical Use Case for make cnc router | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Frame and components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Higher cost than wood materials | Medium |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications | Exceptional strength and rigidity | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| MDF | Router tables and enclosures | Cost-effective and easy to machine | Susceptible to moisture damage | Low |
| Plywood | Structural and aesthetic components | Good balance of strength and weight | Quality can vary significantly | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to build or source CNC routers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material can help in making informed purchasing decisions that align with specific operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for make cnc router
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of CNC Routers?
Manufacturing a CNC router involves several critical stages, each contributing to the overall quality and functionality of the final product. These stages include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
Material Preparation
The first step is selecting the right materials, which typically include aluminum, steel, and various composites. Aluminum is favored for its lightweight and durability, while steel may be used in areas requiring higher strength. The material preparation stage involves cutting, machining, and sometimes anodizing the raw materials to enhance their properties.
Precision is vital during this phase. Accurate measurements and cuts ensure that all components fit together correctly during assembly. Advanced CNC machining processes may be employed to achieve high tolerances, reducing the need for extensive adjustments later on.
How Are CNC Router Components Formed?
The forming process generally involves several techniques tailored to the specific components of the CNC router. Key techniques include:
- Machining: This includes milling, turning, and drilling operations to create complex shapes and features on components like brackets and frames.
- Welding: For structural components, welding may be used to join metal parts, ensuring they can withstand operational stresses.
- Casting and Forging: Some manufacturers may utilize casting for complex shapes, while forging provides increased strength for critical components.
Each technique has its advantages and must be chosen based on the desired properties of the final product. For instance, welded structures may be more robust but require careful inspection for flaws.
What Does the Assembly Process Entail for CNC Routers?
Assembly is a crucial stage where the prepared components come together to form the CNC router. This process typically involves several steps:
- Sub-assembly: Smaller components, such as motors, control systems, and linear guides, are assembled before being integrated into the main structure.
- Main Assembly: The frame and moving parts are assembled, ensuring alignment and fit. This is where precision tools and jigs are often used to maintain accuracy.
- Integration of Electronics: The electrical components are installed, including stepper motors, drivers, and the control system. Proper wiring and connections are essential to avoid future operational issues.
Quality assurance checkpoints are critical during this stage to catch any misalignments or defects early in the process.
How Is the Finishing Process Conducted for CNC Routers?
Finishing processes may include surface treatments such as anodizing, powder coating, or painting to enhance aesthetics and corrosion resistance. These treatments not only improve the appearance but also contribute to the longevity of the machine.
Additionally, final inspections are conducted to ensure all components are functioning correctly and meet specified tolerances. This step often involves testing the router’s capabilities before it leaves the manufacturing facility.
What Quality Assurance Standards Are Relevant for CNC Router Manufacturing?
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of CNC router manufacturing, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. The most relevant standards include:
- ISO 9001: This international standard focuses on quality management systems and is widely recognized across various industries. Compliance indicates a commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking demonstrates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is essential for market access in the European Union.
- API Standards: For specialized CNC routers used in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in CNC Router Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity and performance. Common QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection verifies that incoming materials meet specified standards before they are used in production. It helps prevent defects from the outset.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During assembly and machining, IPQC ensures that processes are followed correctly and that components are manufactured to specifications. This may involve measuring tolerances and conducting visual inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes thorough testing to confirm that it operates as intended. This may include running the CNC router through various operations to ensure precision and reliability.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control Processes?
B2B buyers need to ensure that their suppliers have robust quality control processes in place. Here are effective methods for verification:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, processes, and quality control measures firsthand. This can include reviewing documentation related to quality management systems.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards. These reports should outline testing methods, results, and any corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an impartial assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These inspections often involve comprehensive evaluations of materials, processes, and final products.
What Quality Control Nuances Should International B2B Buyers Consider?
When dealing with international suppliers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of specific quality control nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality control. Understanding these cultural differences can help buyers navigate potential challenges in communication and expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Each country may have unique regulations regarding manufacturing standards. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations as well as international standards.
- Logistics and Transportation: Quality assurance doesn’t stop at manufacturing. Buyers must consider how products will be transported and whether additional quality checks are necessary to mitigate risks during shipping.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for CNC routers is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on these elements, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘make cnc router’
Introduction
This practical sourcing guide is designed to assist international B2B buyers in procuring CNC routers. With the growing demand for precision engineering and manufacturing capabilities across sectors, understanding the sourcing process is crucial. This checklist will streamline your procurement journey, ensuring you select the right components and suppliers for building a CNC router that meets your specific needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the procurement process, clearly outline the technical specifications of your CNC router. Consider dimensions, cutting capabilities, and the types of materials you plan to work with. This foundational step ensures that you are aligned with your operational requirements and can communicate effectively with suppliers.
- Dimensions: Determine the size of the work area you need, as this will impact the type of router you build.
- Capabilities: Decide if you need features like a moving gantry or a stationary table, which will affect the design and complexity.
Step 2: Research and Identify Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers who specialize in CNC router components. Look for companies with a strong reputation in the industry, focusing on those who have experience in your region, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Supplier Reputation: Check online reviews and testimonials from other B2B buyers.
- Local Considerations: Understand local import regulations that may affect sourcing.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing, it’s crucial to vet suppliers thoroughly. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in a similar industry or region. Don’t just rely on their website; engage with their customer service to assess their responsiveness and support capabilities.
- Certification Checks: Verify if they have relevant certifications, such as ISO, that ensure quality standards.
- Performance History: Inquire about their experience with similar projects and their ability to meet deadlines.
Step 4: Request Samples and Specifications
Once you have shortlisted suppliers, request samples of key components along with their specifications. This step is essential for evaluating the quality of materials and ensuring they meet your technical requirements.
- Material Quality: Assess the durability and compatibility of materials with your intended applications.
- Technical Documentation: Ensure you receive detailed specifications and installation guidelines.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Conditions
Engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Clear agreements will help avoid misunderstandings later in the procurement process and ensure you get the best value for your investment.
- Volume Discounts: Inquire about bulk purchasing options if you plan to order multiple units.
- Warranty and Support: Ensure that warranties are clearly outlined and that you understand the after-sales support available.
Step 6: Finalize Your Order and Logistics
After negotiating terms, finalize your order and coordinate logistics for shipping and delivery. Pay attention to the logistics partners used by the supplier, as this can affect delivery timelines and costs.
- Shipping Options: Evaluate different shipping methods based on cost and delivery speed.
- Customs and Duties: Be aware of any import taxes or customs duties that may apply to your order.
Step 7: Establish a Feedback Loop
After receiving your CNC router components, establish a feedback loop with your supplier. This ongoing communication can help resolve any issues quickly and improve the relationship for future orders.
- Performance Review: Share insights on the quality and performance of the components.
- Future Needs: Discuss any upcoming projects or needs to foster a collaborative partnership.
Following this checklist will not only facilitate a smoother procurement process but also ensure that you build a CNC router that enhances your operational efficiency and precision in manufacturing.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for make cnc router Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Sourcing a CNC Router?
When considering the sourcing of a CNC router, understanding the cost structure is essential for effective budgeting and pricing strategy. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used significantly affect the overall cost. This includes aluminum extrusions, linear rails, ball screws, and electronic components. Higher-grade materials can increase durability and precision but will also raise the initial investment.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct labor for assembly and indirect labor for design, engineering, and project management. In regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of South America and Africa, this can be a significant area for cost savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other operational costs associated with running a facility. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overhead costs, influencing the overall price.
-
Tooling: Depending on the design complexity, tooling costs can vary. Custom tooling for specific CNC applications can be a considerable expense, but investing in high-quality tooling can enhance production efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing a robust QC process is crucial to ensure product reliability. This may involve additional testing and inspection costs, which should be factored into the total pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, which can vary by region and shipping terms (Incoterms), must be considered. For international buyers, customs duties and taxes may also impact overall expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the standard margins in the CNC router market can help buyers negotiate better terms.
How Do Price Influencers Impact CNC Router Sourcing?
Several factors can influence the price of CNC routers, particularly for international B2B buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide discounts based on order volume. Larger orders can lead to significant savings, making it beneficial for companies planning to scale.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom features or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Products with certifications for quality and safety often come at a premium. However, these certifications can enhance trust and reliability in the product.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge higher prices but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for international buyers. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total cost, as they determine who is responsible for shipping and insurance.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize CNC Router Sourcing Costs?
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency in sourcing CNC routers:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and terms. Suppliers may have flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO rather than just the purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime when calculating the overall investment.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Utilize platforms that provide insights into different suppliers, including their pricing structures and customer reviews. This can help identify the best options.
-
Leverage Local Partnerships: For buyers in Africa and South America, forming partnerships with local distributors can reduce logistics costs and improve supply chain efficiency.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Keeping abreast of industry trends can provide insights into pricing fluctuations and emerging suppliers, aiding in more informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for CNC routers can vary widely based on specifications, supplier, and market conditions. This analysis provides a framework for understanding potential costs but should not be considered definitive. Buyers are encouraged to conduct their own research and obtain quotes to ensure accurate budgeting for their specific requirements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing make cnc router With Other Solutions
Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing and fabrication, businesses are continually seeking solutions that enhance productivity while minimizing costs. The ‘make CNC router’ presents a versatile option for precise machining tasks. However, it is essential to consider alternative technologies that can fulfill similar requirements. This analysis provides a comparative overview of the ‘make CNC router’ against other viable solutions, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and operational contexts.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Make CNC Router | 3D Printer | Laser Cutter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision for milling, drilling, and routing | Excellent for intricate designs and prototyping | Superior cutting speed and precision for flat materials |
| Cost | Moderate (parts and assembly) | Varies widely (low to high) | High initial investment and maintenance costs |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires design and assembly skills | Generally user-friendly; plug-and-play options available | Moderate; requires setup and calibration |
| Maintenance | Moderate; DIY repairs possible | Low; minimal upkeep required | High; lens and mirrors need regular cleaning |
| Best Use Case | Woodworking, metal parts, signage | Prototyping, small-scale production | Engraving, cutting, and marking materials |
Detailed Breakdown
3D Printer
3D printing technology has gained traction for its ability to create complex geometries and prototypes rapidly. It excels in producing intricate designs with minimal waste. The ease of use is a significant advantage, especially with user-friendly models available for immediate deployment. However, while the initial cost can be low for basic models, professional-grade printers can be expensive. Additionally, 3D printers are primarily limited to specific materials like plastics and resins, making them less versatile than CNC routers for various machining tasks.
Laser Cutter
Laser cutting technology provides exceptional speed and precision, particularly for flat materials like wood, acrylic, and metals. It is ideal for applications requiring detailed engraving and cutting. However, the initial investment can be substantial, particularly for high-quality machines. Maintenance can also be demanding, as components such as lenses and mirrors require regular cleaning and replacement. While laser cutters are excellent for specific applications, they do not offer the same versatility for diverse machining processes as CNC routers.
Conclusion
Choosing the right solution depends on a thorough assessment of business needs, budget, and operational goals. The ‘make CNC router’ stands out for its versatility and precision across various materials, making it an ideal choice for businesses engaged in woodworking, metal fabrication, and signage. In contrast, 3D printers and laser cutters serve specific niches—rapid prototyping and precision cutting, respectively. By evaluating the comparative aspects outlined in this analysis, B2B buyers can align their choice with their production requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency in their operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for make cnc router
What Are the Essential Technical Properties of CNC Routers?
When evaluating CNC routers for business purposes, understanding their technical specifications is crucial. Here are some key properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material used in the construction of CNC routers significantly impacts their durability and performance. Common materials include aluminum, steel, and various plastics. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers. In contrast, steel offers greater rigidity, which is essential for high-precision applications. B2B buyers should assess the material grade to ensure it aligns with their operational needs and longevity expectations. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension. In CNC machining, tight tolerances (often ±0.01 mm) are vital for achieving precision in manufacturing parts. High tolerance levels ensure that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. For businesses, especially in industries like aerospace or automotive, tight tolerances can be the difference between operational efficiency and costly rework. -
Travel Distance
– This specification indicates the maximum distance the router’s cutting head can move along the X, Y, and Z axes. For instance, a travel distance of 730 mm (X) and 650 mm (Y) allows for larger workpieces to be processed. Understanding travel distances is essential for B2B buyers to ensure the CNC router can accommodate their specific project sizes without requiring additional setups. -
Spindle Power
– The spindle power, typically measured in kilowatts (kW), determines the cutting ability of the CNC router. A more powerful spindle can handle tougher materials and faster feed rates, which is crucial for productivity. B2B buyers should consider their material processing needs to select a spindle power that optimizes both speed and efficiency, ultimately affecting their bottom line. -
Drive Mechanism
– CNC routers utilize various drive mechanisms, including rack and pinion, lead screws, and ball screws. Ball screws, for example, offer high precision and low friction, making them ideal for applications requiring accuracy. Understanding the drive mechanism is important for buyers as it affects the machine’s performance, maintenance requirements, and overall cost of ownership.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the CNC Router Industry?
Familiarizing yourself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms you should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the CNC router industry, buyers often source components from OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility. Understanding OEM relationships can help B2B buyers secure reliable suppliers for their CNC needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. For CNC routers, MOQs can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer. B2B buyers should be aware of MOQs to manage their inventory costs effectively and ensure they can meet production demands without overcommitting financially. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other information for specific products. In the context of CNC routers, an RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and features from multiple vendors. This process is critical for making informed purchasing decisions and securing the best value. -
Incoterms
– Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers when negotiating shipping and delivery terms, as they clarify who bears the risk and costs at various stages of the shipping process. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time from placing an order until the product is delivered. In the CNC router market, lead times can vary based on the complexity of the machine and the manufacturer’s production capacity. Buyers should consider lead times in their project planning to avoid delays in production.
By understanding these properties and terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing CNC routers, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and profitability.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the make cnc router Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the CNC Router Sector?
The CNC router market is witnessing significant growth driven by advancements in technology and an increasing demand for automation in manufacturing processes. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek efficiency and precision, the adoption of CNC routers is accelerating. Key trends include the rise of DIY CNC kits, which cater to small-scale manufacturers and hobbyists, allowing them to build custom solutions tailored to their specific needs. Furthermore, the integration of IoT and AI technologies into CNC machines enhances their functionality, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which is particularly appealing to B2B buyers looking to optimize production.
Moreover, international buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing CNC routers that offer versatility and multi-functionality. Machines capable of performing various tasks—such as milling, cutting, and engraving—are in high demand, allowing companies to maximize their investment. The competitive landscape is also shifting, with many manufacturers offering modular systems that can be easily upgraded, ensuring longevity and adaptability as market demands evolve.
How Is Sustainability Impacting Sourcing Trends in the CNC Router Sector?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the CNC router sector. Environmental impacts associated with manufacturing processes and the sourcing of materials are under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to ethical practices and sustainable production methods. This includes using recycled materials, minimizing waste, and implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
Additionally, certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wood sourcing are gaining traction among international buyers. These certifications not only assure buyers of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability but also enhance brand reputation in markets where consumers are increasingly eco-conscious. As a result, companies that adopt sustainable sourcing strategies are likely to gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
How Has the CNC Router Sector Evolved Over Time?
The evolution of the CNC router sector is marked by significant technological advancements and a shift in manufacturing paradigms. Initially, CNC routers were limited to industrial applications, primarily in large-scale manufacturing settings. However, the democratization of technology has led to the development of affordable, user-friendly CNC systems that cater to small businesses and DIY enthusiasts.
The introduction of open-source designs and community-driven platforms has further accelerated this trend, allowing users to share knowledge and resources. As a result, CNC routers have transformed into versatile tools used across various industries, including woodworking, metal fabrication, and even art. This evolution reflects a broader movement towards customization and flexibility in manufacturing, aligning with the needs of international B2B buyers who seek to adapt quickly to changing market demands.
In summary, understanding these dynamics—market growth driven by technology, the importance of sustainability, and the historical context of CNC routers—enables B2B buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing machines for their operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of make cnc router
-
How do I choose the right CNC router for my business needs?
When selecting a CNC router, consider your specific application requirements, such as the materials you will be working with (wood, metal, etc.), the size of the projects, and the desired precision. Assess the machine’s specifications, including cutting area, spindle power, and speed. Additionally, evaluate the software compatibility for design and control, as well as the ease of use for your operators. Finally, consider the manufacturer’s reputation and customer support, especially for ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. -
What are the key features to look for in a CNC router?
Key features to evaluate include the router’s build quality, motion system (gantry vs. moving table), and rigidity, which affect precision and durability. Look for advanced features such as automatic tool changers, programmable spindle speeds, and integrated safety systems. Additionally, consider the software compatibility for CAD/CAM applications and the availability of spare parts. A strong support network for training and technical assistance is also essential for maximizing your investment. -
What is the typical lead time for CNC router orders?
Lead times for CNC routers can vary significantly based on the manufacturer, customization requirements, and order volume. Generally, standard models may have a lead time of 4 to 12 weeks, while customized or larger machines could take longer. It’s crucial to communicate your timeline needs with suppliers upfront to ensure they can meet your delivery expectations. Additionally, factor in any potential delays due to shipping logistics, especially for international orders. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for CNC routers?
MOQs can vary widely among suppliers, with some offering single units while others may require bulk orders to reduce costs. For B2B buyers, understanding the MOQ is essential for budgeting and planning inventory. If you are a smaller business, look for manufacturers that cater to low-volume orders or consider forming partnerships with other companies to meet MOQ requirements. Always clarify the terms before placing an order to avoid unexpected costs. -
How can I vet a CNC router supplier?
To vet a CNC router supplier, start by researching their reputation within the industry. Look for customer reviews, case studies, and testimonials that highlight their product quality and service reliability. It’s beneficial to request references from previous clients. Additionally, evaluate their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO. If possible, arrange a visit to their manufacturing facility to assess their production processes and quality control measures. -
What payment terms are typical when sourcing CNC routers internationally?
Payment terms can differ by supplier, but common arrangements include upfront deposits (usually 30-50%) with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment through escrow services for added security. Ensure that the payment methods align with your financial capabilities and discuss any flexibility in terms. Always document the agreed-upon terms in a contract to protect both parties. -
How do I ensure quality assurance (QA) for my CNC router?
To ensure QA, request detailed specifications and quality standards from your supplier before production. Implement a third-party inspection process to verify that the CNC router meets your requirements before shipment. Additionally, inquire about the manufacturer’s testing protocols, warranty policies, and post-sale support. Establish a clear communication channel for addressing any quality concerns that may arise during production and delivery. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing CNC routers?
When importing CNC routers, consider the shipping method (air vs. sea), customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that the supplier provides the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Work with a reliable freight forwarder familiar with the regulations in your destination country to navigate logistics efficiently. Additionally, account for lead times and any potential delays in transit when planning your production schedule.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 7 Make Cnc Router Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Instructables – 3D CNC Router
Domain: instructables.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Overall dimensions: X: 1050mm, Y: 840mm, Z: 400mm; Travel: X: 730mm, Y: 650mm, Z: 150mm; Electronics: 3x 3 Nm Nema 23 Stepper Motors, 3x DM556 Leadshine stepper motor driver, 36V power supply, Breakout Board, 5V power supply, Ethernet Smoothstepper (recommended), ON/OFF switch, Shielded 18/4 Awg wire, 3x Proximity sensors; Spindle options: Kress FME 800, Bosch Colt, Dewalt Compact Router; Mechanic…
2. OpenBuilds – CNC Router Builds
Domain: builds.openbuilds.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: CNC Router Builds, OpenBuilds Part Store, Categories include Cartesian Style CNC, Delta Mills, X/Y Table Style CNC Mill, Other Style CNC Mills. Notable builds include: 5 x 10 Wall Mountable CNC under $3000, OpenBuilds MiniMite Router, upgraded OpenBuilds Lead 1515, Gerber 404 Retrofit, Workbee Queen 1500×1000 CNC Router with upgrades, and various DIY projects. Features include linear rails, Nema m…
3. BuildYourCNC – CNC Machines & Components
Domain: buildyourcnc.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: BuildYourCNC offers a wide range of products including CNC machines, laser machines, 3D resin printers, CNC electronics, and various components. Key categories include CNC plans, laser cutters and engravers, turnkey systems, controllers, stepper motors and drivers, power supplies, and mechanical components like lead screws and bearings. They also provide CNC software, spindles and VFDs, cutting to…
4. V1E – DIY CNC Router Guide
Domain: forum.v1e.com
Registered: 2006 (19 years)
Introduction: This company, V1E – DIY CNC Router Guide, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
5. Maker Forums – 3018 CNC Controller Issues
Domain: forum.makerforums.info
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Homemade desktop CNC built using a 3018 controller; utilizes GRBL controller software; issues with axis direction (X and Z reversed); G-code created in Easel; operated via cellphone.
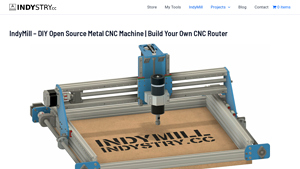
6. Indystry – IndyMill CNC Machine
Domain: indystry.cc
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: IndyMill is a DIY open-source metal CNC machine project developed by Nikodem Bartnik, designed as an upgrade to the Dremel CNC. It aims to be easy to build and replicate worldwide, using widely available components and comprehensive documentation. The machine has a working area of approximately 520x400x115mm and outside dimensions of 760x660x360mm. Parts required include various profiles, lead scr…
7. All3DP – DIY CNC Router Guide
Domain: all3dp.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: DIY CNC Router/Machine: How to Build Your Own, Author: Andreas Giencke, Updated: Feb 6, 2023, Description: A guide for building a DIY CNC router, suitable for makers, highlighting the challenges involved.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for make cnc router
In the dynamic landscape of CNC router manufacturing, strategic sourcing stands out as a crucial driver of competitive advantage. By understanding the diverse components required for building CNC routers—such as motors, spindles, and rails—international buyers can leverage a global supply chain to enhance product quality while optimizing costs. This approach not only fosters innovation but also ensures that businesses can respond swiftly to market demands, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Investing time in evaluating suppliers and understanding their capabilities can yield significant long-term benefits. Establishing relationships with manufacturers who prioritize quality and reliability will ultimately lead to superior machine performance and reduced downtime. As the CNC market continues to evolve, being proactive in sourcing high-quality materials and components will enable businesses to stay ahead of the competition.
Looking forward, international buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships that align with their strategic goals. The potential for growth in CNC applications is immense, and by committing to strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves to capitalize on emerging opportunities in diverse markets. Take the next step in your CNC journey—connect with reputable suppliers and innovate your operations today.